A study of the dynamic extraction method for granular flow thickness based on digital image processing
-
摘要:
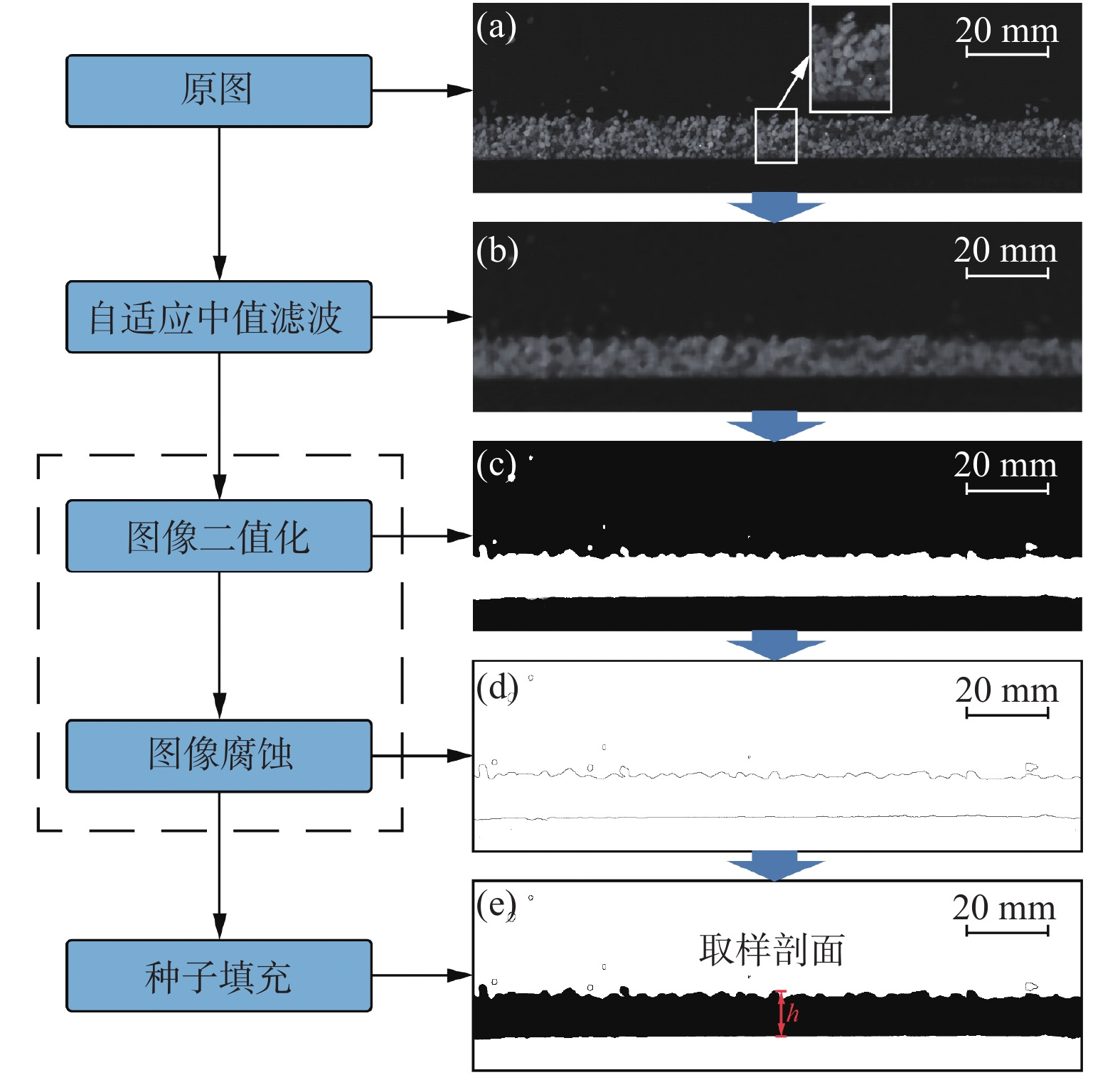
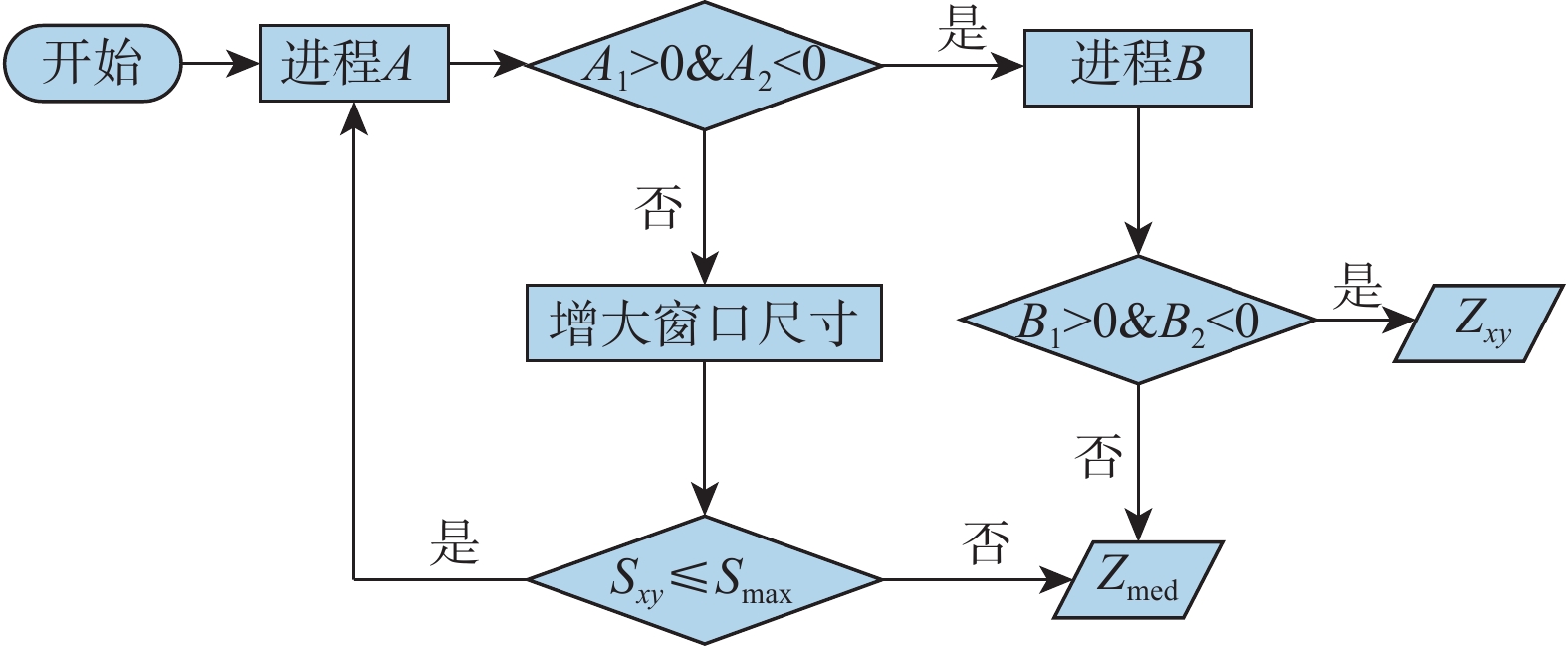
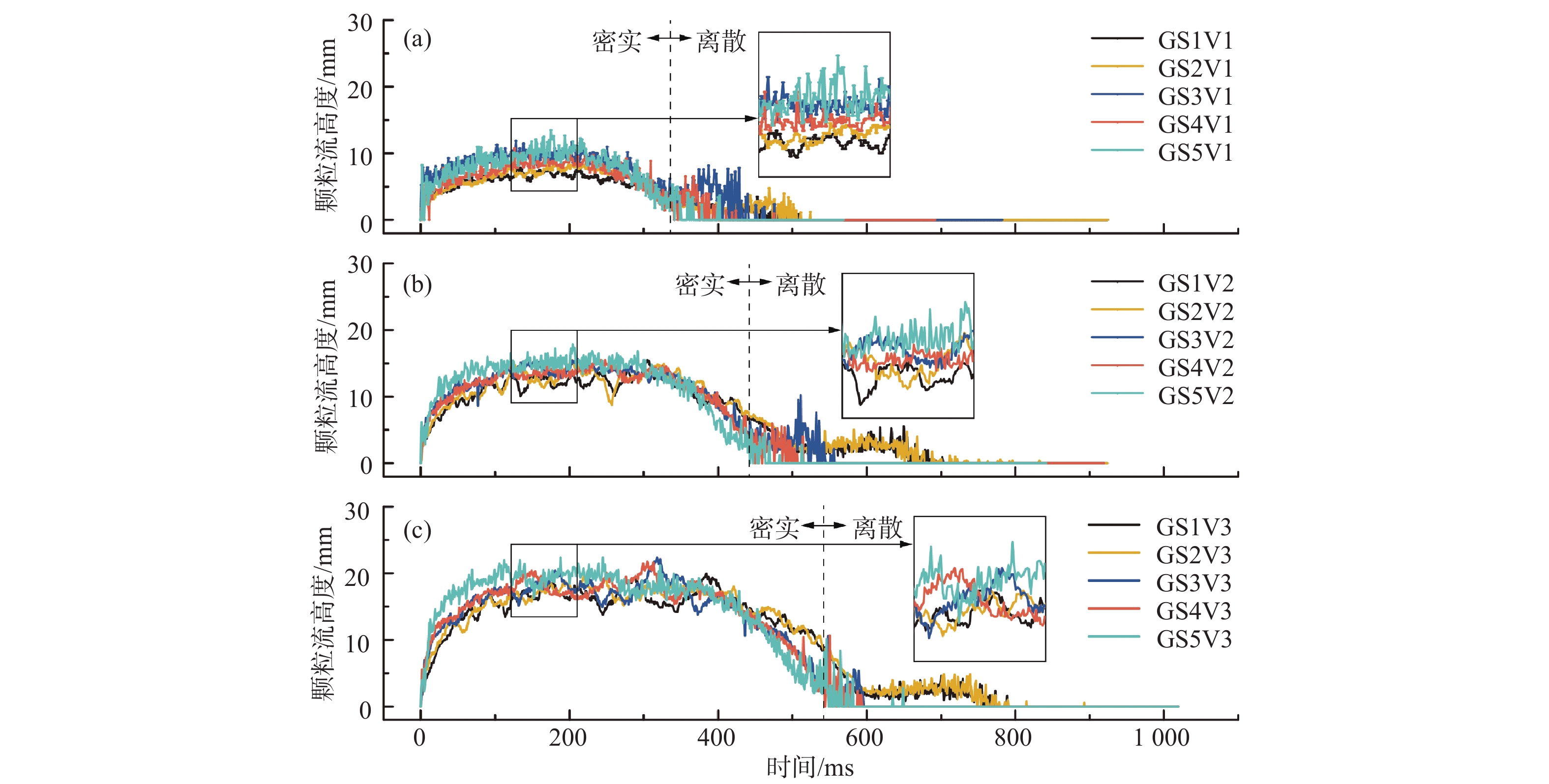
颗粒流厚度及其演化趋势是碎屑流物理模型试验中重点关注的要素。目前试验中颗粒流厚度的监测主要有传感器监测、机械原件测量、人工测读等方法。随着计算机跨学科的应用及计算机数字图像处理技术的成熟,越来越多的数字图像处理技术被应用于工程地质领域。以颗粒流斜槽试验为依托,基于自适应中值滤波、图像二值化、图像腐蚀及种子填充等数字图像处理方法,对高速相机所采集的颗粒流图像序列进行处理分析并编制了相关程序,实现了连续提取颗粒流运动过程中的厚度值。分析结果表明:基于数字图像处理方法提取的颗粒流厚度在颗粒流主体区段与实测厚度值相吻合,在颗粒流尾部由于颗粒离散会存在一定的偏差,主要是由于部分三维空间中的颗粒在二维图像中呈现出重叠的形式,造成颗粒连续的假象。总体而言,通过该方法获取的颗粒流厚度值在一定条件下具有较高的精度,相比于其他方法具有效率高、获取参数多、采样频率高、扰动低等优势,可作为颗粒流试验中流态参数动态获取的常规方法之一。
Abstract:The granular flow thickness and its evolution trend are key factors in analyses of the physical model experiments of avalanches. At present, the measurements of granular flow thickness mainly include sensor monitoring, mechanical measurement and manual measurement. With the development of computer technology, digital image processing methods have been applied in more and more subjects including engineering geology. In this paper, a series of granular chute flow experiments are conducted for the extraction of granular flow thicknesses. Based on the digital image processing methods including adaptive median filter, image binarization, image erosion and seed filling, the granular flow image sequence recorded by the high-speed camera is processed and analysed with related codes compiled, thereby achieving continuous extraction of flow thickness during the granular flow propagation. The results show that the granular flow thicknesses extracted with the digital image processing methods are consistent with the measured true thicknesses in the main bodies of the granular flows. Some deviations appear in the tail of granular flow accompanied by significant particle dispersions. The deviations are mainly attributed to the fact that some particles in the three-dimensional space show overlapping phenomenon in the two-dimensional image, which results in the illusion of granular continuity. In general, the granular flow thicknesses obtained with the digital image processing methods is of a high accuracy in the densely packed granular flows. Compared with other methods, this method is of higher efficiency, higher sampling rate and lower disturbance on granular flows. In addition, additional parameters, such as velocities and displacement, can be obtained simultaneously. Therefore, this method can be used as one of the conventional methods to obtain kinematic parameters in granular flow experiments.
-

-
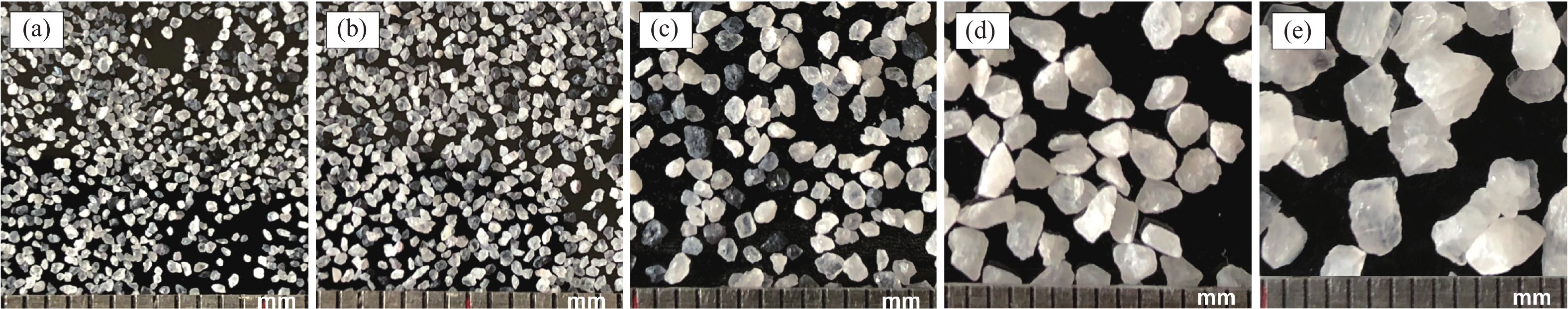
表 1 试验工况设置及颗粒物理参数
Table 1. Test condition setting and physical properties of the granular material
编号 粒径/
mm平均粒径/
mm基底摩擦/
(°)内摩擦角
/(°)颗粒密度
/(g·cm−3)容积率
GS1 [0.10,0.25) 0.175 22.90 36.39 2.66 0.62 GS2 [0.25,0.50) 0.375 22.55 36.71 0.62 GS3 [0.5,1.0) 0.75 22.20 39.44 0.62 GS4 [1,2) 1.50 22.03 39.32 0.61 GS5 [2,5) 3.50 21.93 40.27 0.60 -
[1] HUNGR O, LEROUEIL S, PICARELLI L. The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update[J]. Landslides,2014,11(2):167 − 194. doi: 10.1007/s10346-013-0436-y
[2] HUTCHINSON J N. General report: morphological and geotechnical parameters of landslides in relation to geology and hydrogeology[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Landslides. Lausanne: 1988: 3−35.
[3] 程谦恭, 张倬元, 黄润秋. 高速远程崩滑动力学的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 山地学报,2007,25(1):72 − 84. [CHENG Qiangong, ZHANG Zhuoyuan, HUANG Ruiqiu. Study on dynamics of rock avalanches: state of the art report[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2007,25(1):72 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.01.007
[4] LI H J, XU Q, HE Y S, et al. Prediction of landslide displacement with an ensemble-based extreme learning machine and copula models[J]. Landslides,2018,15(10):2047 − 2059. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1020-2
[5] 郑光, 许强, 巨袁臻, 等. 2017年8月28日贵州纳雍县张家湾镇普洒村崩塌特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(1):223 − 240. [ZHENG Guang, XU Qiang, JU Yuanzhen, et al. The Pusacun rockavalanche on August 28, 2017 in Zhangjiawan Nayongxian, Guizhou: characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(1):223 − 240. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 彭双麒, 许强, 郑光, 等. 碎屑流堆积物粒度分布与运动特性的关系—以贵州纳雍普洒村崩塌为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(4):129 − 136. [PENG Shuangqi, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Relationship between particle size distribution and movement characteristics of rock avalanche deposits: a case study of the Pusa village rock avalanche in Nayong of Guizhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(4):129 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] FORTERRE Y, POULIQUEN O. Long-surface-wave instability in dense granular flows[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2003,486:21 − 50. doi: 10.1017/S0022112003004555
[8] ZHOU G G D, LI S, SONG D R, et al. Depositional mechanisms and morphology of debris flow: physical modelling[J]. Landslides,2019,16(2):315 − 332. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1095-9
[9] SAVAGE S B, LUN C K K. Particle size segregation in inclined chute flow of dry cohesionless granular solids[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,1988,189:311 − 335. doi: 10.1017/S002211208800103X
[10] ROGNON P G, CHEVOIR F, BELLOT H, et al. Rheology of dense snow flows: Inferences from steady state chute-flow experiments[J]. Journal of Rheology,2008,52(3):729 − 748. doi: 10.1122/1.2897609
[11] BRYANT S K, TAKE W A, BOWMAN E T. Observations of grain-scale interactions and simulation of dry granular flows in a large-scale flume[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2015,52(5):638 − 655. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2013-0425
[12] ANCEY C. Dry granular flows down an inclined channel: Experimental investigations on the frictional-collisional regime[J]. Physical Review E,2001,65:011304. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.65.011304
[13] RUSSELL A S, JOHNSON C G, EDWARDS A N, et al. Retrogressive failure of a static granular layer on an inclined plane[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2019,869:313 − 340. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2019.215
[14] SAINGIER G, DEBOEUF S, LAGRÉE P Y. On the front shape of an inertial granular flow down a rough incline[J]. Physics of Fluids,2016,28(5):053302. doi: 10.1063/1.4948401
[15] TAKAGI D, MCELWAINE J N, HUPPERT H E. Shallow granular flows[J]. Physical Review E,2011,83(3):031306. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.83.031306
[16] SADJADPOUR M, CAMPBELL C S. Granular chute flow regimes: mass flowrates, flowrate limits and clogging[J]. Advanced Powder Technology,1999,10(2):175 − 185. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8831(08)60448-3
[17] AUGENSTEIN D A, HOGG R. An experimental study of the flow of dry powders over inclined surfaces[J]. Powder Technology,1978,19(2):205 − 215. doi: 10.1016/0032-5910(78)80029-1
[18] 万保峰, 袁水华, 苏建平. 基于纹理分析的滑坡遥感图像识别[J]. 地矿测绘,2009,25(2):11 − 14. [WAN Baofeng, YUAN Shuihua, SU Jianping. Remote sensing image recognition of landslide based on texture analysis[J]. Surveying and Mapping of Geology Rsearch and Mineral Resources,2009,25(2):11 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9394.2009.02.004
[19] FAN X M, XU Q, SCARINGI G. Brief communication: Post-seismic landslides, the tough lesson of a catastrophe[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2018,18(1):397 − 403. doi: 10.5194/nhess-18-397-2018
[20] 涂新斌, 王思敬. 图像分析的颗粒形状参数描述[J]. 岩土工程学报,2004,26(5):659 − 662. [TU Xinbin, WANG Sijing. Particle shape descriptor in digital image analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2004,26(5):659 − 662. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2004.05.018
[21] 苗得雨, 白晓红. 基于Matlab的土体SEM图像处理方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(6):141 − 146. [MIAO Deyu, BAI Xiaohong. Microstructure of soil using SEM images based on Matlab[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(6):141 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 吴凯, 倪万魁, 刘海松, 等. 压实黄土强度特性与微观结构变化关系研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(5):62 − 69. [WU Kai, NI Wankui, LIU Haisong, et al. Research on the relationships between the strength properties of compacted loess and microstructural changes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(5):62 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张嘎, 张建民, 梁东方. 土与结构接触面试验中的土颗粒细观运动测量[J]. 岩土工程学报,2005,27(8):903 − 907. [ZHANG Ga, ZHANG Jianmin, LIANG Dongfang. Measurement of soil particle movement in soil-structure interface test[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2005,27(8):903 − 907. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.08.010
[24] 彭双麒, 许强, 郑光, 等. 白格滑坡-碎屑流堆积体颗粒识别与分析[J]. 水利水电技术,2020,51(2):144 − 154. [PENG Shuangqi, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Recognition and analysis of deposit body grain of Baige landslide-debris flow[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2020,51(2):144 − 154. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] WHITE D J, TAKE W A, BOLTON M D. Soil deformation measurement using particle image velocimetry (PIV) and photogrammetry[J]. Géotechnique,2003,53(7):619 − 631.
[26] STANIER S A, BLABER J, TAKE W A, et al. Improved image-based deformation measurement for geotechnical applications[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2016,53(5):727 − 739. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2015-0253
[27] STANIER S A, WHITE D J. Improved image-based deformation measurement in the centrifuge environment[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal,2013,36(6):20130044. doi: 10.1520/GTJ20130044
[28] 王烜, 张永泽, 李嘉. 数字图像处理技术在固—液两相流试验中的应用[J]. 水动力学研究与进展,1999,14(2):210 − 218. [WANG Xuan, ZHANG Yongze, LI Jia. Application of digital image processing technique in solid/fluid two-phase flow experiment[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics,1999,14(2):210 − 218. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] GONZALEZ R, WOODS R. 数字图像处理[M]. 3版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2011: 208-406.
GONZALEZ R, WOODS R. Digital image processing[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronice Industry, 2011: 208-406. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: