Particle identification and statistical methods of a rock avalanche accumulation body based on the particle analysis system
-
摘要:
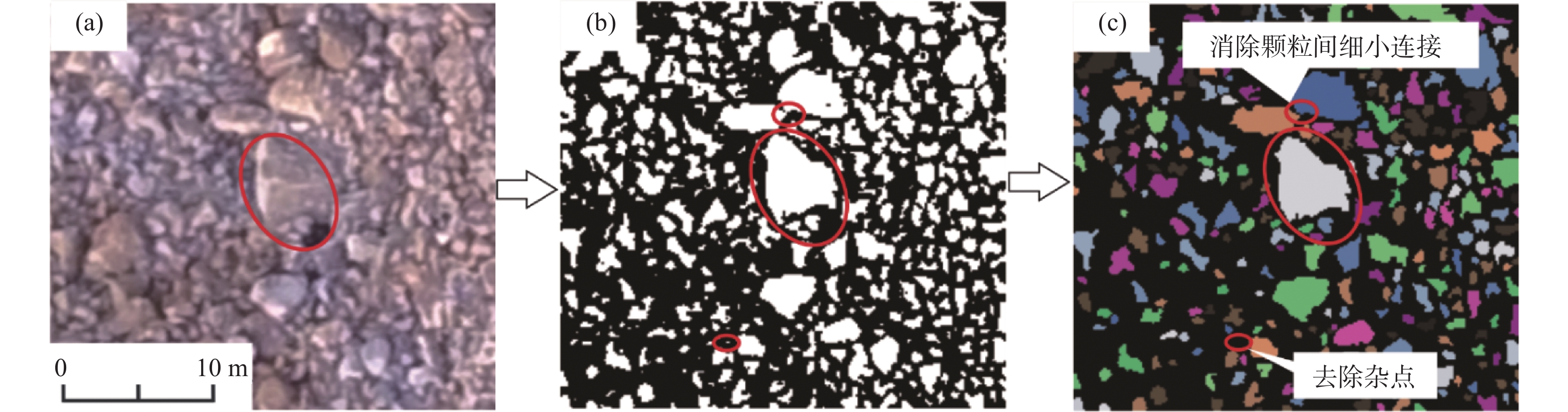
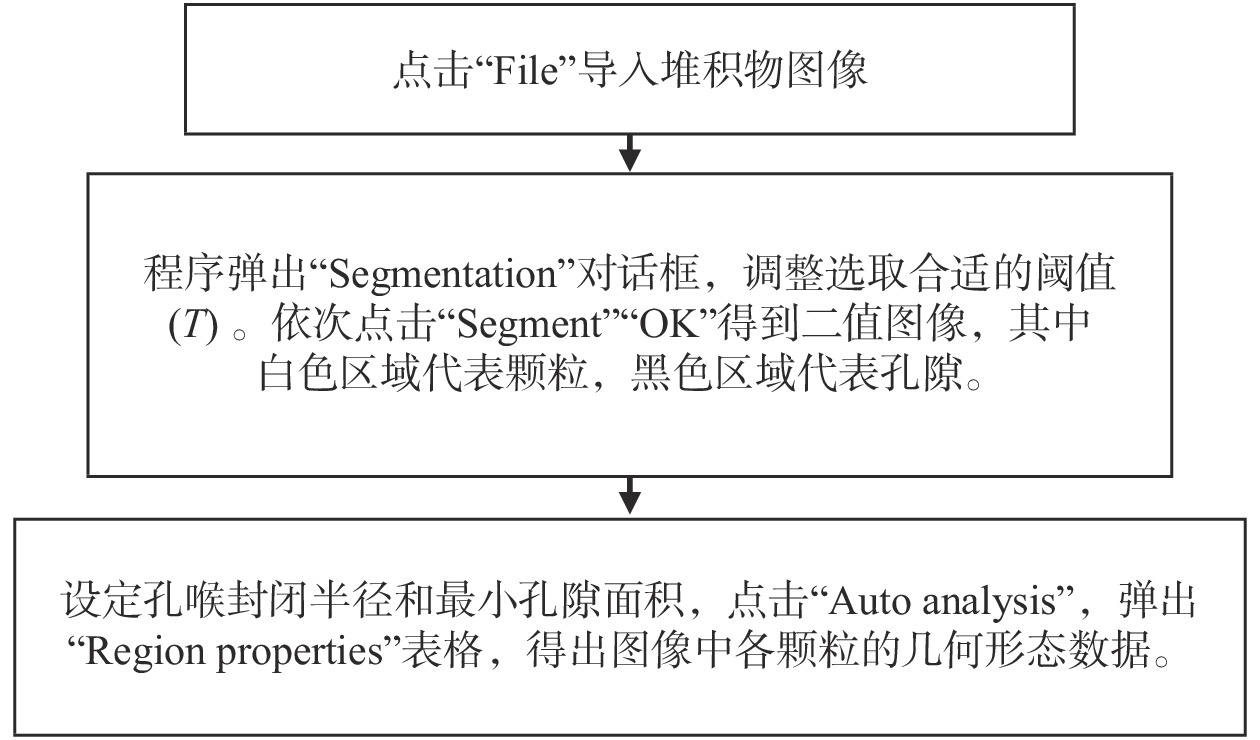
碎屑流堆积物颗粒识别和统计是碎屑流灾害的研究重点。文章基于图像处理孔隙(颗粒)及裂隙图像识别与分析系统(PCAS),以贵州纳雍普洒村崩塌-碎屑流为例,结合纳雍崩塌堆积物粒径实测结果,通过阐释识别过程中阈值、孔喉封闭半径、最小孔隙面积的参数意义,研究PCAS软件在碎屑流颗粒识别与统计中的应用,并提出了颗粒识别时这些参数的选取方法。分析结果表明:(1)PCAS能自动准确地识别碎屑流堆积物颗粒与孔隙,相比人工计数更精细,所识别堆积物各区小颗粒比重较大,0~2 m颗粒粒径各区占比都在50%以上;(2)当阈值为170(像素)时能获得精细的二值图像,颗粒与孔隙得到了准确地区分;(3)不同参数取值下获得堆积物颗粒粒径分布结果不同,碎屑流堆积物颗粒识别宜采用较大的孔喉封闭半径和较小孔隙面积,当二者比值为3/30(像素)时能更好地反应颗粒粒径分布情况;(4)PCAS具有较高的可行性,统计结果显示,各粒径含量变化趋势与人工统计相近,两种统计方法各粒径占比、分布规律基本吻合,说明利用PCAS可以实现对崩塌碎屑流颗粒粒径分布的高效便捷分析。
-
关键词:
- 碎屑流 /
- 孔隙(颗粒)及裂隙图像识别与分析系统 /
- 堆积体 /
- 颗粒识别 /
- 纳雍崩塌
Abstract:Particle identification and statistics of rock avalanche deposits are the focus of researches on rock avalanche disasters. Based on the image processing PCAS particle recognition system, taking the collapse-rock avalanche of the Pusa Village in Nayong of Guizhou Province as an example, combined with the measured results of the particle size of the Nayong collapse, the parameter values of threshold (T), pore throat closing radius (r) and minimum pore area (S0) during the identification process are explained. The application of PCAS software to the identification and statistics of rock avalanche particles is studied, and the selection methods of these parameters are proposed. The analysis results show that (1) PCAS can automatically and accurately identify debris flow accumulation particles and pores, which are more precise than manual counting. Small particles in each area of the recognized accumulation have a large proportion, and the proportion of 0~2 m particles in each area is more than 50%. (2) When the threshold value is 170 (pixels), a fine binary image can be obtained, and the particles and the pores are accurately distinguished. (3) The particle size distribution results of the deposits obtained under different parameter values are different, and the particle identification of the rock avalanche deposits should adopt larger r and S0. When r/S0=3/30 (pixels), the particle size distribution can be better reflected. (4) PCAS is of the high feasibility and the statistical results show that the variation trend of each particle size content is similar to that of artificial statistics. The proportion and distribution of particle sizes in the two statistical methods are basically consistent with each other, which is of great significance for the efficient and convenient analysis of particle size distribution of collapse-rock avalanche.
-
Key words:
- rock avalanche /
- PCAS /
- accumulation body /
- particle identification /
- rock avalanche in Nayong
-

-
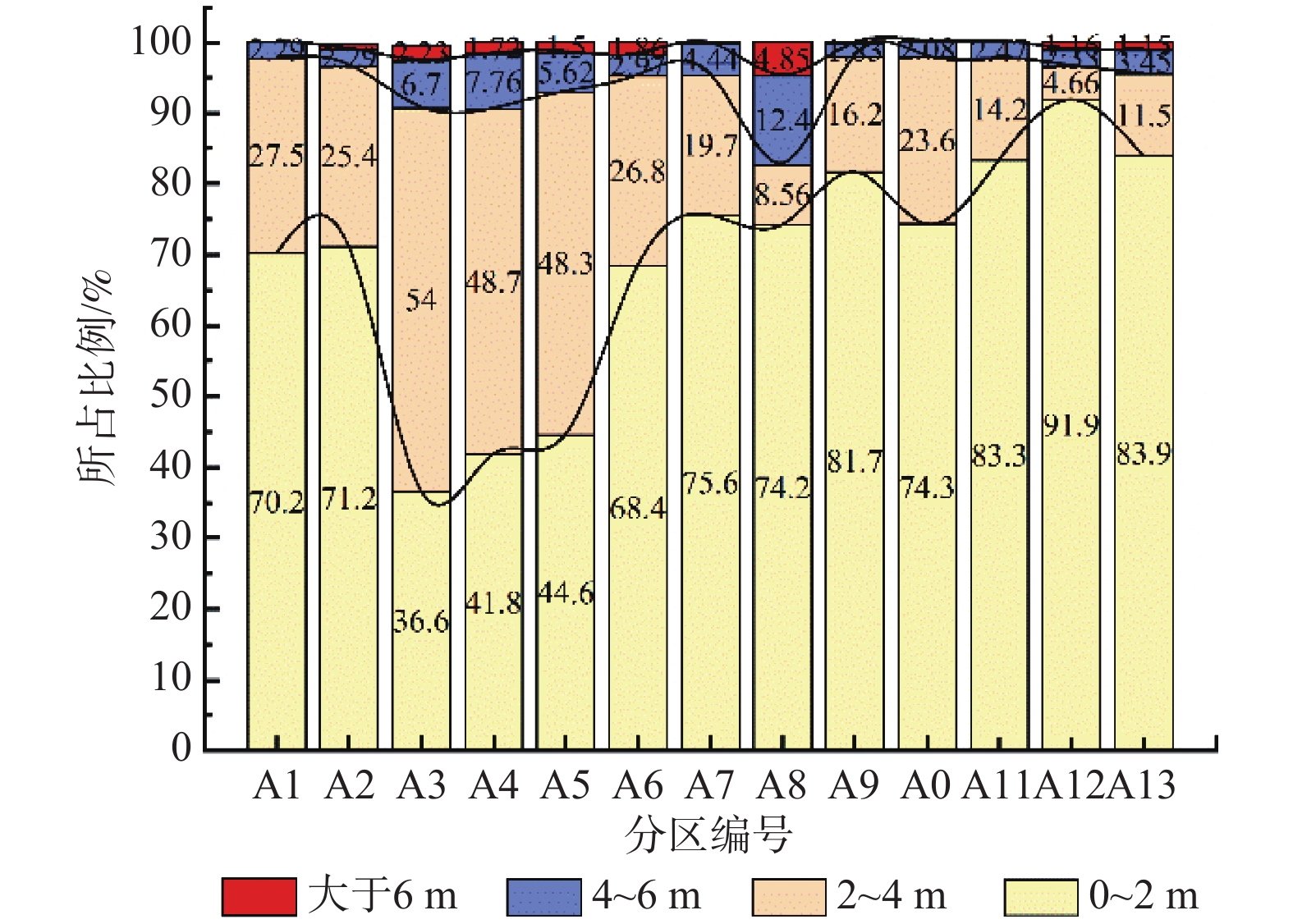
图 3 崩塌堆积分区示意图[2]
Figure 3.
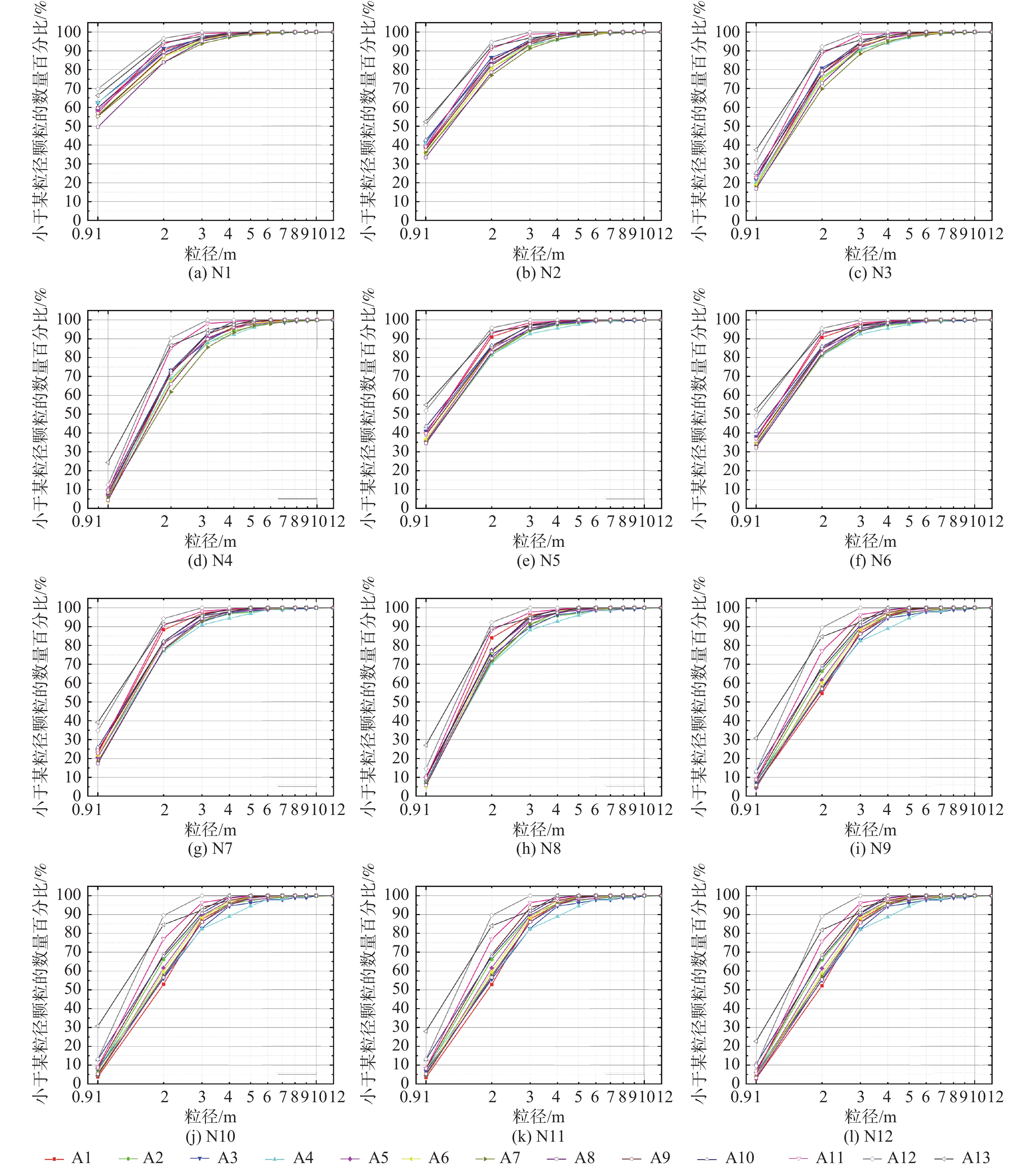
图 4 分区颗粒粒径累计曲线[2]
Figure 4.
表 1 三个参数的组合情况
Table 1. Combinations of the three parameters
颗粒粒径累计
曲线编号阈值(T) 孔喉封闭
半径(r)最小孔隙面积
(S0)N1 170 1 10 N2 20 N3 30 N4 40 N5 2 10 N6 20 N7 30 N8 40 N9 3 10 N10 20 N11 30 N12 40 -
[1] FRANCIS, AMP P W, BAKER M C W. Mobility of pyroclastic flows[J]. Nature, 1977, 270:164 − 165.
[2] 彭双麒, 许强, 郑光, 等. 碎屑流堆积物粒度分布与运动特性的关系—以贵州纳雍普洒村崩塌为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(4):129 − 136. [PENG Shuangqi, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Relationship between particle size distribution and movement characteristics of rock avalanche deposits: A case study of the Pusa village rock avalanche in Nayong of Guizhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(4):129 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] TOMIOKA S, KOZAKI T, TAKAMATSU H, et al. Analysis of microstructural images of dry and water-saturated compacted bentonite samples observed with X-ray micro CT[J]. Applied Clay Science,2010,47(1/2):65 − 71.
[4] 李建胜, 王东, 康天合. 基于显微CT试验的岩石孔隙结构算法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2010,32(11):1703 − 1708. [LI Jiansheng, WANG Dong, KANG Tianhe. Algorithmic study on rock pore structure based on micro-CT experiment[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2010,32(11):1703 − 1708. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 吴义祥. 工程粘性土微观结构的定量评价[J]. 地球学报,1991,12(2):143 − 151. [WU Yixiang. Quantitative approach on micro-structure of engineering clay[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,1991,12(2):143 − 151. (in Chinese)
[6] 施斌, 李生林, TOLKACHEV M. 黏性土微观结构SEM图象的定量研究[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学,1995,25(6):666 − 672. [SHI Bin, LI Shenglin, TOLKACHEV M. Quantitative research on SEM image of the microstructure of cohesive soil[J]. Science in China (Series A),1995,25(6):666 − 672. (in Chinese)
[7] 涂新斌, 王思敬, 岳中琦. 香港风化花岗岩细观结构研究方法[J]. 工程地质学报, 2003, 11(4): 428 − 434.
TU Xinbin, WANG Sijing, YUE Zhongqi. Methods for study of microstructure of weathered granite, Hong Kong[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2003, 11(4): 428 − 434. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 梁双华, 孙如华, 李文平. 基于Mapinfo 和Photoshop 的粘性土扫描图像处理[J]. 河南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 26(1): 55 − 58.
LIANG Shuanghua, SUN Ruhua, LI Wenping. Using Mapinfo and Photoshop to study SEM images of clay[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science & Technology (Natural Science), 2005, 26(1): 55 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] BAI B J, ELGMATI M, ZHANG H, et al. Rock characterization of Fayetteville shale gas plays[J]. Fuel,2013,105:645 − 652. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.09.043
[10] 彭双麒, 许强, 李骅锦, 等. 基于高精度图像识别的堆积体粒径分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(6):1290 − 1301. [PENG Shuangqi, XU Qiang, LI Huajin, et al. Grain size distribution analysis of landslide deposits with reliable image identification[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(6):1290 − 1301. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 彭双麒, 许强, 郑光, 等. 白格滑坡-碎屑流堆积体颗粒识别与分析[J]. 水利水电技术,2020,51(2):144 − 154. [PENG Shuangqi, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Recognition and analysis of deposit body grain of Baige Landslide-Debris Flow[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2020,51(2):144 − 154. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 刘春, 许强, 施斌, 等. 岩石颗粒与孔隙系统数字图像识别方法及应用[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(5):925 − 931. [LIU Chun, XU Qiang, SHI Bin, et al. Digital image recognition method of rock particle and pore system and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018,40(5):925 − 931. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] PRAKONGKEP N, SUDDHIPRAKARN A, KHEORUENROMNE I, et al. SEM image analysis for characterization of sand grains in Thai paddy soils[J]. Geoderma,2010,156(1/2):20 − 31.
[14] BENAVENTE N, PINA P. Morphological segmentation and classification of marble textures at macroscopical scale[J]. Computers and Geosciences,2009,35(6):1194 − 1204. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2008.04.008
[15] GONZALEZ, WOODS R C, RICHARD E. Digital image processing[M]. 2nd ed. New Jersey: Upper Saddle River, 2002.
[16] YU W W, HE F, XI P. A rapid 3D seed-filling algorithm based on scan slice[J]. Computers and Graphics,2010,34(4):449 − 459. doi: 10.1016/j.cag.2010.05.005
[17] 王国章, 李滨, 冯振, 等. 重庆武隆鸡冠岭岩质崩滑-碎屑流过程模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(5):101 − 106. [WANG Guozhang, LI Bin, FENG Zhen, et al. Simulation of the process of the Jiguanling rock avalanche in Wulong of Chongqing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(5):101 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 袁小一, 许强, 程谦恭, 等. 高速远程滑坡-碎屑流超前冲击气浪分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(6):113 − 119. [YUAN Xiaoyi, XU Qiang, CHENG Qiangong,et al. An analysis of air-blasts induced by rock avalanche[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(6):113 − 119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 郑光. 滑坡-碎屑流远程运动距离研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018.
ZHENG Guang. Study on the long-run out distance of rock avalanche[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: