Research on hydrogeological parameter inversion of an aquitard based on multi-source data: A case study of a silt layer in the Hohhot Basin
-
摘要:
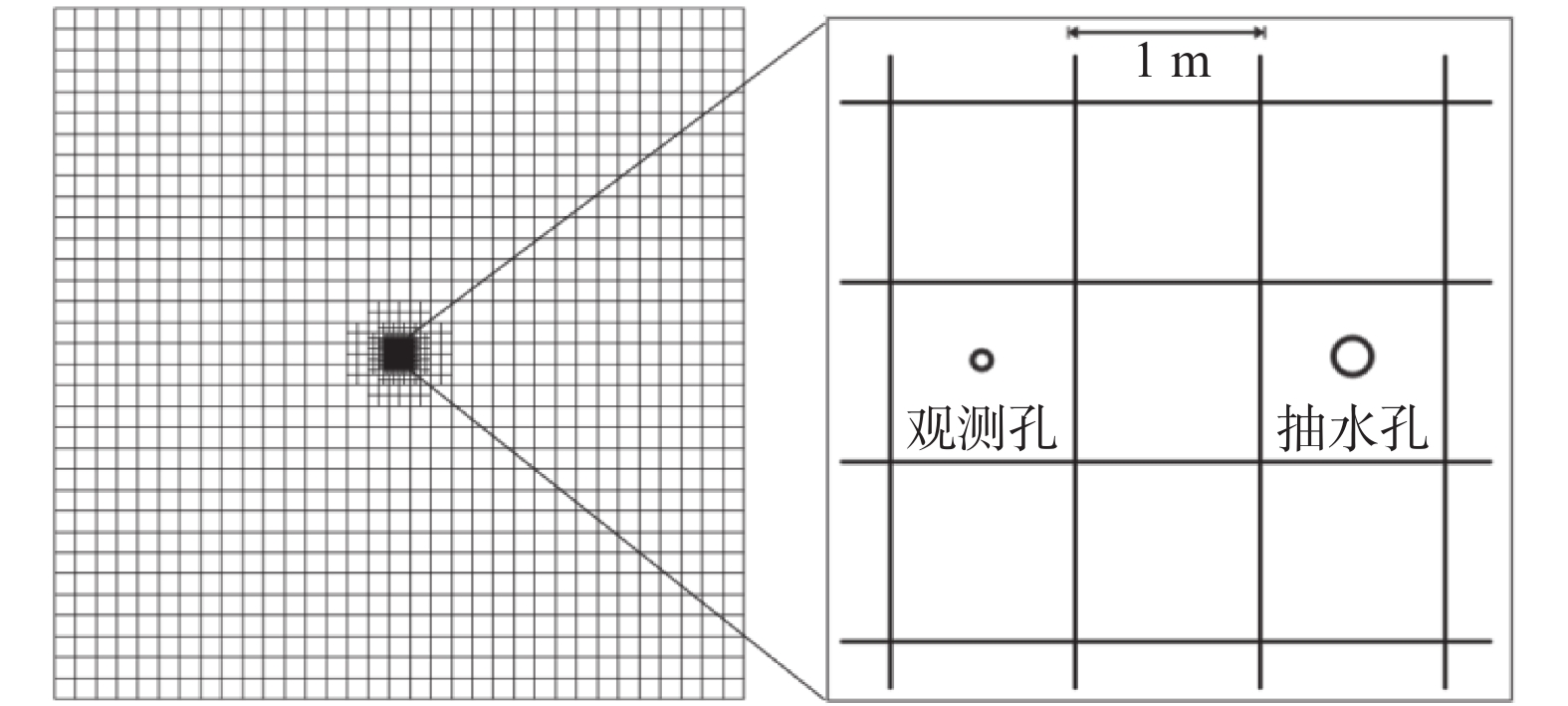
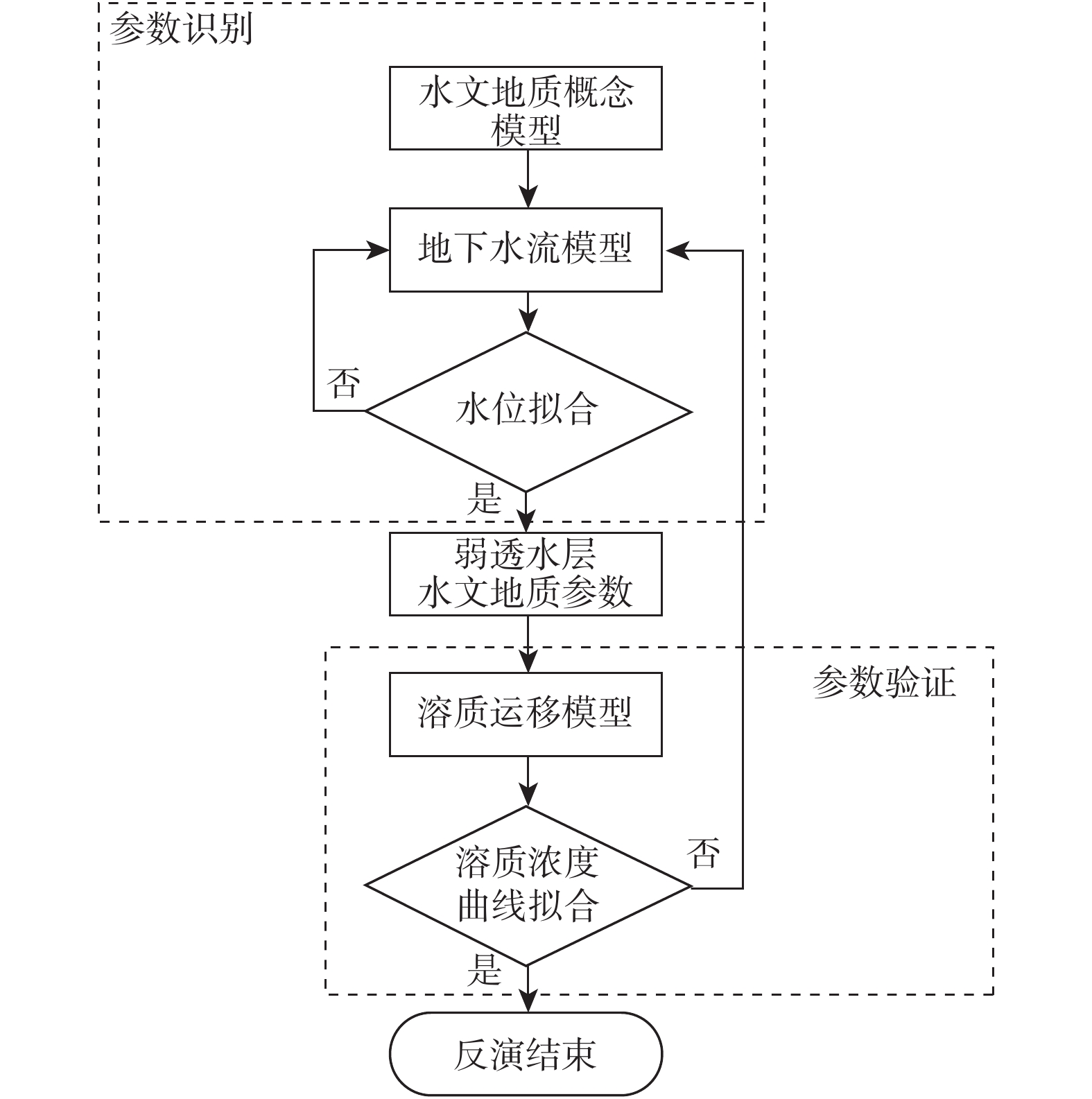
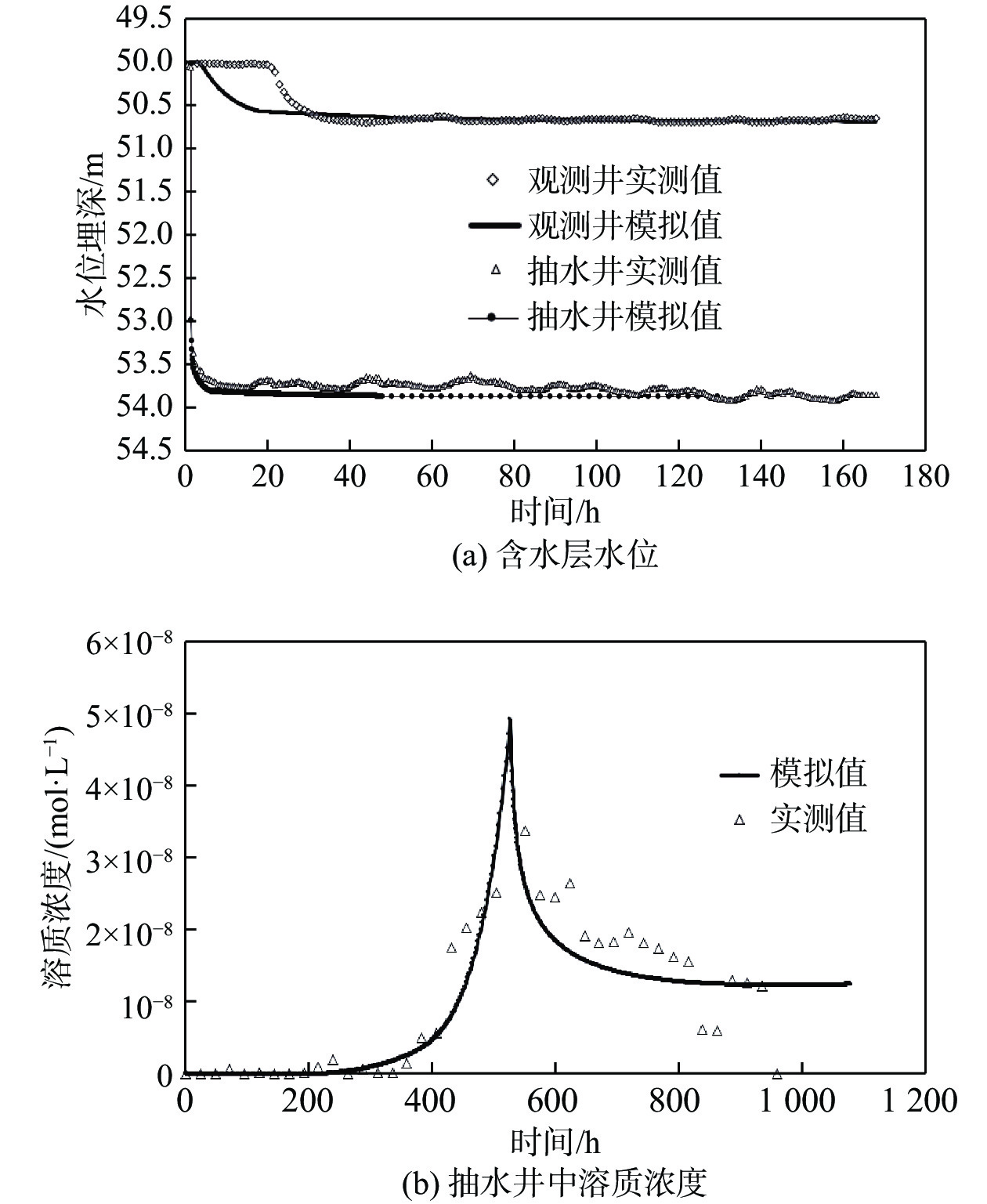
弱透水层是含水层系统的重要组成部分,其水文地质参数的准确获取一直以来都是研究难点,传统室内试验难以克服应力状态及环境变化对土层参数的影响,因此如何在原位状态下评价其水文地质参数有着重要意义。选取呼和浩特盆地某淤泥层为研究对象,基于抽水试验和溶质运移试验获得的多源数据,采用基于控制体积有限差分法的非结构化网格(Unstructured Grid)方法,建立三维地下水流-溶质运移耦合模型,对弱透水层水文地质参数进行反演。结果显示:模型计算的抽水井中水位和溶质浓度变化规律与实际观测数据能够较好拟合,模型识别出的抽水含水层渗透参数(4.8 m/d)与通过解析法计算得出的结果(4.17 m/d)相近,建立的数值模型符合实际水文地质条件;反演得到淤泥质弱透水层垂向渗透系数为1.2×10−4 m/d、储水率为1.0×10−5 m−1。基于多源数据的参数反演方法可为弱透水层参数研究提供借鉴。
-
关键词:
- 数值模拟 /
- 弱透水层 /
- MODFLOW-USG /
- 多源数据 /
- 参数反演
Abstract:An aquitard is an important part of an aquifer system. It is always difficult to determine the hydrogeological parameters of the aquitard. Traditional laboratory tests are difficult to overcome the influence of stress state and environmental change on the aquitard layer parameters. Therefore, evaluation of hydrogeological parameters under in-situ state is of great significance. This article selects a silt layer in the Hohhot Basin, and primarily designs and carries out pumping tests and solute transport tests. The unstructured grid with the controlled volume finite difference method is used to establish a 3D coupling model of groundwater flow and solute transport. Groundwater levels and concentration data are used to estimate the hydrogeological parameters of the aquitard. The results show that the variation in groundwater levels and solute concentrations in the pumping wells calculated by the model can fit well with the actual observation data, and the coefficient of permeability of the pumping aquifer identified by the model (4.8 m/d) is similar to the analytical result (4.17 m/d). The numerical model conforms to the actual hydrogeological conditions. The vertical hydraulic conductivity of the aquitard studied in this paper is 1.2×10−4 m/d, and the specific storage is 1.0×10−5 m−1. The method presented in this paper may provide references for the parameter determination of an aquitard.
-
Key words:
- numerical modeling /
- aquitard /
- MODFLOW-USG /
- multi-source data /
- parameter inversion
-

-
表 1 主要水文地质参数表
Table 1. Main hydrogeological parameters
参数 K/(m·d−1) Kz/(m·d−1) Ss/m−1 I层 III层 II层 I层 II层 III层 参数值 1.92 4.8 1.2×10−4 1.5×10−6 1.0×10−5 2.0×10−6 确定方法 经验值 经验值 反演 经验值 反演 经验值 -
[1] 陈晨, 文章, 梁杏, 等. 江汉平原典型含水层水文地质参数反演[J]. 地球科学,2017,42(5):727 − 733. [CHEN Chen, WEN Zhang, LIANG Xing, et al. Estimation of hydrogeological parameters for representative aquifers in Jianghan Plain[J]. Earth Science,2017,42(5):727 − 733. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 程林, 韩龙喜, 刘晓华, 等. 一维地下水溶质运移模型多参数反演[J]. 水资源保护,2014,30(3):5 − 8. [CHENG Lin, HAN Longxi, LIU Xiaohua, et al. Multi-parameter inversion of one-dimensional groundwater solute transport model[J]. Water Resources Protection,2014,30(3):5 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 杨建民, 郑刚. 用水位恢复数据反演越流承压含水层参数[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(6):1602 − 1606. [YANG Jianmin, ZHENG Gang. Parameter estimation for leaky aquifers using residual drawdowns[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2008,29(6):1602 − 1606. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.06.032
[4] 易立新, 徐鹤. 地下水数值模拟[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009.
YI Lixin, XU He. Numerical simulation of groundwater[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[5] EL OSTA M, HUSSEIN H, TOMAS K. Numerical simulation of groundwater flow and vulnerability in wadi el-natrun depression and vicinities, west Nile delta, Egypt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India,2018,92(2):235 − 247. doi: 10.1007/s12594-018-0986-7
[6] 郝奇琛. 中国内陆盆地地下水流与水盐运移耦合模拟研究 : 以柴达木盆地典型剖面为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
HAO Qichen. Coupled modeling of salt movement and groundwater flow in inland basin: A case study in Qaidam basin, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 肖勇, 邵景力, 顾晓敏, 等. 北京昌平平原区地下水污染特征[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2015,13(2):252 − 256. [XIAO Yong, SHAO Jingli, GU Xiaomin, et al. Characteristics of groundwater pollution in Changping Plain of Beijing[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2015,13(2):252 − 256. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 顾晓敏, 张戈, 郝奇琛, 等. 基于TOUGH2的柴达木盆地诺木洪剖面地下水流模拟[J]. 干旱区地理,2016,39(3):548 − 554. [GU Xiaomin, ZHANG Ge, HAO Qichen, et al. Application of TOUGH2 in groundwater numerical simulation of Qaidam Basin[J]. Arid Land Geography,2016,39(3):548 − 554. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 陈晓恋, 张美雁, 文章, 等. 裂隙含水层水文地质参数反演—以黑龙江七台河市应急水源地为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(5):32 − 37. [CHEN Xiaolian, ZHANG Meiyan, WEN Zhang, et al. Application of numerical simulation to estimate the hydraulic parameters infractured media: A case study in emergency water area of Qitaihe City, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(5):32 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 毛喜云, 张强, 于升才, 等. 基于AquiferTest和ModFlow求解哈尔滨河漫滩地区水文地质参数[J]. 天津建设科技,2017,27(6):56 − 59. [MAO Xiyun, ZHANG Qiang, YU Shengcai, et al. Inversion of hydrogeological parameters in Harbin River floodplain based on Aquifer Test and Modflow[J]. Tianjin Construction Science and Technology,2017,27(6):56 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3197.2017.06.020
[11] 李贵仁. 某铁矿岩溶裂隙含水层水文地质参数反演[J]. 勘察科学技术,2019(1):42 − 46. [LI Guiren. Inversion of hydrogeological parameters of Karst fissure aquifer in an iron mine[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology,2019(1):42 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2019.01.010
[12] SZABÓ N P. A genetic meta-algorithm-assisted inversion approach: hydrogeological study for the determination of volumetric rock properties and matrix and fluid parameters in unsaturated formations[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2018,26(6):1935 − 1946. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1749-7
[13] MOHARIR K, PANDE C, PATIL S. Inverse modelling of aquifer parameters in basaltic rock with the help of pumping test method using MODFLOW software[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2017,8(6):1385 − 1395. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2016.11.017
[14] 李兆峰, 周志芳, 李明远, 等. 弱透水层释水过程中水力参数响应规律[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2017,45(4):340 − 344. [LI Zhaofeng, ZHOU Zhifang, LI Mingyuan, et al. Variation of hydraulic parameters of aquitard during water release[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences),2017,45(4):340 − 344. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] WU Jichun, ZENG Xiankui. Review of the uncertainty analysis of groundwater numerical simulation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(25):3044 − 3052. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5950-8
[16] 张泽鹏, 朱玉晨, 郝奇琛, 等. 呼和浩特盆地地下水流系统变异机制及其资源效应[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):63 − 68. [ZHANG Zepeng, ZHU Yuchen, HAO Qichen, et al. A study on variation mechanism of groundwater flow system in the Hohhot basin and its resources effect analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):63 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张翼龙. 呼和浩特盆地开采胁迫下的地下水系统响应及适应性对策研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2012.
ZHANG Yilong. Aquifer system response and its adaptability countermeasures to exploitation in the Hohhot basin[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 赵瑞科, 曹文庚, 杨会峰, 等. 呼和浩特盆地地下水演化特征研究[J]. 人民黄河,2018,40(5):78 − 82. [ZHAO Ruike, CAO Wengeng, YANG Huifeng, et al. Study on evolution characteristics of groundwater in Hohhot Basin[J]. Yellow River,2018,40(5):78 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2018.05.017
[19] 曹文庚, 张翼龙, 李政红, 等. 呼和浩特市大青山山前倾斜平原地质环境问题形成机理研究[J]. 现代地质,2013,27(2):468 − 474. [CAO Wengeng, ZHANG Yilong, LI Zhenghong, et al. Formation mechanism of geological environment issue in piedmont clinoplain of Daqing mountain, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience,2013,27(2):468 − 474. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.028
[20] 陆丽华, 侯岳岚, 程亚平, 等. 地表水-地下水溶质运移耦合模拟研究: 以某赤泥堆场项目地下水环境影响评价为例[J]. 地下水,2019,41(6):1 − 4. [LU Lihua, HOU Yuelan, CHENG Yaping, et al. Study of solute transport simulation considering the coupling of groundwater and surface water: A case study of an environmental impact assessment of a red mud disposal site on groundwater[J]. Ground Water,2019,41(6):1 − 4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] Panday S, Langevin C D, Niswonger R G, et al. MODFLOW-USG version 1: An unstructured grid version of MODFLOW for simulating groundwater flow and tightly coupled processes using a control volume finite-difference formulation[R]. Washington DC: US Geological Survey, 2013.
[22] 周念清, 杨一流, 江思珉. 非结构网格化方法求解地下水流数值模型[J]. 勘察科学技术,2016(1):14 − 17. [ZHOU Nianqing, YANG Yiliu, JIANG Simin. Solving groundwater numerical model with unstructured grid method[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology,2016(1):14 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2016.01.004
[23] 杜新强, 常翠, 冶雪艳. 地下水流三维数值模拟中弱透水层初始水位的推求方法分析[J]. 黑龙江水专学报,2008,35(4):94 − 97. [DU Xinqiang, CHANG Cui, YE Xueyan. Analysis on the method to the initial groundwater level of aquitard during three dimensional transient numerical simulation of groundwater flow[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Hydraulic Engineering,2008,35(4):94 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-008X.2008.04.026
[24] 王超, 束龙仓, 鲁程鹏. 渗透系数空间变异性对低渗透地层中地下水溶质运移的影响[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2014,42(2):137 − 142. [WANG Chao, SHU Longcang, LU Chengpeng. Impacts of spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity on solute transport in groundwater of low-permeability stratum[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences),2014,42(2):137 − 142. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 王小丹, 凤蔚, 王文科, 等. 基于HYDRUS-1D模型模拟关中盆地氮在包气带中的迁移转化规律[J]. 地质调查与研究,2015,38(4):291 − 298. [WANG Xiaodan, FENG Wei, WANG Wenke, et al. Migrating and transforming rule of nitrogen in unsaturated zone in Guanzhong basin based on HYDRUS-1D model[J]. Geological Survey and Research,2015,38(4):291 − 298. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2015.04.008
[26] 田振东. 基于Visual MODFLOW的卫河河水污染对地下水影响研究[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2016.
TIAN Zhendong. Based on visual MODFLOW research on between the Wei river water pollution to groundwater[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: