An experimental study of the dynamic compaction method based on relay drainage in foundation treatment of the coastal backfill area
-
摘要:
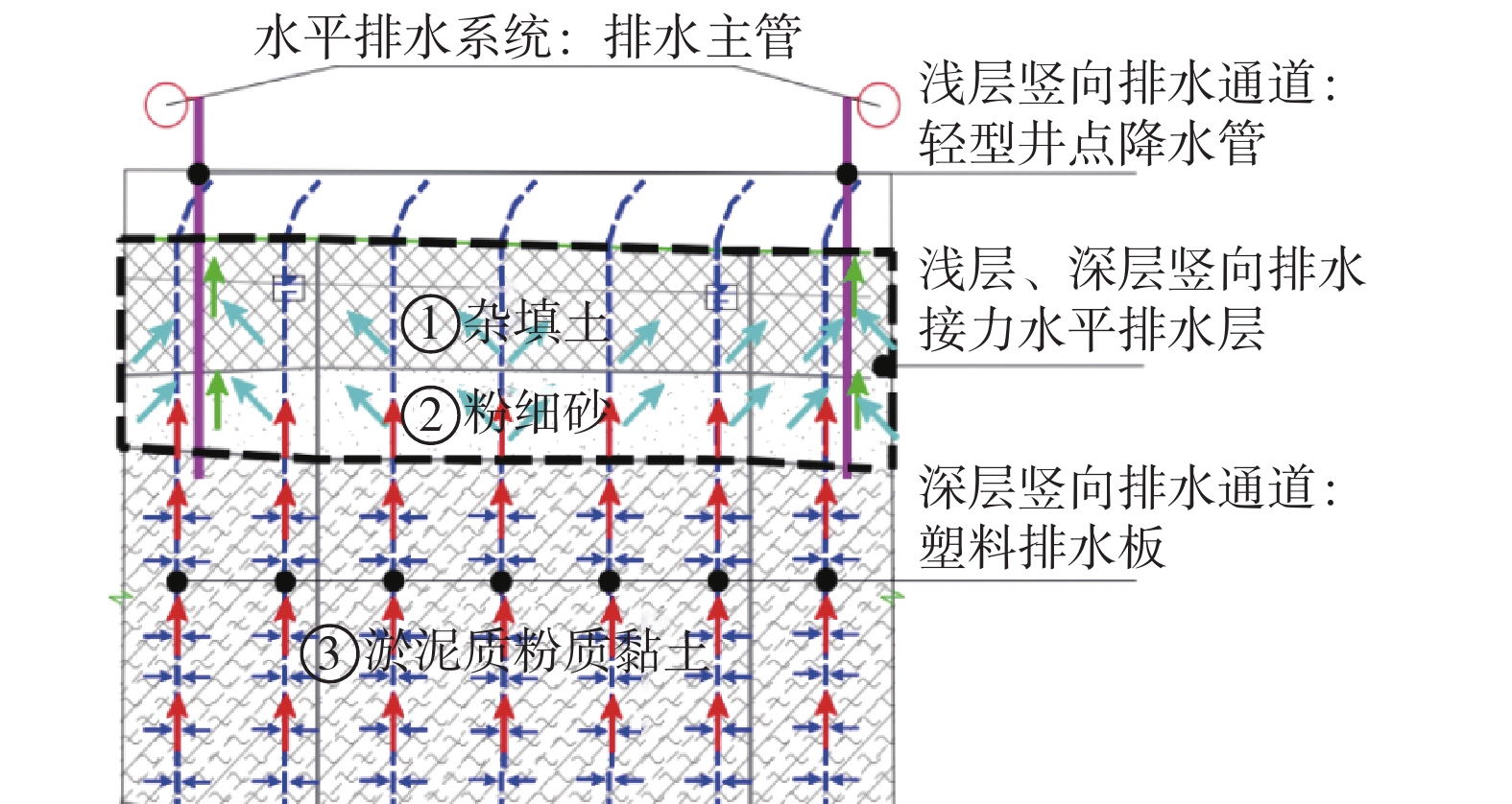
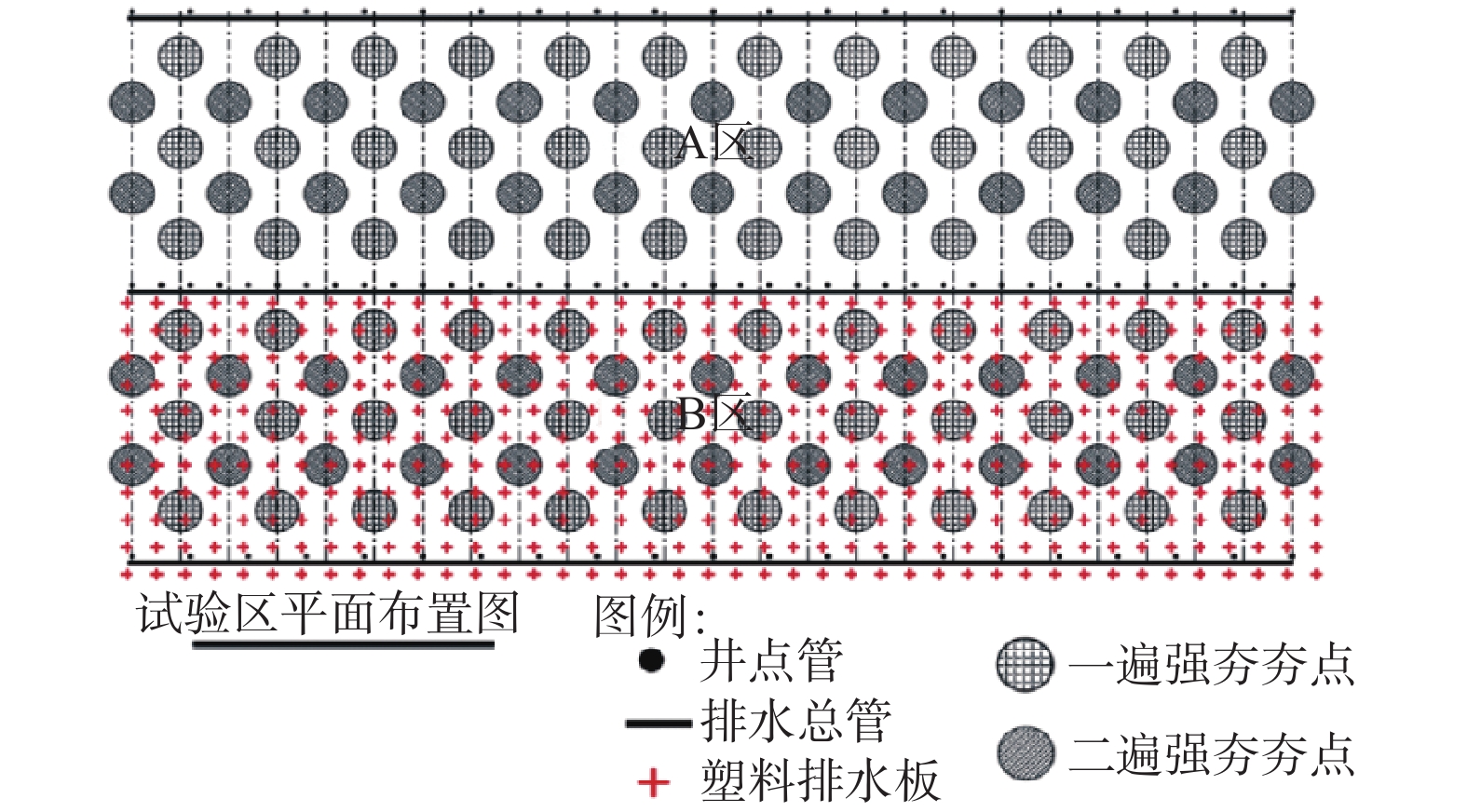
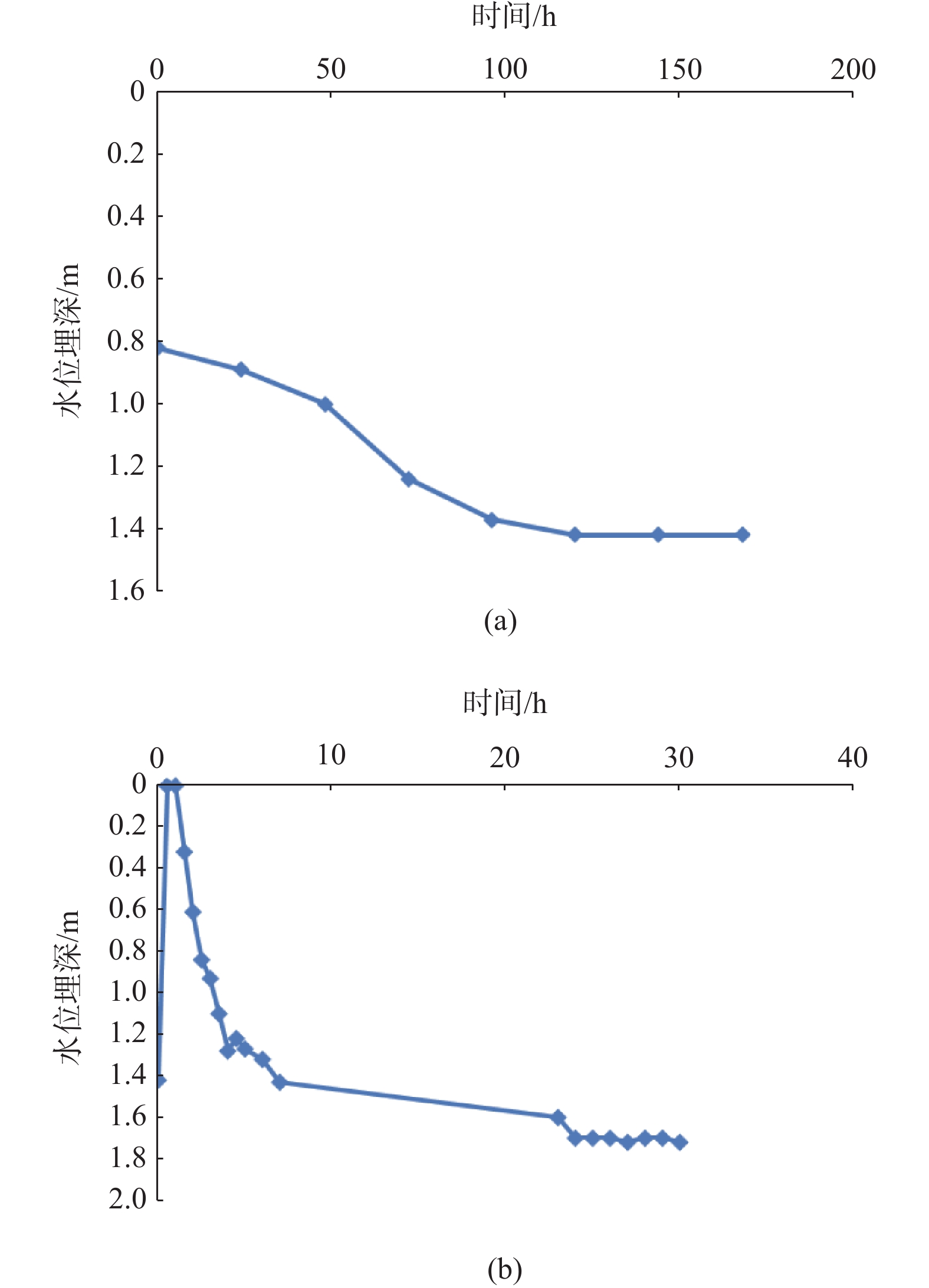
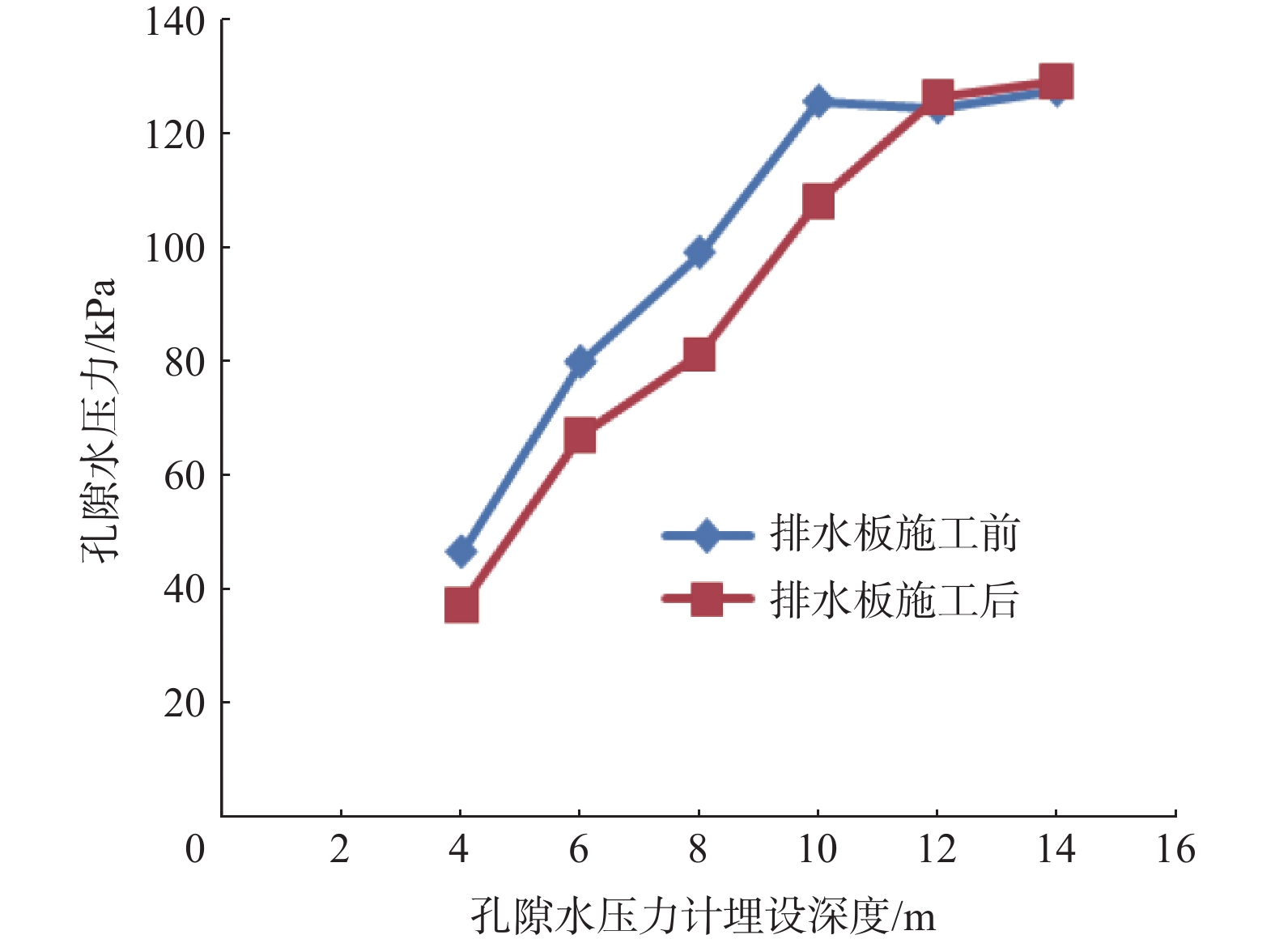
本文对山东半岛海岸带滨海杂填土、饱和粉细砂、淤泥质土等特殊复杂地层地基处理方法进行了研究。以经济高效的强夯法为基础,提出复杂地层整体排水概念,设计了浅层、深层竖向排水和水平排水的接力排水系统,并进行了现场试验研究。监测数据表明,强夯荷载作用下,接力排水系统整体协同排水,可快速排出各个地层中地下水、消散超孔隙水压力。7 h左右可基本消除强夯引起的地下水上升及孔隙水压力消散。持续降水,地表沉降为上部土体厚度的0.7%~2.0%。强夯动力荷载作用下,表层土体压缩为上部土体厚度的8.7%~10.9%。埋深3~7 m土体沉降约为土体厚度的5‰、3‰,埋深7~10 m土体沉降为土体厚度的2‰。检测数据表明,在强夯有效影响深度内地基处理效果明显,土体工程性状改善明显。表层承载力及变形模量满足设计要求,4 m以下淤泥承载力平均值略低于设计要求,下部淤泥质土计算平均固结度为77%。夯后1个月监测数据表明,地表沉降量在25 mm以内,已逐步趋于稳定,分层沉降、孔隙水压力数值整体稳定略有下降。
Abstract:The studies of foundation treatment methods are carried out for the special and complex foundation in the fill, saturated silty fine sand and silt in the coastal backfill area of the coastal zone of the Shandong Peninsula. Based on the economical and efficient dynamic compaction method, the concept of integrated combined drainage is put forward. The relay drainage system of the shallow and deep vertical drainage channels and their relay horizontal drainage channels are designed, and field tests are undertaken. The monitoring data show that under the dynamic compaction load, the relay drainage system can coordinate drainage as a whole, which can quickly discharge the groundwater to dissipate the excess pore water pressure. The rise of groundwater level and dissipation of pore water pressure caused by dynamic compaction can be basically eliminated in about 7 hours. With continuous precipitation, the surface settlement is 0.7%~2.0% of the thickness of the upper soil mass. Under the dynamic load of dynamic compaction, the surface soil is compressed to 8.7%~10.9% of the thickness of the upper soil. The soil settlement is about 5 ‰ and 3 ‰ of the soil thickness at the buried depth of 3~7 m, and 2 ‰ of the soil thickness is at the buried depth of 7~10 m. The test data show that in the effective depth of dynamic compaction, the effect of foundation treatment is obvious, the engineering properties and the degree of consolidation of foundation are improved. The surface bearing capacity and deformation modulus meet the design requirements, the average bearing capacity of silt below 4 m is slightly lower than the design requirements, and the average degree of consolidation of mucky soil is 77%. The monitoring data of one month after tamping shows that the surface subsidence is within 25 mm, which tends to be stable, the layered settlement and pore water pressure are stable and slightly decreased.
-

-
表 1 场区地层概况
Table 1. Layers in the site
地层名称 平均厚度/m 性状简述 杂填土 2.0 湿—很湿,松散,风化砂、碎石,
碎石粒径80~160 mm粉细砂 2.0 饱和,松散,颗粒级配较差 淤泥质土 8.5 黑灰色,有腥臭味,流塑—软塑 粉质黏土 1.6 黑灰色,软—可塑,含少量细砂 中粗砂 2.1 饱和,稍密—中密,颗粒级配差 全风化花岗岩 2.0 结构大部破坏,岩芯砂土状 表 2 分层沉降监测值
Table 2. Monitoring data of layered settlement
初始埋深值/m 第一遍夯前沉降值/mm/占土层厚度比值/‰ 第一遍夯后沉降值/mm/占土层厚度比值/‰ 第二遍夯前沉降值/mm/占土层厚度比值/‰ 第二遍夯后沉降值/mm/占土层厚度比值/‰ 3.3 1.0/0.3 19.0/5.8 0.0/0.0 9.0/2.7 5.5 1.0/0.5 11.0/5.0 2.0/0.9 7.0/3.2 7.0 1.0/0.7 6.0/4.0 0.0/0.0 5.0/3.3 9.0 5.0/0.25 3.0/1.5 1.0/0.5 5.0/2.5 10.9 0.0/0.0 4.0/2.1 4.0/2.1 8.0/4.2 12.9 0.0/0.0 4.0/2.0 0.0/0.0 2.0/1.0 14.9 2.0/0.1 0.0/0.0 0.0/0.0 1.0/0.5 表 3 持续降水地表沉降、平均夯沉量监测数据
Table 3. Surface settlement by pumping and ramming settlement
点号 初始高程
/m持续抽水沉降量
/mm强夯后沉降量
/mm总沉降量
/mm1 4.26022 10.99 437.3 448.29 2 3.86569 17.01 401.3 418.31 3 4.23462 6.24 426.5 432.74 4 4.07414 7.25 376.2 383.45 5 4.46802 8.96 349.7 358.66 平均值 10.09 398.2 408.29 表 4 夯前、夯后土体物理参数对比
Table 4. Difference in soil parameters before and after ramming
取样深度/m 孔隙比e 湿密度ρ0/(g·cm−3) 含水率W/% 压缩模量Es1-2/ MPa 黏聚力c/ kPa
(剪切试验)内摩擦角φ/(°)
(剪切试验)夯前 夯后 夯前 夯后 夯前 夯后 夯前 夯后 夯前 夯后 夯前 夯后 5.3~5.5 2.123 1.369 1.48 1.70 68.1 45.9 2.33 3.01 2.0 4.6 1.6 2.6 6.5~6.7 2.403 1.264 1.48 1.78 71.8 34.1 2.38 2.93 3.2 5.1 2.2 2.5 7.5~7.7 1.418 0.938 1.67 1.81 48.3 34.2 3.58 3.76 3.8 8.2 2.2 3.7 9.0~9.2 1.432 1.185 1.67 1.79 49.0 42.2 3.70 3.71 4.2 7.4 3.2 4.2 10.0~10.2 1.389 1.186 1.67 1.78 45.5 42.0 3.13 3.35 5.3 6.4 4.2 4.3 11.0~11.2 1.039 0.953 1.82 1.81 37.7 33.8 3.96 3.52 4.7 7.5 2.5 4.7 12.0~12.3 1.058 1.095 1.79 1.90 32.4 33.4 3.99 3.90 6.2 5.9 3.6 3.8 平均值 1.552 1.141 1.65 1.80 50.4 37.9 3.29 3.45 4.2 6.4 2.8 3.7 5~10m平均值 1.753 1.188 1.59 1.77 56.5 39.7 3.02 3.35 3.7 6.3 2.7 3.5 表 5 固结试验数据
Table 5. Data of the consolidation test
取样
深度/m先期固结压力Pc/kPa 各级压力下固结稳定后的孔隙比e 25 kPa 50 kPa 100 kPa 200 kPa 上部荷载70 kPa 5.5~5.7 36.0 1.31 1.253 1.13 0.926 1.199 6.8~7.0 36.0 1.26 1.185 1.08 0.919 1.138 7.5~7.7 58.6 0.834 0.793 0.741 0.816 9.1~9.3 54.4 0.929 0.865 0.790 0.901 10.0~10.2 54.0 1.069 1.002 0.905 1.039 11.3~11.5 57.9 1.060 0.992 0.902 1.031 12.0~12.2 65.2 1.133 0.834 0.782 1.001 表 6 载荷试验数据结果
Table 6. Results of the loading tests
试验点
编号试验深度/m 承载力特征值fak/kPa fak对应沉降量s/mm 变形模量E0/MPa 1 0.5 155 4.51 12.5 2 0.5 160 4.01 14.6 3 0.5 150 4.33 12.8 4 4.5 119 0.93 10.3 5 4.5 116 0.98 9.6 6 4.5 120 0.91 10.7 表 7 夯后地表沉降数据
Table 7. Surface subsidence data
点号 停止降水时
地面高程/m0~10 d沉降
量/mm10~20 d沉降
量/mm20~30 d沉降
量/mm累计30 d沉降
量/mm1 4.00522 12.07 5.32 2.80 20.19 2 4.01662 12.96 8.08 3.30 24.34 3 3.88059 13.14 5.12 2.45 20.71 4 4.02969 7.76 4.05 1.62 13.43 5 3.94267 8.93 3.13 2.38 14.44 6 4.00457 5.40 2.95 1.35 9.70 表 8 夯后分层沉降监测值
Table 8. Monitoring data of layered settlement
初始埋深
值/m停止降水时
沉降量/mm0~10 d沉降
量/mm10~20 d沉降
量/mm20~30 d沉降
量/mm3.3 30.0 30.0 29.9 / 5.5 21.1 22.0 / 22.0 12.9 8.3 10.0 10.0 13.2 -
[1] 龚晓南. 地基处理手册[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2008.
GONG Xiaonan. Foundation Treatment Manual [M]. 3ed. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
[2] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑地基处理技术规范: JGJ 79—2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2013.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for ground treatment of buildings: JGJ 79—2012. [S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2013. (in Chinese)
[3] 中国工程建设标准化协会. 强夯地基处理技术规程: CECS 279—2010[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2010.
China Association for Engineering Construction Standardization. Technical specification of dynamic consolidation to ground treatment: CECS 279—2010[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2010. (in Chinese)
[4] 左名麒. 震动波与强夯法机理[J]. 岩土工程学报,1986,8(3):55 − 62. [ZUO Mingqi. Vibration wave and dynamic compaction mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1986,8(3):55 − 62. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1986.03.007
[5] 雷鸣, 王星华, 唐依民. 基于孔压实测资料的真空预压机理及沉降计算探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(6):81 − 85. [LEI Ming, WANG Xinghua, TANG Yimin. Discussion of the mechanism of vacuum preloading and settlement calculation based on measured values of pore water pressure[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(6):81 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.06.016
[6] 刘景锦, 雷华阳, 卢海滨, 等. 真空预压法淤堵泥层形成机理及预测模型研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(3):61 − 71. [LIU Jingjin, LEI Huayang, LU Haibin, et al. A study of siltation mud formation mechanism and prediction model of vacuum preloading method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(3):61 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 董超强. 塑料排水板堆载预压法处理超软土地基固结沉降与稳定性控制研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017.
DONG Chaoqiang. Study on consolidation settlement and stability controlling of super-soft foundation treated by the method of prefabricated vertical drains with preloading[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 叶兴永. 强夯法处理软弱粉土地基试验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2001.
YE Xingyong. The test and study of dynamic consolidation applied in soft silt foundation treatment. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2001. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王越虹. 低能量强夯联合井点降水处理沿海软质地基的应用研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2011.
WANG Yuehong. Application research of coastal soft foundation by low-energy dynamic and dewatering consolidation[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao Technology University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 陈晨. 塑料排水板—强夯法在吹填土地基加固中的应用[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2007.
CHEN Chen. The application of plastic-board drain and dynamic consolidation method for filled foundation[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 韩治勇. 高真空排水+强夯动静耦合软基加固机理研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016.
HAN Zhiyong. Study on the mechanism of high vacuum drainage combined with dynamic compaction for soft foundation consolidation[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 谢伟树. 低能强夯真空排水法孔压消散及沉降计算研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2017.
XIE Weishu. Study on pore pressure dissipation and settlement calculation under low-energy dynamic vacuum compaction[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 谢松高, 陈锦旺. 地面积水情况下层状土壤的水平排水[J]. 水利学报,1965(5):1 − 9. [XIE Songgao, CHEN Jinwang. Horizontal ditch drainage for layered soil with surface ponded water percolated[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,1965(5):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 吴航. 强夯作用下土体动力响应的特性与分析[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2016.
WU Hang. Study on dynamic response of soil under dynamic compaction[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 李广信. 高等土力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004.
LI Guangxin. Advanced Soil Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[16] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for geotechnical testing method: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[17] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 复合地基技术规范: GB/T 50783—2012[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2012.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for composite foundation: GB/T 50783—2012. [S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2012. (in Chinese)
[18] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑地基检测技术规范: JGJ 340—2015[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2015.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for testing of building foundation soils: JGJ 340—2015[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[19] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑变形测量规范: JGJ 8—2016[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2016.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code for deformation measurement of building and structure: JGJ 8—2016[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2016. (in Chinese)
[20] 倪静, 朱颖, 陈有亮, 等. 循环荷载作用下竖向排水板加固软黏土的孔隙水压力累积特性研究[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(2):383 − 389. [NI Jing, ZHU Ying, CHEN Youliang, et al. Cumulative pore water pressure behaviour of soft clays installed with prefabricated vertical drains under cyclic loads[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2016,37(2):383 − 389. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 林敏晖. 静动力排水固结法夯击间隔期间软土固结机理研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2017.
LIN Minhui. Consolidation mechanism between tamping on soft soil Static-dynamic drainage consolidation treatment [D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: