A early warning model of regional landslide in Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province based on logistic regression
-
摘要:
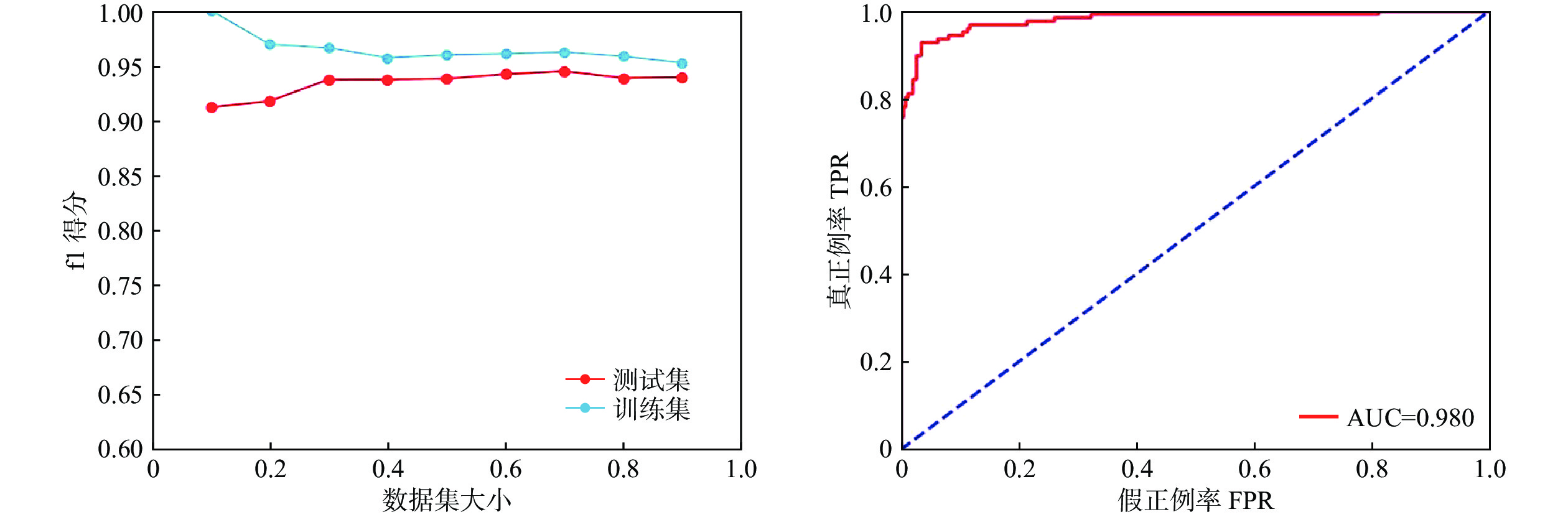
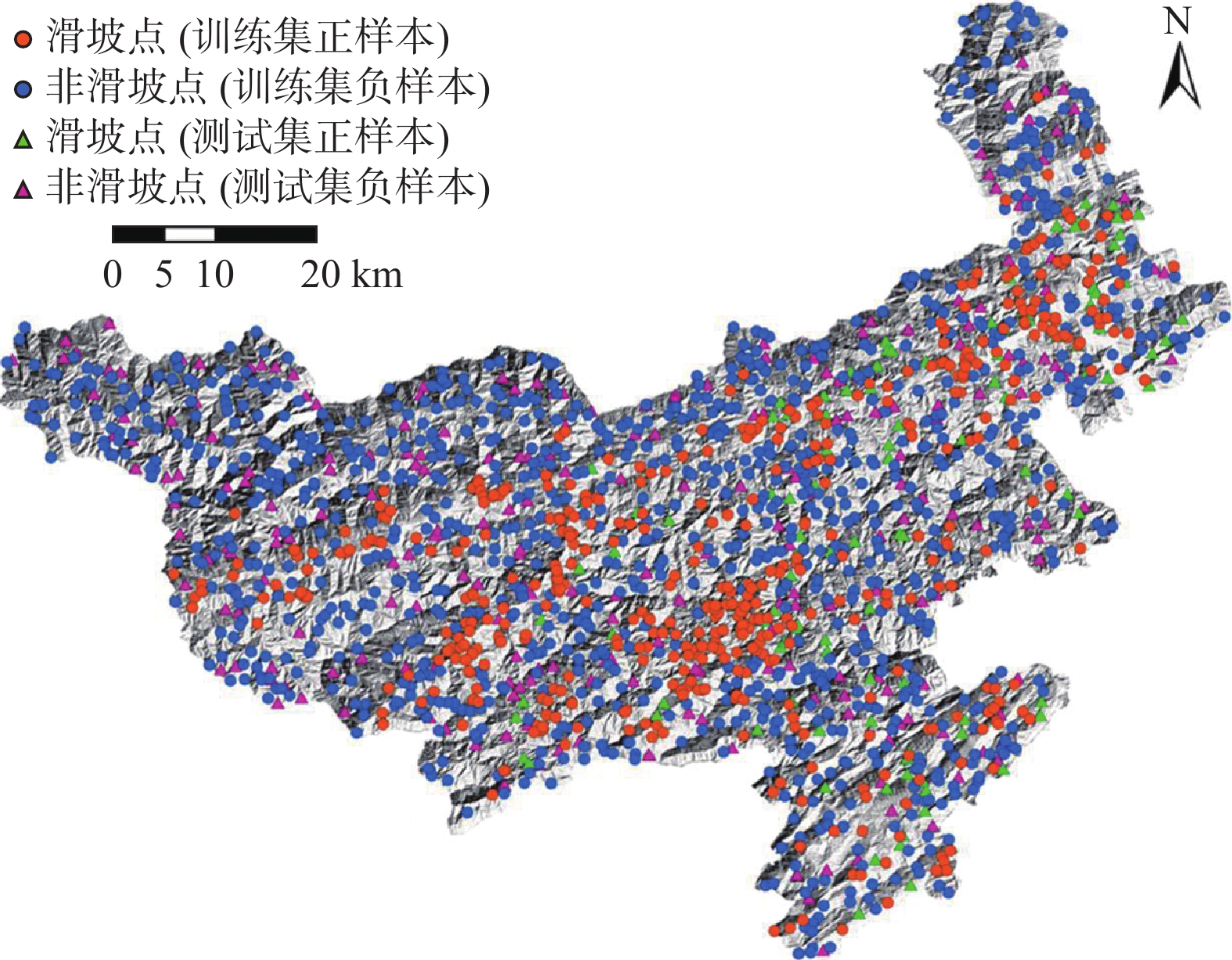
四川省青川县滑坡灾害群发,点多面广,区域滑坡灾害预警是有效防灾减灾的重要手段,预警模型是成功预警的核心。由于研究区滑坡诱发机理复杂、调查监测大数据及分析方法不足等原因,传统区域地质灾害预警模型存在预警精度有限、精细化不足等问题。文章在青川县地质灾害调查监测和降水监测成果集成整理与数据清洗基础上,构建了青川县区域滑坡灾害训练样本集,样本集包括地质环境、降雨等27个输入特征属性和1个输出特征属性,涵盖了青川县近9年(2010—2018年)全部样本,数量达1 826个(其中,正样本613个,负样本1 213个)。基于逻辑回归算法,对样本集进行5折交叉验证学习训练,采用贝叶斯优化算法进行模型优化,采用精确度、ROC曲线和AUC值等指标校验模型准确度和模型泛化能力。其中,ROC曲线也称为“受试者工作特征”曲线;AUC值表示ROC曲线下的面积。校验结果显示,基于逻辑回归算法的模型训练结果准确率和泛化能力均较好(准确率94.3%,AUC为0.980)。开展区域滑坡实际预警时,按训练样本特征属性格式,输入研究区各预警单元27个特征属性,调用预先学习训练好的模型,输出滑坡灾害发生概率,根据输出概率分段确定滑坡灾害预警等级。当输出概率P≥40%且P<60%时,发布黄色预警;当输出概率P≥60%且P<80%时,发布橙色预警;当输出概率P≥80%时,发布红色预警。
Abstract:In Qingchuan County of Sichuan Province, landslide disasters occur in a large number of places and cover a wide range of areas. Early warning of regional landslide disaster is an important means of effective disaster prevention and mitigation, and an early warning model is the core of successful early warning. The traditional regional geological disaster warning model is limited by the lack of big data and analysis methods of the complicated investigation and monitoring mechanism of the landslide in the study areas, and it has some problems, such as limited warning precision and insufficient refinement. In this paper, the training sample set of landslide disaster in Qingchuan County is constructed on the basis of the integrated collation and data cleaning of the results of geological disaster investigation and monitoring and precipitation monitoring. The sample set includes 27 input feature attributes such as geological environment rainfall and 1 output feature attribute, covering the total number of the samples in Qingchuan County in the past 9 years (2010—2018) up to 1826 (613 positive samples, 1213 negative samples). Based on the logistic regression algorithm, the study and training of the sample set is carried out with a 50%-fold cross validation. The Bayesian optimization algorithm is used for model optimization, and the accuracy and model generalization ability of the model are verified by such indicators as accuracy, ROC curve and AUC value. The ROC curve is also known as the “Receiver Operating Characteristic” curve. AUC value represents the area under the ROC curve. The verification results show that the training result model based on logistic regression algorithm is of good accuracy and generalization ability (accuracy 94.3% and AUC 0.980). Finally, it is proposed that in the actual warning of regional landslide, 27 characteristic attributes of each warning unit in the research area are input according to the format of characteristic attributes of training samples, and the pre-learned and trained model is called to output the probability of occurrence of landslide disaster, and the warning level of landslide disaster is segmented according to the output probability. A yellow alert is issued when the output probability P is greater than or equal to 40% and P is less than 60%. An orange alert is issued when the output probability P is greater than or equal to 60% and P is less than 80%. A red alert is issued when the output probability P is greater than or equal to 80%. In the next step, the accuracy of the model will be further verified in the landslide disaster early warning business in Qingchuan county.
-
Key words:
- landslide hazard /
- Early warning model /
- logistic regression /
- model building /
- warning level
-

-
表 1 训练样本输入特征及参数
Table 1. Input characteristics and parameters of the training samples
序号 输入特征 输入特征参数 1 坡度/(°) ①0~10;②10~20;③20~30; ④30~40;⑤≥40 2 坡向/(°) ①0~90;②90~180;③180~270; ④270~360 3 高程/m ①0~800;②800~1200;1200~1600;
④1600~2000;⑤≥20004 地貌类型 ①中低山;②中山;③高中山 5 地层岩性 ①松散堆积层;②软弱-半坚硬薄-中层状岩组;③半坚硬-坚硬薄-中层状岩组;④坚硬-半坚硬中-厚层状岩组;
⑤未知岩性6 距断裂距离/m ①0~500;②500~1000;③1000~1500; ④1500~2000;⑤≥2000 7 年雨量/mm ①0~500;②500~800;③800~1000;
④1000~1200;⑤≥12008 距房屋距离/m ①0~200;②≥200 9 距道路距离/m ①0~200;②≥200 10 距沟谷距离/m ①0~200;②≥200 11 网格单元历史灾点数/个 ①0;②1;③2;④3~4;⑤5~7 12 当日雨量/mm ①<10;②10~25;③25~50; ④50~100;⑤>100 13 前1日雨量/mm ①<10;②10~25;③25~50; ④50~100;⑤>100 14 前2日雨量/mm ①<10;②10~25;③25~50; ④50~100;⑤>100 ... ... ... 27 前15日雨量/mm ①<10;②10~25;③25~50; ④50~100;⑤>100 表 2 不同阈值下的Logistic回归分类结果混淆矩阵
Table 2. Confuse matrix of the result of the logistic regression classification under different thresholds
阈值 实际值 滑坡 非滑坡 0.25 预测值 滑坡 468 58 准确率:0.890 非滑坡 25 910 准确率:0.973 召回率:0.949 召回率:0.940 总精度:0.943 0.5 预测值 滑坡 451 26 准确率:0.945 非滑坡 42 942 准确率:0.957 召回率:0.915 召回率:0.973 总精度:0.953 0.75 预测值 滑坡 423 15 准确率:0.966 非滑坡 70 953 准确率:0.932 召回率:0.858 召回率:0.985 总精度:0.942 表 3 Logistic回归模型分类
Table 3. Logistic regression model classification report
精确率 召回率 f1得分 0 0.949 0.975 0.957 1 0.950 0.883 0.915 准确率 0.943 宏平均 0.944 0.929 0.936 加权平均 0.943 0.943 0.942 表 4 预警等级划分
Table 4. Early warning level division
预警等级 风险等级 概率P 红色预警 风险很高 [80%, 100%] 橙色预警 风险高 [60%, 80%) 黄色预警 风险较高 [40%, 60%) -
[1] 刘传正, 温铭生, 唐灿. 中国地质灾害气象预警初步研究[J]. 地质通报,2004,23(4):303 − 309. [LIU Chuanzheng, WEN Mingsheng, TANG Can. Meteorological early warning of geo-hazards in China based on raining forecast[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2004,23(4):303 − 309. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.04.001
[2] 刘传正, 刘艳辉, 温铭生, 等. 中国地质灾害区域预警方法与应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.
LIU Chuanzheng, LIU Yanhui, WEN Mingsheng, et al. Method and application of regional warning for geo-hazards in China [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing. 2009. (in Chinese)
[3] 刘传正, 刘艳辉, 温铭生, 等. 中国地质灾害气象预警实践: 2003-2012[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(1):1 − 8. [LIU Chuanzheng, LIU Yanhui, WEN Mingsheng, et al. Early warning for regional geo-hazards during 2003-2012, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(1):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] CANNON S H. Rainfall conditions for abundant debris avalanches, San Francisco Bay region, California[J]. California Geology,1985,38(12):267 − 272.
[5] AU S W C. Rain-induced slop instability in Hong Kong[J]. Engineering Geology,1998,51(1):1 − 36.
[6] ALEOTTI P. A warning system for rainfall-induced shallow failures[J]. Engineering geology,2004,73:247 − 265.
[7] 刘艳辉, 刘传正, 连建发, 等. 基于显式统计原理的地质灾害区域预警方法初步研究[J]. 中国地质,2008,35(2):344 − 350. [LIU Yanhui, LIU Chuanzheng, LIAN Jianfa, et al. Preliminary study of geo-hazards regional early warning based on explicit statistical theory[J]. Geology in China,2008,35(2):344 − 350. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.02.020
[8] 刘艳辉, 刘传正, 温铭生, 等. 中国地质灾害气象预警模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2015,23(4):738 − 746. [LIU Yanhui, LIU Chuanzheng, WEN Mingsheng, et al. Study of early warning models for regional geo-hazards in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2015,23(4):738 − 746. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 刘艳辉, 张振兴, 苏永超. 地质灾害承灾载体脆弱性评价方法研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(5):1121 − 1130. [LIU Yanhui, ZHANG Zhenxing, SU Yongchao. Case study of vulnerability evaluation for geo-hazards bearing capacity of a region[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(5):1121 − 1130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘艳辉, 苏永超. 四川青川县区域地质灾害气象风险预警模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):134 − 143. [LIU Yanhui, SU Yongchao. Early-warning model of regional geological disasters based on meteorological factor in Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):134 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 侯圣山, 李昂, 韩冰, 等. 四川雅安地质灾害预警预报及分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2014,25(4):134 − 138. [HOU Shengshan, LI Ang, HAN Bing, et al. An approach of geo-hazard warning system in Ya’an, Sichuan and its analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2014,25(4):134 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 李守定, 白亚恒, 姜越, 等. 基于内外动力耦合成因理论的新疆地质灾害气象预警显式统计模型[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2017,39(2):287 − 300. [LI Shouding, BAI Yaheng, JIANG Yue, et al. An explicit statistical model for meteorological early warning of geological hazards in Xinjiang based on the coupling theory of internal and external dynamics[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2017,39(2):287 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 魏平新, 李秀娟. 广东省突发性地质灾害气象预警实践[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(1):138 − 144. [WEI Pingxin, LI Xiujuan. The meteorologic early warning research of sudden geo-hazard in Guangdong province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(1):138 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 中国地质环境监测院. 城镇化过程中承灾载体脆弱性及脆弱性评价方法研究成果报告[R]. 北京: 中国地质环境监测院, 2018.
China Institute of Geo-Environmental Monitoring. The research report of vulnerability vector and vulnerability assessment method during urbanization[R]. Beijing: China Institute of Geo-Environmental Monitoring, 2018. (in Chinese)
[15] 四川九零九建设工程有限公司. 四川省青川县地质灾害详细调查报告[R]. 成都: 四川九零九建设工程有限公司, 2015.
Sichuan 909 Construction Engineering Co. LTD. A detailed survey report on geological hazards in Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province[R]. Chengdu: Sichuan 909 Construction Engineering Co. LTD, 2015. (in Chinese)
[16] 中国地质环境监测院. 四川青竹江流域地质灾害调查报告[R]. 北京: 中国地质环境监测院, 2016.
China Institute of Geo-Environmental Monitoring. Geo-hazards investigation report of Qingzhujiang River region, Sichuan[R]. Beijing: China Institute of Geo-Environmental Monitoring, 2016. (in Chinese)
[17] 刘艳辉, 肖锐铧, 陈春利, 等. 区域滑坡预警中训练样本集的构建方法、系统及存储介质: 202010829816.0[P].
LIU Yanhui, XIAO Ruihua, CHEN Chunli, et al. Construction method system and storage medium of training sample set in regional landslide early warning: 202010829816.0[P].2020-08-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 韩帅, 孙乐平, 杨艺云, 等. 基于改进K-Means聚类和误差反馈的数据清洗方法[J]. 电网与清洁能源,2020,36(7):9 − 15. [HAN Shuai, SUN Leping, YANG Yiyun, et al. Data cleaning method based on improved K-means clustering and error feedback[J]. Power System and Clean Energy,2020,36(7):9 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 朱力. 决策树算法在山区公路地质灾害风险评估系统中的应用[D]. 重庆: 重庆师范大学, 2019.
ZHU Li. Application of decision tree algorithm in the risk assessment system of mountain highway geological hazards[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] BOSCHETTI A, MASSARON L. Python data science essentials[M]. 2nd ed. Packt Publishing Ltd, 2015.
[21] 赵永红, 王航, 张琼, 等. 滑坡位移监测方法综述[J]. 地球物理学进展,2018,33(6):2606 − 2612. [ZHAO Yonghong, WANG Hang, ZHANG Qiong, et al. A review of monitoring methods for landslide displacement[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2018,33(6):2606 − 2612. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/pg2018BB0464
[22] 张铎, 吴中海, 李家存, 等. 国内外地震滑坡研究综述[J]. 地质力学学报,2013,19(3):225 − 241. [ZHANG Duo, WU Zhonghai, LI Jiacun, et al. A review of seismic landslide studies at home and abroad[J]. Journal of geomechanics,2013,19(3):225 − 241. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2013.03.001
[23] LEE S, RYU J, MIN K, et al. Development and application of landslide susceptibility analysis techniques using geographic information system (GIS)[C]//IGARSS 2000. IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Taking the Pulse of the Planet: The Role of Remote Sensing in Managing the Environment. Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37120). IEEE, 2000, 1: 319−321.
[24] OHLMACHER G C, DAVIS J C. Using multiple logistic regression and GIS technology to predict landslide hazard in northeast Kansas, USA[J]. Engineering geology,2003,69:331 − 343.
[25] 李铁锋, 丛威青. 基于Logistic回归及前期有效雨量的降雨诱发型滑坡预测方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2006,17(1):33 − 35. [LI Tiefeng, CONG Weiqing. Rainfall-induced landslide prediction method based on Logistic regression and early effective rainfall[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazards and Prevention,2006,17(1):33 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.01.008
[26] 孙德亮. 基于机器学习的滑坡易发性区划与降雨诱发滑坡预报预警研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2019.
SUN Deliang. Study on landslide susceptibility regionalization and rainfall-Induced landslide prediction and Early Warning based on machine learning [D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] SNOEK J, LAROCHELLE H, ADAMS R P. Practical bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems,2012,25:2951 − 2959.
[28] 中国地质灾害防治工程行业协会. 地质灾害区域气象风险预警标准(试行): T/CAGHP 039-2018[S]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2018.
China Geological Disaster Prevention Engineering Association. Regional meteorological risk early warning standard for geological disaster (trial): T/CAGHP 039-2018[S]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2018. ](in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: