Enrichment and influencing factors of fluid-mobile elements in breccia serpentinite from serpentinite mud volcanoes in Mariana Forearc
-
摘要:
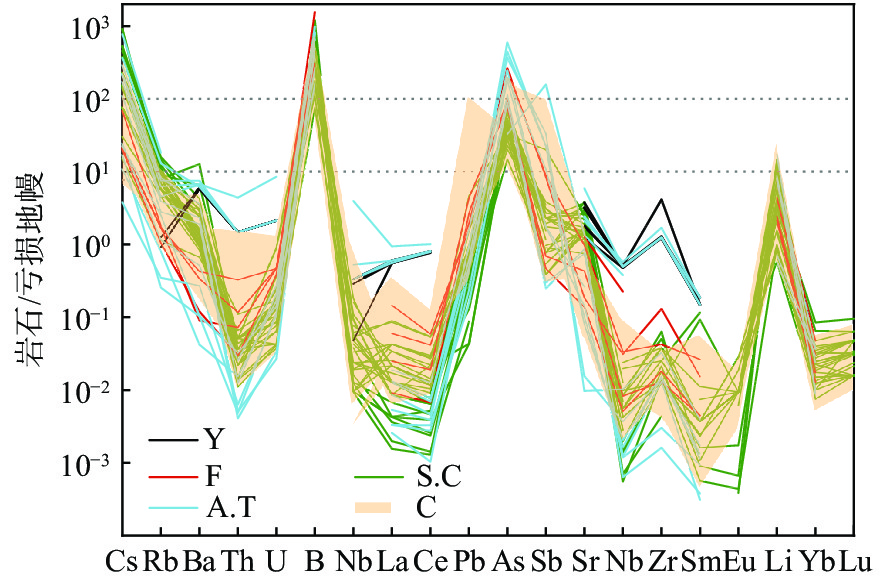
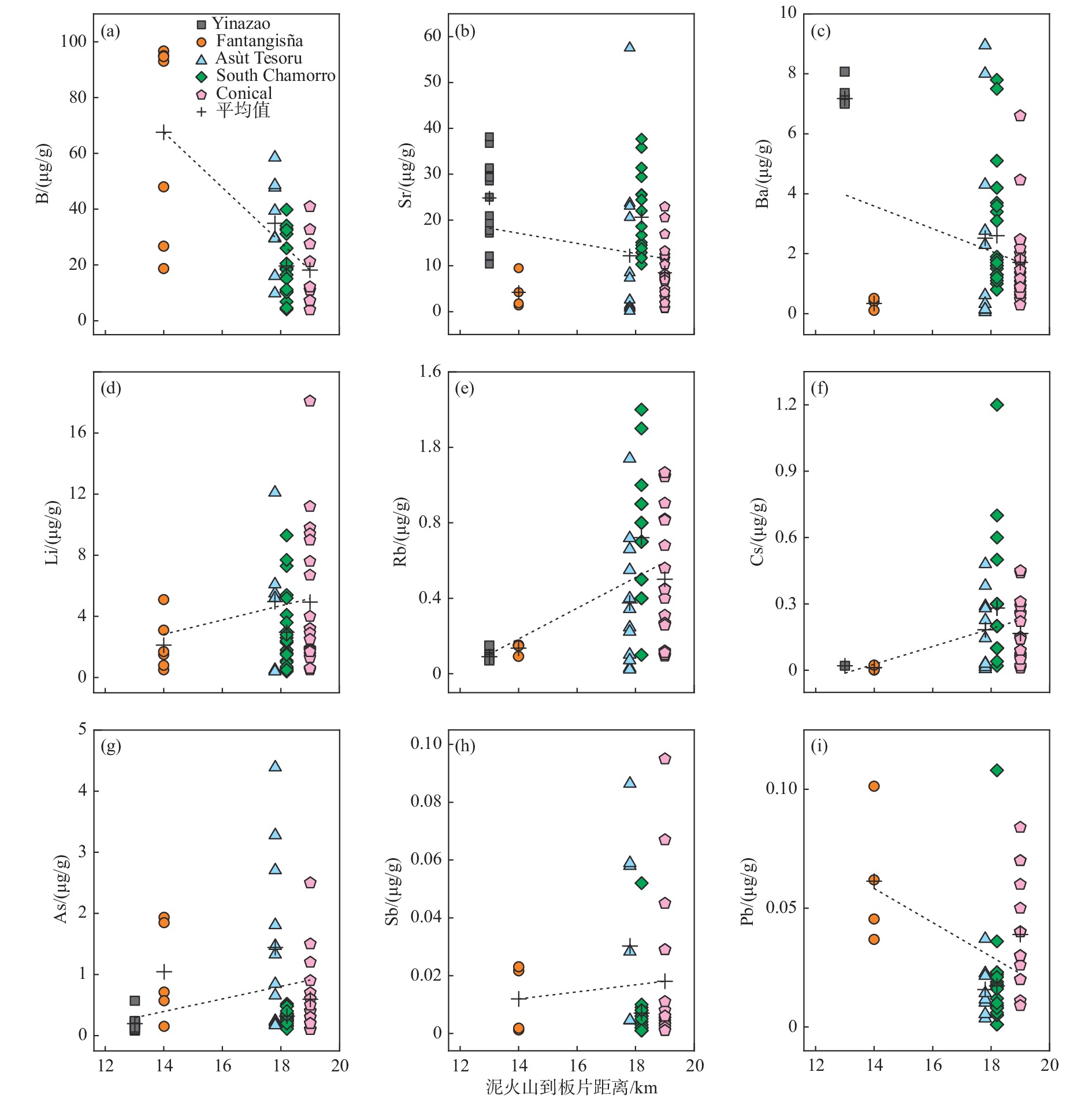
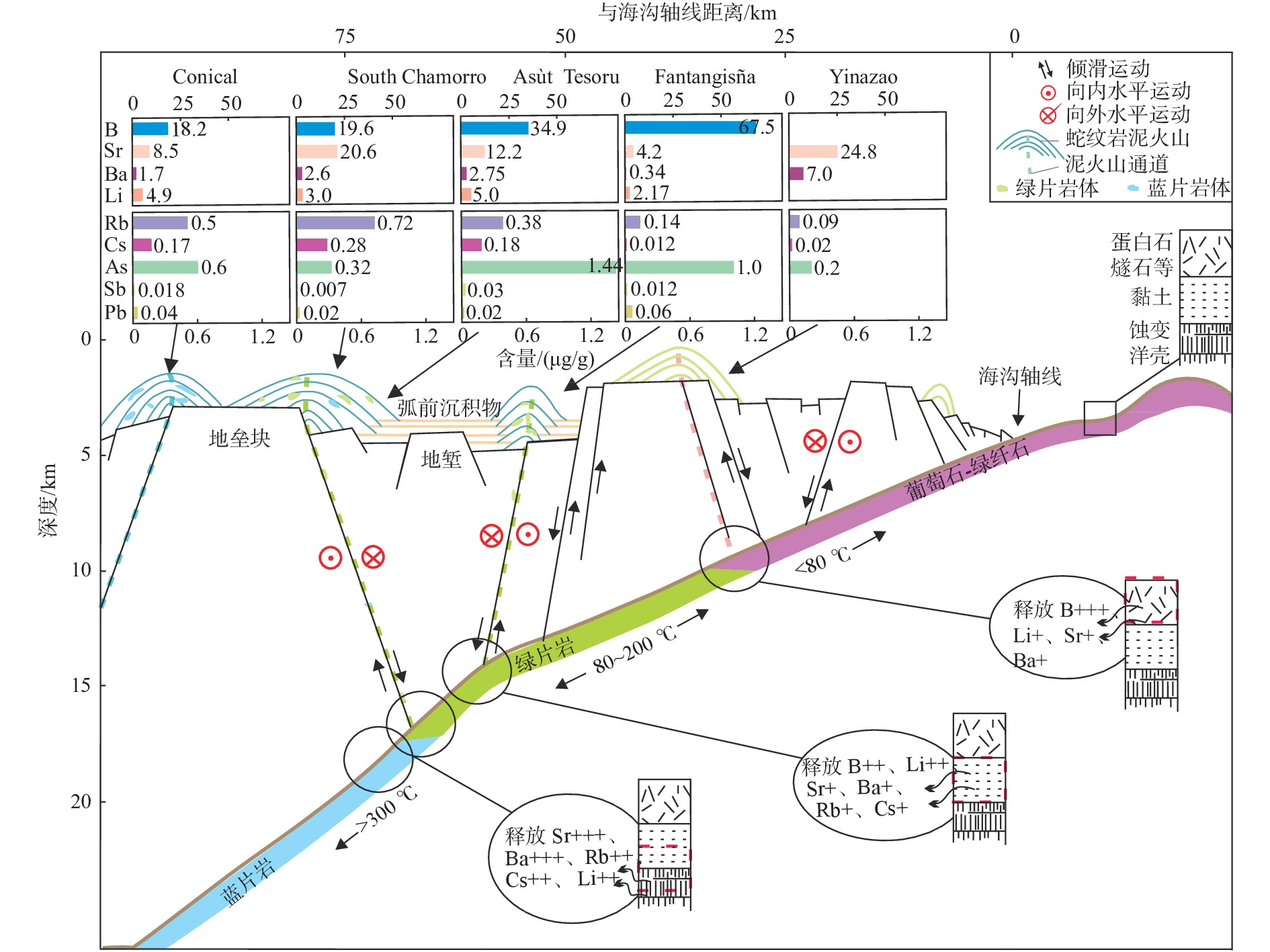
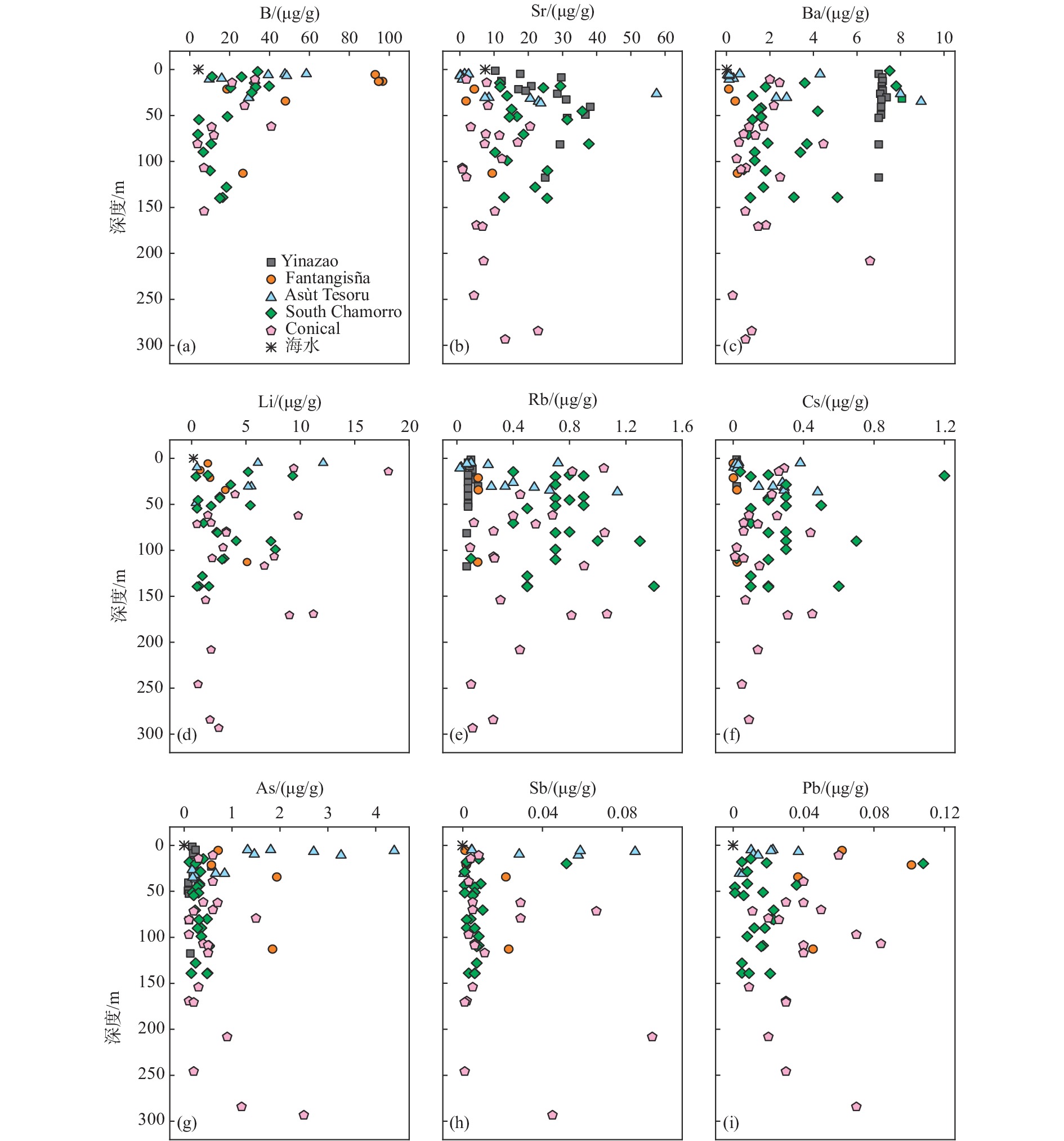
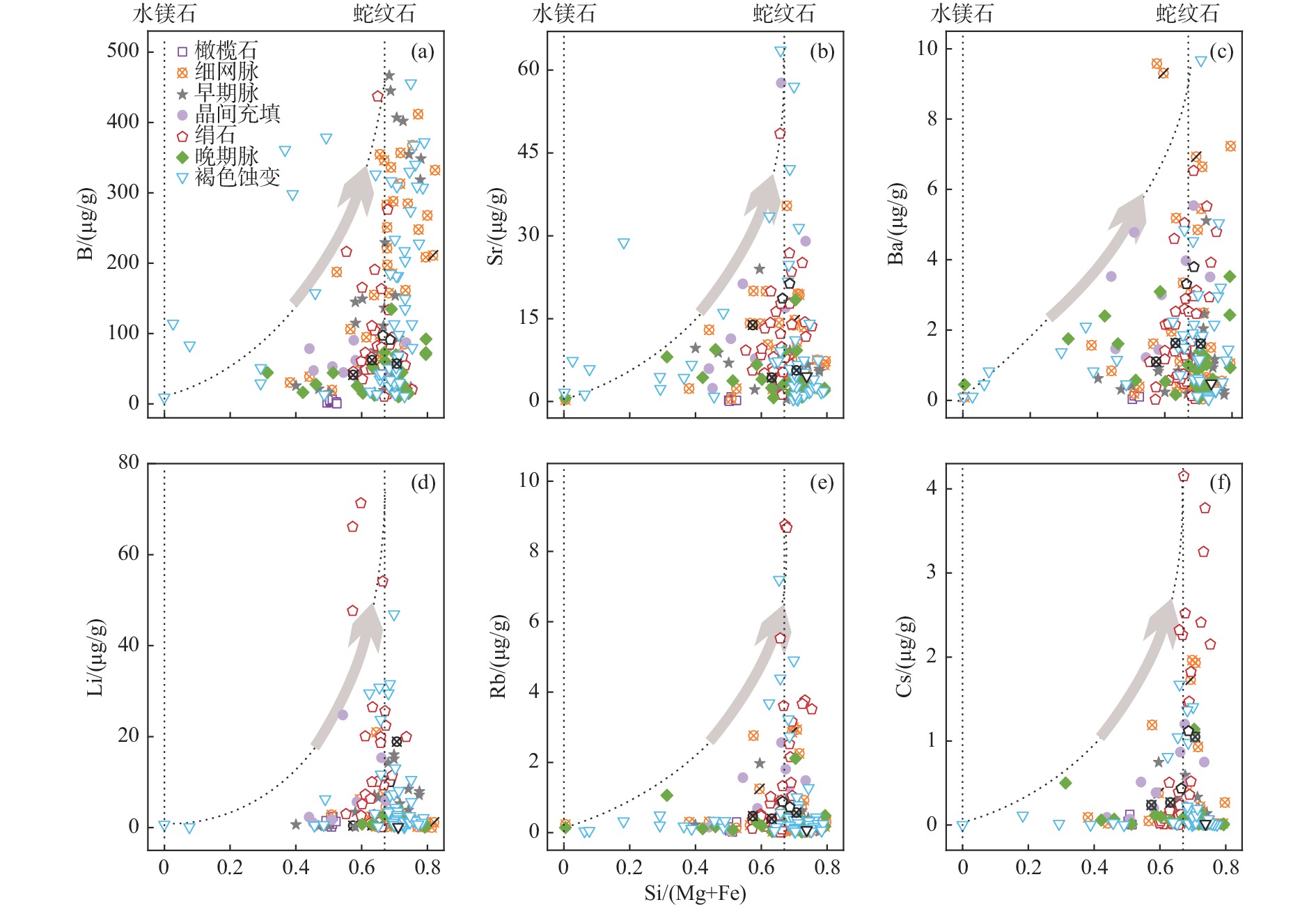
马里亚纳弧前蛇纹岩泥火山被认为是认识俯冲作用的直接窗口,其发育的角砾状蛇纹岩富含的流体流动性元素(FMEs)记录了引起蛇纹石化作用的流体和俯冲带的流体-岩石相互作用及元素循环等信息。本文整理了马里亚纳弧前物源深度逐渐增加的5座蛇纹岩泥火山(Yinazao、Fantangisña、Asùt Tesoru、South Chamorro和Conical)发育角砾蛇纹岩的FMEs数据,通过不同泥火山、同一泥火山不同深度样品及同一块状样微区子样品间的FMEs特征对比,分析了蛇纹岩泥火山引起的蛇纹石化作用的流体性质、来源和形成机制。5座蛇纹岩泥火山角砾蛇纹岩的FMEs均较亏损地幔(DM)显示富集特征:B、Cs、As强烈富集(常>100×DM),Li、Rb、Sb中等富集(>10×DM),Ba、Sr、Pb弱富集(<10×DM)。浅源泥火山角砾蛇纹岩中B、Sr、Ba、Pb含量最高,且由浅源至深源泥火山其含量呈逐渐减少的趋势。而Li、Rb、Cs、As、Sb含量显示相反特征,浅源泥火山的角砾蛇纹岩中含量最低,且从浅源到深源泥火山其含量逐渐增加。不同泥火山角砾蛇纹岩FMEs具有系统性变化特征,反映了俯冲板片衍生流体是其发生蛇纹石化作用的主要流体。离海沟较近的泥火山下部俯冲板片成岩作用以蛋白石脱水为主,形成的板片衍生流体极富B,略富Li、Ba、Sr、Pb;离海沟较远的泥火山下部俯冲板片成岩或进变质作用主要为碳酸盐矿物分解和少量蚀变洋壳脱水及黏土矿物转化,板片衍生流体富Ba、Sr、Li、Rb、Cs;居于上述2类泥火山之间的泥火山,下部俯冲板片主要成岩作用为黏土矿物脱水及转化,板片衍生流体以富集B、Li、Rb、Cs、Ba为特征。海底以下深度<50 m的样品FMEs含量最高,指示海水风化对FMEs含量有一定影响,尤其是B、Sr。同一块角砾蛇纹岩不同微区结构的FMEs含量不同,纯蛇纹石区域其含量最高,指示蛇纹石化产物对FMEs有一定影响;绢石结构中Li、Rb、Cs含量高于橄榄石蚀变的蛇纹石,说明原始矿物类型也对部分FMEs富集有一定影响。
Abstract:The serpentinite mud volcano is considered as a direct window into subduction in Mariana Forearc. Serpentinites in serpentinite mud volcano are rich in water and fluid-mobile elements, and an archive of information about serpentinized fluids, fluid/rock interactions, and element cycles in subduction zones. We reviewed the FME (fluid-mobile element) behaviors of breccia serpentinite collected from five serpentinite mud volcanoes that erupted from the Mariana subduction zone in gradually elevated depths (Yinazao, Fantangisña, Asut Tesoru, South Chamorro, and Conical). We summarized and compared the FME characteristics of breccia serpentinite samples from different mud volcanoes at different depths of the same mud volcano and from microsamples in the same block, aiming at uncovering the features and sources of the serpentinized fluids, and the formation mechanisms of the Mariana forearc serpentine mud volcanoes. The FME characteristics of breccia serpentinite from all five serpentinite mud volcanoes show enrichments compared with those in depleted mantle (DM): strong enrichments of B, Cs, and As (often over 100×DM (depleted mantle)), moderate enrichments of Li, Rb, and Sb(>10×DM), and weak enrichments of Ba, Sr, and Pb(<10×DM). The contents of B, Sr, Ba, and Pb are the highest in breccia serpentinite samples from shallow mud volcano and show a decreasing trend from shallow mud volcano to deep mud volcano. On the contrary, the contents of Li, Rb, Cs, As, and Sb show the opposite trend, and these elements are lowest in breccia serpentinite samples from the shallow mud volcano and increase gradually from shallow mud volcano to deep mud volcano. The systematic variation of FMEs of breccia serpentinite in the five different mud volcanoes indicates that subducted plate-derived fluid is the main serpentinized fluid of the breccia serpentinite. The plate-derived fluid and main serpentinized fluid of Yinazao that is close to the trench, are extremely rich in B and slightly rich in Li, Ba, Sr, and Pb that are originated from opal dehydration processes at subduction interface below 80℃. The plate-derived fluids and the main serpentinized fluids of the farthest serpentinite mud volcanoes are rich in Ba, Sr, Li, Rb, and Cs that are mainly generated by carbonate mineral decomposition and certain altered oceanic crust dehydrated and clay-mineral transformed materials at subduction interface over 200 ℃. The Fantangisña in a moderate distance away from the trench shows plate-derived fluids and serpentinized fluids that featured with enrichment of B, Li, Rb, Cs, and Ba, which should be resulted from clay mineral dehydration and transformation at subduction interface in temperature 80-200 ℃. Samples in the upper 50 mbsf have the highest FME contents, indicating that seawater weathering has an effect on some FMEs, especially B and Sr. The contents of FME varied in different microstructures of the same breccia serpentine with the highest content in pure serpentine area, showing that serpentine products had a certain influence on FMEs. The contents of Li, Rb, and Cs in bastite are higher than those of the serpentine formed by olivine alteration, which proved that the original mineral types also had a certain influence on the enrichment of some FMEs.
-
Key words:
- fluid-mobile elements /
- breccia serpentinite /
- serpentinite mud volcano /
- Mariana Forearc
-

-
表 1 马里亚纳5座蛇纹岩泥火山关键参数
Table 1. Critical parameters from five Mariana serpentinite mud volcanoes
关键参数 Yinazao Fantangisña Asùt Tesoro South Chamorro Conical 到海沟距离/km 55 62 72 78 86 到板片深度/km 13 14 18 18 19 板幔界面温度/℃ 80 150 250 250~300 250~350 孔隙水pH 11.2 11.0 12.5 12.5 12.5 是否发育流体渗漏 是 是(很弱) 是 是 是 钻探航次 IODP 366 IODP 366 IODP 366 ODP 195 ODP 125 全岩数据来源 文献[11,34] 文献[11,34] 文献[11,34] 文献[24,27] 文献[26] 原位数据来源 文献[18] 文献[18] 文献[18] 文献[28] 注:到海沟距离、到板片深度、对应板幔界面温度和孔隙水数据引自文献 [15],流体渗漏情况引自文献 [11,15]。 -
[1] MEVEL C. Serpentinization of abyssal peridotites at mid-ocean ridges[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience,2003,335(10/11):825-852.
[2] 汪小妹,曾志刚,欧阳荷根,等. 大洋橄榄岩的蛇纹岩石化研究进展评述[J]. 地球科学进展,2010,25(6):605-616.
[3] 黄瑞芳,孙卫东,丁兴,等. 基性和超基性岩蛇纹石化的机理及成矿潜力[J]. 岩石学报,2013,29(12):4336-4348.
[4] MOHAMMADI N,AHMADIPOUR H,LENTZ D R,et al. Emplacement of serpentinites in the Chohar Gonbad-Gugher-Baft ophiolitic mélange,southeast Iran:examination of the mineral–chemical,petrologic,and structural features[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences,2016,105(2):537-555. doi: 10.1007/s00531-015-1187-x
[5] NAN J,KING H E,DELEN G,et al. The nanogeochemistry of abiotic carbonaceous matter in serpentinites from the Yap Trench,western Pacific Ocean[J]. Geology,2020,49(3):1-5.
[6] 王先彬. 蛇纹石化作用与地球生命起源/演化的痕迹[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2016,35(2):205-211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.02.001
[7] MCCOLLOM T M,SEEWALD J S. Serpentinites,hydrogen,and life[J]. Elements,2013,9(2):129-134. doi: 10.2113/gselements.9.2.129
[8] 黄瑞芳,孙卫东,丁兴,等. 橄榄岩蛇纹石化过程中氢气和烷烃的形成[J]. 岩石学报,2015,31(7):1901-1907.
[9] PREINER M,XAVIER J,SOUSA F,et al. Serpentinization:connecting geochemistry,ancient metabolism and industrial hydrogenation[J]. Life,2018,8(41):1-22.
[10] DESCHAMPS F,GODARD M,GUILLOT S,et al. Geochemistry of subduction zone serpentinites:a review[J]. Lithos,2013(178):96-127. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.05.019
[11] DEBRET B,ALBERS E,WALTER B,et al. Shallow forearc mantle dynamics and geochemistry:new insights from IODP expedition 366[J]. Lithos,2019(326/327):230-245. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.10.038
[12] 吴凯,袁洪林,吕楠,等. 蛇纹石化和俯冲带蛇纹岩变质脱水过程中流体活动性元素的行为[J]. 岩石学报,2020,36(1):141-153. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.14
[13] PARKINSON I J,PEARCE J A. Peridotites from the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Forearc (ODP Leg 125):evidence for mantle melting and melt-mantle mnteraction in a Supra-Subduction Zone Setting[J]. Journal of Petrology,1998,39(9):1577-1618. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.9.1577
[14] SAVOV I P,S G,RYAN J,et al. Geochemistry of serpentinite muds and metamorphic rocks from the Mariana Forearc,ODP sites 1200 and 778-779,South Chamorro and Conical Seamounts[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program,Scientific Results,2005(195):1-49.
[15] FRYER P , WHEAT C G, WILLIAMS T, et al. Expedition 366 summary[C]//FRYER P , WHEAT C G, WILLIAMS T, et al. Mariana Convergent Margin and South Chamorro Seamount, Proceedings of the International Ocean Discovery Program. College Station: TX (International Ocean Discovery Program), 2018: 1-23.
[16] DILEK Y , MOORES E M, ELTHON D, et al. Ophiolites and oceanic crust: new insights from field studies and Ocean Drilling Program[M]//FRYER P, LOCKWOOD J P, BECKER N, et al. Geological Society of America, 2000: 35-51.
[17] FRYER,PATRICIA. Serpentinite mud volcanism:observations,processes,and implications[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science,2012,4(1):345-373. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-120710-100922
[18] ALBERS E,KAHL W A,BEYER L,et al. Variant across-forearc compositions of slab-fluids recorded by serpentinites:implications on the mobilization of FMEs from an active subduction zone (Mariana Forearc)[J]. Lithos,2020(364/365):1-20.
[19] FRYER P,WHEAT C G,WILLIAMS T,et al. Mariana serpentinite mud volcanism exhumes subducted seamount materials:implications for the origin of life[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society a Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences,2020,378(2165):1-28.
[20] FRYER P,GHARIB J,ROSS K,et al. Variability in serpentinite mudflow mechanisms and sources:ODP drilling results on Mariana forearc seamounts[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2006,7(8):Q08014.
[21] AGRANIER A,LEE C T A,LI Z X A,et al. Fluid-mobile element budgets in serpentinized oceanic lithospheric mantle:insights from B,As,Li,Pb,PGEs and Os isotopes in the Feather River Ophiolite,California[J]. Chemical Geology,2007,245(3/4):230-241. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.08.008
[22] PETERS D,BRETSCHER A,JOHN T,et al. Fluid-mobile elements in serpentinites:constraints on serpentinisation environments and element cycling in subduction zones[J]. Chemical Geology,2017(466):654-666. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.07.017
[23] XIE Z,HATTORI K,DONG Y,et al. In situ characterization of forearc serpentinized peridotite from the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure terrane:behavior of fluid-mobile elements in continental subduction zone[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(4):101-139.
[24] JANOS K,THOMAS P,CARL S,et al. Geochemistry of ocean floor and forearc serpentinites:constraints on the ultramafic input to subduction zones[J]. Journal of Petrology,2012,53(2):235-270. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egr058
[25] HATTORI K H,GUILLOT S. Volcanic fronts form as a consequence of serpentinite dehydration in the forearc mantle wedge[J]. Geology,2003,31(6):525-528. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0525:VFFAAC>2.0.CO;2
[26] SAVOV I P,RYAN J G,D'ANTONIO M,et al. Geochemistry of serpentinized peridotites from the Mariana Forearc Conical Seamount,ODP Leg 125:implications for the elemental recycling at subduction zones[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2005,6(4):1-24.
[27] SAVOV I P,RYAN J G,D'ANTONIO M,et al. Shallow slab fluid release across and along the Mariana arc-basin system:insights from geochemistry of serpentinized peridotites from the Mariana Forearc[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,2007,112(9):1-30.
[28] KAHL W A,JONS N,BACH W,et al. Ultramafic clasts from the South Chamorro serpentine mud volcano reveal a polyphase serpentinization history of the Mariana forearc mantle[J]. Lithos,2015(227):1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.03.015
[29] FRYER P AND MOTTL M. Lithology,mineralogy,and origin of serpentine muds recovered from conical and torishima forearc seamounts:results of Leg 125 Drilling[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results,,1992(125):343-362.
[30] JOHNSTON R M. Fluid-mobile trace element variability of serpentinites and fntrained crustal rocks across the Mariana Forearc system [D]. Jampa: University of South Florida, 2019.
[31] OAKLEY A J,TAYLOR B,FRYER P,et al. Emplacement,growth,and gravitational deformation of serpentinite seamounts on the Mariana Forearc[J]. Geophysical Journal International,2007,170(2):615-634. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03451.x
[32] HULME S M,WHEAT C G,FRYER P,et al. Pore water chemistry of the Mariana serpentinite mud volcanoes:a window to the seismogenic zone[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2010,11(1):Q01X09.
[33] FRYER P B, SALISBURY M H. 1. Leg 195 synthesis: site 1200—serpentinite seamounts of the Izu-Bonin/Mariana convergent plate margin (ODP Leg 125 and 195 drilling results) [J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, 2006(195): 1-30.
[34] D'ANTONIO M,KRISTENSEN M B. Serpentine and brucite of ultramafic clasts from the South Chamorro Seamount (ODP Leg 195,site 1200):inferences for the serpentinization of the Mariana forearc mantle[J]. Mineralogical Magazine,2004,68(6):887-904. doi: 10.1180/0026461046860229
[35] TAMBLYN R,ZACK T,SCHMITT A K,et al. Blueschist from the Mariana forearc records long-lived residence of material in the subduction channel[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2019,519(519):171-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2019.05.013
[36] FRYER P,SABODA K L,JOHNSON L E,et al. Conical Seamount:SeaMARC II,Alvin submersible,and seismic reflection studies[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports,1990(125):69-80.
[37] 刘英俊. 元素地球化学 [M].北京: 科学出版社, 1984: 422-427.
[38] SEYFRIED W E,DIBBLE W E. Seawater-peridotite interaction at 300 ℃ and 500 bars:implications for the origin of oceanic serpentinites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1980,44(2):309-321. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90139-8
[39] SALTERS V,STRACKE A. Composition of the depleted mantle[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems,2004,5(5):1-27.
[40] BENTON L D,RYAN J G,SAVOV I P. Lithium abundance and isotope systematics of forearc serpentinites,Conical Seamount,Mariana forearc:insights into the mechanics of slab-mantle exchange during subduction[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2004,5(8):Q08J12.
[41] SMEDLEY P L,KINNIBURGH D G. A review of the source,behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2002,17(5):517-568. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5
[42] HATTORI K,TAKAHASHI Y,GUILLOT S,et al. Occurrence of arsenic (V) in forearc mantle serpentinites based on X-ray absorption spectroscopy study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2005,69(23):5585-5596. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.07.009
[43] DESCHAMPS F,GUILLOT S,GODARD M,et al. In situ characterization of serpentinites from forearc mantle wedges:timing of serpentinization and behavior of fluid-mobile elements in subduction zones[J]. Chemical Geology,2010,269(3/4):262-277. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.10.002
[44] KELLEY K A,PLANK T,LUDDEN J,et al. Composition of altered oceanic crust at ODP Sites 801 and 1149[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2003,4(6):8910.
[45] LAFAY R,DESCHAMPS F,SCHWARTZ S,et al. High-pressure serpentinites,a trap-and-release system controlled by metamorphic conditions:example from the Piedmont zone of the western Alps[J]. Chemical Geology,2013(343):38-54.
[46] BEBOUT G E. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics of subduction zones[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2007,260(3/4):373-393. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2007.05.050
[47] PLANK T. The chemical composition of subducting sediments [C]//HOLLAND H D, TUREKIAN K K . Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 607-629.
[48] RYAN J G, CHAUVEL C. The subduction-zone filter and the impact of recycled materials on the evolution of the mantle [C]//HOLLAND H D, TUREKIAN K K. Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition). Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 479-508.
[49] KASTNER M, SOLOMON E A, HARRIS R N, et al. Fluid Origins, Thermal Regimes, and Fluid and Solute Fluxes in the Forearc of Subduction Zones [M]//STEIN R, BLACKMAN D K, INAGAKI F, et al. Developments in Marine Geology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 671-733.
[50] WHEAT C G, FOURNIER T, PAUL C, et al. Data report: IODP expedition 366 pore water trace element (V, Mo, Rb, Cs, U, Ba, and Li) compositions [C]//FRYER P, WHEAT C G, WILLIAMS T, et al. Proceedings of the International Ocean Discovery Program. 2018: 1-8.
[51] YOU C F,CASTILLO P R,GIESKES J M,et al. Trace element behavior in hydrothermal experiments:implications for fluid processes at shallow depths in subduction zones[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1996,140(1/4):41-52.
[52] ALBERS E,BACH W,KLEIN F,et al. Fluid–rock interactions in the shallow Mariana forearc:carbon cycling and redox conditions[J]. Solid Earth,2019(10):907-930. doi: 10.5194/se-10-907-2019
[53] BENTON L D, RYAN J G , TERA F. Boron isotope systematics of slab fluids as inferred from a serpentine seamount, Mariana forearc [J]. 2001, 187(3/4): 273-282.
[54] O'HANLEY. Serpentinites: records of tectonic and petrological history [M]//CHARNOCK H, DEWEY J F, CONWAY M S, et al. UK: Oxford University Press: 1996: 1-277.
[55] EVANS B W,HATTORI K,BARONNET A. Serpentinite:what,why,where?[J]. Elements,2013,9(2):99-106. doi: 10.2113/gselements.9.2.99
[56] ALLEN D E,SEYFRIED W E. Compositional controls on vent fluids from ultramafic-hosted hydrothermal systems at mid-ocean ridges:an experimental study at 400°C,500 bars[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2003,67(8):1531-1542. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01173-0
[57] FROST B R,EVANS K A,SWAPP S M,et al. The process of serpentinization in dunite from New Caledonia[J]. Lithos,2013,178(9):24-39.
[58] MCCOLLOM T M,BACH W. Thermodynamic constraints on hydrogen generation during serpentinization of ultramafic rocks[J]. Geochmica et Cosmochimica Acta,2009,73(3):856-875. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.10.032
-




 下载:
下载: