Calculation method and application of formation fracture pressure in Baiyun deepwater area
-
摘要:
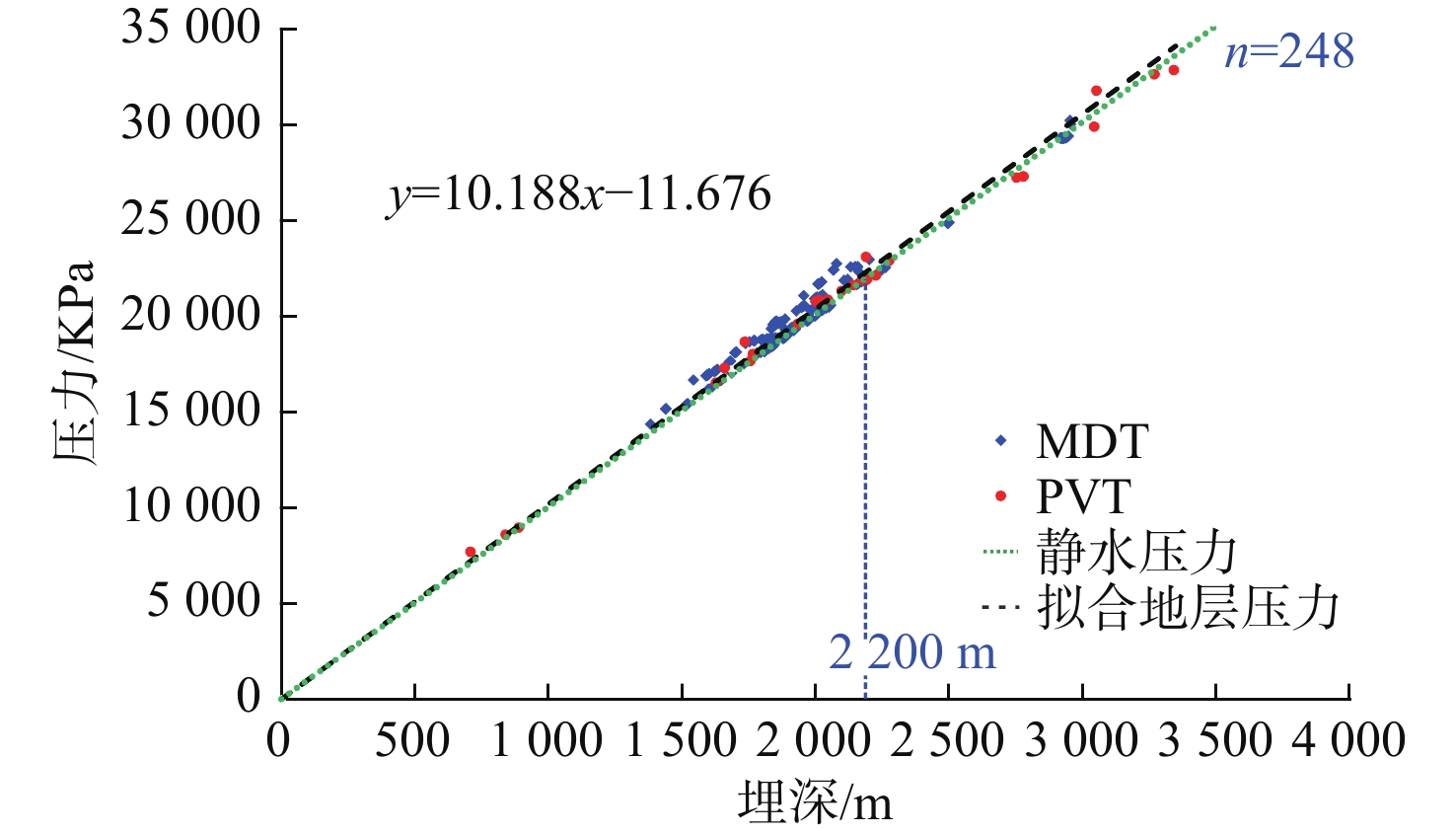
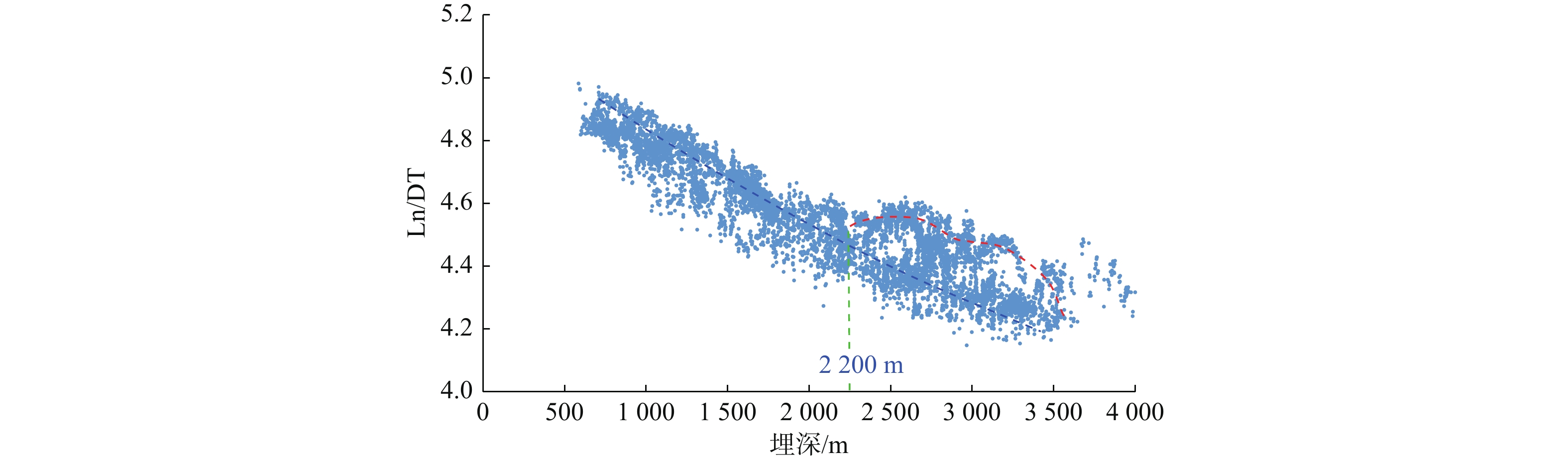
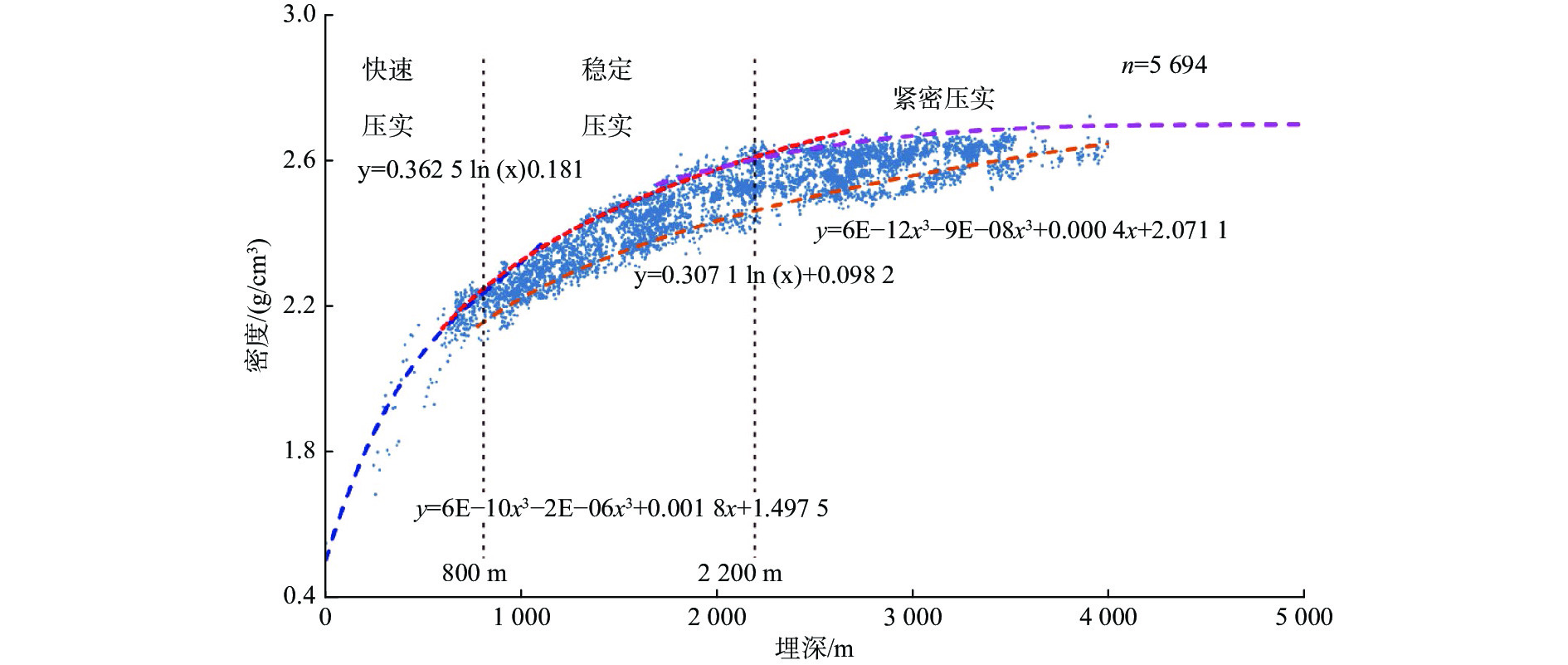
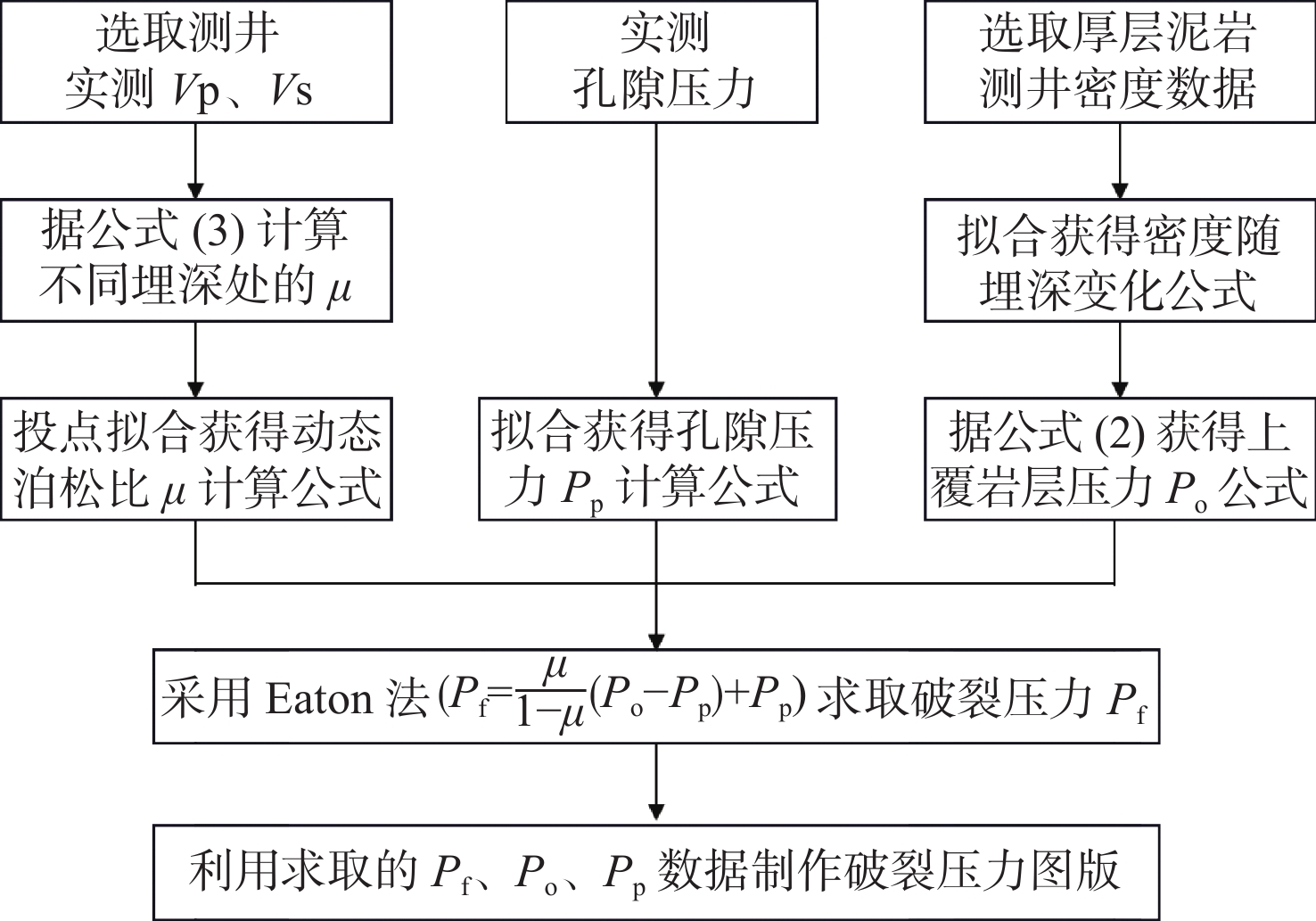
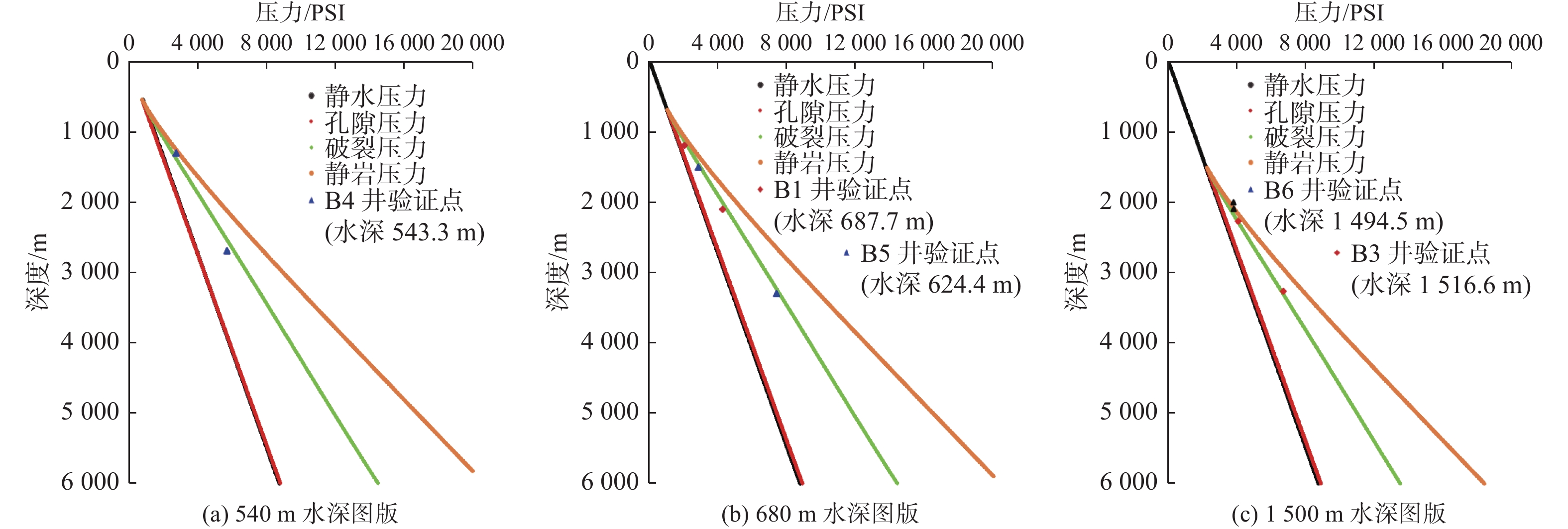
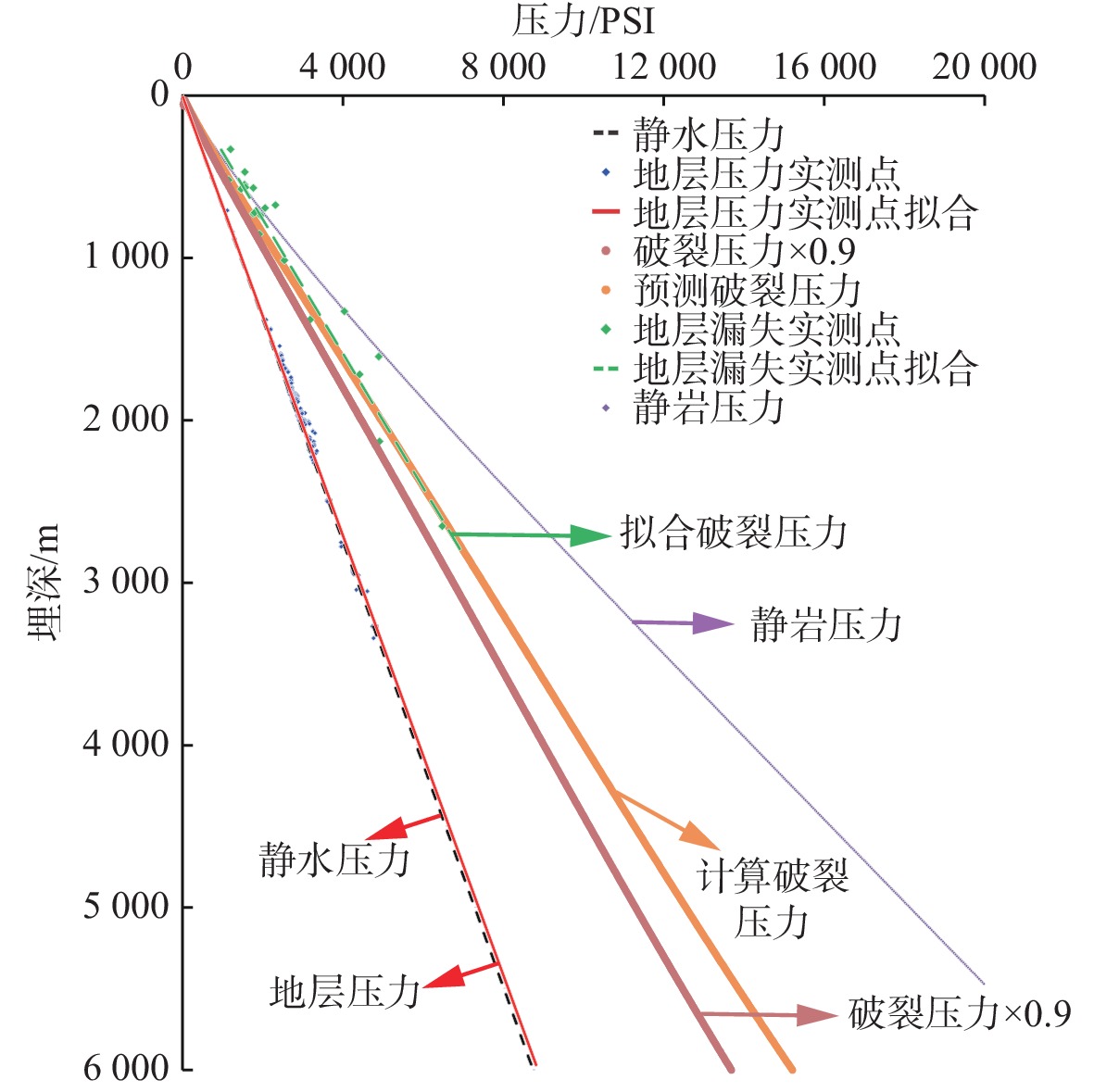
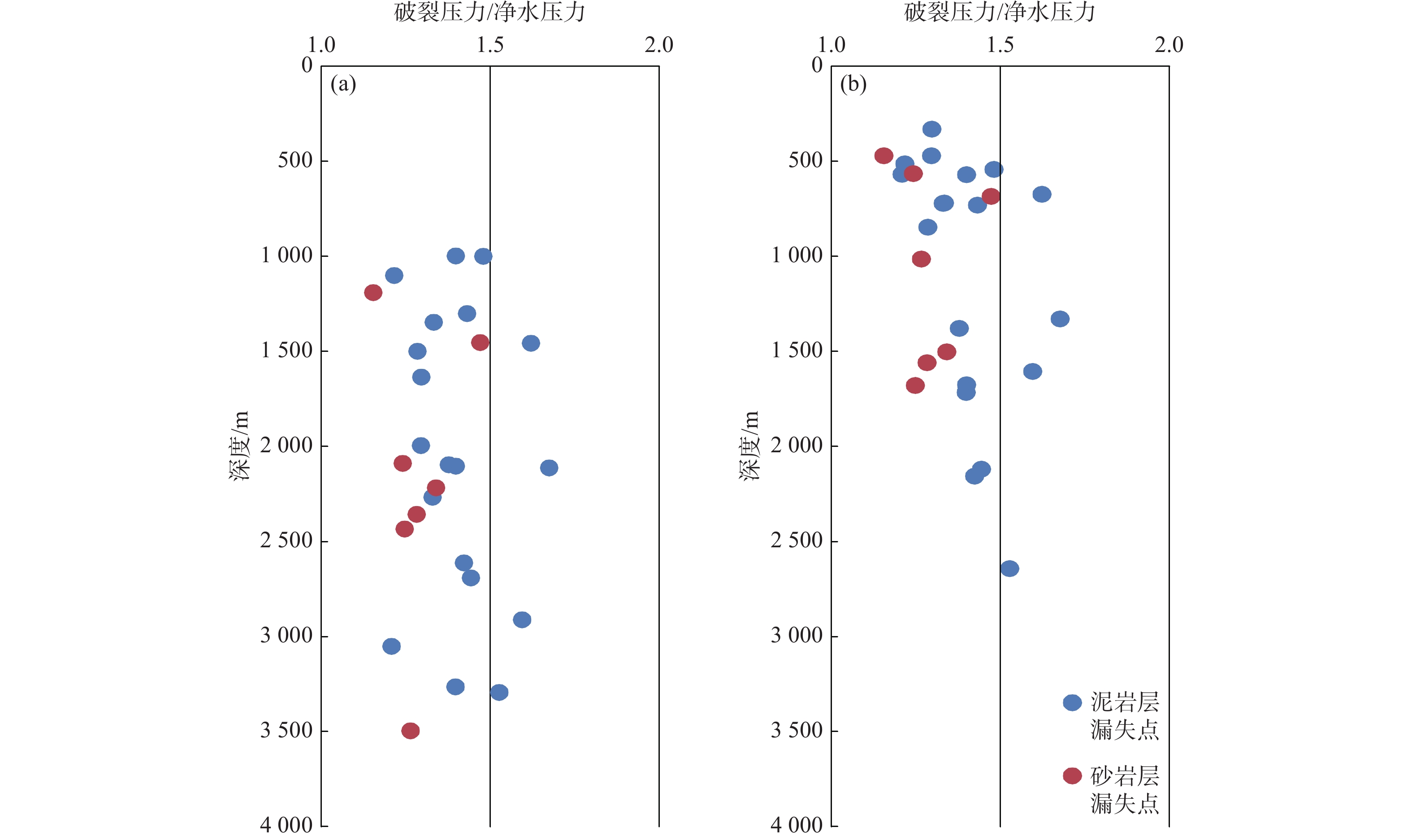
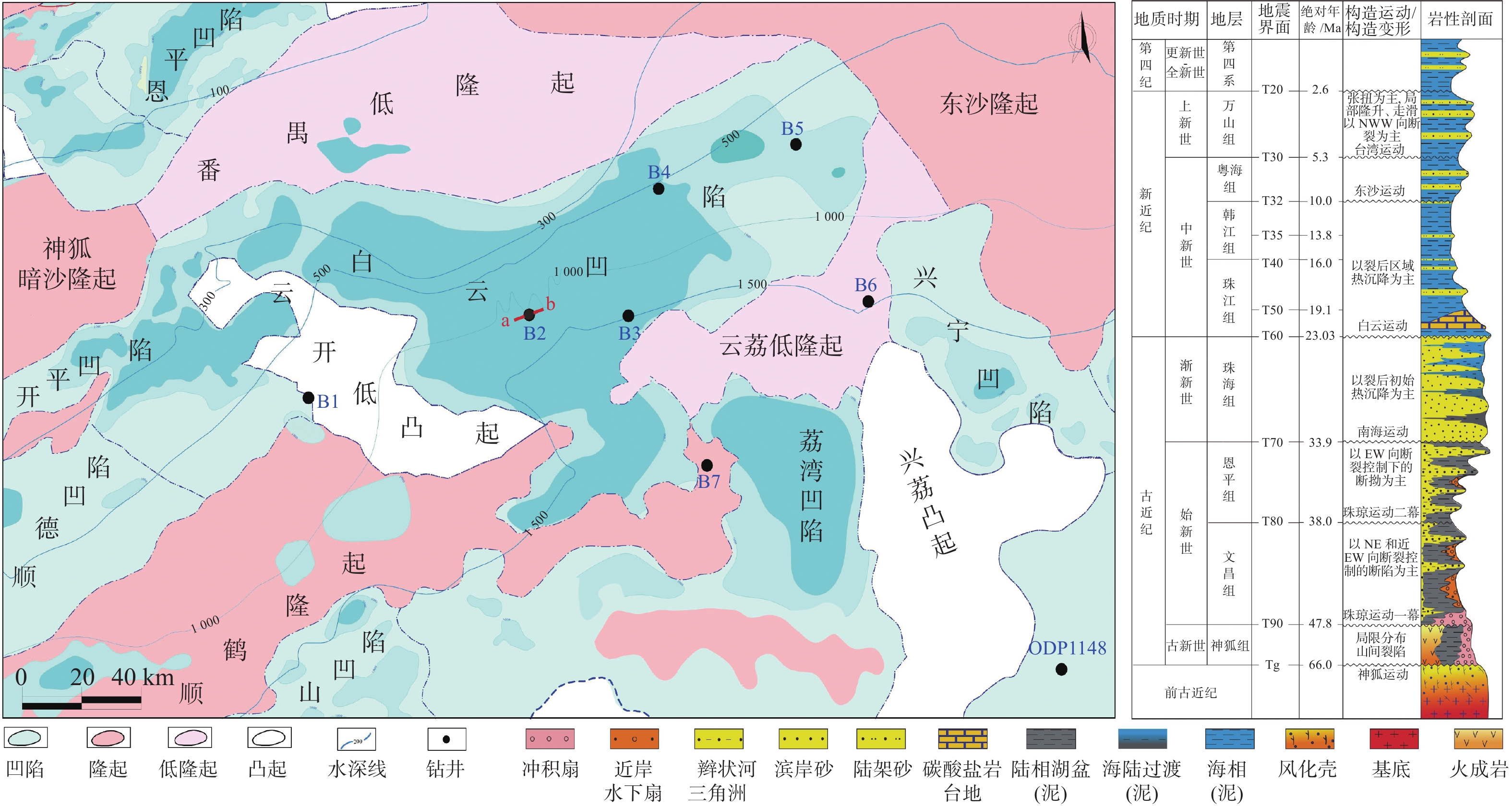
地层破裂压力不仅可以用于钻井设计,也可用于盖层封烃高度、流体底辟区古压力系数等重要参数的计算。本次研究分析整理了白云深水区38口探井的测井数据,构建了泥岩密度随埋深的变化趋势,明确了研究区正常压实泥岩密度随埋深表现出“三段式”(<800、800~1 200、>2 200 m)变化趋势,并拟合出静岩压力及泊松比随深度变化的动态公式。采取Eaton法建立了不同水深条件下的地层破裂压力图版,结果与实钻井地漏测试结果吻合较好。利用编制的破裂压力-深度图版,明确了浅埋藏区圈闭盖层最大封烃高度计算方法,证实深水、超深水区薄盖层依然具备封烃能力;结合油气成藏期次研究,明确了近白云凹陷中心位置B2钻井周边底劈区的最大古压力系数为1.69~1.713。综合分析推测在研究区孔隙压力达到上覆泥岩破裂压力值的90%附近时,超压体系产生裂缝,泥岩盖层受到破坏,油气漏失。
Abstract:Formation fracture pressure can be used not only for drilling design, but also for calculation of important parameters such as hydrocarbon sealing height of caprock and ancient pressure coefficient of fluid diapir area. In this study, the logging data of 38 exploration wells in Baiyun deep-water area are analyzed and sorted, the variation trend of mudstone density with buried depth is constructed, the variation trend of normal compacted mudstone density with buried depth is defined as "Three-stage" (< 800, 800-1200, > 2 200 m), and the dynamic formula of static rock pressure and Poisson's ratio with depth is fitted.The Eaton method is adopted to establish the chart of formation fracture pressure under different water depths, and the results are in good agreement with the leakage pressure obtained by actual drilling.Using the compiled fracture pressure-depth chart, the calculation method of the maximum hydrocarbon sealing height of the trap caprock in shallow buried area is clarified, and it is confirmed that the thin caprock in deep and ultra-deep water areas still has the hydrocarbon sealing ability. Combined with the study of oil and gas accumulation periods, it is clear that the maximum Paleopressure coefficient in the bottom splitting area around B2 well near the center of Baiyun sag is 1.69~1.713.Through comprehensive analysis, it is speculated that when the pore pressure in the study area reaches about 90% of the fracture pressure of the overlying mudstone, the overpressure system will produce cracks, the mudstone caprock will be damaged and oil and gas leakage will occur.
-

-
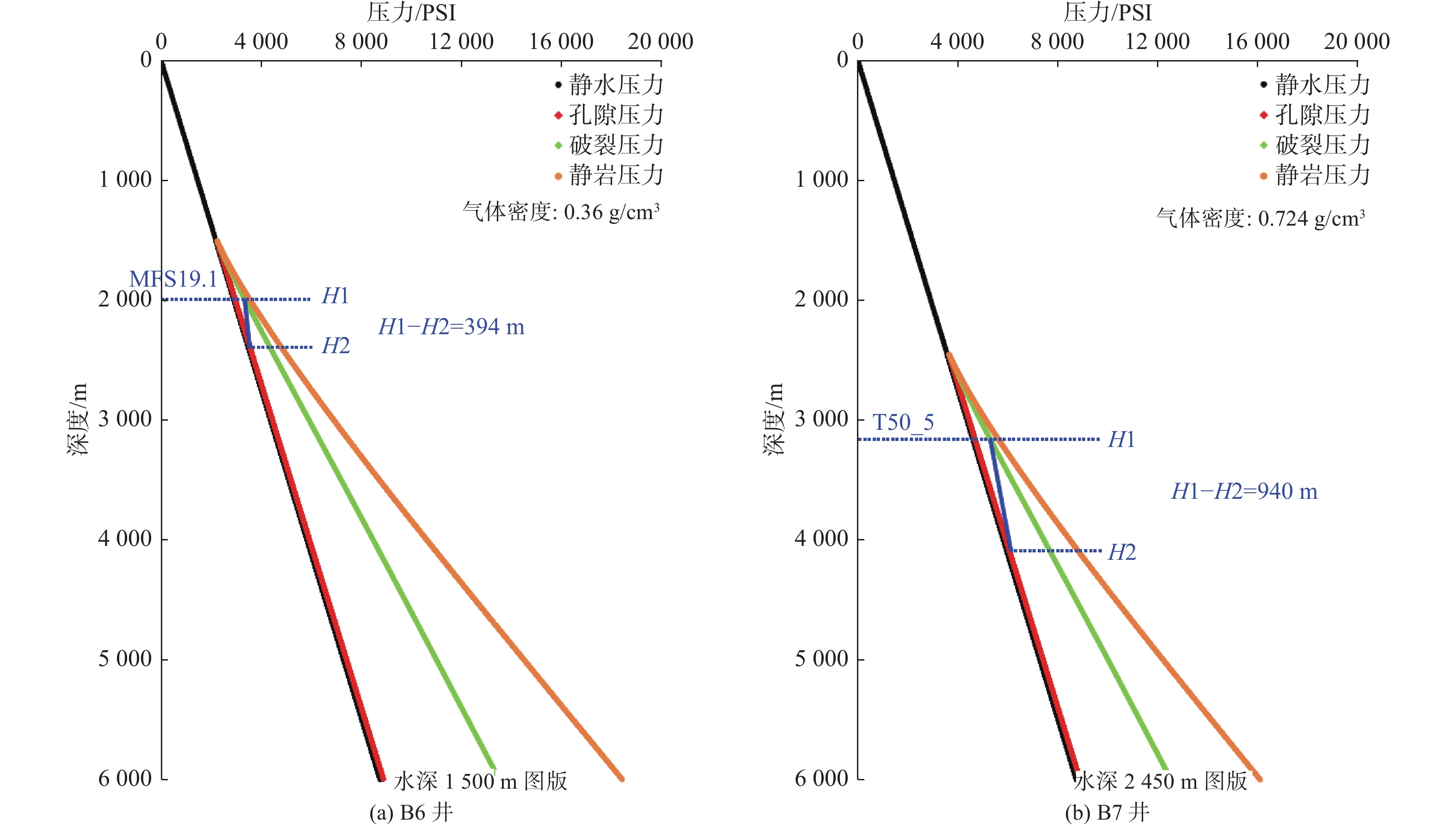
表 1 B6井及B7井盖层封烃高度计算
Table 1. Hydrocarbon sealing height of Well B6 and Well B7 cap
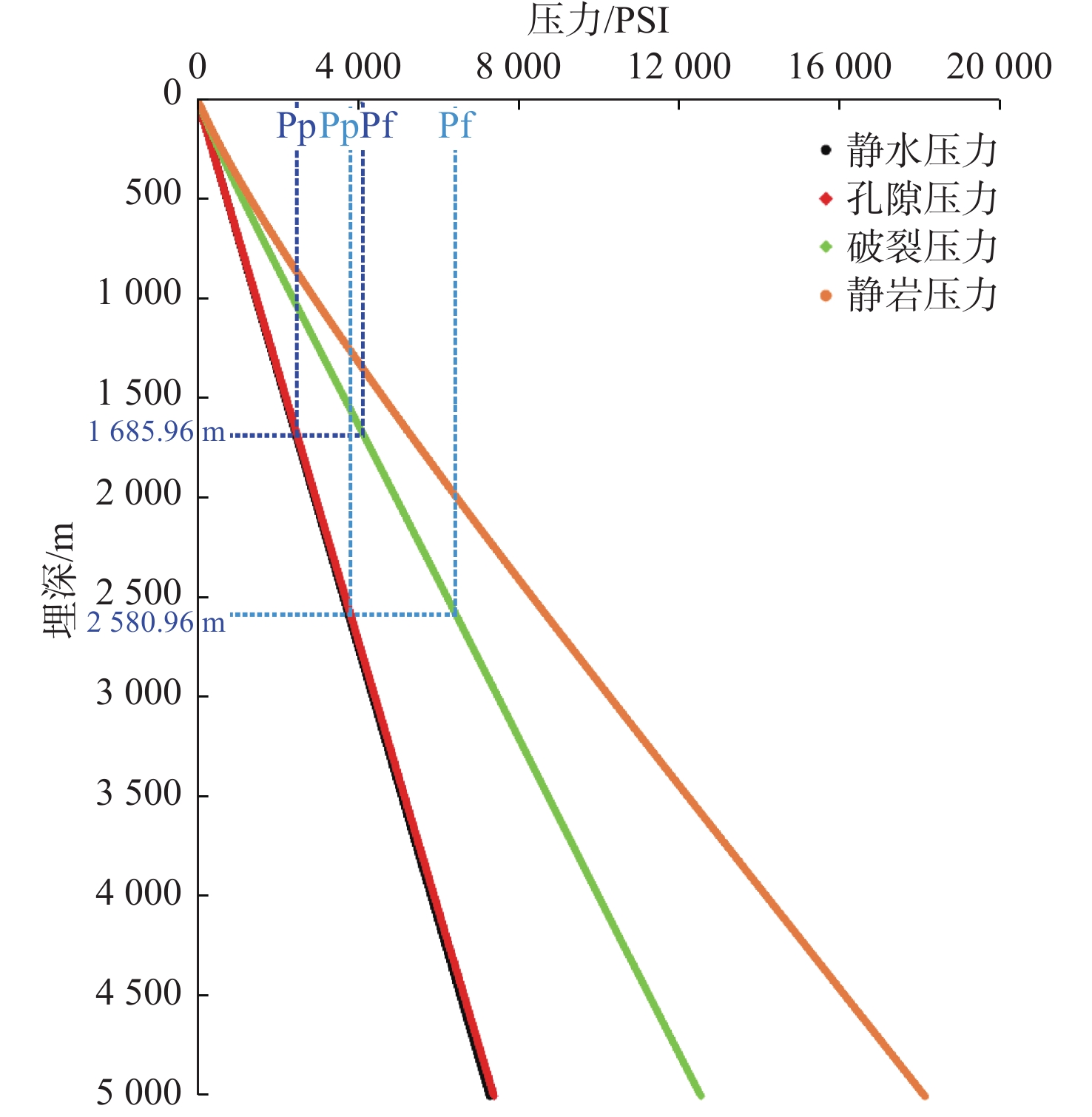
井位 水深/m 盖层地震层位 盖层底深/m 盖层埋深/m 封烃高度/m B6 1 494.5 MFS19.1 1 997.1 502.6 394 B7 2 451.43 T50_5 3 162.5 711.07 940 表 2 白云凹陷B2井区底辟发生时地层古压力系数(破裂/静水)估算
Table 2. Estimation of ancient formation pressure coefficient when the bottom diapir happens in Well B2 area of Baiyun Sag
底辟时间/Ma 封盖层段 底辟发生时封盖层埋深/m 破裂压力/静水压力比值 5 MFS19.1 2 580.96 1.713 10.5 MFS19.1 1 685.96 1.69 -
[1] 柳保军,庞雄,王家豪,等. 珠江口盆地深水区伸展陆缘地壳减薄背景下的沉积体系响应过程及油气勘探意义[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(S1):124-138. doi: 10.7623/syxb2019S1011
[2] 李洪博,郑金云,庞雄,等. 南海北部陆缘差异拆离作用结构样式与控制因素:以珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2020,32(4):24-35.
[3] 庞雄,任建业,郑金云,等. 陆缘地壳强烈拆离薄化作用下的油气地质特征:以南海北部陆缘深水区白云凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(1):27-39.
[4] 庞雄,郑金云,梅廉夫,等. 先存俯冲陆缘背景下珠江口盆地断陷结构的多样性[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(4):1-11.
[5] 邵磊,庞雄,陈长民,等. 南海北部渐新世末沉积环境及物源突变事件[J]. 中国地质,2007,323(6):1022-1031. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.06.008
[6] HUBBERT M K,WILLIS D G. Mechaics of hydraulic fracturing[J]. Petroleum Transactions,1957,210:153-168.
[7] MATTHEWS W R,KELLY J. How to predict formation pressure and fracture gradient from electric and sonic logs[J]. Oil and Gas Journal,1967,65(8):92-106.
[8] 周拿云,杨兆中. 地层破裂压力预测技术综述[J]. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版),2011,13(1):36-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1980.2011.01.011
[9] HAIMSON B,FA IRHURST C. Initiation and extension of hydraulic fractures in rocks[J]. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal,1967,7(6):310-318.
[10] 石杨梦. 川东北须二段裂缝性致密气藏破裂压力预测研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2017.
[11] EATON B A. Fracture gradient prediction and its application in oilfield operations[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology,1969,21(10):1353-1360. doi: 10.2118/2163-PA
[12] ANDERSON R A,INGRAM D S,ZANIER A M. Determining fracture pressure gradient from well log[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology,1973,25(11):1259-1268. doi: 10.2118/4135-PA
[13] STEPHEN R D. Prediction of fracture pressures for wildcat wells[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology,1982,34(4):863-872. doi: 10.2118/9254-PA
[14] 黄荣樽. 地层破裂压力预测模式的探讨[J]. 华东石油学院学报,1984,8(4):335-347.
[15] 李传亮. 射孔完井条件下的岩石破裂压力计算公式[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2002,24(2):37-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2002.02.024
[16] 聂采军,赵军,夏宏权,等. 地层破裂压力测井预测的统计模式研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,2004,15(6):633-636. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2004.06.015
[17] 任岚,赵金洲,胡永全,等. 水力压裂时岩石破裂压力数值计算[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(S2):3417-3422.
[18] 马妮,林正良,胡华锋,等. 页岩地层的破裂压力地震预测方法[J]. 石油物探,2019,58(6):926-934. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2019.06.016
[19] 谢静,吴惠梅,楼一珊,等. 南海深水海域高温高压地层破裂压力预测模型[J]. 断块油气田,2021,28(3):378-382.
[20] 田立新,张忠涛,庞雄,等. 白云凹陷中深层超压发育特征及油气勘探新启示[J]. 中国海上油气,2020,32(6):1-11.
[21] 米立军,张忠涛,庞雄,等. 南海北部陆缘白云凹陷油气富集规律及主控因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(5):902-913.
[22] 郭帅,杨海长,曾清波,等. 白云凹陷恩平组南部物源研究及其油气地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(6):56-63.
[23] 赵毅. 考虑温度影响的深水地层破裂压力研究[D]. 武汉: 长江大学, 2020.
[24] 刘厚彬,孟英峰,王先起,等. 利用测井资料预测地层孔隙压力方法研究综述[J]. 西部探矿工程,2006,122(6):91-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2006.06.045
[25] 秦绪英, 周巍, 陈有明. 地层孔隙压力及破裂压力计算方法研究[C]//中国石化石油勘探开发研究院南京石油物探研究所2004年学术交流会, 中国南京, 2004.
[26] 魏茂安,陈潮,王延江,等. 地层孔隙压力预测新方法[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2007,28(3):395-400. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.03.014
[27] 时贤,程远方,梅伟. 基于测井资料的地层孔隙压力预测方法研究[J]. 石油天然气学报,2012,34(8):94-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2012.08.019
[28] 郭金荣. 他拉哈地区地层孔隙压力及破裂压力预测技术研究[D]. 大庆: 大庆石油学院, 2006.
[29] 邹玮,孙鹏,张书平,等. 西湖凹陷钻前压力预测技术及应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2016,32(8):47-51.
[30] 郑丹,徐思煌,尚小亮. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷泥岩压实特征及其成因[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2010,32(4):372-377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2010.04.008
[31] 张智勇. 苏里格气田低孔低渗地层破裂压力的测井计算方法研究[J]. 国外测井技术,2013,195(3):34-37.
[32] 冯启宁. 用测井资料计算地层破裂压力的公式和方法[J]. 华东石油学院学报,1983,11(3):41-48.
-



 下载:
下载: