Geological structure of Zhusi Depression in ultra-deep water area on the continental margin of the northern South China Sea and its control on the development of source rocks
-
摘要:
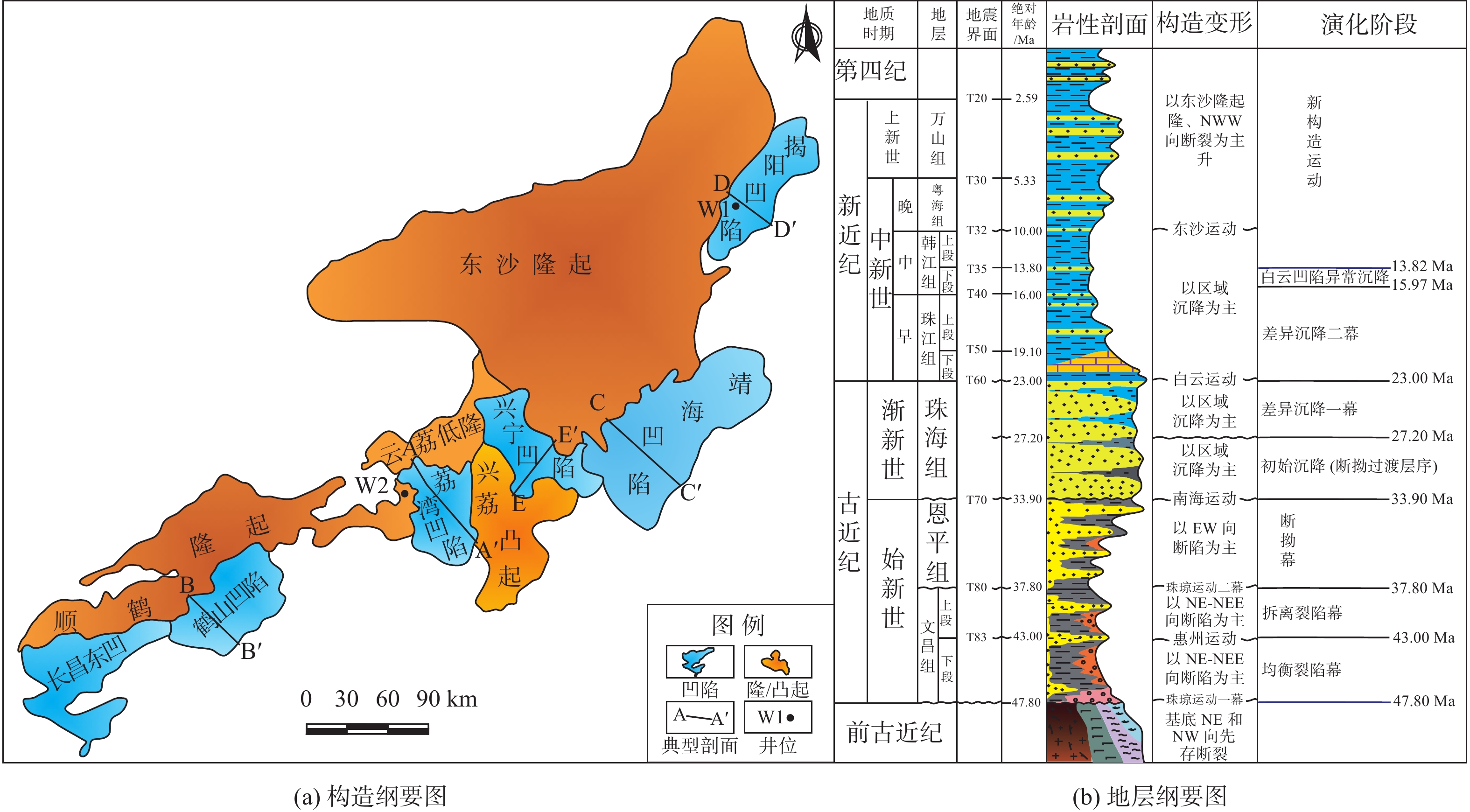
珠江口盆地珠四坳陷整体水深超过1 500 m,属极低勘探程度区域,钻井发现的油气显示证实了该区存在烃源岩。地震资料揭示古近系是主力烃源岩发育层系,沉积厚度及面积均较大。珠四坳陷作为南海北部向超深水迈进的油气勘探新区,其各凹陷的石油地质条件亟待剖析。在珠江口盆地6种断陷形成机制认识的基础上,通过对新采集地震资料的系统分析,将珠四坳陷划分大西洋贫岩浆型大陆边缘的壳间韧性流变型、大西洋富岩浆型大陆边缘的壳上岩浆底侵型、大西洋贫岩浆型大陆边缘的壳上先存拼合型3类断陷结构。运用2Dmove软件及去压实技术恢复各个洼陷沉降速率和伸展速率,结合大量地震剖面深入研究了珠四坳陷地质结构及其对烃源岩发育的影响,明确了不同断陷结构下烃源岩发育背景的差异,以此认为荔湾、鹤山凹陷烃源岩发育条件优越,可作为南海北部超深水地区的重要勘探突破点。
Abstract:The overall water depth of Zhusi Depression in the Pearl River Mouth Basin is more than 1500 m with very low degree of the exploration. The oil and gas revealed by drilling has shown the existence of source rocks in this area, and seismic data present a vast and thick source rocks in the Paleogene strata. As a new oil and gas exploration area marching towards ultra-deep water in the north of the South China Sea, we analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of petroleum geological conditions in each depression. Based on the knowledge of the formation mechanism of six types of fault depressions in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, Zhusi Depression were divided into three representative fault depression structural styles: inter crustal ductile rheological type of Atlantic magma-poor continental margin, supracrustal magmatic underplating type of Atlantic magma-rich continental margin, and pre-existing splicing type of supracrustal magmatic on Atlantic magma-poor continental margin. Using the 2Dmove software and decompaction technology, the subsidence rate and extension rate of each depression were restored. Combining a large number of seismic profiles, the geological structure of Zhusi Depression and its impact on the development of source rocks were studied in depth, and the differences of source rock development background under different fault depression structures were clarified. Results show that the development conditions of source rocks in Liwan and Heshan depressions are superior, which can be regarded as an important exploration breakthrough point in the ultra-deep water area in the north of the South China Sea.
-

-
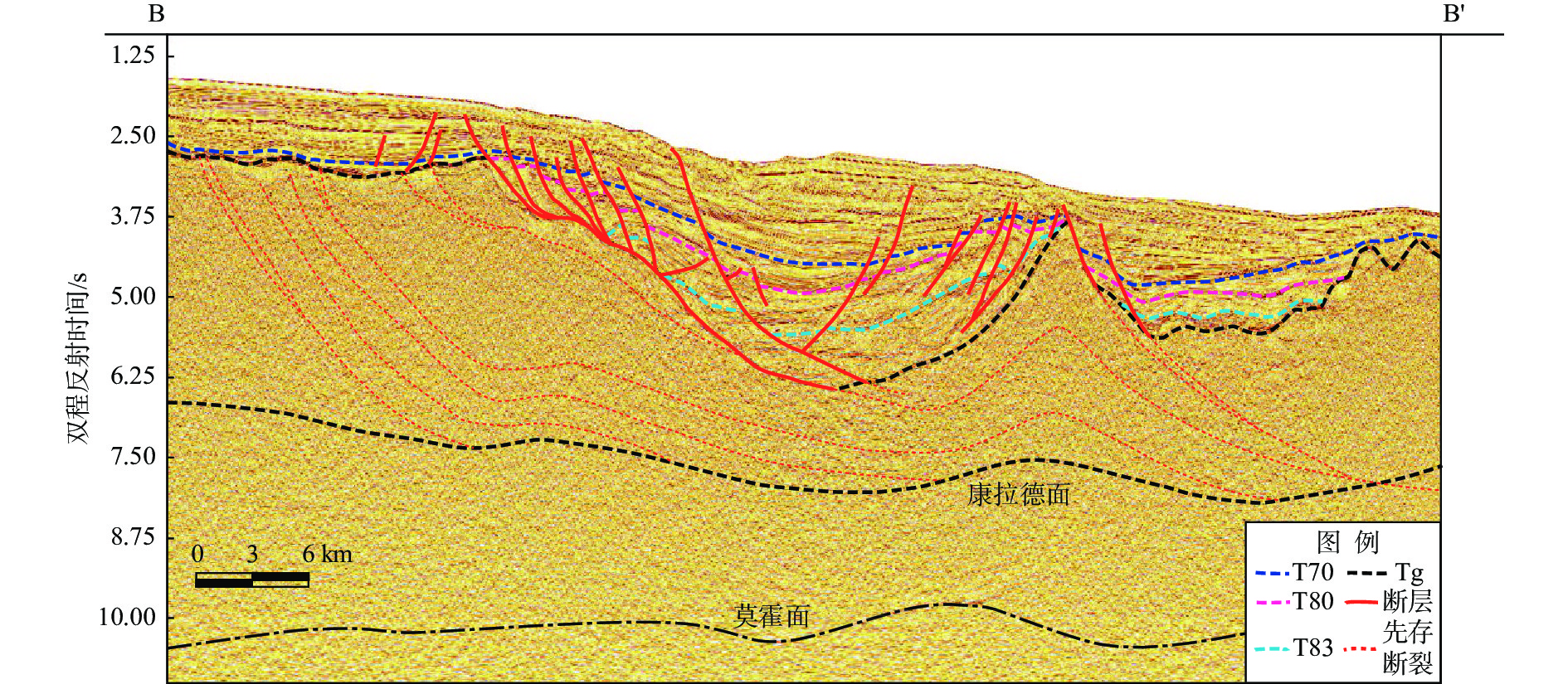
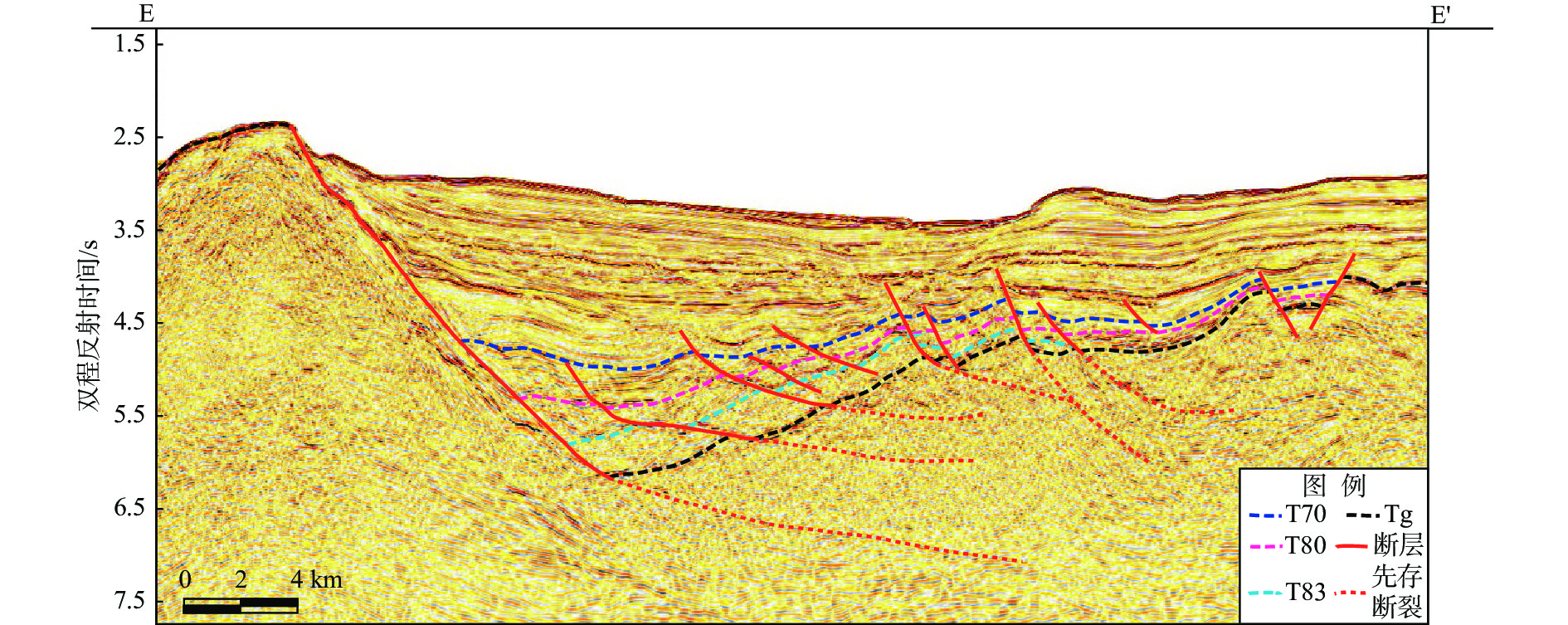
图 2 南海北部陆缘珠四坳陷断陷结构样式[11]
Figure 2.
表 1 珠四坳陷不同凹陷伸展沉降速率统计
Table 1. Statistics of extensional subsidence rates in different sags of Zhusi Depression
凹陷名称 凹陷结构 伸展速率/(m/Ma) 沉降速率/(m/Ma) 荔湾凹陷 壳间韧性流变型 425 371 鹤山凹陷 壳间韧性流变型 529 420 靖海凹陷 壳上岩浆底侵型 330 322 兴宁凹陷 壳上先存拼合型 193 218 揭阳凹陷 壳上先存拼合型 150 197 -
[1] 龚再升. 中国近海大油气田[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997.
[2] 朱伟林,郑金云. 南海北部深水油气新认识[J]. 科技导报,2020,38(18):89-98. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2020.18.014
[3] 吴婷婷,张丽丽,吴哲,等. 珠江口盆地前新生代先存断裂特征及动力背景:以惠州凹陷和番禺4洼为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(6):54-62.
[4] PERON-PINVIDIC G,MANATSCHAL G. The final rifting evolution at deep magma-poor passive margins from Iberia-Newfoundland:a new point of view[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences,2009,98(7):1581-1597. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0337-9
[5] MOHN G,MANATSCHAL G,BELTRANDO M,et al. Necking of continental crust in magma-poor rifted margins:evidence from the fossil Alpine Tethys margins[J]. Tectonics,2012,31(1):1-28.
[6] SUTRA E,MANATSCHAL G,MOHO G,et al. Quantification and restoration of extensional deformation along the Western Iberia and Newfoundland rifted margins[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2013,14(8):2575-2597.
[7] 贾培蒙,张向涛,陈维涛,等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷惠州21古潜山的形成演化及其对深层油气成藏的控制[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(12):27-37. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.187
[8] 庞雄,施和生,朱明,等. 再论白云深水区油气勘探前景[J]. 中国海上油气,2014,26(3):23-29.
[9] 朱筱敏,葛家旺,赵宏超,等. 陆架边缘三角洲研究进展及实例分析[J]. 沉积学报,2017,35(5):945-955.
[10] 庞雄,任建业,郑金云,等. 陆缘地壳强烈拆离薄化作用下的油气地质特征:以南海北部陆缘深水区白云凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(1):27-39. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.01.03
[11] 庞雄,郑金云,梅廉夫,等. 先存俯冲陆缘背景下珠江口盆地断陷结构的多样性[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(4):1-11.
[12] 任建业,庞雄,雷超,等. 被动陆缘洋陆转换带和岩石圈伸展破 裂过程分析及其对南海陆缘深水盆地研究的启示[J]. 地学前缘,2015,22(1):102-114.
[13] 孙珍,刘思青,庞雄,等. 被动大陆边缘伸展-破裂过程研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报,2016,35(1):1-16. doi: 10.11978/2015030
[14] 任建业,庞雄,于鹏,等. 南海北部陆缘深水-超深水盆地成因机制分析[J]. 地球物理学报,2018,61(12):4901-4920. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0558
[15] 庞雄,陈长民,彭大钧,等. 南海北部白云深水区之基础地质[J]. 中国海上油气,2008,20(4):215-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2008.04.001
[16] 米立军,张向涛,庞雄,等. 珠江口盆地形成机制与油气地质[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(s1):1-10. doi: 10.7623/syxb2019S1001
[17] 李洪博,郑金云,庞雄,等. 南海北部陆缘差异拆离作用结构样式与控制因素:以珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2020,32(4):24-35.
[18] 施和生,杜家元,梅廉夫,等. 珠江口盆地惠州运动及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(3):1-15.
[19] 梁杰,刘培,陈维涛,等. 适用于改造型洼陷的烃源规模识别技术:以西江主洼为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(6):78-87.
[20] 刘培,蒋有录,刘华,等. 渤海湾盆地沾化凹陷断层活动与新近系油气成藏关系[J]. 天然气地球科学,2013,24(3):541-547.
[21] 张功成. 南海北部陆坡深水区构造演化及其特征[J]. 石油学报,2010,31(4):528-533. doi: 10.7623/syxb201004002
[22] 赵中贤,周蒂,廖杰,等. 珠江口盆地陆架区岩石圈伸展模拟及裂后沉降分析[J]. 地质学报,2010,84(8):1135-1145.
-



 下载:
下载: