A study of the evaluation of geo-hazards development degree based on time-space coupling
-
摘要:
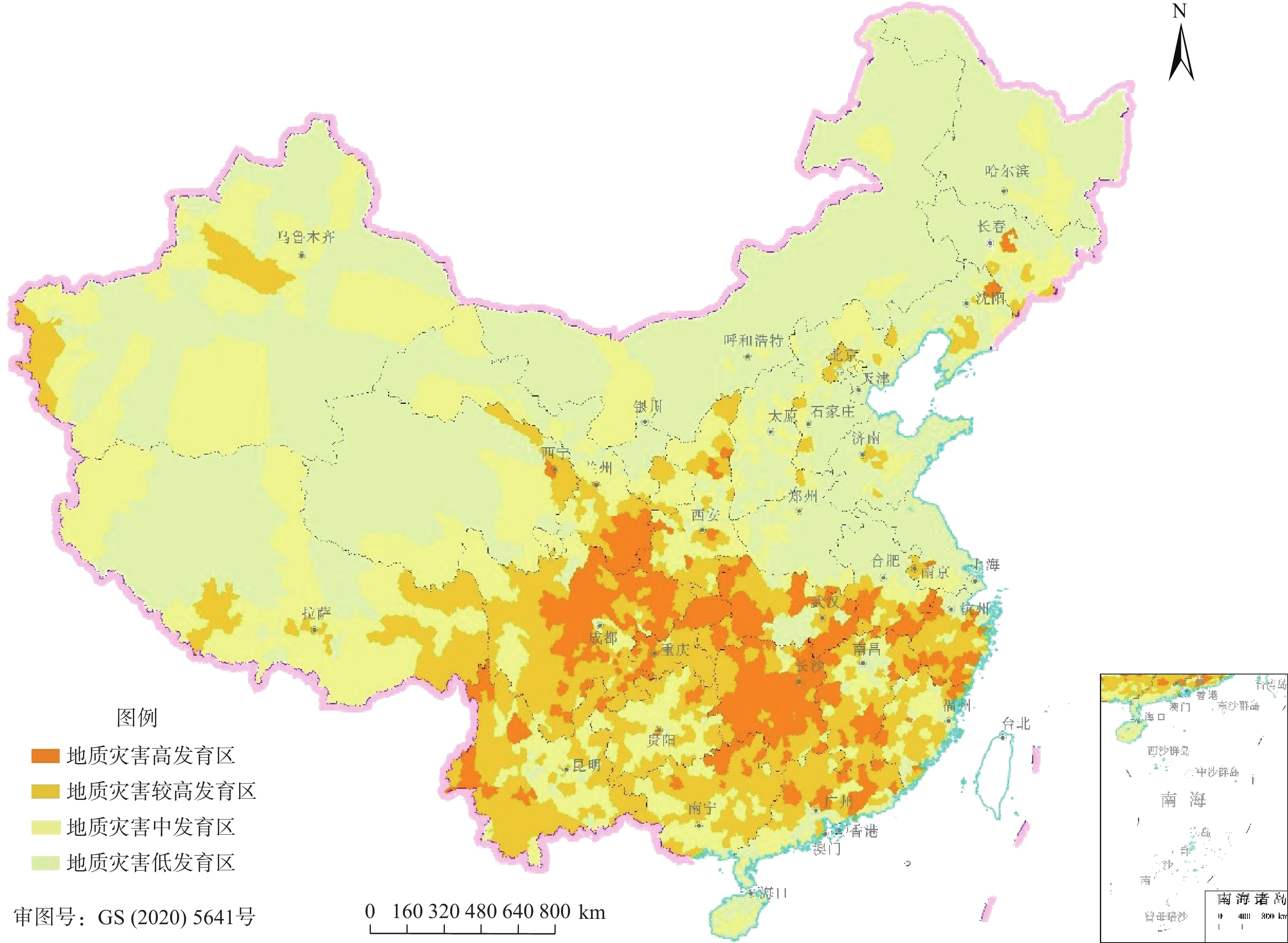
在现有地质灾害综合评价指标体系中,地质灾害发育程度评价因子只包括反映空间维度的点数量、点密度、体积数、体积密度等,不包括反映时间维度的评价因子。文章引入反映时间维度的受灾年份因子充实之。通过对地质灾害体积取中位数对数法、对受灾年份采用概率密度法进行处理和采用熵权法确定评价因子权重来建立时空耦合评价模型;采用斜率法将评价结果划分为高、较高、中、低四级,以反映已发生灾害的发育状况。选取2011—2020年已发生的地质灾害点,评价区域为除香港特别行政区、澳门特别行政区、台湾地区以外的全国31个省份,按此方法对以县域为单元的地质灾害发育程度进行评价与区划。结果表明:地质灾害高发育区共323个县,涉及19个省(自治区、直辖市),主要分布在东南、西南、西北等地。较高发育区共566个县,涉及25个省(自治区、直辖市),主要分布在西南、中南、东南等地。中发育区623个县,涉及30个省(自治区、直辖市),主要包括西北、华北等地。低发育区共1336个县,涉及30个省(自治区、直辖市),主要包括华北、东北、华东等地。本次评价结果与国家防灾部署、灾害发育分布具有较高的吻合度。野外实地调研证明,引入受灾年份后的评价结果较引入前更符合实际情况。
Abstract:The geo-hazards comprehensive evaluation index system was established in the early stage of the team, and the number, the number density, the volume and the volume density, which reflect the spatial dimension, are used to evaluate the development degree of geo-hazards, excluding the evaluation factors reflecting the time dimension. In this paper, disaster years reflecting the time dimension are introduced to enrich the development degree evaluation system of geo-hazards. The median logarithmic method and probability density distribution are respectively used to processing data of disaster years and volume, and the entropy weight is used to determine the weight of evaluation factors. The evaluation models are established and the evaluation results are divided into four levels by the slope method, reflecting the development status of disasters. The geo-hazards occurred in 31provinces in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan) from 2011 to 2020 are taken as examples, the development degree of geo-hazards (landslide, collapse and debris flow) is evaluated and divided according to this method. The results show that the geo-hazards high development areas cover 323 counties in total, involving 19 provinces, mainly occurring in Southeast China, Southwest China and Northwest China. The sub-high development areas cover 566 counties in total, involving 25 provinces, mainly occurring in Southwest China, South Central China and Southeast China. The moderately development areascover 623 counties in total, involving 30 provinces, mainly occurring in Northwest China and North China. The low development areas cover 1336 counties in total, involving 30 provinces, mainly occurring in North China, Northeast China and East China. When compared with the national disaster prevention deployment situation or the geo-hazards distribution, the evaluation results are in good agreement with the reality. In addition, through field investigation, the evaluation results are more consistent with the actual situation.
-

-
表 1 地质灾害发育程度评价体系
Table 1. Evaluation system of development degree of geo-hazards
目标层 指标层 因子层 地质灾害
发育程度
评价滑坡发育程度指数 数量、点密度、体积、体积密度、受灾年份 崩塌发育程度指数 数量、点密度、体积、体积密度、受灾年份 泥石流发育程度指数 数量、点密度、体积、体积密度、受灾年份 表 2 地质灾害规模等级划分标准
Table 2. Scale classification of geo-hazards
灾害类型 巨型 大型 中型 小型 滑坡/104 m3 >1000 100~1000 10~100 <10 崩塌/103 m3 >100 10~100 1~10 <1 泥石流/104 m3 >50 20~50 2~20 <2 表 3 地质灾害规模级数计算
Table 3. Volume assignment of geo-hazards
规模等级 滑坡规模级数 崩塌规模级数 泥石流规模级数 巨型 7.30 6.08 5.95 大型 6.20 5.35 5.34 中型 5.30 4.30 4.60 小型 2.48 2.00 3.00 表 4 滑坡时间系数
Table 4. Landslide time coefficient
置信区间 滑坡受灾
年份/a滑坡受灾县数量
/个滑坡受灾年份
概率密度/%滑坡时间
系数(μ−σ, μ+σ) 1 333 25.00 1 2 239 17.94 1 3 176 13.21 1 4 126 9.46 1 累计 874 65.61 — (μ−1.96σ, μ+1.96σ) 5 143 10.74 1.40 6 109 8.18 1.40 7 88 6.61 1.40 8 63 4.73 1.40 累计 1277 95.87 — (μ−2.58σ, μ+2.58σ) 9 42 3.15 1.46 10 13 0.98 1.46 累计 1332 100 — 表 5 崩塌时间系数
Table 5. Collapse time coefficient
置信区间 崩塌受灾
年数/a崩塌受灾县数量
/个崩塌受灾年份
概率密度/%崩塌时间
系数(μ−σ, μ+σ) 1 242 21.17 1 2 177 15.45 1 3 139 12.14 1 4 108 9.42 1 5 129 11.30 1 累计 794 69.48 — (μ−1.96σ, μ+1.96σ) 6 103 9.03 1.40 7 94 8.25 1.40 8 76 6.69 1.40 累计 1068 93.45 — (μ−2.58σ, μ+2.58σ) 9 52 4.55 1.46 10 23 2.01 1.46 累计 1143 100 — 表 6 泥石流时间系数
Table 6. Debris flow time coefficient
置信区间 泥石流受灾
年数/a泥石流受灾县
数量/个泥石流受灾年份
概率密度/%泥石流时间
系数(μ−σ, μ+σ) 1 371 56.99 1 2 130 10.97 1 累计 501 67.96 — (μ−1.96σ, μ+1.96σ) 3 75 20.52 1.40 4 26 3.99 1.40 5 20 3.07 1.40 累计 622 95.54 — (μ−2.58σ, μ+2.58σ) 6 15 2.30 1.46 7 8 1.23 1.46 8 6 0.92 1.46 累计 651 100 — 表 7 各项评价因子权重
Table 7. Weight of evaluation factors of landslide, collapse and debris flow
权重类别 W1 W2 W3 W4 滑坡 0.25 0.24 0.26 0.25 崩塌 0.23 0.27 0.26 0.24 泥石流 0.24 0.23 0.28 0.25 表 8 地质灾害发育程度指数等级界限值
Table 8. The bound value of the development degree indexs of Geo-hazards
等级 高发育区 较高发育区 中发育区 低发育区 F/10−4 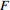 ≥8.0
≥8.03.4≤ 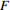 <8.0
<8.00< 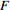 <3.4
<3.4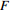 =0
=0表 9 地质灾害发育程度评价结果分省数量统计
Table 9. Quantity statistics by provinces of evaluation results of Geo-hazards development degree
/个 省 份 县个数 高发育区县数 较高发育区县数 中发育区县数 低发育区县数 省 份 县个数 高发育区县数 较高发育区县数 中发育区县数 低发育区县数 北京市 16 0 6 2 8 湖北省 103 33 20 15 35 天津市 16 0 0 1 15 湖南省 122 70 38 4 10 河北省 167 0 5 26 136 广东省 122 15 33 40 34 山西省 117 0 0 33 84 广 西 111 10 49 29 23 内蒙古 103 0 0 8 95 海南省 25 0 0 7 18 辽宁省 100 1 7 13 79 重庆市 38 13 20 1 4 吉林省 60 1 5 14 40 四川省 183 73 75 22 13 黑龙江 128 0 0 12 116 贵州省 88 4 37 44 3 上海市 16 0 0 0 16 云南省 129 13 70 39 7 江苏省 94 1 2 12 79 西 藏 74 0 15 43 16 浙江省 89 16 27 28 18 陕西省 107 11 28 47 21 安徽省 104 15 11 14 64 甘肃省 86 17 21 30 18 福建省 85 6 30 22 27 青海省 44 2 10 17 15 江西省 100 21 41 31 7 宁 夏 22 0 2 5 15 山东省 136 0 6 10 120 新 疆 105 0 7 30 68 河南省 158 1 1 24 132 合 计 2848 323 566 623 1336 注:县个数为中华人民共和国民政部截至2020年12月的统计数据。 表 10 营山县、泸定县、自贡市贡井区引入受灾年份因子前后评价等级差异
Table 10. Different evaluation grades before and after introducing disaster year factor in Yingshan County, Luding County and Gongjing district of Zigong
县名 引入受灾年份因子后等级 未引入受灾年份因子等级 灾害类型 发生数量/起 规模数 点密度/(起·m−2) 规模密度 受灾年数/a 营山县 3 4 滑坡 39 109 0.024 0.067 5 崩塌 2 4 0.001 0.002 1 泸定县 4 3 滑坡 14 38 0.006 0.005 3 崩塌 3 6 0.001 0.003 2 泥石流 41 146 0.019 0.068 8 -
[1] 中华人民共和国国务院. 地质灾害防治条例(国务院令第394号)[Z]. 2003.
[2] 刘传正, 李铁锋, 程凌鹏, 等. 区域地质灾害评价预警的递进分析理论与方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2004,31(4):1 − 8. [LIU Chuanzheng, LI Tiefeng, CHENG Lingpeng, et al. A method to analyze four parameters for assessment and early warning on the regional geo-hazards[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2004,31(4):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2004.04.001
[3] 李媛, 孟晖, 董颖, 等. 中国地质灾害类型及其特征—基于全国县市地质灾害调查成果分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2004,15(2):29 − 34. [LI Yuan, MENG Hui, DONG Ying, et al. Main types and characterisitics of geo-hazard in China:Based on the results of geo-hazard survey in 290 counties[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2004,15(2):29 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.02.005
[4] 张建江. 贵州区域地质灾害发育程度初探[J]. 贵州地质,2009,26(4):317 − 320. [ZHANG Jianjiang. Discussion of regional geologic disaster developing degree in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology,2009,26(4):317 − 320. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2009.04.016
[5] 杨森林, 陈革平, 裴永伟. 贵州地质灾害发育分区[J]. 贵州地质,2011,28(2):131 − 134. [YANG Senlin, CHEN Geping, PEI Yongwei. Zoning of developing condition of geologic disaster in Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Geology,2011,28(2):131 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2011.02.011
[6] 王涛, 吴树仁, 石菊松, 等. 秦岭中部太白县地质灾害发育特征及危险性评估[J]. 地质通报,2013,32(12):1976 − 1983. [WANG Tao, WU Shuren, SHI Jusong, et al. Case study of landslide characteristics and hazard assessment in Taibai County, central Qinling Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2013,32(12):1976 − 1983. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 黄丽, 李奇, 袁华东. 降水对湖北省地质灾害发育程度的影响[J]. 资源环境与工程,2012,26(4):369 − 375. [HUANG Li, LI Qi, YUAN Huadong. Impact of precipitation on the degree of development of geological disasters in Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2012,26(4):369 − 375. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2012.04.012
[8] 李媛, 曲雪妍, 房浩, 等. 地质灾害综合评价指标体系和评价方法研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(5):129 − 132. [LI Yuan, QU Xueyan, FANG Hao, et al. A study of comprehensive evaluation index system and methods for geo-harzard[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(5):129 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王杰涛, 於李军, 刘亚洲. 地质灾害发育强度等级图绘制方法研究[J]. 科技经济导刊,2017(6):27 − 28. [WANG Jietao, YU Lijun, LIU Yazhou. Study on mapping method of development intensity grade of geological hazard[J]. Technology and Economic Guide,2017(6):27 − 28. (in Chinese)
[10] 宋彦辉, 彭建兵. 山区公路地质灾害评价模型探讨[J]. 公路交通科技,2005,22(6):34 − 36. [SONG Yanhui, PENG Jianbing. Discussion on the evaluation model of highway geological disasters in mountainous area[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2005,22(6):34 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2005.06.010
[11] 郭昱. 权重确定方法综述[J]. 农村经济与科技,2018,29(8):252 − 253. [GUO Yu. A review of weight methods[J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology,2018,29(8):252 − 253. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2018.08.171
[12] 贾艳红, 赵军, 南忠仁, 等. 基于熵权法的草原生态安全评价—以甘肃牧区为例[J]. 生态学杂志,2006,25(8):1003 − 1008. [JIA Yanhong, ZHAO Jun, NAN Zhongren, et al. Ecological safety assessment of grassland based on entropy-right method: A case study of Gansu pastoral area[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2006,25(8):1003 − 1008. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2006.08.026
[13] 丁笑舒. 相似度计算中的权重确定方法文献综述[J]. 计算机光盘软件与应用,2015,18(2):106. [DING Xiaoshu. A review of the methods of weight determination in similarity calculation[J]. Computer CD Software and Applications,2015,18(2):106. (in Chinese)
[14] 冯运卿, 李雪梅, 李学伟. 基于熵权法与灰色关联分析的铁路安全综合评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2014, 14(2)
FENG Yunqing, LI Xuemei, LI Xuewei. Comprehensive evaluation method for the railway safety based on the entropy method and the grey relation analysis[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2014, 14(2):73-79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 朱吉祥, 张礼中, 周小元, 等. 基于信息熵的灰色模型在地质灾害评价中的应用—以四川青川县为例[J]. 灾害学,2012,27(1):78 − 82. [ZHU Jixiang, ZHANG Lizhong, ZHOU Xiaoyuan, et al. Application of entropy-based grey model in geological hazard assessment—A case study of Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2012,27(1):78 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2012.01.016
[16] 中华人民共和国国务院. 国家突发地质灾害应急预案[Z]. 2006.
[17] 强菲, 赵法锁, 段钊. 陕南秦巴山区地质灾害发育及空间分布规律[J]. 灾害学,2015,30(2):193 − 198. [QIANG Fei, ZHAO Fasuo, DUAN Zhao. Development and spatial distribution of geological disasters in Qinling-Daba mountains of south Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2015,30(2):193 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2015.02.037
[18] 郭跃, 林孝松. 地质灾害系统的复杂性分析[J]. 重庆师范学院学报(自然科学版),2001,18(4):1 − 7. [GUO Yue, LIN Xiaosong. An analysis of the complexity of geological hazard system[J]. Journal of Chongqing Teachers College (Natural Science Edition),2001,18(4):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 徐海云, 涂雄苓, 罗付岩. 中国突发性地质灾害分布的统计规律[J]. 数理统计与管理,2010,29(6):951 − 960. [XU Haiyun, TU Xiongling, LUO Fuyan. An empirical law of distribution of abrupt geological hazards in China[J]. Journal of Applied Statistics and Management,2010,29(6):951 − 960. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 陈希孺. 数理统计学简史[M]. 长沙:湖南教育出版社, 2002: 112 − 114.
CHEN Xiru. Concise history of statistics[M]. Changsha:Hunan Education Publishing House, 2002: 112 − 114. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: