Characteristics of geothermal water in the Xining Basin and risk of reinjection scaling
-
摘要:
青海西宁盆地中低温地热资源丰富,但热储地层以含黏土矿物的弱胶结砂岩为主,地热水溶解性总固体较高,回灌过程中存在显著的结垢风险。基于对西宁盆地地热成因及资源分布特征分析,采用矿物溶解度法、饱和指数法等方法对典型地热水回灌结垢趋势及风险进行了综合判断。结果表明:西宁盆地“凹中凸”构造有利于地热水在深部热储富集和增温,同时将深部溶解的大量矿物质带到西宁地区中央凸起地带;西宁地区地热储层埋深主要在700~1600 m,水温30~70 ℃,主要为SO4·Cl—Na水化学类型,溶解性总固体1.85×103~4.80×104 mg/L;回灌过程中结垢以碳酸钙结垢为主,当回灌水与地下热水性质相近时,结垢风险主要发生在回灌井筒中,地层结垢风险较小,而当回灌水与地下热水性质差异较大时,不配伍性将导致地层结垢风险大大提高,其中药王泉与DR2005原1∶ 1混合时结垢量最大可达177.57 mg/L,而其他地热水结垢量较小。根据以上特征,提出以下综合解决方案:物理防垢+管材防腐、系统增压防垢+管材防腐和地面预处理+管材防腐,并辅之以阴极保护防腐、优化排量、酸洗井筒等措施,可为今后保障地热水回灌能力措施的制定提供理论依据与技术支持。
Abstract:The Xining Basin in Qinghai Province is rich in geothermal resources of low to medium temperature, but the geothermal reservoir is dominated by weakly consolidated sandstone containing clay minerals, and the geothermal water has high salinity, which causes a significant risk of scaling during reinjection. In this paper, based on the analysis of the geothermal genesis and resource distribution characteristics in the Xining Basin, different methods, such as the mineral solubility method and saturation index method, are used to assess the scaling tendency and risk in typical geothermal water during reinjection. The results show that the “convex in concave” structure of the Xining Basin is beneficial for the enrichment and warming of thermal groundwater in the deep geothermal reservoir, and at the same time, a large number of dissolved minerals are brought to the central bulge in the Xining Basin. The geothermal reservoir in the Xining Bain is mainly buried at a depth of 700−1600 m with water temperature of 30−70 ℃. The hydrochemical type is mainly of SO4·Cl—Na type, and the salinity range from 1.85×103 to 4.80×104 mg/L. The main scaling product during reinjection is CaCO3. When the characteristics of reinjection water and geothermal water are similar, the risk of scaling mainly occurs in the reinjection wellbore, and the risk of formation scaling is relatively small. When the characteristics of reinjection water and geothermal water are quite different, the incompatibility will greatly increase the risk of formation scaling. Among them, when the water from Yaowangquan is mixed with that from DR2005Y by 1∶1, the maximum scaling amount can reach 177.57 mg/L, while the scaling amount from other geothermal water is smaller. Based on the above characteristics, three sets of comprehensive measures are proposed as the follows: physical anti-scaling + pipe anti-corrosion, system pressurization anti-scaling + pipe anti-corrosion and ground pretreatment + pipe anti-corrosion, supplemented by measures such as cathodic protection anticorrosion, optimized displacement, and pickling the wellbore. The results of this study can provide theoretical basis and technical support for the formulation of measures to ensure the reinjection capacity of geothermal water in the future.
-
Key words:
- Xining Basin /
- geothermal water /
- reinjection /
- scaling risk /
- anti-scale
-

-
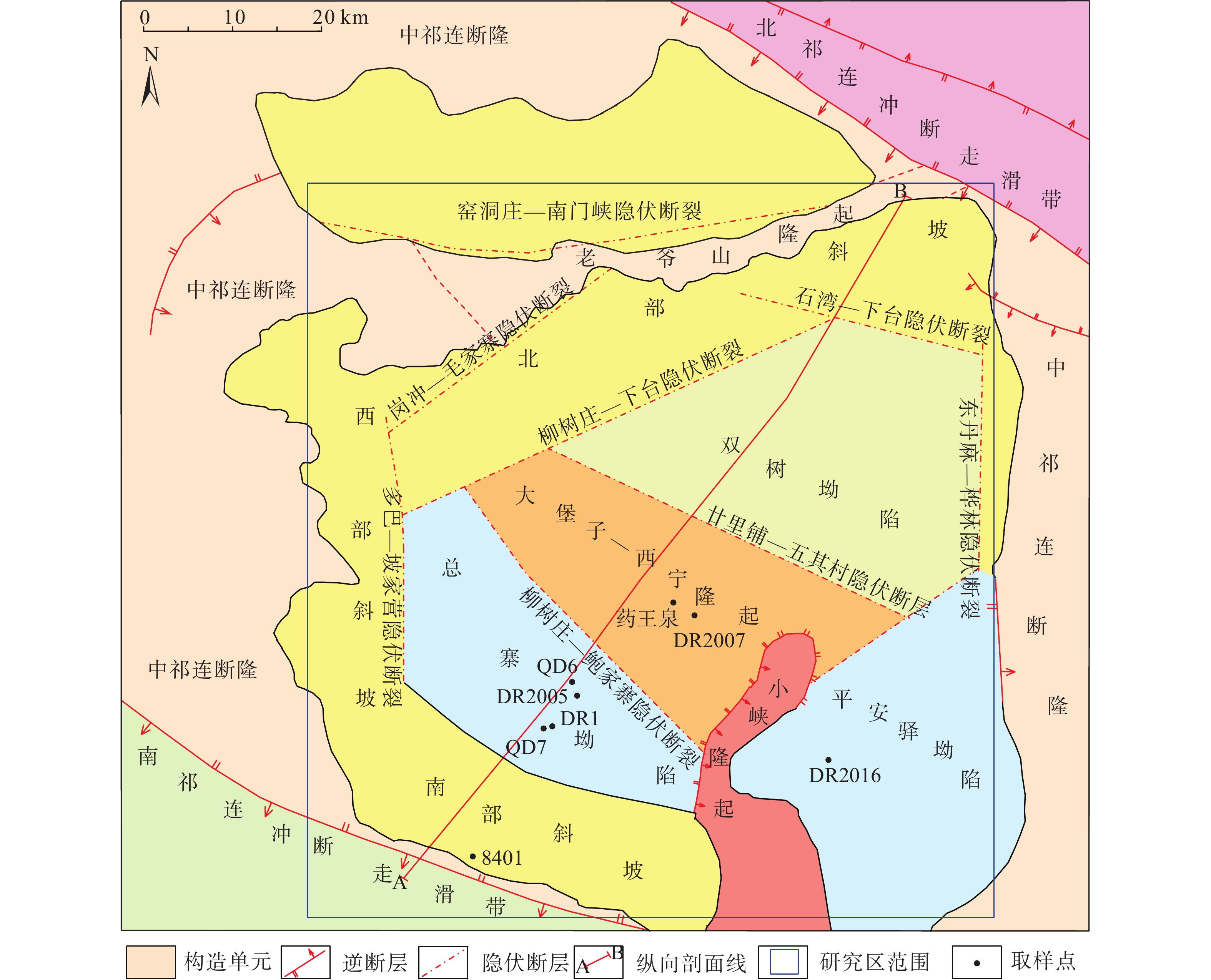
图 1 西宁盆地构造单元划分略图(据文献[19],略有修改)
Figure 1.
图 2 西宁盆地中新生界热储构造概念模型纵向剖面(据文献[18],略有修改)
Figure 2.
表 1 西宁地区主要地热井基本情况
Table 1. Statistics of the major geothermal wells in the Xining area
孔号 位置 试段
位置/m热储
厚度/m含水层岩
性及时代水头
高度/m水头
降深/m涌水量/
(103 m3·d−1)水温
/℃溶解性总
固体/(104mg·L−1)水化学
类型DR1 南川工业园
清水河南500 m745~1600 121.90 粗砂岩、中砂岩,K −19.50 62.38 0.81 59.00 2.30 SO4·Cl—Na 132.30 1.67 61.00 DR2005 城南杜家庄 850~1600 234.30 砂岩、砂砾岩,K、J −15.70 107.38 1.33 61.00 3.42 SO4·Cl—Na 8401 药水滩 − − 碳酸盐岩地层,Jxk +4.45 3.36 0.15 37.00 − − 8701 西宁胜利宾馆 309~720 179.90 砂岩、砂砾岩,K、J +55.84 54.84 3.03 39.50 3.49 SO4·Cl—Na 8601 西宁供热公司 460~698 182.90 砂岩、砂砾岩,K、J +59.98 58.41 2.24 42.20 3.98 SO4·Cl—Na 911 西宁市杨家寨 270~580 251.60 中细砂岩、含砾中细
砂岩、砂砾岩,K、J+63.00 62.00 合流0.86 32.00 3.38 SO4·Cl—Na 8309 西宁彭家寨
地矿局基地325~371 46.36 含砾砂岩,E +22.92 43.33 0.58 27.00 2.16 SO4·Cl—Na CKB1 西宁市小桥
电厂北500m429~468 38.00 砂岩,K − − − 14.00 6.48 Cl·SO4—Na DR2007 新宁花园 474~1030 340.40 砂岩、含砾粗砂岩,
K、J+50.00 自流 0.48 53.00 5.30 SO4·Cl—Na R2 海湖新区 697~1159 196.70 砂岩、砂砾岩,
K、J+61.00 自流 1.89 42.00 2.65 SO4·Cl—Na DR2010 互助县
威远镇1039~1925 362.50 砂岩、砂砾岩,
K、J+27.00 自流 1.40 62.00 3.59 Cl·SO4—Na 表 2 西宁地区典型地热水样水质分析结果
Table 2. Hydrochemical ananlyses of typical geothermal water samples in the Xining area
地热水类型 DR2005 DR2007 DR2016 药王泉 8401 DR2005原 DR2016原 K+/(mg·L−1) 65.81 48.74 80.69 18.22 4.63 124.00 87.40 Na+/(mg·L−1) 1.18×103 1.66×104 1.51×104 3.65×103 20.11 1.11×104 1.26×104 Ca2+/(mg·L−1) 24.04 425.55 549.55 41.36 317.40 270.10 418.00 Mg2+/(mg·L−1) 8.21 140.00 176.11 19.36 93.69 78.30 149.00 Br2+/(mg·L−1) 0.13 <0.02 0.25 <0.02 0 0.05 0 Sr2+/(mg·L−1) 0.37 13.83 48.15 2.97 0 6.10 25.70  /(mg·L−1)
/(mg·L−1)2.81×103 0.70×103 0.75×103 2.82×103 1.31×103 1.41×103 0.70×103 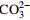 /(mg·L−1)
/(mg·L−1)0 25.42 0 64.71 0 0 0 Cl−/(mg·L−1) 39.97 9.36×103 2.26×104 1.2×103 7.52 6.98×103 1.94×104 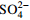 /(mg·L−1)
/(mg·L−1)146.66 2.07×104 1.22×103 4.16×103 45.43 1.42×104 1.17×103 游离CO2/(mg·L−1) 10.81 0 14.19 0 0 30.77 16.70 pH 7.40 8.41 7.20 8.34 6.68 7.56 8.08 溶解性总固体/(mg·L−1) 4.34×103 4.80×104 4.06×104 1.20×104 1.85×103 3.42×104 3.44×104 水化学类型判断 HCO3—Na SO4·Cl—Na Cl—Na SO4·HCO3—Na HCO3—Ca SO4·Cl—Na Cl—Na 备注 水样污染 − − − − 前期测定 前期测定 表 3 回灌井筒内碳酸钙垢过饱和指数及结垢趋势
Table 3. CaCO3 saturation index and scaling trend in wellbore
注入水 DR2005原 DR2007 DR2016 药王泉 8401 过饱和指数 1.19 1.85 0.86 1.80 1.21 结垢趋势/(mg·L−1) 191.78 103.93 151.21 10.29 254.40 表 4 地层内碳酸钙垢过饱和指数及结垢趋势
Table 4. CaCO3 saturation index and scaling trend in formation
注入水在
地层中的
比例/%注入水类别 DR2005原 DR2007 DR2016 药王泉 8401 过饱和
指数0 0 0 0 0 0 10 −0.01 −0.02 0.008 0.11 −0.03 20 −0.02 −0.04 0.013 0.22 −0.06 30 −0.03 −0.06 0.015 0.33 −0.09 40 −0.03 −0.08 0.014 0.43 −0.11 50 −0.04 −0.10 0.012 0.54 −0.13 60 −0.04 −0.11 0.008 0.64 −0.14 70 −0.04 −0.11 0.002 0.74 −0.14 80 −0.03 −0.11 −0.002 0.84 −0.13 90 −0.02 −0.08 −0.004 0.89 −0.07 100 0 0 0 0 0 结垢趋势/(mg·L−1) 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 0 0 4.21 60.16 0 20 0 0 6.59 110.05 0 30 0 0 7.36 147.50 0 40 0 0 6.80 170.49 0 50 0 0 5.26 177.57 0 60 0 0 3.13 168.38 0 70 0 0 0.92 143.90 0 80 0 0 0 106.17 0 90 0 0 0 57.65 0 100 0 0 0 0 0 表 5 地热回灌井筒防腐防垢防堵措施汇总及对比
Table 5. Summary and comparison of anti-corrosion, anti-scaling and anti-blocking measures in geothermal reinjection wellbore
序号 措施 原理 防腐 防垢 防堵 备注 1 地热水预处理(常压/低压) 对尾水进行预结垢、杀菌、曝晒释放
酸性气体、除氧、除颗粒等√ √ √ 设计工艺流程及计算参数指标 2 回灌储层优选 回灌水-地下热水配伍性良好,同层
注采√ 进行配伍性分析,提出储层选择标准 3 系统增压法调pH、加CO2 防止地热水脱气、或恢复地热水溶解
气状态,使地热水结垢欠饱和√ 进行全流程开采-利用-注入温压场计算及结垢趋势分析,确定有效工艺参数 4 适速注入 保持井筒高压低温,减小结垢和腐蚀
趋势,避免泥砂运移√ √ √ 根据地层泥砂运移及井筒结垢和腐蚀趋势优化排量 5 物理防垢新技术 合金短节、HTI电偶层,形成微磁场使水分子极性化降低结垢趋势,或释放
大量负电子中和金属离子√ √ 基于电化学、胶体理论,已发展至第三代(磁场式-静电场式-电子场) 6 管材选择 不锈钢、非金属、防腐防垢内衬 √ √ 玻璃钢管材+不锈钢筛网 7 阴极保护 锌作为牺牲阳极 √ 可大大降低局部腐蚀 8 近井-井筒定期酸洗 溶解井筒及近井地层结垢物,提高
近井渗透率√ √ 对井筒管材有一定要求,投入大 9 近井酸化压裂 提高近井吸水能力 √ 对井筒管材有一定要求,投入大,对固结程度较差的地层压裂效果不敢保证 表 6 地热水回灌井综合防腐防垢防堵建议
Table 6. Suggestions for comprehensive anti-corrosion, anti-scaling and anti-blocking in geothermal water reinjection wells
方案 地面-井筒 地层 备注/特点 方案1 物理防垢+管材防腐 同层注采/配伍性储层 预防工艺简单,对系统温压变化要求不高,系统封闭无O2 方案2 系统增压防垢+管材防腐 同层注采/配伍性储层 需保持系统高压,防止脱气生垢,能耗增加,系统封闭无O2 方案3 地面预处理+管材防腐 同层注采/配伍性储层 占用面积大、工艺流程复杂,需脱氧 辅助措施 阴极保护防腐、优化排量降低井筒
结垢和腐蚀趋势、酸洗井筒除垢酸化压裂提高近井吸水能力、
优化排量防止泥砂颗粒运移经济性及技术可行性有待论证 -
[1] 拓明明, 周训, 郭娟, 等. 重庆温泉及地下热水的分布及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(1):165 − 172. [TA Mingming, ZHOU Xun, GUO Juan, et al. Occurrence and formation of the hot springs and thermal groundwater in Chongqing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(1):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 王洁青, 周训, 李晓露, 等. 云南兰坪盆地羊吃蜜温泉水化学特征与成因分析[J]. 现代地质,2017,31(4):822 − 831. [WANG Jieqing, ZHOU Xun, LI Xiaolu, et al. Hydrochemistry and formation of the Yangchimi hot spring in the Lanping Basin of Yunnan[J]. Geoscience,2017,31(4):822 − 831. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.04.016
[3] 薛宇泽, 陶鹏飞, 韩元红. 渭河盆地中深层地热资源开发存在问题及改进措施[J]. 资源环境与工程,2020,34(3):428 − 431. [XUE Yuze, TAO Pengfei, HAN Yuanhong. The problem and improvement measures of middle and deep geothermal resources development in Weihe Basin[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2020,34(3):428 − 431. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 马正孔. 砂岩地热尾水回灌技术的研究[J]. 华北国土资源,2018(4):72 − 73. [MA Zhengkong. The research on reinjection technology of geothermal tail water into sandstone[J]. Huabei Land and Resources,2018(4):72 − 73. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7487.2018.04.030
[5] 梅博, 郭亮, 王鹏, 等. 地热井尾水回灌技术及其应用进展[J]. 中国资源综合利用,2018,36(1):168 − 170. [MEI Bo, GUO Liang, WANG Peng, et al. The technology and application of water recharge in the tail water of geothermal well[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization,2018,36(1):168 − 170. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] ZHANG L, CHAO J H, GENG S H, et al. Particle migration and blockage in geothermal reservoirs during water reinjection: Laboratory experiment and reaction kinetic model[J]. Energy,2020,206:118234. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.118234
[7] 杨亚军, 丁桂伶, 徐巍, 等. 基于示踪试验及动态数据的北京小汤山地区地热资源量评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):196 − 200. [YANG Yajun, DING Guiling, XU Wei, et al. Tracer test and geothermal resource quantity evaluation based on dynamic data in the Xiaotangshan area of Beijing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):196 − 200. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张薇, 王贵玲, 刘峰, 等. 中国沉积盆地型地热资源特征[J]. 中国地质,2019,46(2):255 − 268. [ZHANG Wei, WANG Guiling, LIU Feng, et al. Characteristics of geothermal resources in sedimentary basins[J]. Geology in China,2019,46(2):255 − 268. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 洪增林, 张银龙, 周阳. 关中盆地南部山前中深层地热资源赋存特征及应用[J]. 中国地质,2019,46(5):1224 − 1235. [HONG Zenglin, ZHANG Yinlong, ZHOU Yang. Research on the modes of occurrence and application of geothermal resources in the middle and deep layers of the piedmont area in southern Guanzhong Basin[J]. Geology in China,2019,46(5):1224 − 1235. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12029/gc20190522
[10] 孟宪级, 白丽萍, 齐金生. 地热水结垢趋势的判断[J]. 工业水处理,1997,17(5):6 − 7. [MENG Xianji, BAI Liping, QI Jinsheng. The judgment of scaling tendency in geothermal water in China[J]. Industrial Water Treatment,1997,17(5):6 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.1997.17(5).6
[11] 曹倩, 方朝合, 李云, 等. 国内外地热回灌发展现状及启示[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2021,43(2):203 − 211. [CAO Qian, FANG Chaohe, LI Yun, et al. Development status of geothermal reinjection at home and abroad and its enlightenment[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology,2021,43(2):203 − 211. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 戴群, 王聪, 罗杨, 等. 砂岩地热储层回灌堵塞机理研究及治理对策[J]. 精细石油化工进展,2017,18(6):10 − 13. [DAI Qun, WANG Cong, LUO Yang, et al. Research on sandstone geothermal reservoir reinjection plugging mechanism and measures against it[J]. Advances in Fine Petrochemicals,2017,18(6):10 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8348.2017.06.003
[13] 刘明言. 地热流体的腐蚀与结垢控制现状[J]. 新能源进展,2015,3(1):38 − 46. [LIU Mingyan. A review on controls of corrosion and scaling in geothermal fluids[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy,2015,3(1):38 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2015.01.007
[14] 豆肖辉, 张大磊, 荆赫, 等. 不锈钢在低温地热水环境中的腐蚀与结垢行为[J]. 腐蚀与防护,2020,41(7):61 − 66. [DOU Xiaohui, ZHANG Dalei, JING He, et al. Corrosion and scaling behavior of stainless steel in low-temperature geothermal water environment[J]. Corrosion & Protection,2020,41(7):61 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11973/fsyfh-202007010
[15] 马致远, 侯晨, 席临平, 等. 超深层孔隙型热储地热尾水回灌堵塞机理[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(5):133 − 139. [MA Zhiyuan, HOU Chen, XI Linping, et al. Reinjection clogging mechanism of used geothermal water in a super-deep-porous reservoir[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(5):133 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王连成. 天津市新近系馆陶组地热流体回灌研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
WANG Liancheng. A study of geothermal reinjection in the Guantao reservoir in Tianjin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 赵季初. 鲁北砂岩热储地热尾水回灌试验研究[J]. 山东国土资源,2013,29(9):23 − 30. [ZHAO Jichu. Lubei geothermal tail water reinjection experiments in sandstone reservoir[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,2013,29(9):23 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2013.09.005
[18] 赵振, 于漂罗, 陈惠娟, 等. 青海省西宁地热田成因分析及资源评价[J]. 中国地质,2015,42(3):803 − 810. [ZHAO Zhen, YU Piaoluo, CHEN Huijuan, et al. Genetic analysis and resource evaluation of the Xining geothermal field in Qinghai Province[J]. Geology in China,2015,42(3):803 − 810. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.03.029
[19] 尚小刚. 青海省威远镇地热田热储特征及其开发利用潜力评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.
SHANG Xiaogang. Development use and potential evaluation of the thermal reservoir characteristics and geothermal resources of geothermal field in Weiyuan town, Qinghai Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 马致远, 李嘉祺, 翟美静, 等. 沉积型和火山型地热流体的同位素水文地球化学对比研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):9 − 18. [MA Zhiyuan, LI Jiaqi, ZHAI Meijing, et al. A comparative study of isotopic hydrogeochemistry of geothermal fluids of sedimentary basin type and volcanic type[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):9 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 蔡义汉. 地热直接利用[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2004.
CAI Yihan. Geothermal direct-use[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 2004.(in Chinese)
[22] 李义曼, 庞忠和. 地热系统碳酸钙垢形成原因及定量化评价[J]. 新能源进展,2018,6(4):274 − 281. [LI Yiman, PANG Zhonghe. Carbonate calcium scale formation and quantitative assessment in geothermal system[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy,2018,6(4):274 − 281. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2018.04.004
[23] 任加国, 武倩倩. 水文地球化学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014.
REN Jiaguo, WU Qianqian. Hydro-geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014.(in Chinese)
[24] 柴蕊. 天津市周良庄地热田地下热水的水化学及钙华研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2006.
CHAI Rui. A study of hydrochemistry and tufa in thermal groundwater in the Zhouliangzhuang geothermal fileld, Tianjin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 刘光启. 化工物性算图手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002.
LIU Guangqi. The manual of calculation about chemical physical properties[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002.(in Chinese)
[26] 李雪娇. 硫酸钡结垢影响因素及化学阻垢实验研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2015.
LI Xuejiao. Experimental research on influencing factors of barium sulfate scaling and chemical scale inhibition[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] ODDO J E, TOMSON M B. Why scale forms and how to predict[J]. SPE Production & Facilities,1997,9(1):47 − 54.
[28] ODDO J E, TOMSON M B. Simplified calculation of CaCO3 saturation at high temperatures and pressures in brine solutions[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology,1982,34(7):1583 − 1590. doi: 10.2118/10352-PA
[29] 王磊, 唐红伟, 高雨. 油气田地面集输系统结垢预测模型研究[J]. 管道技术与设备,2012(3):12 − 13. [WANG Lei, TANG Hongwei, GAO Yu. Study of gathering system scaling prediction[J]. Pipeline Technique and Equipment,2012(3):12 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9614.2012.03.005
[30] 贾红育, 曲志浩. 注水开发油田油层结垢趋势研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2001,28(1):89 − 91. [JIA Hongyu, QU Zhihao. A study on formation scaling tendency for waterflooding oilfields[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2001,28(1):89 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2001.01.029
[31] 陈易, 徐燕来, 王闰, 等. 油田注水硫酸盐垢结垢趋势预测研究[J]. 内江科技,2012,33(5):23. [CHEN Yi, XU Yanlai, WANG Run, et al. Research on prediction of sulfate scaling trend in oilfield water injection[J]. Neijiang Science & Technology,2012,33(5):23. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1436.2012.05.020
[32] 韩淑彬. G104区块注水井井筒结垢机理及防垢技术研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2016.
HAN Shubin. Research on scaling mechanism and anti-scaling technology of water injection well in G104 block[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 刘明言, 朱家玲. 地热能利用中的防腐防垢研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2011,30(5):1120 − 1123. [LIU Mingyan, ZHU Jialing. Progress of corrosion and fouling prevention in utilization of geothermal energy[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2011,30(5):1120 − 1123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载:





