Evolution characteristics of total dissolved solids in the groundwater level funnel area in the Hufu piedmont plain
-
摘要:
为揭示滹滏平原漏斗核心区地下水溶解性总固体(TDS)增大对水位下降的响应特征以及驱动TDS增大的主要化学组分,应用地学数理统计分析、时间序列异变分析和GIS空间特征分析技术,分析了近50年(1972—2017)研究区地下水水位埋深、TDS及化学组分变化特征。结果表明:(1)随着水位降幅变化,地下水TDS增幅具有阶段性变化特征,在漏斗形成初期(1972—1980年),地下水水位年均降幅最大,TDS年均增幅也最大;中期(1981—2000年)地下水水位年均降幅最小,TDS年均增幅也最小;末期(2001—2017年)地下水水位年均降幅居中,TDS年均增幅也居中。(2)随着水位埋深增大,漏斗核心区地下水水位埋深大小对TDS增大影响呈递减效应。漏斗形成初期水位埋深9.10~23.20 m,中期水位埋深13.40~42.28 m,末期水位埋深21.41~50.29 m,漏斗核心区地下水水位年均降幅每增大1.0 m条件下,TDS年均增幅分别增大21.96 ,13.54 ,12.32 mg/L。(3)自初期、中期至末期,地下水中Na+、
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ Abstract:In order to reveal the response characteristics of total dissolved solids (TDS) increase to groundwater level decline and the main chemical components that drive TDS to increase in the core area of the groundwater level funnel in the Hufu piedmont plain, geological statistical analysis, time series variation analysis and GIS spatial feature analysis technology are applied to analyze the variation characteristics of groundwater level depth, TDS and chemical compositions in the study area in the past 50 years (1972-2017). The results show that (1) the increase of TDS is characterized by stages along with the decrease of groundwater levels. In the initial stage of the funnel formation (1972-1980), the annual decrease of groundwater levels was the largest, and the annual increase of groundwater TDS was also the largest. In the middle period (1981-2000), the average annual decrease of groundwater level was the lowest, and the average annual increase of groundwater TDS was also the lowest. At the end of the period (2001-2017), the average annual decline of groundwater level was in the middle, and the average annual increase of groundwater TDS was also in the middle. (2) The influence of groundwater level on the increasing TDS presents a decreasing effect with the increase of the depth of groundwater level. For each increase of groundwater level of 1.0 m, the average growth rate of groundwater TDS increased by 21.96 mg/L at the initial stage of the funnel formation (the groundwater level buried depth ranged from 9.10 m to 23.20 m), the average growth rate of groundwater TDS increased by 13.54 mg/L at the middle stage (the groundwater level buried depth ranged from 13.40 m to 42.28 m), and the average growth rate of groundwater TDS increased by 12.32 mg/L at the end stage (the groundwater level buried depth ranged from 21.41 m to 50.29 m). (3) The increase of concentrations of Na+ and
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ -

-
表 1 漏斗形成不同时期地下水水位变化特征
Table 1. Characteristics of groundwater level changes in different stages of the funnel formation
漏斗形成阶段 地下水水位年均降幅特征值 Ⅰ区水位年均
降幅/mⅡ区 Ⅲ区 水位年均
降幅/m与Ⅰ区水位年均降幅的比值 水位年均
降幅/m与Ⅰ区水位年均降幅的比值 初期
(1972—1980年)最小值 −0.76 −0.30 2.53 −0.17 4.47 最大值 −2.54 −2.39 1.06 −1.73 1.47 平均值 −1.68 −1.57 1.07 −1.13 1.49 中期
(1981—2000年)最小值 −0.30 −0.14 2.14 −0.20 1.50 最大值 −0.88 −0.87 1.01 −1.04 0.85 平均值 −0.63 −0.43 1.47 −0.52 1.21 末期
(2001—2017年)最小值 −0.66 −0.25 2.64 −0.24 2.75 最大值 −1.15 −1.14 1.01 −1.02 1.13 平均值 −0.94 −0.56 1.68 −0.75 1.25 注:负值表示水位下降,初、中、末期分别相对1972年、1980年和2000年地下水水位的年均降幅。 表 2 研究区漏斗形成不同时期地下水TDS演变特征
Table 2. Characteristic of groundwater salinity changes in different stages of the funnel formation
漏斗形成阶段 地下水TDS
及年均增幅特征值Ⅰ区TDS Ⅱ区 Ⅲ区 TDS 与Ⅰ区
的比值TDS 与Ⅰ区
的比值初期
(1973—1980年)TDS/(mg·L−1) 最小值 471 634 0.74 342 1.38 最大值 997 954 1.05 613 1.63 平均值 736 737 1.00 518 1.42 年均增幅/(mg·L−1) 最小值 26.53 24.58 1.08 5.09 5.21 最大值 49.51 47.86 1.03 30.69 1.61 平均值 36.04 35.00 1.03 23.34 1.54 中期
(1981—2000年)TDS/(mg·L−1) 最小值 625 711 0.88 462 1.35 最大值 1231 1353 0.91 738 1.67 平均值 913 933 0.98 626 1.46 年均增幅/(mg·L−1) 最小值 2.50 3.87 0.65 2.64 0.95 最大值 18.33 19.97 0.92 7.82 2.34 平均值 8.88 9.81 0.91 5.40 1.64 末期
(2001—2017年)TDS/(mg·L−1) 最小值 828 804 1.03 700 1.18 最大值 1379 1729 0.80 897 1.54 平均值 1064 1087 0.98 804 1.32 年均增幅/(mg·L−1) 最小值 4.65 1.51 3.08 3.11 1.50 最大值 24.32 26.87 0.91 27.14 0.90 平均值 10.79 10.97 0.98 12.91 0.84 注:初期、中期和末期地下水TDS年均增幅的初值分别为1973年、1980年和2000年研究区相应监测点地下水TDS监测值。 表 3 漏斗核心区地下水TDS与主要化学组分相关性
Table 3. Correlation between TDS and main chemical components in the funnel core area
主要化学组分 与TDS相关系数(R2) 初期 中期 末期 Na+ 0.20 0.37 0.16 Ca2+ 0.63 0.72 0.68 Mg2+ 0.56 0.55 0.38 Cl− 0.22 0.37 0.37 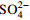
0.16 0.23 0.04 
0.20 0.18 0.17 表 4 不同时期地下水TDS增幅中主要化学组分增幅贡献比率
Table 4. Variation characteristics of the increment contribution ratio of main chemical components in groundwater salinity increment in different periods
漏斗形成阶段 水化指标 TDS Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ 
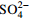
Cl− 化学组分含量比值 r1 r2 r3 r4 初期(1972—1980年) 增幅/(mg·L−1) 324 17 45 16 94 70 80 2.21 0.28 0.26 0.30 占TDS增幅比率/% / 5.14 14.10 5.13 29.17 21.63 24.84 中期(1981—2000年) 增幅/(mg·L−1) 175 11 24 8 49 41 42 1.89 0.33 0.28 0.35 占TDS增幅比率/% / 6.27 13.86 4.46 27.89 23.60 23.93 末期(2001—2017年) 增幅/(mg·L−1) 151 15 20 6 40 37 33 1.45 0.42 0.44 0.43 占TDS增幅比率/% / 9.98 13.07 4.17 26.68 24.14 21.96 注:r1为(Ca2++Mg2+)和 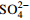 当量浓度比值,r2为Na+和Ca2+当量浓度比值,r3为
当量浓度比值,r2为Na+和Ca2+当量浓度比值,r3为
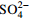 和
和
 当量浓度比值,r4为Na+和
当量浓度比值,r4为Na+和
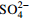 当量浓度比值。
当量浓度比值。
-
[1] 李凤林, 杨先铎, 杨天申, 等. 石家庄城市供水水文地质勘测报告[R]. 石家庄: 河北省地质局水文地质观测总站, 1965.
LI Fenglin, YANG Xianduo, YANG Tianshen, et al. Hydrogeological survey report of Shijiazhuang City water Supply[R]. Shijiazhuang: Hydrogeological Observation Station of Hebei Geology Bureau, 1965. (in Chinese)
[2] 张光辉, 费宇红, 张行南, 等. 滹沱河流域平原区地下水流场异常变化与原因[J]. 水利学报,2008,39(6):747 − 752. [ZHANG Guanghui, FEI Yuhong, ZHANG Xingnan, et al. Abnormal variation of groundwater flow field in plain area of Hutuo River basin and analysis on its cause[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2008,39(6):747 − 752. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2008.06.017
[3] 王金哲, 张光辉, 母海东, 等. 人类活动对浅层地下水干扰程度定量评价及验证[J]. 水利学报,2011,42(12):1445 − 1451. [WANG Jinzhe, ZHANG Guanghui, MU Haidong, et al. Quantitative valuation and validation of the influence degree of human activities on shallow groundwater[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2011,42(12):1445 − 1451. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 冯慧敏, 张光辉, 王电龙, 等. 近50年来石家庄地区地下水流场演变驱动力分析[J]. 水利学报,2014,45(2):180 − 186. [FENG Huimin, ZHANG Guanghui, WANG Dianlong, et al. Analysis on driving force for groundwater flow field evolution in Shijiazhuang Area in recent 50 years[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2014,45(2):180 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 冯慧敏. 石家庄平原区地下水流场演变特征与尺度效应[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2015.
FENG Huimin. Groundwater flow field evolution characteristic and size effect of Shijiazhuang plain[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张光辉, 田言亮, 王电龙, 等. 冀中山前农业区地下水位强降弱升特征与机制[J]. 水科学进展,2015,26(2):227 − 232. [ZHANG Guanghui, TIAN Yanliang, WANG Dianlong, et al. Sharp decline and sluggish rise of shallow groundwater level in the Central Hebei piedmont agricultural region[J]. Advances in Water Science,2015,26(2):227 − 232. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张千千, 王慧玮, 王龙, 等. 滹沱河冲洪积扇地区地下水硬度升高的机理研究[J]. 环境科学与技术,2018,41(增刊2):62 − 68. [ZHANG Qianqian, WANG Huiwei, WANG Long, et al. Increasing mechanism of groundwater total hardness (TH) in the hutuo river alluvial-pluvial fan[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,41(Sup2):62 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张小文, 何江涛, 刘丹丹, 等. 滹沱河冲洪积扇浅层地下水水质外界胁迫作用分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(5):48 − 56. [ZHANG Xiaowen, HE Jiangtao, LIU Dandan, et al. An analysis of the stress effects and methods of the shallow groundwater quality in the Hutuo River alluvial fan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(5):48 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王磊, 何江涛, 张振国, 等. 基于信息筛选和拉依达准则识别地下水主要组分水化学异常的方法研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2018,38(3):919 − 929. [WANG Lei, HE Jiangtao, ZHANG Zhenguo, et al. Research on the method to identify the outliers of the main components of groundwater based on the information screening coupled with PauTa criterion[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2018,38(3):919 − 929. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 单晓杰, 何江涛, 张小文, 等. 基于人为活动影响识别的区域地下水水质演化预测: 以石家庄地区为例[J]. 现代地质,2020,34(1):189 − 198. [SHAN Xiaojie, HE Jiangtao, ZHANG Xiaowen, et al. Prediction of regional groundwater quality evolution affected by human activities: A case study of Shijiazhuang area[J]. Geoscience,2020,34(1):189 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李亚松, 张兆吉, 费宇红, 等. 河北省滹沱河冲积平原地下水质量及污染特征研究[J]. 地球学报,2014,35(2):169 − 176. [LI Yasong, ZHANG Zhaoji, FEI Yuhong, et al. Groundwater quality and contamination characteristics in the hutuo river plain area, Hebei Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2014,35(2):169 − 176. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.02.07
[12] 程中双. 强烈开采含水层的水化学和同位素响应及其水文地质指示: 以石家庄山前平原为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2015.
CHENG Zhongshuang. Chemical and isotopic response to intensive groundwater exploitation and its implications: A case study in the piedmont plain, Shijiazhuang[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 田夏. 滹沱河超采区地下水水化学演变特征与模拟[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.
TIAN Xia. Study on the chemical characteristics and simulation of groundwater in overdrafted zone of the Hutuo River Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] YAN M J, WANG Q, TIAN Y L, et al. The dynamics and origin of groundwater salinity in the northeast Hufu Plain[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(16):1 − 15.
[15] RINA K, SINGH C K, DATTA P S, et al. Erratum to: Geochemical modelling, ionic ratio and GIS based mapping of groundwater salinity and assessment of governing processes in Northern Gujarat, India[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2013,70(5):2421 − 2422. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2821-1
[16] 费宇红, 陈树娥, 刘克岩. 滹沱河断流区水环境劣变特征与地下调蓄潜力[J]. 水利学报,2001(11):41 − 44. [FEI Yuhong, CHEN Shue, LIU Keyan. characteristics of inferior variation of water environment in Hutuohe River dried-up area[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2001(11):41 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2001.11.007
[17] 李婉珠. 石家庄市地下水环境演化规律研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄经济学院, 2009.
LI Wanzhu. Research of environmental evolution of groundwater of Shijiazhuang City[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang University of Economics, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张学礼. 滹沱河流域水环境变迁与区域社会发展研究(1949-2009)[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2018.
ZHANG Xueli. Research on water environmental transition and regional social development in Hutuo River basin(1949-2009)[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王晓玮, 邵景力, 王卓然, 等. 西北地区地下水水量-水位双控指标确定研究: 以民勤盆地为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):17 − 24. [WANG Xiaowei, SHAO Jingli, WANG Zhuoran, et al. A study of the determination of indicators of dual control of groundwater abstraction amount and water table in northwest China: a case study of the Minqin Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):17 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 田夏, 李亚松, 费宇红, 等. 滹沱河超采区地下水硫酸盐来源识别及迁移转化[J]. 科学技术与工程,2020,20(7):2583 − 2589. [TIAN Xia, LI Yasong, FEI Yuhong, et al. Sulfate source identification, migration and transformation in the groundwater over-exploited area of the hutuo river basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(7):2583 − 2589. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.07.008
[21] 张小文, 何江涛, 彭聪, 等. 地下水主要组分水化学异常识别方法对比: 以柳江盆地为例[J]. 环境科学,2017,38(8):3225 − 3234. [ZHANG Xiaowen, HE Jiangtao, PENG Cong, et al. Comparison of identification methods of main component hydrochemical anomalies in groundwater: a case study of Liujiang basin[J]. Environmental Science,2017,38(8):3225 − 3234. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王水献, 王云智, 董新光. 焉耆盆地浅层地下水埋深与TDS时空变异及水化学的演化特征[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2007,26(5):90 − 93. [WANG Shuixian, WANG Yunzhi, DONG Xinguang. The spatio-temporal variation of shallow groundwater TDS, depth and it's evolvement characteristic of water chemistry in Yanqi basin[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2007,26(5):90 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 赵江涛, 周金龙, 高业新, 等. 新疆焉耆盆地平原区地下水溶解性总固体时空演化[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(5):120 − 125. [ZHAO Jiangtao, ZHOU Jinlong, GAO Yexin, et al. Spatial-temporal evolution of total dissolved solids of groundwater in plain area of Yanqi Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2016,32(5):120 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.05.017
[24] 王雨山, 李戍, 李海学, 等. 海原盆地地下水咸化特征和控制因素[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):10 − 17. [WANG Yushan, LI Shu, LI Haixue, et al. Groundwater salinization characteristics and controlling factors in the Haiyuan Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):10 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 章旭, 郝红兵, 刘康林, 等. 西藏加查象牙泉水文地球化学特征及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):1 − 9. [ZHANG Xu, HAO Hongbing, LIU Kanglin, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation of the Ivory spring in Jiacha County of Xizang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 张千千, 王慧玮, 翟天伦, 等. 滹沱河冲洪积扇地下水硝酸盐的污染特征及污染源解析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(6):110 − 117. [ZHANG Qianqian, WANG Huiwei, ZHAI Tianlun, et al. Characteristics and source apportionment of groundwater nitrate contamination in the Hutuo River alluvial-pluvial fan regions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(6):110 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] YI Q, STEWART M. Prediction of groundwater quality trends resulting from anthropogenic changes in southeast Florida[J]. Ground Water,2018,56(1):46 − 61. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12544
[28] 张光辉, 刘中培, 连英立, 等. 河北平原地下水质变及农药化肥施用量变化影响[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2009,7(2):50 − 54. [ZHANG Guanghui, LIU Zhongpei, LIAN Yingli, et al. Variation of groundwater quality and influence of pesticide and fertilizer on Hebei plain[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2009,7(2):50 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 张英, 刘春燕, 王金翠, 等. 快速城镇化进程中典型冲洪积扇地下水化学演变特征及影响因素解析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2019,17(5):172 − 179. [ZHANG Ying, LIU Chunyan, WANG Jincui, et al. Analysis of characteristics and influencing factors of groundwater chemical evolution of typical alluvial fans of rapid urbanization[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2019,17(5):172 − 179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载:


