Assessment of resources and ecological risks induced by groundwater utilization in the unconfined aquifer in the western Jilin Province: A case study in the Taoer River catchment
-
摘要:
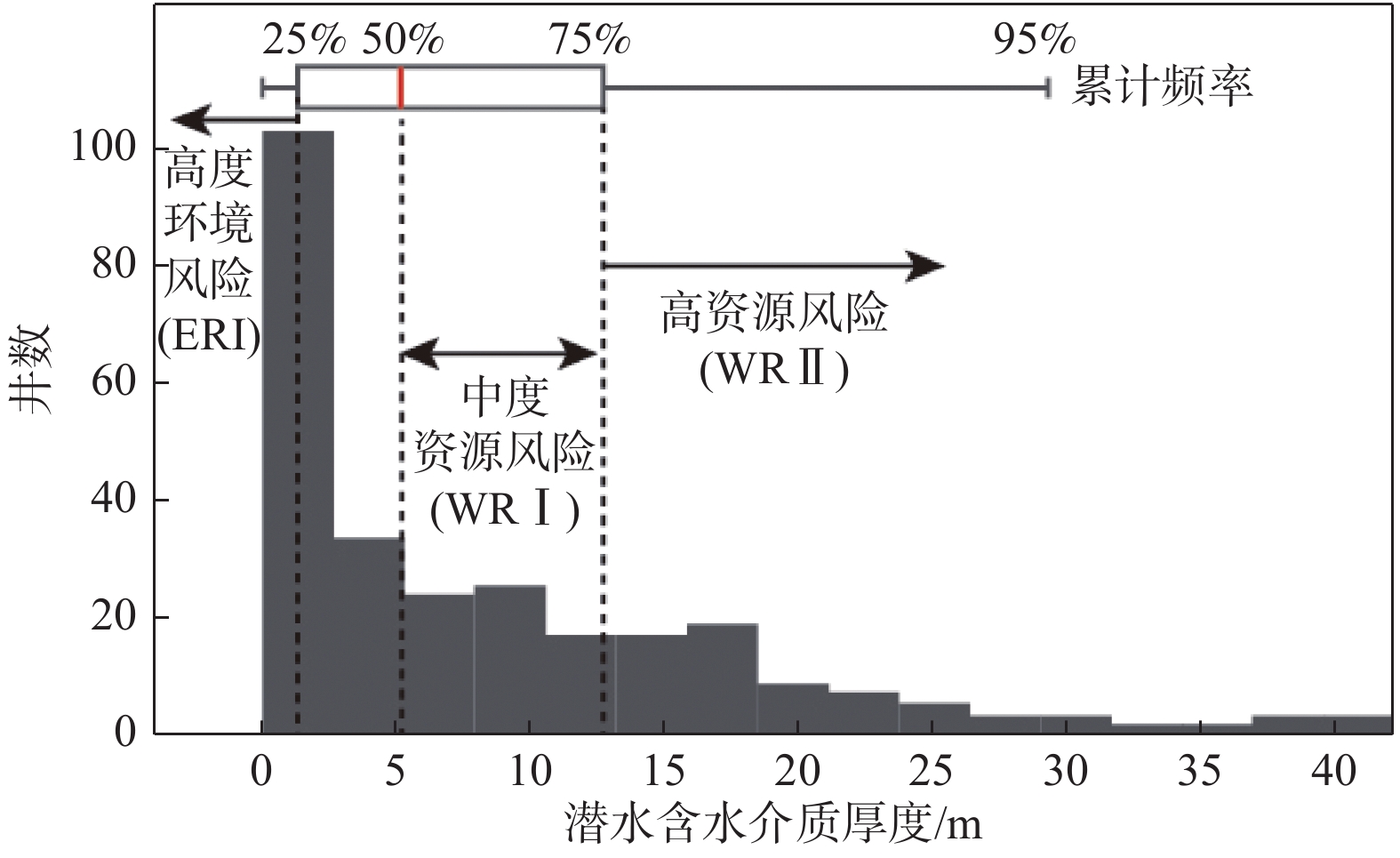
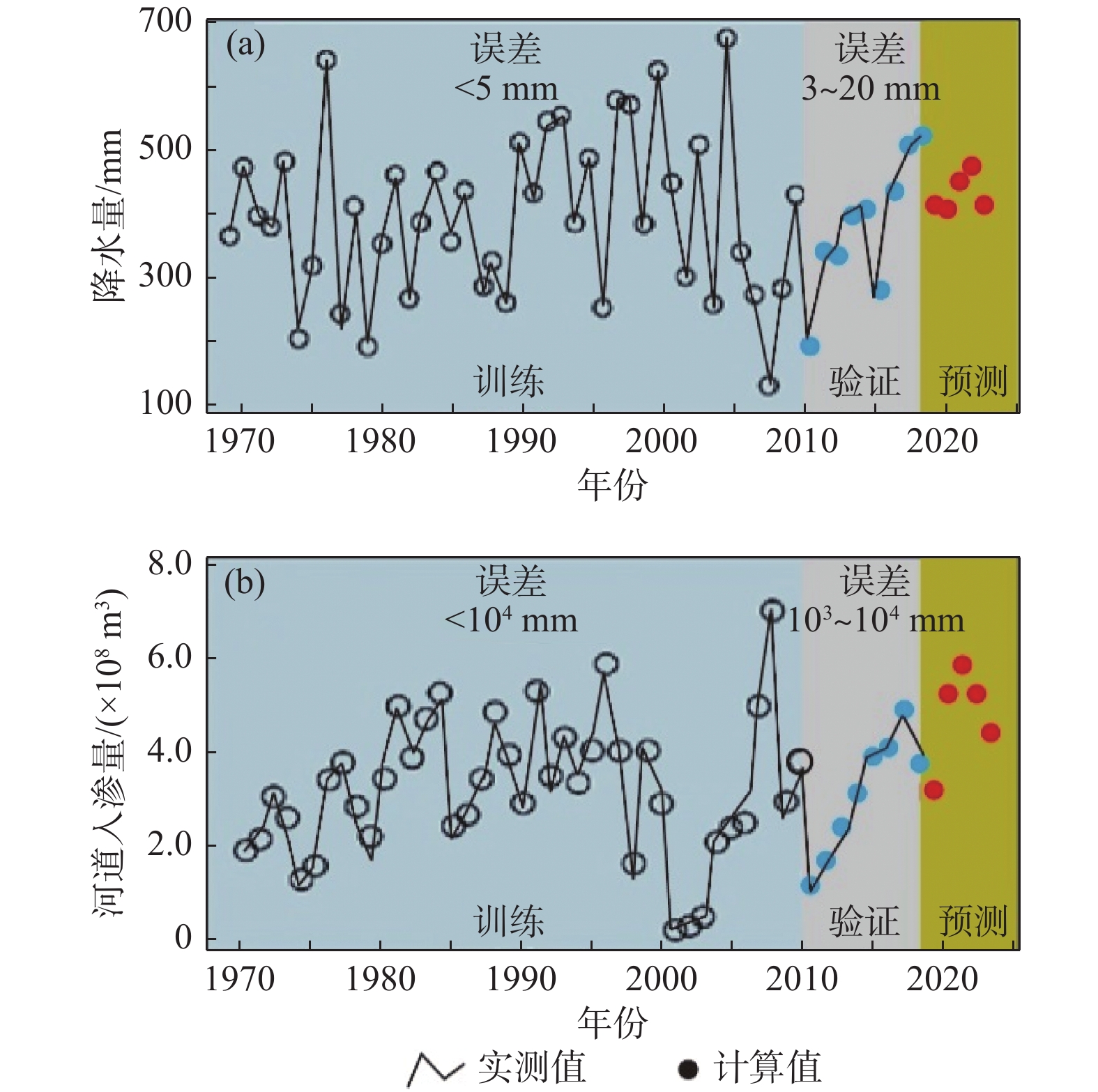
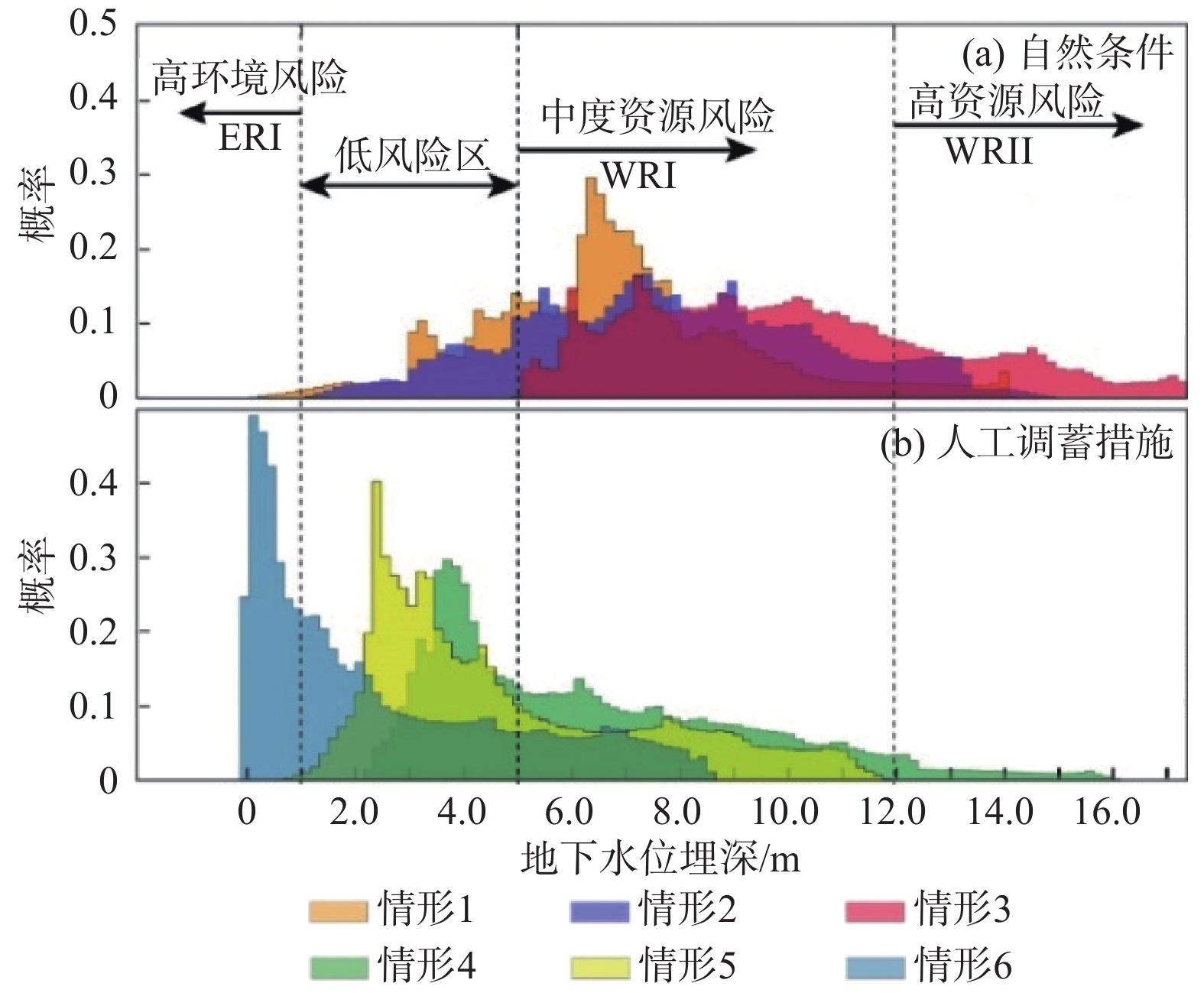
吉林省西部是我国主要粮食产区,但区内农业水利规划管理同时面临潜水资源与生态环境双重风险。近20年来,区内曾尝试多种水资源利用模式,但缺少不同模式应用效果的定量化对比。文章建立了不同水资源利用模式,对比分析各模式的水资源与次生盐碱化风险。以洮儿河流域为例,采用循环神经网络预测2019—2023年该地区大气降水和地表水对地下水补给量;通过随机数值模拟预测现状开采、连续干旱、无序开采、地下水库建设、节水灌溉、旱田改水田6种情形下,区内潜水水位空间分布特征。以防止次生盐碱化为目标,定义水位埋深上限为1 m;以含水介质厚度为参考,定义水位埋深下限为12 m。遴选适合吉林省西部地区地下水资源可持续利用模式。结果显示:无序开采是导致区内水资源枯竭的主要诱因;地下水库建设和旱改水工程有助于潜水资源维护,但长期运行可加剧生态环境风险。节水灌溉(净采强度为2.0×108~3.0×108 m3/a)是降低区内水资源风险和生态环境风险的最佳方式。文章采用的神经网络—随机模拟分析方法成功预测了地下水位变化驱动因子和地下水位中长期变化趋势,为我国干旱半干旱地区潜水资源利用方案制定提供了新方法。
Abstract:The western part of Jilin Province is one of the major agriculture zones in China. It is located in a semi-arid zone with limited and unreliable water resources, and also with serious soil salinization. It is of critical importance to manage the groundwater levels in the unconfined aquifer, considering both the risks of water resources and the ecological problems related to the shallow buried depth of groundwater levels. However, there is still lack of quantitative risk analyses on the current strategies of water use in this area. In this study the recurrent neural network is used to predict the rainfall and river flux from 2019 to 2023, which are then used as the input variables in the stochastic groundwater flow models to predict the spatial distribution of groundwater levels in the unconfined aquifer. The groundwater levels under six scenarios, including the present-day recharge and discharge, drought, chaos extraction, managed aquifer recharge, drip irrigation and paddy farming, are calculated. Following a risk assessment, the drip irrigation with a net extraction rate ranging from 2.0×108 to 3.0×108 m3/a is considered as the best strategy for groundwater resources utilization, which can effectively prevent the water resources in the unconfined aquifer from being over-exploited (with the buried depth of greater than 12 m), and also maintain the depth of groundwater table of greater than 1m to reduce the risk of soil salinization. Meanwhile, chaos extraction inducing the water resources depletion is the major factor, and both the managed aquifer recharge and paddy farming are helpful in water resources conservation, but may worse the soil salinization. The methodology employed in this study can be widely used in other arid and semi-arid areas for groundwater resources management.
-

-
表 1 不同分区内渗透系数、给水度概率分布[28]
Table 1. Probability distribution of coefficient of permeability and specific yield in different zones
分区 渗透/ (m·d−1) 给水度 均值 方差 概率分布 均值 方差 概率分布 I 30.5 2.3 对数正态 0.13 0.05 正态 II 35.8 1.8 对数正态 0.14 0.04 正态 III 25.7 5.0 对数正态 0.12 0.05 正态 IV 28.3 3.2 对数正态 0.10 0.05 正态 V 20.6 2.2 对数正态 0.10 0.04 正态 VI 23.8 1.7 对数正态 0.10 0.04 正态 表 2 不同工况条件下研究区域补给量与开采量取值范围
Table 2. Ranges of recharge and exploration rate under different scenarios
序号 工况 补给量/
(×108 m3·a−1)开采量/
(×108 m3·a−1)概率分布 情形1 维持现状 4.7~8.0 3.8~6.9 均匀 情形2 干旱 0.0~5.0 3.8~6.9 均匀 情形3 无序开采 4.7~8.0 4.0~11.0 均匀 情形4 地下水库调蓄 4.7~8.0 3.8~6.9 均匀 情形5 节水灌溉 4.0~7.0 2.0~3.0 均匀 情形6 旱改水工程 7.0~10.0 3.8~6.9 均匀 -
[1] 神祥金, 吴正方, 杜海波. 近50年来吉林西部半干旱区气候变化特征[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2014,25(2):190 − 196. [SHEN Xiangjin, WU Zhengfang, DU Haibo. Characteristics of climatic change in semiarid region of western Jilin in recent 50a[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2014,25(2):190 − 196. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2014.02.033
[2] 李海毅, 汤洁, 斯蔼. 分形理论在吉林西部干旱指数预测中的应用[J]. 东北师大学报(自然科学版),2007,39(1):126 − 130. [LI Haiyi, TANG Jie, SI Ai. Application of fractal theory in forecasting the drought index in the west of Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2007,39(1):126 − 130. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1832.2007.01.026
[3] 戴长雷. 地下水库调控研究—以饮马河中游为例[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2006.
DAI Changlei. Study on groundwater reservoir regulation with a case of the middle reaches of Yinma river[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 林年丰, 汤洁. 松嫩平原环境演变与土地盐碱化、荒漠化的成因分析[J]. 第四纪研究,2005,25(4):474 − 483. [LIN Nianfeng, TANG Jie. Study on the environment evolution and the analysis of causes to land salinization and desertification in Songnen plain[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2005,25(4):474 − 483. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.04.011
[5] 肖霄. 吉林省洮儿河扇形地地下水库人工调蓄理论与技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.
XIAO Xiao. Research on the theory and technology of groundwater reservoir artificial regulation of Taoer River alluvial fan in Jilin province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 黄彦, 司振江, 李芳花, 等. 大型灌区节水改造技术集成研究与示范[J]. 水利科学与寒区工程,2018,1(6):8 − 14. [HUANG Yan, SI Zhengjiang, LI Fanghua, et al. Research and demonstration of key technologies for water saving reform in large scale irrigation aera[J]. Hydro Science and Cold Zone Engineering,2018,1(6):8 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3305.2018.06.002
[7] 范语思, 李月芬, 张玉树, 等. 吉林西部县域“旱改水”时空演变特征及驱动机制分析[J]. 世界地质,2020,39(2):444 − 451. [FAN Yusi, LI Yuefen, ZHANG Yushu, et al. Analysis on spatiotemporal evolution and its driving mechanism of conversion from dryland into paddy field at County scale in western Jilin Province[J]. Global Geology,2020,39(2):444 − 451. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2020.02.020
[8] 汤洁, 陈静书, 李昭阳, 等. 吉林西部盐碱农田有机碳矿化和激发效应对氮磷添加的响应[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(3):1−11.
TANG Jie, CHEN Jingshu, LI Zhaoyang, et al. Response of organic carbon mineralization and priming effect to nitrogen and phosphorus addition in saline-alkali farmland of western Jilin province, China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2020, 50(3):1−11.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 杨沁瑜, 张尧, 刘家福. 基于蚁群模型的吉林西部土地利用安全格局情景模拟研究[J]. 长春师范大学学报, 2020, 39 (2), 97−103.
YANG Qinyu, ZHANG Yao, LIU Jiafu. Simulation of land use security pattern in western Jilin province based on ant colony model[J]. Journal of Changchun Normal University, 2020, 39 (2): 97−103.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 才源, 曹扬, 李子勇, 等. 吉林省西部盐碱地状况的调查与分析[J]. 农业与技术, 2019, 39(19): 48−52.
CAI Yuan, CAO Yang, LI Ziyong, et al. Survey and analysis of saline soil distribution in Western Jilin Province[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2019, 39(19): 48−52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 鲍硕超, 王清, 卞建民. 吉林省大安地区盐渍土室内冻胀试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(6): 1701−1707.
BAO Shuochao, WANG Qing, BIAN Jianmin. Indoor frost heaving experiment of saline soil in Da'an area, Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(6): 1701−1707. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 卞建民, 刘彩虹, 杨晓舟. 吉林西部大安灌区土壤贮水能力空间变异特征及土壤水分有效性[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(2): 554−563.
BIAN Jianmin, LIU Caihong, YANG Xiaozhou. Spatial distribution of soil water storage capacity and soil water availability in West Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(2): 554−563. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 张瑜, 徐子棋, 杨献坤. 不同改良剂对吉林西部重度盐碱土的改良及牧草的增产[J]. 森林工程,2020,36(2):25 − 34. [ZHANG Yu, XU Ziqi, YANG Xiankun. Effects of different soil amendments on the soil improving and the forage grass yield increasing on the severe saline-alkali soil in the western Jilin Province[J]. Forest Engineering,2020,36(2):25 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2020.02.005
[14] LI Y F, GONG H Y, LI S J, et al. Ecological stoichiometry homeostasis of six microelements in leymus chinensis growing in soda saline-alkali soil[J]. Sustainability,2020,12(10):4226. doi: 10.3390/su12104226
[15] 章光新, 邓伟, 何岩. 洮儿河流域地下水TDS时空变异特征研究[J]. 水土保持学报,2005,19(2):122 − 124. [ZHANG Guangxin, DENG Wei, HE Yan. Characteristics of spatial and temporal variation of TDS of groundwater in tao'er river basin[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2005,19(2):122 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.02.032
[16] 朱琳, 苏小四. 吉林西部地区第四系潜水水质影响因素的R型因子分析[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2006,28(1):51 − 56. [ZHU Lin, SU Xiaosi. Application of R-mode analysis in determining influencing factors of quaternary unconfined groundwater quality in west area of Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2006,28(1):51 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2006.01.011
[17] 王宇, 卢文喜, 卞建民, 等. 三种地下水位动态预测模型在吉林西部的应用与对比[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(3):886−891.
WANG Yu, LU Wenxi, BIAN Jianmin, et al. Comparison of three dynamic models for groundwater in western Jilin and the application[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2015, 45(3):886−891.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 卞建民, 汤洁, 封灵, 等. 吉林西部砷中毒区水文地球化学特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2009,36(5):80 − 83. [BIAN Jianmin, TANG Jie, FENG Ling, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics in the arsenic poisoning area in western Jilin Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2009,36(5):80 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.05.018
[19] POORNIMA S, PUSHPALATHA M. Prediction of rainfall using intensified LSTM based recurrent neural network with weighted linear units[J]. Atmosphere,2019,10(11):1 − 18.
[20] 陈荦, 张幼宽, 王长申. 基于时间序列分析的辛安泉流量变化研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2012, 39(1):19−23.
CHEN Luo, ZHANG Youkuan, WANG Changshen. A study of evolution of the discharge of the Xin'an Spring with time series analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2012, 39(1):19−23.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 凤蔚, 祁晓凡, 李海涛, 等. 雄安新区地下水水位与降水及北太平洋指数的小波分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2017, 44(6): 1−8.
FENG Wei, QI Xiaofan, LI Haitao, et al. Wavelet analysis between groundwater level regimes and precipitation,North Pacific Index in the Xiongan New Area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(6): 1−8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 姜瑶, 徐宗学, 王静. 基于年径流序列的五种趋势检测方法性能对比[J]. 水利学报, 2020, 51 (7): 1−13.
JIANG Yao, XU Zongxue, WANG Jing. Comparison among five methods of trend detection for annual runoff series[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2020, 51 (7): 1−13 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 杨果岳, 方明, 孙希望, 等. 基于递归图理论的沉降时间序列可预测分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(1):158 − 164. [YANG Guoyue, FANG Ming, SUN Xiwang, et al. Predictability analysis of the settlement time series based on the theory of recurrence plots[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(1):158 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] CONNOR J T, MARTIN R D, ATLAS L E. Recurrent neural networks and robust time series prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks,1994,5(2):240 − 254. doi: 10.1109/72.279188
[25] KINGMA D P, BA J L. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[M]. Toronto: International Conference on Learning Representations, 2015.
[26] NEUMAN S P. Theory of flow in unconfined aquifers considering delayed response of the water table[J]. Water Resources Research,1972,8(4):1031 − 1045. doi: 10.1029/WR008i004p01031
[27] Diersch, H J G. FEFLOW: finite element modeling of flow, mass and heat transport in porous and fractured media[M]. Germany: Springer Science & Business Media, 2013:10-68.
[28] 陈社明. 吉林西部浅层地下水系统对旱改水工程的响应研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2013.
CHEN Sheming. The effect of dry land to wet land on shallow aquifer in western Jilin province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] REHFELDT K R, BOGGS J M, GELHAR L W. Field study of dispersion in a heterogeneous aquifer: 3. Geostatistical analysis of hydraulic conductivity[J]. Water Resources Research,1992,28(12):3309 − 3324. doi: 10.1029/92WR01758
-




 下载:
下载: