Investigating weathering features of sandstones in the Yungang Grottoes based on SEM images and micro-scale flow model
-
摘要:
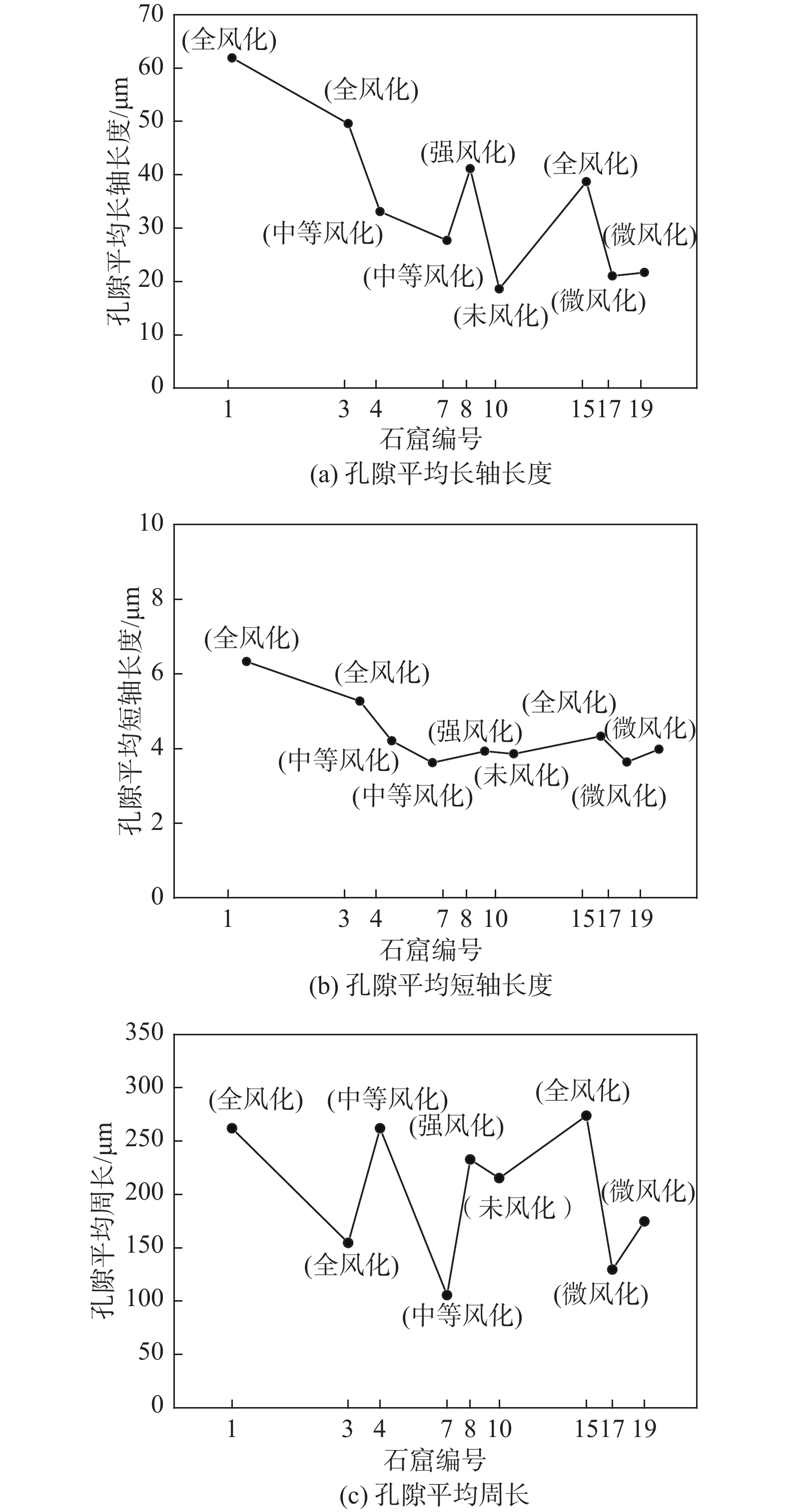
风化作用、岩石微观结构、岩石微观渗流特性定量关系的研究是石窟文物有效保护的重要基础,砂岩风化作用严重影响了岩体上石窟文物的有效保护。本次研究使用扫描电镜(SEM)获得云冈石窟不同窟体砂岩的微观图像,根据图像增强和图像分割技术得到了岩石中颗粒和孔隙的数字特征参数,从微观角度建立了反映孔喉连接特性的渗流模型,得到了不同窟体岩石的局部水力传导系数,分析了数字特征参数、水力传导系数、风化作用之间的关系。结果表明,风化作用对石窟砂岩微观结构具有很大影响;砂岩孔隙平均长轴长度大小对应的风化程度分别是全风化或强风化、中等风化、微风化或未风化,长度分别为大于40 μm、25~35 μm、15~25 μm;风化程度越高、水力传导系数越大,随着风化程度的增高、水力传导系数的范围为1 × 10−9~1 × 10−4 cm/s;水力传导系数与孔喉尺寸、孔喉连通性密切相关;孔喉半径比增大时、水力传导系数也增大。
Abstract:The quantitative relationship among the weathering, microscale structure, and microscale flow properties is a fundamental issue for the efficient preservation of the cultural relics in the grottoes. Sandstone weathering may affect the efficient preservation of the cultural relics in the grotto rocks. In this study, the microscopic images of the sandstones of various grottoes in the Yungang Grottoes are obtained by Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM), and the digital characteristic parameters of the particles and pores in the rock are obtained by using the image enhancement and image segmentations. A flow model reflecting the characteristics of the pore-throat connection is also established in the microscopic scale. The local hydraulic conductivity coefficients of the rocks at various grottoes are then obtained. The relationship among the hydraulic conductivity coefficients, digital characteristic parameters, and weathering levels is further explored. The results show that the weathering much affects the microstructure of the grotto sandstones; the corresponding great-small order of the weathering for the average long axeses of pores are the complete or high weathering, the moderate weathering, and the slight weathering or fresh sandstones, respectively, with the axeses of greater than 40 μm, 25 to 35 μm, and 15 to 25 μm. The higher levels of weathering will result in the greater hydraulic conductivities ranging from 1×10−9 to 1×10−4 cm/s; the hydraulic conductivity is closely related to the size and connectivity of the pore-throats; and the increases in the pore-throat radius ratios will result in the increase in the hydraulic conductivities.
-

-
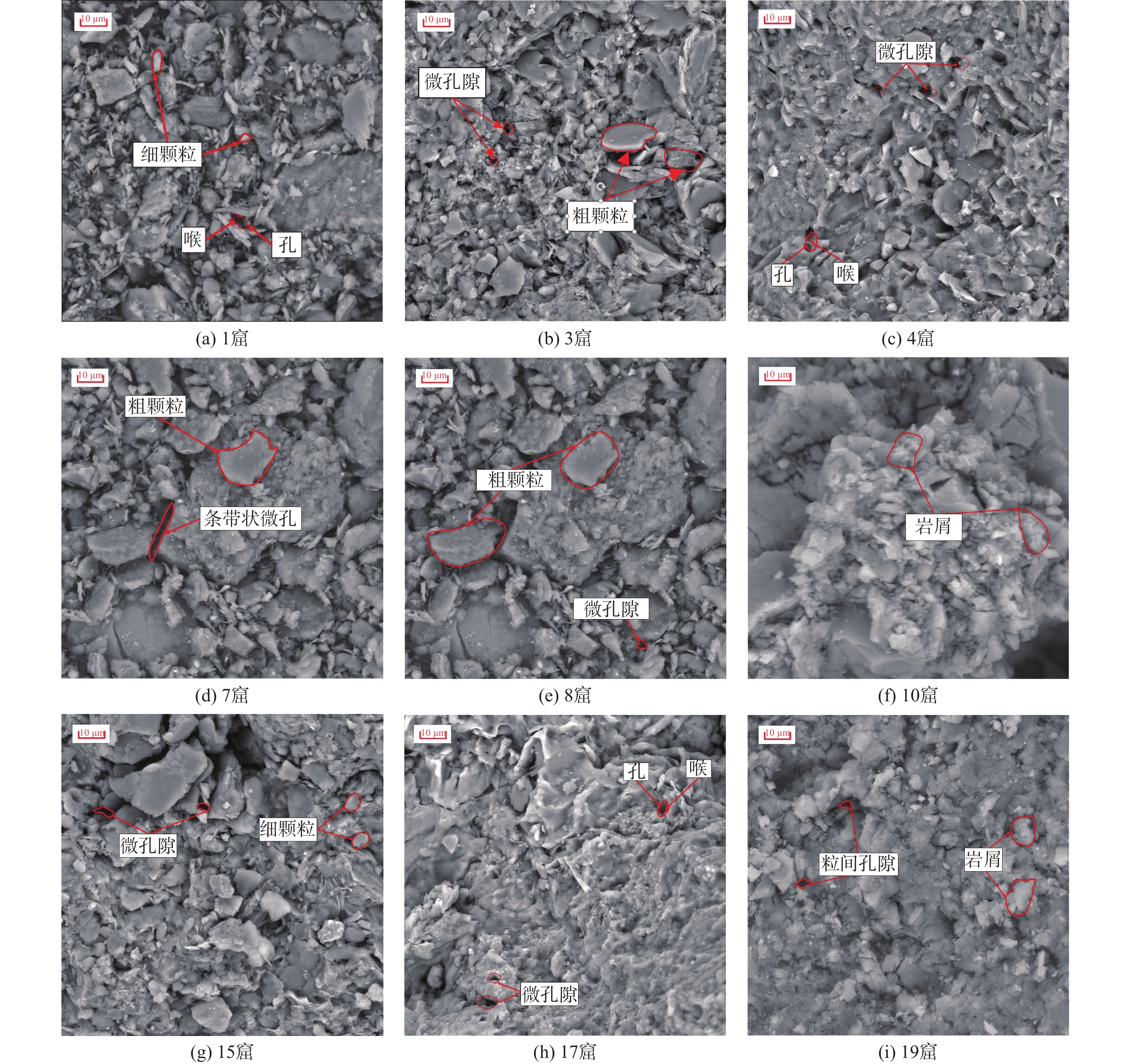
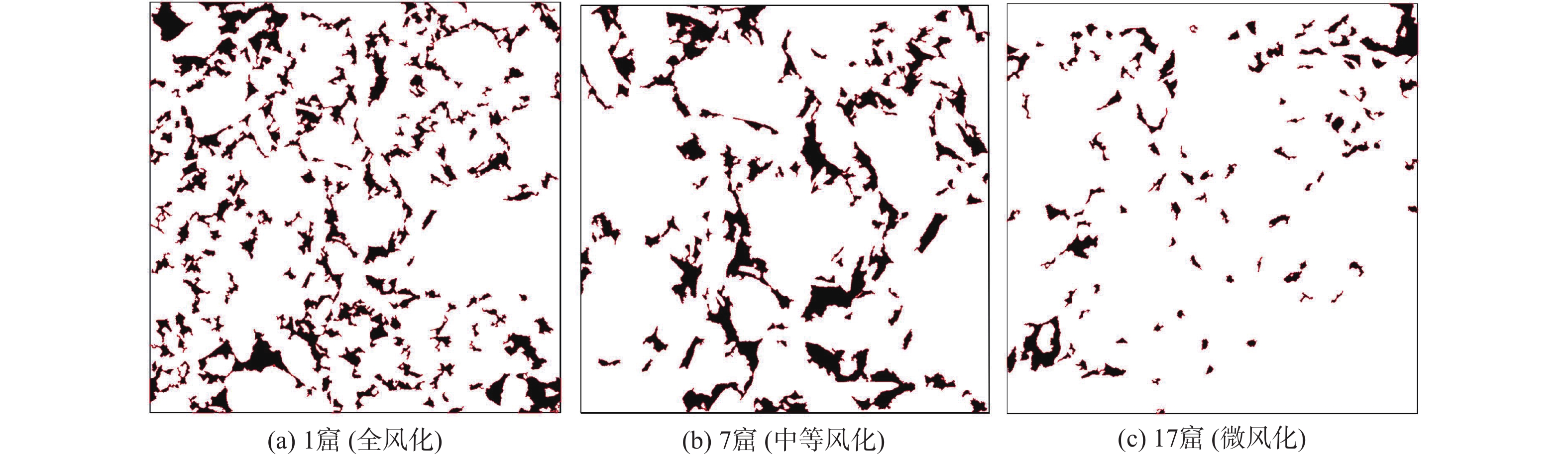
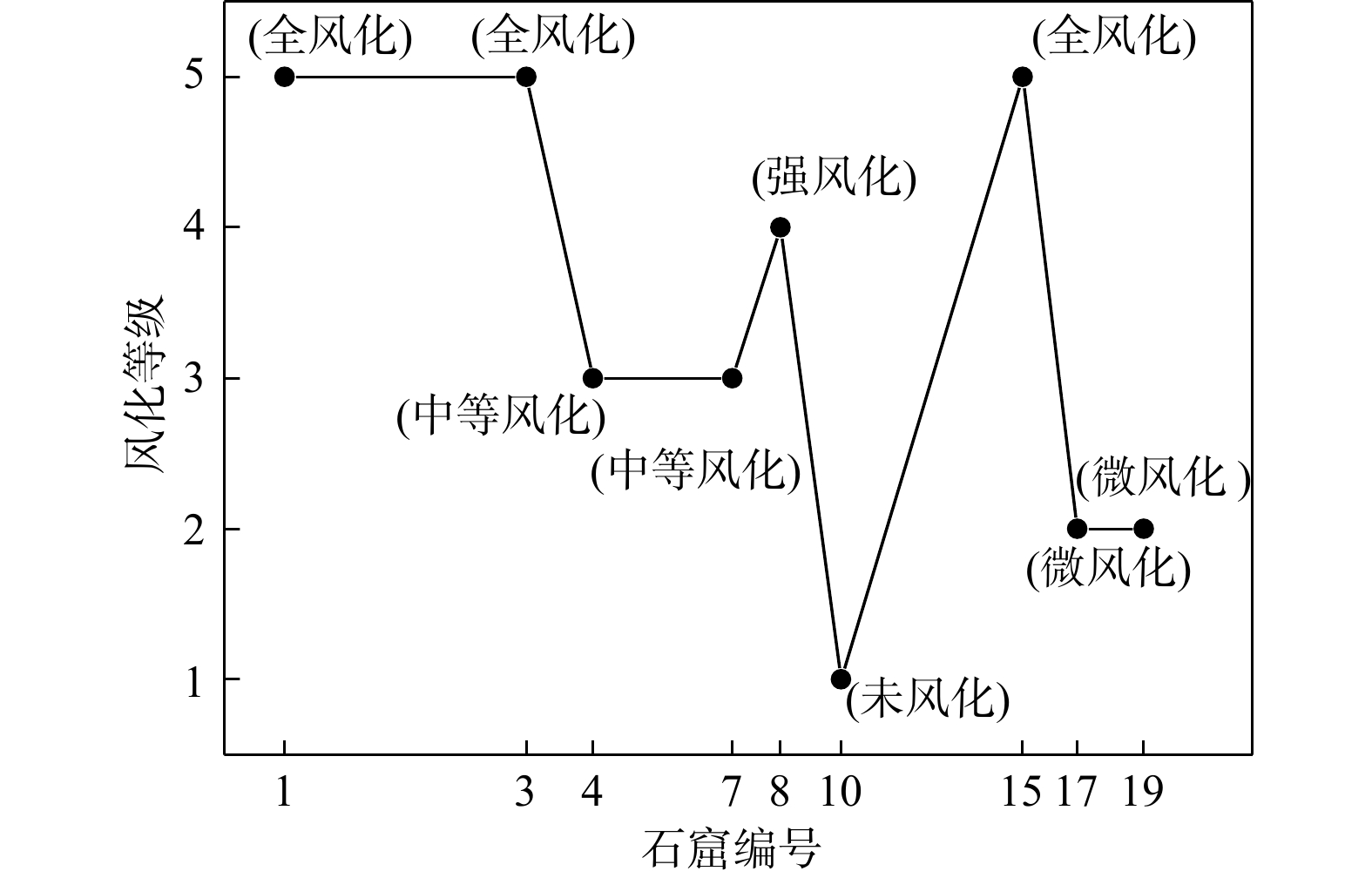
图 1 不同窟的砂岩风化等级[9]
Figure 1.
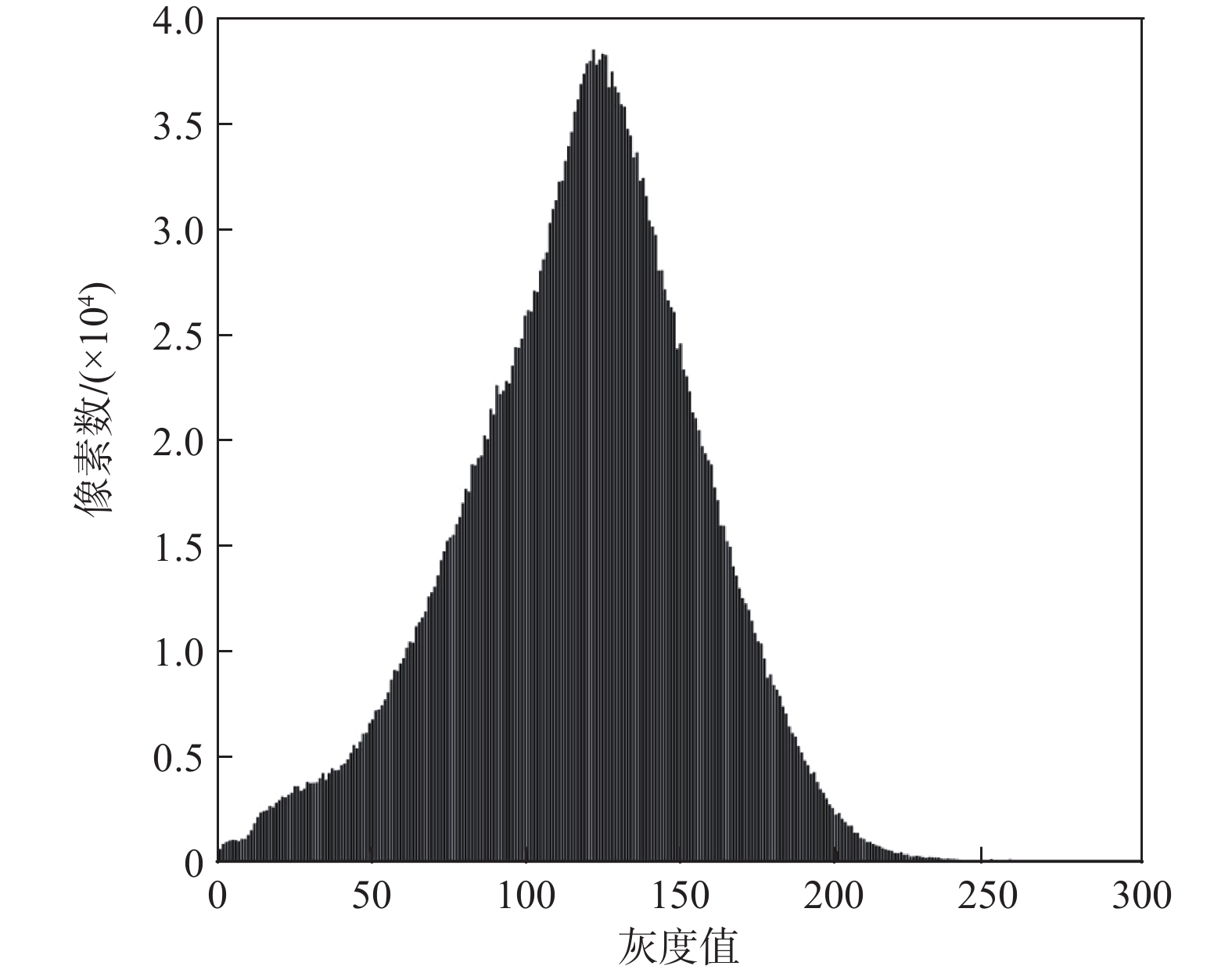
图 3 由图2(d)得到的灰度直方图
Figure 3.
表 1 不同窟砂岩样品SEM图像的数字特征参数
Table 1. Digital parameters of SEM images for sandstone samples in various grottoes
石窟编号 颗粒数量/个 颗粒平均粒径/μm 颗粒平均圆度 面孔隙率/% 1 305 10.65 0.42 36.85 3 419 14.74 0.48 30.13 4 214 8.47 0.43 14.32 7 189 4.98 0.40 17.32 8 286 9.48 0.45 31.38 10 79 4.43 0.26 18.38 15 331 16.94 0.52 33.22 17 128 2.47 0.29 19.89 19 72 4.91 0.34 12.20 表 2 不同窟体砂岩SEM图像的孔隙特征参数
Table 2. Pore digital parameters of SEM images for sandstones in various grottoes
石窟
编号ri/(10−6 m) ro/(10−6 m) d/(10−6 m) η/(10−6 m2·s−1) 1 61.90 6.33 101.42 1.42 3 49.02 5.27 84.81 1.38 4 33.11 4.21 51.98 1.38 7 27.72 3.62 39.32 1.30 8 41.17 3.93 69.58 1.38 10 18.01 3.86 31.80 1.30 15 58.73 4.33 125.27 1.42 17 21.03 3.64 40.83 1.34 19 21.69 3.98 51.94 1.34 表 3 不同窟体砂岩的风化特征参数
Table 3. Weathering characteristic parameters for sandstones in various grottoes
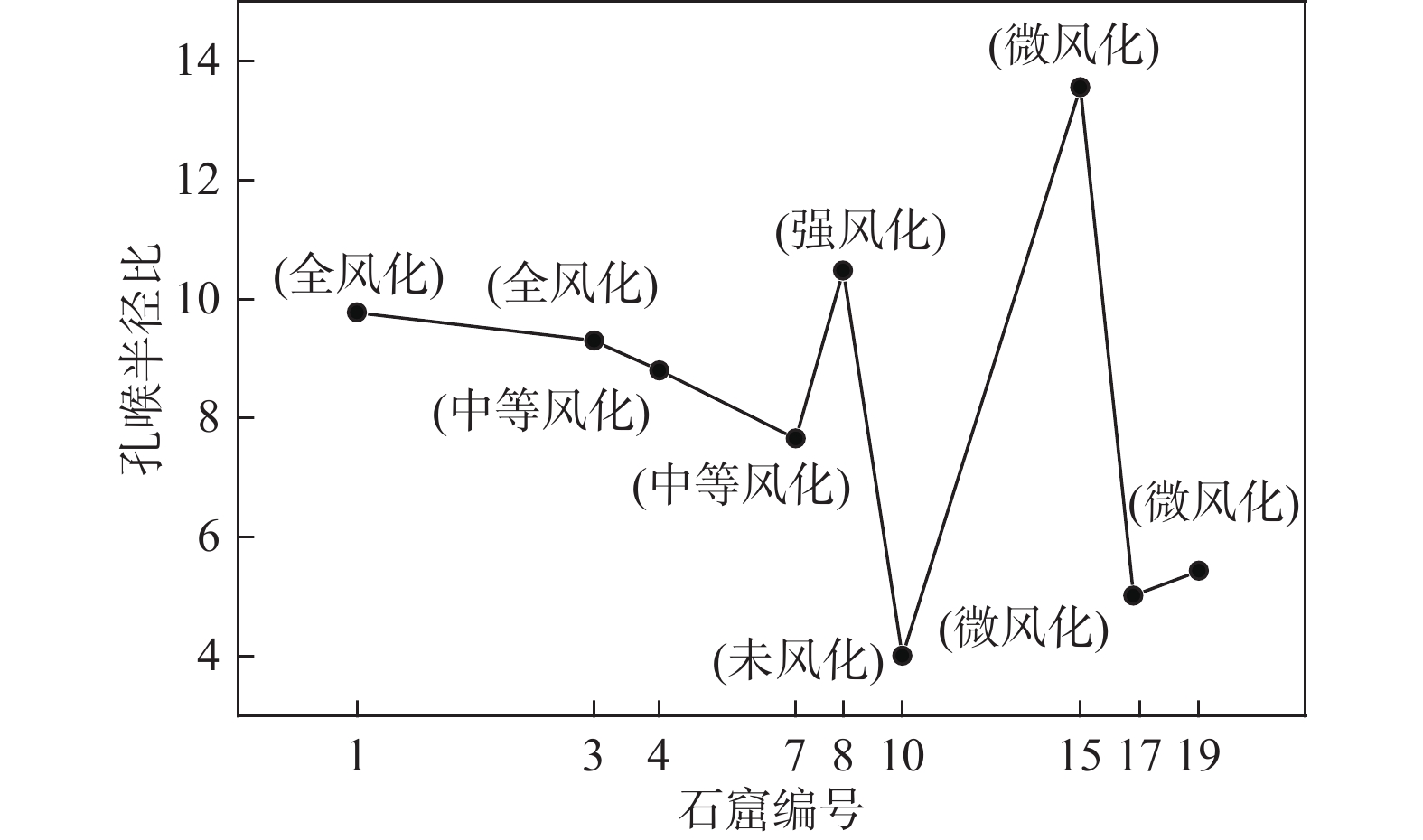
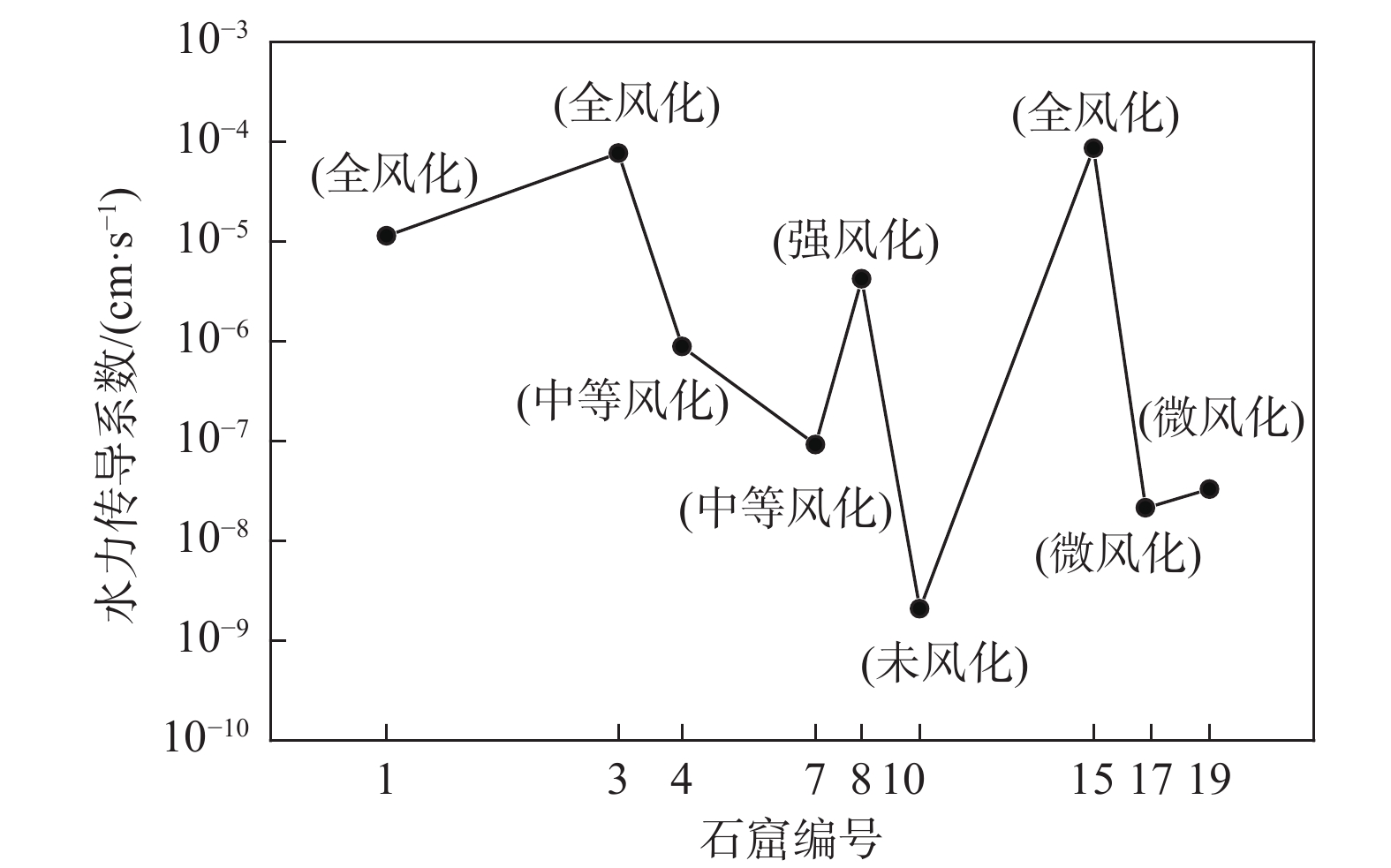
石窟编号 孔喉半径比 水力传导系数/(cm·s−1) 1 9.78 1.14 × 10−5 3 9.30 7.71 × 10−5 4 8.80 8.86 × 10−7 7 7.66 9.23 × 10−8 8 10.48 4.23 × 10−6 10 4.01 2.09 × 10−9 15 13.56 8.64 × 10−5 17 5.02 2.14 × 10−8 19 5.44 3.31 × 10−8 -
[1] 孙寅森, 郭少斌. 基于图像分析技术的页岩微观孔隙特征定性及定量表征[J]. 地球科学进展,2016,31(7):751 − 763. [SUN Yinsen, GUO Shaobin. Qualitative and quantitative characterization of shale microscopic pore characteristics based on image analysis technology[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2016,31(7):751 − 763. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2016.07.0751.
[2] 张鹏飞, 卢双舫, 李俊乾, 等. 基于扫描电镜的页岩微观孔隙结构定量表征[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2018,42(2):19 − 28. [ZHANG Pengfei, LU Shuangfang, LI Junqian, et al. Quantitative characterization of microscopic pore structure for shales using scanning electron microscopy[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science),2018,42(2):19 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 张吉群, 胡长军, 和冬梅, 等. 孔隙结构图像分析方法及其在岩石图像中的应用[J]. 测井技术,2015,39(5):550 − 554. [ZHANG Jiqun, HU Changjun, HE Dongmei, et al. Image analysis method of pore structure and its application in rock image[J]. Well Logging Technology,2015,39(5):550 − 554. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 周宏伟, 谢和平. 多孔介质孔隙度与比表面积的分形描述[J]. 西安矿业学院学报,1997,17(2):97 − 102. [ZHOU Hongwei, XIE Heping. Fractal description of porosity and specific surface area of porous media[J]. Journal of Xi’an Mining Institute,1997,17(2):97 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 唐朝生, 施斌, 王宝军. 基于SEM土体微观结构研究中的影响因素分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2008,30(4):560 − 565. [TANG Chaosheng, SHI Bin, WANG Baojun. Factors affecting analysis of soil microstructure using SEM[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2008,30(4):560 − 565. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2008.04.016
[6] BENAVENTE D, PLA C, CUETO N, et al. Predicting water permeability in sedimentary rocks from capillary imbibition and pore structure[J]. Engineering Geology,2015,195:301 − 311. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.06.003
[7] BERNABÉ Y, LI M, MAINEULT A. Permeability and pore connectivity: a new model based on network simulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth,2010,115(B10):B10203. doi: 10.1029/2010JB007444
[8] NISHIYAMA N, YOKOYAMA T. Estimation of permeability of sedimentary rocks by applying water-expulsion porosimetry to Katz and Thompson model[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,177:75 − 82. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.05.016
[9] 孟田华, 杨成全, 卢玉和, 等. SEM和X-Ray对云冈石窟石雕风化物的分析[J]. 山西大同大学学报(自然科学版),2014,30(4):17 − 21. [MENG Tianhua, YANG Chengquan, LU Yuhe, et al. Analysis of the Yungang grottoes weathered stone with SEM and X-ray approaches[J]. Journal of Shanxi Datong University (Natural Science Edition),2014,30(4):17 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 谢云鹏, 陈秋南, 黄小城, 等. 深埋隧道炭质板岩微观结构及单轴压缩试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):96 − 102. [XIE Yunpeng, CHEN Qiunan, HUANG Xiaocheng, et al. An experimental study of microstructure and uniaxial compression test of carbonaceous slate in a deep buried tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):96 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 王光谦, 孙其诚. 颗粒物质及其多尺度结构统计规律[J]. 工程力学,2009,26(增刊2):1 − 7. [WANG Guangqian, SUN Qicheng. Granular matter and the scaling laws[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2009,26(Sup2):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 李日运, 吴林峰. 岩石风化程度特征指标的分析研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(22):3830 − 3833. [LI Riyun, WU Linfeng. Research on characteristic indexes of weathering intensity of rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(22):3830 − 3833. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.22.018
[13] BARAKA-LOKMANE S, MAIN I G, NGWENYA B T, et al. Application of complementary methods for more robust characterization of sandstone cores[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2009,26(1):39 − 56. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.11.003
[14] THEODOROPOULOU M A, SYGOUNI V, KAROUTSOS V, et al. Relative permeability and capillary pressure functions of porous media as related to the displacement growth pattern[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow,2005,31(10/11):1155 − 1180.
[15] 谢渊, 王剑, 江新胜, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地下白垩统含水层储水岩石特征与介质结构研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2005,32(2):11 − 19. [XIE Yuan, WANG Jian, JIANG Xinsheng, et al. Structure of water-bearing media and characteristics of water-bearing rocks of the Lower Cretaceous aquifer in the Ordos Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2005,32(2):11 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.02.002
[16] 杨建, 康毅力, 李前贵, 等. 致密砂岩气藏微观结构及渗流特征[J]. 力学进展,2008,38(2):229 − 236. [YANG Jian, KANG Yili, LI Qiangui, et al. Characters of micro-structure and percolation in tight sandstone gas reservoirs[J]. Advances in Mechanics,2008,38(2):229 − 236. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 郭永春, 谢强, 文江泉. 红层软岩结构特征与工程评价初探[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(6):86 − 90. [GUO Yongchun, XIE Qiang, WEN Jiangquan. Engineering criterion of structure-stability of soft rocks of red beds[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(6):86 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.06.017
[18] DESBOIS G, URAI J L, KUKLA P A, et al. High-resolution 3D fabric and porosity model in a tight gas sandstone reservoir: a new approach to investigate microstructures from mm- to nm-scale combining argon beam cross-sectioning and SEM imaging[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2011,78(2):243 − 257. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2011.06.004
[19] HAMMECKER C, MERTZ J D, FISCHER C, et al. A geometrical model for numerical simulation of capillary imbibition in sedimentary rocks[J]. Transport in Porous Media,1993,12(2):125 − 141. doi: 10.1007/BF00616976
[20] BENAVENTE D, LOCK P, ÁNGELES GARCÍA DEL CURA M, et al. Predicting the capillary imbibition of porous rocks from microstructure[J]. Transport in Porous Media,2002,49(1):59 − 76. doi: 10.1023/A:1016047122877
[21] TSAKIROGLOU C D, IOANNIDIS M A. Dual-porosity modelling of the pore structure and transport properties of a contaminated soil[J]. European Journal of Soil Science,2008,59(4):744 − 761. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2007.01019.x
[22] 黄继忠. 云冈石窟地质特征研究[J]. 东南文化,2003(5):91 − 93. [HUANG Jizhong. A study on the geological character of Yungang grotto[J]. Southeast Culture,2003(5):91 − 93. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-179X.2003.05.016
[23] CAI J C, ZHANG Z E, WEI W, et al. The critical factors for permeability-formation factor relation in reservoir rocks: Pore-throat ratio, tortuosity and connectivity[J]. Energy,2019,188:116051. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.116051
-



 下载:
下载: