Estimation of groundwater evapotranspiration rate in the loess phreaticaquifer by removing the barometric effect
-
摘要:
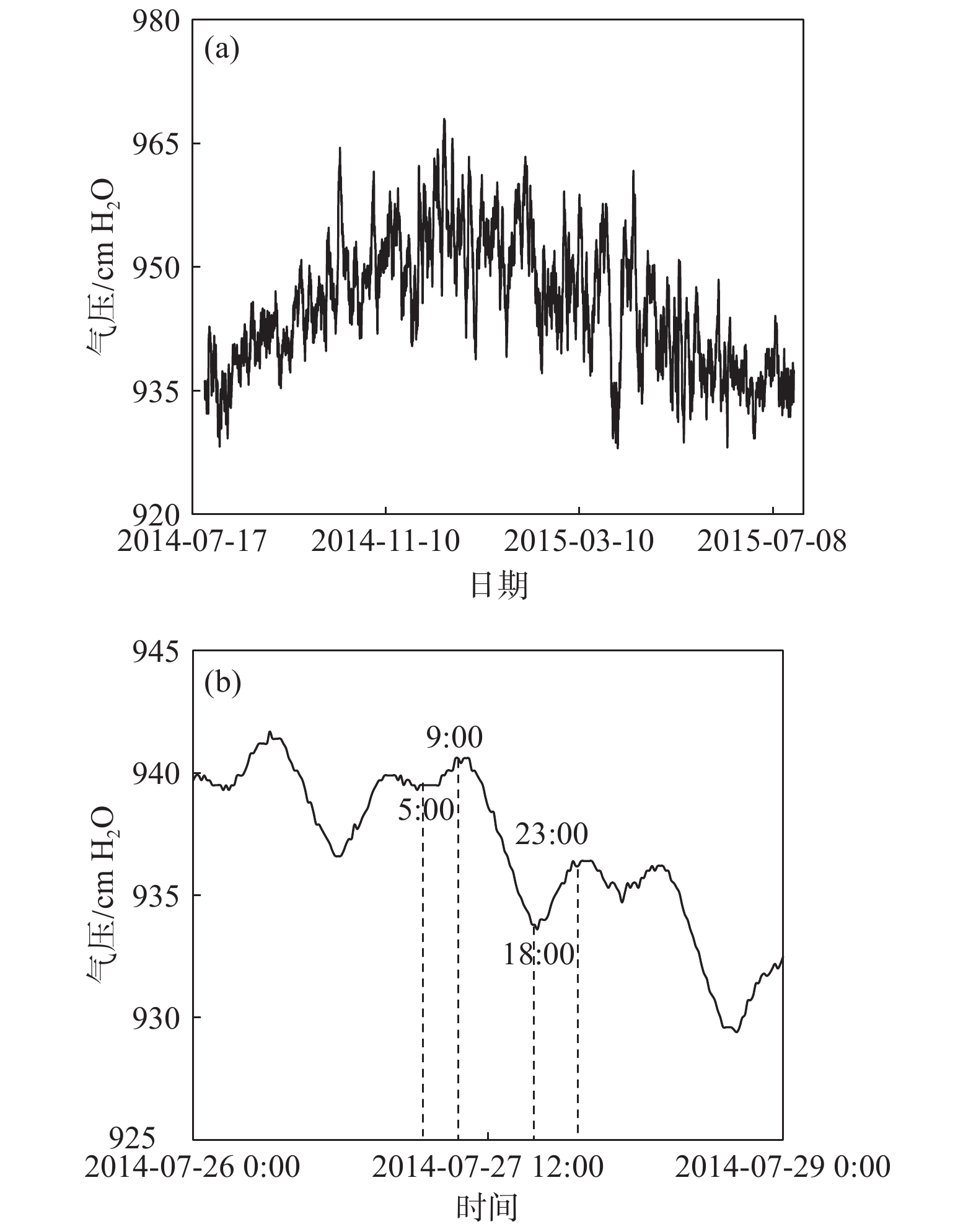
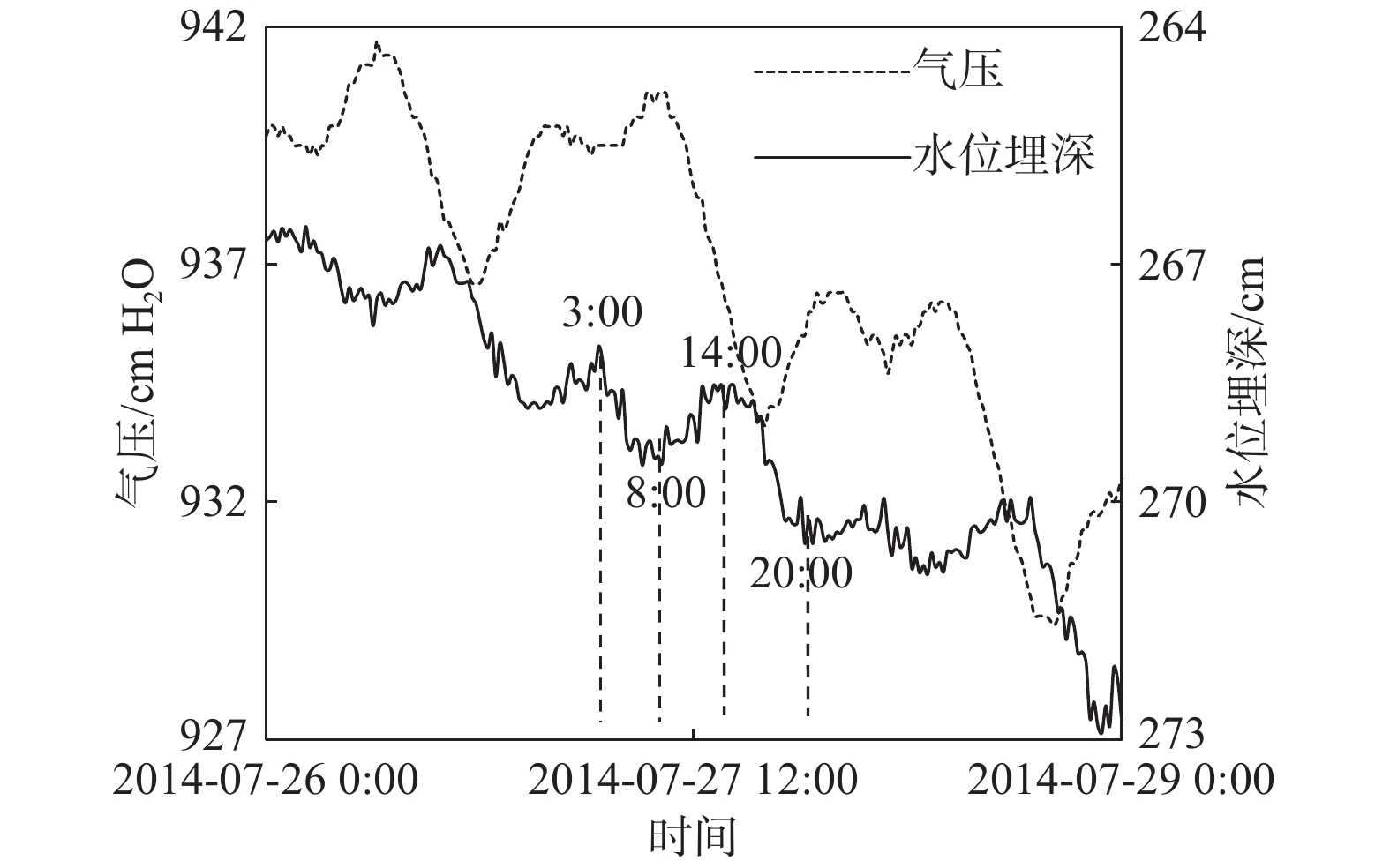
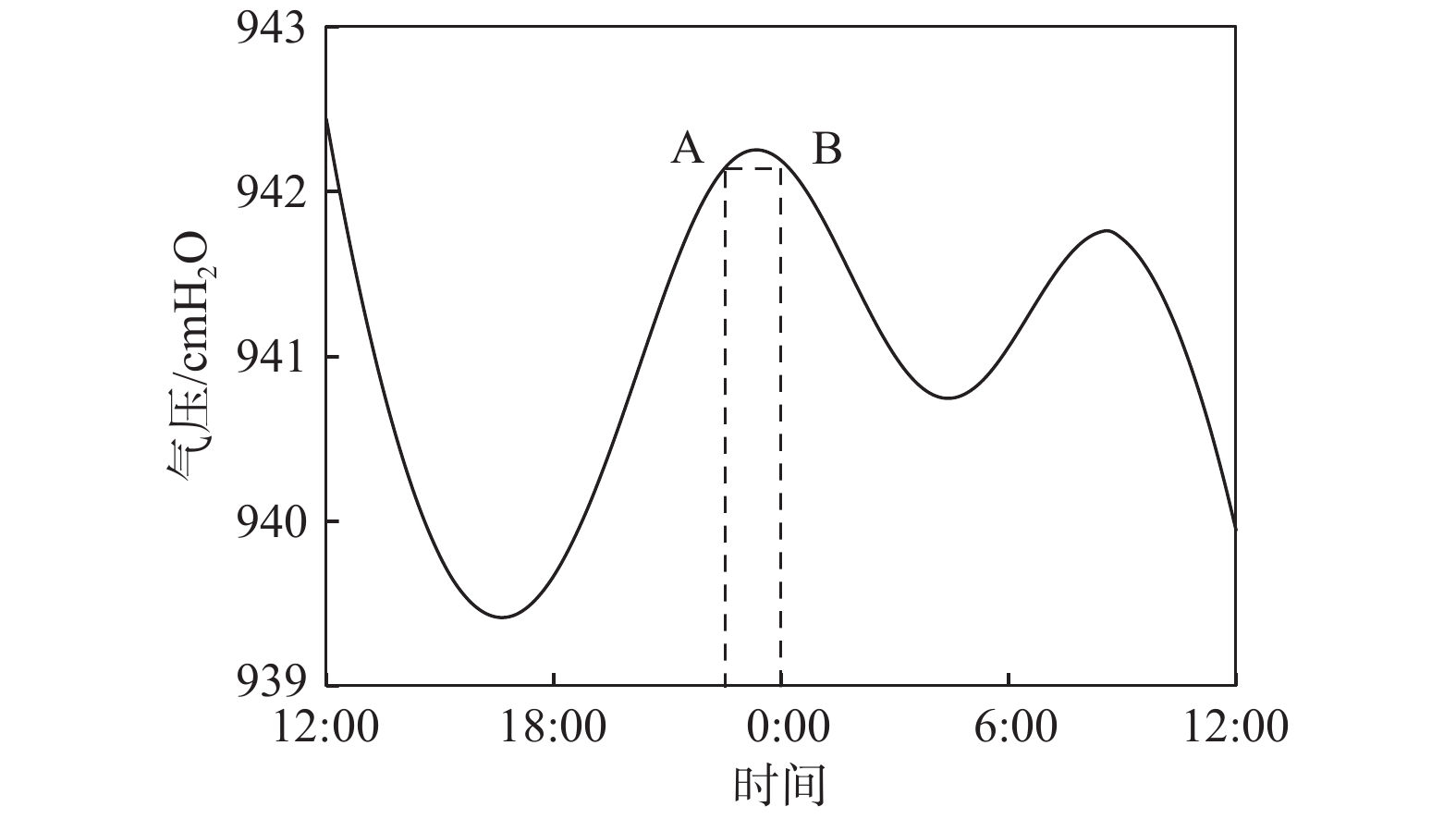
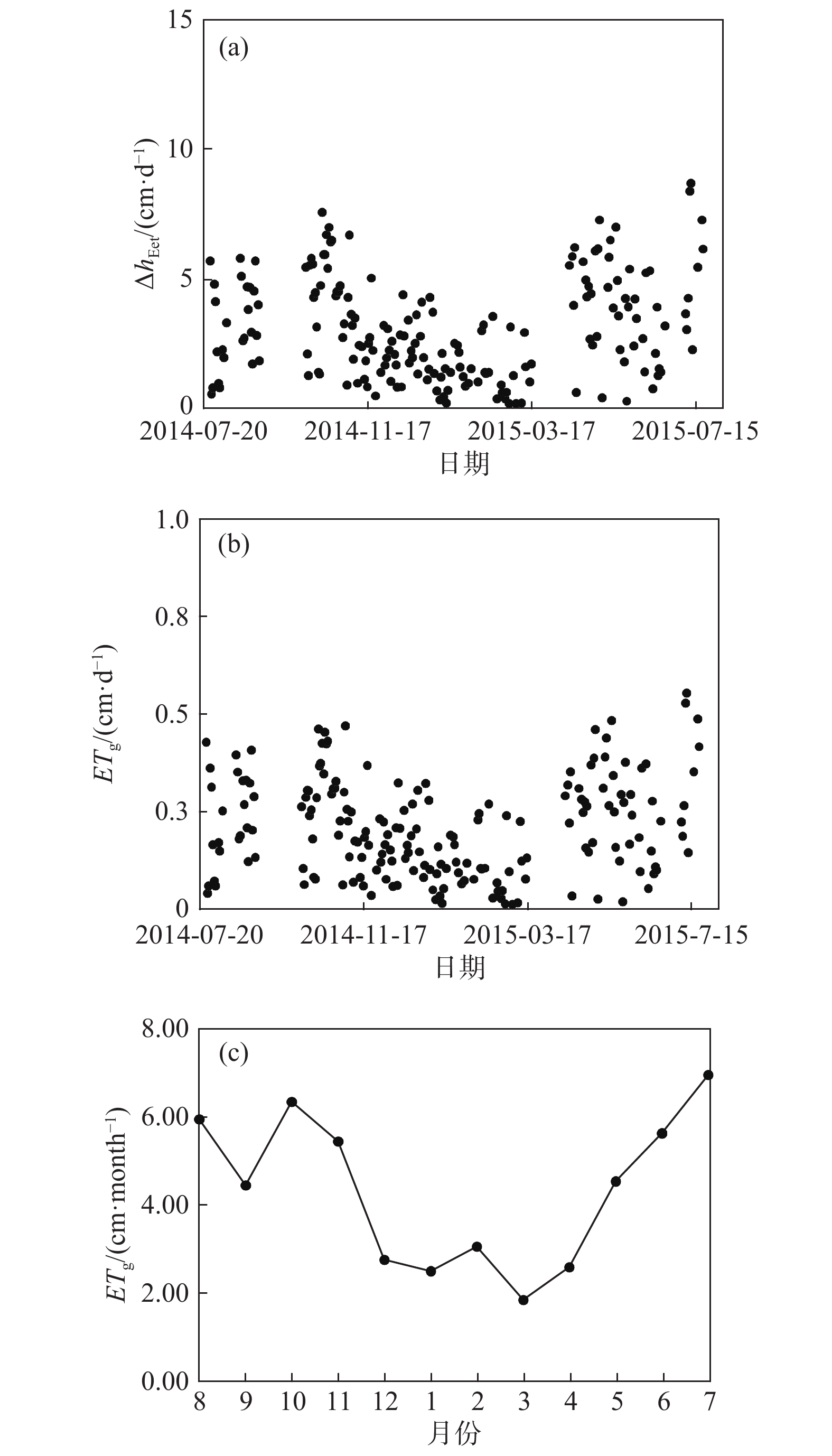
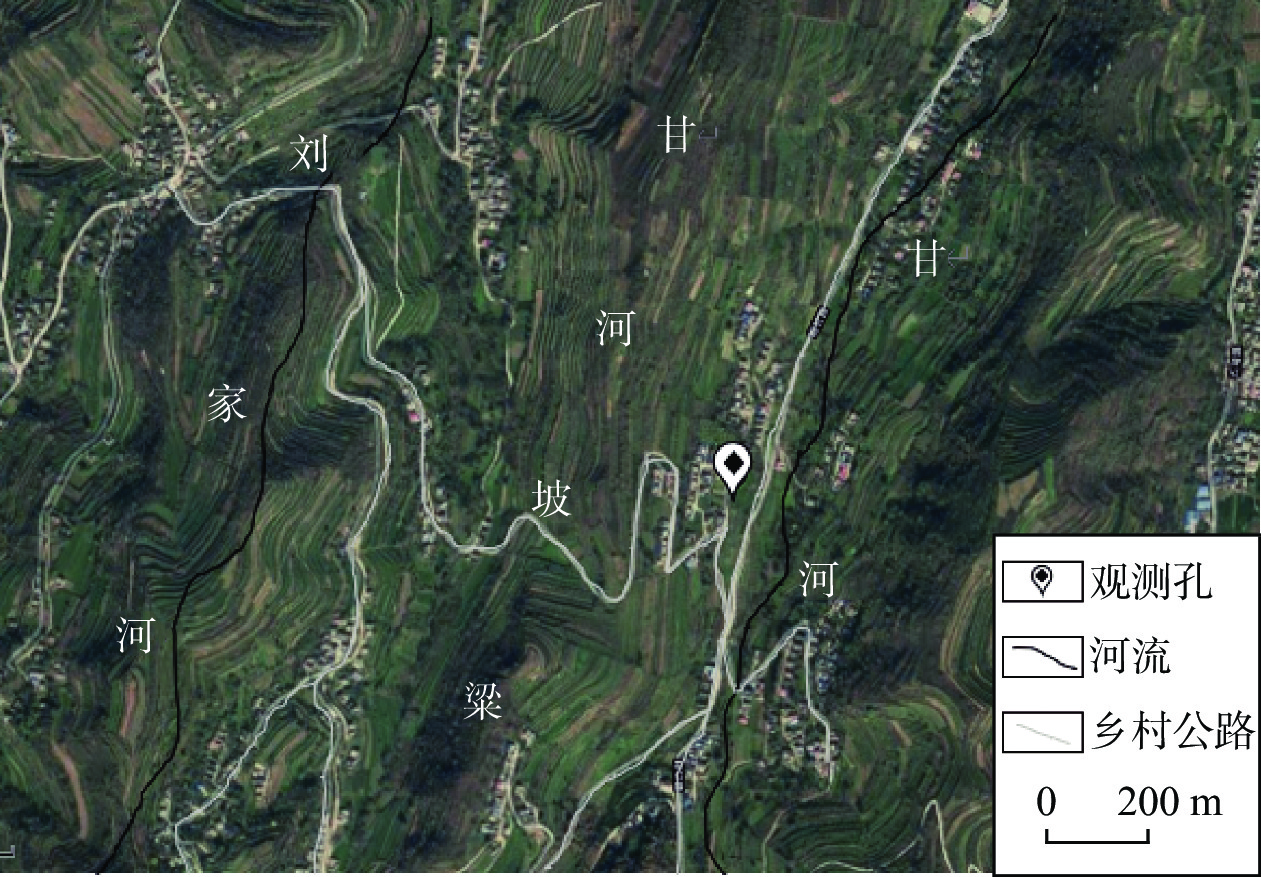
潜水蒸发蒸腾(ETg)是干旱半干旱地区浅埋深地下水最主要的排泄方式,也是地下水系统中重要的均衡项。如果存在气压效应,用于估算地下水蒸发蒸腾强度的传统水位波动法则不适用。以黄土潜水为例,提出了一种基于水位变化和大气压变化规律的水位图方法,用于消除气压效应以获取潜水蒸发蒸腾强度。研究表明,大气压变化通常在午夜前,一般为22:00—24:00,会出现一个峰值,该时间段气压效应可以忽略,而且潜水蒸发蒸腾强度最小,此时潜水位的变化速率相当于净补给速率;在获取潜水净补给强度后,选择第二个时间段,0:00—4:00,此时潜水蒸发蒸腾强度最小,且气压一般处于连续下降阶段,可以用来估算气压效应系数。在此基础上,可利用水位均衡和水位波动法方便地估算潜水蒸发蒸腾强度。该方法数据获取容易,估算结果也较为准确。
Abstract:Groundwater evapotranspiration (ETg) is the most important dischargeway of shallow groundwater in arid and semi-arid areas, and also is a significant component of the water budget in groundwater systems. When groundwater levelsare interfered with barometric effect, the traditional water table fluctuation method for estimation of the ETg rate cannot be directly employed.This paper proposes a hydrographical method for removing the barometric effect on the ETg rateestimation using water-table fluctuations based on the changes ingroundwater levels and barometric pressure.The results illustrate that thechangesin barometric pressure usually reach the peak before midnight, generally between 22:00 and 24:00 when the barometric effect can be ignored, and the evapotranspiration rate is the minimum and therefore thegroundwater level changes rate at this time interval is equivalent to the net recharge rate. Furthermore, the second time period between 0:00 and 4:00 when the ETg rate is negligible and the barometric pressure is generally in a continuous decline, is then selected to estimate the barometric efficiency. On the basis of these analyses, the ETg rate can be readily estimated by the groundwater level balance method and the water table fluctuation method. The data required in theproposed methodare easy to obtain and the estimated ETg ratesare relatively accurate.
-

-
表 1 水均衡法计算结果和实际结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of the calculated values by the water balance method with the actual results
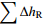 /cm
/cm
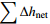 /cm
/cm
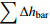 /cm
/cm
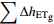 /cm
/cm
254.8 −65.6 −63.3 195.8 计算水位变化量/cm 实测水位变化量/cm 绝对误差/cm 相对误差/% −69.9 −76.3 −6.4 8.4 -
[1] CARRETERO S C, KRUSE E E. Relationship between precipitation and water-table fluctuation in a coastal dune aquifer: northeastern coast of the Buenos Aires Province, Argentina[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2012,20(8):1613 − 1621. doi: 10.1007/s10040-012-0890-y
[2] BUTLER J J JR, KLUITENBERG G J, WHITTEMORE D O, et al. A field investigation of phreatophyte-induced fluctuations in the water table[J]. Water Resources Research,2007,43(2):W02404.
[3] WHITE W N. A method of estimating ground-water supplies based on discharge by plants and evaporation from soil: Results of investigations in Escalante Valley, Utah[R]. Washington DC: US Geological Survey, 1932. Survey, 1932.
[4] GRIBOVSZKI Z, KALICZ P, KUCSARA M, et al. Evapotranspiration calculation on the basis of the riparian zone water balance[J]. Acta Silvatica et Lignaria Hungarica,2008,4:95 − 106.
[5] CHENG D H, DUAN J B, QIAN K, et al. Groundwater evapotranspiration under psammophilous vegetation covers in the Mu Us Sandy Land, Northern China[J]. Journal of Arid Land,2017,9(1):98 − 108. doi: 10.1007/s40333-016-0095-7
[6] CHENG D H, LI Y, CHEN X H, et al. Estimation of groundwater evapotranspiration using diurnal water table fluctuations in the Mu Us Desert, Northern China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2013,490:106 − 113. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.03.027
[7] 贾伍慧, 尹立河, 王晓勇, 等. 利用改进的Loheide方法计算地下水的蒸散发量[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):48 − 51. [JIA Wuhui, YIN Lihe, WANG Xiaoyong, et al. Quantifying groundwater evapotranspiration by the modified loheide method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):48 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] ROJSTACZER S, RILEY F S. Response of the water level in a well to earth tides and atmospheric loading under unconfined conditions[J]. Water Resources Research,1990,26(8):1803 − 1817. doi: 10.1029/WR026i008p01803
[9] 李海龙, 宋金颖, 万力, 等. 承压含水层井孔储存效应对气压波动引起的井孔水位波动的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(4):1 − 6. [LI Hailong, SONG Jinying, WAN Li, et al. The response of well-aquifer systems to barometric loading[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(4):1 − 6. (in Chinese)
[10] 王丽亚, 郭海朋, 李文鹏, 等. 气压对观测井水位的影响及校正方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2012,39(6):29 − 34. [WANG Liya, GUO Haipeng, LI Wenpeng, et al. Impact of atmospheric loading on the water level in a well and methods for calibrating it[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2012,39(6):29 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 赵丹, 王广才. 地下水位气压效应的消除及主要气压影响分波的识别[J]. 中国科学(技术科学),2013,43(1):79 − 86. [ZHAO Dan, WANG Guangcai. Removing barometric pressure effects from groundwater level and identifying main influential constituents[J]. Scientia Sinica Techologica,2013,43(1):79 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/ze2013-43-1-79
[12] 张子广, 盛艳蕊, 张素欣, 等. 井水位对气压扰动的响应[J]. 地震研究,2010,33(2):170 − 175. [ZHANG Ziguang, SHENG Yanrui, ZHANG Suxin, et al. Response of water level on the well to air pressure perturbation[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,2010,33(2):170 − 175. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2010.02.008
[13] TOLL N J, RASMUSSEN T C. Removal of barometric pressure effects and earth tides from observed water levels[J]. Groundwater,2007,45(1):101 − 105. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2006.00254.x
[14] BREDEHOEFT J D. Response of well-aquifer systems to earth tides[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,1967,72(12):3075 − 3087. doi: 10.1029/JZ072i012p03075
[15] QUILTY E G, ROELOFFS E A. Removal of barometric pressure response from water level data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth,1991,96(B6):10209 − 10218. doi: 10.1029/91JB00429
[16] BUTLER JR J J, JIN W, MOHAMMED G A, et al. New insights from well responses to fluctuations in barometric pressure[J]. Groundwater,2011,49(4):525 − 533. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2010.00768.x
[17] 耿杰, 周斌, 张昭栋. 深井水位气压效率和相关系数在中强地震前的变化特征[J]. 西北地震学报,2002,24(3):257 − 261. [GENG Jie, ZHOU Bin, ZHANG Zhaodong. The characteristics of anomalous variations on barometric pressure efficiency and interrelation coefficient of groundwater level in deep wells before moderate and strong earthquakes[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,2002,24(3):257 − 261. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张昭栋, 郑金涵, 张广城, 等. 承压井水位对气压动态过程的响应[J]. 地球物理学报,1989,32(5):539 − 549. [ZHANG Zhaodong, ZHENG Jinhan, ZHANG Guangcheng, et al. Response of water level of pressure well to dynamic process of barometric pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,1989,32(5):539 − 549. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1989.05.006
[19] 张昭栋, 郑金涵, 耿杰, 等. 地下水潮汐现象的物理机制和统一数学方程[J]. 地震地质,2002,24(2):208 − 214. [ZHANG Zhaodong, ZHENG Jinhan, GENG Jie, et al. Physical mechanism and unitary mathematical equation for tidal phenomena of ground water[J]. Seismology and Geology,2002,24(2):208 − 214. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.02.008
[20] 齐丽军. 利用地下水水位波动提取地下水蒸发蒸腾和降雨入渗补给强度[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2017.
QI Lijun. Extraction of groundwater evapotranspiration and rainfall infiltration supplement intensity by groundwater level fluctuation [D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] CHENG D H, WANG Y H, DUAN J B, et al. A new analytical expression for ultimate specific yield and shallow groundwater drainage[J]. Hydrological Processes,2015,29(8):1905 − 1911. doi: 10.1002/hyp.10306
[22] DAI A G, WANG J H. Diurnal and semidiurnal tides in global surface pressure fields[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,1999,56(22):3874 − 3891. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1999)056<3874:DASTIG>2.0.CO;2
[23] SCHILLING K E, KINIRY J R. Estimation of evapotranspiration by reed canary grass using field observations and model simulations[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2007,337(3/4):356 − 363.
[24] BURT T P. Diurnal variations in stream discharge and through flow during a period of low flow[J]. Journal of Hydrology,1979,41(3/4):291 − 301.
-



 下载:
下载: