Response of Dongying Port project change to seabed erosion and siltation since 1985
-
摘要:
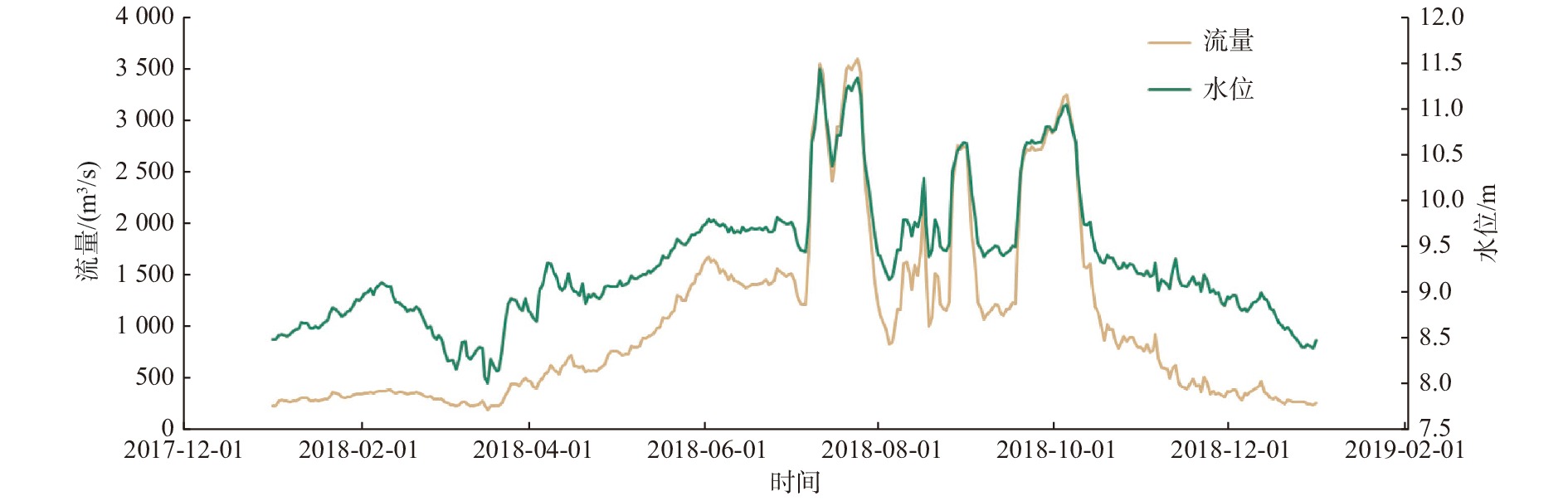
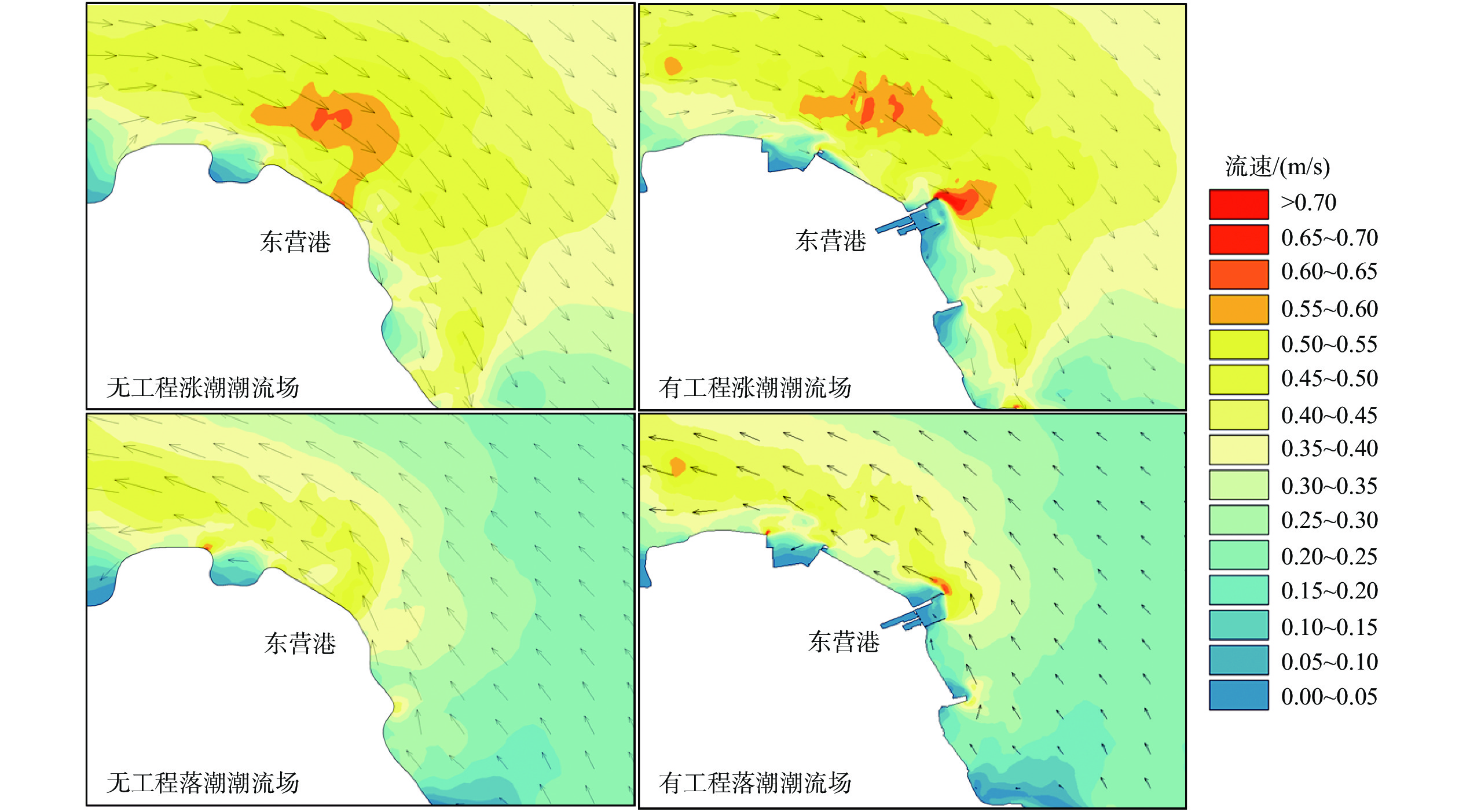
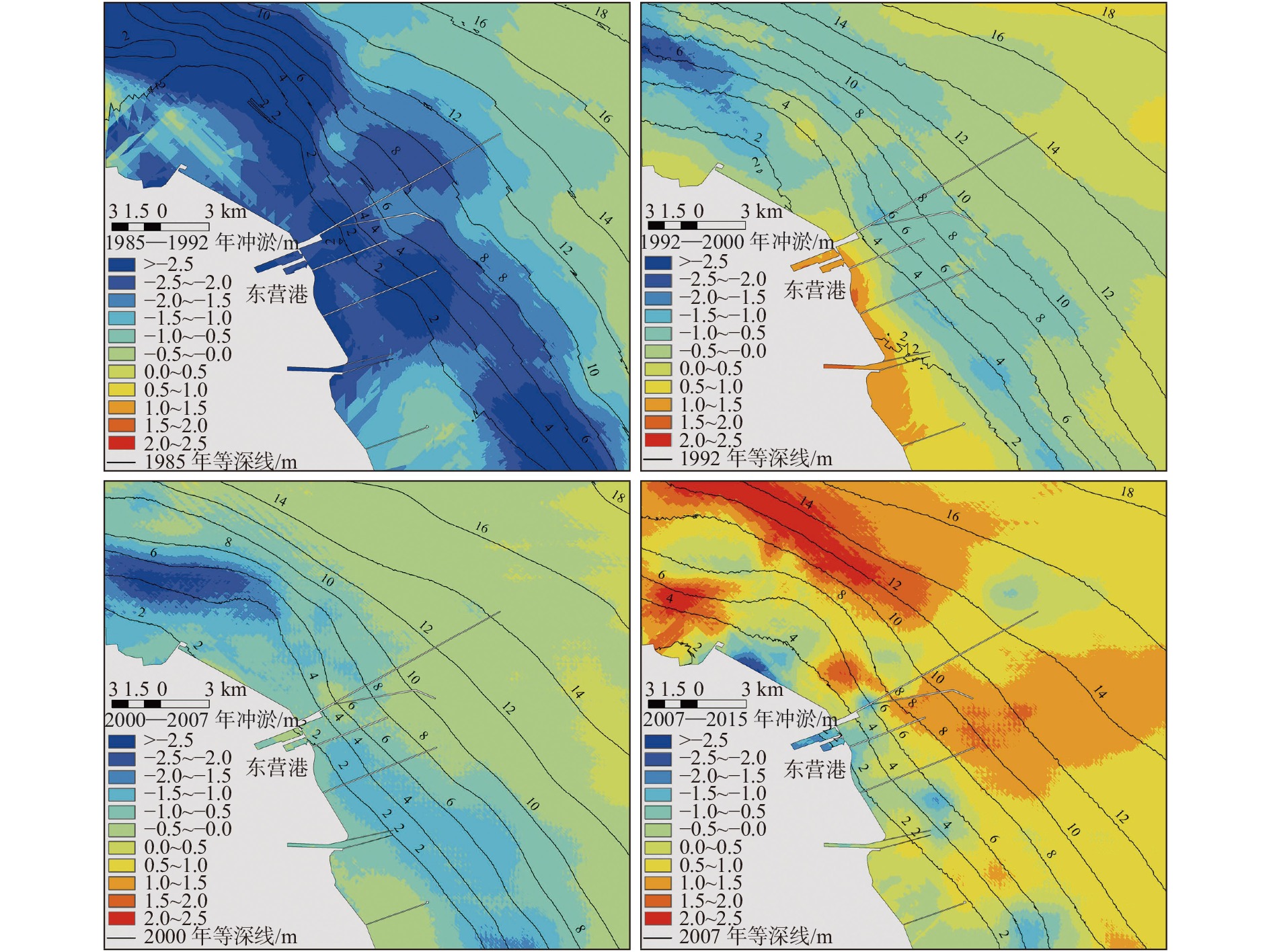
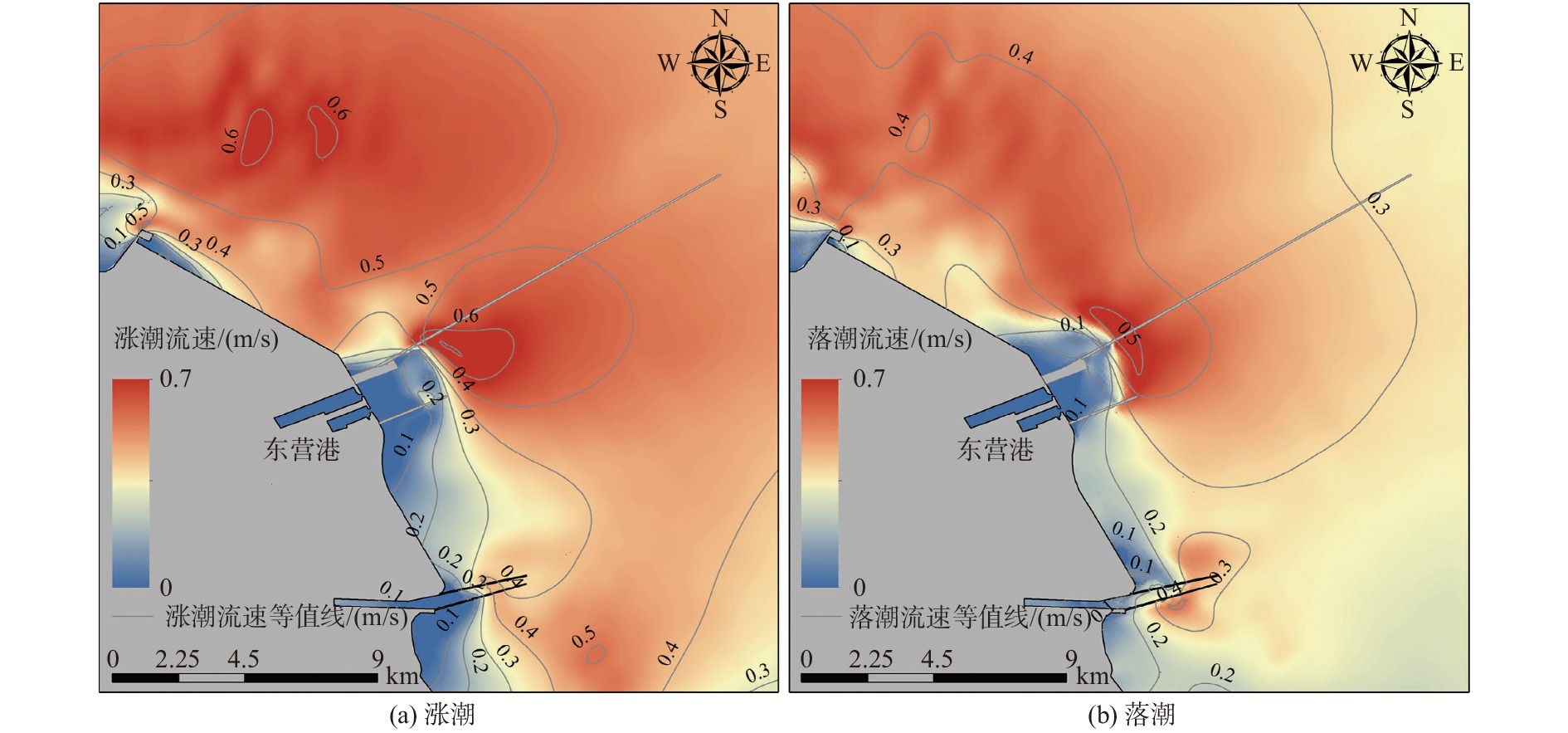
河口三角洲区域地质环境脆弱,对环境变化响应敏感,三角洲港口冲淤演变受工程结构影响较大。黄河三角洲的东营港区域以粉砂质海岸为主,区域内泥沙运移活跃,此类区域港口建设的关键问题在于工程结构导致的海床冲淤变化。通过东营港建港以来实测水深数据构建水下地形数字高程模型(DEM),并结合水动力数值模拟,探讨了东营港冲淤演变过程和工程影响。结果表明,由于波浪和潮流导致的海底地形变化,东营港近岸海域的冲淤演变形势已从单一侵蚀转变到近岸侵蚀、离岸淤积的新情势;工程结构影响局地潮流流速和流向,口门处出现高速横流,最大流速可达0.7 m/s;高流速导致北防波堤的堤头位置出现直径约1 km的冲刷坑;工程结构的遮蔽区有促淤效应,遮蔽区大小与潮流流向、工程结构-岸线夹角有关,但在波浪、余流的作用下,2007—2015年工程结构遮蔽区依旧存在0.5 m以上的侵蚀。持续的侵蚀作用使海域防波堤和海堤的不稳定性加剧,迫切需要加强检测与防护。
Abstract:The geological environment in estuarine delta region is fragile and sensitive to natural and anthropological changes, and the evolution of alluvial siltation in delta port is influenced by engineering structures. Dongying Port in the Yellow River Delta is dominated by silty sands and active sediment transport. The key issue of engineering in such an area is the change of sea bed flushing and siltation caused by engineering structure. By applying the digital elevation model (DEM) of underwater topography constructed by the measured bathymetry data since the construction of Dongying Port in combination of numerical hydrodynamic simulation, the evolution of the siltation process and engineering impact of Dongying Port were explored. Results show that, due to the change of seafloor topography caused by waves and tides, the situation of siltation in the near-shore area of Dongying Port has evolved from single erosion to near-shore erosion and offshore siltation. The engineering structure affected the local tidal flow velocity and direction, and a high-speed cross-current with a maximum velocity of 0.7 m/s appeared at the mouth gate, which led to a scour pit with a diameter of about 1 km at the head of the north breakwater. The sheltered area of the engineering structure had a siltation-promoting effect, and the size of the sheltered area was related to the tidal flow direction and the angle between the engineering structure and the shoreline. However, under the action of waves and residual currents, more than 0.5 m erosion still existed in the sheltered area from 2007 to 2015. The persistent erosion has increased the instability of sea breakwaters and seawalls. Therefore, it is urgent to strengthen the detection and protection of the port.
-

-
[1] SYVITSKI J,KETTNER A J,OVEREEM I,et al. Sinking deltas due to human activities[J]. Nature Geoscience,2009,2(10):681-686. doi: 10.1038/ngeo629
[2] MOHANYT P K,BARIK S K,KAR P K,et al. Impacts of ports on shoreline change along Odisha coast[J]. Procedia Engineering,2015,116:647-654. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.08.339
[3] SUMER B M,WHITEHOUSE R,TØRUM A. Scour around coastal structures:a summary of recent research[J]. Coastal Engineeering,2001,44:153-190. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3839(01)00024-2
[4] 赵捷,何青,虞志英,等. 长江口北槽深水航道回淤泥沙来源分析[J]. 泥沙研究,2014,19(5):18-24. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2014.05.006
[5] 刘杰,程海峰,韩露,等. 长江口12.5 m深水航道回淤年际变化及成因[J]. 水科学进展,2019,30(1):65-75.
[6] EL-ASMAR H M,WHITE K. Changes in coastal sediment transport processes due to construction of New Damietta Harbour,Nile Delta,Egypt[J]. Coastal Engineering (Amsterdam),2002,46(2):127-138. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3839(02)00068-6
[7] 陈沈良,张国安,谷国传. 黄河三角洲海岸强侵蚀机理及治理对策[J]. 水利学报,2004,35(7):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2004.07.001
[8] FU Y T,CHEN S L,JI H Y,et al. The modern Yellow River Delta in transition:Causes and implications[J]. Marine Geology,2021,436:106-476.
[9] 李孟国,曹祖德. 粉沙质海岸泥沙问题研究进展[J]. 泥沙研究,2009,14(2):72-80. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2009.02.012
[10] 周永东,陈沈良,谷国传. 东营港海域表层沉积物分布及其运移趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2009,29(3):31-38.
[11] 李文涛. 东营港内航道淤积问题分析[J]. 海岸工程,2001(1):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2001.01.001
[12] 罗宗杰,吴建政,胡日军,等. 东营港海域冲淤特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2016,32(12):40-45. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2016.12006
[13] 陈兆林,李卫国,刘锐,等. 东营港海区悬沙特征及冲淤分析[J]. 海洋工程,2009,27(2):110-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2009.02.017
[14] 李典,徐振坤,肖立敏,等. 东营港水动力要素及泥沙运动特性[J]. 中国港湾建设,2017,37(6):7-10. doi: 10.7640/zggwjs201706002
[15] 刘锐. 东营港建设与施工技术[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社股份有限公司, 2016: 10-11.
[16] TAYLOR K E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2001,106(D7):7183-7192. doi: 10.1029/2000JD900719
[17] 刘锐,韩志远,刘涛. 东营港拟建航道沿线滩面沉积物特性及航道可挖性分析[J]. 水道港口,2013,34(2):118-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2013.02.008
[18] SHI C,ZHANG D,YOU L. Sediment budget of the Yellow River Delta,China:the importance of dry bulk density and implications to understanding of sediment dispersal[J]. Marine Geology,2003,199(1/2):13-25. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00159-2
[19] 李东风,李泽刚. 钓口河故道分洪入海泥沙对东营港影响的计算研究[J]. 人民黄河,1998,20(3):8-9.
[20] 陈沈良,张国安,陈小英,等. 黄河三角洲飞雁滩海岸的侵蚀及机理[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2005,25(3):9-14. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2005.03.002
[21] 彭俊,刘锋,陈沈良. 黄河三角洲强侵蚀岸段海域的悬沙输运机理研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2015,20(5):44-50. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2015.05.008
[22] 吴宋仁. 海岸动力学[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2000: 52.
[23] 李向阳,陈沈良,胡静,等. 黄河三角洲孤东海域沉积物及水动力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2008,28(1):43-49. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2008.01.008
[24] 佐藤昭二, 田中则男. 波浪作用下水平床面上泥沙运动[C]//第九届海岸工程会议论文集, 1962: 95-100.
[25] 李平,朱大奎. 波浪在黄河三角洲形成中的作用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1997,17(2):40-47. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1997.02.006
[26] 胡志毅. 丁坝挑角对周围流场及局部冲刷影响的三维数值模拟研究[D]. 西安: 西北农林科技大学, 2021.
-




 下载:
下载: