A review of the advances in water source composition and observation methods of evapotranspiration
-
摘要:
地表蒸散发是地下水-地表水-土壤-植物-大气连续体(GSSPAC)中水分和能量传输的纽带,也是研究陆面水量平衡的关键环节。受气象条件、地质地貌、水文地质条件和人类活动的影响,蒸散发过程机理复杂、时空变异性大,是目前水循环研究的热点之一。在大量文献调研的基础上,本文综合分析了国内外学者围绕蒸散发水源组成和测定方法方面取得的研究成果,得到以下认识:(1)蒸散发的水分来源及其组成逐渐明确,地表水(河流、湖泊等)、土壤水、地下水和植被截留的水分是蒸散发主要的水分来源;(2)蒸散发测定方法可分为水文学方法、植物生理学方法、微气象学方法和同位素方法等,这些方法在研究蒸散发过程和驱动机制等方面具有优势;(3)不同蒸散发测定方法适用的时空尺度不同,可以综合多种测定方法获取更为可靠的蒸散发数据。根据蒸散发测定研究的现状,下一步应该加强GSSPAC系统中水分运移耦合机制的研究,并加强多学科交叉研究,进一步厘清水分、能量和物质循环和流动的相互作用机制。另外,通过不同气候和地貌单元上监测网络的建设,可以获取多重影响因素交互下的蒸散发变化规律与基础数据,以期为大尺度、精细化蒸散发研究提供支撑。
Abstract:Evapotranspiration is the link of water and energy transfer in the continuum of groundwater, surface water, soil, plants and the atmosphere (GSSPAC). Evapotranspiration is also a key in the study of land surface water balance. Affected by meteorological conditions, geological landforms, hydrogeological conditions and human activities, the mechanism of evapotranspiration process is complex, and its temporal and spatial variability is quite large. Based on many published journal papers, this paper comprehensively analyzes water resources and observation methods for evapotranspiration proposed by scholars at home and abroad. The results show that (1) surface water (rivers, lakes, etc.), soil water, groundwater and vegetation intercepted water are the major water sources of evapotranspiration. (2) The methods for measuring evapotranspiration can be divided into hydrology method, plant physiology method, micro-meteorological method and isotope method. These methods have advantages in studying the process and driving mechanism of evapotranspiration. (3) Different evapotranspiration measurement methods are suitable for different spatiotemporal scales, and more reliable evapotranspiration data can be obtained by integrating various measurement methods. According to the current situation of evapotranspiration researches, the next step is to strengthen the coupling mechanism researches of water transport in the GSSPAC system, and strengthen interdisciplinary researches to further clarify the interaction mechanism of water, energy and material cycle and flow. In addition, through the construction of monitoring network on different climate and geomorphic units, we can gain basic data of evapotranspiration variation under the interaction of multiple influencing factors, which can support large-scale and refined evapotranspiration researches.
-
Key words:
- evapotranspiration /
- water cycle /
- water source /
- observation methods
-

-
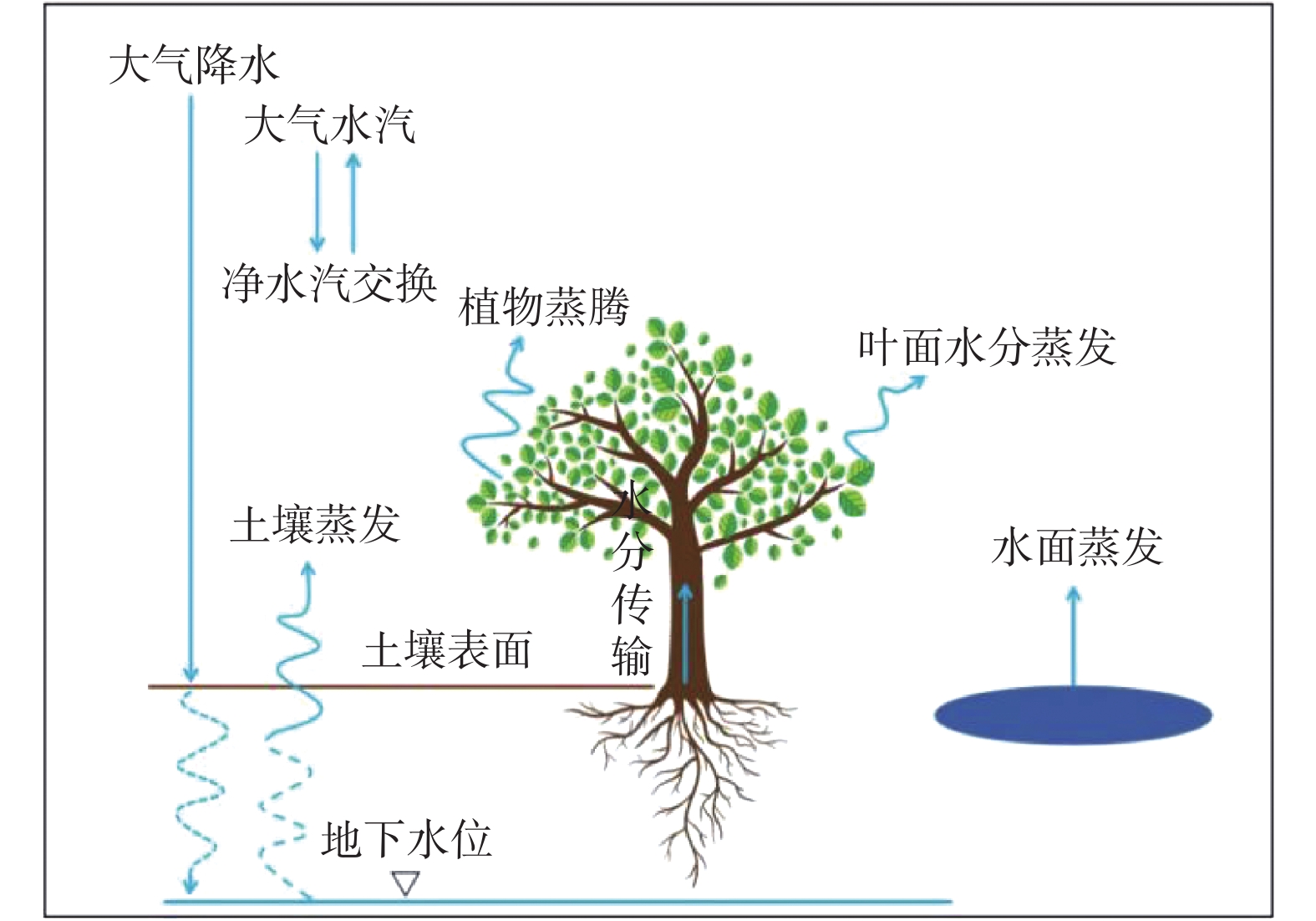
图 1 陆面的蒸散发组成(改自Zhang等[1])
Figure 1.
-
[1] ZHANG J H, BAI Y, YAN H, et al. Linking observation, modelling and satellite-based estimation of global land evapotranspiration[J]. Big Earth Data,2020,4(2):94 − 127. doi: 10.1080/20964471.2020.1743612
[2] WANG K C, DICKINSON R E, WILD M, et al. Evidence for decadal variation in global terrestrial evapotranspiration between 1982 and 2002: 1. Model development[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,2010,115(D20):D20112. doi: 10.1029/2009JD013671
[3] JASECHKO S, SHARP Z D, GIBSON J J, et al. Terrestrial water fluxes dominated by transpiration[J]. Nature,2013,496:347 − 350. doi: 10.1038/nature11983
[4] MAXWELL R M, CONDON L E. Connections between groundwater flow and transpiration partitioning[J]. Science,2016,353:377 − 380. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf7891
[5] SWINBANK W G. An experimental study of eddy transports the lower atmosphere[M]. Melbourne: Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization, 1955.
[6] 郭小娇, 石建省. 水分蒸散发研究国内外进展与趋势[J]. 地质论评,2019,65(6):1473 − 1486. [GUO Xiaojiao, SHI Jiansheng. Global review of the research progress and trend of evapotranspiration[J]. Geological Review,2019,65(6):1473 − 1486. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 杨瀚凌, 罗维均, 王彦伟, 等. 不同尺度下蒸散量测算方法的应用及展望[J]. 地球环境学报,2020,11(1):31 − 44. [YANG Hanling, LUO Weijun, WANG Yanwei, et al. Application and prospect of evapotranspiration measuring methods under different scales[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2020,11(1):31 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 尹剑, 欧照凡, 付强, 等. 区域尺度蒸散发遥感估算—反演与数据同化研究进展[J]. 地理科学,2018,38(3):448 − 456. [YIN Jian, OU Zhaofan, FU Qiang, et al. Review of current methodologies for regional evapotranspiration estimation: inversion and data assimilation[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2018,38(3):448 − 456. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 张圆, 贾贞贞, 刘绍民, 等. 遥感估算地表蒸散发真实性检验研究进展[J]. 遥感学报,2020,24(8):975 − 999. [ZHANG Yuan, JIA Zhenzhen, LIU Shaomin, et al. Advances in validation of remotely sensed land surface evapotranspiration[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing,2020,24(8):975 − 999. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] LI X, LIU S M, LI H X, et al. Intercomparison of six upscaling evapotranspiration methods: from site to the satellite pixel[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres,2018,123(13):6777 − 6803. doi: 10.1029/2018JD028422
[11] XU Y, XU Y P, WANG Y F, et al. Spatial and temporal trends of reference crop evapotranspiration and its influential variables in Yangtze River Delta, Eastern China[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2017,130(3/4):945 − 958.
[12] 李晓媛, 于德永. 蒸散发估算方法及其驱动力研究进展[J]. 干旱区研究,2020,37(1):26 − 36. [LI Xiaoyuan, YU Deyong. Progress on evapotranspiration estimation methods and driving forces in arid and semiarid regions[J]. Arid Zone Research,2020,37(1):26 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] MASSON-DELMOTTE, ZHAI P, PÖRTHER H O, et al. Global warming of 1.5 °C[R]. 2018.
[14] 薛阳, 金晓媚, 朱晓倩. 宁夏沿黄经济区蒸散量变化特征及水均衡方法验证[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(3):27 − 32. [XUE Yang, JIN Xiaomei, ZHU Xiaoqian. Variation of evapotranspiration of Ningxia Yellow River economic zone and the validation using water budget method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(3):27 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 朱晓倩, 金晓媚, 张绪财, 等. 格尔木河流域山前平原区蒸散量的分布特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5):55 − 64. [ZHU Xiaoqian, JIN Xiaomei, ZHANG Xucai, et al. Distribution characteristics of evapotranspiration in the valley piedmont plain of the Golmud River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(5):55 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] MIRALLES D G, BRUTSAERT W, DOLMAN A J, et al. On the use of the term “evapotranspiration”[J]. Water Resources Research,2020,56(11):e2020WR028055.
[17] WEI Z, YOSHIMURA K, WANG L, et al. Revisiting the contribution of transpiration to global terrestrial evapotranspiration[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2017,44(6):2792 − 2801. doi: 10.1002/2016GL072235
[18] 杨建锋, 李宝庆, 刘士平, 等. 地下水对农田腾发过程作用研究进展[J]. 农业工程学报,2000,16(4):45 − 49. [YANG Jianfeng, LI Baoqing, LIU Shiping, et al. Review on progress of effects of groundwater on evapotranspiration in farmland[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2000,16(4):45 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 席丹, 王文科, 赵明, 等. 玛纳斯河流域山前平原区蒸散发时空异质性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):25 − 34. [XI Dan, WANG Wenke, ZHAO Ming, et al. Analyses of the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of evapotranspiration in the piedmont of the Manas River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):25 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] MA Z T, WANG W K, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Assessing bare-soil evaporation from different water-table depths using lysimeters and a numerical model in the Ordos Basin, China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2019,27(7):2707 − 2718. doi: 10.1007/s10040-019-02012-0
[21] 李红寿, 汪万福, 张国彬, 等. 用拱棚法对极干旱区GSPAC水分运转的分析[J]. 干旱区地理,2010,33(4):572 − 579. [LI Hongshou, WANG Wanfu, ZHANG Guobin, et al. GSPAC water movement by greenhouse method in the extremely dry area[J]. Arid Land Geography,2010,33(4):572 − 579. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 许文豪, 尹立河, 贾伍慧, 等. 环境因素对毛乌素沙地旱柳树干液流的影响分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):102 − 108. [XU Wenhao, YIN Lihe, JIA Wuhui, et al. Impact of environmental factors on the Sap flow of willows in the Muus Sandland[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(2):102 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 刘昌明. 土壤-植物-大气系统水分运行的界面过程研究[J]. 地理学报,1997,52(4):366 − 373. [LIU Changming. Study on interface processes of water cycle in soil plant atmosphere continuum[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,1997,52(4):366 − 373. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 杨建锋, 李宝庆, 李运生, 等. 浅地下水埋深区潜水对SPAC系统作用初步研究[J]. 水利学报,1999,30(7):27 − 32. [YANG Jianfeng, LI Baoqing, LI Yunsheng, et al. Preliminary studies on groundwater effects on SPAC system in shallow groundwater field[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,1999,30(7):27 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] WANG W K, LI J T, WANG W M, et al. Estimating streambed parameters for a disconnected river[J]. Hydrological Processes,2014,28(10):3627 − 3641. doi: 10.1002/hyp.9904
[26] DALTON J. Experimental Essays[M]. USD: University of Hawaii Press, 1802: 392-395.
[27] BOWEN I S. The ratio of heat losses by conduction and by evaporation from any water surface[J]. Physical Review,1926,27(6):779. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.27.779
[28] WANG T I, OCHS G R, CLIFFORD S F. A saturation-resistant optical scintillometer to measure Cn2[J]. JOSA,1978,68(3):334 − 338. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.68.000334
[29] 张珂, 鞠艳, 李致家. 金沙江流域实际蒸散发遥感重建及时空特征分析[J]. 水科学进展, 2020,32(2):182-191.
ZHANG Ke, JU Yan, LI Zhijia. Satellite-based reconstruction and spatiotemporal variability analysis of actual evapotranspiration in the Jinshajiang basin, China[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2020,32(2):182-191.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] CHEN J L, TAPLEY B, SEO K W, et al. Improved quantification of global mean ocean mass change using GRACE satellite gravimetry measurements[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2019,46(23):13984 − 13991. doi: 10.1029/2019GL085519
[31] 赵华. 不同尺寸蒸渗仪测定农田蒸散量的对比及冠层阻力的模拟研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2015.
ZHAO Hua. Measurement of crop evapotranspiration via lysimeters with different diameters and simulation of canopy resistance[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 王文科, 宫程程, 张在勇, 等. 旱区地下水文与生态效应研究现状与展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2018,33(7):702 − 718. [WANG Wenke, GONG Chengcheng, ZHANG Zaiyong, et al. Research status and prospect of the subsurface hydrology and ecological effect in arid regions[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2018,33(7):702 − 718. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 王文科, 李俊亭, 侯莉莉, 等. 温差条件下的蒸发模拟试验系统: CN202442980U[P]. 2012-09-19.
WANG Wenke, LI Junting, HOU Lili, et al. Evaporation simulation test system under temperature difference condition: CN202442980U[P]. 2012-09-19.(in Chinese)
[34] 王文科, 李俊亭, 王哲, 等. 咸水水面蒸发试验系统: CN202442936U[P]. 2012-09-19.
WANG Wenke, LI Junting, WANG Zhe, et al. Water surface evaporation testing system for salt water: CN202442936U[P]. 2012-09-19.(in Chinese)
[35] 李俊亭, 王文科, 王哲, 等. 水面蒸发试验系统: CN202443138U[P]. 2012-09-19.
LI Junting, WANG Wenke, WANG Zhe, et al. Water surface evaporation testing system: CN202443138U[P]. 2012-09-19.(in Chinese)
[36] 申圆圆, 李俊亭, 王文科, 等. 全自动蒸发降水计量用数据采集装置: CN203721111U[P]. 2014-07-16.
SHEN Yuanyuan, LI Junting, WANG Wenke, et al. Automatic data acquisition device for measurement of evaporation and rainfall: CN203721111U[P]. 2014-07-16.(in Chinese)
[37] 杨泽元. 地下水引起的表生生态效应及其评价研究——以秃尾河流域为例[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2004.
YANG Zeyuan. Study on supergene ecological effect excited by groundwater and its evaluation —take Tuwei river drainage as an example[D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 赵贵章. 鄂尔多斯盆地风沙滩地区包气带水—地下水转化机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2011.
ZHAO Guizhang. Study on transformation mechanism of vadose zone water-groundwater in the wind-blown sand area of the Ordos basin[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] 黄金廷. 半干旱区蒸散发对地下水变化响应机制研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2013.
HUANG Jinting. The responses of evapotranpiration to the groundwater changes in the semi-arid area[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[40] 张蕾. 水面蒸发尺度效应及其与气象要素关系研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2015.
ZHANG Lei. The relationship between the water surface evaporation scale effect and its meteorological parameters[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] 祁泽学. 水面蒸发盐度效应及影响因素研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2015.
QI Zexue. Study on the water evaporation salinity effect and the influencing factors[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] 安可栋. 旱区土气界面水热传输机理及对包气带水热运移的影响[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016.
AN Kedong. Mechanism of heat and water transfer at the land-atmosphere interface and its effects on the heat and water flow in vadose zone in an arid region[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[43] 李婉歆. 不同岩性饱和裸土潜在蒸发量规律研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2017.
LI Wanxin. The law of potential evaporation between different saturated soils[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[44] 李合生. 现代植物生理学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006.
LI Hesheng. Modern plant physiology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[45] NOURI H, BEECHAM S, KAZEMI F, et al. A review of ET measurement techniques for estimating the water requirements of urban landscape vegetation[J]. Urban Water Journal,2013,10(4):247 − 259. doi: 10.1080/1573062X.2012.726360
[46] ALLEN R G, PEREIRA L S, HOWELL T A, et al. Evapotranspiration information reporting: I. Factors governing measurement accuracy[J]. Agricultural Water Management,2011,98(6):899 − 920. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2010.12.015
[47] GARRATT J R, HICKS B B. Micrometeorological and PBL experiments in Australia[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology,1990,50(1/2/3/4):11 − 29.
[48] BALDOCCHI D. ‘Breathing’ of the terrestrial biosphere: lessons learned from a global network of carbon dioxide flux measurement systems[J]. Australian Journal of Botany,2008,56(1):1-26. doi: 10.1071/BT07151
[49] 于贵瑞, 张雷明, 孙晓敏. 中国陆地生态系统通量观测研究网络(ChinaFLUX)的主要进展及发展展望[J]. 地理科学进展,2014,33(7):903 − 917. [YU Guirui, ZHANG Leiming, SUN Xiaomin. Progresses and prospects of Chinese terrestrial ecosystem flux observation and research network (ChinaFLUX)[J]. Progress in Geography,2014,33(7):903 − 917. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[50] WILSON K B, HANSON P J, MULHOLLAND P J, et al. A comparison of methods for determining forest[J]. Australian Journal of Botany,2001,56(1):153 − 168.
[51] FOKEN T. The energy balance closure problem: an overview[J]. Ecological Applications,2008,18(6):1351 − 1367. doi: 10.1890/06-0922.1
[52] ZHANG H, ZHANG H S. Comparison of turbulent sensible heat flux determined by large-aperture scintillometer and eddy covariance over urban and suburban areas[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology,2015,154(1):119 − 136. doi: 10.1007/s10546-014-9965-8
[53] 孙根厚, 胡泽勇, 王介民, 等. 那曲地区两种空间尺度感热通量的对比分析[J]. 高原气象,2016,35(2):285 − 296. [SUN Genhou, HU Zeyong, WANG Jiemin, et al. Comparison analysis of sensible heat fluxes at two spatial scales in Naqu area[J]. Plateau Meteorology,2016,35(2):285 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[54] LIU S M, XU Z W, ZHU Z L, et al. Measurements of evapotranspiration from eddy-covariance systems and large aperture scintillometers in the Hai River Basin, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2013,487:24 − 38. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.02.025
[55] 吴友杰, 杜太生. 基于氧同位素的玉米农田蒸散发估算和区分[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(4):127 − 134. [WU Youjie, DU Taisheng. Estimating and partitioning evapotranspiration of maize farmland based on stable oxygen isotope[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020,36(4):127 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[56] STOY P C, ELMADANY T S, FISHER J B, et al. Reviews and syntheses: Turning the challenges of partitioning ecosystem evaporation and transpiration into opportunities[J]. Biogeosciences,2019,16(19):3747 − 3775. doi: 10.5194/bg-16-3747-2019
[57] WU Y J, DU T S, DING R S, et al. Multiple methods to partition evapotranspiration in a maize field[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology,2017,18(1):139 − 149. doi: 10.1175/JHM-D-16-0138.1
[58] KEELING C D. The concentration and isotopic abundances of atmospheric carbon dioxide in rural areas[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1958,13(4):322 − 334. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(58)90033-4
[59] CRAIG H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters[J]. Science,1961,133(3465):1702 − 1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
[60] HSIEH J C C, CHADWICK O A, KELLY E F, et al. Oxygen isotopic composition of soil water: Quantifying evaporation and transpiration[J]. Geoderma,1998,82(1/2/3):269 − 293.
-



 下载:
下载: