Experimental simulation of the carbonate dissolution process under different occurrence conditions
-
摘要:
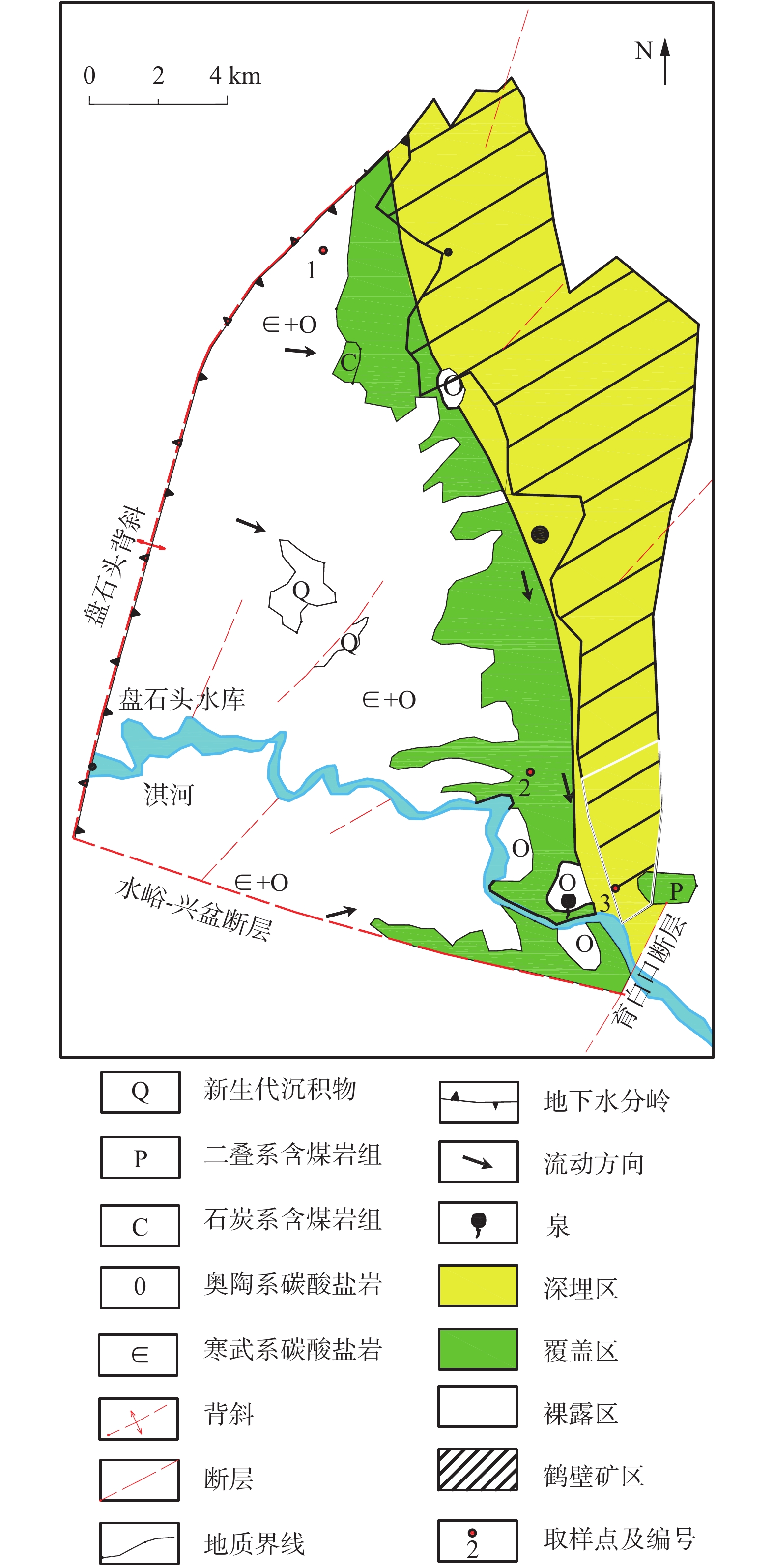
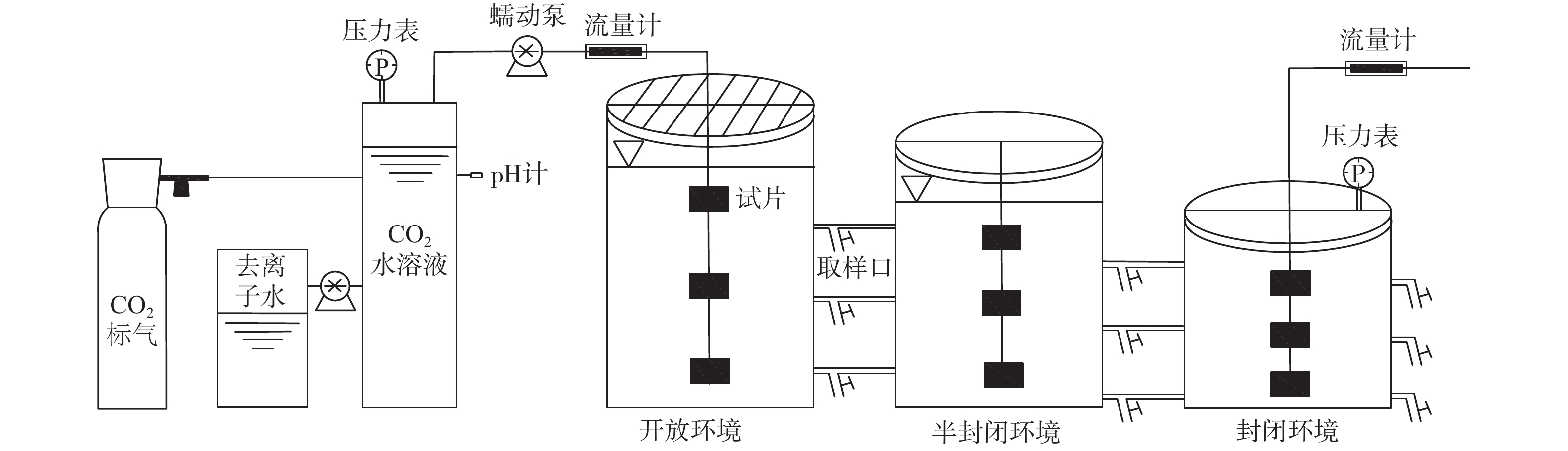
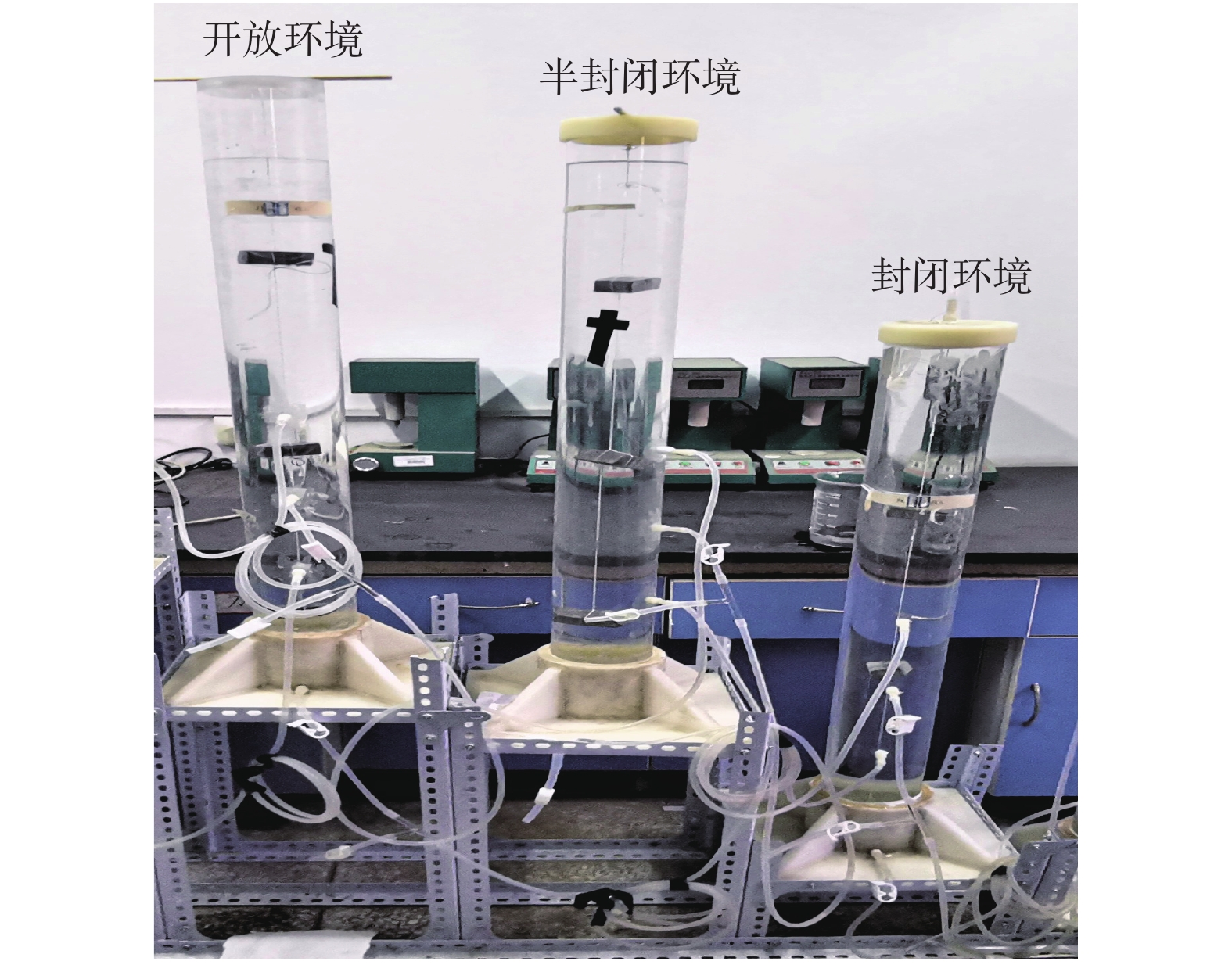
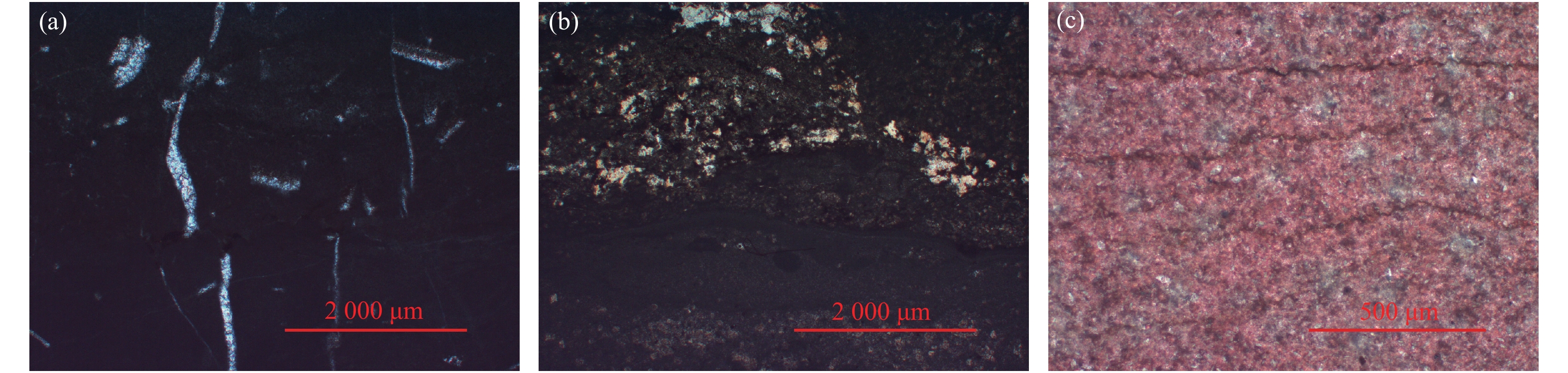
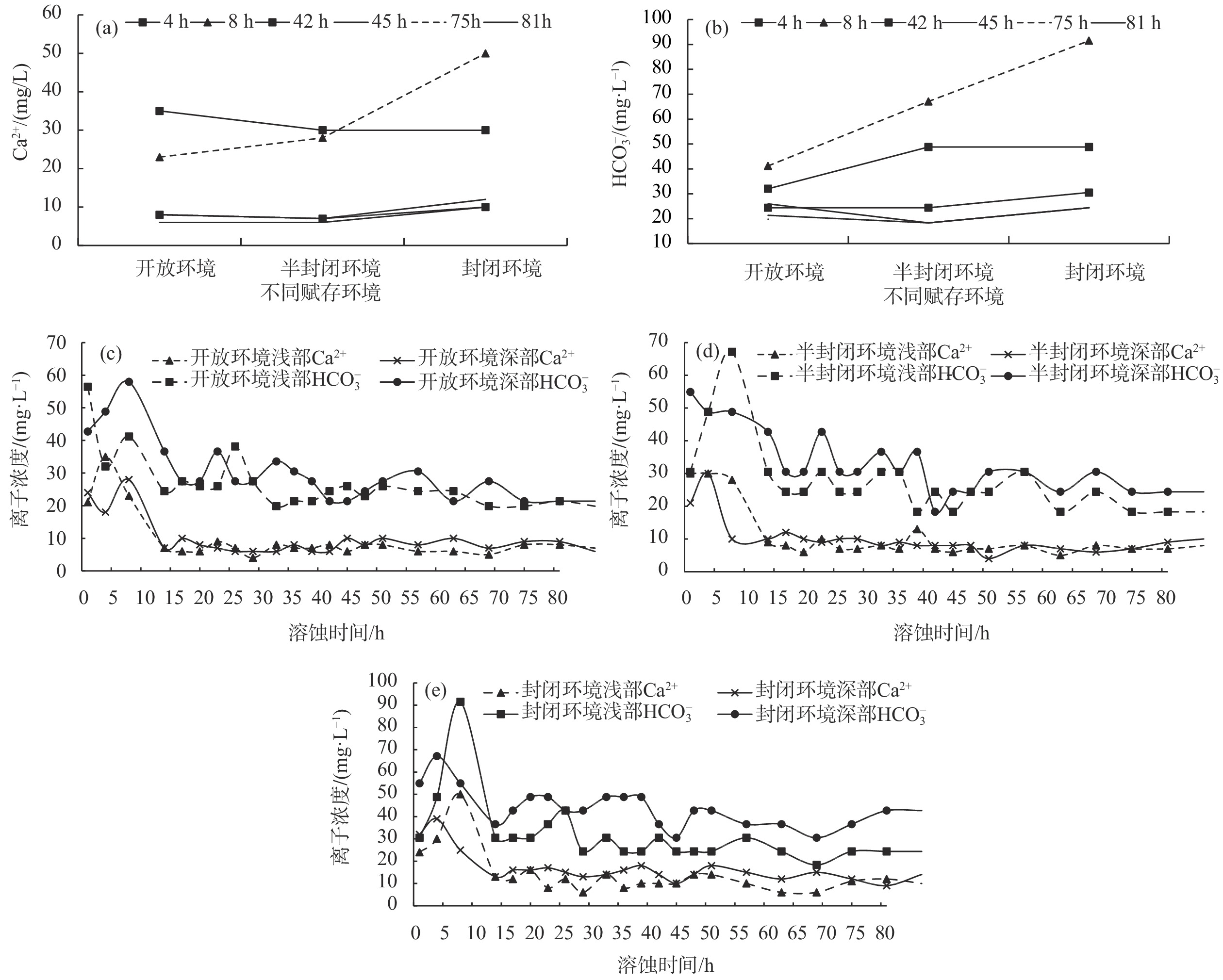
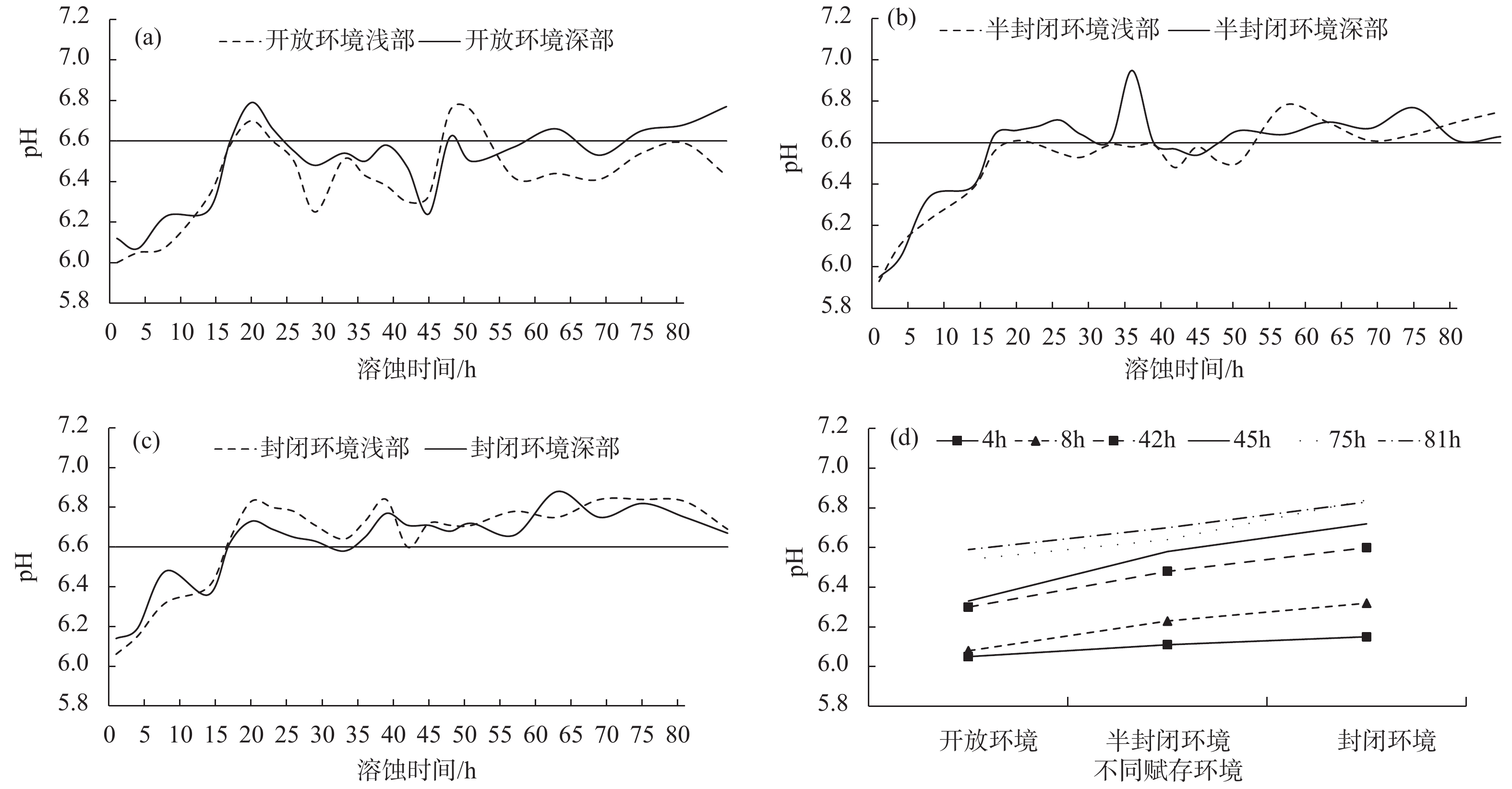
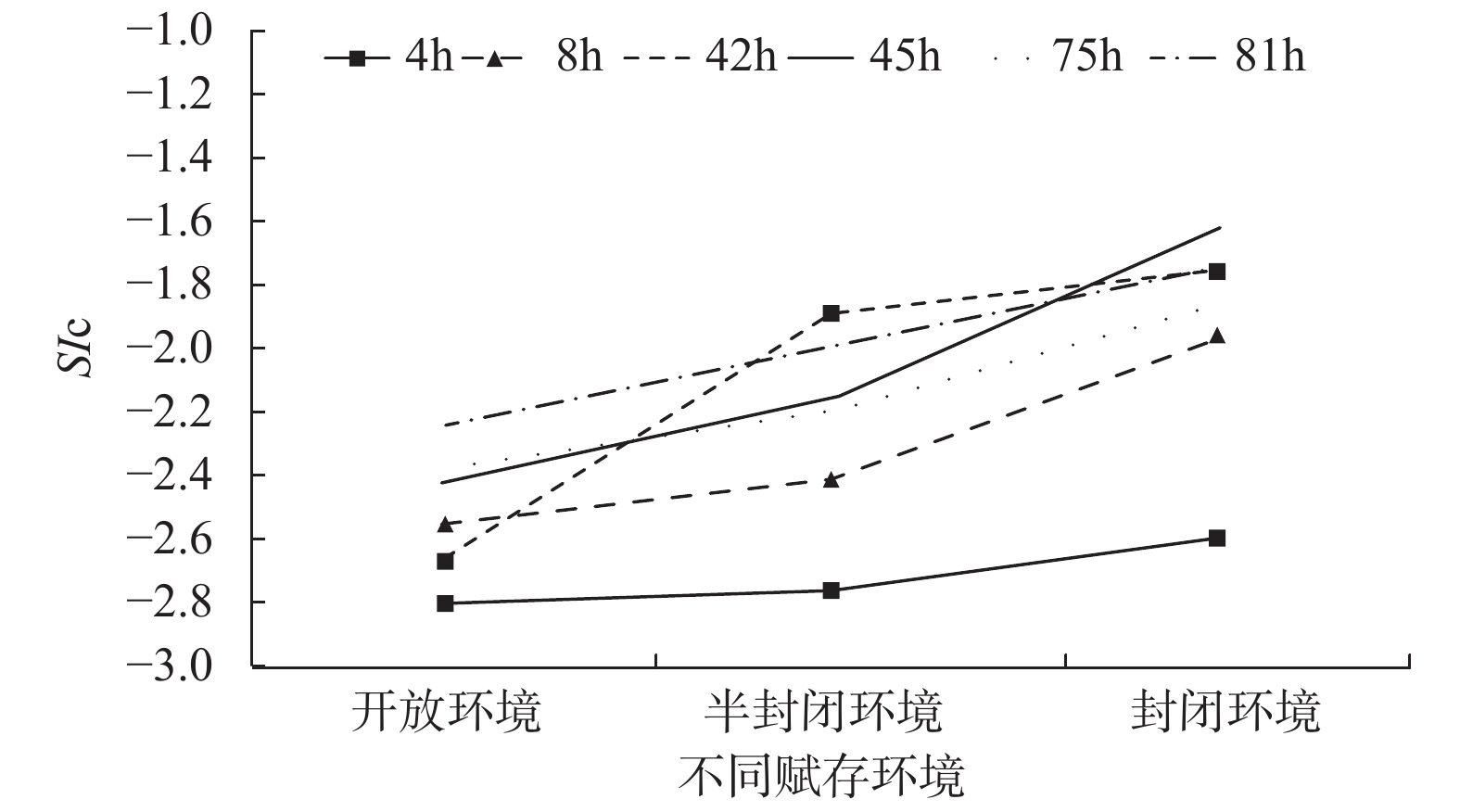
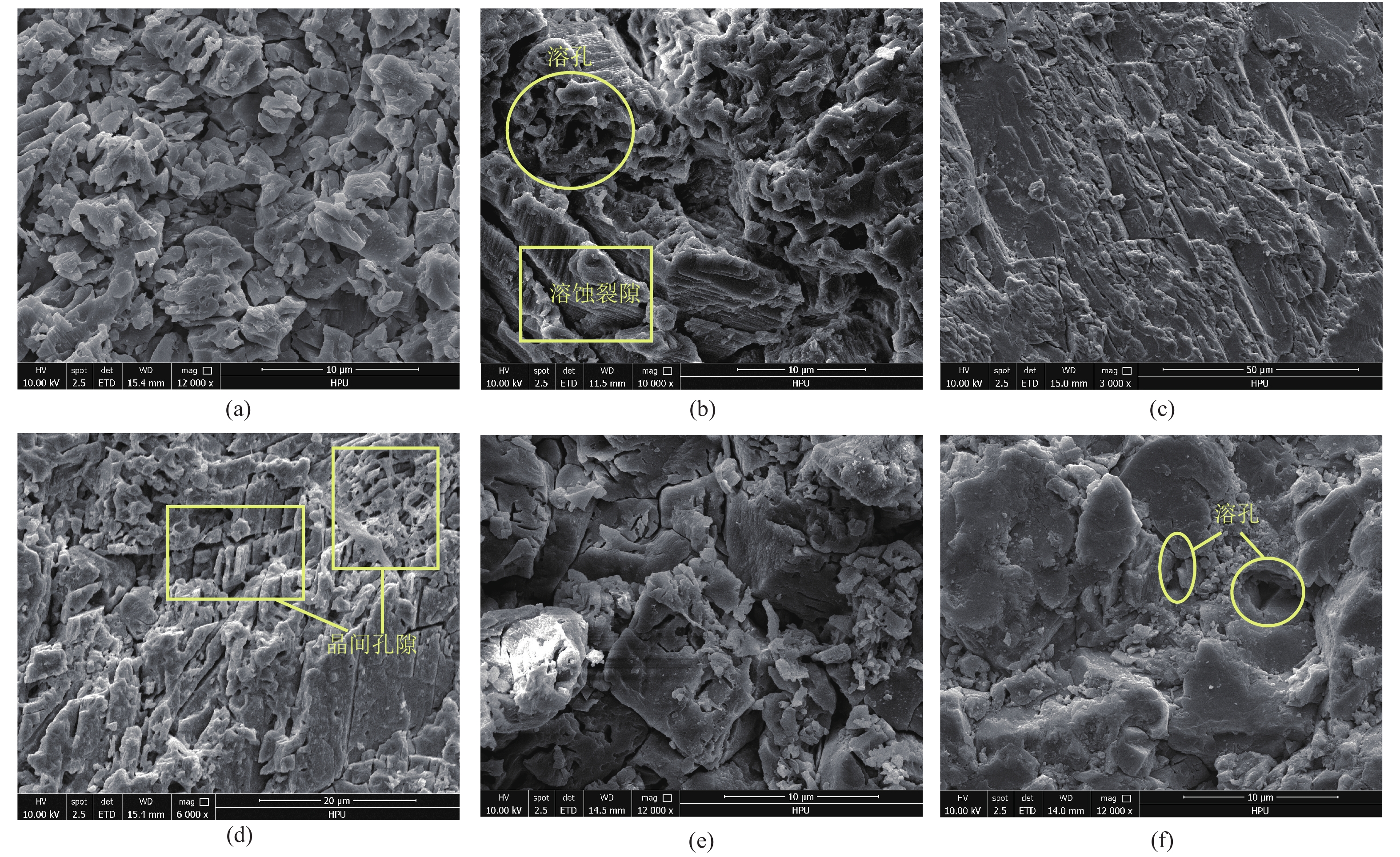
目前,有关碳酸盐岩溶蚀过程的研究多集中在单一环境平衡状态下,不同赋存环境、微观尺度上的研究较少。鉴于此,为探讨不同赋存环境下碳酸盐岩溶蚀过程及微观变化特征,借助研制的岩溶水系统不同赋存环境下水岩相互作用模拟装置,选取典型岩溶水系统开放环境、半封闭环境与封闭环境的岩样,以CO2溶液为酸性流体介质,开展室内溶蚀模拟试验,研究岩溶水中特征组分的变化规律进行模拟实验,并从宏观和微观尺度,研究岩溶水系统不同赋存环境下的碳酸盐岩溶蚀变化特征。结果显示:不同赋存环境下Ca2+、
${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ Abstract:At present, the researches on the dissolution process of carbonate rocks are mostly concentrated on a single environmental equilibrium state, and the researches in different occurrence environments and at a micro scale are relatively weak. In order to explore the dissolution process and the micro change characteristics of carbonate rocks in different occurrence environments, with the help of the developed simulation device of water-rock interaction in different occurrence environments of karst groundwater systems, the indoor dissolution simulation test of the representative rock samples of karst groundwater systems is carried out in the typical open environment, semi-closed environment and closed environment. CO2 solution is used as the acid fluid medium. The changes and control factors of characteristic components in karst groundwater are examined, and the characteristics of the dissolution of representative minerals in different occurrence environments of karst groundwater systems are explored from the macro and micro perspectives. The results show that the spatial variation characteristics of the contents of Ca2+ and
${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ -
Key words:
- occurrence environment /
- carbonate rock /
- corrosion characteristics /
- microstructure
-

-
表 1 试验岩样岩性组分含量
Table 1. Statistics of lithologic components of the test rock samples
试验编号 采集位置 岩性 组分含量 矿物含量 CaO/% MgO/% 酸不溶物/% 方解石/% 白云石/% 试验一 1 泥晶含云灰岩 53.21 0.139 1.23 91 6 1 泥晶含云灰岩 53.21 0.139 1.23 91 6 1 泥晶含云灰岩 53.21 0.139 1.23 91 6 试验二 1 泥晶含云灰岩 53.21 0.139 1.23 91 6 2 泥晶灰岩 51.83 0.662 2.37 92 3 3 泥微晶含石英白云岩 31.87 13.4 1.94 4 85 表 2 各反应物生成物的热力学数据
Table 2. Thermodynamic data of the reactant products
反应物或产物 标准摩尔焓/(kJ·mol−1) 标准摩尔熵/(kJ·mol−1) 摩尔体积/(cm2·mol−1) 临界温度/K 临界压力/Pa Cp系数或Cp a b c CaCO3 −1 208.22 92.68 36.934 104.5 0.0219 2.59×106 CO2 −393.52 213.69 24465 304.41 7.20×106 44.22 8.79×10−3 8.620×105 Ca2+ −542.6 −56.43 18.5 H2O −286.021 69.91 18.069 647.15 2.28×107 30.5 0.0103 0 0 H+ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 表 3 试验变量表
Table 3. Test variables
试验批号 赋存环境 岩样岩性 pH 溶蚀时间/h 岩块表面流速/(m·s−1) 介质 试验一 开放环境 泥晶含云灰岩 6 80 5.4×10−3 碳酸水 半封闭环境 泥晶含云灰岩 封闭环境 泥晶含云灰岩 试验二 开放环境 泥晶含云灰岩 6 80 5.4×10−3 碳酸水 半封闭环境 泥晶灰岩 封闭环境 泥微晶含石英白云岩 表 4 不同赋存环境下岩样溶蚀结果
Table 4. Dissolution results of the rock samples in different environments
试验号 埋深 开放环境 半封闭环境 封闭环境 总溶蚀率/
(mg·cm−2)剥蚀速率/
(mm·a−1)总溶蚀率/
(mg·cm−2)剥蚀速率/
(mm·a−1)总溶蚀率/
(mg·cm−2)剥蚀速率/
(mm·a−1)试验一 20 cm 3.19 1.34 2.11 0.89 1.85 0.78 40 cm 3.24 1.36 2.23 0.94 1.87 0.79 60 cm 2.42 1.02 2.34 0.99 2.27 0.96 均值 2.95 1.24 2.23 0.94 2.00 0.84 试验二 20 cm 2.74 1.15 0.58 0.24 0.68 0.29 40 cm 3.52 1.48 1.60 0.67 0.60 0.25 60 cm 3.42 1.44 1.18 0.50 0.56 0.24 均值 3.23 1.36 1.12 0.47 0.61 0.26 -
[1] 梁永平, 赵春红. 中国北方岩溶水功能[J]. 中国矿业,2018,27(增刊2):297 − 299. [LIANG Yongping, ZHAO Chunhong. Karst water function in northern China[J]. China Mining Magazine,2018,27(Sup2):297 − 299. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 柳广弟. 石油地质学[M]. 4版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2009: 153 − 165.
LIU Guangdi. Petroleum geology [M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2009: 153 − 165. (in Chinese)
[3] 李振拴. 中国北方喀斯特水源地勘探方法研究[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2000.
LI Zhenshuan. Study on the exploration method of karst water source in North China[M]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Publishing House, 2000. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 韩德馨, 杨起. 中国煤田地质学[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1984.
HAN Dexin, YANG Qi. China coalfield geology[M]. Beijing: Coal Industry Press, 1984. (in Chinese)
[5] 武强, 董东林, 傅耀军, 等. 煤矿开采诱发的水环境问题研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2002,31(1):19 − 22. [WU Qiang, DONG Donglin, FU Yaojun, et al. Research on water pollution induced by coal mining[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2002,31(1):19 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2002.01.005
[6] BISCHOFF J L, DICKSON F W. Seawater-basalt interaction at 200 ℃ and 500 bars: Implications for origin of sea-floor heavy-metal deposits and regulation of seawater chemistry[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters,1975,25(3):385 − 397.
[7] 张寿越. 碳酸岩系的溶蚀与岩溶的发育—以湖北、四川、广西等省(区)为例[J]. 地质学报,1979,53(3):247 − 261. [ZHANG Shouyue. The corrosion of carbonate rocks and development of karst (with Hubei, Sichuan, Guangxi as examples)[J]. Acta Geological Sinica,1979,53(3):247 − 261. (in Chinese)
[8] DOVE P M, CRERAR D A. Kinetics of quartz dissolution in electrolyte solutions using a hydrothermal mixed flow reactor[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1990,54(4):955 − 969. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90431-J
[9] 韩宝平. 任丘油田碳酸盐岩溶蚀实验研究[J]. 中国岩溶,1988,7(1):83 − 90. [HAN Baoping. Study on the simulation of carbonate rock' s corrosion in Renqiu oilfield[J]. Carsologica Sinica,1988,7(1):83 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 邵东梅. 不同水流速度下温度对奥陶系碳酸盐岩溶蚀速度的影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2012,40(3):62 − 65. [SHAO Dongmei. Influence of temperature on dissolution rate in Ordovician carbonate rock in different water flow rate[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2012,40(3):62 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2012.03.015
[11] 于奭, 严毅萍, 张春来, 等. 酸雨对碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率影响的试验研究[J]. 桂林理工大学学报,2011,31(4):539 − 544. [YU Shi, YAN Yiping, ZHANG Chunlai, et al. Experimental study on carbonate dissolution rate influenced by acid rain[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology,2011,31(4):539 − 544. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2011.04.010
[12] 范明, 蒋小琼, 刘伟新, 等. 不同温度条件下CO2水溶液对碳酸盐岩的溶蚀作用[J]. 沉积学报,2007,25(6):825 − 830. [FAN Ming, JIANG Xiaoqiong, LIU Weixin, et al. Dissolution of carbonate rocks in CO2 solution under the different temperatures[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2007,25(6):825 − 830. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.06.002
[13] 佘敏, 寿建峰, 沈安江, 等. 从表生到深埋藏环境下有机酸对碳酸盐岩溶蚀的实验模拟[J]. 地球化学,2014,43(3):276 − 286. [SHE Min, SHOU Jianfeng, SHEN Anjiang, et al. Experimental simulation of dissolution for carbonate rocks in organic acid under the conditions from epigenesis to deep burial environments[J]. Geochimica,2014,43(3):276 − 286. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 郭静芸, 毕鑫涛, 方然可, 等. 可溶岩化学溶蚀试验方法研究综述[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):24 − 34. [GUO Jingyun, BI Xintao, FANG Ranke, et al. Advaces in the chemical dissolution methods of soluble rocks[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):24 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 黄荷, 陈植华, 王涛, 等. 岩溶矿区水文地球化学特征及其水源指示意义[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(1):19 − 26. [HUANG He, CHEN Zhihua, WANG Tao, et al. Groundwater source identification incarbonate-hosted deposit using hydrogechemistry, hydrogen and oxygen isotope method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(1):19 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王兴山, 张捷, 秦中. 岩石侵蚀速率测算方法研究综述及展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2013,28(4):447 − 454. [WANG Xingshan, ZHANG Jie, QIN Zhong. Methods for measuring erosion rate of rock: an overview[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2013,28(4):447 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2013.04.0447
[17] LIN Y, REN H X, WU Y Z, et al. The evolution of hydrogeochemical characteristics of a typical piedmont karst groundwater system in a coal-mining area, Northern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2019,78(18):1 − 17.
[18] 唐伟, 曹建华, 杨会, 等. 外源水对碳酸盐侵蚀速率研究—以桂林毛村地下河为例[J]. 地球与环境,2014,42(2):207 − 212. [TANG Wei, CAO Jianhua, YANG Hui, et al. Research on carbonate rock corrosion rate by allogenic water as exemplified by the Maocun subterranean river in Guilin[J]. Earth and Environment,2014,42(2):207 − 212. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 武亚遵, 潘春芳, 林云, 等. 鹤壁矿区奥陶系灰岩地下水水文地球化学特征及反向模拟[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2018,29(4):25 − 32. [WU Yazun, PAN Chunfang, LIN Yun, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and its reverse simulation of Ordovician Limestone groundwater in Hebi Mining area[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2018,29(4):25 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 武亚遵, 潘春芳, 林云, 等. 典型华北型煤矿区主要充水含水层水文地球化学特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(5):191 − 199. [WU Yazun, PAN Chunfang, LIN Yun, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and controlling factors of main water filled aquifers in the typical North China coalfield[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(5):191 − 199. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 刘再华, Chris GROVES, 袁道先, 等. 水-岩-气相互作用引起的水化学动态变化研究—以桂林岩溶试验场为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2003,30(4):13 − 18. [LIU Zaihua, GROVES C, YUAN Daoxian, et al. Study on the hydrochemical variations caused by the water-rock-gas interaction—an example from the Guilin Karst Experimental Site[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2003,30(4):13 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.04.003
[22] 陈如冰, 罗明明, 罗朝晖, 等. 三峡地区碳酸盐岩化学组分与溶蚀速率的响应关系[J]. 中国岩溶,2019,38(2):258 − 264. [CHEN Rubing, LUO Mingming, LUO Zhaohui, et al. Response relationship between chemical composition and dissolution rate of carbonate rocks in the Three Gorges Area[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2019,38(2):258 − 264. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 苏悦, 胡晓农, 曹建华, 等. 桂林市毛村流域碳酸盐岩溶蚀实验研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2019,38(1):63 − 65. [SU Yue, HU Xiaonong, CAO Jianhua, et al. Experimental research on carbonate rock erosion by Maocun river basin in Guilin[J]. Coal technology,2019,38(1):63 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 闫志为, 张志卫, 王佳佳. 硫酸水对方解石和白云石矿物的溶蚀作用[J]. 水资源保护,2009,25:79 − 82. [YAN Zhiwei, ZHANG Zhiwei, WANG Jiajia. Corrosion of calcite and dolomite in sulfurice acid water[J]. Water Resources Protection,2009,25:79 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 佘敏, 寿建峰, 贺训云, 等. 碳酸盐岩溶蚀机制的实验探讨:表面溶蚀与内部溶蚀对比[J]. 海相油气地质,2013,18(5):55 − 61. [SHE Min, SHOU Jianfeng, HE Xunyun, et al. Experiment of dissolution mechanism of carbonate rocks:surface dissolution and internal dissolution[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2013,18(5):55 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 刘再华, W. Dreybrodt, 韩军, 等. CaCO3-CO2-H2O岩溶系统的平衡化学及其分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2005, 24(1):3 − 16. [LIU Zaihua, W Dreybrodt, HAN Jun, et al. Equilibrium chemistry of the CaCO3-CO2-H2O system and discessions[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2005, 24(1):3 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 曹建华, 王福星, 何师意, 等. 广西弄岗自然保护区碳酸盐岩表面内生地衣保水性岩溶意义[J]. 地球学报,1995,16(4):419 − 431. [CAO Jianhua, WANG Fuxing, HE Shiyi, et al. Hydrological effect and karst significance of endolithic lichens on the surface of carbonate rocks in the Longgang natural reserve, Guangxi[J]. Journal of Earth,1995,16(4):419 − 431. (in Chinese)
[28] 翁金桃. 桂林岩溶与碳酸盐岩[M]. 重庆: 重庆出版社, 1987: 1 − 180.
WENG Jintao. Karat and carbonnate rocks in Guilin.[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing Press, 1987: 1 − 180. (in Chinese)
[29] 余逍逍, 史文兵, 王小明, 等. 基于数字图像处理技术的溶蚀岩体细观变形破坏机制模拟研究[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(3):409 − 416. [YU Xiaoxiao, SHI Wenbing, WANG Xiaoming, et al. Simulation on mesoscopic deformation and failure mechanism of dissolved rock mass using digital image processing technology[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020,39(3):409 − 416. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 武亚遵, 林云, 万军伟, 等. 酸盐岩单裂隙渗流—溶蚀耦合模型及其参数敏感性分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2016,35(1):81 − 86. [WU Yazun, LIN Yun, WAN Junwei, et al. Coupled fluid flow and dissolution model and associated parameter sensitivity analysis in a single carbonate rock fracture[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2016,35(1):81 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 毛亮, 于青春, 王敬霞, 等. 降雨对裂隙型岩溶含水系统演化影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 中国岩溶,2017,36(1):42 − 48. [MAO Liang, YU Qingchun, WANG Jingxia, et al. Numerical simulation of precipitation impact on fractured karst system evolution[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2017,36(1):42 − 48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] SONG Chao, LIU Changli, ZHANG Yun, et al. Impact of animal manure addition on the weathering of agricultural lime in acidic soils: The agent of carbonate weathering[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2017,5(2):202 − 212.
[33] LIU Changli, ZHANG Yun, SONG Chao, et al. Effect of Farmyard Manure Application on Dissolution of Carbonate Rocks and Its Eco-environmental Impact[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2013,1(1):60 − 69.
-




 下载:
下载: