Advances in researches on ammonia, nitrite and nitrate on migration and transformation in the groundwater level fluctuation zone
-
摘要:
三氮是我国地下水中典型污染物,其在包气带和含水层中的迁移转化过程受到高度关注。近几年,地下水位波动带中的三氮迁移转化已经成为新的研究领域。在综合运用文献计量分析法,定量分析相关研究趋势的基础上,系统总结地下水位波动带形成及特点,梳理波动带中三氮迁移转化过程及生物地球化学过程最新研究表述及成果,并对今后可能的研究热点和方向进行了展望。现有研究表明:水位波动带中环境指标如土壤含水率、氧化还原电位、溶解氧和有机质含量均表现出一定的分带性规律,微生物菌群结构和功能基因更多样化,并呈现一定的分布特征。随着地下水位波动,包气带中的三氮易浸溶进入地下水并发生迁移。地下水位上升,硝化作用减弱,反硝化作用增强;地下水位下降,硝化作用增强,反硝化作用减弱。为完善水位波动带三氮迁移转化过程研究,应进一步关注:(1)将水化学演化分析与分子生物学高通量测序方法相结合,深入探究水位波动带三氮转化与微生物作用机理;(2)除关注硝化、反硝化作用外,增加异化还原、同化还原和厌氧氨氧化等作用过程的研究;(3)细化分析更多情境、更多影响因素的水位波动过程,识别水位波动带三氮转化的关键影响要素。
Abstract:Ammonia, nitrite and nitrate are typical pollutants in shallow groundwater and in the vadose zone, and their migration and transformation processes are highly concerned. In recent years, new studies have focused on the three-nitrogen in the groundwater level fluctuation zone. This paper comprehensively uses the literature measurement analysis method to quantitatively analyze the related research trends, and systematically summaries the latest research results of the formation and characteristics of the groundwater level fluctuation zone, the migration and transformation process of the three-nitrogen and their biogeochemical processes in the fluctuation zone. The results show that environmental indicators such as soil moisture content, redox potential, contents of dissolved oxygen and organic matter in the groundwater level fluctuation zone have remarkable zoning rules, and the microbial community structure and functional genes are more diversified with obvious layers. As the groundwater levels fluctuate, the three-nitrogen in the vadose zone is easy to leach into the groundwater and migrate. As the groundwater levels rise, nitrification weakens, denitrification enhances, and as the groundwater levels drop, nitrification enhances, and denitrification weakens. Finally, this paper prospects the research hotspots and directions in the future: (1) the groundwater chemical evolution analysis is combined with the high-throughput sequencing method of molecular biology to explore the three-nitrogen transformation and microbial action mechanism in the groundwater level fluctuation zone. (2) In addition to nitrification and denitrification, the researches on dissimilation reduction, assimilation reduction and anaerobic ammonia oxidation processes are increased. (3) The groundwater level fluctuation process with more scenarios and influencing factors are analyzed, and the key influencing factors of the three nitrogen transformation in the groundwater level fluctuation zone are identified.
-

-
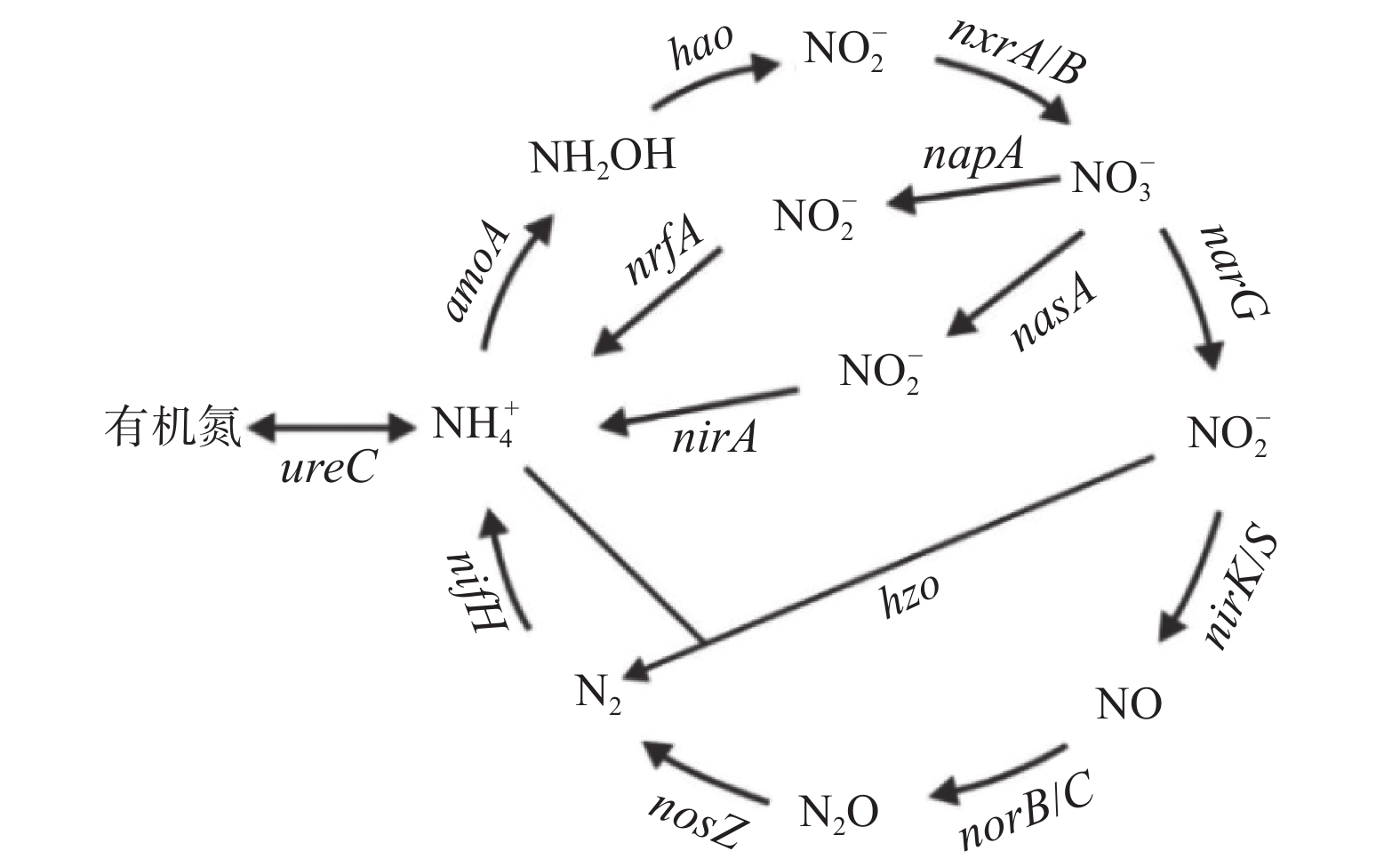
图 1 氮循环过程及其关键微生物功能基因[10]
Figure 1.
表 1 参与三氮转化的主要功能基因信息
Table 1. Main functional gene information of the three-nitrogen transformation
基因代号 基因全称(KEGG数据库直系同源蛋白编码) 主要作用 具体参与过程 参考文献 AOA/AOB -amoA 氨单加氧酶基因(K10944、K10945) 硝化作用 将  氧化为 NH2OH
氧化为 NH2OH
[29, 46] hao 羟胺氧化还原酶基因(K10535) 硝化作用 将NH2OH 氧化为 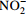
[10, 47] nxrA/B 亚硝酸盐氧化还原酶基因(K00370、K00371) 硝化作用 将 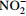 氧化为
氧化为
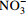
[10] narG 硝酸盐还原酶基因(K00370) 反硝化作用 将 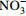 还原为
还原为
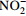
[29] nirK/nirS 亚硝酸盐还原酶基因(K00368、K15864) 反硝化作用 将 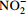 还原为NO
还原为NO
[11, 29, 46] norB/norC 一氧化氮还原酶基因(K04561、K02305) 反硝化作用 将NO还原为 N2O [11] nosZ 氧化亚氮还原酶基因(K00376) 反硝化作用 将N2O还原为 N2 [11, 34] nasA/nasB、narB 硝酸盐同化还原酶(K00372、K00360、K00367) 同化还原作用 将 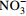 还原为
还原为
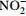
[18] nirA 亚硝酸盐同化还原酶基因(K00366) 同化还原作用 将 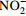 还原为
还原为

[10] napA/napB 硝酸盐异化还原酶基因(K02567、K02568) 异化还原作用 将 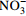 还原为
还原为
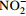
[11] nrfA/nrfH,nirB/nirD 亚硝酸盐异化还原酶基因(K03385、K15876、K00362、K00363) 异化还原作用 将 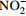 还原为
还原为

[10-11] -
[1] 穆恩林, 欧阳如琳, 董四方, 等. 地下水水位管理研究进展综述[J]. 地下水,2019,41(3):33 − 34. [MU Enlin, OUYANG Ruolin, DONG Sifang, et al. Summary of research progress on groundwater level management[J]. Ground Water,2019,41(3):33 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2019.03.012
[2] 王嘉瑜, 蒲生彦, 胡玥, 等. 地下水污染风险预警等级及阈值确定方法研究综述[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):43 − 50. [WANG Jiayu, PU Shengyan, HU Yue, et al. Review on the determination methods for early warning grade and threshold of groundwater pollution risk[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 赵辉, 陈文芳, 崔亚莉. 中国典型地区地下水位对环境的控制作用及阈值研究[J]. 地学前缘,2010,17(6):159 − 165. [ZHAO Hui, CHEN Wenfang, CUI Yali. Control function of groundwater table on the environment of typical areas in China and the study of thresholds[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2010,17(6):159 − 165. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 孟祥菲. 地下水位波动带铁猛含量变化规律研究: 以沈阳黄家水源地为例[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015.
MENG Xiangfei. Study on variation of Fe and Mn content in fluctuation zone of groundwater level —an example in Shenyang Huangjia water[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 杨洋. 考虑地下水位波动的土层污染物运移模型研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2015.
YANG Yang. Research on the model of contaminant migration in soil considering groundwater level fluctuation[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李翔, 席北斗, 姜永海, 等. 水位波动带氮素迁移转化规律[J]. 环境工程学报,2013,7(12):4703 − 4708. [LI Xiang, XI Beidou, JIANG Yonghai, et al. Nitrogen migration and transformation in fluctuation belt of water table[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2013,7(12):4703 − 4708. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] ACHARYA B S, HALIHAN T, ZOU C B, et al. Vegetation controls on the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of deep moisture in the unsaturated zone: A hydrogeophysical evaluation[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):1 − 10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x
[8] DUAN Y H, GAN Y Q, WANG Y X, et al. Temporal variation of groundwater level and arsenic concentration at Jianghan Plain, central China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2015,149:106 − 119. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.12.001
[9] KUYPERS M M M, MARCHANT H K, KARTAL B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology,2018,16(5):263 − 276. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2018.9
[10] 王朱珺, 王尚, 刘洋荧, 等. 宏基因组技术在氮循环功能微生物分子检测研究中的应用[J]. 生物技术通报,2018,34(1):1 − 14. [WANG Zhujun, WANG Shang, LIU Yangying, et al. The applications of metagenomics in the detection of environmental microbes involving in nitrogen cycle[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2018,34(1):1 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] LIU Y Y, LIU C X, NELSON W C, et al. Effect of water chemistry and hydrodynamics on nitrogen transformation activity and microbial community functional potential in hyporheic zone sediment columns[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2017,51(9):4877 − 4886.
[12] 赵磊, 刘慧. 江汉油田波动带土壤氮循环功能菌群分析[J]. 环境科学与技术,2018,41(11):49 − 53. [ZHAO Lei, LIU Hui. Analysis of soil nitrogen functional bacteria in the volatility zone of Jianghan oilfield[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,41(11):49 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] HSIEH P C, HSU H T, LIAO C B, et al. Groundwater response to tidal fluctuation and rainfall in a coastal aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2015,521:132 − 140. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.11.069
[14] 李阳, 乔玲, 张景华, 等. 怀柔应急备用水源地下水位及水质分析[J]. 北京水务,2018(4):20 − 23. [LI Yang, QIAO Ling, ZHANG Jinghua, et al. Analysis of groundwater level and water quality of emergency standby water sources in Huairou[J]. Beijing Water,2018(4):20 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] CHEN A Q, LEI B K, HU W L, et al. Temporal-spatial variations and influencing factors of nitrogen in the shallow groundwater of the near shore vegetable field of Erhai Lake, China[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research,2018,25(5):4858 − 4870.
[16] 王玉刚, 肖笃宁, 李彦, 等. 新疆三工河流域尾闾绿洲地下水变化与土壤积盐的响应[J]. 生态学报,2007,27(10):4036 − 4044. [WANG Yugang, XIAO Duning, LI Yan, et al. Response of salt accumulation in soil to groundwater changes at the oasis in the lower reaches of Sangong River, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2007,27(10):4036 − 4044. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.10.011
[17] KOHFAHL C, MASSMANN G, PEKDEGER A. Sources of oxygen flux in groundwater during induced bank filtration at a site in Berlin, Germany[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2008,17(3):571 − 578.
[18] REZANEZHAD F, COUTURE R M, KOVAC R, et al. Water table fluctuations and soil biogeochemistry: An experimental approach using an automated soil column system[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2014,509:245 − 256. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.036
[19] FARNSWORTH C E, VOEGELIN A, HERING J G. Manganese oxidation induced by water table fluctuations in a sand column[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2012,46(1):277 − 284.
[20] BÖHLKE J K, WANTY R, TUTTLE M, et al. Denitrification in the recharge area and discharge area of a transient agricultural nitrate plume in a glacial outwash sand aquifer, Minnesota[J]. Water Resources Research,2002,38(7):10 − 1.
[21] 林广宇. 地下水位变动带石油烃污染物的迁移转化规律研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014.
LIN Guangyu. Study on migration and transformation of petroleum hydrocarbons in zone of intermittent saturation[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] LIU Y C, FEI Y H, Meng S H, et al. Hydrochemical evolution of groundwater and soils in the water-level-fluctuation zone[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2019,78(22):1 − 12.
[23] SCHIMEL J, BALSER T C, WALLENSTEIN M. Microbial stress-response physiology and its implications for ecosystem function[J]. Ecology,2007,88(6):1386 − 1394. doi: 10.1890/06-0219
[24] JOST D, HABERER C M, GRATHWOHL P, et al. Oxygen transfer in a fluctuating capillary fringe: impact of microbial respiratory activity[J]. Vadose Zone Journal,2015,14(5):1 − 14.
[25] HUANG P, ZHANG J B, ZHU A N, et al. Nitrate accumulation and leaching potential reduced by coupled water and nitrogen management in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,610/611:1020 − 1028. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.127
[26] 吕晓立, 刘景涛, 周冰, 等. 塔城盆地地下水“三氮”污染特征及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(2):42 − 50. [LYU Xiaoli, LIU Jingtao, ZHOU Bing, et al. Distribution and source of nitrogen pollution in groundwater in the Tacheng Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(2):42 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] LI X, LI J, XI B D, et al. Effects of groundwater level variations on the nitrate content of groundwater: a case study in Luoyang area, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2015,74(5):3969 − 3983. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4016-4
[28] RASIAH V, ARMOUR J D, NELSON P N. Nitrate in shallow fluctuating groundwater under sugarcane: Quantifying the lateral export quantities to surface waters[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment,2013,180:103 − 110.
[29] ZHANG D, CUI R Y, FU B, et al. Shallow groundwater table fluctuations affect bacterial communities and nitrogen functional genes along the soil profile in a vegetable field[J]. Applied Soil Ecology,2020,146:103368. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.103368
[30] WANG Y, LI K, TANAKA T S T, et al. Soil nitrate accumulation and leaching to groundwater during the entire vegetable phase following conversion from paddy rice[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems,2016,106(3):325 − 334. doi: 10.1007/s10705-016-9807-9
[31] TERANES J L, BERNASCONI S M. The record of nitrate utilization and productivity limitation provided by δ15N values in lake organic matter—A study of sediment trap and core sediments from Baldeggersee, Switzerland[J]. Limnology & Oceanography,2000,45(4):801 − 813.
[32] 杜涛. 南水北调入京后北京西南地区地下水水质演变的实验模拟研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2004.
DU Tao. A study of test simulation on groundwater quality evolution after the south-to-north water transfering in southwestern area, Beijing[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 杨雪琴, 连英丽, 颜庆云, 等. 滨海湿地生态系统微生物驱动的氮循环研究进展[J]. 微生物学报,2018,58(4):633 − 648. [YANG Xueqin, LIAN Yingli, YAN Qingyun, et al. Microbially-driven nitrogen cycling in coastal ecosystems[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica,2018,58(4):633 − 648. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 邓闵. 精养池塘碳氮循环特征及有机碳源对生物絮团降氮作用的影响机制[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018.
DENG Min. The carbon and nitrogen cycling characteristic of intensitive pond and the influence of organic carbon sources on the nitrogen removal of biofloc[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] LEININGER S, URICH T, SCHLOTER M, et al. Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils[J]. Nature,2006,442(7104):806 − 809. doi: 10.1038/nature04983
[36] LIU S, HU B L, HE Z F, et al. Ammonia-oxidizing archaea have better adaptability in oxygenated/hypoxic alternant conditions compared to ammonia-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2015,99(20):8587 − 8596. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6750-7
[37] GUBRY-RANGIN C, HAI B, QUINCE C, et al. Niche specialization of terrestrial archaeal ammonia oxidizers[J]. PNAS,2011,108(52):21206 − 21211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109000108
[38] YANG Y D, REN Y F, WANG X Q, et al. Ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria responding differently to fertilizer type and irrigation frequency as revealed by Illumina Miseq sequencing[J]. Journal of Soils & Sediments,2018,18(3):1029 − 1040.
[39] MORALES S E, COSART T, HOLBEN W E. Bacterial gene abundances as indicators of greenhouse gas emission in soils[J]. The ISME Journal,2010,4(6):799 − 808. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.8
[40] 王薇, 蔡祖聪, 钟文辉, 等. 好氧反硝化菌的研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报,2007,18(11):2618 − 2625. [WANG Wei, CAI Zucong, ZHONG Wenhui, et al. Research advances in aerobic denitrifiers[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2007,18(11):2618 − 2625. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] MOSIER A C, FRANCIS C A. Denitrifier abundance and activity across the San Francisco Bay estuary[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports,2010,2(5):667 − 676. doi: 10.1111/j.1758-2229.2010.00156.x
[42] HUANG S, CHEN C, WU Q, et al. Distribution of typical denitrifying functional genes and diversity of the nirS-encoding bacterial community related to environmental characteristics of river sediments[J]. Biogeosciences Discussions,2011,8(3):5251 − 5280. doi: 10.5194/bgd-8-5251-2011
[43] GARDNER W S, MARK J M, SOONMO A, et al. Nitrogen fixation and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) support nitrogen dynamics in Texas estuaries[J]. Limnology & Oceanography,2006,51(1):558 − 568.
[44] WANG H N, GUNSALUS R P. The nrf A and nir B nitrite reductase operons in Escherichia coli are expressed differently in response to nitrate than to nitrite[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2000,182(20):5813 − 5822. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.20.5813-5822.2000
[45] 胡晓婷, 程吕, 林贤彪, 等. 沉积物硝酸盐异化还原过程的温度敏感性与影响因素—以长江口青草沙水库为例[J]. 中国环境科学,2016,36(9):2624 − 2632. [HU Xiaoting, CHENG Lyu, LIN Xianbiao, et al. Temperature sensitive and controlling factors of dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in sediments of Qingcaosha reservoir, Yangtze Esturay[J]. China Environmental Science,2016,36(9):2624 − 2632. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.09.011
[46] 崔荣阳, 雷宝坤, 张丹, 等. 浅层地下水升降对菜地土壤剖面硝化/反硝化微生物丰度的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2019,39(9):3099 − 3106. [CUI Rongyang, LEI Baokun, ZHANG Dan, et al. Effects of shallow groundwater fluctuations on the abundances of nitrification and denitrification microbes in the soil profile of vegetable field[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2019,39(9):3099 − 3106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[47] 陈春兰, 吴敏娜, 魏文学. 长期施用氮肥对土壤细菌硝化基因多样性及组成的影响[J]. 环境科学,2011,32(5):1489 − 1496. [CHEN Chunlan, WU Minna, WEI Wenxue. Effect of long-term application of nitrogen fertilizer on the diversity of nitrifying genes (amoA and Hao) in paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science,2011,32(5):1489 − 1496. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[48] 刘若萱, 贺纪正, 张丽梅. 稻田土壤不同水分条件下硝化/反硝化作用及其功能微生物的变化特征[J]. 环境科学,2014,35(11):4275 − 4283. [LIU Ruoxuan, HE Jizheng, ZHANG Limei. Response of nitrification/denitrification and their associated microbes to soil moisture change in paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science,2014,35(11):4275 − 4283. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: