Spatio-temporal change of coastal current around Shandong Peninsula and transport characteristics of suspended matter
-
摘要:
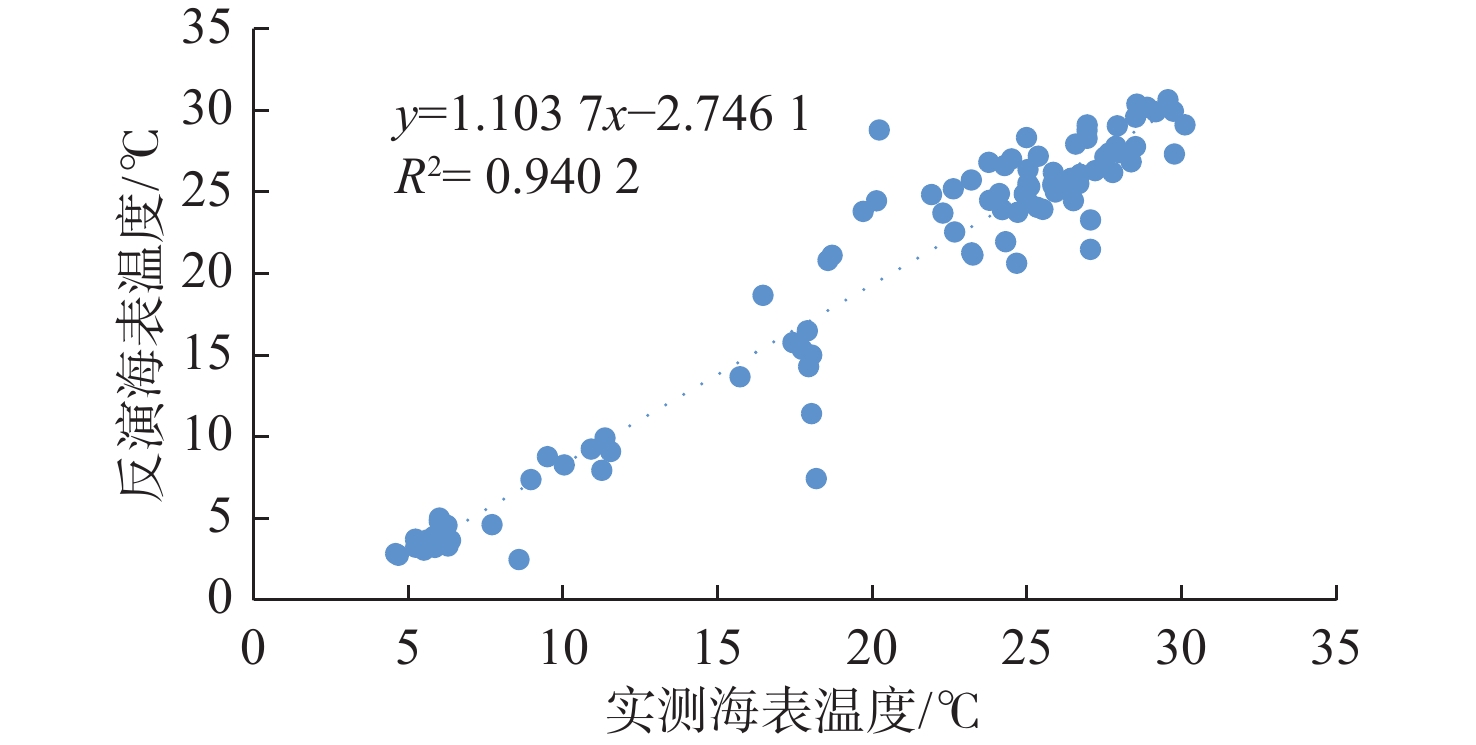
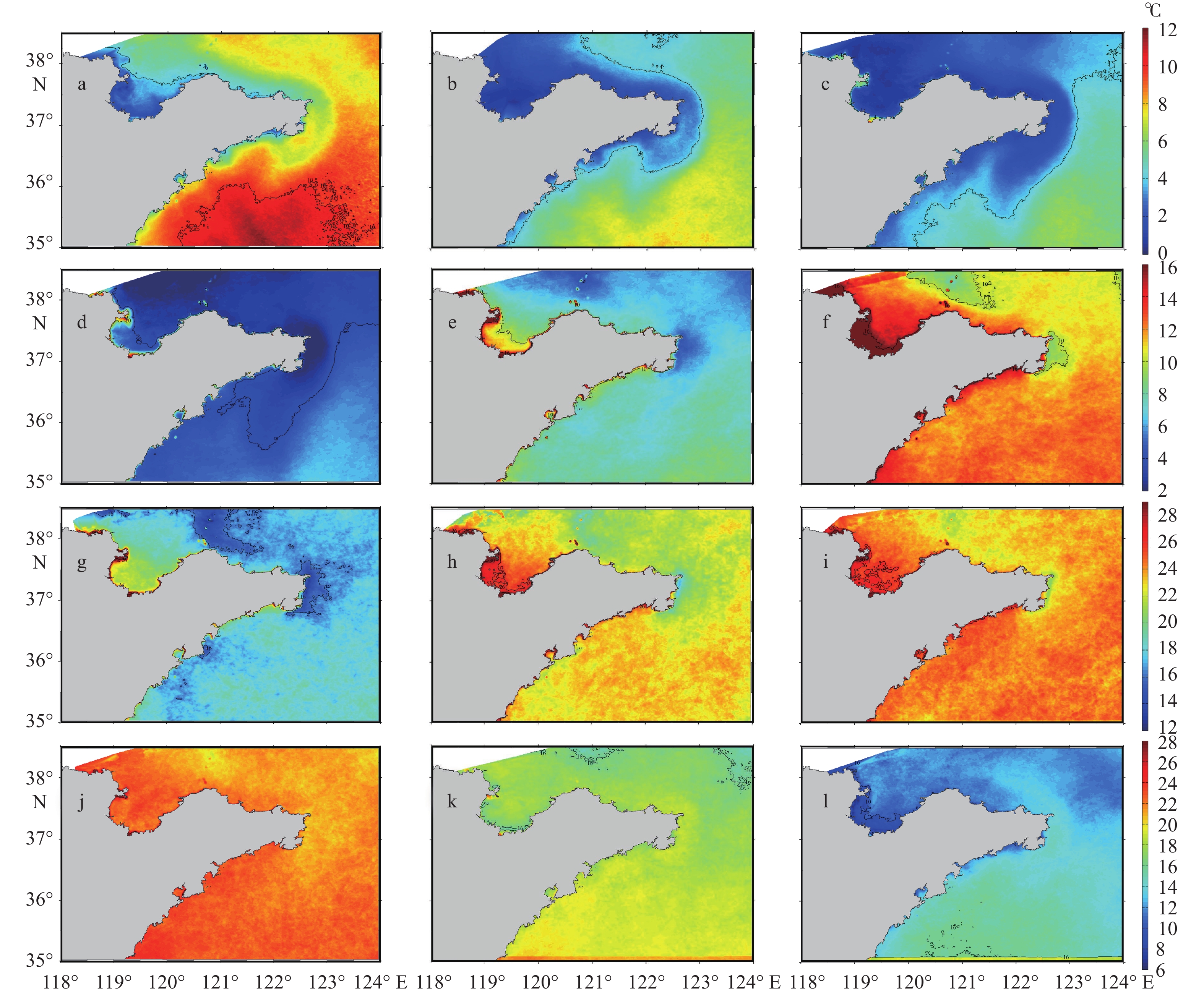
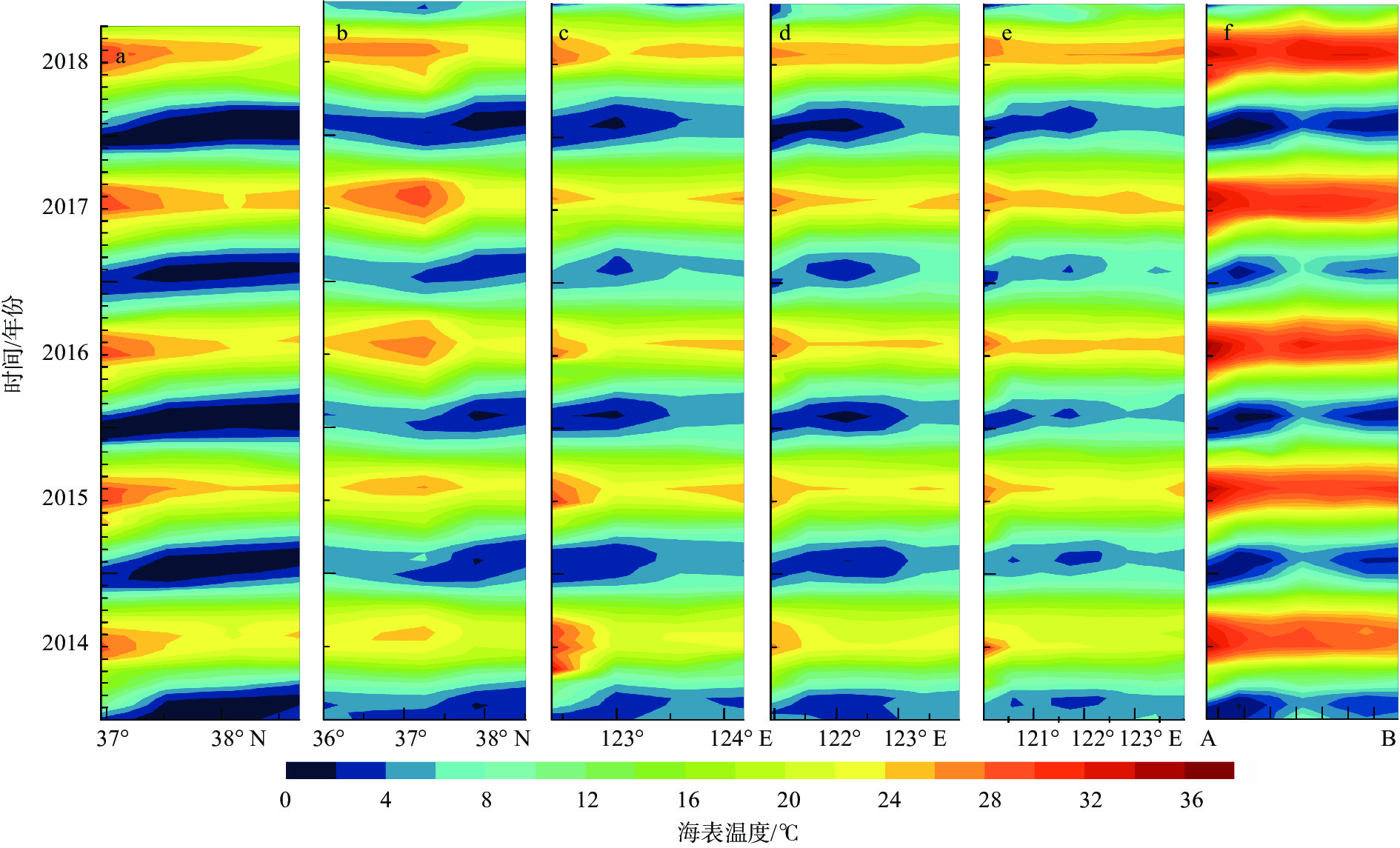
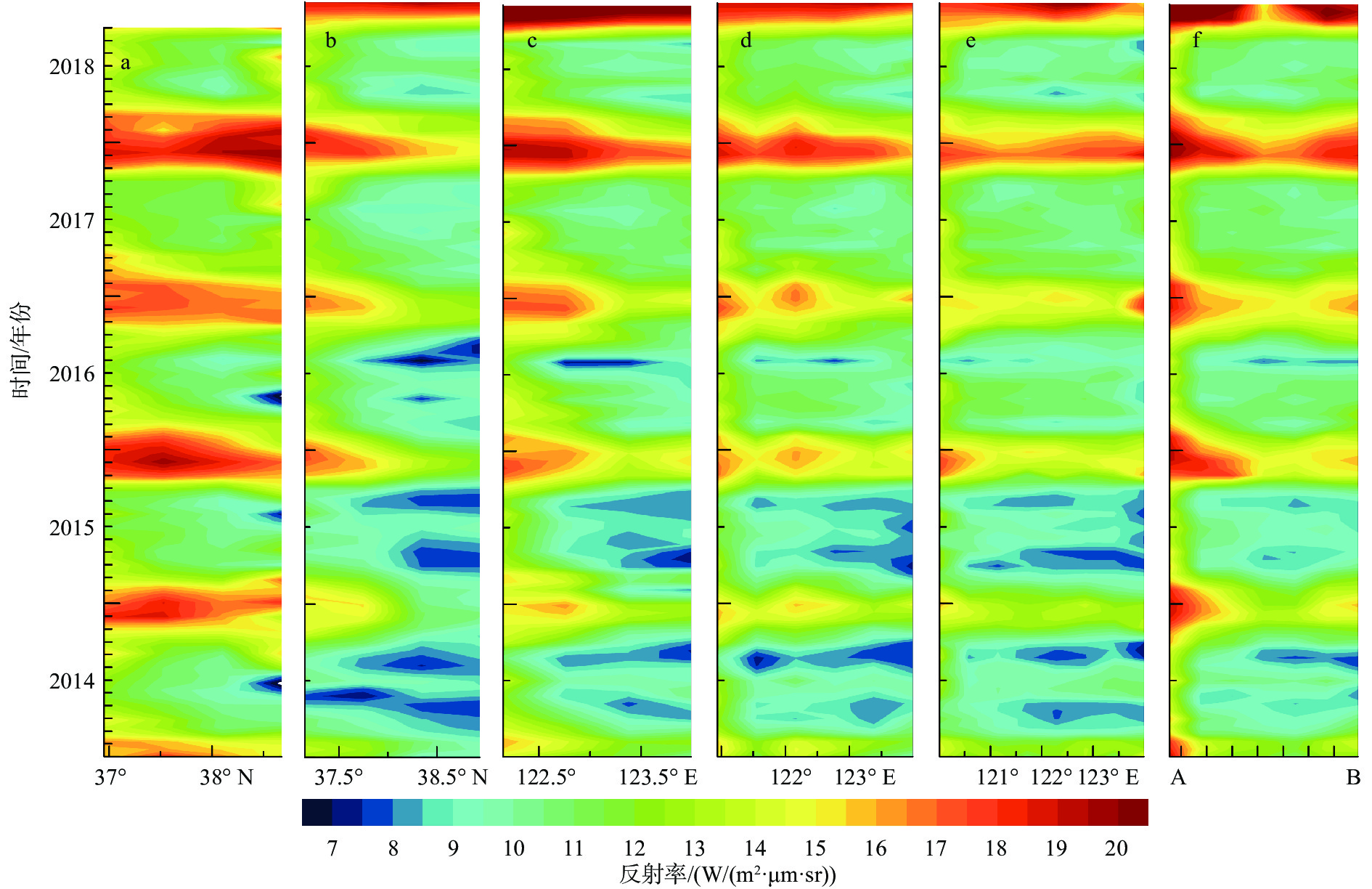
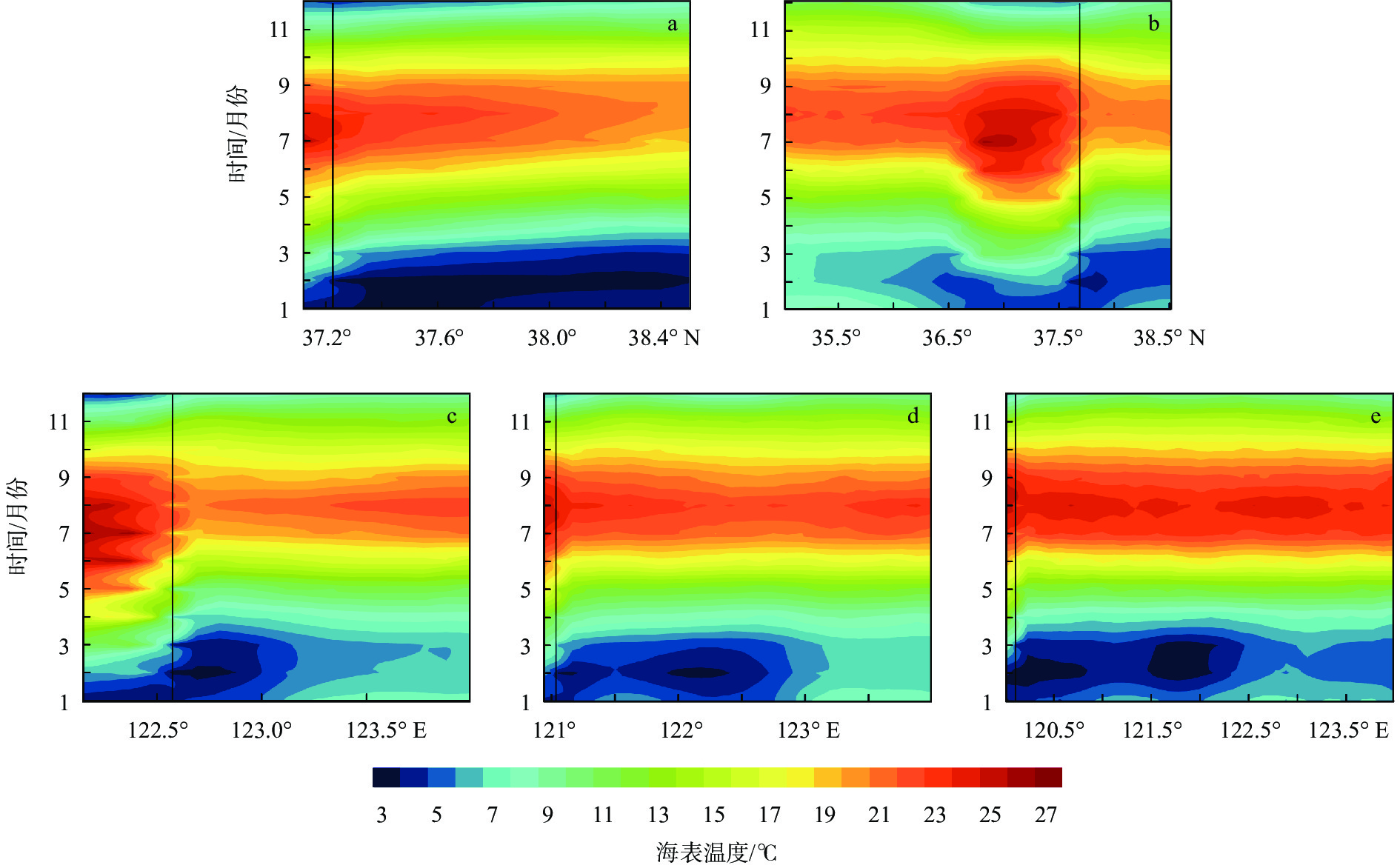
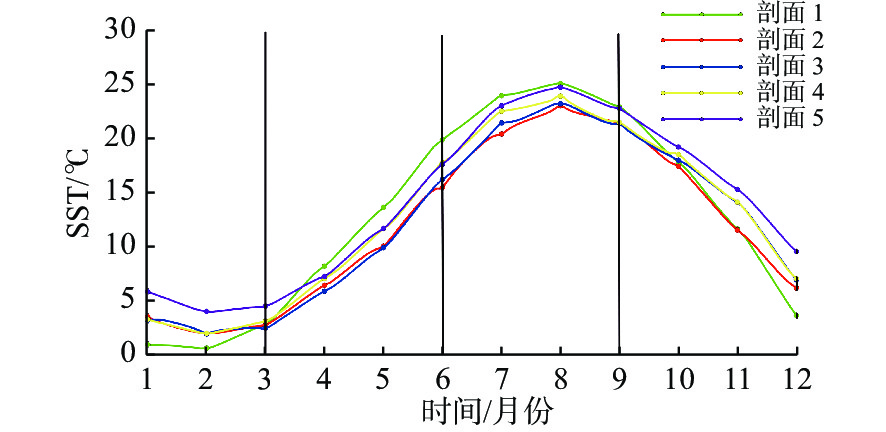
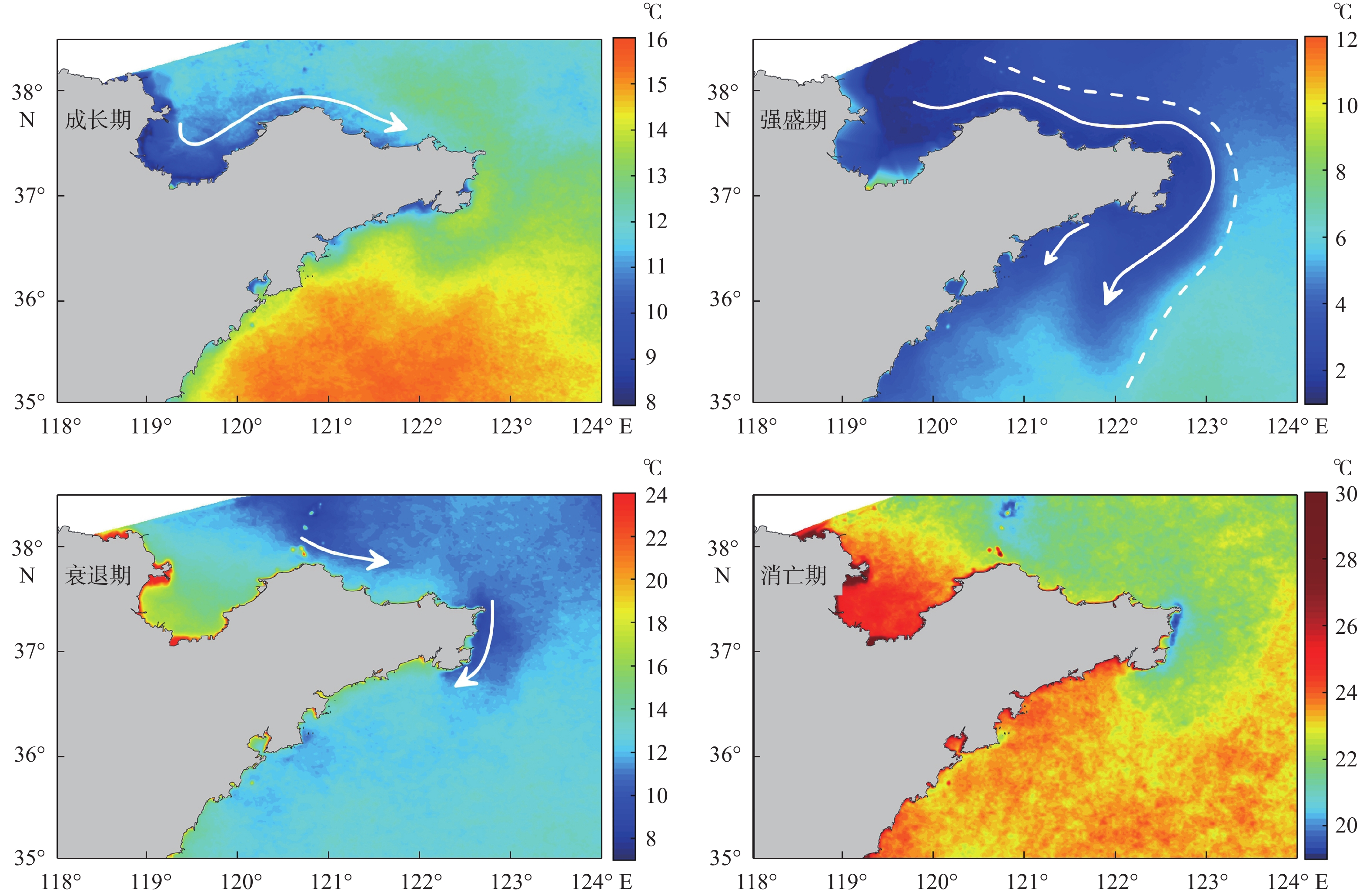
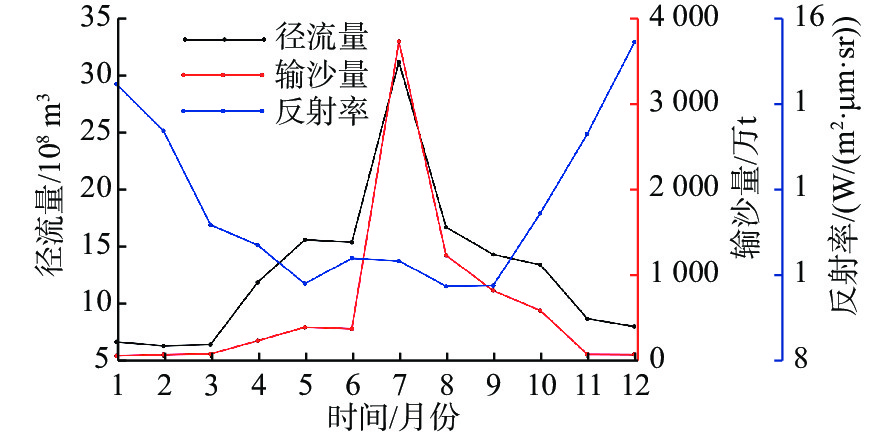
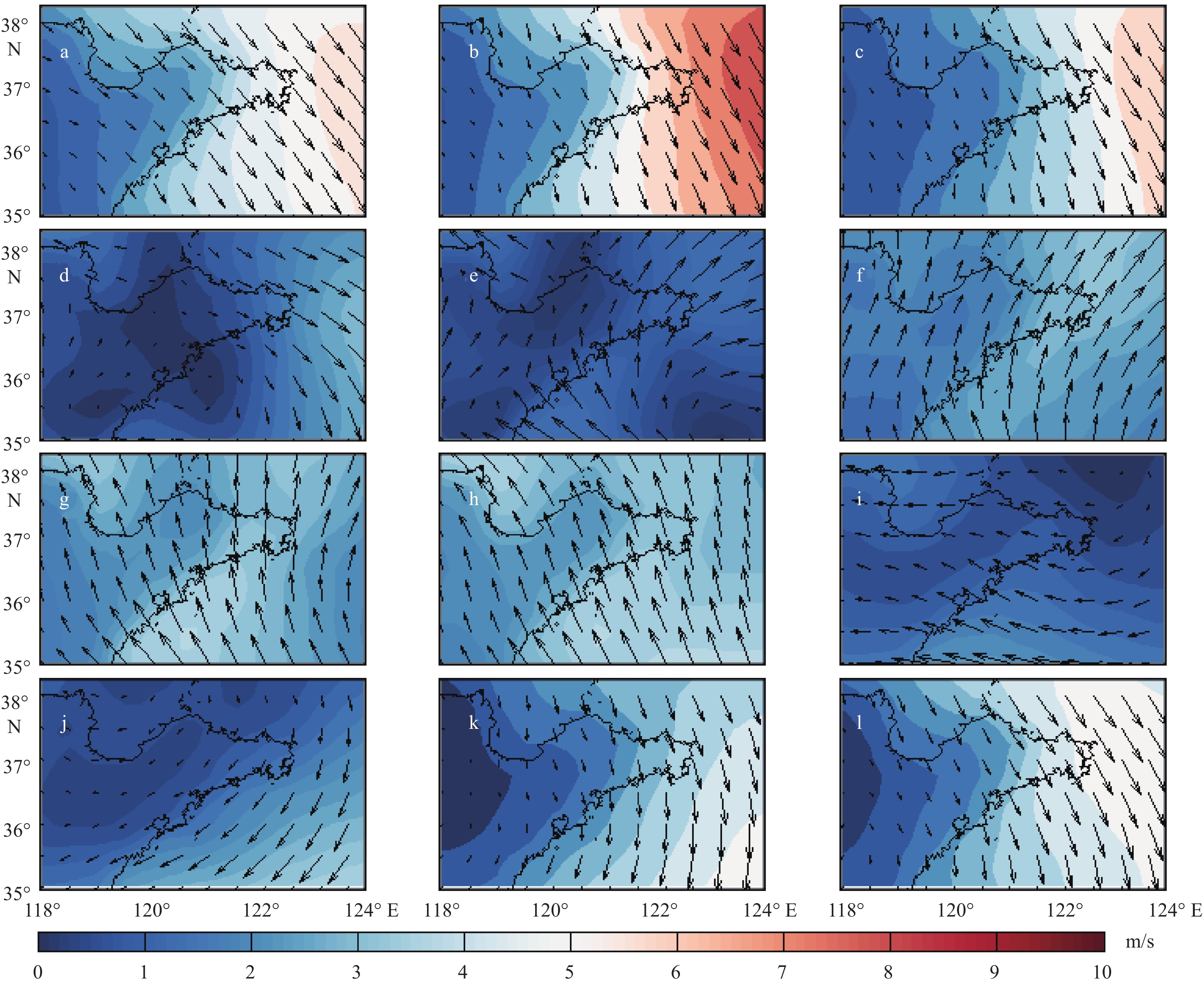
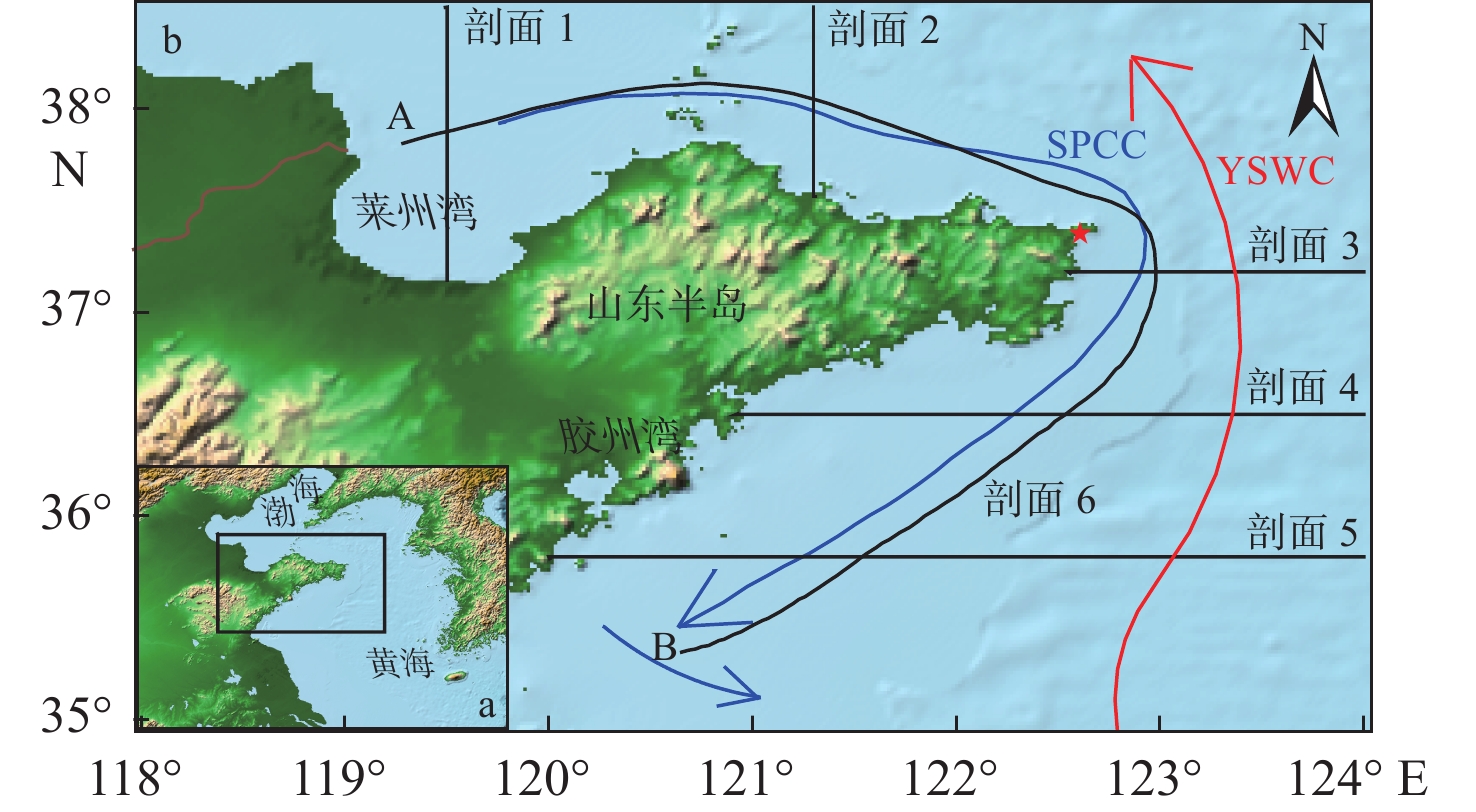
基于2014—2018年NOAA/AVHRR遥感数据,在山东半岛海域选取6条剖面,结合海表温度和表层悬浮体的时空变化特征,详细研究了山东半岛沿岸流的年周期变化规律与移动路径。研究结果表明,山东半岛沿岸流年周期变化可分为4个阶段:成长期(10—12月)时开始形成于黄河口附近,沿莱州湾南部向东运移;强盛期(次年1—3月)时山东半岛沿岸流完全成型,扩散带最宽,鼎盛时期北部可以至38°N附近,东部可以至123°E附近,在35°~36°N附近分成NE—SW向的2个分支,主干部分最远可到达胶州湾东部海域,余流沿岸向西南方向转折;衰退期(4—6月)时沿岸流强度减弱,只在山东半岛北部和东部小范围内有微弱的显示;消亡期(7—9月)时基本消失。山东半岛沿岸流在冬季时对悬浮体扩散具有强烈的驱动作用,使其在黄河口南侧与山东半岛北岸-成山头东部海域分别形成呈“弧形”和“条带状”分布的2个高浓度区域。
-
关键词:
- 山东半岛沿岸流 /
- NOAA/AVHRR /
- 海表温度 /
- 表层悬浮体
Abstract:Based on NOAA/AVHRR remote sensing data from 2014 to 2018, six sections were selected in the sea area around Shandong Peninsula, East China. Combined with the temporal and spatial variation characteristics of sea surface temperature and concentration of surface suspension matter, the annual periodic variation and movement path of the coastal current at the six sections were studied. Results show that the annual periodic variation of the coastal current along Shandong Peninsula could be divided into four stages. The first is the growth stage (October to December), during which coastal currents are originated near the Yellow River estuary and move eastward along the southern Laizhou Bay. The second is the mature stage (January to March of the next year), during which the coastal currents are fully formed, and had the widest diffusion zone reaching near 38°N in the north and 123°E in the east. Two branches from northeast to southwest near 35°~36°N could be recognized. The main part reached the eastern sea area of Jiaozhou Bay, and the residual current turned southwest. The third is the decline stage (April to June), during which the intensity of coastal currents weakened but showing only a small range in the north and east of Shandong Peninsula. The fourth is the extinction stage (July to September), and they largely disappeared. In winter, Shandong Peninsula coastal current had a strong driving effect on the diffusion of surface suspension, by which two high-concentration areas in the patterns of "arc" and "strip" distribution were formed in the south of the Yellow River Estuary, and in the area between the north shore of Shandong Peninsula and the east of Chengshantou, respectively.
-

-
[1] 张春桂,张星,曾银东,等. 台湾海峡海表面温度的遥感反演及精度检验[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2008,30(2):153-160. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2008.02.019
[2] YANG Z S,LIU J P. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2007,240(1):169-176.
[3] 杨作升,高文兵. 黄东海陆架悬浮体向其东部深海区输送的宏观格局[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),1992,14(2):81-90.
[4] 秦蕴珊,李凡,郑铁民,等. 南黄海冬季海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋科学,1986,10(6):1-7.
[5] 郑铁民,赵一阳,李凡,等. 南黄海夏季海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),1990,12(6):749-757.
[6] LIU X M,QIAO L L,ZHONG Y,et al. Pathways of suspended sediments transported from the Yellow River Mouth to the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2020,236:106639. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106639
[7] QIAO L L,ZHONG Y,WANG N,et al. Seasonal transportation and deposition of the suspended sediments in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea and the related mechanisms[J]. Ocean Dynamics,2016,66(5):751-766. doi: 10.1007/s10236-016-0950-2
[8] 王保铎. 夏、秋季黄海典型断面悬浮体分布特征及环境意义[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2013.
[9] 王勇智,乔璐璐,杨作升,等. 夏、冬季山东半岛东北部沿岸悬浮物输送机制的初步研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2012,17(5):49-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.05.008
[10] 王勇智,张永强,孙惠凤. 山东半岛东部海域悬浮体分布季节变化及其冬季输送通量研究[J]. 沉积学报,2019,37(3):541-549. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2018.169
[11] LU J,QIAO F L,WANG X H,et al. Modeling the Yellow River sediment flux and its deposition patterns under climatological conditions[J]. Ocean Dynamics,2013,63(6):709-722. doi: 10.1007/s10236-013-0626-0
[12] 孙湘平. 中国近海区域海洋学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2006.
[13] 乔方利. 中国区域海洋学-物理海洋学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2012.
[14] GUAN B X. Patterns and structures of the currents in Bohai, Huanghai and East China Seas[C]//ZHOU D, LIANG Y B, ZENG C K. Oceanology of China seas.Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1994: 17-26.
[15] 温国义,李广雪,赵东波,等. 根据AVHRRSST探讨中国北部海域冬季环流演变[J]. 海洋环境科学,2008,27(S2):19-23.
[16] 鲍献文,李娜,姚志刚,等. 北黄海温盐分布季节变化特征分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2009,39(4):553-562.
[17] 窦衍光,李军,杨守业. 山东半岛东部海域表层沉积物元素组成及物源指示意义[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2012,1(34):109-119.
[18] YUAN D L,ZHU J R,LI C,et al. Cross-shelf circulation in the Yellow and East China Seas indicated by MODIS satellite observations[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2008,70(1/2):134-149. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2007.04.002
[19] BIAN C,JIANG W S,QUAN Q,et al. Distributions of suspended sediment concentration in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea based on field surveys during the four seasons of 2011[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2013,121/122:24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.03.013
[20] 韦钦胜,于志刚,冉祥滨,等. 黄海西部沿岸流系特征分析及其对物质输运的影响[J]. 地球科学进展,2011,26(2):145-156.
[21] 藏政晨,王厚杰,薛佐,等. 黄海近岸锋面的时空变化及其对沉积物输运和沉积的影响[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2015,31(7):1-10. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2015.07001
[22] MASK A C,O'BRIEN J J,PRELLER R. Wind-driven effects on the Yellow Sea Warm Current[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,1998,103(C13):30713-30729. doi: 10.1029/1998JC900007
[23] 姜杰. 遥感技术在海岸带海洋地质环境综合调查中的应用[J]. 海洋地质动态,2006,22(5):30-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2006.05.008
[24] 李艳彬. 中红外数据反射信息反演研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学, 2018.
[25] 余伟豪. NOAA卫星同期观测数据综合分析及应用研究[D]. 廊坊: 防灾科技学院, 2019.
[26] 熊学军. 中国近海海洋: 物理海洋与海洋气象[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2012.
[27] 刘雪. 基于遥感的中国东部海域悬浮泥沙季节变化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[28] LIU X,LI G X,MA Y Y,et al. Distribution and diffusion of surface suspended matter off the East China Shore,2010[J]. Geological Journal,2016,51(S1):49-59.
[29] 王辉武,于非,吕连港,等. 冬季黄海暖流区的空间变化和年际变化特征[J]. 海洋科学进展,2009,27(2):140-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.02.003
[30] MARTIN J M,ZHANG J,SHI M C,et al. Actual flux of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment to the Western Pacific Ocean[J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research,1993,31(3):243-254. doi: 10.1016/0077-7579(93)90025-N
[31] 鲍献文,李真,王勇智,等. 冬、夏季北黄海悬浮物分布特征[J]. 泥沙研究,2010,15(2):48-56. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2010.02.009
[32] 刘传玉. 中国东部近海温度锋面的分布特征和变化规律[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2009.
-



 下载:
下载: