Spatio-temporal change and influencing factors of evapotranspiration in the Huaihe River Basin based on MODIS evapotranspiration data
-
摘要:
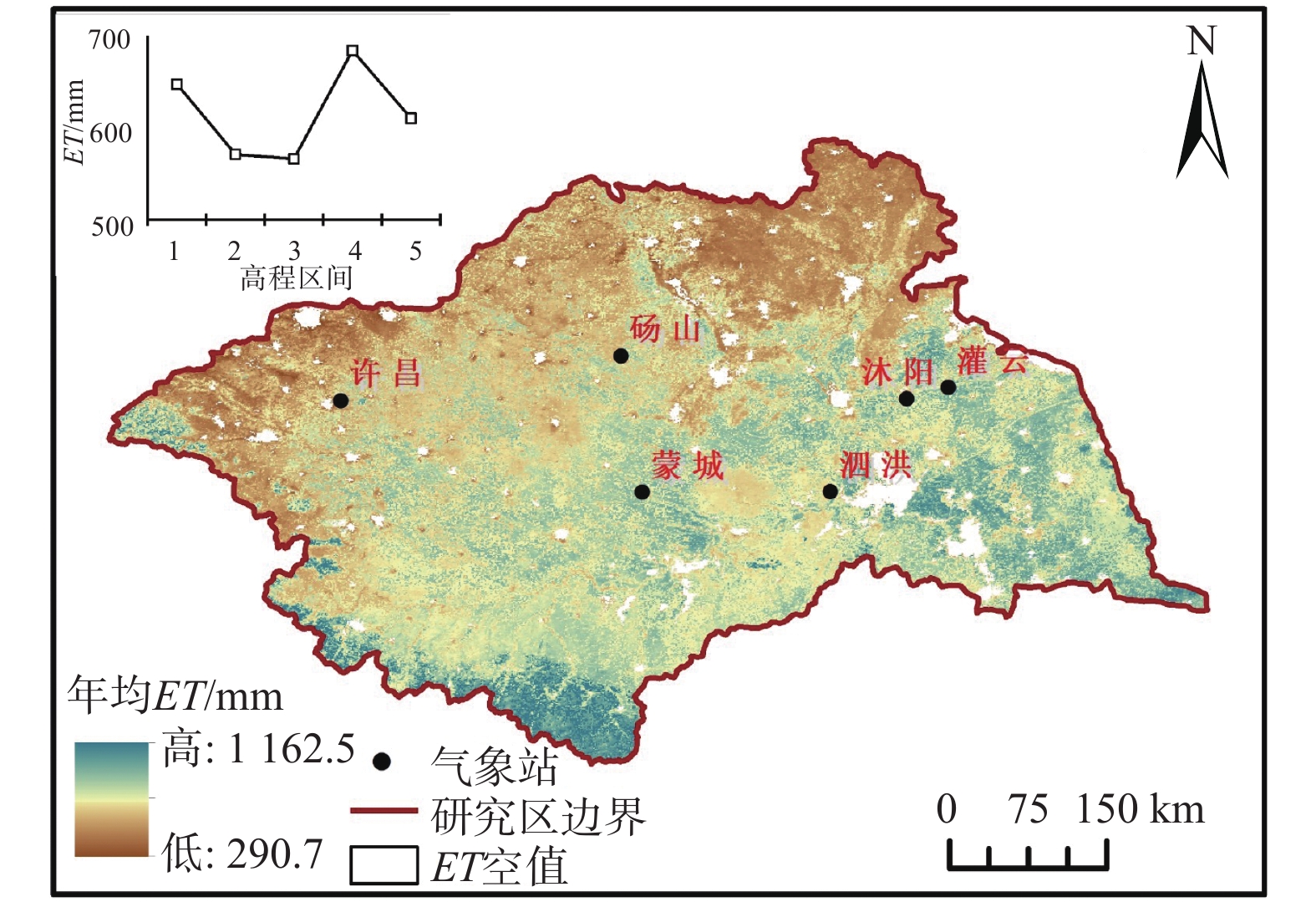
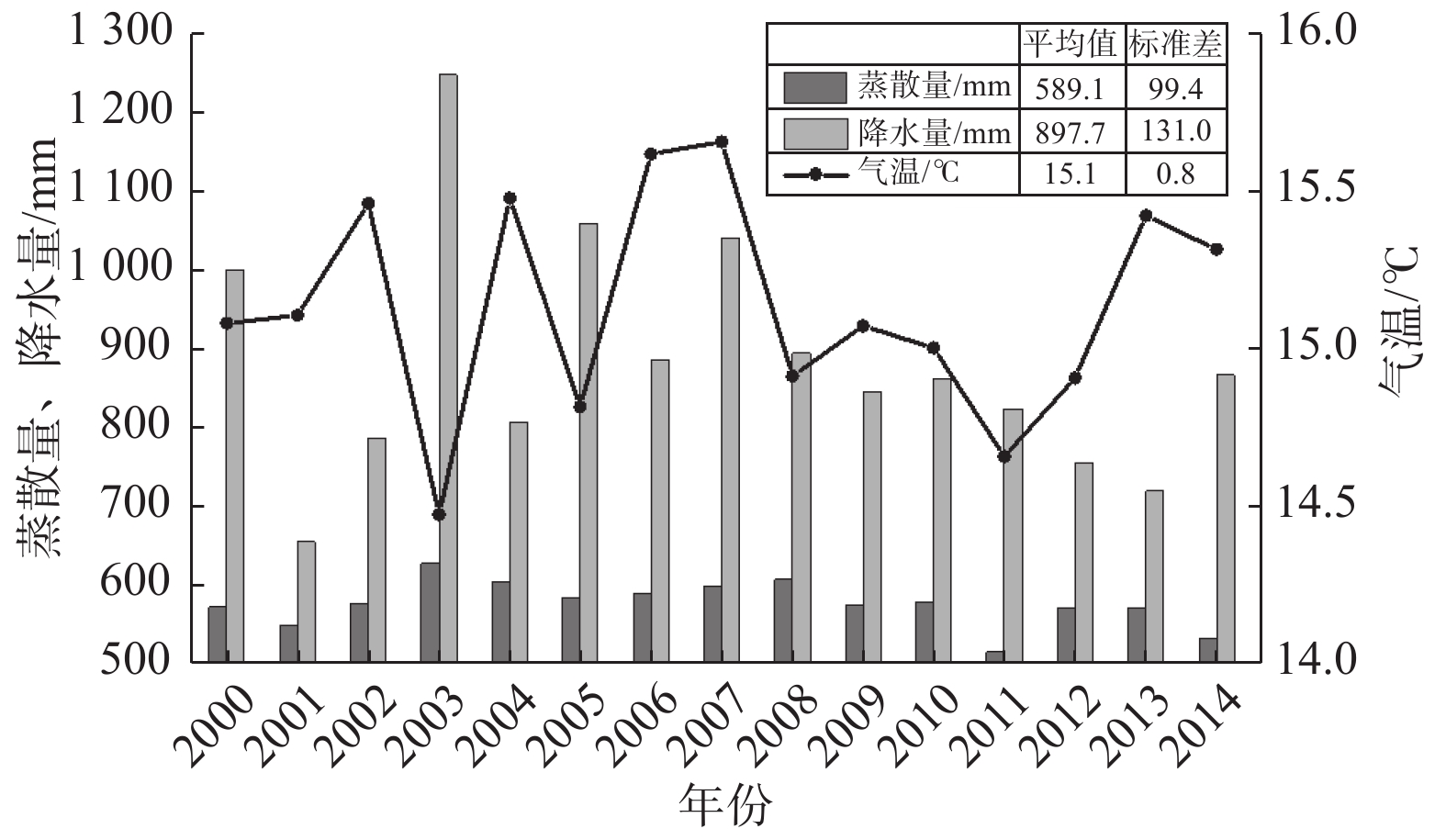
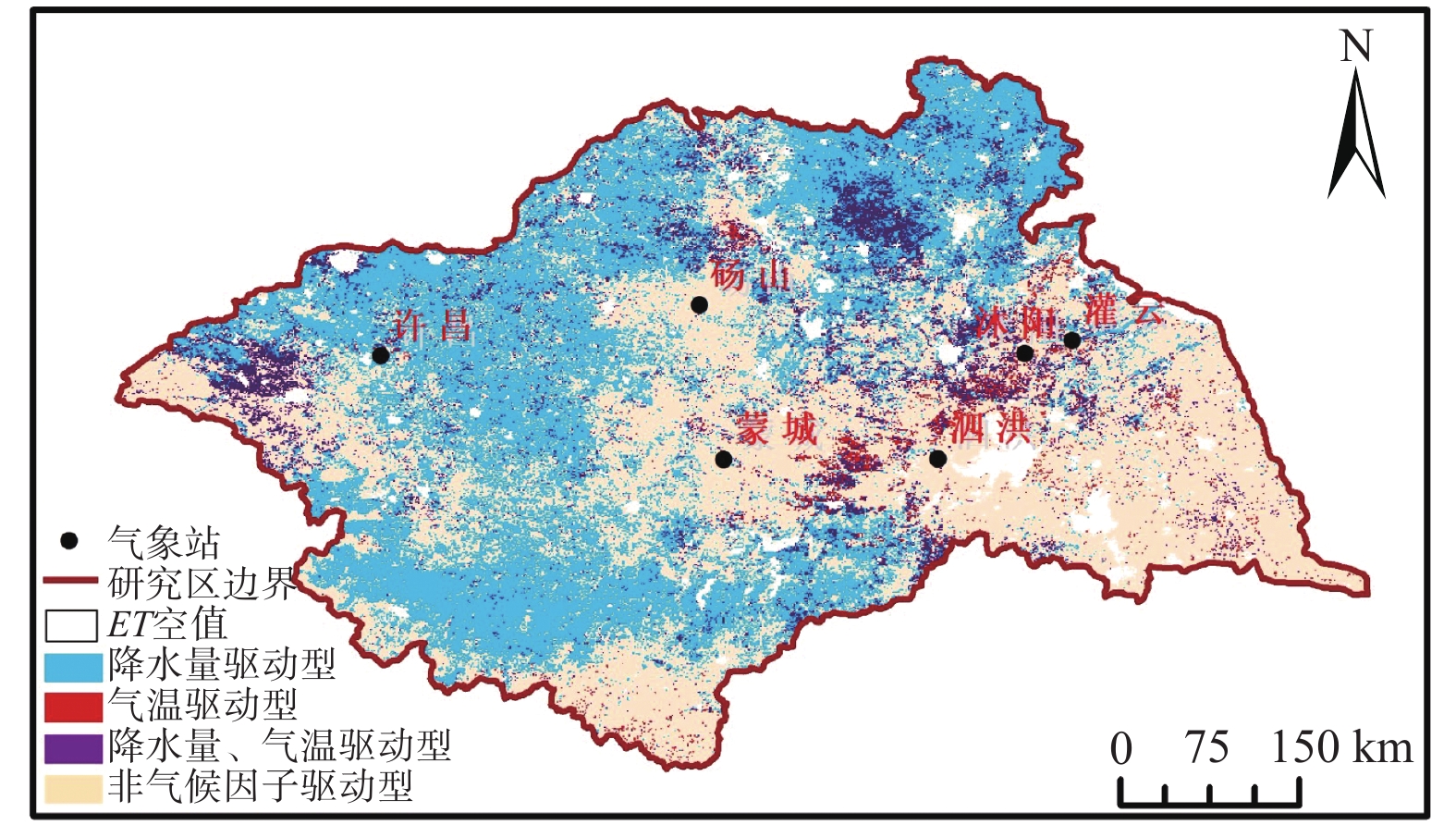
淮河流域作为我国重要的粮食产地,其水资源利用情况具有很高的研究价值。利用MODIS蒸散发数据产品(MOD16/ET)、降水和气温时序数据以及土地利用数据,探讨了淮河流域2000—2014年蒸散量时空变化特征及其对气候变化、土地利用的响应。结果表明:淮河流域蒸散量在空间上表现为南高北低,蒸散量多年均值为589.1 mm,夏季最高,冬季最低。整体而言,淮河流域15年间蒸散量具有先增加后减少的趋势;趋势分析结果显示,31.4%的地区蒸散量呈显著或极显著减少趋势,5.4%的地区蒸散量呈显著或极显著增加趋势,63.2%的地区蒸散量无显著变化。从蒸散量的气候因子分区看,52.0%的区域表现为非气候因子驱动型,44.1%的地区为降水驱动型,双因子驱动型和气温驱动型范围很小,面积占比分别为2.4%、1.5%,表明人类活动对蒸散发的影响巨大。四种植被覆盖土地利用蒸散量均值表现为林地>水田>旱地>草地。根据2000—2014年土地利用转变引起蒸散量变化的统计结果,草地转变为水田时蒸散量明显增加,旱地转变为草地、林地转变为旱地后蒸散量明显减少。
Abstract:The Huaihe River Basin is an important grain production area in China, and the utilization of water resources in the basin is of great research value. To explore the spatial-temporal characteristics of evapotranspiration (ET) in the Huaihe River Basin from 2000 to 2014 and its response to climate change and land use, MOD16/ET products, precipitation and temperature data, and land use data are used in this article. The results show that ET is high in the south and low in the north of the study area. The annual average ET is 589.1 mm, the seasonal change of ET decreases in this order: summer (257.4 mm) > spring (144.6 mm) > autumn (121.8 mm) > winter (66.3 mm). EThas an increasing trend at first and then a decreasing trend over the 15 years. According to the results of trend analysis, 31.4 % of the regions showed a significant or extremely significant decreasing trend of ET, 5.4% of the regions showed a significant or extremely significant increasing trend of ET, and 63.2% of the regions showed no significant change. Analyses of the driving climatic factors on ET change shows that about 52.0% of the study area was impacted by non-climatic driving factor, while 44.1% was driven by precipitation, and 2.4% and 1.5% were separately driven by the two climate factors and temperature, indicating that the ET change in this region is mainly affected by human activities. The average value of ET of the four types of vegetation coverage land use decreased in this order: woodland (639.29 mm) > paddy field (633.24 mm) > dry land (568.72 mm) > grassland (556.37 mm). According to the statistical results of ETof different land use types from 2000 to 2014, the conversion of grassland to paddy fields significantly increases ET, and the conversion of dry land to grassland and woodland to dry land significantly reduces ET.
-

-
表 1 变化趋势等级
Table 1. Variation trend level
变化等级 极显著减少 显著减少 不显著变化 显著增加 极显著增加 条件  <0且
<0且
 <0且
<0且
P>0.05  >0且
>0且
 >0且
>0且
P≤0.01 0.01<P≤0.05 0.01<P≤0.05 P≤0.01 表 2 淮河流域蒸散发驱动分区准则
Table 2. Rules of regionalization for the drivers of ET change
蒸散发驱动类型 分区准则 t检验(降水) t检验(气温) F检验 降水驱动型 t≥t0.05 F≥F0.05 气温驱动型 t≥t0.05 F≥F0.05 气温、降水驱动型 t≤t0.05 t≤t0.05 F≥F0.05 非气候因子驱动型 F≤F0.05 表 3 不同地貌类型划分及其蒸散量数据统计
Table 3. Classification of different geomorphic types and ET data statistics
序号 高程/m 地貌类型 平均ET/mm 标准差/mm 1 ≤20 平原 647.1 72.5 2 (20,200] 丘陵 571.2 84.6 3 (200,500] 低山 566.2 167.0 4 (500,1500] 中山 683.6 142.0 5 >1500 高山 610.1 91.7 表 4 淮河流域不同土地利用类型年均蒸散量统计
Table 4. Annual average ET of different land use types in the Huaihe River Basin
年份 水田 旱地 林地 草地 面积/
(104 km2)均值/mm 总量/
(108 m3)面积/
(104 km2)均值/mm 总量/
(108 m3)面积/
(104 km2)均值/mm 总量/
(108 m3)面积/
(104 km2)均值/mm 总量/
(108m3)2000年 4.56 633.24 289.02 14.04 568.72 798.36 1.82 639.29 116.63 0.97 556.37 53.76 2005年 4.56 636.26 289.35 13.96 582.38 812.90 1.83 656.59 120.39 0.95 561.65 53.39 2010年 4.51 664.50 299.77 13.90 570.22 792.41 1.84 662.17 121.72 0.95 556.24 52.85 2014年 4.49 603.27 270.75 13.80 533.41 736.35 1.83 616.47 113.18 0.96 507.93 48.63 -
[1] ZHENG C, WANG Q. Spatiotemporal variations of reference evapotranspiration in recent five decades in the arid land of Northwestern China[J]. Hydrological Processes,2014,28(25):6124 − 6134. doi: 10.1002/hyp.10109
[2] 席丹, 王文科, 赵明, 等. 玛纳斯河流域山前平原区蒸散发时空异质性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):25 − 34. [XI Dan, WANG Wenke, ZHAO Ming, et al. Analyses of the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of evapotranspiration in the piedmont of the Manas River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):25 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] CHENG L Z, YANG M X, WANG X J, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of terrestrial evapotranspiration in the upper Taohe River Basin from 2001 to 2018 based on MOD16 ET data[J]. Advances in Meteorology,2020:1 − 17.
[4] AGUILAR AL, FLORES H, CRESPO G, et al. Performance assessment of MOD16 in evapotranspiration evaluation in Northwestern Mexico[J]. Water,2018,10(7):901 − 914.
[5] 王松, 田巍, 刘小莽, 等. 不同蒸散发产品在汉江流域的比较研究[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2018,16(3):1 − 9. [WANG Song, TIAN Wei, LIU Xiaomang, et al. Comparisons of various evapotranspiration products in the Hanjiang River Basin[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science &Technology,2018,16(3):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 黄瑾, 王文, 崔巍, 等. 云贵地区几种潜在蒸散发产品质量评估[J]. 人民长江,2019,50(12):73 − 79. [HUANG Jin, WANG Wen, CUI Wei, et al. Evaluation of several evapotranspiration products over Yunnan-Guizhou region in China[J]. Yangtze River,2019,50(12):73 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 邓兴耀, 刘洋, 刘志辉, 等. 中国西北干旱区蒸散发时空动态特征[J]. 生态学报,2017,37(9):2994 − 3008. [DENG Xingyao, LIU Yang, LIU Zhihui, et al. Temporal-spatial dynamic change characteristics of evapotranspiration in arid region of Northwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2017,37(9):2994 − 3008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 马梓策, 于红博, 张巧凤. 2000-2017年锡林河流域地表蒸散量的时空特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2020(3):18 − 24. [MA Zice, YU Hongbo, ZHANG Qiaofeng. Spatio-temporal characteristics of evapotranspiration and its influencing factors in Xilin River Basin from 2000 to 2017[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2020(3):18 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 邱丽莎, 张立峰, 何毅, 等. 2000-2018年祁连山蒸散发时空变化及影响因素[J]. 水土保持研究,2020,27(3):210 − 217. [QIU Lisha, ZHANG Lifeng, HE Yi, et al. Spatiotemporal variations of evapotranspiration and influence factors in Qilian Mountain from 2000 to 2018[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,27(3):210 − 217. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 薛明慧. 基于MOD16数据的河南省和山东省干旱的时空分布特征[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报,2020,15(2):81 − 87. [XUE Minghui. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of drought in Henan and Shandong provinces based on MOD16[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment,2020,15(2):81 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张高强. 乌审召盆地植被、蒸散与地下水的相互关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.
ZHANG Gaoqiang. The relationships among vegetation, evapotranspiration and groundwater in the Wushenzhao Basin, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 高瑜莲, 柳锦宝, 柳维扬. 基于混合型线性双源遥感蒸散模型的南疆绿洲地区干旱研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2019,37(6):231 − 237. [GAO Yulian, LIU Jinbao, LIU Weiyang, et al. Analysis of drought in the oasis of Southern Xinjiang based on the hybrid linear dual source remote sensing evapotranspiration model[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2019,37(6):231 − 237. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 蒙雨, 但文红, 王焕. 基于MOD16的乌江流域地表蒸散发时空特征及影响因素[J]. 水土保持研究,2020,27(6):139 − 145. [MENG Yu, DAN Wenhong, WANG Huan. Spatiotemporal characteristics of evapotranspiration and its affecting factors in Wujiang Basin based on MOD16[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,27(6):139 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 温媛媛, 赵军, 王炎强, 等. 基于MOD16的山西省地表蒸散发时空变化特征分析[J]. 地理科学进展,2020,39(2):255 − 264. [WEN Yuanyuan, ZHAO Jun, WANG Yanqiang, et al. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of surface evapotranspiration in Shanxi Province based on MOD16[J]. Progress in Geography,2020,39(2):255 − 264. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.02.007
[15] 梁红闪, 王丹, 郑江华. 伊犁河流域地表蒸散量时空特征分析[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2020,39(7):100 − 110. [LIANG Hongshan, WANG Dan, ZHENG Jianghua. Temporal and spatial characteristics of surface evapotranspiration in the Ili River Basin[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2020,39(7):100 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 黄葵, 卢毅敏, 魏征, 等. 土地利用和气候变化对海河流域蒸散发时空变化的影响[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2019,21(12):1888 − 1902. [HUANG Kui, LU Yimin, WEI Zheng, et al. Effects of land use and climate change on spatiotemporal changes of evapotranspiration in Haihe River Basin[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science,2019,21(12):1888 − 1902. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李鑫川, 徐金梦, 朱玲玉, 等. 2000—2016年淮河流域叶面积指数时空变化特征[J]. 水土保持,2019,7(4):71 − 79. [LI Xinchuan, XU Jinmeng, ZHU Lingyu, et al. Variations of LAI in Huaihe River Basin during 2000—2016[J]. Open Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,7(4):71 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12677/OJSWC.2019.74010
[18] 孟丹, 李小娟, 宫辉力, 等. 京津冀地区NDVI变化及气候因子驱动分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2015,17(8):1001 − 1007. [MENG Dan, LI Xiaojuan, GONG Huili, et al. Analysis of spatial-temporal change of NDVI and its climatic driving factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolis circle from 2001 to 2013[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2015,17(8):1001 − 1007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 褚荣浩, 申双和, 李萌, 等. 小型与E-601型蒸发皿蒸发量对比分析及其折算系数—以江苏省为例[J]. 气象科学,2018,38(2):247 − 257. [CHU Ronghao, SHEN Shuanghe, LI Meng, et al. Comparative analysis of small and E-601 pan evaporation and its conversion coefficient: Taking Jiangsu Province as an example[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences,2018,38(2):247 − 257. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 任芝花, 黎明琴, 张纬敏. 小型蒸发器对E-601B蒸发器的折算系数[J]. 应用气象学报,2002(4):508 − 514. [REN Zhihua, LI Mingqin, ZHANG Weimin. Conversion coefficient of smail evaporation pan into E-601B pan in China[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science,2002(4):508 − 514. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 姜艳阳, 王文, 周正昊. MODIS MOD16蒸散发产品在中国流域的质量评估[J]. 自然资源学报,2017,32(3):517 − 528. [JIANG Yanyang, WANG Wen, ZHOU Zhenghao. Evaluation of MODIS MOD16 evapotranspiration product in Chinese river basins[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2017,32(3):517 − 528. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王耕, 李素娟, 张兴国. 基于DEM的淮河源地貌形态类型划分[J]. 水土保持通报,2012,38(2):292 − 296. [WANG Geng, LI Sujuan, ZHANG Xingguo. Classification of geomorphic forms of Huaihe River source based on DEM[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2012,38(2):292 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王润元, 杨兴国, 张九林, 等. 陇东黄土高原土壤储水量与蒸发和气候研究[J]. 地球科学进展,2007(6):625 − 635. [WANG Runyuan, YANG Xingguo, ZHANG Jiulin, et al. A study of soil water and land surface evaporation and climate on Loess Plateau in the Eastern Gansu Province[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2007(6):625 − 635. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: