Microcosmic pore characteristics evolution of the cement improved frozen soil after thawing compression
-
摘要:
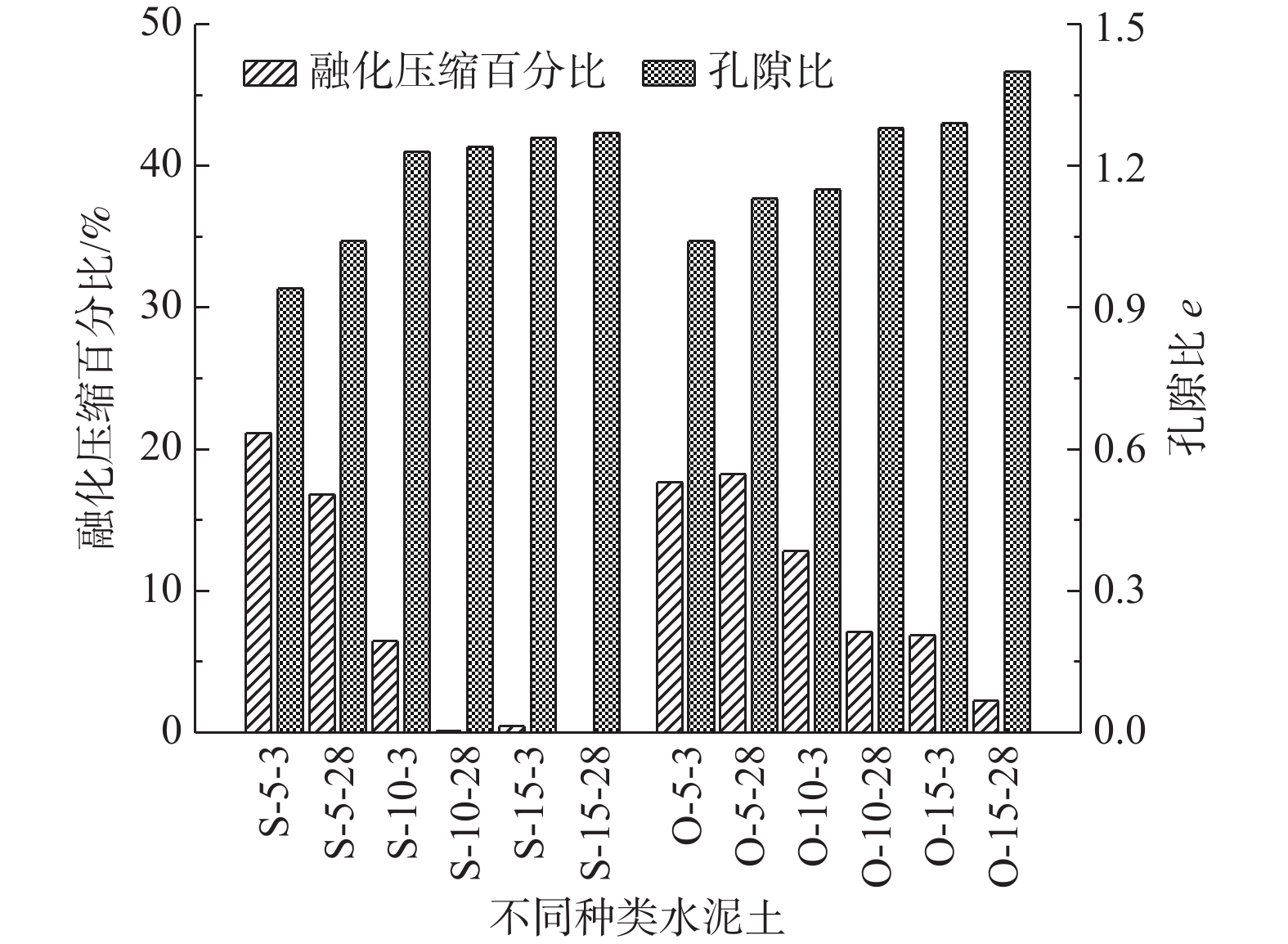
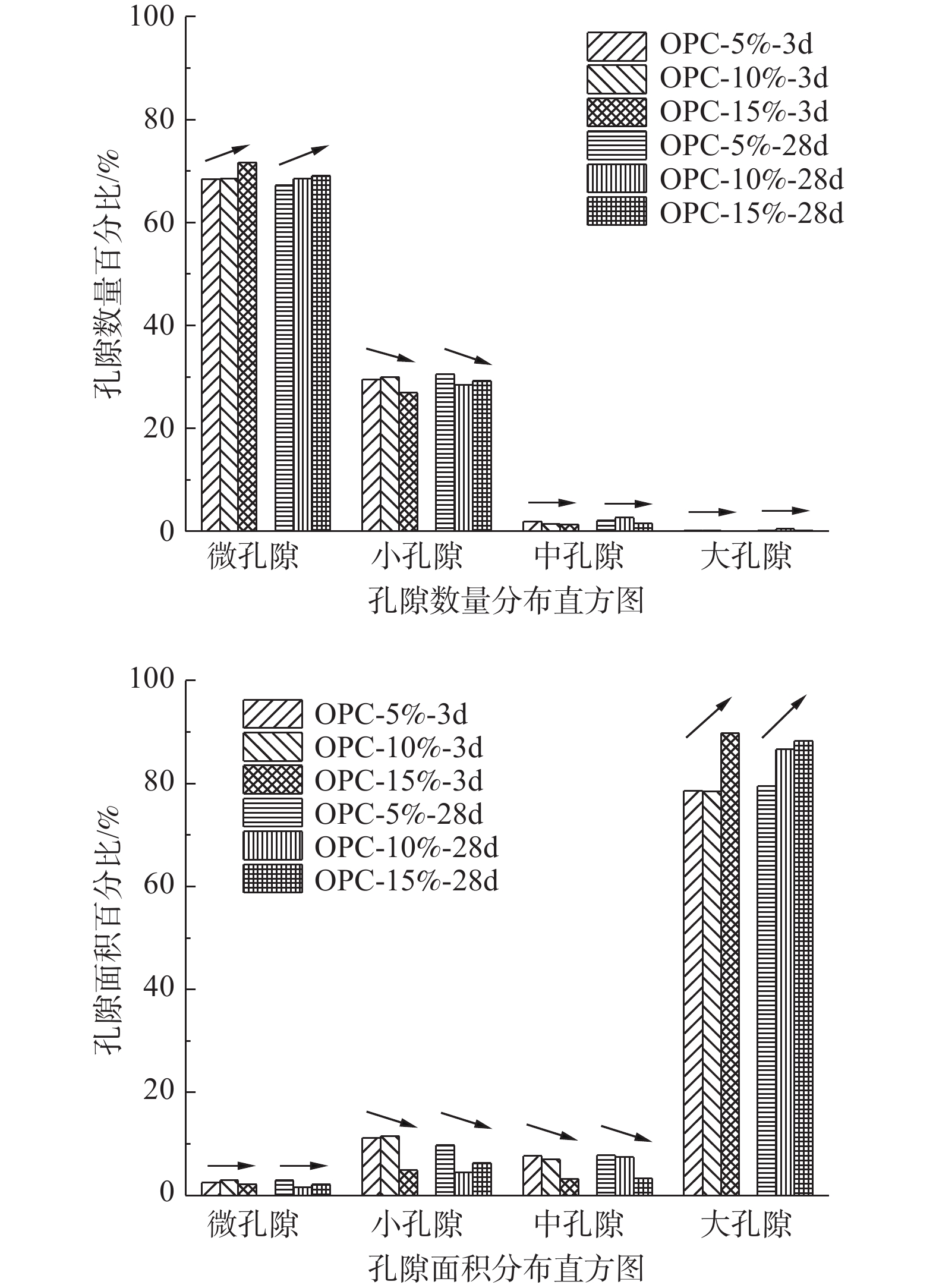
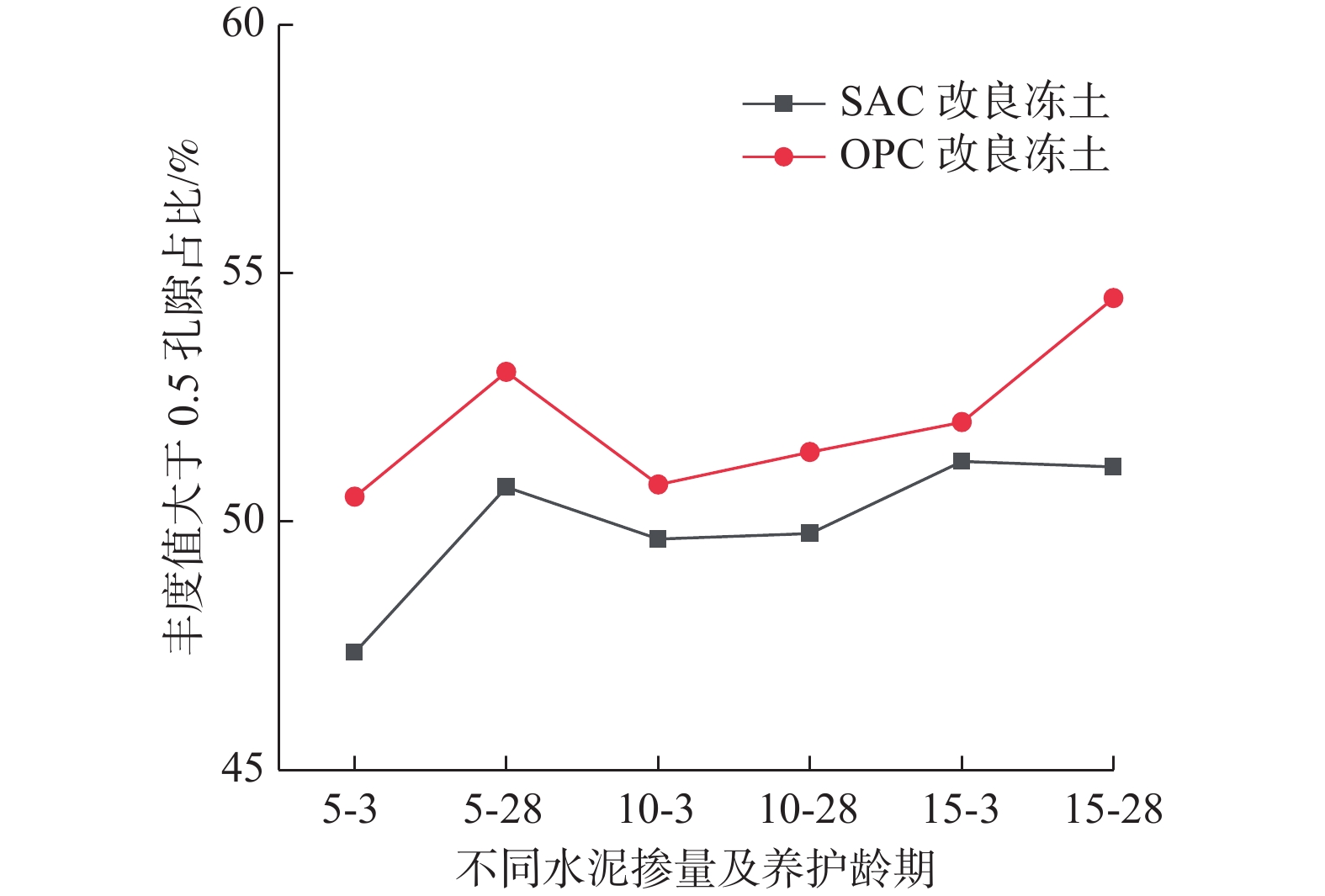
水泥改良冻土在融化压缩下的微观孔隙演变特征研究,对了解水泥改良冻土的过程具有重要意义。将水泥改良后的冻土进行融化压缩实验,通过冷冻干燥法对试验后的土样进行电镜样品制取并获取其微观特征图像。对试验土样进行比重测试,得到土样真实的三维孔隙比。最后以真实孔隙比作参考,确定图像分割所选取的灰度值并提取其孔隙特征。结合融化压缩试验结果,对水泥改良冻土的孔隙数量、面积、定向角及丰度值随改良土压缩量的变化关系进行了分析。研究结果表明:经过水泥改良后的冻土,大孔隙结构强度增大明显;随着水泥掺量及养护龄期的增加,孔隙比与孔隙面积变大,压缩量变小;随着土体压缩量的增大,孔隙的定向角分布逐渐由均匀状向锯齿状发展;土样压缩过程中,丰度值大于0.5的孔隙发生压缩明显,孔隙逐渐趋于细长状,并且随着压缩量的增大,孔隙丰度值的分布越来越趋于正态分布。孔隙微观结构演变研究为阐释水泥改良冻土宏观力学特性增强的机制提供了科学依据。
Abstract:The research on microcosmic characteristics evolution of the cement improved frozen soil under thawing compression is of great significance to understand the process of the improvement. In this study, Thawing compression test is conducted with the cement treated frozen soil. The specimens of SEM are prepared with the method of freezing- drying and the microscopic characteristic images are obtained. The real three-dimensional pore ratio is obtained by the specific gravity test. The gray value is selected for image segmentation as the reference of the real pore ratio and the microscopic pore characteristic is extracted. Based on the results of the compression test, the pore characteristics, such as the diameter, quantity, area, directional angle and abundance, are quantitatively analyzed. The results show that the strength of macropore structures is enhanced when the frozen soil is improved by cement, causing an increasing pore ratio and pore area, and a decreasing compression. With the development of the compression, the orientation angle distribution of the pores transfers from the originally uniform style to the serrated style. The pores tend to be elongated with the compaction of the pores with the abundance value greater than 0.5 while the whole pore abundances tend gradually to be normal distribution. The research on microstructure evolution provides a scientific basis for interpreting the mechanism of the enhancement on the macroscopic mechanical properties of the cement improved frozen soil.
-

-
表 1 不同水泥土的比重结果
Table 1. Different soil-cement specific gravity results
掺量/% SAC OPC 3 d 28 d 3 d 28 d 5 2.935 3.016 2.988 3.013 10 2.948 3.027 3.017 3.025 15 2.954 3.034 3.034 3.033 -
[1] 张虎, 张建明, 苏凯, 等. 高温-高含冰量冻土原位旁压蠕变试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2013,43(6):1950 − 1957. [ZHANG Hu, ZHANG Jianming, SU Kai, et al. In-situ pressuremeter creep test on high-temperature and high ice-rich permafrost[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2013,43(6):1950 − 1957. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张虎, 张建明, 苏凯, 等. 冻土原位旁压蠕变试验粘弹性模型分析[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程,2013,35(6):22 − 27. [ZHANG Hu, ZHANG Jianming, SU Kai, et al. Viscoelastic model analysis of in situ pressuremter creep test in permafrost[J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering,2013,35(6):22 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] YAO X L, QI J L, ZHANG J M, et al. A one-dimensional creep model for frozen soils taking temperature as an independent variable[J]. Soils and Foundations,2018,58(3):627 − 640.
[4] ZHANG Z L, ZHANG J M, ZHANG H. Effects and mechanisms of ionic soil stabilizers on warm frozen soil[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering,2018,43(10):5657 − 5666.
[5] ZHANG Z L, ZHANG H, ZHANG J M, et al. Effectiveness of ionic polymer soil stabilizers on warm frozen soil[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2019,23(7):2867 − 2876.
[6] CHAI M T, ZHANG J M. Improvement of compressibility and thaw-settlement properties of warm and ice-rich frozen soil with cement and additives[J]. Materials,2019,12(7):1068.
[7] CHAI M T, ZHANG H, ZHANG J M, et al. Effect of cement additives on unconfined compressive strength of warm and ice-rich frozen soil[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,149:861 − 868.
[8] 孙杲辰, 张建明, 党迎生, 等. 高温冻土固化前后结构性变化对融化压缩特性影响[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2020,52(2):17 − 25. [SUN Gaochen, ZHANG Jianming, DANG Yingsheng, et al. Structural properties changes before and after solidification and their effects on melting and compression characteristics of high warm and frozen soil[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2020,52(2):17 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11918/201810121
[9] SUN G C, ZHANG J M, DANG Y S, et al. Microstructure and strength features of warm and ice-rich frozen soil treated with high-performance cements[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2019,16(6):1470 − 1482.
[10] 廖一蕾, 张子新, 肖时辉, 等. 水泥加固黏性土微观特征试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(增刊 2):4318 − 4327. [LIAO Yilei, ZHANG Zixin, XIAO Shihui, et al. Microstructure research on cement stabilized clays[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(Sup 2):4318 − 4327. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 黄春霞, 黄敏, 蔡伟, 等. 不同黏粒含量粉土的微观结构研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2020,42(4):758 − 764. [HUANG Chunxia, HUANG Min, CAI Wei, et al. Microstructure of silt with different clay contents[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2020,42(4):758 − 764. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 周晖, 房营光, 禹长江. 广州软土固结过程微观结构的显微观测与分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(增刊 2):3830 − 3837. [ZHOU Hui, FANG Yingguang, YU Changjiang. Micro-structure observation and analysis of Guangzhou soft soil during consolidation process[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(Sup 2):3830 − 3837. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 张先伟, 孔令伟, 郭爱国, 等. 基于SEM和MIP试验结构性黏土压缩过程中微观孔隙的变化规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(2):406 − 412. [ZHANG Xianwei, KONG Lingwei, GUO Aiguo, et al. Evolution of microscopic pore of structured clay in compression process based on SEM and MIP test[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(2):406 − 412. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.02.021
[14] DELAGE P. Microstructure features in the behaviour of engineered barriers for nuclear waste disposal[C]// Experimental Unsaturated Soil Mechanics. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2007, 112: 11-32.
[15] 谢定义, 齐吉琳. 土结构性及其定量化参数研究的新途径[J]. 岩土工程学报,1999,21(6):3 − 5. [XIE Dingyi, QI Jilin. Soil structure characteristics and new approach in research on its quantitative parameter[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1999,21(6):3 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 陈正汉, 方祥位, 朱元青, 等. 膨胀土和黄土的细观结构及其演化规律研究[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(1):1 − 11. [CHEN Zhenghan, FANG Xiangwei, ZHU Yuanqing, et al. Research on meso-structures and their evolution laws of expansive soil and loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2009,30(1):1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.01.001
[17] 叶为民, 万敏, 陈宝, 等. 干湿循环条件下高压实膨润土的微观结构特征[J]. 岩土工程学报,2011,33(8):1173 − 1177. [YE Weimin, WAN Min, CHEN Bao, et al. Micro-structural behaviors of densely compacted GMZ01 bentonite under drying/wetting cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2011,33(8):1173 − 1177. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张先伟, 孔令伟, 李峻, 等. 黏土触变过程中强度恢复的微观机理[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(8):1407 − 1413. [ZHANG Xianwei, KONG Lingwei, LI Jun, et al. Microscopic mechanism of strength increase of clay during thixotropic process[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,36(8):1407 − 1413. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201408005
[19] 王东伟, 陆武萍, 唐朝生, 等. 砂土微观结构样品制备技术及量化方法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(12):4783 − 4792. [WANG Dongwei, LU Wuping, TANG Chaosheng, et al. Sample preparation technique and microstructure quantification method for sandy soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(12):4783 − 4792. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 施斌, 姜洪涛. 粘性土的微观结构分析技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2001,20(6):864 − 870. [SHI Bin, JIANG Hongtao. Research on the analysis techniques for clayey soil microstructure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2001,20(6):864 − 870. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2001.06.025
[21] 侯超群, 席瑶, 孙志彬, 等. 基于IPP图像处理的膨胀土微观结构定量研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(2):156 − 161. [HOU Chaoqun, XI Yao, SUN Zhibin, et al. A quantitative study of microstructure of expansive soil based on IPP image processing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(2):156 − 161. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 张季如, 祝杰, 黄丽, 等. 固结条件下软黏土微观孔隙结构的演化及其分形描述[J]. 水利学报,2008,39(4):394 − 400. [ZHANG Jiru, ZHU Jie, HUANG Li, et al. Evolution of micro pore structure of soft clay and its fractal features under consolidation[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2008,39(4):394 − 400. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2008.04.002
[23] 房后国, 刘娉慧, 袁志刚. 海积软土固结过程中微观结构变化特征分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2007,34(2):49 − 52. [FANG Houguo, LIU Pinhui, YUAN Zhigang. Analysis on characteristics of microstructure change during marine soft soil consolidation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2007,34(2):49 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2007.02.012
[24] GRIFFITHS F J, JOSHI R C. Change in pore size distribution due to consolidation of clays[J]. Géotechnique,1989,39(1):159 − 167.
[25] 王宝军, 施斌, 蔡奕, 等. 基于GIS的黏性土SEM图像三维可视化与孔隙度计算[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(1):251 − 255. [WANG Baojun, SHI Bin, CAI Yi, et al. 3D visualization and porosity computation of clay soil SEM image by GIS[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2008,29(1):251 − 255. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.01.047
[26] 袁则循, 毛灵涛, 赵丹. 基于数字地形模型土微结构三维孔隙度的计算方法[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2011,30(5):734 − 737. [YUAN Zexun, MAO Lingtao, ZHAO D. Computation method on 3D porosity of soil microstructure based on digital terrain model[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science),2011,30(5):734 − 737. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 赵柯迪. 大连高城山地区粘性土微观结构研究[D]. 大连: 辽宁师范大学, 2019.
ZHAO Kedi. Study on microstructure of cohesive soil in Gaocheng mountain area, Dalian[D]. Dalian: Liaoning Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 中华人民共和国建设部. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T 50123—1999 [S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 1999.
Ministry of Construction of the People's Republic of China. Standard for soil test method: GB/T 50123—1999[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
[29] 袁中夏, 王兰民, 邓津. 电镜图像在黄土结构性研究中应用的几个问题[J]. 西北地震学报,2005,27(2):115 − 121. [YUAN Zhongxia, WANG Lanmin, DENG Jin. Several problems on application of SEM image in the structure properties study of loess[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,2005,27(2):115 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 雷祥义, 王书法. 黄土的孔隙大小与湿陷性[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1987,14(5):15 − 18. [LEI Xiangyi, WANG Shufa. Size of loess pores in relation to collapsibility[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1987,14(5):15 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 胡建伟, 谢永江, 刘子科, 等. 纳米C-S-H/PCE对硅酸盐–硫铝酸盐复合水泥凝结硬化的影响[J/OL]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文): 1−12. [2020-05-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1218.tu.20200517.1459.004.html.
HU Jianwei, XIE Yongjiang, LIU Zike, et al. Effect of nano-C-S-H/PCE on the setting and hardening process of portland-sulphoaluminate composite cement[J/OL]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering: 1−12. [2020-05-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1218.tu.20200517.1459.004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: