An analysis of flow-like motion of avalanches based on physical modeling experiments
-
摘要:
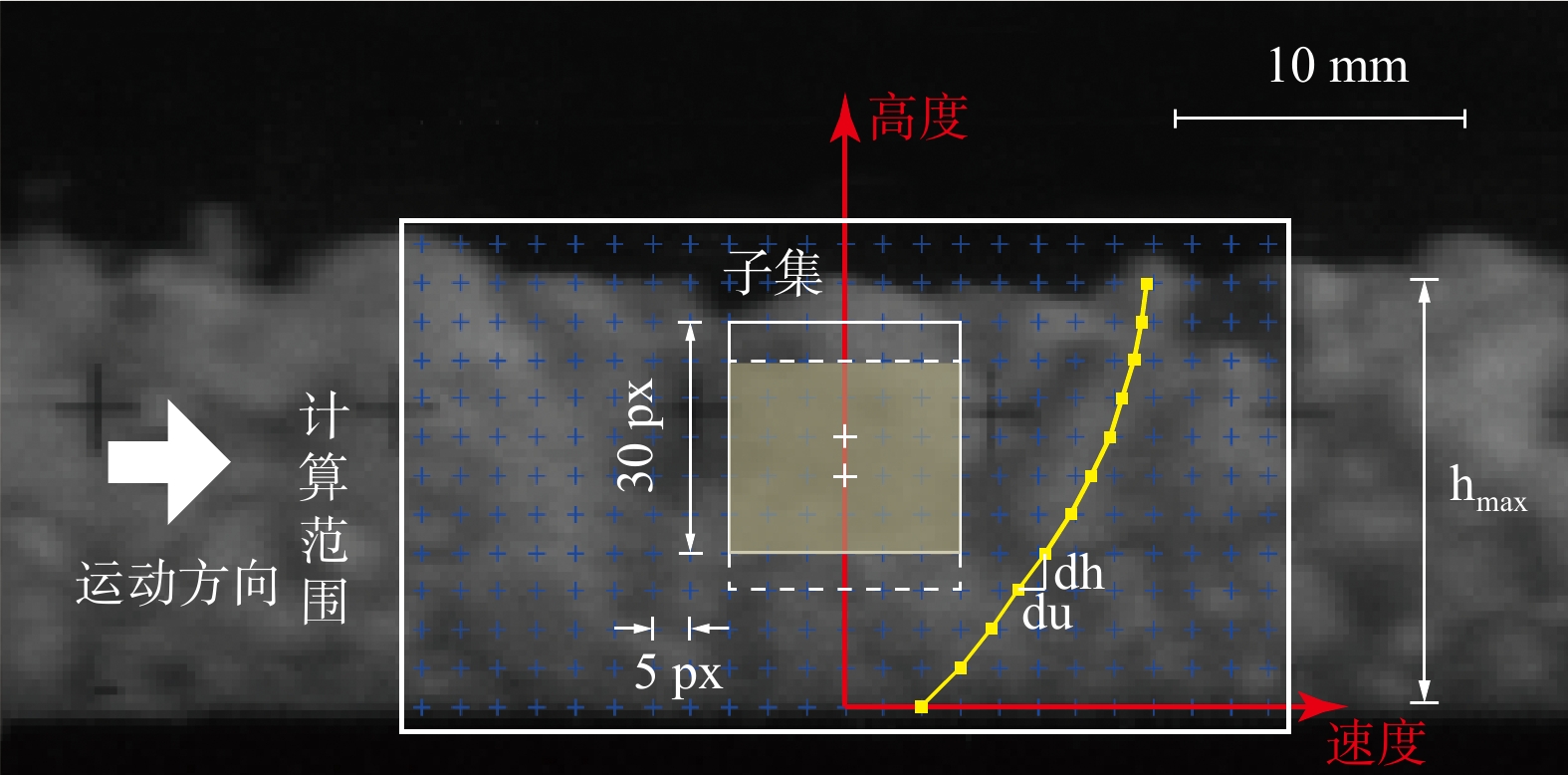
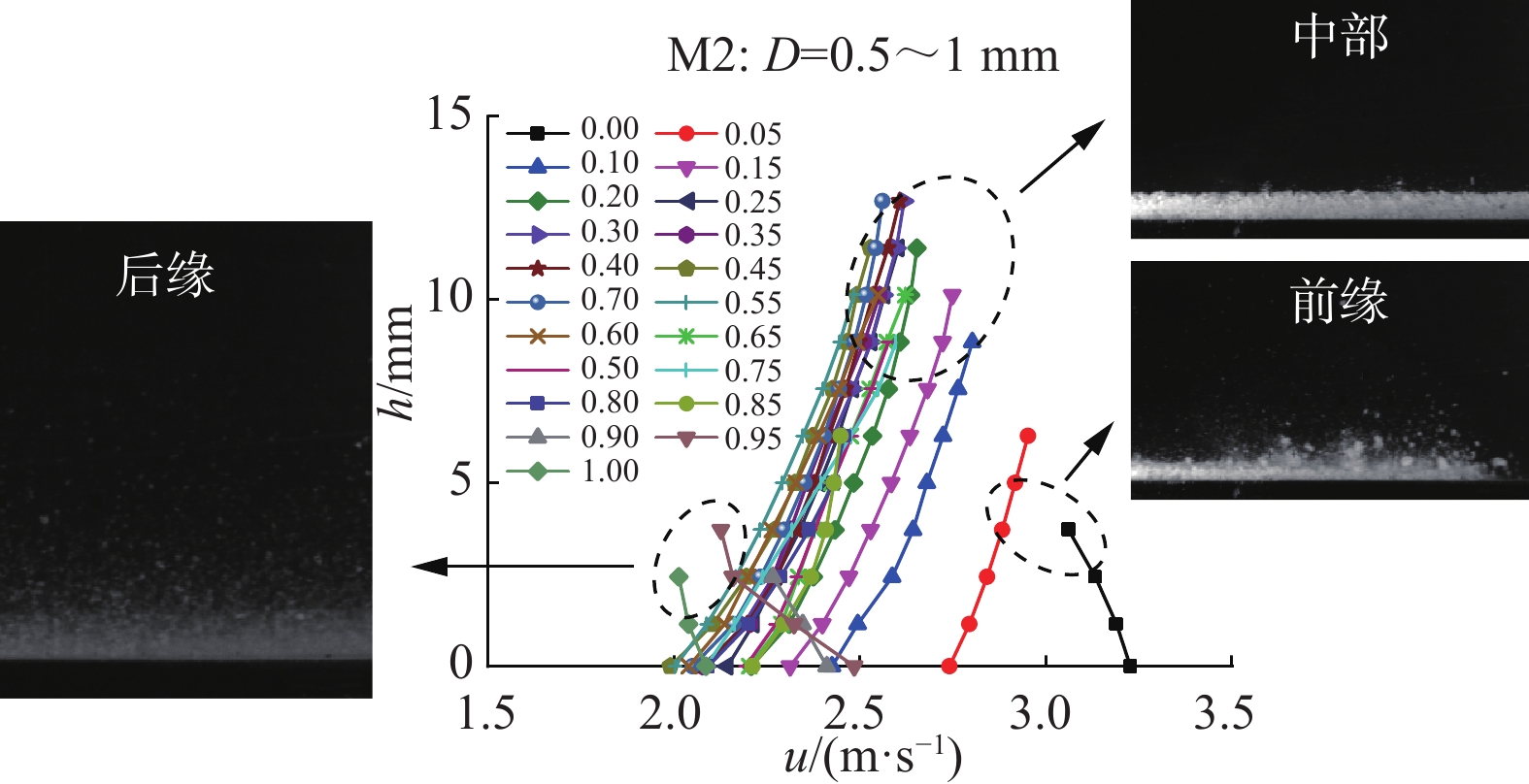
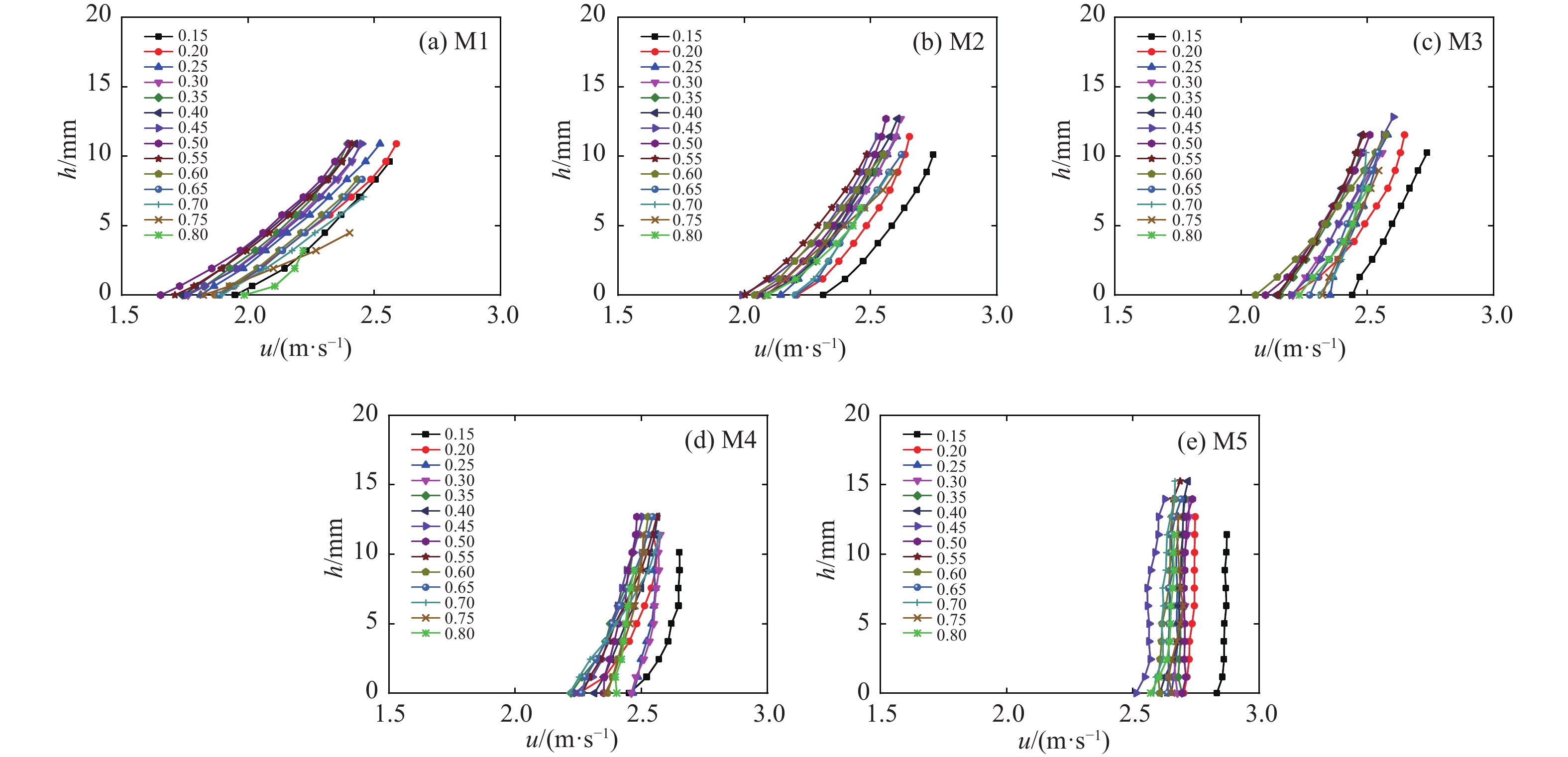
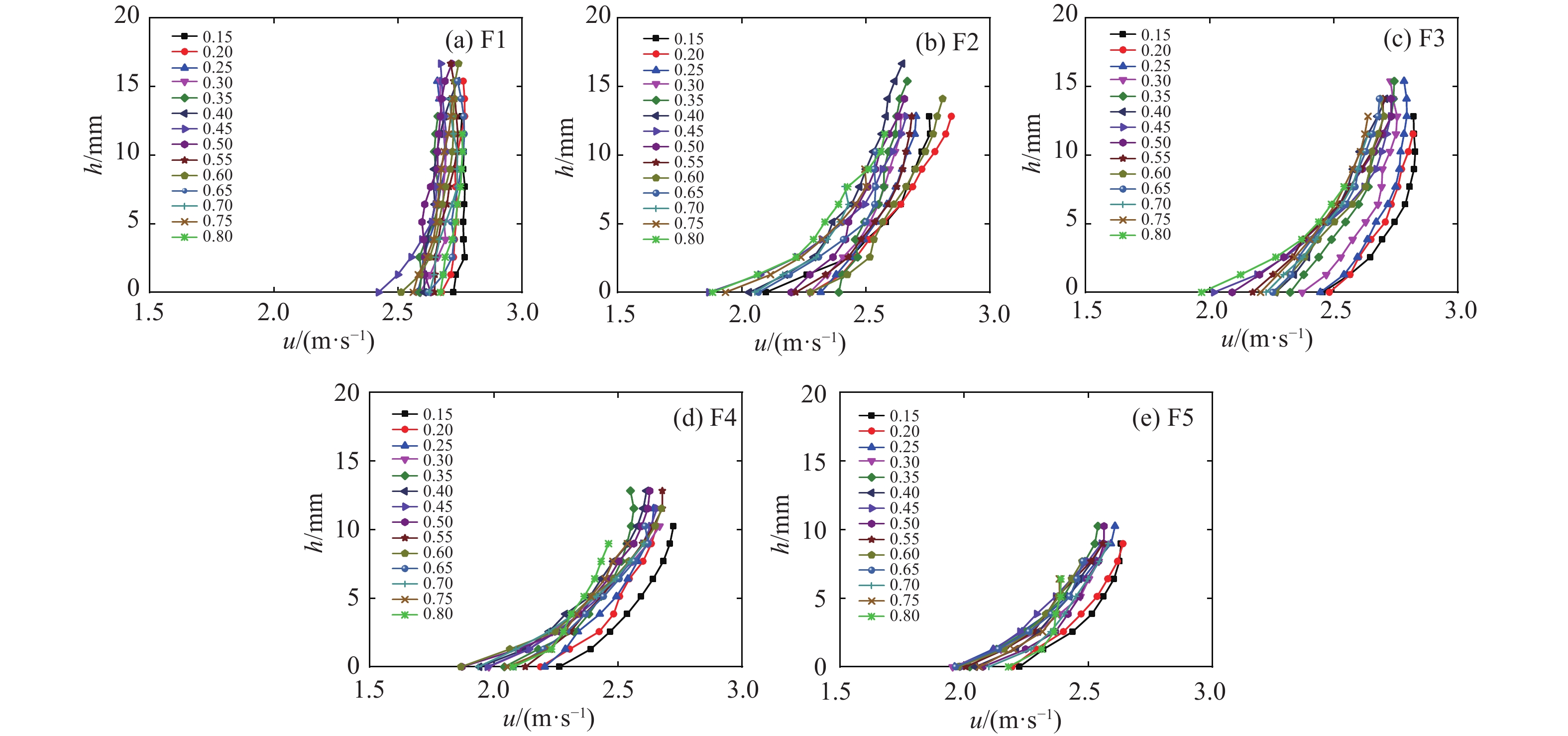
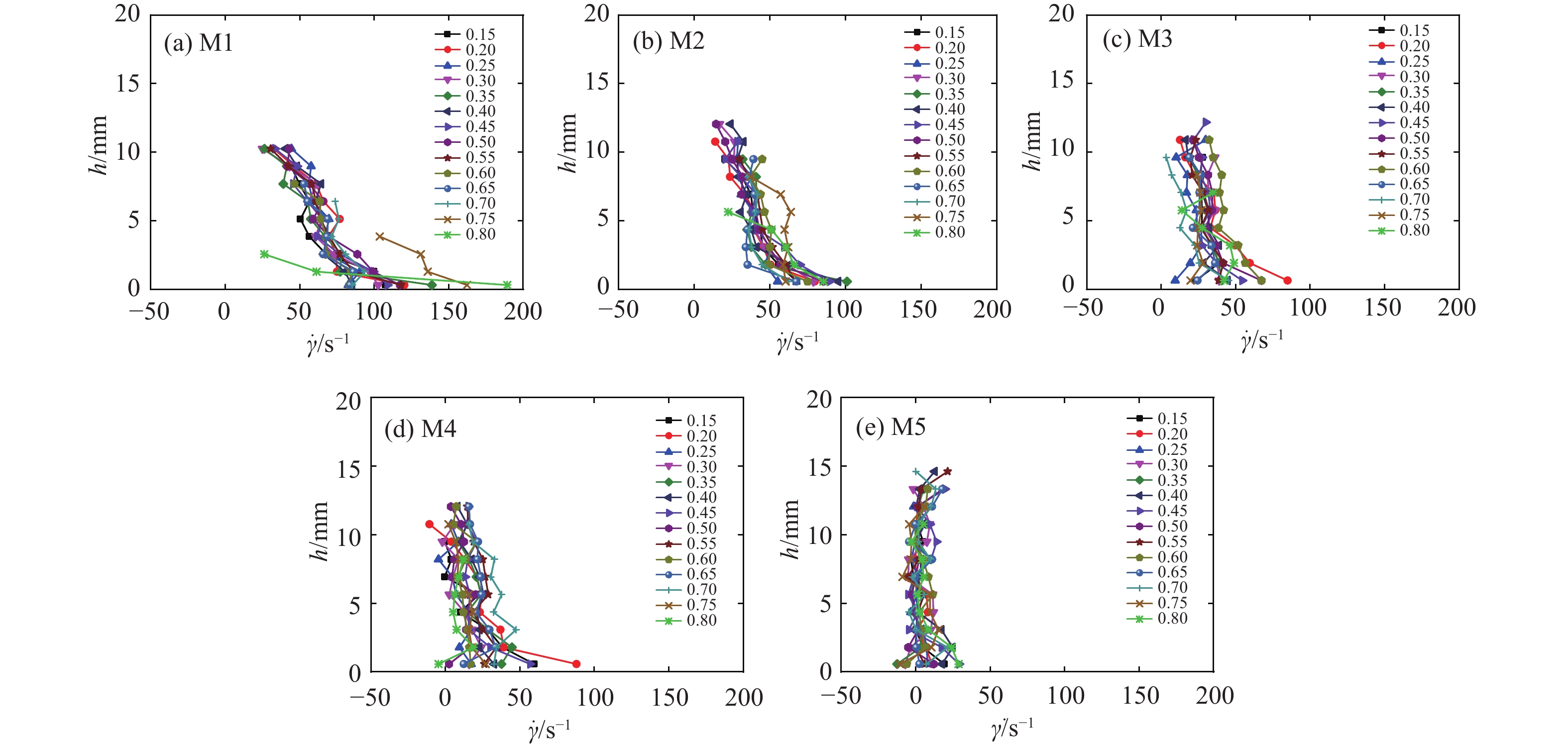
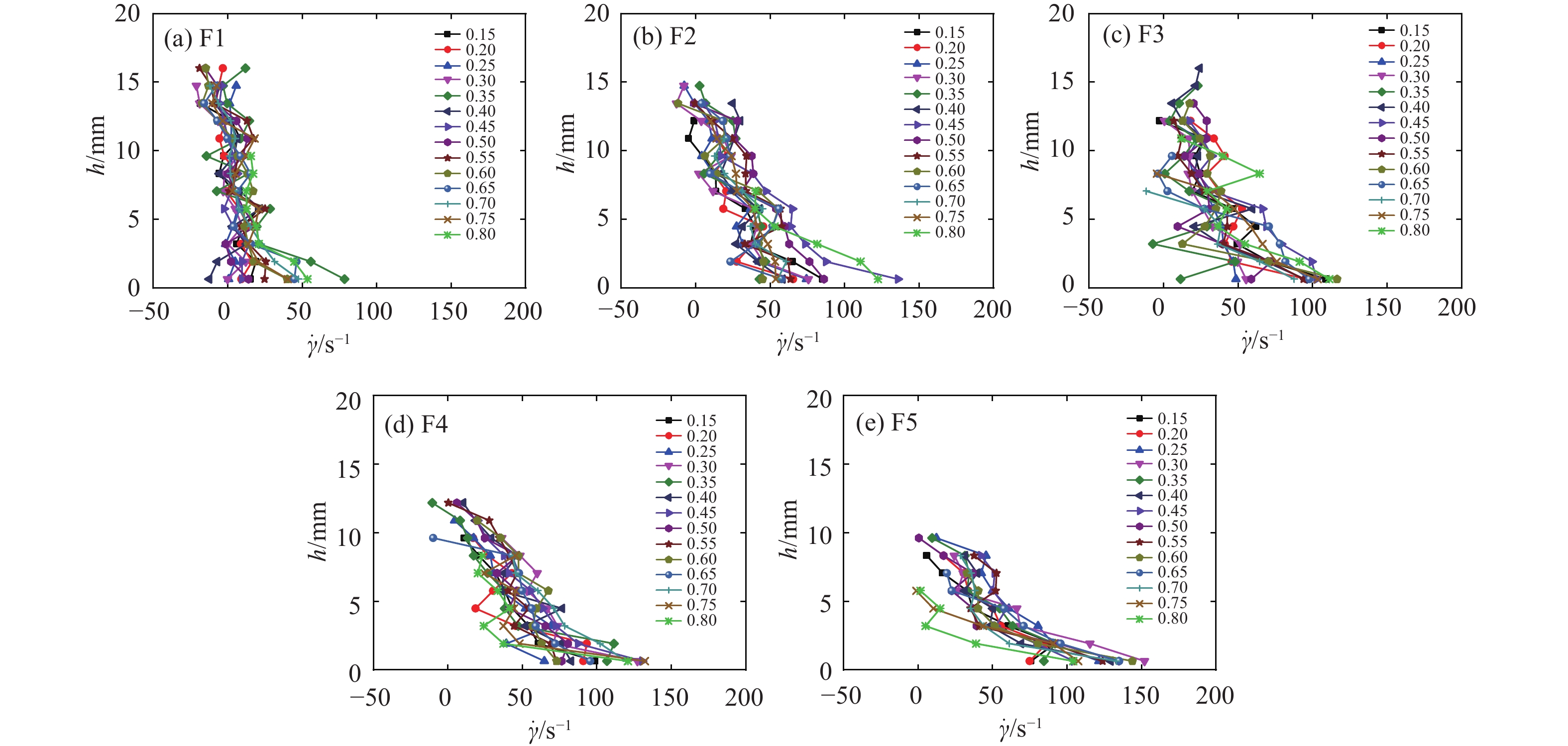
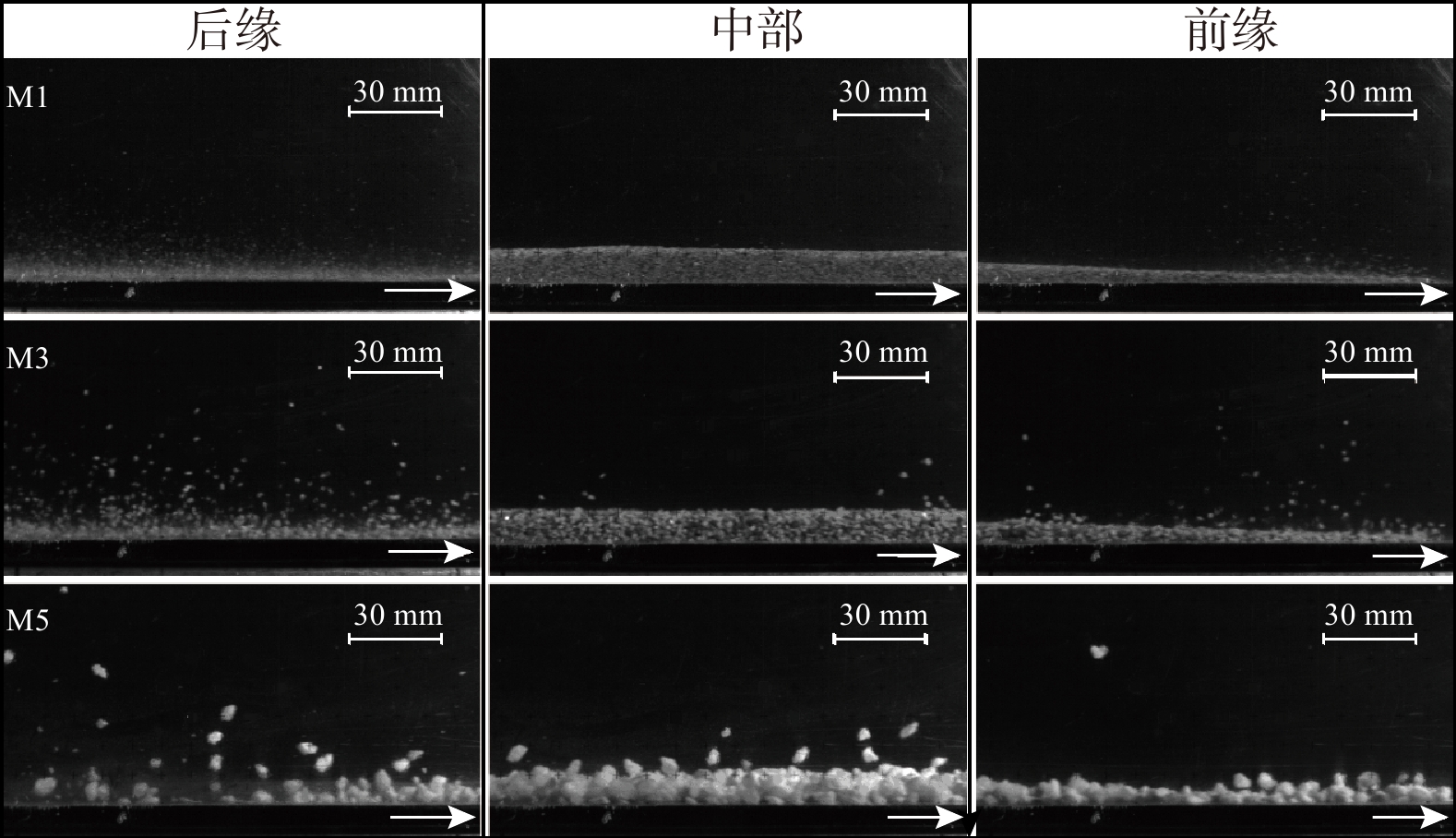
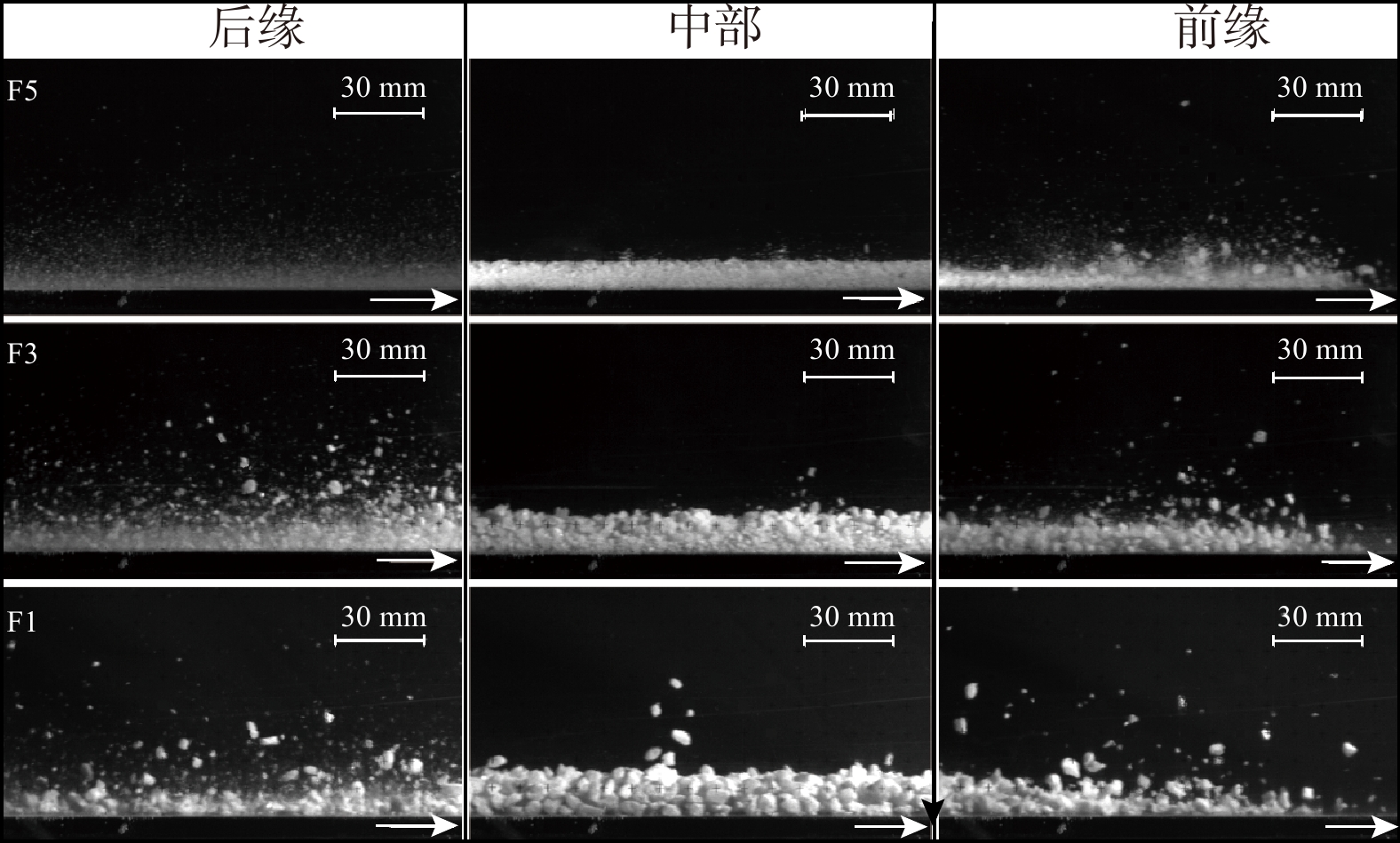
流态化运动是高速远程滑坡的主要运动形式,是揭示高速远程滑坡运动机理的重要基础。基于粒子图像测速(PIV)分析方法,采用物理模型试验对不同粒径组成条件下的颗粒流内部的速度分布、剪切变形及流态特征进行了研究,并对高速远程滑坡流态化运动特征进行了讨论分析。结果表明:碎屑流流态化运动特征与颗粒粒径呈显著的相关性,随着粒径的减小或细颗粒含量的增加,颗粒流底部相对于边界的滑动速度以及整体的运动速度均呈逐渐减小的趋势,颗粒流内部剪切变形程度增加,颗粒的运动形式由“滑动”向“流动”转变;当颗粒粒径较小或细颗粒含量较高时,颗粒流内部剪切速率增大的趋势在颗粒流底部更加显著,反映了粒径减小有助于促进颗粒流内部剪切向底部的集中;在同一颗粒流的不同运动阶段及不同纵向深度,其流态特征具有显著差别,颗粒流前缘及尾部主要呈惯性态,颗粒间以碰撞作用为主,而主体部分则主要呈密集态,颗粒间以摩擦接触作用为主;在颗粒流表面及底部,颗粒间相互作用方式主要是碰撞作用,中间部分则以摩擦作用为主;对于不同粒径的颗粒流,随着粒径的增大或粗颗粒含量的增加,颗粒流内部颗粒的碰撞作用加强,颗粒流整体趋于向惯性态转变。
Abstract:Flow-like motion is the main forms of rock avalanche emplacement, which is the foundation to reveal the dynamic mechanisms of rock avalanches. In this paper, a series of physical modeling experiments based on the Particle Image Velocimetry(PIV)analysis method are conducted to research the internal velocity distribution, internal shear behavior and flow regimes of the granular flow under different grain size conditions. The flow-like motion of rock avalanches and the corresponding deposit features are further discussed and analyzed based on the experimental results. The research results show that the flow-like motion of the granular flow is significantly correlated with the grain size. With the decreasing grain size or the increasing fine particles content, the slip velocity at the bottom of the granular flow and the bulk velocity decrease gradually, the degree of internal shear of the granular flow increases, and the motion form of the granular materials changes from “sliding” to “flowing”. When the grain size is smaller or the content of fine particles is higher, the increasing trend of the internal shear rate is more prominent at the bottom of the granular flow, which indicates that the reduction in grain size promotes shear localization at the bottom of the granular flow. The granular flow regime is different at different locations of the granular flow. The leading and trailing edges of the granular flow are mainly inertial regime, and the interaction between particles is dominated by collisions, while the particle interactions in the main body is dominated by frictional contact. On the surface and bottom of the granular flow, the interaction between particles is mainly collision, while particle interaction in the middle part is mainly frictional contact. For the granular flow with different grain sizes, with the increasing grain size and coarse particles content, the particle collisions in the granular flow are enhanced, and the flow regimes tend to be more inertial.
-
Key words:
- granular flow /
- flow-like motion /
- shear rate /
- flow regime /
- rock avalanche
-

-
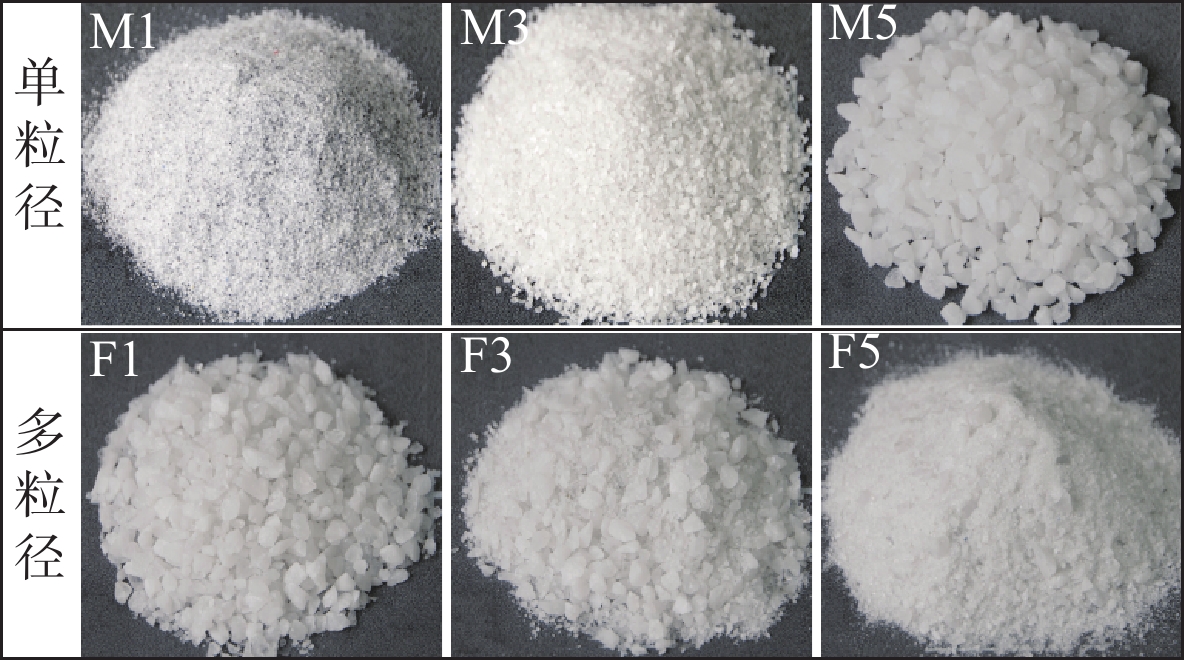
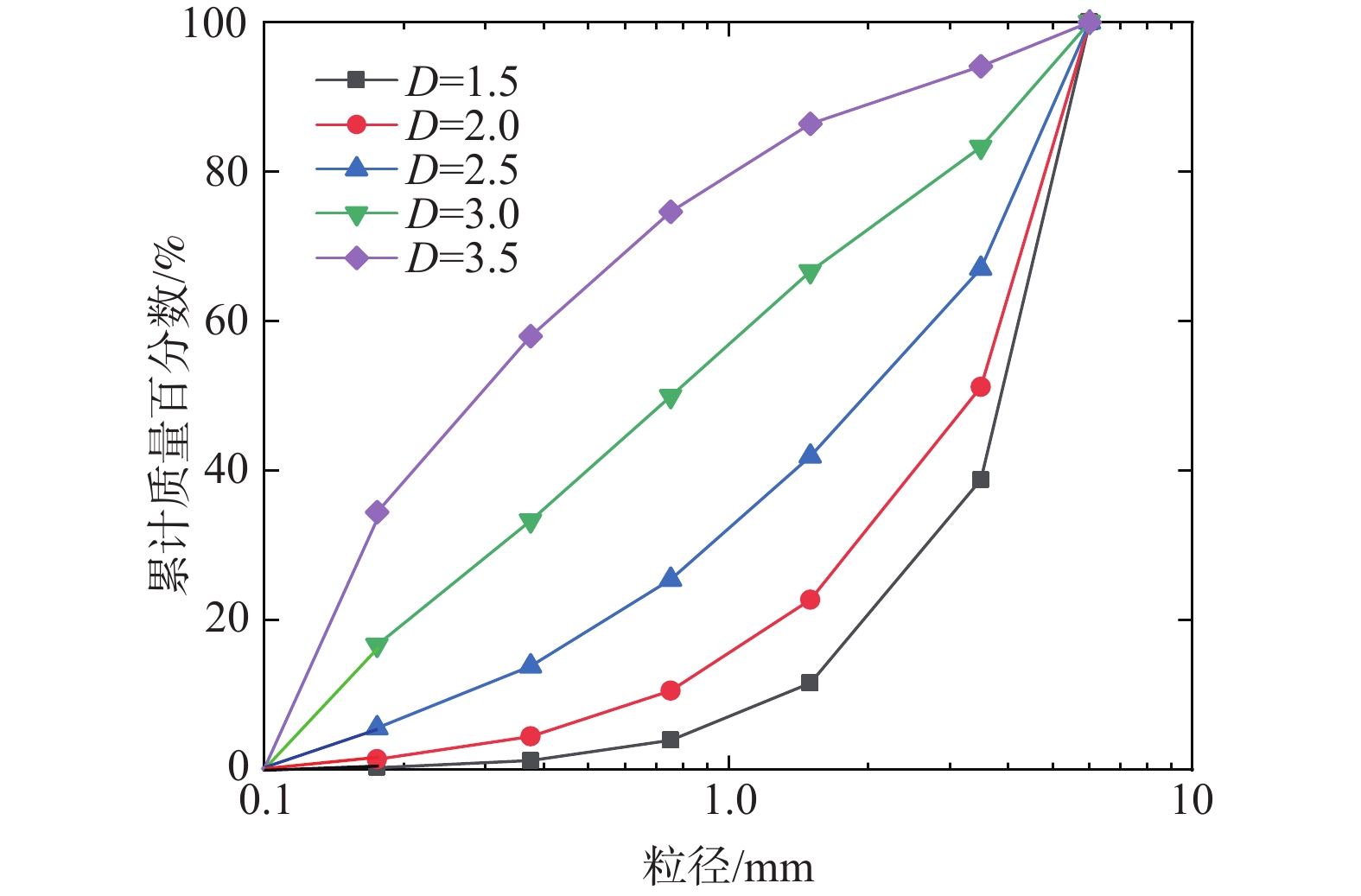
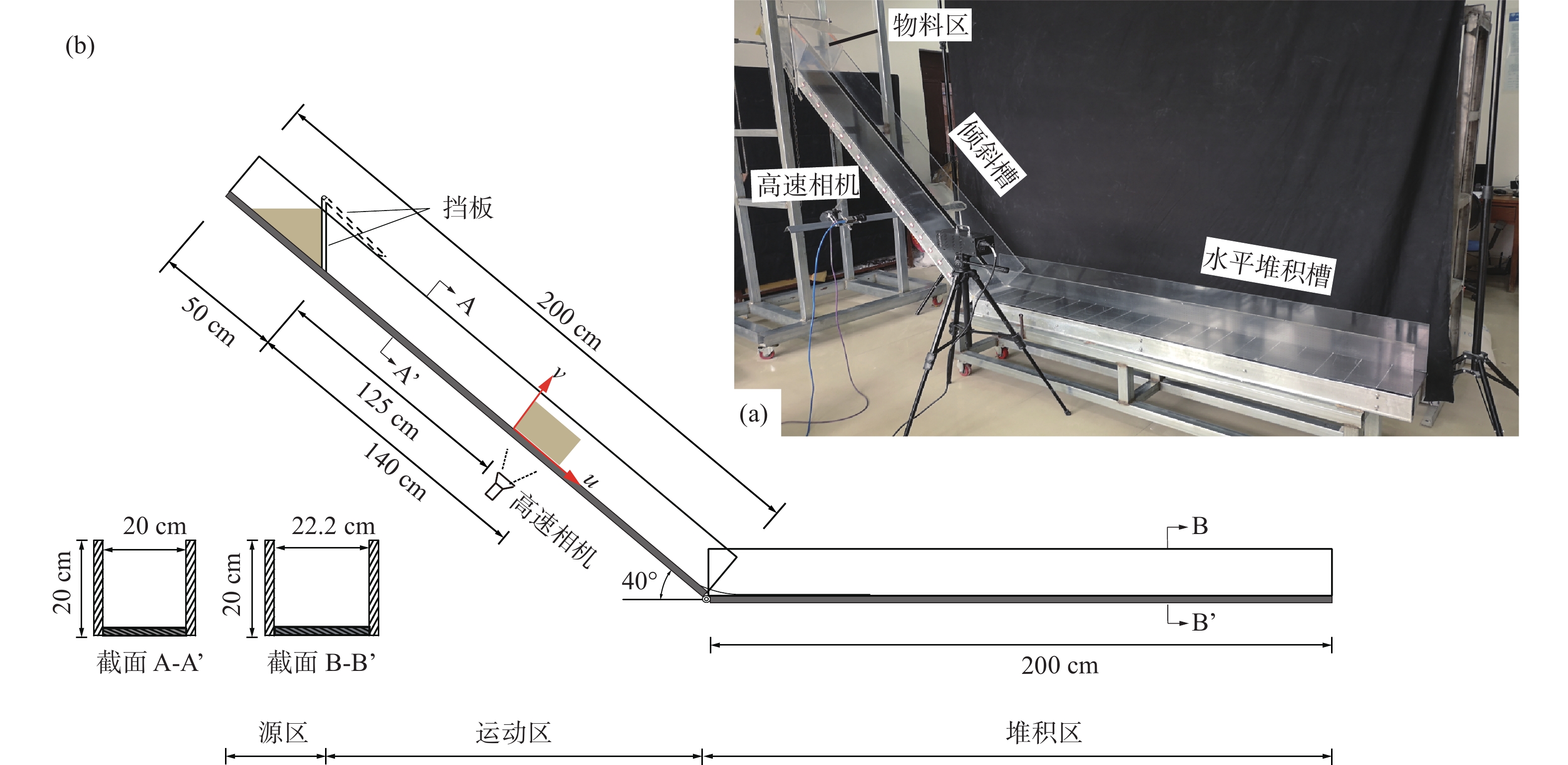
表 1 试验工况设计
Table 1. Design of experimental conditions
粒径组成 编号 工况条件 平均粒径/mm 内摩擦角/(°) 质量/kg 单粒径 M1 d=0.25~0.5 mm 0.38 26.7 8 M2 d=0.5~1 mm 0.75 28.2 M3 d=1~2 mm 1.5 28.1 M4 d=2~5 mm 3.5 31.0 M5 d=5~7 mm 6.0 33.0 多粒径 F1 D=1.5 3.96 32.2 F2 D=2.0 3.41 31.4 F3 D=2.5 2.14 30.6 F4 D=3.0 0.75 28.4 F5 D=3.5 0.30 28.1 -
[1] HEIM. Landslides and human lives[M]. Vancouver, B C: Bitech Publishers, 1932: 80 − 88.
[2] 程谦恭, 张倬元, 黄润秋. 高速远程崩滑动力学的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 山地学报,2007,25(1):72 − 84. [CHENG Qiangong, ZHANG Zhuoyuan, HUANG Runqiu. Study on dynamics of rock avalanches: state of the art report[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2007,25(1):72 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.01.007
[3] 陈达, 许强, 郑光, 等. 基于颗粒识别分析系统的碎屑流堆积物颗粒识别和统计方法研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):60 − 69. [CHEN Da, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Particle identification and statistical methods of a rock avalanche accumulation body based on the particle analysis system[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):60 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 陈禄俊, 邢爱国, 陈龙珠, 等. 高速远程滑坡飞行数值分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2008,35(5):1 − 6. [CHEN Lujun, XING Aiguo, CHEN Longzhu, et al. Numerical analysis on the flying of highspeed and long runout landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2008,35(5):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2008.05.002
[5] 温铭生, 陈红旗, 张鸣之, 等. 四川茂县"6·24"特大滑坡特征与成因机制分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(3):1 − 7. [WEN Mingsheng, CHEN Hongqi, ZHANG Mingzhi, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism analysis of the "6·24" catastrophic landslide of the June 24 of 2017, at Maoxian, Sichuan[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(3):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 戴兴建, 殷跃平, 邢爱国. 易贡滑坡-碎屑流-堰塞坝溃坝链生灾害全过程模拟与动态特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):1 − 8. [DAI Xingjian, YIN Yueping, XING Aiguo. Simulation and dynamic analysis of Yigong rockslide-debris avalanche-dam breaking disaster chain[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] KENT P E. The transport mechanism in catastrophic rock Falls[J]. Journal of Geology,1966,74(1):79 − 83. doi: 10.1086/627142
[8] 王玉峰, 许强, 程谦恭, 等. 高速远程滑坡裹气流态化动力学特性实验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(2):268 − 274. [WANG Yufeng, XU Qiang, CHENG Qiangong, et al. Experimental study of dynamical shearing behaviors of rock avalanche debris under the effect of entrapped gas[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(2):268 − 274. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] MELOSH H J. The physics of very large landslides[J]. Acta Mechanica,1986,64(1/2):89 − 99.
[10] 王玉峰, 程谦恭, 朱圻. 汶川地震触发高速远程滑坡–碎屑流堆积反粒序特征及机制分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(6):1089 − 1106. [WANG Yufeng, CHENG Qiangong, ZHU Qi. Inverse grading analysis of deposit from rock avalanches triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(6):1089 − 1106. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.06.002
[11] DAVIES T R, MCSAVENEY M J. The role of rock fragmentation in the motion of large landslides[J]. Engineering Geology,2009,109(1/2):67 − 79.
[12] GASSEN W V, CRUDEN D M. Momentum transfer and friction in the debris of rock avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1989,26(4):623 − 628. doi: 10.1139/t89-075
[13] SASSA K. Geotechnical model for the motion of landslides[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on landslides. Rotterdam: A A Balkema, 1988, 37 − 55.
[14] HUNGR O. A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides, debris flows, and avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1995,32(4):610 − 623. doi: 10.1139/t95-063
[15] 李坤, 王玉峰, 程谦恭, 等. 分形粒径分布对颗粒流粒径分选的影响规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(2):330 − 343. [LI Kun, WANG Yufeng, CHENG Qiangong, et al. Effects of fractal particle size distribution on segregation of granular flows[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(2):330 − 343. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] HUNGR O, LEROUEIL S, PICARELLI L. The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update[J]. Landslides,2014,11(2):167 − 194. doi: 10.1007/s10346-013-0436-y
[17] SAVAGE S B, HUTTER K. The motion of a finite mass of granular material down a rough incline[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,1989,199:177 − 215. doi: 10.1017/S0022112089000340
[18] ARMANINI A. Granular flows driven by gravity[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research,2013,51(2):111 − 120. doi: 10.1080/00221686.2013.788080
[19] LI K, WANG Y F, LIN Q W, et al. Experiments on granular flow behavior and deposit characteristics: Implications for rock avalanche kinematics[J]. Landslides,2021,18(5):1779 − 1799. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01607-z
[20] DAVIES T R, MCSAVENEY M J. Runout of dry granular avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1999,36(2):313 − 320. doi: 10.1139/t98-108
[21] MANZELLA I, LABIOUSE V. Flow experiments with gravel and blocks at small scale to investigate parameters and mechanisms involved in rock avalanches[J]. Engineering Geology,2009,109(1/2):146 − 158.
[22] 王玉峰, 许强, 程谦恭, 等. 复杂三维地形条件下滑坡–碎屑流运动与堆积特征物理模拟实验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(9):1776 − 1791. [WANG Yufeng, XU Qiang, CHENG Qiangong, et al. Experimental study on the propagation and deposit features of rock avalanche along 3D complex topography[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(9):1776 − 1791. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 郝明辉, 许强, 杨兴国, 等. 高速滑坡–碎屑流颗粒反序试验及其成因机制探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(3):472 − 479. [HAO Minghui, XU Qiang, YANG Xingguo, et al. Physical modeling tests on inverse grading of particles in high speed landslide debris[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(3):472 − 479. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 李祥龙, 唐辉明, 熊承仁, 等. 基底刮铲效应对岩石碎屑流停积过程的影响[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(5):1527 − 1534. [LI Xianglong, TANG Huiming, XIONG Chengren, et al. Influence of substrate ploughing and erosion effect on process of rock avalanche[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(5):1527 − 1534. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.05.039
[25] 陆鹏源, 侯天兴, 杨兴国, 等. 滑坡冲击铲刮效应物理模型试验及机制探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(6):1225 − 1232. [LU Pengyuan, HOU Tianxing, YANG Xingguo, et al. Physical modeling test for entrainment effect of landslides and the related mechanism discussion[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(6):1225 − 1232. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 张志东, 樊晓一, 姜元俊. 滑源区粒序分布及颗粒粒径对碎屑流冲击作用的影响研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):49 − 59. [ZHANG Zhidong, FAN Xiaoyi, JIANG Yuanjun. Particle sequence distribution and the effect of particle size on the impact effect in a fluidized landslide-debris flow[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):49 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] CROSTA G B, FRATTINI P, FUSI N. Fragmentation in the val pola rock avalanche, Italian Alps[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2007,112(F1):F01006.
[28] SAMMIS C, KING G, BIEGEL R. The kinematics of gouge deformation[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics,1987,125(5):777 − 812. doi: 10.1007/BF00878033
[29] SILBERT L E, ERTAŞ D, GREST G S, et al. Granular flow down an inclined plane: Bagnold scaling and rheology[J]. Physical Review E,2001,64(5):51302.
[30] DUFRESNE A, PRAGER C, BÖSMEIER A. Insights into rock avalanche emplacement processes from detailed morpho-lithological studies of the Tschirgant deposit (Tyrol, Austria)[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2016,41(5):587 − 602. doi: 10.1002/esp.3847
-



 下载:
下载: