The well determination for geothermal resource explorationin typical islands in Xiaoguan Island, Qingdao
-
摘要:
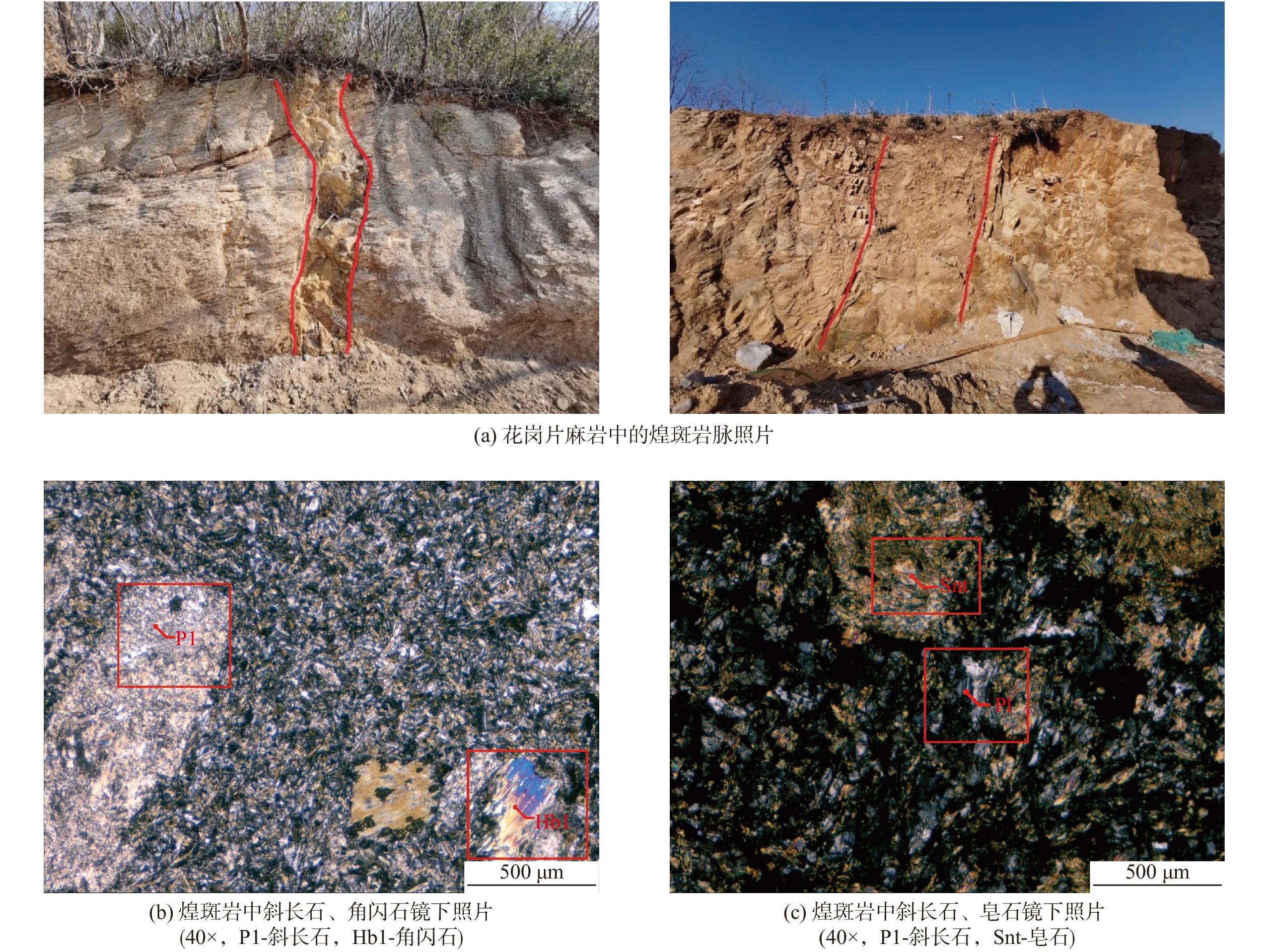
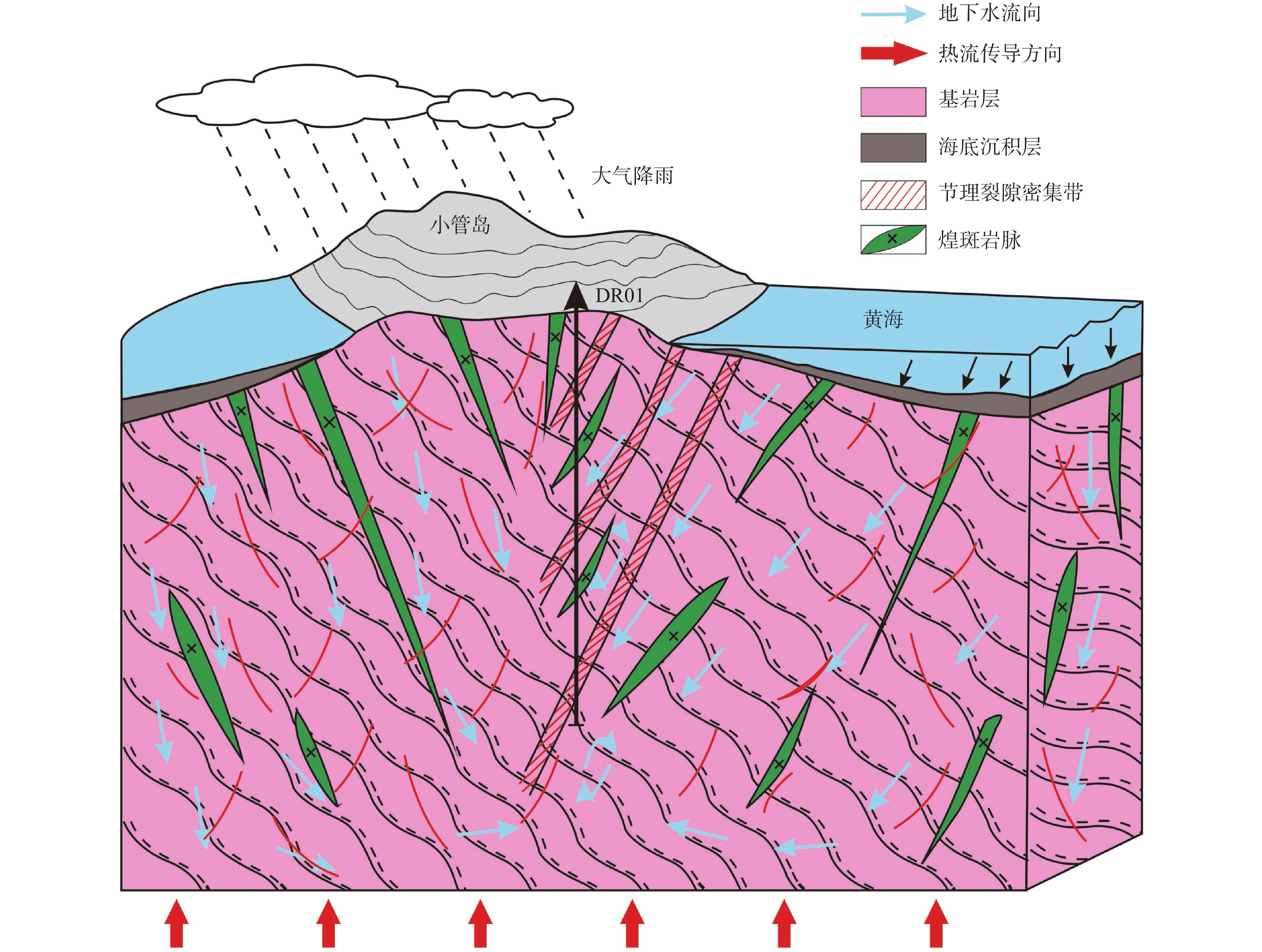
海岛地区地质环境条件相对较复杂,地形起伏较大,地貌类型多样,地热地质条件特殊,选用合适的地热资源勘查定井的方法,对地热资源的勘查开发具有重要意义。以典型海岛−青岛市小管岛的地热资源勘查工作为例,综合分析小管岛地热地质条件,对比分析地热资源勘查物探方法的优缺点,有针对性地采用音频大地电磁测深(AMT)和高精度电磁频谱法(MES)相结合的勘查定井方法进行地热资源勘查。综合2种物探方法解释成果,获取研究区热储概念模型,确定地热井位置,成功施工1500 m地热井1眼,出水量121.2 m3/d,孔底温度39.2 ℃。根据小管岛地热资源勘查实例表明,采用AMT法和MES法在海岛地区进行地热资源勘查是可行的、有效的。
Abstract:The geological environment conditions in island area are relatively complex, with large topographical fluctuations, various types of landforms, and special geothermal geological conditions. Choosing appropriate methods for geothermal resource exploration and well location is of great significance for the exploration and development of geothermal resources. Taking the geothermal resource exploration on Xiaoguan Island in Qingdao City as an example, we comprehensively analyzed the geothermal condition and compared the advantages and disadvantages of geophysical prospecting methods for geothermal resource exploration. Besides, by combining audio magnetotelluric (AMT) sounding method with high precision electromagnetic spectrum (MES) method, we interpreted the results of the two geophysical prospecting methods, obtained a conceptual model of thermal storage in the island area, identified the location of geothermal wells, and successfully constructed a 1500 m-deep geothermal well with a daily water output of 121.2 m3 and a 39.2 ℃ of bottom hole temperature. This study justified the feasibility and effectiveness of applying AMT and MES methods to explore geothermal resources in the island area.
-
Key words:
- typical islands /
- geothermal resources /
- exploration and well location methods /
- AMT method /
- MES method
-

-
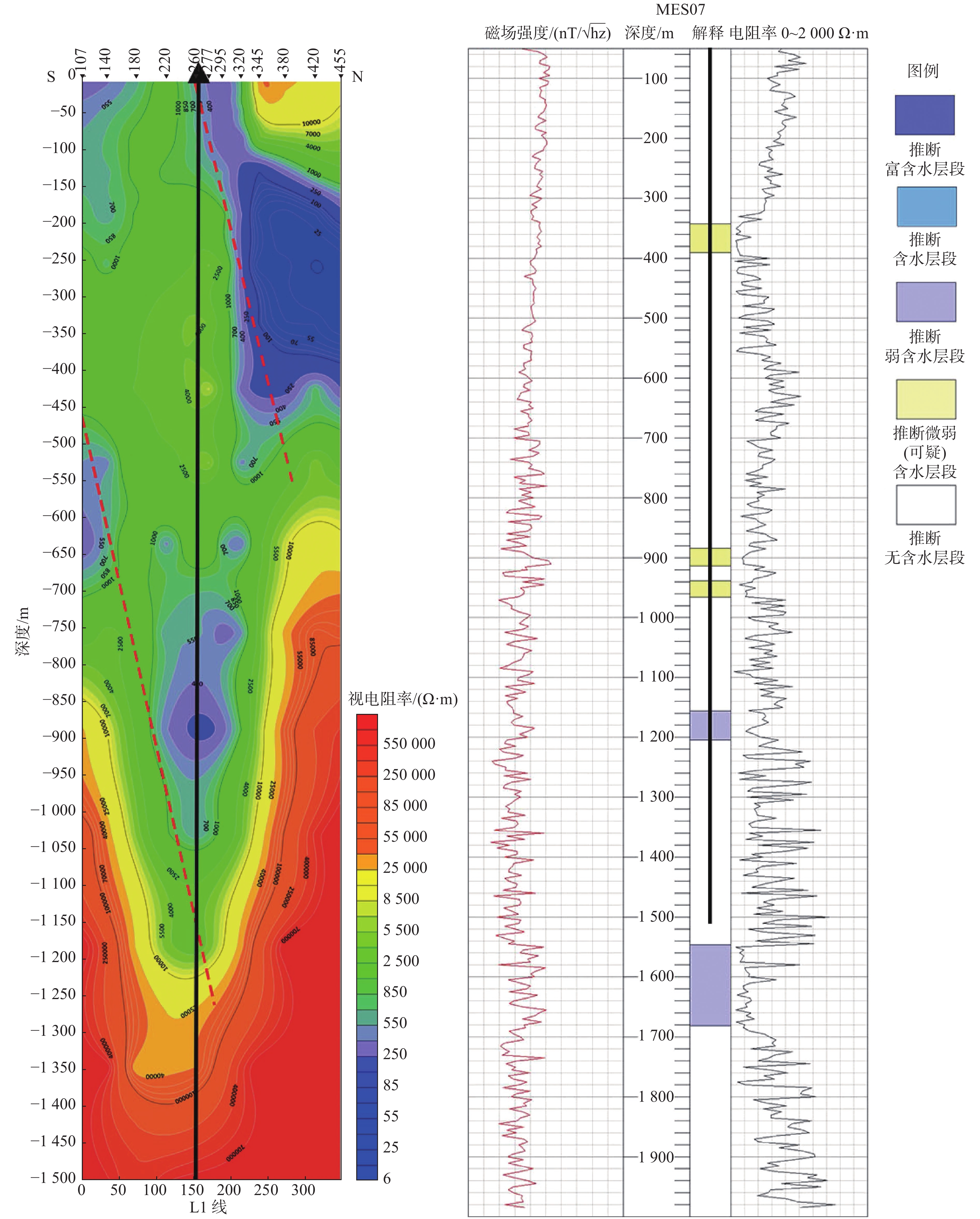
表 1 MES测深解译结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of MES sounding interpretation results
推断的含水层 探明的含水层 分析总结 含水层1 342~390 m 含水层1 351.33~357.15 m 存在且基本一致 含水层2 884~913 m 含水层2 617.75~622.55 m 存在但深度有偏差 含水层3 938~965 m / / 煌斑岩分布段 含水层4 1 180~1 200 m 含水层3 1 170.40~1 178.75 m 存在且基本一致 含水层5 1546~1 681 m 含水层4 1 437.45~1 448.70 m 有待验证 注:“/”为无内容。 -
[1] 刘桂仪, 刘洪华, 陈奂良, 等. 地热资源勘查实务[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 2021.
[2] 李常锁,杨磊,高卫新,等. 济南北部地热田地热地质特征浅析[J]. 山东国土资源,2008,24(4):39-43.
[3] 韩立民,王爱香. 保护海岛资源:科学开发和利用海岛[J]. 海洋开发与管理,2004,6:30-33.
[4] 李迎朋. 河北省海岛地热综合利用方式探究[J]. 陕西建筑,2020,9:1-3.
[5] 陈大磊,于嘉宾,王阳,等. 音频大地电磁测量法(AMT)在莒县地区地热勘查中的应用[J]. 山东国土资源,2016,32(12):58-61.
[6] 雷晓东,杨全合,李晨,等. 北京凤河营地热田东北部综合地球物理勘探[J]. 物探与化探,2004,39(4):249-255.
[7] 徐光辉,黄力军,刘瑞德. 应用可控源音频大地电磁测深于北京水文地质勘查[J]. 物探与化探,2005,29(6):523-525.
[8] 万明浩,王家林,吴健生,等. 江苏句容-常州地区综合地球物理研究[J]. 地球物理学报,1993,36:791-797.
[9] 吴璐萍,石昆法,李荫槐,等. 可控源音频大地电磁法在地下水勘查中的应用研究[J]. 地球物理学报,1996,39(5):712-717.
[10] 叶益信,邓居智,方根显. 高频大地电磁测深(EH-4) 在热储构造勘查中的试验研究:以抚州地热区为例[J]. 地质与勘探,2011,47(4):649-653.
[11] 汪琪,赵志鹏,尹秉喜,等. 电磁测深MT法在平原深部地热调查中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报,2016,13(6):782-787.
[12] 王佳龙,张宝松,陈基炜,等. 大地电磁测深不同反演方法的应用效果对比:以安徽皖江地区页岩气调查为例[J]. 华东地质,2020,41(1):79-87.
[13] 柳建新, 童孝忠, 郭荣文, 等. 大地电磁测深法勘探: 资料处理、反演与解释[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.
[14] 李帝铨,胡艳芳. 强干扰矿区中广域电磁法与CSAMT探测效果对比[J]. 物探与化探,2015,39(5):967-972.
[15] 陈斌. CSAMT法与微动测深法在漳州某区地热资源勘探中的应用[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2021,1:64-69.
[16] 秦福锋,许丙彩,冯英明,等. 日照东部地区地热资源成因分布规律及勘查定井方法研究[J]. 山东国土资源,2021,37(9):36-45.
-




 下载:
下载: