Experimental research on the influence of mica on strength of cement-reinforced soft clay
-
摘要:
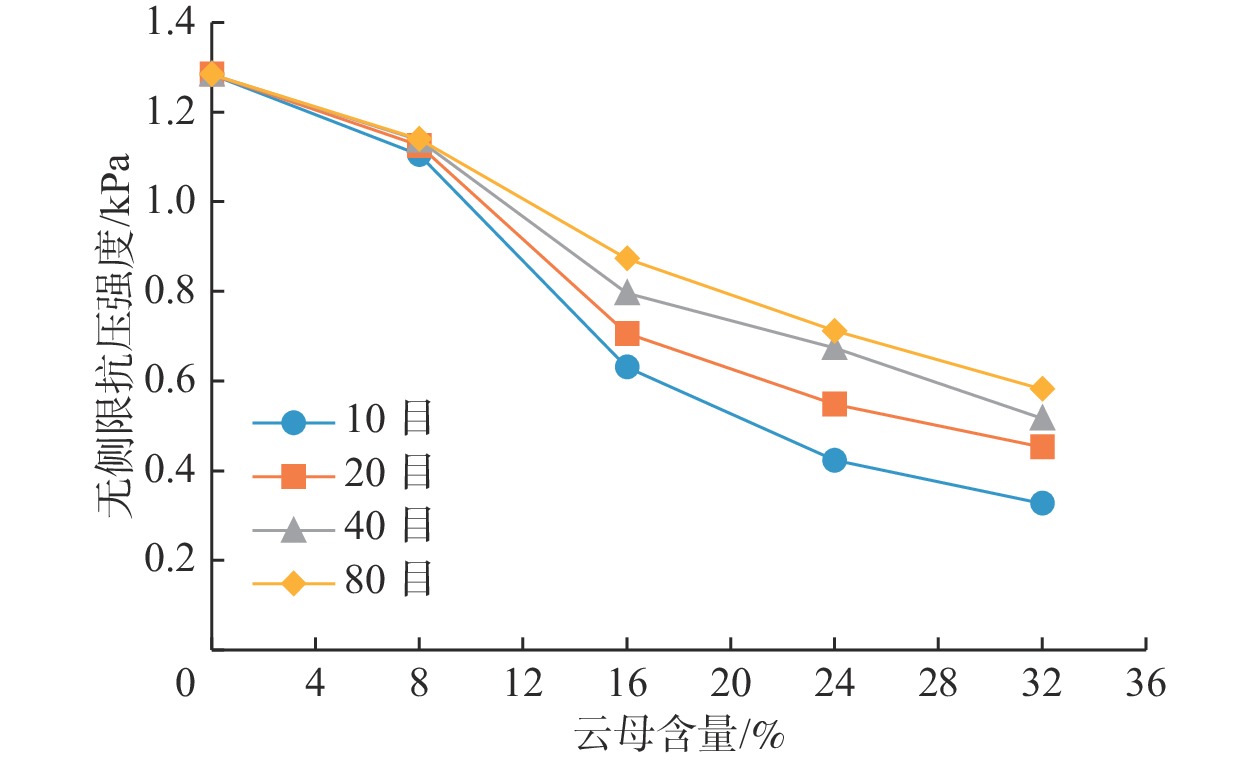
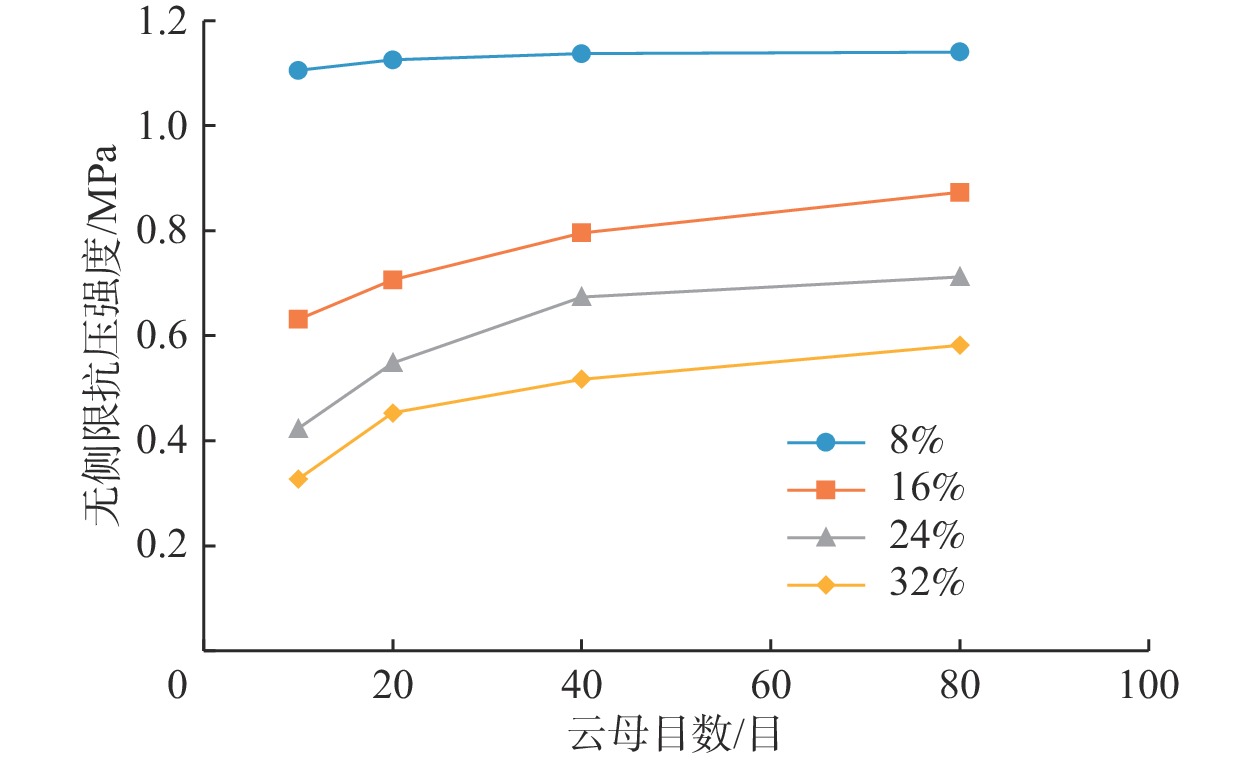
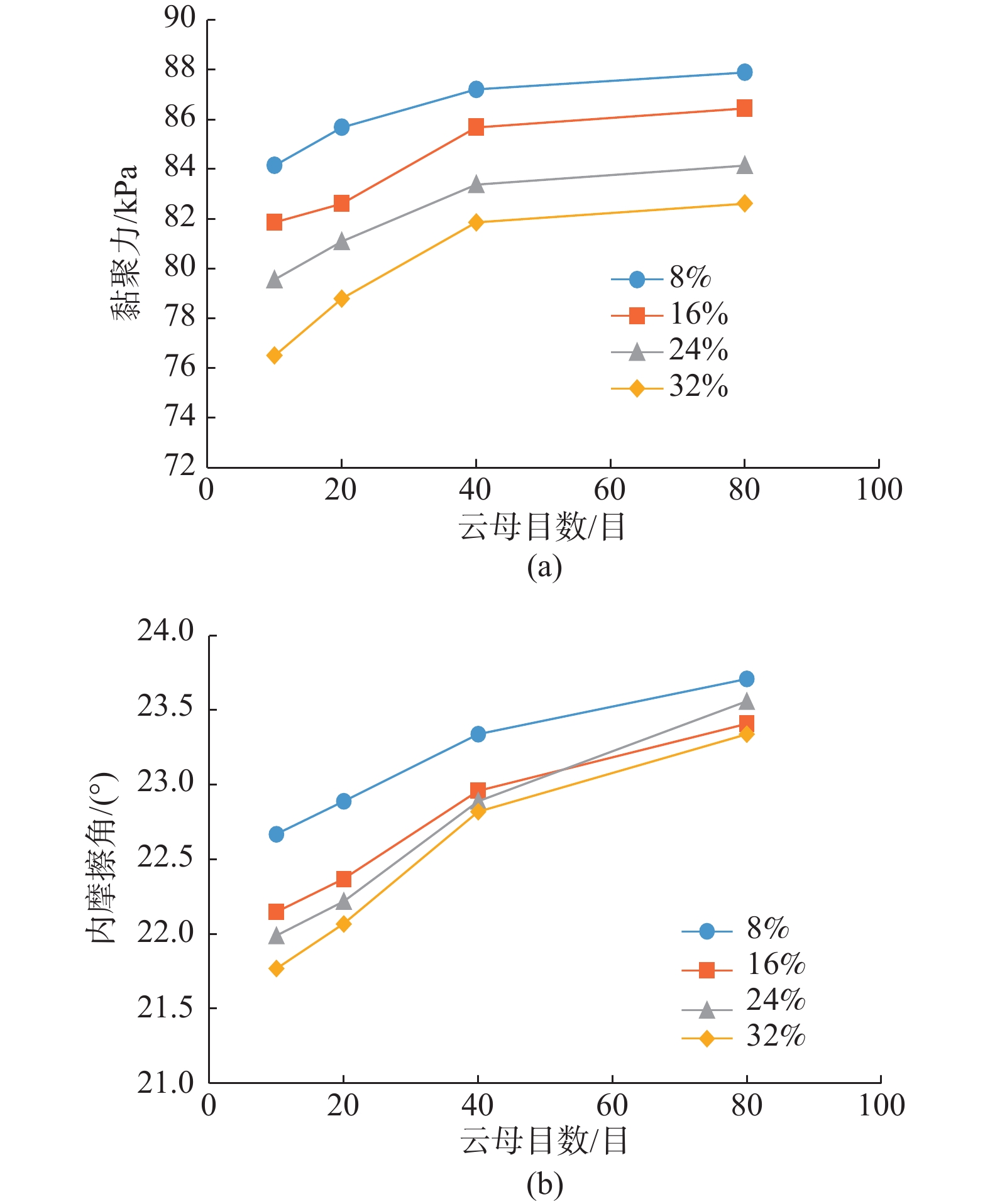
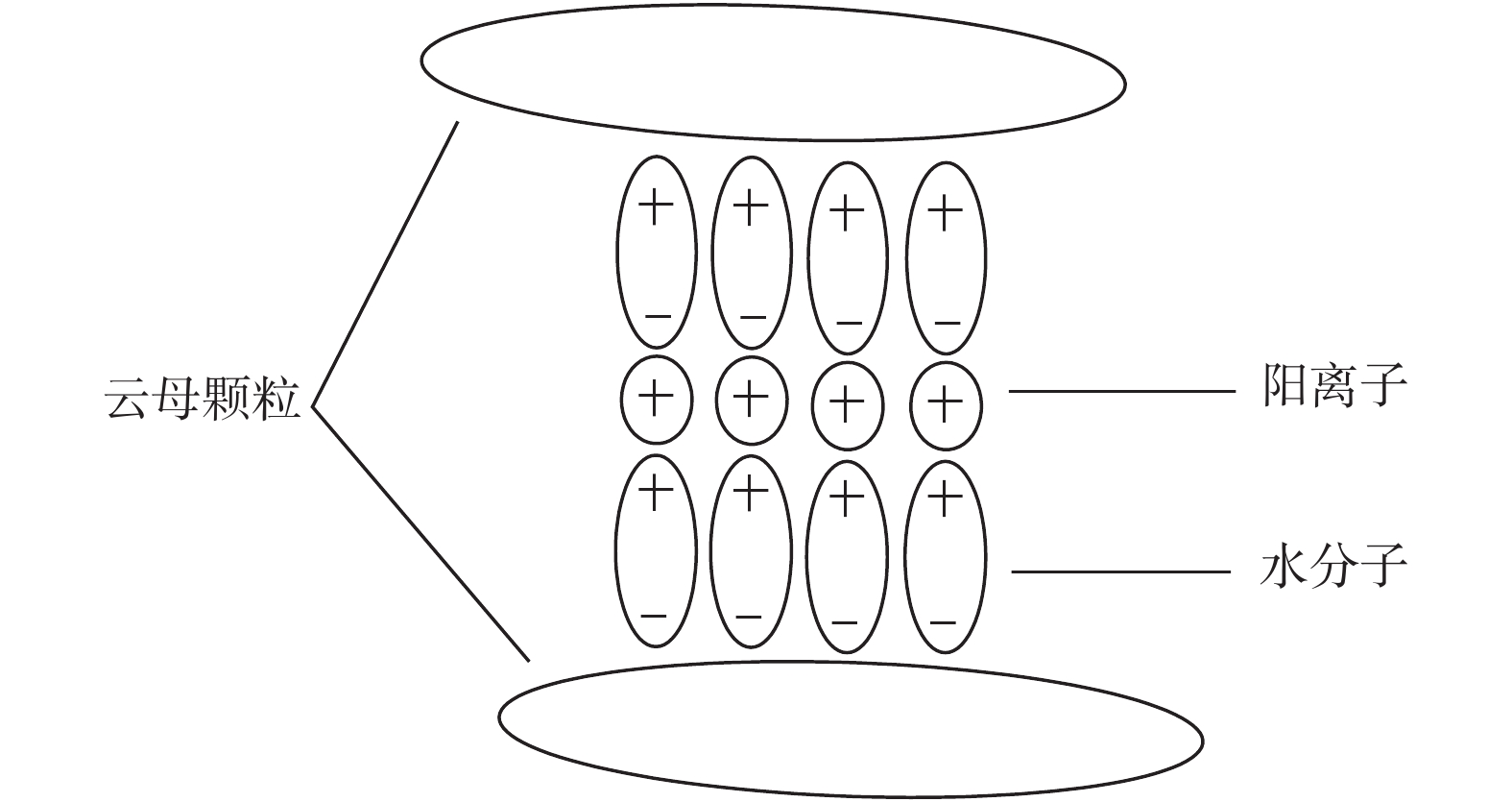
软黏土具有压缩性强、承载能力低的特点,实际工程中多用水泥作为固化剂对软黏土进行加固。云母是软黏土中较为常见的一种片状矿物,其含量和颗粒大小会影响水泥加固后的软黏土即水泥软黏土的强度。通过无侧限抗压强度试验和直接剪切试验研究云母含量及目数对水泥软黏土抗压强度及抗剪强度的影响,提出了云母含量、目数与水泥软黏土抗压强度、抗剪强度指标值之间的关系。试验中云母目数设定为10,20,40,80目共4个梯度,云母含量设定为0%、8%、16%、24%、32%共5个梯度。试验结果表明,云母含量的增加以及云母目数的减小会导致水泥软黏土无侧限抗压强度和抗剪强度的降低,且其对无侧限抗压强度的不利影响更为显著。含10目32%云母的水泥软黏土的强度减少量最大,此时无侧限抗压强度为0.33 MPa,是不含云母水泥软黏土的25.5%;黏聚力为76.5 kPa,比不含云母时减少了12.24 kPa;内摩擦角由不含云母时的23.71°降低至21.77°。云母自身的片状形态及其对水泥水解水化作用、离子交换作用的阻碍是造成水泥软黏土强度降低的主要原因。
Abstract:Soft clay is of the characteristics of strong compressibility and low bearing capacity. Cement is used as curing agent to strengthen soft clay in engineering. Mica is a kind of mineral widely distributed in soft clay, and its content and particle size will affect the strength of the cement-reinforced soft clay. The influence law among the mica content and mica mesh number on strength of the cement-reinforced soft clay is studied based on direct shear tests and unconfined compressive strength tests. Based on the experimental data, the mathematical relationship between the content and mesh number of mica and soil-cement strength is established. The number of mica meshes in the experiment is 10, 20, 40 and 80 mesh, and the mica content is set as 0%, 8%, 16% and 32%. The results show that as the content of mica increases or the number of mica meshes decreases, the unconfined compressive strength and shear strength of the cement-reinforced soft clay show a decreasing trend, and the effect of mica on the unconfined compressive strength is more significant. When the number of mica mesh in the cement soft clay is 10 mesh and the content is 32%, the strength of the cement soft clay decreases the most. In this case, the unconfined compressive strength of 0.33 MPa is 25.5% of that of the cement soft clay without mica, the cohesion is 76.5 kPa, which is 12.24 kPa less than that of the cement soft clay without mica, and the internal friction angle decreases from 23.71° to 21.77°. It is speculated that the lamellar morphology of mica and adverse effect on cement hydration are the main reasons for the decrease of the cement soil strength.
-
Key words:
- mica /
- cement-reinforced soft clay /
- compressive strength /
- cohesion /
- internal friction angle
-

-
表 1 我国部分沿海地区软黏土中云母含量占比情况
Table 1. Percentage of mica content in soft clay in some areas
表 2 云母的主要化学成分
Table 2. Chemical compositions of mica
成分 SiO2 Al2O3 K2O Na2O MgO Fe2O3 含量/% 44~50 20~33 9~11 1~2 1~2 2~6 表 3 软土的基本物理性质
Table 3. Physic-mechanical indices of soft soil
天然密度ρ/(g·cm−3) 黏聚力c/kPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 含水率w/% 孔隙比e 1.71 19 8.2 68 1.79 表 4 软黏土的矿物成分
Table 4. Mineral compositions of soft clay
/% 石英 钾长石 斜长石 蒙脱石 伊蒙混层 伊利石 高岭石 绿泥石 32.4 1.7 15.4 1.0 3.8 26.7 9.5 9.5 表 5 水泥软黏土强度试验结果
Table 5. Results of the cement-reinforced soft clay strength
云母含量/% 云母目数 10目 20目 40目 80目 qu/MPa c/kPa φ/(°) qu/MPa c/kPa φ/(°) qu/MPa c/kPa φ/(°) qu/MPa c/kPa φ/(°) 0 1.28 88.74 23.71 1.28 88.74 23.71 1.28 88.74 23.71 1.28 88.74 23.71 8 1.11 84.15 22.22 1.13 85.68 22.45 1.14 87.21 23.34 1.14 87.90 23.71 16 0.63 81.86 22.15 0.71 82.62 22.37 0.79 85.68 22.96 0.87 86.46 23.41 24 0.42 79.56 21.99 0.55 81.09 22.22 0.67 83.39 23.04 0.71 84.15 23.56 32 0.33 76.50 21.77 0.45 78.80 22.07 0.52 81.86 23.12 0.58 82.62 23.34 表 6 水泥软黏土强度试验统计值
Table 6. Test statistics of strength of the cement soft clay
抗压强度qu/MPa 黏聚力c/kPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 云母目数0,含量0% 1.28 88.74 23.71 云母目数10,含量32% 0.33 76.50 21.77 差值 0.95 12.24 1.94 强度损失比 74.2% 13.8% 8.2% -
[1] 赵春彦, 黄启友, 郎锋, 等. 单因素和多因素作用下的水泥土强度评估模型试验研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2018,15(11):2788 − 2795. [ZHAO Chunyan, HUANG Qiyou, LANG Feng, et al. Experimental study on strength evaluation model of cement soil under single factor and multi factors[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2018,15(11):2788 − 2795. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 刘宝臣, 李翠娟, 潘宗源, 等. 水泥搅拌法改良桂林红黏土力学性质试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(4):633 − 638. [LIU Baochen, LI Cuijuan, PAN Zongyuan, et al. Laboratory test for mechanical properties of Guilin red clay mixed with cement[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(4):633 − 638. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.04.022
[3] 黄英豪, 朱伟, 张春雷, 等. 固化淤泥重塑土力学性质及其强度来源[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(5):1352 − 1356. [HUANG Yinghao, ZHU Wei, ZHANG Chunlei, et al. Mechanical characteristics and strength source of remolded solidified dredged material[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2009,30(5):1352 − 1356. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.05.029
[4] 车东日. 水泥混合上海软弱黏性土性状的试验研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2012.
CHE Dongri. Laboratory investigation on the behavior of cement mixed soft clayey soil of Shanghai[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 袁建议, 潘拥军, 汪春峰, 等. 水泥土搅拌桩力学参数的试验分析[J]. 湖北理工学院学报,2013,29(6):42 − 45. [YUAN Jianyi, PAN Yongjun, WANG Chunfeng, et al. Experimental analysis of mechanical parameters of cement- soil mixing pile[J]. Journal of Hubei Polytechnic University,2013,29(6):42 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4565.2013.06.011
[6] 李振龙, 潘殿琦, 杨书红, 等. 海相淤泥特性水泥土搅拌桩强度影响因素及其变化规律的试验研究[J]. 长春工程学院学报(自然科学版),2015,16(3):16 − 19. [LI Zhenlong, PAN Dianqi, YANG Shuhong, et al. The test study on influencing factors and changing rules to cement-soil mixing pile strength in marine silt characteristics[J]. Journal of Changchun Institute of Technology (Natural Sciences Edition),2015,16(3):16 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 陈中学, 李文广, 任涛, 等. 水泥土无侧限抗压强度试验分析[J]. 公路交通技术,2016,32(5):4 − 8. [CHEN Zhongxue, LI Wenguang, REN Tao, et al. Unconfined compressive strength test analysis for cement soil[J]. Technology of Highway and Transport,2016,32(5):4 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 吴家琦, 侯蕊, 李幻, 等. 水泥改良海相沉积淤泥质软黏土无侧限抗压强度试验研究[J]. 路基工程,2019(6):73 − 77. [WU Jiaqi, HOU Rui, LI Huan, et al. Study on cement modified marine sediment silty soft clay by unconfined compressive strength test[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2019(6):73 − 77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 芮凯军, 李俊才, 杨宇, 等. 不同土质水泥土性质的室内试验[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版),2019,41(2):173 − 178. [RUI Kaijun, LI Juncai, YANG Yu, et al. Laboratory tests on properties of cement soil with different soils[J]. Journal of Nanjing Tech University (Natural Science Edition),2019,41(2):173 − 178. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 陈慧娥, 王清. 有机质对水泥加固软土效果的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(增刊2):5816 − 5821. [CHEN Hui’e, WANG Qing. Influences of organic matter on the effects of consolidating soft soil with cement[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(Sup2):5816 − 5821. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 邢皓枫, 徐超, 叶观宝, 等. 可溶盐离子对高含盐水泥土强度影响的机理分析[J]. 中国公路学报,2008,21(6):26 − 30. [XING Haofeng, XU Chao, YE Guanbao, et al. Mechanism analysis of influence of soluble salt ions on strength of salt-rich cement-soil[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2008,21(6):26 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2008.06.005
[12] 傅小姝, 王江营, 张贵金, 等. 不同pH值下水泥土力学与渗透特性试验研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2017,14(8):1639 − 1646. [FU Xiaoshu, WANG Jiangying, ZHANG Guijin, et al. Experimental study about mechanic and permeability of soil-cement in different pH value[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2017,14(8):1639 − 1646. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2017.08.010
[13] 杨爱武, 闫澍旺, 杜东菊, 等. 碱性环境对固化天津海积软土强度影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(9):2930 − 2934. [YANG Aiwu, YAN Shuwang, DU Dongju, et al. Experimental study of alkaline environment effects on the strength of cement soil of Tianjin marine soft soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(9):2930 − 2934. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.09.040
[14] 徐金明, 黄亮, 涂齐亮, 等. 使用微观试验确定软土中晶质矿物的类型与含量[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(1):103 − 110. [XU Jinming, HUANG Liang, TU Qiliang, et al. Determination of types and contents of minerals included in soft soil using microscopic experiments[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(1):103 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 赵云. 宁波软土的热物性和热固结特性研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2018.
ZHAO Yun. An investigation on the thermal and thermo-consolidation behaviour of Ningbo soft soil[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李晋骅. 真空预压加固南沙软土过程中排水板淤堵行为试验研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2015.
LI Jinhua. Experimental study on clogging behavior of PVD in Nansha soft clay improved by vacuum preloading[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张可能, 王彦之, 胡惠华, 等. 洞庭湖砂纹淤泥质土固结过程微观结构变化[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(1):96 − 102. [ZHANG Keneng, WANG Yanzhi, HU Huihua, et al. An analysis of microstructure changes in sand grain mucky soil of Dongting Lake during consolidation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(1):96 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 周晖. 矿物成分对软土强度性质的影响分析[J]. 工业建筑,2013,43(7):61 − 64. [ZHOU Hui. Analysis of mineral composition impact on soft soil’s strength properties[J]. Industrial Construction,2013,43(7):61 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部.水泥土配合比设计规程: JGJ/T 233—2011[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Specification for mix proportion design of cement soil: JGJ/T 233—2011[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2011. (in Chinese)
[20] 张跃, 袁代国. 水泥土加固机理及不同成因类型软土配合比试验[J]. 化工矿物与加工,2003,32(5):28 − 29. [ZHANG Yue, YUAN Daiguo. Reinforcement mechanism of cemented soil and test of mixture ratio of different types of soft clay[J]. Industrial Minerals and Processing,2003,32(5):28 − 29. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7524.2003.05.010
[21] 黄新, 周国钧. 水泥加固土硬化机理初探[J]. 岩土工程学报,1994,16(1):62 − 68. [HUANG Xin, ZHOU Guojun. Hardening mechanism of cement-stabilized soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1994,16(1):62 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1994.01.008
-




 下载:
下载: