Erosion and deposition evolution of the abandoned Diaokou course of the Yellow River and influential factors
-
摘要:
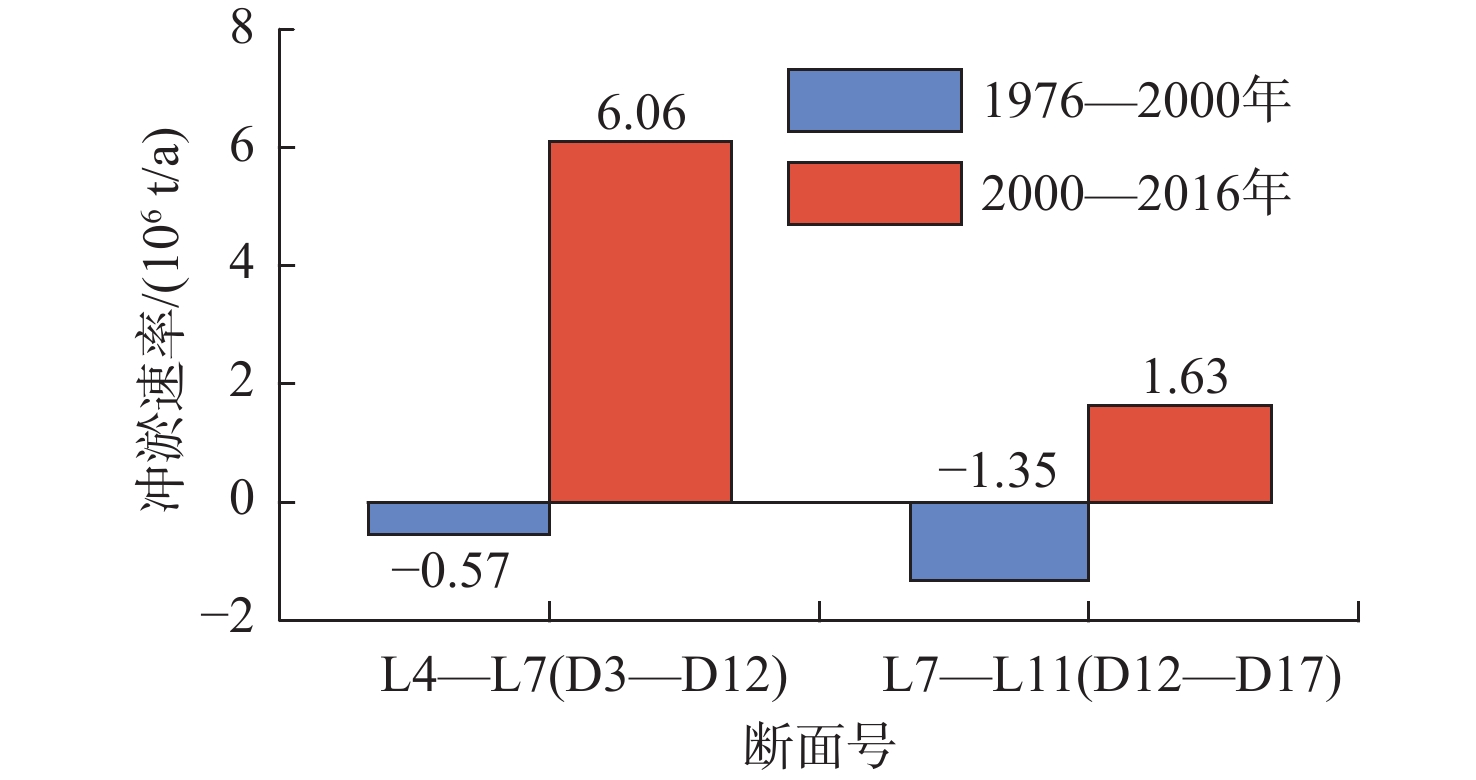
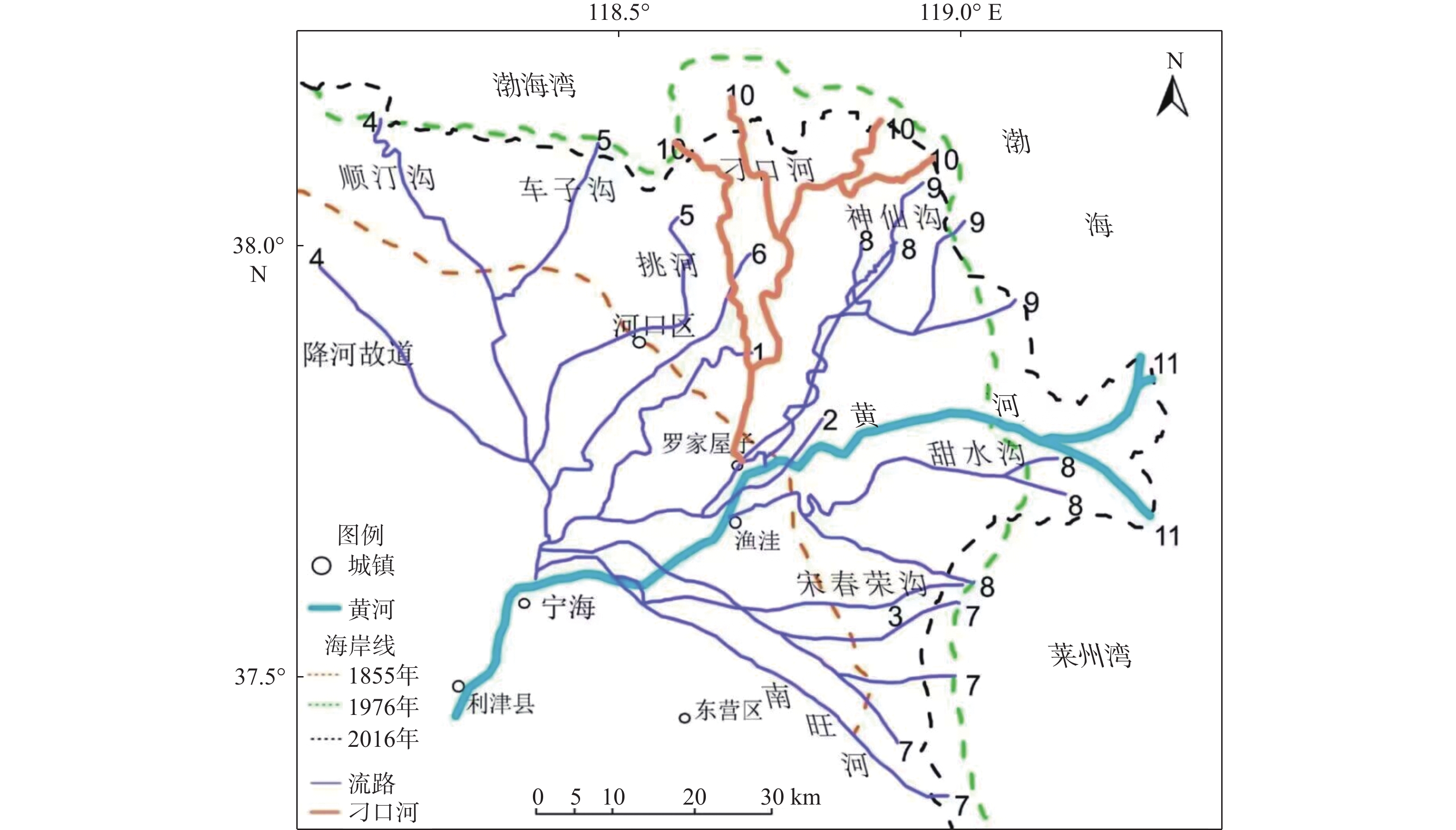
刁口流路是黄河1964年至1976年期间的行水流路,在1976年黄河人为改道清水沟后废弃,在1992年将其作为备用流路。依据不同年份刁口废弃流路的高程测量数据,计算了不同时期刁口废弃流路的冲淤量,分析了刁口废弃流路不同时段的冲淤变化特征,探讨了刁口废弃流路冲淤变化的受控机制。研究结果表明,1976—2000年,刁口废弃流路河道整体处于冲刷状态,冲刷速率约为1.92×106 t/a;2000—2016年,河道整体处于淤积状态,淤积速率约为7.99×106 t/a。刁口废弃河道的冲淤在空间上存在明显的差异,2000—2016年,以断面D20为分界线,向海一侧的河段呈现冲刷状态,河道槽蓄量增加;而向陆一侧的河段呈现淤积状态,河道槽蓄量减少。废弃河道的冲淤演化除受生态调水、海洋动力侵蚀等影响外,更多地受到河道周边油田开发以及两岸的农田和林业发展等因素的影响。因此,从维持河道行水能力的角度来看,亟需对河道开展维护修缮,以保证刁口流路作为黄河入海备用流路的适宜性。
Abstract:From 1964 to 1976, the Yellow River flowed through the Diaokou course into the Bohai Sea. In 1976, the Diaokou course was abandoned and replaced by an artificial diversion to the Qingshuigou course. Based on the measured elevation data of the abandoned Diaokou course in years of 1976, 2000, and 2016, we calculated the volume of erosion and deposition along the Diaokou course at different stages, described the spatial distribution of erosion and deposition of the Diaokou course, and discussed the potential impact factors on the Diaokou course evolution over the last 40 years after its abandonment. The results indicate that during 1976-2000, the Diaokou course experienced erosion at rate of ~1.92×106 t/a, and during 2000-2016, the Diaokou course was silted at deposition rate of ~7.99×106 t/a. The erosion and deposition along the Diaokou course present significant spatial difference during 2000-2016. Taking section D20 as the boundary, the seaward river section was in scouring state, and the storage capacity of river channel increased; while the landward section was in siltation state, and the storage capacity of the river channel decrease. The evolution of erosion and sedimentation in the Diaokou course was not only affected by the ecological water diversion and marine dynamic erosion, but also by the development of nearby oil fields, farming, and forestation. Therefore, to maintain the water flow capacity of the Diaokou course, cleaning up the Diaokou course is urgent to ensure good condition of the Diaokou course as a backup waterway of the Yellow River seaward empting.
-

-
表 1 1964—1976年刁口河流路淤积断面设立及实测情况
Table 1. Establishment and measurement of sedimentation cross-section of the Diaokou course from 1964 to 1976
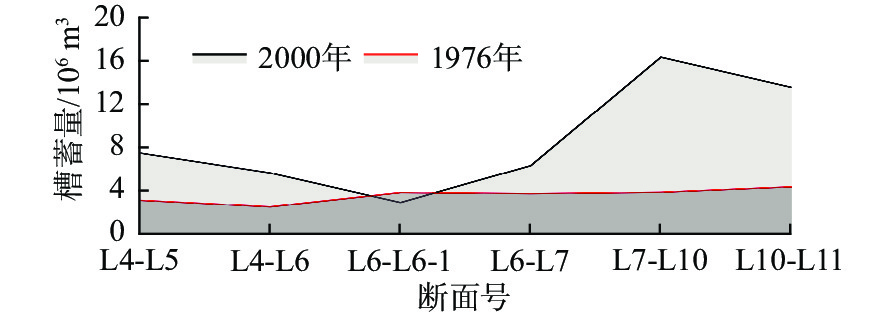
断面名称 设立日期 停测日期 断面长度/m 说明 L4 1965年4月 1976年8月 11 463 L5 1965年4月 1976年8月 10 457 L6 1965年4月 1976年8月 9 624 L6-1 1966年5月 1976年8月 8 168 原刁口河水位站位于L6-1右岸 L7 1965年4月 1976年8月 10 114 L10 1966年8月 1976年8月 8 855 拟建刁口水文站站址位于L10北 1 km L11 1968年5月 1976年8月 8 202 表 2 1976年与2000年河道槽蓄量对比
Table 2. Comparison in channel storage capacity between 1976 and 2000
断面号 1976年槽蓄量
/106 m32000年槽蓄量
/106 m31976—2000年
槽蓄量/106 m3冲淤速率
/(10 6 t/a)L5—L4 3.14 7.51 4.37 −0.27 L6—L5 2.53 5.67 3.14 −0.20 L6-1—L6 3.86 2.93 −0.93 0.06 L7—L6-1 3.76 6.35 2.59 −0.16 L10—L7 3.88 16.31 12.43 −0.78 L11—L10 4.38 13.55 9.17 −0.57 L4—L11 21.52 52.32 30.82 −1.93 表 3 2000年与2016年刁口流路河道槽蓄量对比
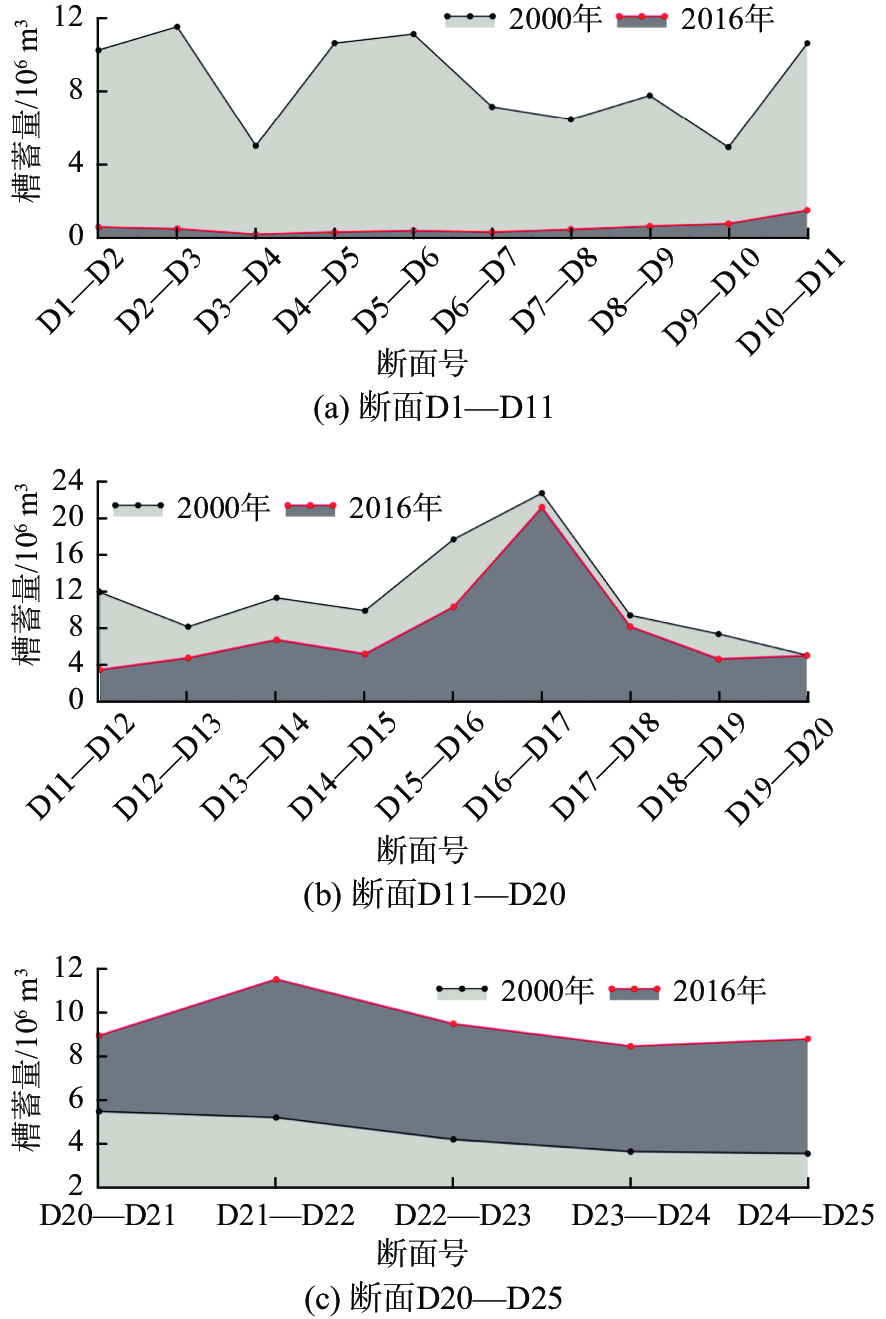
Table 3. Comparison in channel storage capacity of the Diaokou course between 2000 and 2016
断面号 2000年槽蓄
量/106 m32016年槽蓄
量/106 m32000—2016年
槽蓄量/106 m3冲淤速率
/(106 t/a)D1—D11 85.33 5.23 −80.10 7.92 D11—D20 105.24 71.16 −34.08 2.29 D20—D25 22.14 47.23 25.09 −2.24 -
[1] CUI B L,LI X Y. Coastline change of the Yellow River estuary and its response to the sediment and runoff (1976–2005)[J]. Geomorphology,2011,127(1/2):32-40.
[2] 王鸿翔,赵颖异,刘静航,等. 近50年黄河下游水沙情势演变及其影响因素分析[J]. 水力发电,2020,46(9):48-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2020.09.011
[3] AMOROS C. The concept of habitat diversity between and within ecosystems applied to river side-arm restoration[J]. Environmental Management,2001,28(6):805-817. doi: 10.1007/s002670010263
[4] 王开荣,李岩,于守兵,等. 黄河刁口河备用流路现状及保护工程措施探讨[J]. 中国水利,2017(1):15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2017.01.005
[5] 庞家珍. 黄河三角洲流路演变及对黄河下游的影响[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,1994(3):539-545. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.1994.03.001
[6] 赵翰卿,付志国. 大型河流—三角洲沉积储层精细描述方法[J]. 石油学报,2000,21(4):109-113. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.04.021
[7] 李胜利,于兴河,姜涛,等. 河流辫-曲转换特点与废弃河道模式[J]. 沉积学报,2017,35(1):1-9.
[8] 刘波,赵翰卿,王良书,等. 古河流废弃河道微相的精细描述[J]. 沉积学报,2001,19(3):394-398. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.03.013
[9] 张本华. 曲流河储层构型中废弃河道的识别及其分布模式:以孤岛油田馆上段为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2013,20(3):18-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2013.03.005
[10] ZHANG G Z,LI Y,WEI X,et al. Causes and typical control model of wind-drift sandy lands in abandoned channel of the Yellow River[J]. Forestry Studies in China,2006,8(1):59-64. doi: 10.1007/s11632-006-0011-x
[11] WU X,WANG H J,BI N S,et al. Evolution of a tide-dominated abandoned channel:a case of the abandoned Qingshuigou course,Yellow River[J]. Marine Geology,2020,422(7/26):106-116.
[12] LI Z Y,WANG H J,JEFFREY A N,et al. Modeling the infilling process of an abandoned fluvial-deltaic distributary channel:an example from the Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Geomorphology,2020,361(6):107-204.
[13] 吴晓,范勇勇,王厚杰,等. 三角洲废弃河道演化过程及受控机制:以黄河刁口废弃河道为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(2):22-29.
[14] 葛海燕. 刁口河尾闾黄河三角洲自然保护区生态补水效果评估[J]. 山东林业科技,2012,42(5):34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2724.2012.05.010
[15] 薛菲. 刁口河生态调水对湿地地下水矿化度的影响[J]. 中国科技信息,2015,13(Z3):48-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8972.2015.13.014
[16] 王春华,张娜,何敏,等. 黄河刁口河流路恢复运用目标与时机[J]. 人民黄河,2016,38(3):33-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2016.03.010
[17] 安催花,唐梅英,陈雄波,等. 黄河河口综合治理面临的问题与对策[J]. 人民黄河,2013,35(10):60-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2013.10.020
[18] XUE C T. Historical changes in the Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Marine Geology,1993,113(3):321-330.
[19] WANG H J,YANG Z S,LI G,et al. Wave climate modeling on the abandoned Huanghe (Yellow River) Delta lobe and related deltaic erosion[J]. Journal of Coastal Research,2006,22(4):906-918.
[20] SAITO Y,YANG Z,HORI K. The Huanghe (Yellow River) and Changjiang (Yangtze River) deltas:a review on their characteristics,evolution and sediment discharge during the Holocene[J]. Geomorphology,2001,41(2/3):219-231.
[21] ZHENG S,HAN S S,TAN G M,et al. Morphological adjustment of the Qingshuigou channel on the Yellow River Delta and factors controlling its avulsion[J]. Catena,2018,166:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.03.009
[22] JIA Y G,ZHENG J W,YUE Z Q,et al. Tidal flat erosion of the Huanghe River Delta due to local changes in hydrodynamic conditions[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2014,33(7):116-124. doi: 10.1007/s13131-014-0501-y
[23] WANG H J,WANG A M,BI N S,et al. Seasonal distribution of suspended sediment in the Bohai Sea,China[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2014,90:17-32. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.03.006
[24] 姜朝. 断面法计算冲淤量的数学基础及实际应用中的局限性[C]//全国测绘科技信息网中南分网第二十八次学术信息交流会论文集. 河南开封, 2014.
[25] 申冠卿,姜乃迁,张原锋,等. 黄河下游断面法与沙量法冲淤计算成果比较及输沙率资料修正[J]. 泥沙研究,2006,31(1):32-37. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.01.005
[26] 韩其为. 淤积物干容重的分布及其应用[J]. 泥沙研究,1997,22(2):10-16. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.1997.02.002
[27] 付云霞,管勇,王晓丹,等. 大型河口三角洲地面沉降机制研究:以黄河三角洲为例[J]. 海岸工程,2021,40(2):83-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2021.02.001
[28] 谭晋钰,黄海军,刘艳霞. 黄河三角洲沉积物压实固结及其对地面沉降贡献估算[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2014,34(5):33-38.
[29] 刘桂卫,黄海军,杜廷芹,等. 黄河三角洲地区地面沉降驱动因素研究[J]. 海洋科学,2011,35(8):43-50.
[30] 李华伟. 谈刁口河的开发与保护[C]//建设生态水利 推进绿色发展论文集. 南京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2018: 331-336.
[31] 黄安定,蒋雪中,陈沈良. 黄河三角洲北部自然保护区生态补沙定量分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(12):15-21. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2019.221
-



 下载:
下载: