Hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution mechanism of karst groundwater in the catchment area of the Sangu Spring
-
摘要:
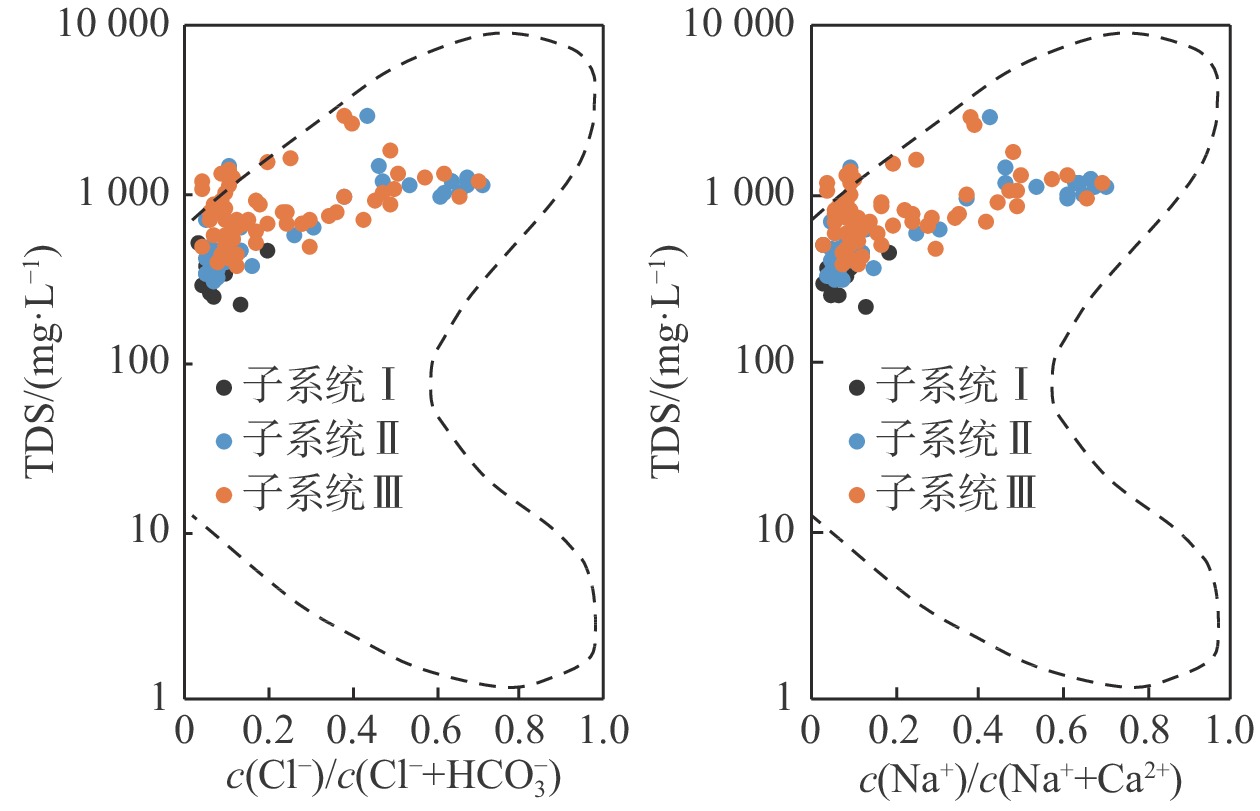
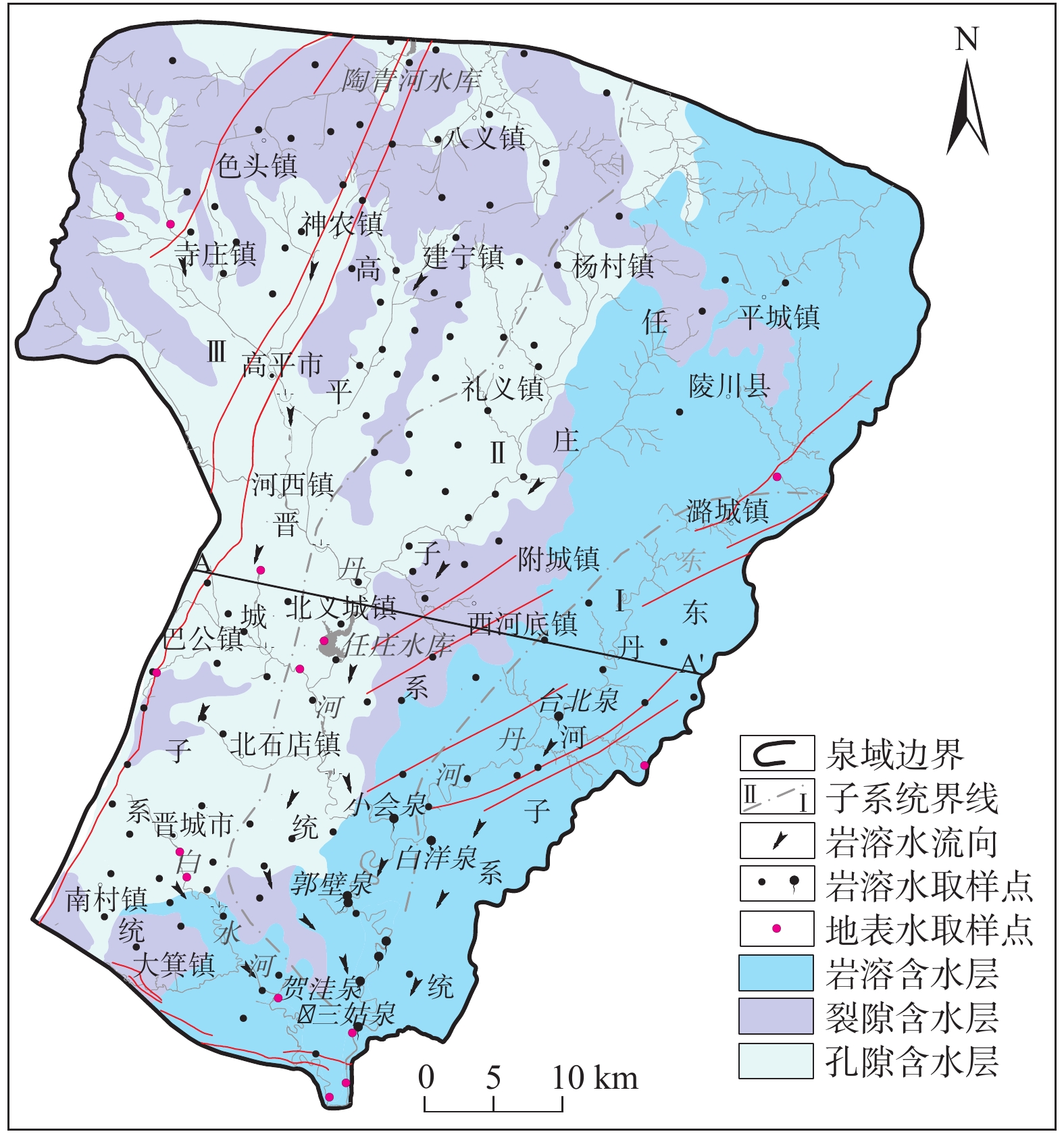
三姑泉域岩溶地下水对晋东南地区居民生活及煤炭基地建设起着重要支撑作用。受煤炭资源大规模开采及人类活动加剧的影响,岩溶地下水水化学环境演变剧烈。通过分析三姑泉域的125 个岩溶地下水、14 个地表水及14个雨水样品,综合利用统计分析、变异系数分析、氢氧稳定同位素、Gibbs模型、离子相关关系、矿物饱和指数及因子分析,确定岩溶地下水的补给来源,分析三个子系统间岩溶水水化学特征、差异及形成演化机制。结果表明:岩溶水δD值为−77‰~−42‰,δ18O值为−10.6‰~−4.5‰,且沿大气降雨线分布,显示岩溶地下水以大气降水入渗补给为主。子系统Ⅰ与子系统Ⅱ和子系统Ⅲ具有明显不同的水化学特征和水文地球化学演化进程。子系统Ⅰ岩溶水为低TDS软水,73%为HCO3—Ca(Mg)型水;子系统Ⅱ、子系统Ⅲ为低TDS软水—高TDS硬水,水化学类型复杂,36%~40%为HCO3·SO4—Ca·Mg型水,24%~45%为SO4·HCO3—Ca型水。因子分析表明,区域岩溶地下水化学形成演化主要受控于水-岩作用、人类活动、地表水和局部裂隙水渗漏的影响。水-岩作用使得岩溶水化学组分以
${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{NO}}_3^-$ Abstract:The karst groundwater in the catchment area of the Sangu Spring plays an important supporting role in the residents' living and coal base construction in southeastern Shanxi Province.With the large-scale coal mining and the intensification of human activities, the hydrochemistry of the regional karst groundwater has changed drastically. In this study, 125 karst groundwater, 14 surface water and 14 rain water samples were collected and tested. The descriptive statistical analysis, coefficient of variation analysis, hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes, Gibbs model, ion correlation, mineral saturation index and factor analysis are comprehensively used to determine the replenishment sources of the karst groundwater, the differences of hydrochemical characteristics and evolution mechanism among the subsystems. The results show that the δD and δ18O values of the karst groundwater range from −77‰ to −42‰ and from −10.6‰ to −4.5‰, respectively, and the data points fall near the local meteoric water line (LMWL), indicating that the karst groundwater are mainly recharged by infiltration from precipitation. The hydrochemical characteristics and hydrogeochemical evolution processes between subsystems Ⅰ and Ⅱ-Ⅲwere obviously different. The karst groundwater of subsystem Ⅰhas low salinity and is soft water, and 73% of the groundwater is of HCO3—Ca(Mg) type. However, the karst groundwater in subsystems Ⅱ and Ⅲ changes from low salinity and soft water to high salinity and hard water, and 36% to 40% of the water is of HCO3·SO4—Ca·Mg type and 24% to 45%, of SO4·HCO3—Ca type. Factor analyses show that the hydrochemical evolution processes of the regional karst groundwater are mainly controlled by water-rock interactions, human activities, leakage of surface water and local fissure water. Hydrochemical compositions of
< span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144440.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144440.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144440.png'/ > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144600.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144455.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144455.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144455.png'/ > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144600.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144455.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144455.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144455.png'/ > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144531.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144531.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202004059_Z-20210115144531.png'/ > -

-
表 1 岩溶水和地表水水化学参数
Table 1. Statistical parameters of the dissolved chemical components of karst groundwater and surface water
项目 岩溶地下水 东丹河子系统(Ⅰ) 任庄子系统(Ⅱ) 晋城-高平子系统(Ⅲ) 地表水 最小值 最大值 均值 Cv 最小值 最大值 均值 Cv 最小值 最大值 均值 Cv 最小值 最大值 均值 Cv 最小值 最大值 均值 Cv 总硬度 175.10 1324.00 474.34 0.47 175.10 431.90 296.48 0.21 264.70 1315.00 414.60 0.47 246.00 1324.00 548.51 0.41 159.10 983.80 444.61 0.54 TDS 218.70 2781.00 751.21 0.60 218.70 510.20 338.81 0.23 301.70 2781.00 731.46 0.66 371.40 2762.00 852.59 0.51 218.90 1540.00 759.06 0.54 pH 7.08 8.57 7.74 0.03 7.43 7.89 7.62 0.02 7.08 8.57 7.82 0.04 7.20 8.53 7.72 0.03 7.42 8.61 7.96 0.04 Ca2+ 49.37 455.00 132.88 0.56 49.37 148.60 88.27 0.26 74.87 394.00 118.08 0.56 53.60 455.00 151.38 0.53 38.30 250.40 121.19 0.53 Mg2+ 12.59 80.10 34.49 0.40 12.59 24.98 18.45 0.19 16.90 80.10 29.05 0.35 18.02 77.90 41.21 0.30 9.19 86.95 34.49 0.59 K+ 0.15 16.56 1.33 1.34 0.40 2.74 1.12 0.51 0.35 7.42 1.09 1.05 0.15 16.56 1.51 1.45 1.55 33.54 9.78 0.87 Na+ 3.32 304.00 51.72 1.35 3.32 25.27 7.28 0.74 4.42 304.00 67.77 1.20 5.04 284.00 51.84 1.28 4.30 165.60 76.84 0.62 Cl− 0.36 224.00 25.40 1.16 2.50 27.07 9.91 0.67 0.36 118.70 22.26 1.10 5.36 224.00 30.64 1.10 6.07 239.30 74.27 0.82 
21.86 1731.00 269.23 0.98 21.86 107.50 50.10 0.45 26.28 1731.00 253.36 1.18 53.92 1322.00 326.30 0.75 66.08 850.50 281.55 0.73 
146.00 441.10 299.80 0.15 159.00 321.00 270.22 0.18 146.00 428.00 294.30 0.13 208.00 441.10 309.49 0.15 134.50 422.00 239.28 0.35 
0.20 209.50 19.41 1.17 3.92 85.60 16.31 1.23 3.76 209.50 21.40 1.46 0.20 98.30 18.90 0.87 1.88 124.40 27.14 1.21 F− 0.10 2.10 0.54 0.68 0.10 0.52 0.23 0.54 0.18 1.53 0.51 0.71 0.26 2.10 0.63 0.59 0.50 1.70 0.85 0.41 耗氧量 0.20 10.40 1.49 1.09 0.37 6.40 1.35 1.36 0.29 4.80 1.27 0.81 0.20 10.40 1.65 1.13 1.08 24.00 5.18 1.15 注:pH、变异系数(Cv)为无量纲;其余单位为mg/L;总硬度以CaCO3计。 表 2 岩溶水各参数因子载荷矩阵
Table 2. Rotated component matrix and extraction sums of squared loadings
项目 F1 F2 F3 F4 总硬度 0.863* −0.363 −0.046 0.240 TDS 0.943* −0.052 0.103 −0.167 pH 0.197 0.867* 0.396 −0.142 Ca2+ 0.820* −0.425 0.086 0.214 Mg2+ 0.504 0.635* −0.469 0.239 K+ 0.218 −0.240 −0.212 −0.378 Na+ 0.500 0.226 0.227 0.699* Cl− 0.512 −0.484 0.468 0.642* 
0.926* −0.031 −0.025 −0.205 
0.295 0.810* 0.008 0.311 
0.268 −0.529 0.526* 0.054 F− 0.409 0.394 0.649* −0.083 SI−CaCO3 0.455 0.609* 0.415 0.313 SI−CaMg(CO3)2 0.386 0.738* 0.283 0.296 SI−CaSO4·2H2O 0.949* −0.044 −0.106 0.013 SI−CaSO4 0.949* −0.044 −0.106 0.013 SI−NaCl 0.512 −0.050 0.243 0.336 SI−CaF2 0.456 0.263 0.594* −0.009 特征值 8.410 2.845 2.054 1.583 贡献率/% 46.721 15.808 11.409 8.792 累积贡献率/% 46.721 62.529 73.938 82.729 注:*为主因子中具有较高载荷。 -
[1] KOLLARITS S, KUSCHNIG G, VESELIC M, et al. Decision-support systems for groundwater protection: innovative tools for resource management[J]. Environmental Geology,2006,49(6):840 − 848. doi: 10.1007/s00254-006-0179-3
[2] GHASEMIZADEH R, HELLWEGER F, BUTSCHER C, et al. Review: Groundwater flow and transport modeling of karst aquifers, with particular reference to the North Coast Limestone aquifer system of Puerto Rico[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2012,20(8):1441 − 1461. doi: 10.1007/s10040-012-0897-4
[3] 何守阳, 朱立军, 董志芬, 等. 典型岩溶地下水系统地球化学敏感性研究[J]. 环境科学,2010,31(5):1176 − 1182. [HE Shouyang, ZHU Lijun, DONG Zhifang, et al. Study on geochemical susceptivity of groundwater system in representative karstic regions[J]. Environmental Science,2010,31(5):1176 − 1182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘再华, 袁道先. 中国典型表层岩溶系统的地球化学动态特征及其环境意义[J]. 地质论评,2000,46(3):324 − 327. [LIU Zaihua, YUAN Daoxian. Features of geochemical variations in typical epikarst systems of China and their environmental significance[J]. Geological Review,2000,46(3):324 − 327. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.03.014
[5] 徐尚全, 杨平恒, 殷建军, 等. 重庆雪玉洞岩溶地下河地球化学敏感性研究[J]. 环境科学,2013,34(1):77 − 83. [XU Shangquan, YANG Pingheng, YIN Jianjun, et al. Research on the sensitivity of geochemical of underground river in Chongqing Xueyu cave[J]. Environmental Science,2013,34(1):77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张超, 张保祥, 张吉圣, 等. 肥城市岩溶水水化学特征及形成机制[J]. 中国岩溶,2018,37(5):698 − 707. [ZHANG Chao, ZHANG Baoxiang, ZHANG Jisheng, et al. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of karst water in Feicheng City[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2018,37(5):698 − 707. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 霍俊伊, 于奭, 张清华, 等. 湘西峒河流域水化学特征及无机碳通量计算[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):64 − 72. [HUO Junyi, YU Shi, ZHANG Qinghua, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and estimation of the Dissolved inorganic carbon flux in the Donghe River Basin of western Hunan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):64 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 殷晓曦, 陈陆望, 谢文苹, 等. 采动影响下矿区地下水主要水-岩作用与水化学演化规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(5):33 − 39. [YIN Xiaoxi, CHEN Luwang, XIE Wenping, et al. Main water-rock interactions and hydrochemical evolution in the aquifers under the mining-induced disturbance in a mining district[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(5):33 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 黄奇波, 覃小群, 程瑞瑞, 等. 左江中游岩溶峰林区河流交互带水化学特征与控制因素[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5):1 − 8. [HUANG Qibo, QIN Xiaoqun, CHENG Ruirui, et al. Hydrochenmical characteristics and control factors of karst hyporheic zones in the karst peak forest region of the middle reaches of the Zuo River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(5):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘英学, 梁韵, 乔梁. 邢台百泉岩溶地下水系统水-岩反应特征分析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2009,7(4):63 − 66. [LIU Yingxue, LIANG Yun, QIAO Liang. Analysis on water-rock reaction characteristics of groundwater system in Xingtai-Baiquan springs[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2009,7(4):63 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1683.2009.04.018
[11] 邓启军, 李方红, 李伟, 等. 蒲阳河流域地下水水化学及同位素特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):8 − 14. [DENG Qijun, LI Fanghong, LI Wei, et al. The chemical and isotopes characteristic of groundwater in Puyang river basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):8 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张军以, 王腊春, 苏维词, 等. 岩溶地区人类活动的水文效应研究现状及展望[J]. 地理科学进展,2014,33(8):1125 − 1135. [ZHANG Junyi, WANG Lachun, SU Weici, et al. Status and prospect of the hydrological effects of human activities in the Karst area[J]. Progress in Geography,2014,33(8):1125 − 1135. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2014.08.013
[13] 刘绍华, 郭芳, 姜光辉, 等. 桂林市峰林平原区岩溶水文地球化学特征[J]. 地球与环境,2015,43(1):55 − 65. [LIU Shaohua, GUO Fang, JIANG Guanghui, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of peak forest plain in Guilin City, China[J]. Earth and Environment,2015,43(1):55 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 黄科云, 刘德深, 马祖陆, 等. 云南鹤庆西山岩溶地下水主要离子雨季和旱季对比及来源分析[J]. 地球与环境,2015,43(2):183 − 189. [HUANG Keyun, LIU Deshen, MA Zulu, et al. Major ion chemistry and their sources of karstic ground water from the Heqing west mountain, China during flood and dry seasons[J]. Earth and Environment,2015,43(2):183 − 189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 蔡月梅, 蔡五田, 刘金巍, 等. 河南省某大型水源地岩溶水水化学及同位素特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(5):41 − 47. [CAI Yuemei, CAI Wutian, LIU Jinwei, et al. Chemical and isotopic characteristics of the karst groundwater in the wellfield in Henan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(5):41 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李慧清. 晋城市三姑泉域地下水生态现状分析及修复对策[J]. 山西水利科技,2018(2):61 − 64. [LI Huiqing. Analysis on the groundwater ecological status in the Sanguquan spring-feeding area of Jincheng City and restoration countermeasures[J]. Shanxi Hydrotechnics,2018(2):61 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8139.2018.02.020
[17] 王振兴, 李向全, 侯新伟, 等. 煤炭开采条件下三姑泉域岩溶含水层保护评价[J]. 中国岩溶,2019,38(1):28 − 39. [WANG Zhenxing, LI Xiangquan, HOU Xinwei, et al. Karst aquifer protection evaluation to the Sangu spring basin under the condition of coal mining[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2019,38(1):28 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 刘晓红, 张永波. 山西晋城三姑泉域地下水资源评价[J]. 太原科技大学学报,2009,30(3):261 − 263. [LIU Xiaohong, ZHANG Yongbo. Groundwater resources evaluation on Sangu spring region of Jincheng of Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Science and Technology,2009,30(3):261 − 263. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2057.2009.03.019
[19] 刘晓红, 张永波. 山西晋城三姑泉域岩溶地下水水质评价[J]. 山西建筑,2009,35(5):173 − 174. [LIU Xiaohong, ZHANG Yongbo. On the karst underwater water quality assessment of Sanguquan in Jincheng of Shanxi[J]. Shanxi Architecture,2009,35(5):173 − 174. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2009.05.108
[20] 许志峰, 张志祥, 刘晓霞. 三姑泉域水环境质量评价及水污染控制对策[J]. 地下水,2012,34(4):87 − 90. [XU Zhifeng, ZHANG Zhixiang, LIU Xiaoxia. Water environmental quality assessment and strategy for water pollution control in Sangu spring basin[J]. Ground Water,2012,34(4):87 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 侯新伟, 李向全, 王振兴, 等. 晋东能源基地水文地质环境地质调查报告[R]. 石家庄: 中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所, 2016: 45-189.
HOU Xinwei, LI Xiangquan, WANG Zhenxing, et al. Hydrogeological and environment geological survey report of Jindong energy base[R]. Shijiazhuang: Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, 2016: 45-189. (in Chinese)
[22] 黄平华, 陈建生, 宁超, 等. 焦作矿区地下水水化学特征及其地球化学模拟[J]. 现代地质,2010,24(2):369 − 376. [HUANG Pinghua, CHEN Jiansheng, NING Chao, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and hydrogeochemical modeling of groundwater in the Jiaozuo mining district[J]. Geoscience,2010,24(2):369 − 376. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.02.023
[23] PIPER A M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union,1944,25(6):914 − 928. doi: 10.1029/TR025i006p00914
[24] 韦虹, 吴锦奎, 沈永平, 等. 额尔齐斯河源区融雪期积雪与河流的水化学特征[J]. 环境科学,2016,37(4):1345 − 1352. [WEI Hong, WU Jinkui, SHEN Yongping, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of snow meltwater and river water during snow-melting period in the headwaters of the Ertis River, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Science,2016,37(4):1345 − 1352. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] CAROL E, MAS-PLA J, KRUSE E. Interaction between continental and estuarine waters in the wetlands of the northern coastal plain of Samborombón Bay, Argentina[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2013,34:152 − 163. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.03.006
[26] HUANG G X, SUN J C, ZHANG Y, et al. Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2013,463/464:209 − 221. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.078
[27] LIU F, SONG X F, YANG L H, et al. The role of anthropogenic and natural factors in shaping the geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Subei Lake basin, Ordos energy base, Northwestern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2015,538:327 − 340. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.057
-










 下载:
下载: