Late Pleistocene delta and its controlling factors on the shelf of Yinggehai Basin in the northwestern South China Sea
-
摘要:
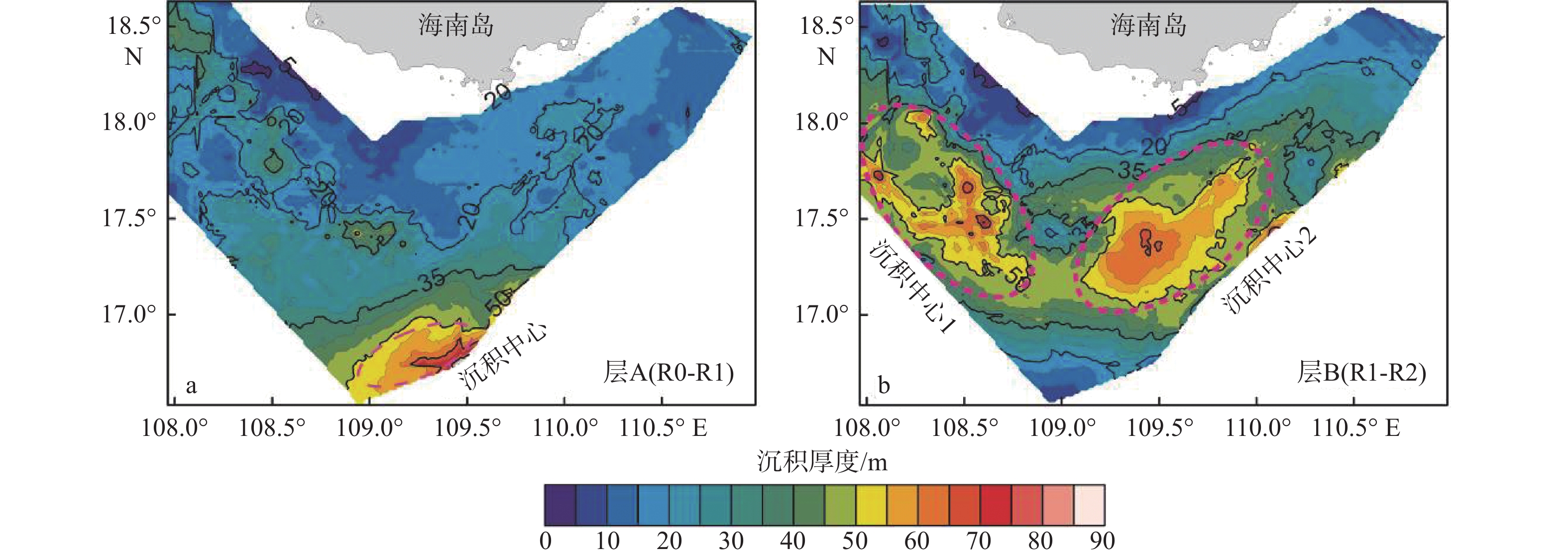
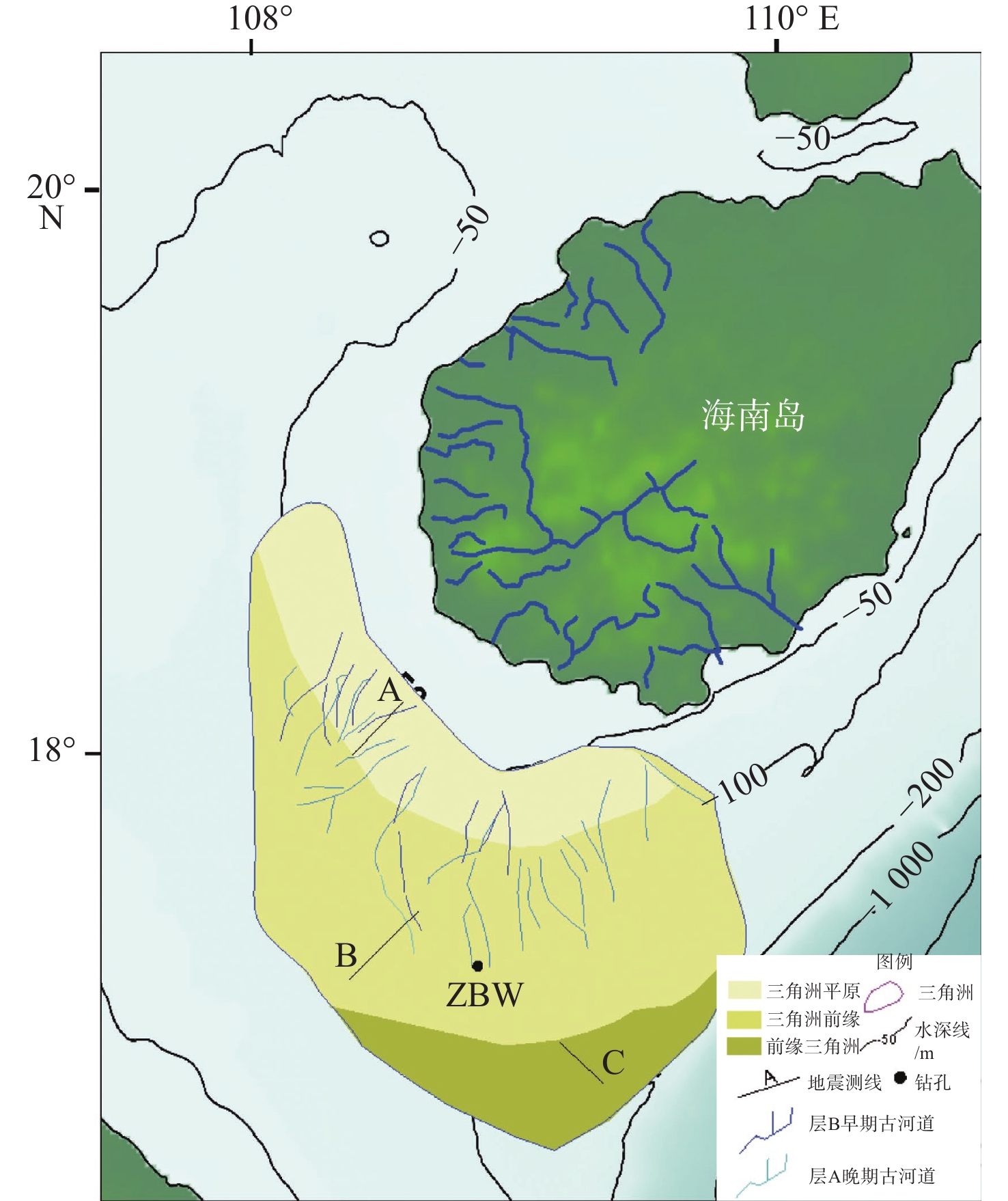
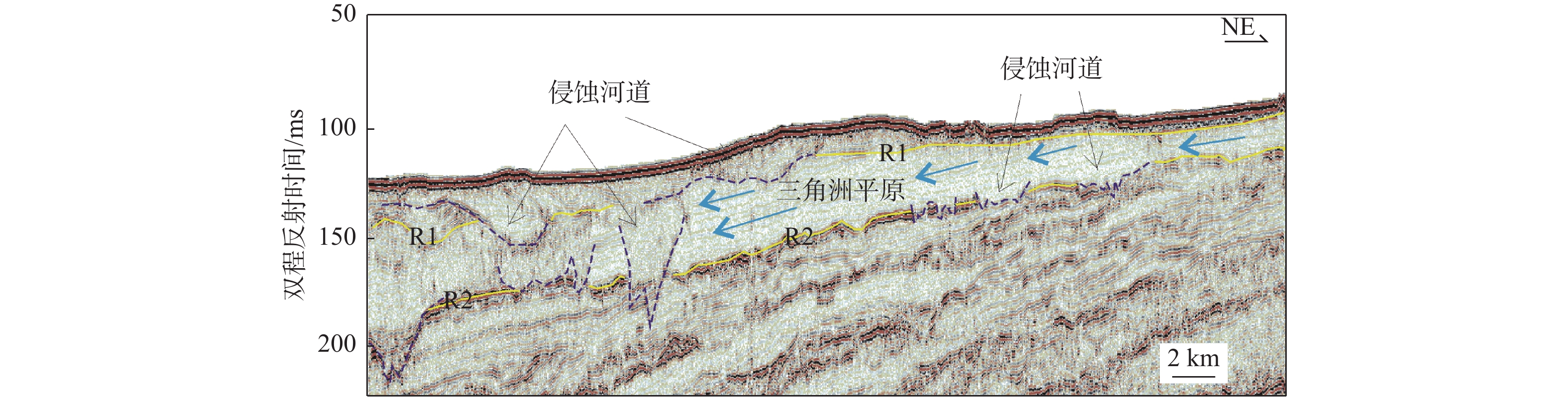
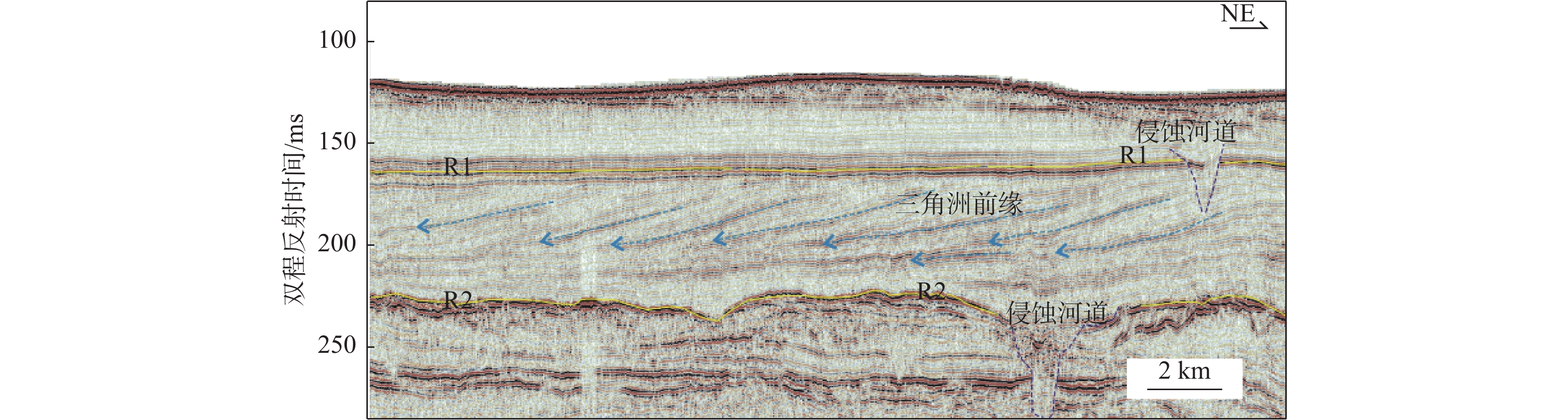
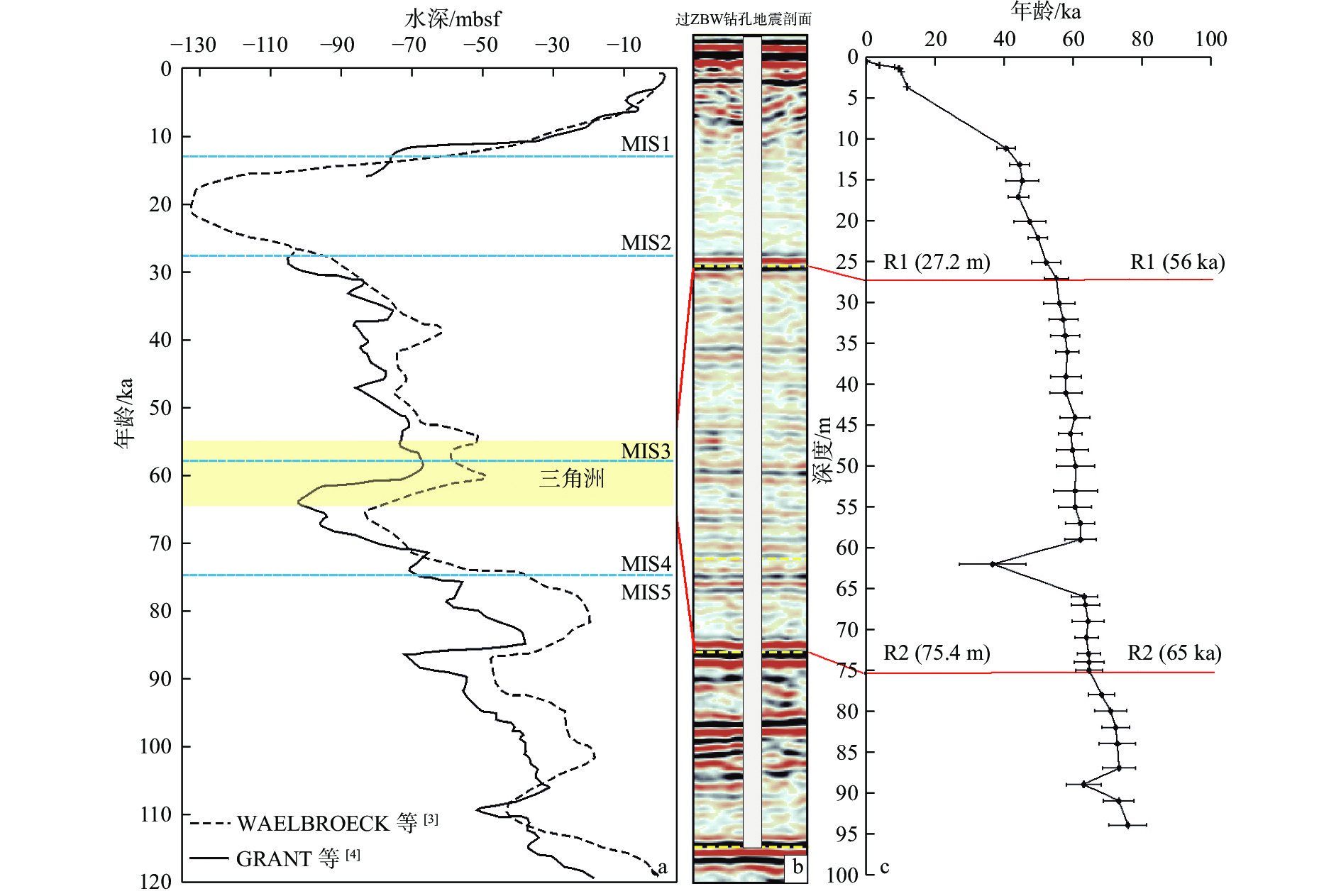
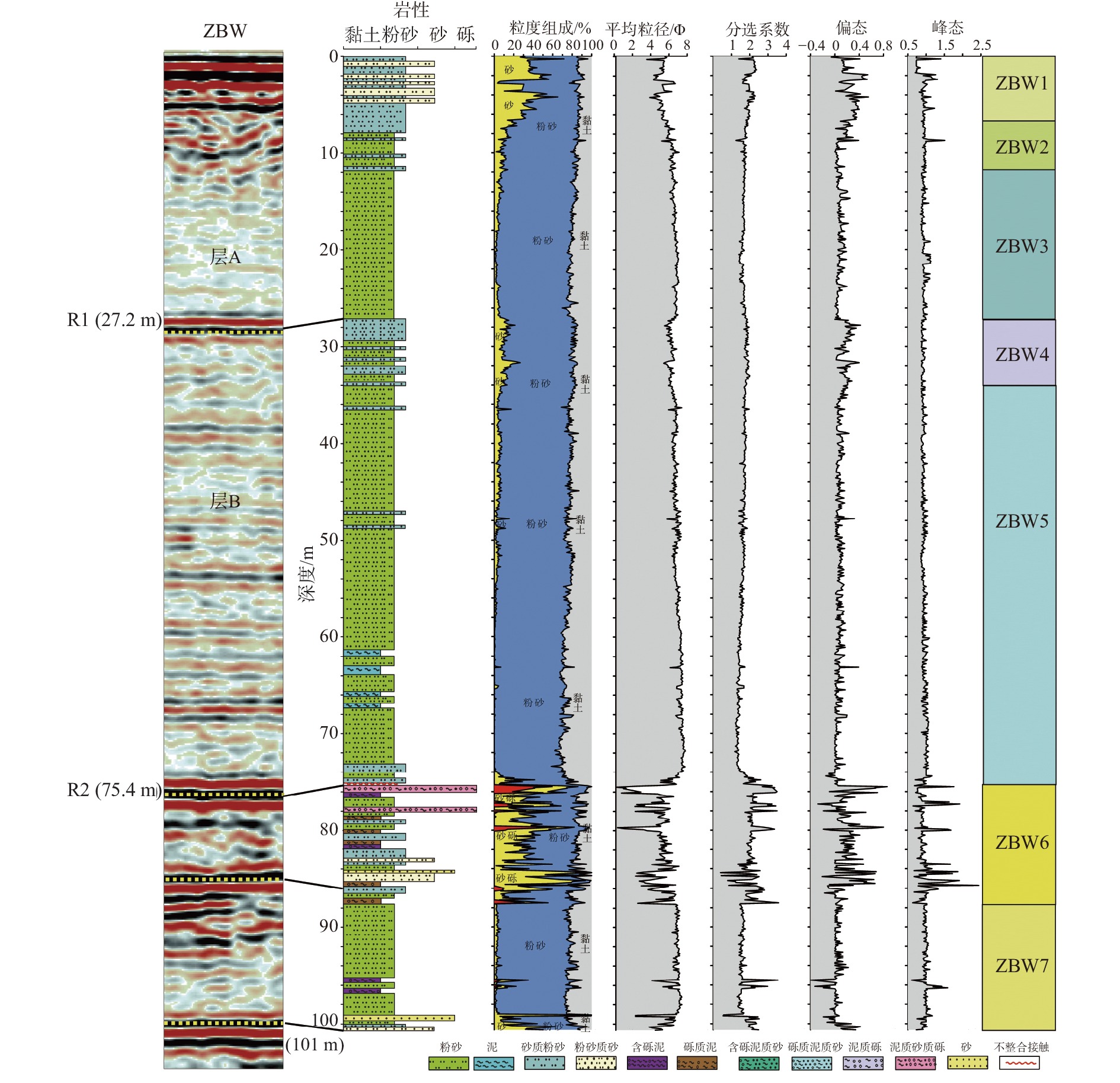
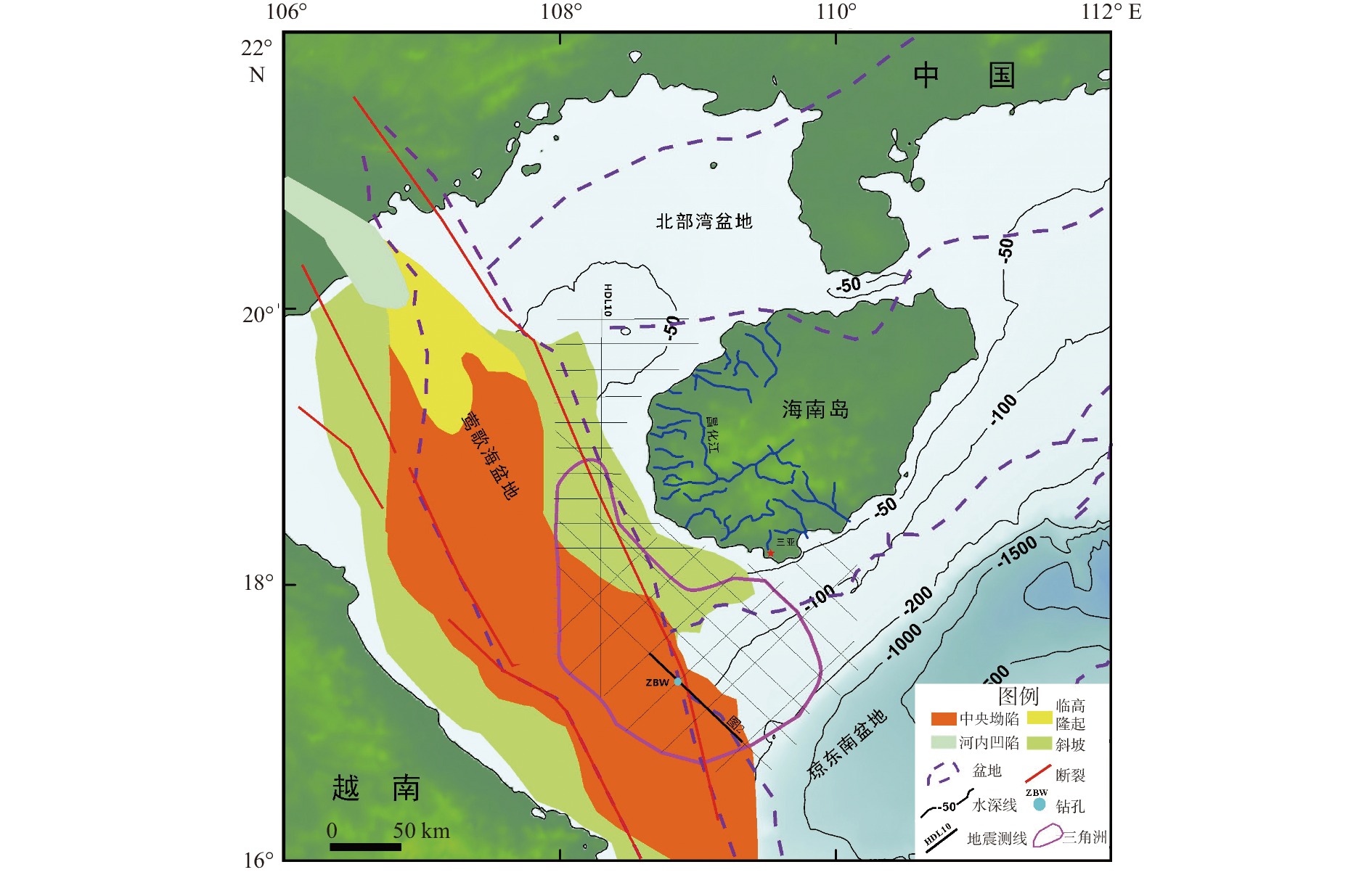
莺歌海盆地陆架区作为南海北部的一个重要地质构造单元,记录了第四纪以来沉积和海平面变化的丰富信息。通过对研究区高分辨率单道地震剖面的解释,结合深水区钻孔资料,分析了该地区晚第四纪地层的沉积特征,研究区浅部地层划分出层A和层B 2套地层单元,并进一步对研究区三角洲平原、三角洲前缘和前三角洲3种沉积亚相的地震特征进行了解释分析。钻孔AMS14C与光释光测年结果表明,三角洲形成于晚更新世65~56 ka,即MIS4晚期—MIS3早期。结合钻孔岩性和有孔虫分布特征以及区域地质、沉积背景等资料,开展了三角洲形成的控制因素分析,认为莺歌海盆地的构造和古地貌、海南岛隆升、物源供给、海平面变化、古季风对三角洲的形成发育具有重要的控制作用。
Abstract:The continental shelf area of the Yinggehai Basin in the northwestern of the South China Sea is an important tectonic unit bearing rich information on sedimentation and sea level changes since the Quaternary. Based on the interpretation of the high-resolution single-channel seismic profiling in this area, combined with the drilling data in the deep water area, the sedimentary characteristics of the Late Quaternary strata in the area were analyzed. The shallow stratum of the study area could be divided into two stratigraphic units: unit A and unit B. The seismic characteristics of the delta plain, delta front, and front delta in the study area were recognized and analyzed. The age-dating results using accelerator mass spectrometry 14C and optically stimulated luminescence indicate that the delta formed during 65~56 kaBP of the Late Pleistocene. Combined with regional geology and sedimentary background, the control factors of delta formation were analyzed. It is believed that the structure and paleo-geomorphology of the Yinggehai Basin, the uplift of Hainan Island, the supply of provenance, and sea level change are important factors controlling the formation of delta.
-
Key words:
- Yinggehai Basin /
- Late Pleistocene /
- continental shelf /
- delta /
- South China Sea
-

-
表 1 ZBW钻孔AMS14C年代测试结果
Table 1. AMS 14C dating results of ZBW core
野外编号 深度/m 测试物 14C年龄/aBP 校正年龄/cal aBP 实验室编号 ZBW-5 0.3 贝壳 190±30 610±30 Beta-451891 ZBW-6 0.8 贝壳 3 850±30 4 260±30 Beta-451892 ZBW-7 1.08 贝壳 8 340±30 8 750 ±30 Beta-451893 ZBW-8 1.23 贝壳 9 440±30 9 860±30 Beta-451894 ZBW-9 1.26 贝壳 9 850±30 10 260±30 Beta-451895 ZBW-11 1.65 贝壳 10 190±30 10 550±30 Beta-451897 ZBW-12 3.51 贝壳 11 790± 40 12 230± 40 Beta-451898 ZBW-4 3.88 贝壳 37 770±180 38 170 ±180 Beta-451890 ZBW-14 6.50 贝壳 > 43 500 Beta-451900 ZBW-15 10.60 贝壳 > 43 500 Beta-451901 ZBW-16 28.90 贝壳 > 43 500 Beta-451902 表 2 ZBW 孔OSL 年代测试结果
Table 2. OSL dating results of ZBW core
样品编号 深度/m OSL年龄/ka 误差/ka 样品编号 深度/m OSL年龄/ka 误差/ka ZBWO-1 11.1 41.04 ±2.69 ZBWO-20 55.1 61.14 ±4.73 ZBWO-2 13 44.88 ±2.84 ZBWO-21 57.1 62.49 ±4.12 ZBWO-3 15.1 45.73 ±4.69 ZBWO-22 59 62.53 ±4.46 ZBWO-4 17 44.56 ± 3.00 ZBWO-23 62 37.14 ±9.43 ZBWO-5 20.1 47.85 ±4.60 ZBWO-24 65.6 63.65 ±3.74 ZBWO-6 22.1 50.16 ±2.67 ZBWO-25 67 64.05 ±4.04 ZBWO-7 25.1 52.7 ±4.23 ZBWO-26 69 64.76 ±4.61 ZBWO-8 27.1 55.62 ±3.25 ZBWO-27 71 64.28 ±3.34 ZBWO-9 30.1 56.52 ±4.44 ZBWO-28 73 64.99 ±3.30 ZBWO-10 32 57.6 ±4.14 ZBWO-29 74 65.05 ±4.15 ZBWO-11 34 58.06 ±4.24 ZBWO-30 75 65.11 ±3.83 ZBWO-12 36 58.67 ±3.27 ZBWO-31 78 68.74 ±3.79 ZBWO-13 39 58.27 ±4.27 ZBWO-32 80 71.34 ±4.62 ZBWO-14 41 58.33 ±4.57 ZBWO-33 82 72.84 ±3.96 ZBWO-15 44 61.01 ±4.21 ZBWO-34 84 73.26 ±5.15 ZBWO-16 46.1 59.7 ±3.33 ZBWO-35 87 73.83 ±4.70 ZBWO-17 48.1 60.28 ±4.54 ZBWO-36 89 63.47 ±5.01 ZBWO-18 50.1 61.22 ±5.38 ZBWO-37 91 73.65 ±4.35 ZBWO-19 53.1 61.1 ±6.23 ZBWO-38 94.1 76.27 ±5.43 -
[1] 汪品先. 冰期时的中国海:研究现状与问题[J]. 第四纪研究,1990,10(2):111-124.
[2] YAO Y,HARFF J,MEYER M,et al. Reconstruction of paleocoastlines for the northwestern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Science in China (Series D):Earth Sciences,2009,52:1127-1136. doi: 10.1007/s11430-009-0098-8
[3] WAELBROECK C,LABEYRIE L,MICHEL E,et al. Sea-level and deep water temperature changes derived from benthic foraminifera isotopic records[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2002,21:295-305. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00101-9
[4] GRANT K M,ROHLING E J,BAR-MATTHEWS M,et al. Rapid coupling between ice volume and polar temperature over the past 150 000 years[J]. Nature,2012,495:744-747.
[5] 罗宪林,李春初,罗章仁. 海南岛南渡江三角洲的废弃与侵蚀[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2000,22(3):55-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2000.03.008
[6] 陈泓君,黄文凯,吴峧岐. 南海西北部晚第四纪典型地震相-沉积相特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2013,29(11):1-7.
[7] 陈泓君,彭学超,朱本铎,等. 南海1:100万海南岛幅海洋区域地质调查与编图成果综述[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2014,34(6):95-107.
[8] 时培兵,褚庆忠,陈小哲,等. 红河三角洲沉积相及其形成模式研究[J]. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版),2016,18(2):18-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1980.2016.02.005
[9] 姚衍桃,詹文欢,刘再峰,等. 珠江三角洲的新构造运动及其与三角洲演化的关系[J]. 华南地震,2008,28(1):29-40.
[10] 韦成龙,张珂,余章馨,等. 珠江口外海域与珠江三角洲晚更新世以来的地层层序对比[J]. 沉积学报,2015,33(4):713-723.
[11] 宗永强,黄光庆,熊海仙,等. 珠江三角洲晚第四纪地层、海平面变化与构造运动的关系[J]. 热带地理,2016,36(3):326-333.
[12] PORBSKI S J,STEEL R J. Shelf-margin deltas:their stratigraphic significance and relation to deepwater sands[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2003,62(3/4):283-326.
[13] UROZA C A,STEEL R J. A highstand shelf-margin delta system from the Eocene of West Spitsbergen,Norway[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2008,203(3/4):229-245.
[14] GONG C L,WANG Y M,PYLES D R,et al. Shelf-edge trajectories and stratal stacking patterns:their sequence-stratigraphic significance and relation to styles of deep-water sedimentation and amount of deep-water sandstone[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2015,99(7):1211-1243. doi: 10.1306/01311513229
[15] CATTANEO A,CORREGGIARI A,LANGONE L,et al. The late-Holocene Gargano subaqueous delta,Adriatic shelf:sediment pathways and supply fluctuations[J]. Marine Geology,2003,193:61-91. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00614-X
[16] CATTANEO A,TRINCARDI F,ASIOLI A,et al. The Western Adriatic shelf clinoform:energy-limited bottom set[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2007,27:506-525. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.11.013
[17] 许冬,龙江平,钱江初,等. 海南岛近海海域7个沉积岩芯的现代沉积速率及其分布特征[J]. 海洋学研究,2008,26(3):9-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.03.002
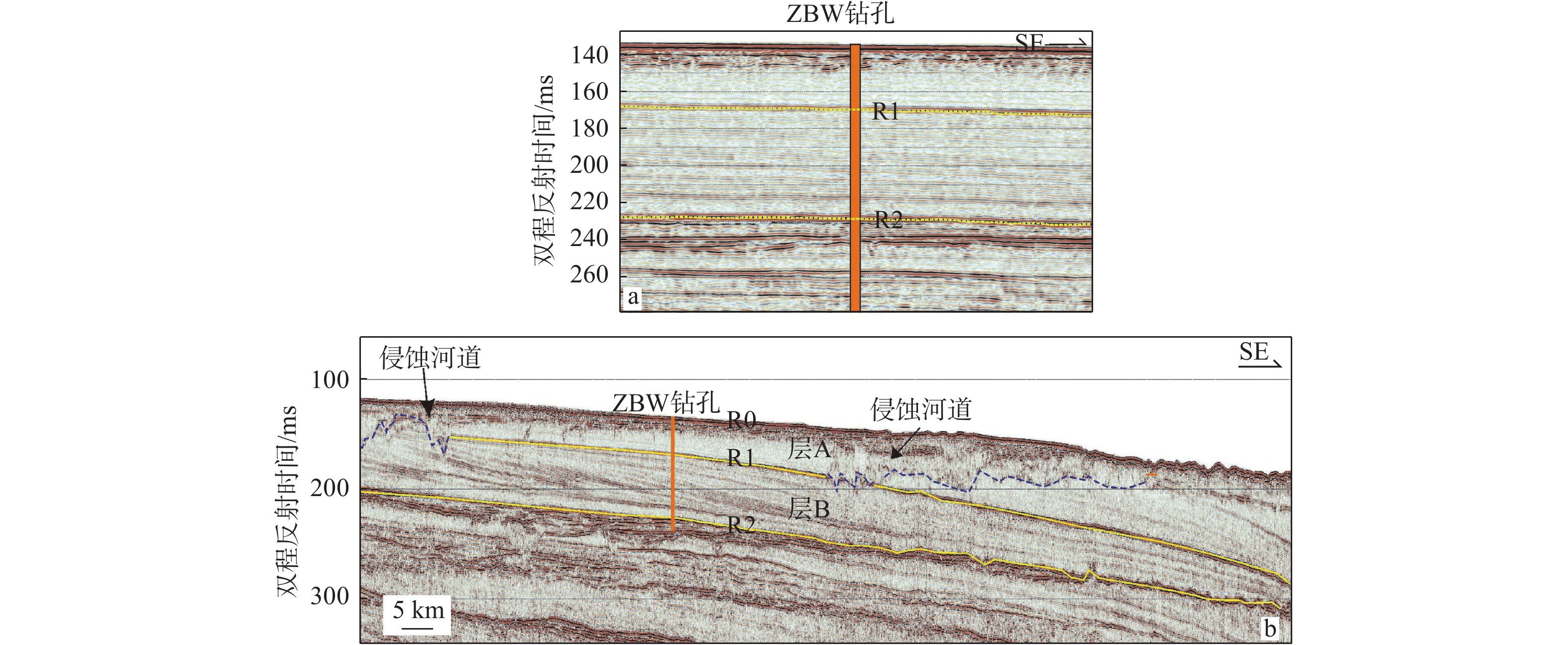
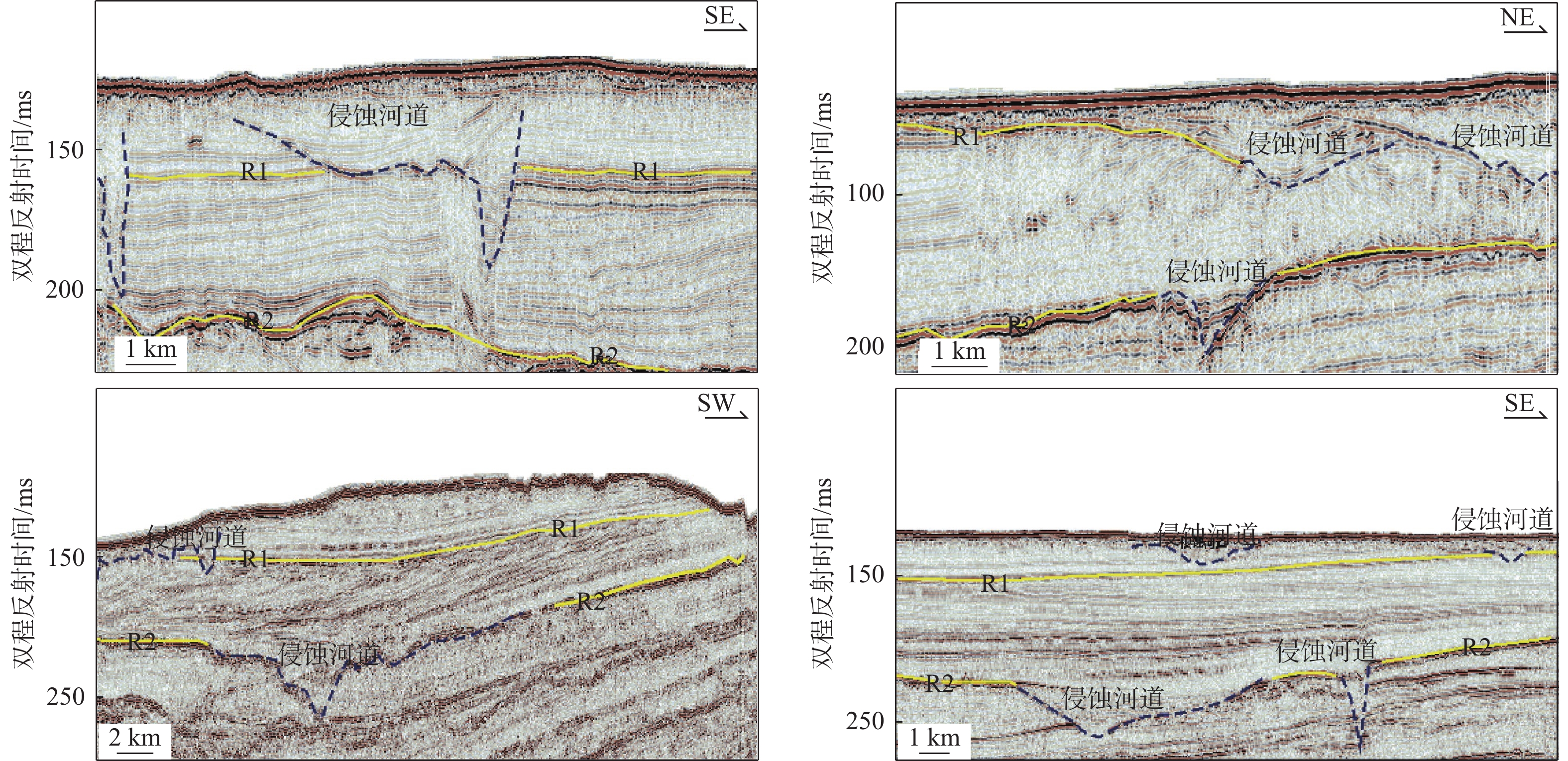
[18] 黄文凯,陈泓君,邱燕. 南海西北部莺歌海盆地晚更新世三角洲地震地层反射特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2015,31(8):10-15.
[19] CHEN H J, HARFF J, QIU Y, et al. Last Glacial Cycle and seismic stratigraphic sequences offshore western Hainan Island, NW South China Sea[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 2016, 429(1):99-121.
[20] FENG Y,ZHAN W,CHEN H,et al. Seismic characteristics and sedimentary record of the late Pleistocene delta offshore southwestern Hainan Island,northwestern South China Sea[J]. Interpretation,2018,6(4):31-43.
[21] 孙珍,钟志洪,周蒂. 莺歌海盆地构造演化与强烈沉降机制的分析和模拟[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2007,32(3):347-356.
[22] ZHU M,GRAHAM S,MCHARGUE T. The Red River Fault zone in the Yinggehai Basin,South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics,2009,476:397-417. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.06.015
[23] 郝芳,李思田,龚再升,等. 莺歌海盆地底辟发育机理与流体幕式充注[J]. 中国科学(D辑),2001,31(6):471-476.
[24] 谢玉洪,范彩伟. 莺歌海盆地东方区黄流组储层成因新认识[J]. 中国海上油气,20l0,22(6):354-386.
[25] 夏伦煜,麦文,赖霞红,等. 莺歌海-琼东南盆地第四系初步研究[J]. 中国海上油气(地质),1989,3(3):21-28.
[26] 李纯泉. 莺歌海盆地流体底辟构造及其对天然气成藏的贡献[J]. 中国海上油气(地质),2000,14(4):253-257.
[27] 朱俊江,詹文欢,唐诚,等. 红河断裂带活动性研究[J]. 华南地震,2003,23(2):13-19.
[28] 刘宝明,夏斌,李绪宣,等. 红河断裂带东南的延伸及其构造演化意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑),2006(10):914-924.
[29] 杨鹏,夏斌,蔡周荣,等. 南海北部莺歌海盆地成因机制:与渭河盆地构造对比分析的启示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2017,37(6):65-75.
[30] ALLEN C R,GILLESPIE A R,YUAN H,et al. Red River and associated faults,Yunnan Province,China:Quaternary geology,slip rates,and seismic hazard[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,1984,95(6):85-94.
[31] LELOUP P H,LACASSIN R,TAPPONNIER P,et al. The Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone (Yunnan,China),Tertiary transform boundary of Indochina[J]. Tectonophysics,1995,251:3-84. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(95)00070-4
[32] LELOUP P H,ARNAUD N,LACASSIN R,et al. New constraints on the structure,thermochronology,and timing of the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone,SE Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2001,106:6683-6732. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900322
[33] 宋维宇. 莺歌海盆地反转构造变形特征及其动力学演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2012,32(2):77-83.
[34] 范彩伟. 莺歌海大型走滑盆地构造变形特征及其地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,42(5):190-199.
[35] RANGIN C, KLEIN M, ROQUES D, et al. The Red River fault system in the Tonkin Gulf, Vietnam [J]. Tectonophysics, 1995, 243: 209-222.
[36] CLIFT P D, SUN Z. The sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the Yinggehai-Song Hong basin and the southern Hainan margin, South China Sea: implications for Xizang uplift and monsoon intensification[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 2006, 111(6): 232-241.
[37] 徐辉龙,丘学林,孙金龙. 莺歌海盆地新构造运动与超压体系喷溢油气成藏作用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2006,26(3):93-100. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2006.03.013
[38] MURRAY A S,OLLEY J M. Precision and accuracy in the optically stimulated luminescence dating of sedimentary quartz[J]. Geochronometria,2002,21:1-16.
[39] FENG Y,ZHAN W,CHEN H,et al. Seismic characteristics and sedimentary record of the late Pleistocene delta offshore south-western Hainan Island,northwestern South China Sea[J]. Interpretation,2018,6:31-43.
[40] ZHANG J,TOMCZAKC M,LI C,et al. Paleo-ecological changes and sedimentary evolution of the Hainan Delta,NW South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2021,209:104-685.
[41] 陈泓君,黄文凯,邱燕. 海南岛西南海域晚第四纪古水深反演[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2017,36(6):128-139.
[42] 邱中建, 龚再升. 中国油气勘探(第四卷): 近海油气区[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社/地质出版社 , 1999: 911-963.
[43] 詹文欢,朱俊江,孙宗勋 等. 南海西北部壳体新构造运动及其演化模式[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2001,25(4):353-360.
[44] 崔涛, 解习农, 任建业, 等. 莺歌海盆地异常裂后沉降的动力学机制[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 33(3): 349-356.
[45] 孙珍,钟志洪,周蒂,等. 红河断裂带的新生代变形机制及莺歌海盆地的实验证据[J]. 热带海洋学报,2003,22(2):1-9.
[46] 裴健翔,陈杨,郝德峰,等. 莺歌海盆地中央坳陷中新世海底扇识别及其形成控制因素[J]. 东北石油大学学报,2016,40(5):45-54.
[47] YAN Q,METCALFE I,SHI X. U-Pb isotope geochronology and geochemistry of granites from Hainan Island (northern South China Sea margin) :constraints on late Paleozoic-Mesozoic tectonic evolution[J]. Gondwana Research,2017,49:333-349. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.06.007
[48] TAN M T,DUNG L V,BACH L D,et al. Pliocene–Quaternary evolution of the continental shelf of central Vietnam based on high resolution seismic data[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2014,79:529-539. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.08.001
[49] JIANG T,CAO L,XIE X,et al. Sun H Insights from heavy minerals and zircon U-Pb ages into the middle Miocene-Pliocene provenance evolution of the Yinggehai Basin,northwestern South China Sea[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2015,327:32-42. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.07.011
[50] LEI C,REN J,STERNAI P,et al. Structure and sediment budget of Yinggehai-Song Hong Basin,South China Sea:implications for Cenozoic tectonics and river basin reorganization in Southeast Asia[J]. Tectonophysics,2015,655:177-190. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.05.024
[51] 龚再升, 李思田, 谢泰俊, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 1-510.
[52] YAN Y,CARTER A,PALK C,et al. Understanding sedimentation in the Song Hong-Yinggehai Basin,South China Sea[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2011,12:1-15.
[53] 田成静,欧阳婷萍,朱照宇,等. 海南岛周边海域表层沉积物磁化率空间分布特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 热带地理,2013,33(6):666-673.
[54] 丁国瑜. 海南岛第四纪地质的几个问题[C]//刘东生, 刘敏厚, 吴子荣, 等. 第四纪地质问题. 北京: 科学出版社, 1964: 207-233.
[55] 刘瑞华,张仲英. 海南岛的新构造运动特征[J]. 热带地理,1989,9(2):174-182.
[56] 张军龙,田勤俭,李峰,等. 海南岛北西部新构造特征及其演化研究[J]. 地震,2008,28(3):85-94.
[57] 王颖, 周旅复. 海南岛西北部火山海岸的研究[J]. 地理学报, 1990, 45(3): 321-330.
[58] 胡亚轩,郝明,秦姗兰,等. 海南岛现今三维地壳运动与断裂活动性研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2018,61(6):2310-2321. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0274
[59] MILLIMAN J, FARNSWORTH K. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean: A Global Synthesis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011:298-301.
[60] LIU Z,ZHAO Y,COLIN C,et al. Source-to sink transport processes of fluvial sediments in the South China Sea[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2016,153:238-273. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.005
[61] ZHUO H,WANG Y,SHI H,et al. Contrasting fluvial styles across the mid-Pleistocene climate transition in the northern shelf of the South China Sea:evidence from 3D seismic data[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2015,129:128-146. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.10.012
[62] 陈隆勋, 朱乾根, 罗会帮, 等. 东亚季风[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1991: 28-101.
[63] 汪品先. 十五万年来的南海[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 1995: 96-107.
[64] CHEN M H,TU X,ZHENG F,et al. Relations between sedimentary sequence and paleo climate changes during last 200 ka in the southern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2000,45:1334-1340. doi: 10.1007/BF03182915
[65] 徐建,汪品先,黄宝琦,等. 南海南部普林虫与“中更新世革命”[J]. 地球科学,2004,29(1):7-14.
[66] 刘志飞,COLIN C,黄维,等. 珠江流域盆地表层沉积物的黏土矿物及其对南海沉积物的贡献[J]. 科学通报,2007,52(4):448-456.
[67] WANG L,WANG P X. Late Quaternary paleoceanography of the South China Sea:glacial-interglacial contrasts in an enclosed basin[J]. Paleoceanography,1990,5(1):77-90. doi: 10.1029/PA005i001p00077
[68] WANG L,SARNTHEIN M,ERLENKEUSER H,et al. East Asian monsoon climate during the late Pleistocene:high- resolution sediment records from the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology,1999,156:245-284. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00182-0
[69] WANG P,TIAN J,CHENG X. Transition of Quaternary glacial cyclicity in deep-sea records at Nansha,the South China Sea[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences,2001,44(10):926-933. doi: 10.1007/BF02907085
[70] SUN X,LUO Y,HUANG F,et al. Deep-sea pollen from the South China Sea:Pleistocene indicators of East Asian monsoon[J]. Marine Geology,2003,201:97-118. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00211-1
[71] 汪品先,翦知湣,赵泉鸿,等. 南海演变与季风历史的深海证据[J]. 科学通报,2003,48(21):2228-2239.
[72] 刘志飞, COLIN C, TRENTESAUX A, 等. 南海南部晚第四纪东亚季风演化的黏土矿物记录[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2004, 34(3): 272- 279.
[73] 郑洪波,杨文光,贺娟,等. 南海的氧同位素3期[J]. 第四纪研究,2008,28(1):68-78.
[74] WANG P,WANG L,BIAN Y,et al. Late Quaternary paleoceanography of the South China Sea:surface circulation and carbonate cycles[J]. Marine Geology,1995,127:145-165. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(95)00008-M
[75] TAMBURINI F,ADATTE T,FöLLMI K,et al. Investigating the history of East Asian monsoon and climate during the last glacial–interglacial period (0~140 000 years):mineralogy and geochemistry of ODP Sites 1143 and 1144,South China Sea.[J]. Marine Geology,2003,201:147-168. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00214-7
-



 下载:
下载: