Influence of reduced sediment supply on the particle size distribution on tidal flats of the Yellow River Delta: a physical experimental study
-
摘要:
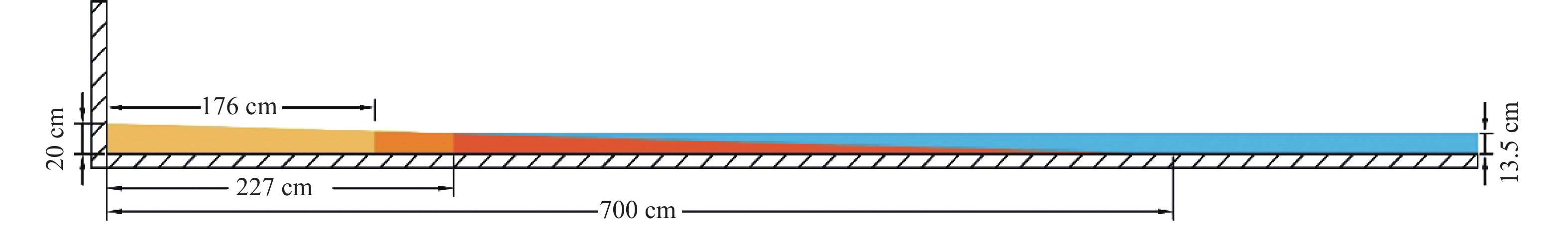
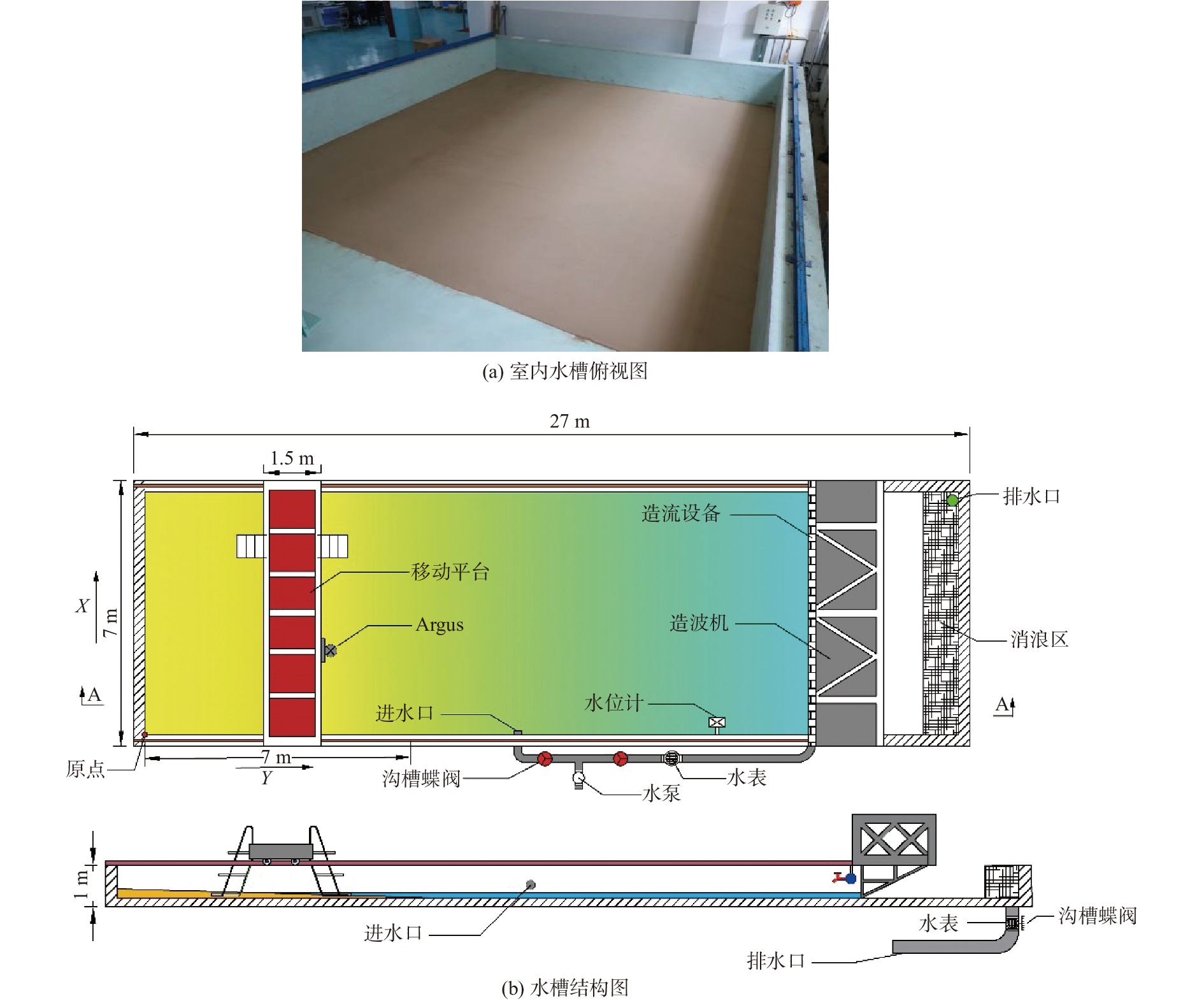
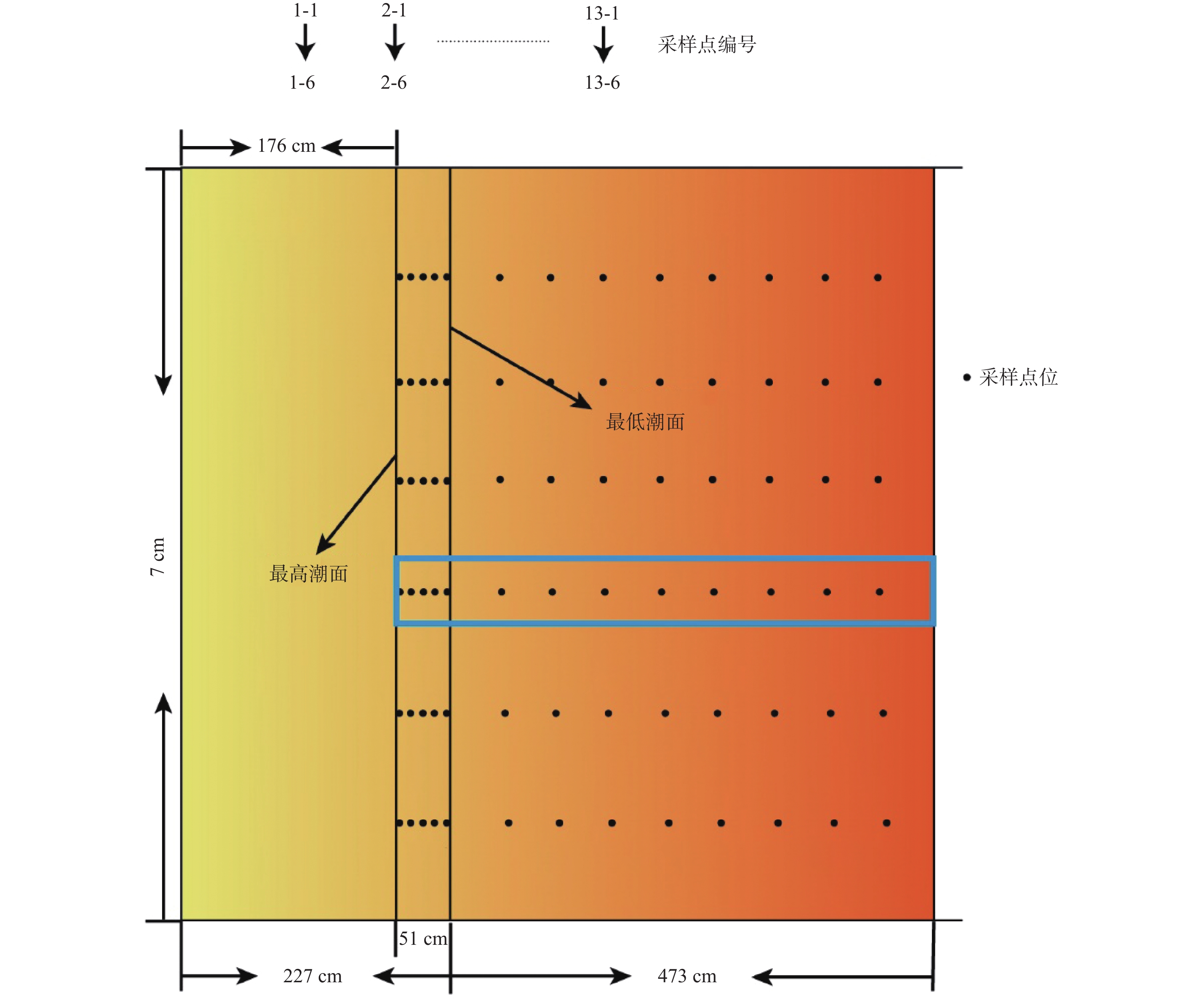
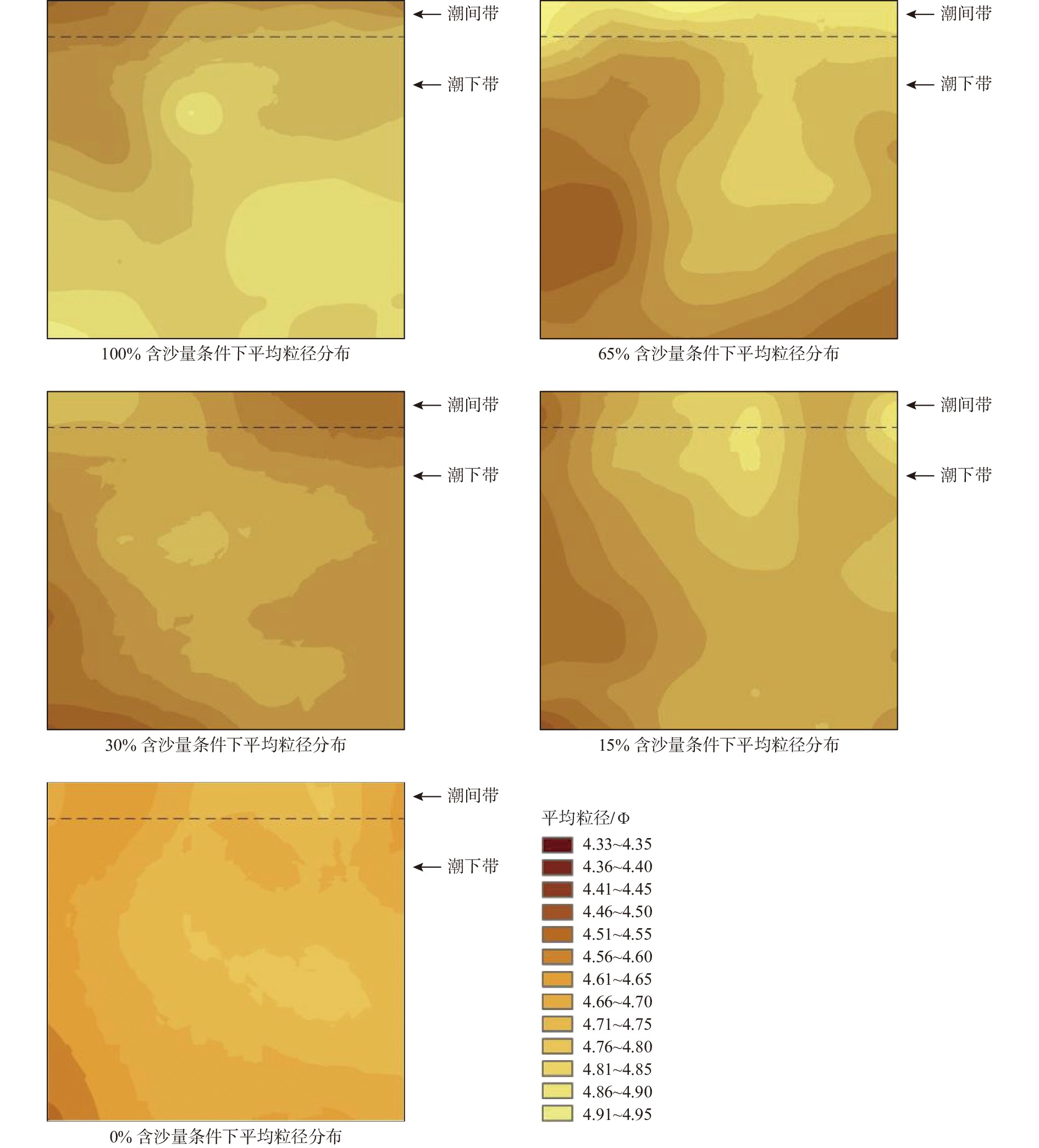
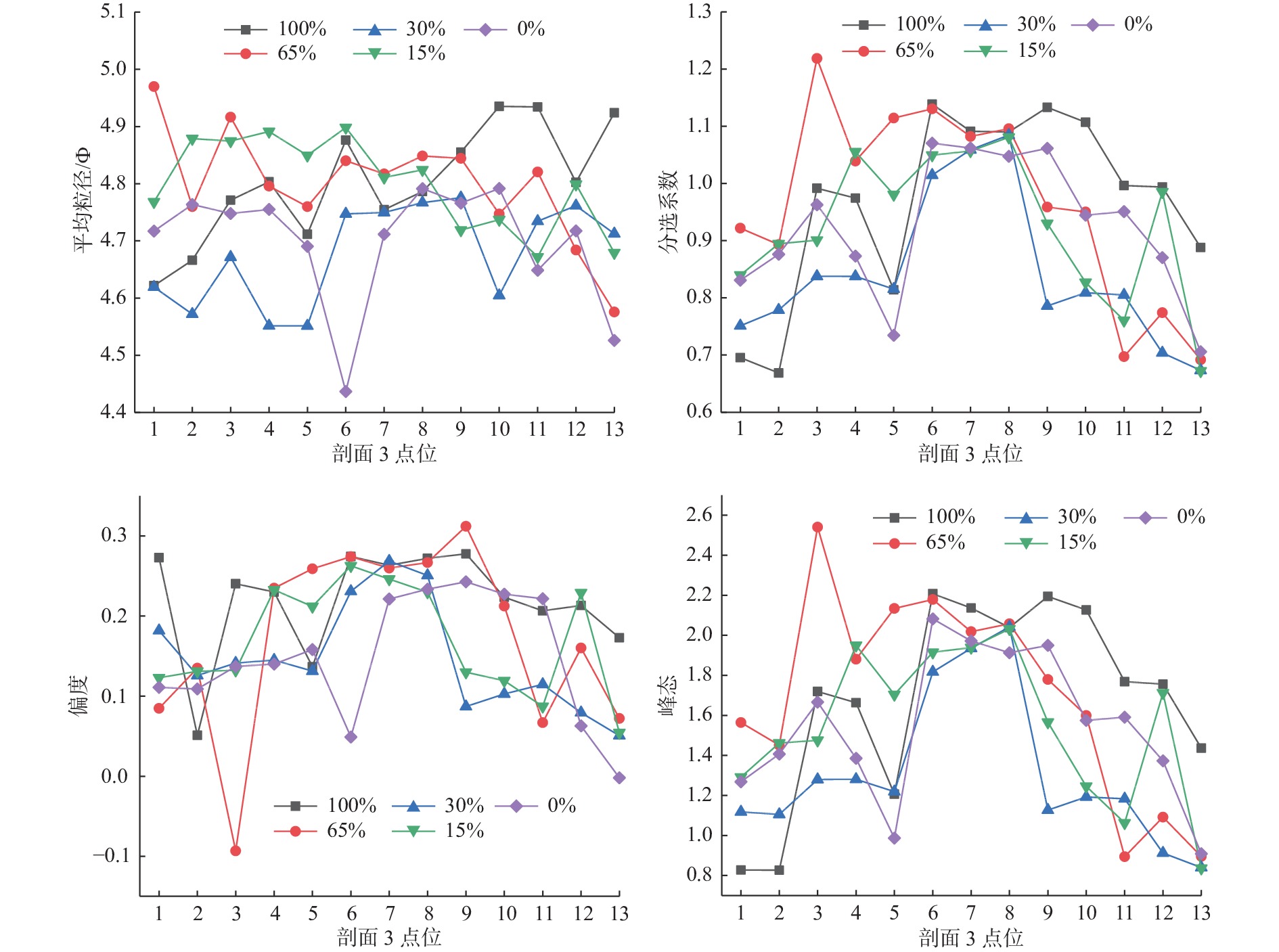
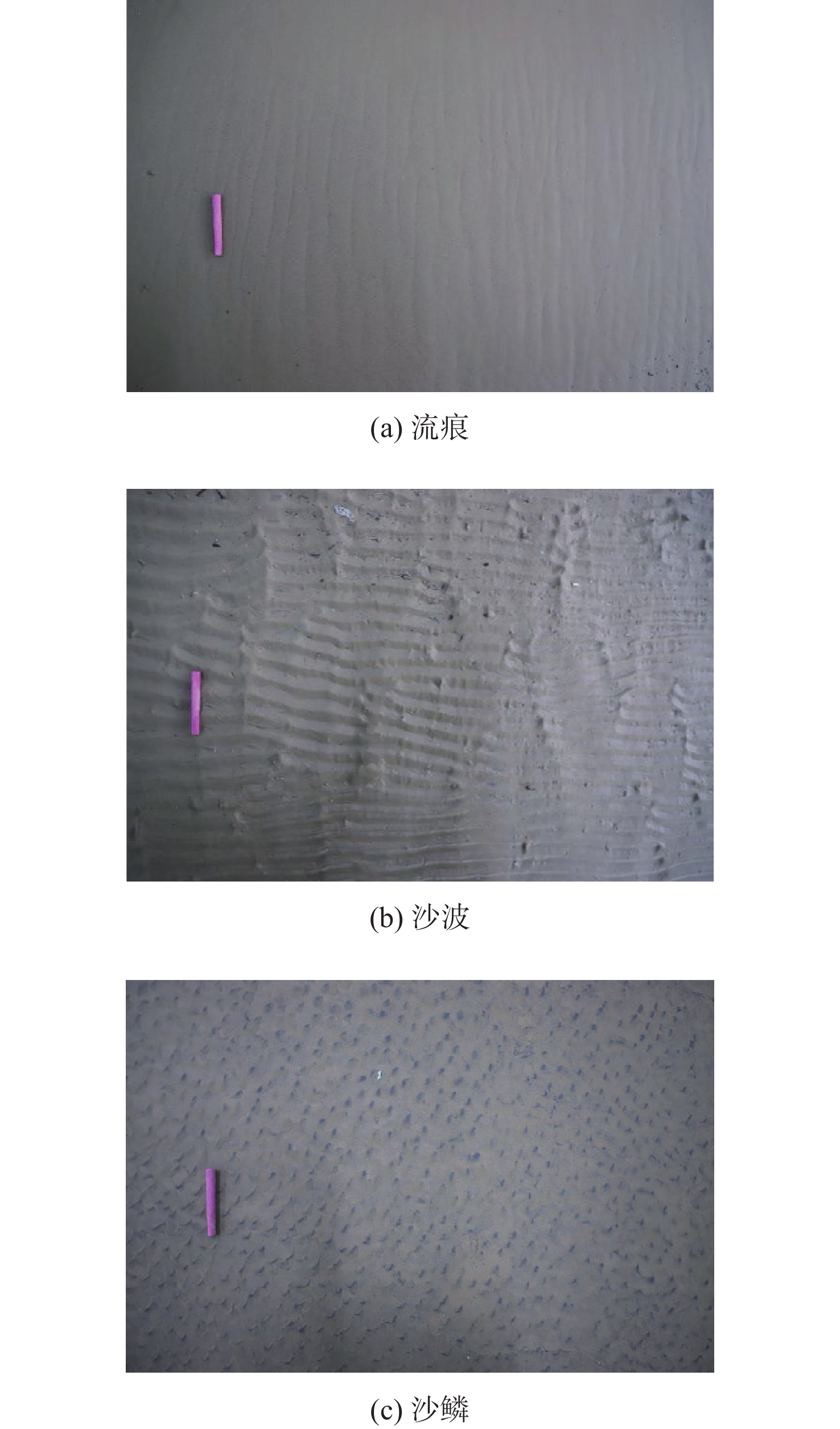
为探究不同悬沙浓度下潮滩粒度特征的变化,对黄河三角洲潮滩进行了物理模拟实验。使用采自研究区的潮滩表层沉积物,设定与实际潮滩尺寸按比例缩小的室内水槽以及波浪潮汐动力模拟,对不同悬沙浓度条件(0~14.9 kg/m3)下的模拟“潮滩”进行粒度分析。结果表明,随着悬沙浓度的减少,潮滩粒度特征发生了明显变化。随着含沙量的减少,整个潮滩的细颗粒沉积物分布范围减小,总体上沉积物呈现粗化特征,但颗粒较大的极粗粉砂的分布同样减少;在不同含沙量条件下,分选系数、偏度和峰度均值总体呈现出潮下带上部高、潮间带和潮下带下部低的特征,反映了模拟的潮间带上部和潮下带前缘的分选较潮滩中部更好的特征。含沙量的变化同样影响了模拟潮滩的微地貌形态,随着含沙量的降低,潮滩微地貌逐渐侵蚀破碎。潮滩物理模型实验有助于快速再现潮滩冲淤形态和变化特征,使特定条件下潮滩的变化具备可预见性,从而为人类有针对性地进行生产活动提供参考。
Abstract:To explore the variation of grain size distribution in tidal flat under different suspended sediment concentrations, physical simulation experiments in flume were conducted for tidal flat of the Yellow River Delta. With the sediments (15 t) collected from the tidal flat surface in the field, an indoor flume was designed in a scaled-down size proportional to the real case, in which wave/tidal dynamic parameters were set, and the grain size distributions under different suspended sediment concentrations (0~14.9 kg/m3) were measured and analyzed. Results show that the characteristics of grain size distribution of tidal flat changed obviously with the decrease of suspended sediment concentration. With the decrease of sediment concentration, the distribution range of fine-grained sediments in the whole “tidal flat” decreased in a general coarsening trend; however, that of very coarse particles also decreased. Under different sediment concentrations, the average sorting coefficient, skewness, and kurtosis were generally greater in the upper intertidal zone than those in the intertidal zone and the lower subtidal zone, reflecting better sorting in the upper intertidal zone and the frontal subtidal zone than in the middle tidal flat. In addition, with the decrease in sediment concentration, the micro-topography of the “tidal flat” was gradually eroded and broken. This physical model experiment of tidal flat is able to reproduce quickly the variation in topography of erosion and deposition under different sand supplies and parameters, with which any changes of tidal flat under specific conditions can be simulated for better prediction in real cases as a reference for safe operation of human activities in similar tidal flat areas.
-
Key words:
- grain size /
- sedimentary dynamics /
- sedimentary environment /
- Yellow River Delta
-

-
表 1 不同含沙量条件下沉积物的各粒级分布
Table 1. Distribution of sediment grain size under different sand content conditions
/% 含沙量 极粗砂 粗砂 中砂 细砂 极细砂 粗粉砂 中粉砂 细粉砂 极细粉砂 黏土 100%
含沙量范围
均值0~5.4
0.100~0.74
0.050~0.46
0.050~0.85
0.3011.45~28.14
17.2237.59~55.46
43.7014.96~34.59
27.850.04~9.08
4.820~3.37
2.020.58~3.3
2.0665%含沙量 范围
均值0~3.97
0.150~1.21
0.050~2.86
0.070~3.78
0.338.16~24.85
17.1734.78~54.97
46.1818.57~39.07
27.800.27~10.94
3.710~2.60
1.360.68~2.73
1.6130%含沙量 范围
均值0~1.05
0.040~0.63
0.040~0.54
0.050~0.75
0.2110.7~27.48
18.9442.07~55.99
47.6116.61~33.72
26.350.13~6.21
3.050~2.53
1.270.62~2.38
1.2215%含沙量 范围
均值0~3.81
0.220~0.89
0.090~2.68
0.190~1.31
0.368.51~25.91
17.9738.97~53.3
44.9120.28~35.06
26.980.58~8.19
4.140.92~2.98
1.950.83~2.81
1.630%含沙量 范围
均值0~1.82
0.180~1.1
0.120~2.2
0.210~7.05
0.6010.45~30.6
18.4837.1~54.88
45.6212.98~32.88
26.050~5.93
3.590~2.6
1.910.6~2.46
1.67表 2 不同含沙量条件下沉积物粒度参数
Table 2. Indicators of particle size distribution under different sand concentrations
含沙量 平均粒径/Ф 分选系数 偏度 峰态 100% 范围
均值4.46~5.08(4.76) 0.64~1.36
(0.95)0.05~0.44
(0.20)0.77~2.26
(1.62)65% 范围
均值4.45~5.18(4.75) 0.65~1.22
(0.90)-0.09~0.40
(0.16)0.66~2.54
(1.50)30% 范围
均值4.35~4.92(4.67) 0.60~1.23
(0.87)-0.10~0.31
(0.15)0.68~2.52
(1.39)15% 范围
均值4.33~5.02(4.72) 0.62~1.14
(0.89)0.08~0.30
(0.23)0.71~2.23
(1.44)0% 范围
均值4.31~4.84(4.68) 0.60~1.10
(0.91)0.00~0.30
(0.17)0.67~2.13
(1.51) -
[1] 张云峰,张振克,张华兵,等. 长江口启东嘴潮滩沉积特征及对人类活动的响应[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2021,43(3):62-69.
[2] 王庆,王小鲁,李雪艳,等. 黄河三角洲南部废弃三角洲潮间滩涂表层沉积粒度特征及其粗化现象[J]. 第四纪研究,2017,37(2):353-367. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2017.02.13
[3] 杨立建,马小川,贾建军,等. 近百年来黄河改道及输沙量变化对山东半岛泥质楔沉积物粒度特征的影响[J]. 海洋学报,2020,42(1):78-89.
[4] 戴仕宝,杨世伦,郜昂,等. 近50年来中国主要河流入海泥沙变化[J]. 泥沙研究,2007(2):49-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2007.02.008
[5] 李贺,黄翀,张晨晨,等. 1976年以来黄河三角洲海岸冲淤演变与入海水沙过程的关系[J]. 资源科学,2020,42(3):486-498. doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.03.07
[6] 李松,王厚杰,张勇,等. 黄河在调水调沙影响下的入海泥沙通量和粒度的变化趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2015,31(7):20-27.
[7] 袁萍,毕乃双,吴晓,等. 现代黄河三角洲表层沉积物的空间分布特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(2):49-57.
[8] MURALI R M, RESHMA K N, KUMAR S S, et al. Spatio-temporal coastal morphological changes of Godavari Delta region in the east coast of India. 2020, 95(sp1): 626-631.
[9] 司月君,李保生,李志文,等. 北部湾海岸现代风沙与海滩沙粒度特征对比[J]. 中国沙漠,2020,40(6):43-52.
[10] 唐丽,董玉祥. 华南海岸现代风成沙与海滩沙的粒度特征差异[J]. 中国沙漠,2015,35(1):14-23. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2014.00114
[11] 周曾,陈雷,林伟波,等. 盐沼潮滩生物动力地貌演变研究进展[J]. 水科学进展,2021,32(3):470-484.
[12] 伊锋,李雪艳,许国纯,等. 潮滩干湿转换的地貌发育物理模型及动力机制[J]. 海洋通报,2020,39(3):372-380.
[13] PENG J,CHEN S,DONG P. Temporal variation of sediment load in the Yellow River basin,China,and its impacts on the lower reaches and the river delta[J]. Catena,2010,83(2/3):135-147.
[14] 岳保静,廖晶,高茂生,等. 山东半岛砂质海滩动力地貌演化特征[J]. 海洋科学,2017,41(4):118-127. doi: 10.11759/hykx20161107001
[15] HOITINK A J F,WANG Z B,VERMEULEN B,et al. Tidal controls on river delta morphology[J]. Nature Geoscience,2017,10(7):637-645.
[16] 王爱军,陈坚. 厦门吴冠海岸潮间带沉积物粒度特征及其沉积动力学涵义[J]. 热带海洋学报,2006,25(6):28-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2006.06.005
[17] 周良勇,李安龙,龚淑云,等. 黄河口附近海域表层悬浮体分布及粒度特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2007,27(5):33-38.
[18] 伊锋. 黄河入海泥沙减少对潮滩地貌冲淤影响的物理模型研究[D]. 烟台: 鲁东大学, 2020.
[19] 高抒. 潮滩沉积记录正演模拟初探[J]. 第四纪研究,2007,27(5):750-755. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.05.016
[20] FOLK P I,WARD W D. Brazos River bar:a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1957,27(1):3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[21] FAJAR Y,SUWARSONO,TAUFIK M,et al. Analysis of the dynamics of coastal landform change based on the integration of remote sensing and GIS techniques:implications for tidal flooding impact in Pekalongan,central Java,Indonesia[J]. Quaestiones Geographicae,2019,38(3):17-29. doi: 10.2478/quageo-2019-0025
[22] 张海平,周星星,代文. 空间插值方法的适用性分析初探[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2017,33(6):14-18,105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2017.06.003
[23] 张长宽,黄婷婷,陶建峰,等. 江苏海岸潮滩剖面形态与动力泥沙响应关系[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(3):245-251. doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2020.03.009
[24] 王俊辉,姜在兴,张元福,等. 三角洲沉积的物理模拟[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2013,34(6):758-764. doi: 10.11743/ogg20130607
[25] 戴仕宝,杨世伦,蔡爱民. 51年来珠江流域输沙量的变化[J]. 地理学报,2007,62(5):545-554. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2007.05.011
[26] 陈静,赵宝成,战庆. 长江口水下三角洲北部近百年沉积物粒度组成及其对水动力环境的响应[J]. 沉积学报,2014,32(4):692-699.
[27] 张我华,蔡袁强,吴昌灿. 岸滩侵蚀的环境工程观念[J]. 安全与环境学报,2002,2(3):8-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2002.03.002
-



 下载:
下载: