A new technique for seismic dominant signal extraction in fault shadow zone and its application in TT Block, Xihu Sag, East China Sea
-
摘要:
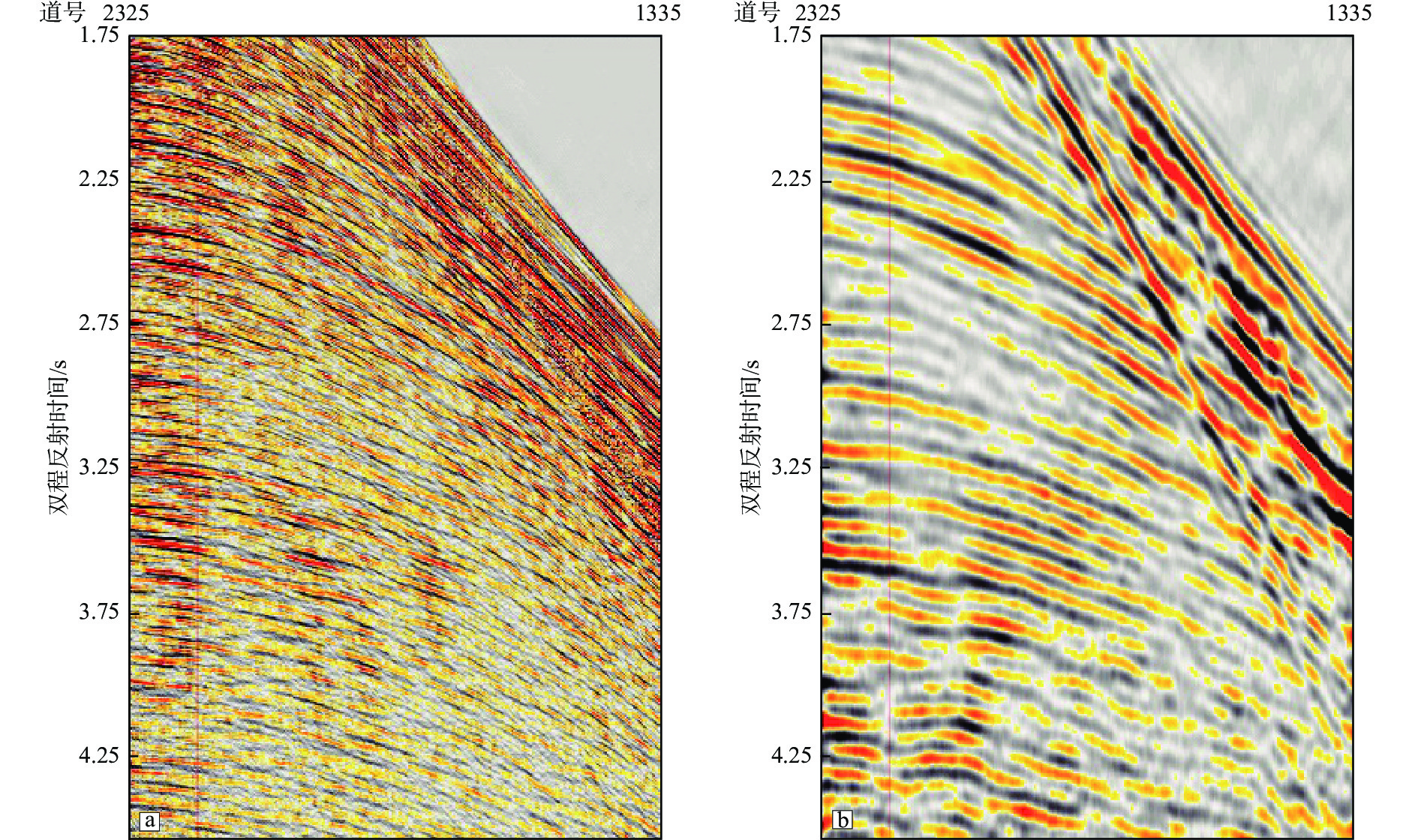
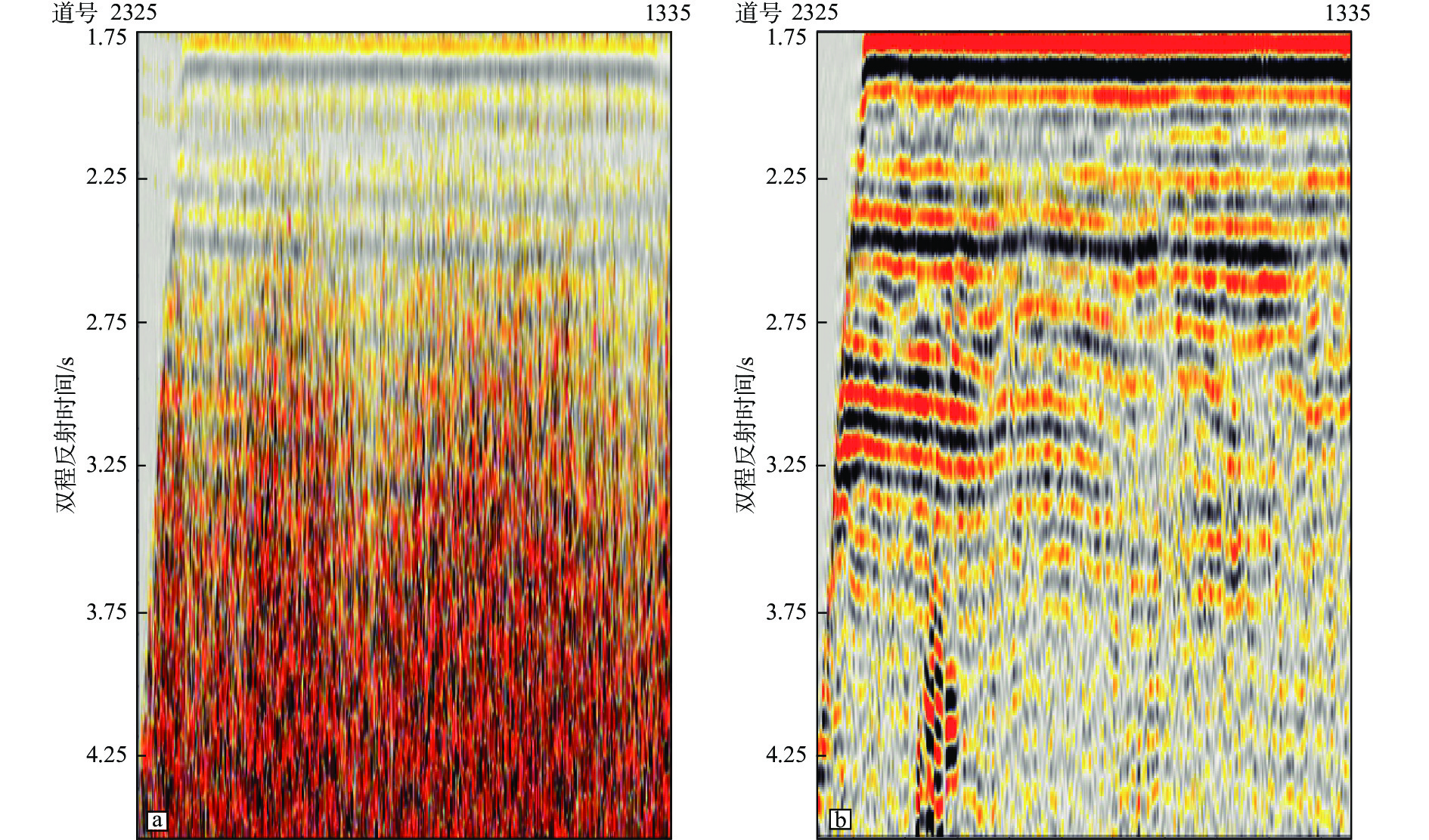
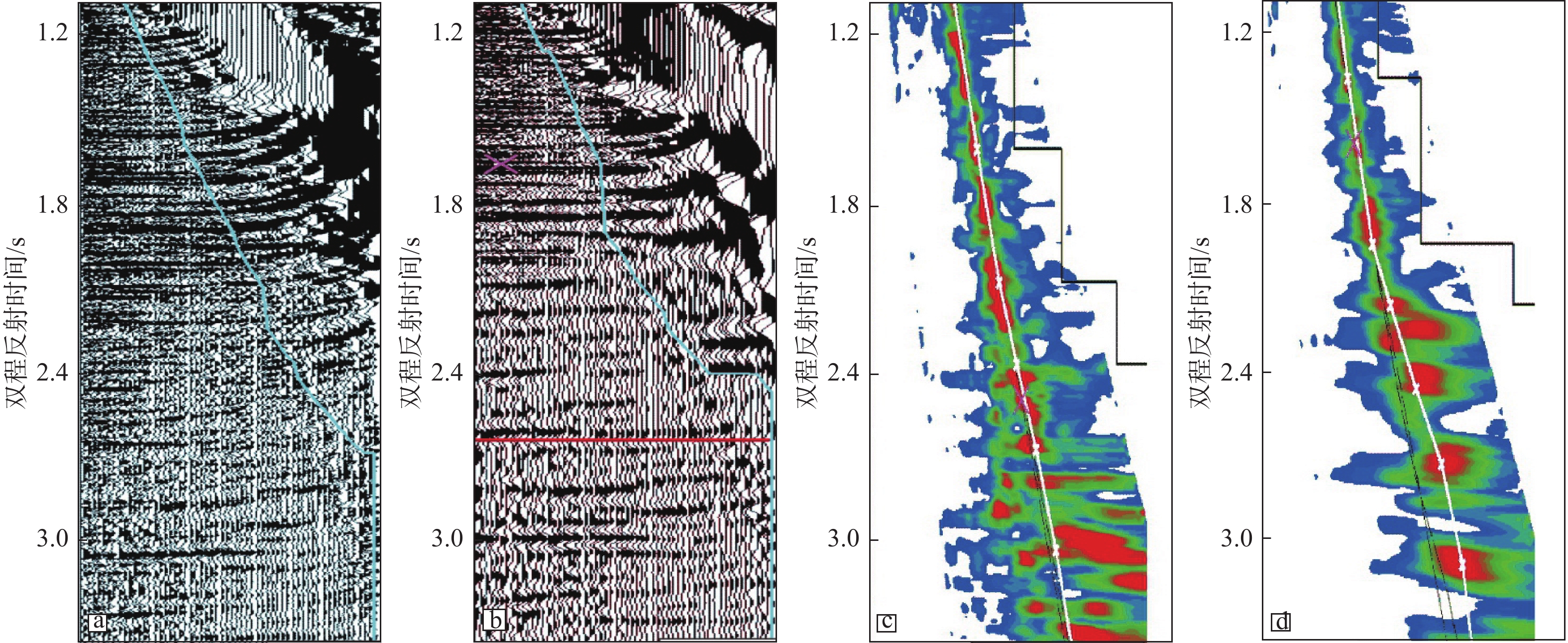
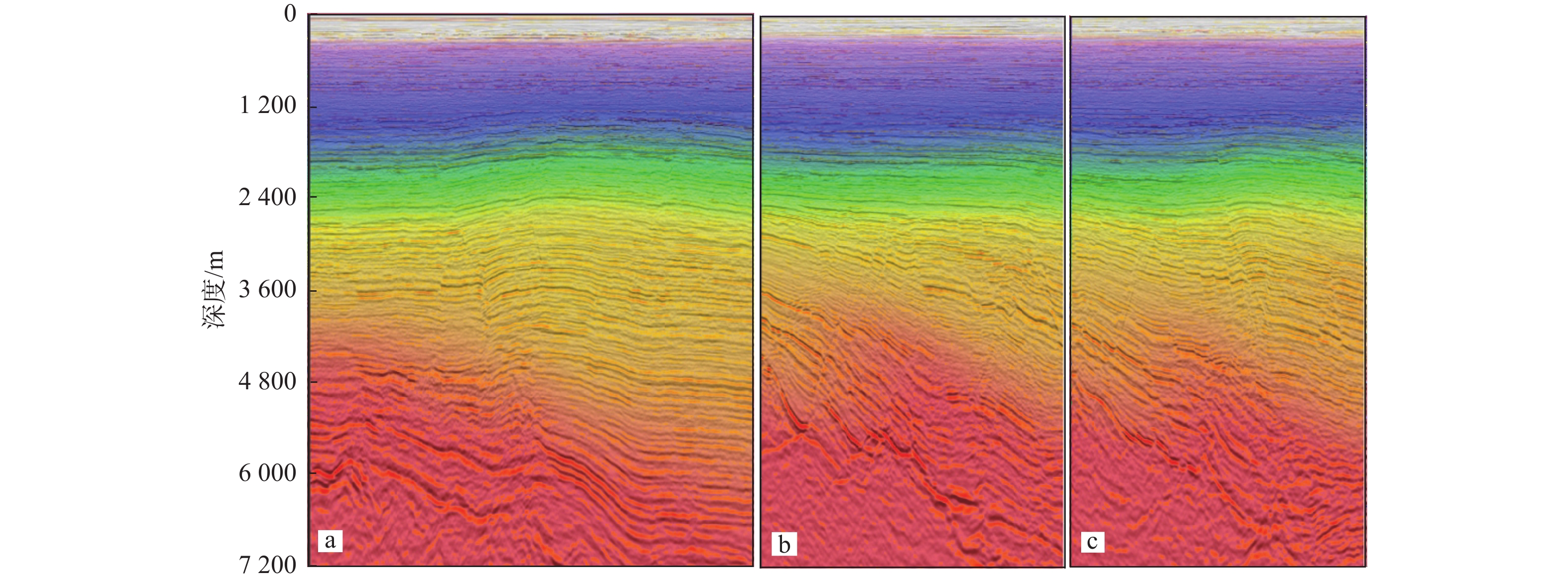
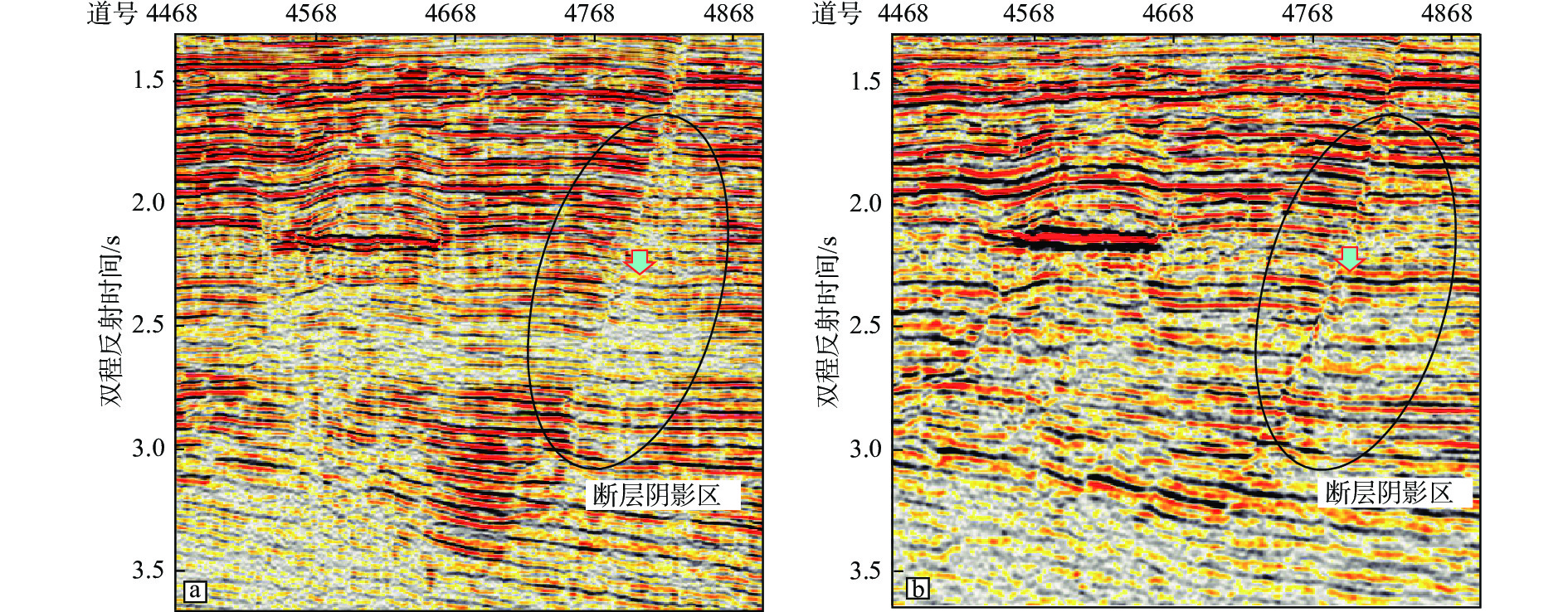
在复杂断块地区,地震成像受断层的影响,断层下盘同相轴出现“上拉”、“下拉”或者同相轴错断的现象,极大地影响了断层圈闭构造高点的确定以及圈闭幅度的准确判断。开展针对复杂断层的高精度速度建模和高精度成像技术被认为是解决断层阴影区成像的主要处理技术解决方案。立足于地震采集信号自身的属性信息,充分挖掘地震信号的潜力,提出广角反射的折射线性去噪技术、中低频有效信号提取技术和优势信号精细速度建模技术,在西湖TT区目标评价中取得了良好的效果,明显减低了断层阴影对目标构造形态的影响,提高了构造圈闭定位的准确性。应用结果表明:通过准确的PSDM速度模型结合断层阴影区优势信号的提取,获得更聚焦的反射能量,断层阴影区弱振幅区得到消除,有效改善了断裂阴影区的成像效果。
Abstract:In complex fault block areas, seismic imaging is affected by faults, resulting in the phenomenon of "pull up", "pull down", or displacement of same phase axis in the footwall of the fault, which greatly affects the determination of the structural highs of fault traps and the accurate judgment of trap amplitude. High-precision velocity modeling and high-precision imaging for complex faults were considered the main processing technological solutions for imaging the shadow zones of faults. Based on the attributes of the seismic acquisition signal, we fully explored the potential of seismic signal and proposed techniques for refractive linear denoising for wide angle reflection, the medium- and low-frequency effective signal extraction, and the dominant signal fine velocity modeling, which have achieved good outcome in the target evaluation for the TT area of Xihu Sag in East China Sea, significantly reduced the influence of fault shadow on the target structural morphology and improved the accuracy of fault trap locating. The application results show that by combining accurate PSDM (pre-stack depth migration) velocity model and the extraction of dominant signal of fault shadow zone, more focused reflection energy could be obtained, the weak amplitude zone of the fault shadow zone was eliminated, and the imaging effect of the fault shadow zone was effectively improved.
-
Key words:
- fault shadow zone /
- dominant signal /
- velocity modeling /
- imaging /
- fault trap
-

-
表 1 地震采集参数
Table 1. Seismic acquisition parameters
测线
方向电缆长度 记录道数 电缆间距/m 最大纵向
炮检距/m最大横向
炮检距/m横纵比 纵向覆盖
次数横向覆盖
次数气枪深度/m 电缆深度/m 30/210° 5 000 m/缆,共8缆 398道/缆,
共8缆75 5 200 270 0.05 50 1 5 6 -
[1] STUART F,赵改善. 断层阴影问题:机理与消除方法[J]. 石油物探译丛,1997,9(2):51-55.
[2] 陈祖银,张霞,邓海东,等. 断层阴影识别技术研究及应用效果分析[J]. 物探化探计算技术,2021,43(5):579-583.
[3] 侯凯,熊书权,杨天笑,等. 南海东部某油田地震成像畸变下的构造恢复[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(5):76-84.
[4] 姜岩,程顺国,王元波,等. 大庆长垣油田断层阴影地震正演模拟及校正方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2019,54(2):320-329.
[5] 刘南,李熙盛,侯月明,等. 模型正演在断层阴影带内构造研究中的作用[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2016,38(5):65-74.
[6] 宋亚民,戴朝强,姜建,等. 南海东部地区断层阴影带构造落实方法及其应用研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术,2021,43(3):296-303.
[7] 涂齐催,娄敏,毛云新,等. 基于构造-流体耦合约束的变速成图方法及其在东海A气田挖潜阶段的成功应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(12):56-63.
[8] 汪生好,李黎,蒋玉婷,等. 少井条件下低缓畸变构造精细研究及油气勘探启示[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(6):63-69.
[9] 白海军,程学欢,赵超,等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷断层阴影带成像技术与实践[J]. 石油物探,2022,61(2):329-338.
[10] 宋亚民,戴朝强,张丽萍,等. 恩平凹陷南部斜坡断层阴影带构造恢复方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2020,35(6):2194-2202.
[11] 孙维昭,王中凡,张智. 断层阴影的正演模拟、识别与校正:以尼日尔Termit盆地为例[J]. 地球物理学进展,2022,37(4):1593-1604.
[12] 白海军,袁阳,杨登锋,等. 海上三维双方位融合处理技术在番禺4洼的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(3):82-88.
[13] 张振波,罗伟. 拖缆宽方位与双方位效果分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(3):66-73.
[14] 朱明,何敏,张振波,等. 海上二次三维双方位地震资料联合成像[J]. 中国海上油气,2016,28(6):15-20.
[15] 胡高伟,邓勇,潘光超,等. 双方位、高密度地震资料在文昌凹陷勘探中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展,2019,34(6):2444-2450.
[16] 朱江梅,李列,杨薇,等. 多方位角地震资料在文昌凹陷勘探开发中的应用分析[J]. 地球物理学进展,2013,28(5):2587-2596.
[17] 胡光辉,李熙盛,郭丽,等. 构造约束全波形反演及其海上资料应用[J]. 石油物探,2018,57(4):592-596.
[18] 李黎,沈水荣,吴意明,等. 全波形反演与断控层析反演联合速度建模:以南海东部A油田为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2020,32(5):107-113.
[19] 张在金,陈可洋,范兴才,等. 井控与构造约束条件下的网格层析速度建模技术及应用[J]. 石油物探,2020,59(2):208-217.
[20] 彭海龙,邓勇,赫建伟,等. 基于断层与层位约束的3D速度建模方法在消除断层阴影中的应用研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2017,32(6):2520-2526.
-



 下载:
下载: