Advances in field testing of the effective absolute permeability of gas hydrate reservoirs
-
摘要:
天然气水合物作为一种新型的非常规能源具有较大的资源潜力。天然气水合物储层的有效绝对渗透率常被选为天然气水合物降压开采效果评价的关键指标,指标大小需要在现场进行测试加以确定。首先对国内外典型地区天然气水合物储层有效绝对渗透率的现场测试实例进行梳理,然后介绍了地层测试和核磁共振测井等现场测试方法,最后总结了目前水合物储层有效渗透率现场测试仍存在的主要问题并给出未来的研究建议,期望为天然气水合物储层现场测试技术的发展提供参考。
Abstract:Natural gas hydrates have been widely treated as a potential energy. The effective absolute permeability of gas hydrate reservoirs is a crucial parameter reflecting the productivity, and it needs to be tested in the field. Advances in field testing of the effective absolute permeability of gas hydrate reservoirs in the world were reviewed. In addition, field-testing methods including wireline formation test and nuclear magnetic resonance logging were introduced, and challenges in on-site testing were addressed. Finally, suggestions were given to develop new field testing methods for future studies.
-
Key words:
- natural gas hydrate /
- permeability /
- well testing /
- nuclear magnetic resonance /
- hydrate saturation
-

-
图 1 阿拉斯加北部陆坡冻土区爱尔伯特山水合物储层测井曲线[30]
Figure 1.
图 2 阿拉斯加北部陆坡冻土区爱尔伯特山水合物储层MDT压力测试井底压力变化曲线[34]
Figure 2.
图 3 墨西哥湾北部海域KC151-2随钻测井曲线[39]
Figure 3.
图 4 计算获得的墨西哥湾北部海域KC151-2井位水合物储层有效绝对渗透率分布曲线[39]
Figure 4.
图 5 日本2013年首次海洋水合物试采AT1-MC监测井的测井曲线及有效绝对渗透率分布情况[42]
Figure 5.
图 6 日本南海海槽MITI海域由核磁共振测井数据计算的有效渗透率分布情况[46]
Figure 6.
图 7 印度Krishna-Godavari盆地NGHP-02-23-C井MDT压力测试结果[49]
Figure 7.
图 8 印度Krishna-Godavari盆地NGHP-02-23-C井MDT测试数据的压力瞬变分析结果[49]
Figure 8.
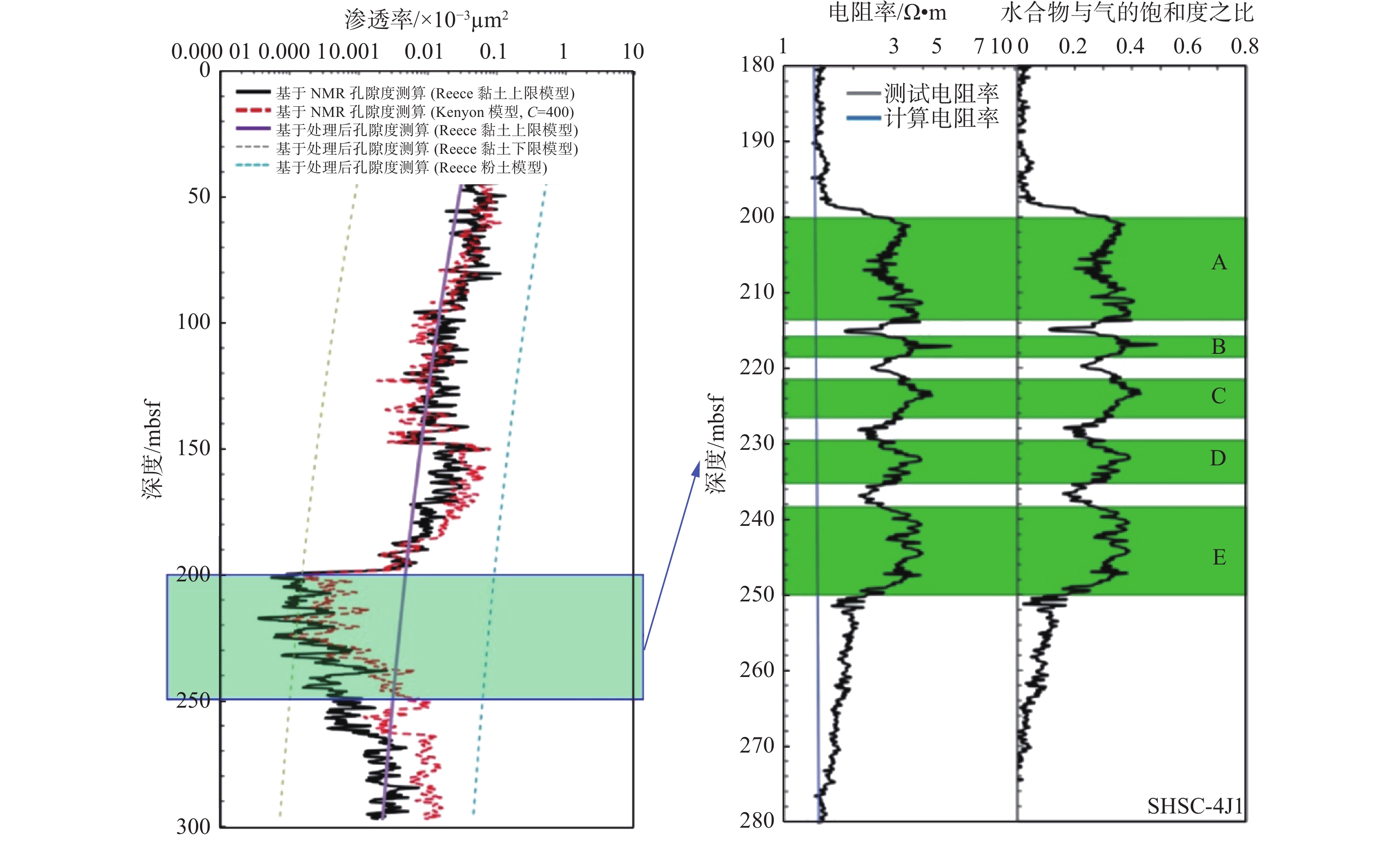
图 9 基于SHSC-4J1测井数据获得的南海北部海域储层有效绝对渗透率与水合物饱和度及气体饱和度数据[50]
Figure 9.
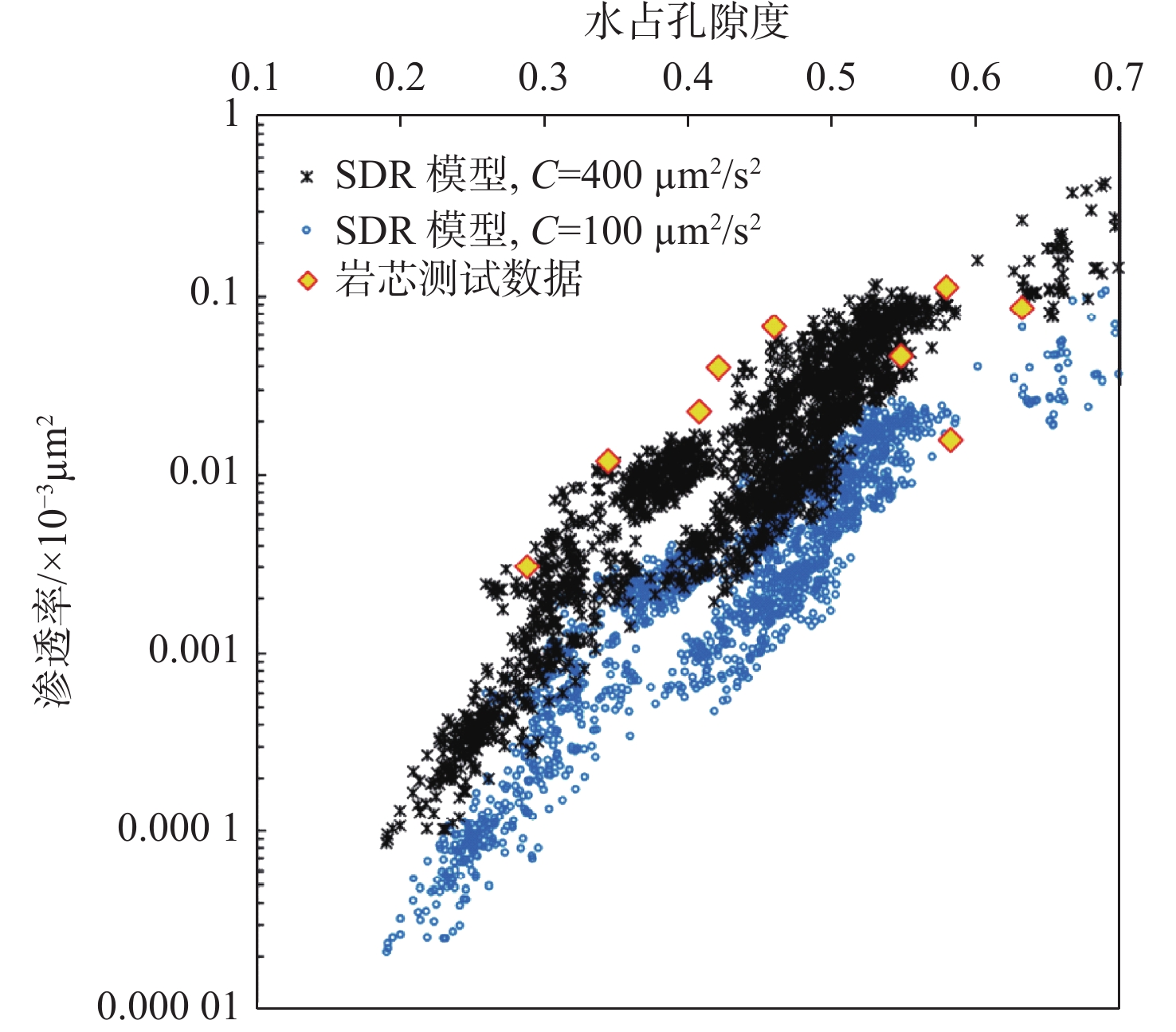
图 10 基于核磁共振测井数据采用SDR模型计算水合物储层有效绝对渗透率结果与保压岩芯测试数据对比情况[50]
Figure 10.
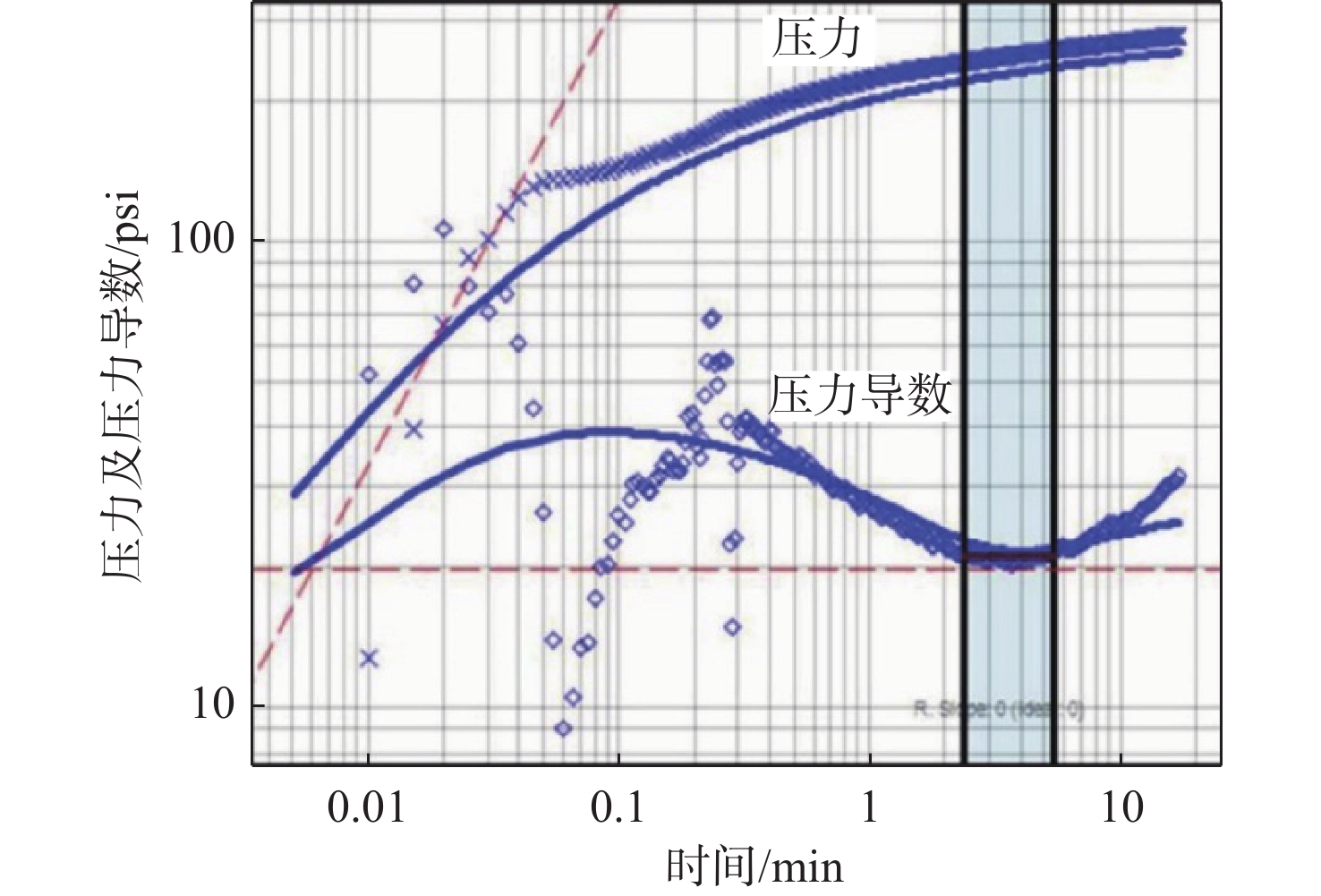
图 11 电缆地层测试流动形态图及其对应的压力导数特征图形[55]
Figure 11.
-
[1] 刘昌岭,郝锡荦,孟庆国,等. 气体水合物基础特性研究进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(9):1-10.
[2] SHAIBU R,SAMBO C,GUO B et al. An assessment of methane gas production from natural gas hydrates:challenges,technology,and market outlook[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research,2021,5(3):318-332. doi: 10.46690/ager.2021.03.07
[3] GIAVARINI C, HESTER K. Gas hydrate: immense energy potential and environmental challenges[M]. London: Springer Press, 2011: 30-56.
[4] CUI Y,LU C,WU M et al. Review of exploration and production technology of natural gas hydrate[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research,2018,2(1):53-62. doi: 10.26804/ager.2018.01.05
[5] 王力峰,付少英,梁金强,等. 全球主要国家水合物探采计划与研究进展[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(3):439-448. doi: 10.12029/gc20170303
[6] 张洋,李广雪,刘芳. 天然气水合物开采技术现状[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2016,32(4):63-68.
[7] 张旭辉,鲁晓兵,李鹏. 天然气水合物开采方法的研究综述[J]. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学,2019,49(3):034604.
[8] MAKOGON Y F,HOLDITCH S A,MAKOGON T Y. Russian field illustrates gas-hydrate production[J]. Oil and Gas Journal,2005,103:43-47.
[9] NUMASAWA M, YAMAMOTO K, YASUDA M et al. Objectives and operation overview of the 2007 JOGMEC/NRCAN/AURORA Mallik 2L-38 gas hydrate production test[C]. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Vancouver, 2008.
[10] BOSWELL R,SCHODERBEK D,COLLETT T S et al. The Iġnik Sikumi Field Experiment,Alaska North Slope:design,operations,and implications for CO2–CH4 exchange in gas hydrate reservoirs[J]. Energy and Fuels,2017,31(1):140-153.
[11] 王平康,祝有海,卢振权,等. 青海祁连山冻土区天然气水合物研究进展综述[J]. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学,2019,49(3):034606.
[12] YAMAMOTO K, TERAO Y, FUJII T et al. Operational overview of the first offshore production test of methane hydrates in the Eastern Nankai Trough[C]//Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, 2014.
[13] YAMAMOTO K,WANG X X,TAMAKI M et al. The second offshore production of methane hydrate in the Nankai Trough and gas production behavior from a heterogeneous methane hydrate reservoir[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(45):25987-26013. doi: 10.1039/C9RA00755E
[14] LI J F,YE J L,QIN X W et al. The first offshore natural gas hydrate production test in South China Sea[J]. China Geology,2018,1(1):5-16. doi: 10.31035/cg2018003
[15] YE J L,QIN X W,XIE W W et al. The second natural gas hydrate production test in the South China Sea[J]. China Geology,2020,3(2):197-209. doi: 10.31035/cg2020043
[16] 李守定,李晓,王思静,等. 天然气水合物原位补热降压充填开采方法[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):282-293.
[17] 窦斌,秦明举,蒋国盛,等. 利用地热开采南海天然气水合物的技术研究[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2011,27(10):49-52,58.
[18] 孙致学,朱旭晨,刘垒,等. 联合深层地热甲烷水合物开采方法及可行性评价[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(2):146-156.
[19] 吴能友,李彦龙,万义钊,等. 海域天然气水合物开采增产理论与技术体系展望[J]. 天然气工业,2020,40(8):100-115. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.008
[20] 吴能友,黄丽,胡高伟,等. 海域天然气水合物开采的地质控制因素和科学挑战[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2017,37(5):1-11.
[21] 王自豪,万义钊,刘乐乐,等. 含水合物沉积物相对渗透率研究进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(2):14-29. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2020.124
[22] LIU L L,LU X B,ZHANG X H. A theoretical model for predicting the spatial distribution of gas hydrate dissociation under the combination of depressurization and heating without the discontinuous interface assumption[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2015,133:589-601. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.07.005
[23] HUANG L,SU Z,WU N Y et al. Analysis on geologic conditions affecting the performance of gas production from hydrate deposits[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2016,77:19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.05.034
[24] SUN J X,NING F L,LEI H W et al. Wellbore stability analysis during drilling through marine gas hydrate-bearing sediments in Shenhu area:a case study[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2018,170:345-367. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.06.032
[25] LIU L L,LU X B,ZHANG X H et al. Numerical simulations for analyzing deformation characteristics of hydrate-bearing sediments during depressurization[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research,2017,1(3):135-147. doi: 10.26804/ager.2017.03.01
[26] 蔡建超,夏宇轩,徐赛,等. 含水合物沉积物多相渗流特性研究进展[J]. 力学学报,2020,52(1):208-223. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-362
[27] 刘乐乐,刘昌岭,吴能友,等. 天然气水合物储层岩心保压转移与测试进展[J]. 地质通报,2021,40(2-3):408-422.
[28] REN X W,GUO Z Y,NING F L et al. Permeability of hydrate-bearing sediments[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2020,202:103100. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103100
[29] 管家明,李栋梁,梁德青,等. 天然气水合物储层渗透率研究进展[J]. 新能源进展,2021,9(1):25-34.
[30] WINTERS W,WALKER M,HUNTER R et al. Physical properties of sediment from the Mount Elbert Gas Hydrate Stratigraphic Test Well,Alaska North Slope[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2011,28:361-380. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.01.008
[31] COLLETT T, JOHNSON A, KNAPP C et al. Natural gas hydrates—energy resource potential and associated geologic hazards[M]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 2009.
[32] KENYON B,KLEINBERG R,STRALEY C et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging technology for the 21st century[J]. Oilfield review,1995,7:19-33.
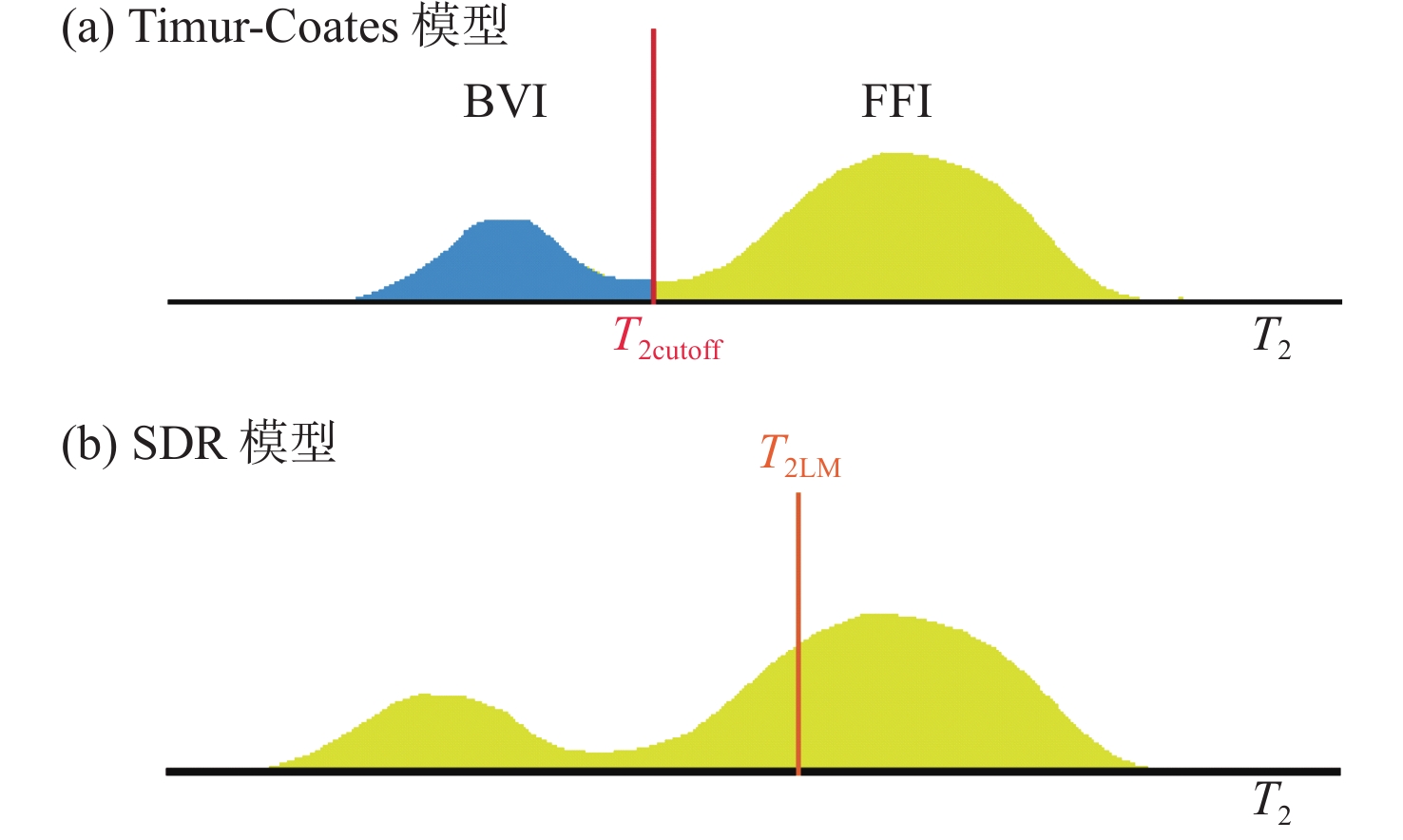
[33] STAMBAUGH B J. NMR tools afford new logging choices[J]. Oil Gas Journal,2000,98:45-52.
[34] ANDERSON B,HANCOCK S,WILSON S et al. Formation pressure testing at the Mount Elbert Gas Hydrate Stratigraphic Test Well,Alaska North Slope:operational summary,history matching,and interpretations[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2011,28:478-492. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.02.012
[35] RUPPEL C,BOSWELL R,JONES E. Scientific results from Gulf of Mexico Gas Hydrates Joint Industry Project Leg 1 drilling:introduction and overview[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2008,25:819-829. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.02.007
[36] COLLETT T S,LEE M W,ZYRIANOVA M V et al. Gulf of Mexico Gas Hydrate Joint Industry Project Leg II logging-while-drilling data acquisition and analysis[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2012,34:41-61. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.08.003
[37] BOSWELL R,COLLETT T S,FRYE M et al. Subsurface gas hydrates in the northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2012,34:4-30. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.10.003
[38] FLEMINGS P B,PHILLIPS S C,BOSWELL R et al. Pressure coring a Gulf of Mexico deep-water turbidite gas hydrate reservoir:initial results from The University of Texas–Gulf of Mexico 2-1 (UT-GOM2-1) Hydrate Pressure Coring Expedition[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2020,104:1847-1876. doi: 10.1306/05212019052
[39] FANG Y,FLEMINGS P B,DAIGLE H et al. Petrophysical properties of the Green Canyon Block 955 hydrate reservoir inferred from reconstituted sediments:implications for hydrate formation and production[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2020,104:1997-2028. doi: 10.1306/01062019165
[40] DAIGLE H,DUGAN B. Extending NMR data for permeability estimation in fine-grained sediments[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2009,26:1419-1427. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.02.008
[41] DUGAN B. Fluid flow in the Keathley Canyon 151 Mini-Basin,northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2008,25:919-923. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.12.005
[42] FUJII T,SUZUKI K,TAKAYAMA T et al. Geological setting and characterization of a methane hydrate reservoir distributed at the first offshore production test site on the Daini-Atsumi Knoll in the eastern Nankai Trough,Japan[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2015,66:310-322. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.02.037
[43] YAMAMOTO K. Overview and introduction: Pressure core-sampling and analyses in the 2012–2013 MH21 offshore test of gas production from methane hydrates in the eastern Nankai Trough[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 66(Part 2): 296-309.
[44] KONNO Y,YONEDA J,EGAWA K et al. Permeability of sediment cores from methane hydrate deposit in the Eastern Nankai Trough[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2015,66:487-495. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.02.020
[45] DAI S, BOSWELL R, WAITE W F et al. What has been learned from pressure cores [C]. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Gas Hydrate, Denver, 2017.
[46] UCHIDA T,TSUJI T. Petrophysical properties of natural gas hydrates-bearing sands and their sedimentology in the Nankai Trough[J]. Resource Geology,2004,54:79-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2004.tb00189.x
[47] COLLETT T S,BOSWELL R,Cochran J R et al. Geologic implications of gas hydrates in the offshore of India:Results of the National Gas Hydrate Program Expedition 01[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2014,58:3-28. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.021
[48] COLLETT T S,BOSWELL R,WAITE W F et al. India National Gas Hydrate Program Expedition 02 Summary of Scientific Results:gas hydrate systems along the eastern continental margin of India[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,108:39-142. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.05.023
[49] KUMAR P,COLLETT T S,YADAV U S et al. Formation pressure and fluid flow measurements in marine gas hydrate reservoirs,NGHP-02 expedition,offshore India[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,108:609-618. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.035
[50] KANG D,LU J A,ZHANG Z et al. Fine-grained gas hydrate reservoir properties estimated from well logs and lab measurements at the Shenhu gas hydrate production test site,the northern slope of the South China sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2020,122:104676. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104676
[51] 刘能强. 实用现代试井解释方法[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008.
[52] 韩永新, 孙贺东, 邓兴梁, 等. 实用试井解释方法[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2016.
[53] 冯永仁,左有祥,王健,等. 地层测试技术及其应用的进展与挑战[J]. 测井技术,2019,43(3):217-227.
[54] 高永德,孙殿强,杨冬,等. 基于电缆地层测试资料储层有效渗透率计算方法研究[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(2):137-142.
[55] CANTINI S, BAKDINI D, BERETTA E et al. Reservoir permeability from wireline formation testers[C]. SPE 164924 paper presented at the EAGE Annual Conference & Exhibition incorporating SPE Europec, United Kingdom, 10-13 June 2013.
[56] DUSSAN E B and SHARMA Y. Analysis of the pressure response of a single-probe formation tester[J]. SPE Formation Evaluation,1992,7(2):151-156. doi: 10.2118/16801-PA
[57] STEWART G and WITTMANN M. Interpretation of the pressure response of the repeat formation tester[C]. SPE 8362 paper presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Las Vegas, Nevada, United States, September 1979.
[58] MORAN J H and FINKLEA E E. Theoretical analysis of pressure phenomena associated with the wireline formation tester[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology,1962,14(8):899-908. doi: 10.2118/177-PA
[59] KASAP E,Huang K,SHWE T et al. Formation-rate-analysis technique:combined drawdown and buildup analysis for wireline formation test data[J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering,1999,2(3):271-280.
[60] MANIVANNAN S. Measuring permeability vs depth in the unlined section of a wellbore using the descent of a fluid column made of two distinct fluids: inversion workflow, laboratory & in-situ tests[D]. NNT: 2018SACLX086, Université Paris Saclay, 2018.
[61] KLEINBERG R L, KENYON W E, MITRA P P. Mechanism of NMR relaxation of fluids in rock[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 1994(Series A), 108: 206-214.
[62] KORB J-P. Nuclear magnetic relaxation of liquids in porous media[J]. New Journal of Physics,2011,13:035016. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/13/3/035016
[63] KLEINBERG R L,FLAUM C,GRIFFIN D D et al. Deep sea NMR:Methane hydrate growth habit in porous media and its relationship to hydraulic permeability,deposit accumulation,and submarine slope stability[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2003,108:2508.
[64] KLEINBERG R L,FLAUM C,STRALEY C et al. Seafloor nuclear magnetic resonance assay of methane hydrate in sediment and rock[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2003,108:2137.
[65] SAUMYA S,NARASIMHAN B,SINGH J et al. Acquisition of Logging-While-Drilling (LWD) multipole acoustic log data during the India National Gas Hydrate Program (NGHP) Expedition 02[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,108:562-569. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.10.011
[66] LIU L,ZHANG Z,LIU C et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse surface relaxivity in quartzitic sands containing gas hydrate[J]. Energy & Fuels,2021,35:6144-6152.
[67] MOHNKE O,HUGHES B. Jointly deriving NMR surface relaxivity and pore size distributions by NMR relaxation experiments on partially desaturated rocks[J]. Water Resource Research,2014,50:5309-5321. doi: 10.1002/2014WR015282
[68] KENYON W E. Nuclear magnetic resonance as a petrophysical measurement[J]. Nuclear Geophysics,1992,6:153-171.
[69] COATES G R,GALFORD J,MARDON D et al. A new characterization of bulk-volume irreducible using magnetic resonance[J]. The Log Analyst,1998:39.
[70] WEI D F,LIU X P,HU X X. Applicability of classical permeability estimation models based on nmr logging in tight sandstones[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2013,772:814-818. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.772.814
[71] XIAO L,LIU X P,ZOU C C et al. Comparative study of models for predicting permeability from nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logs in two Chinese tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Acta Geophysica,2014,62(1):116-141. doi: 10.2478/s11600-013-0165-6
[72] HOU J, ZHAO E M, LIU Y G, et al. Pressure-transient behavior in class Ⅲ hydrate reservoirs[J]. Energy, 2019, 170: 391–402.
-




 下载:
下载: