A numerical simulation study of the effect of the vadose zone with lenses on LNAPL migration under the fluctuating water table
-
摘要:
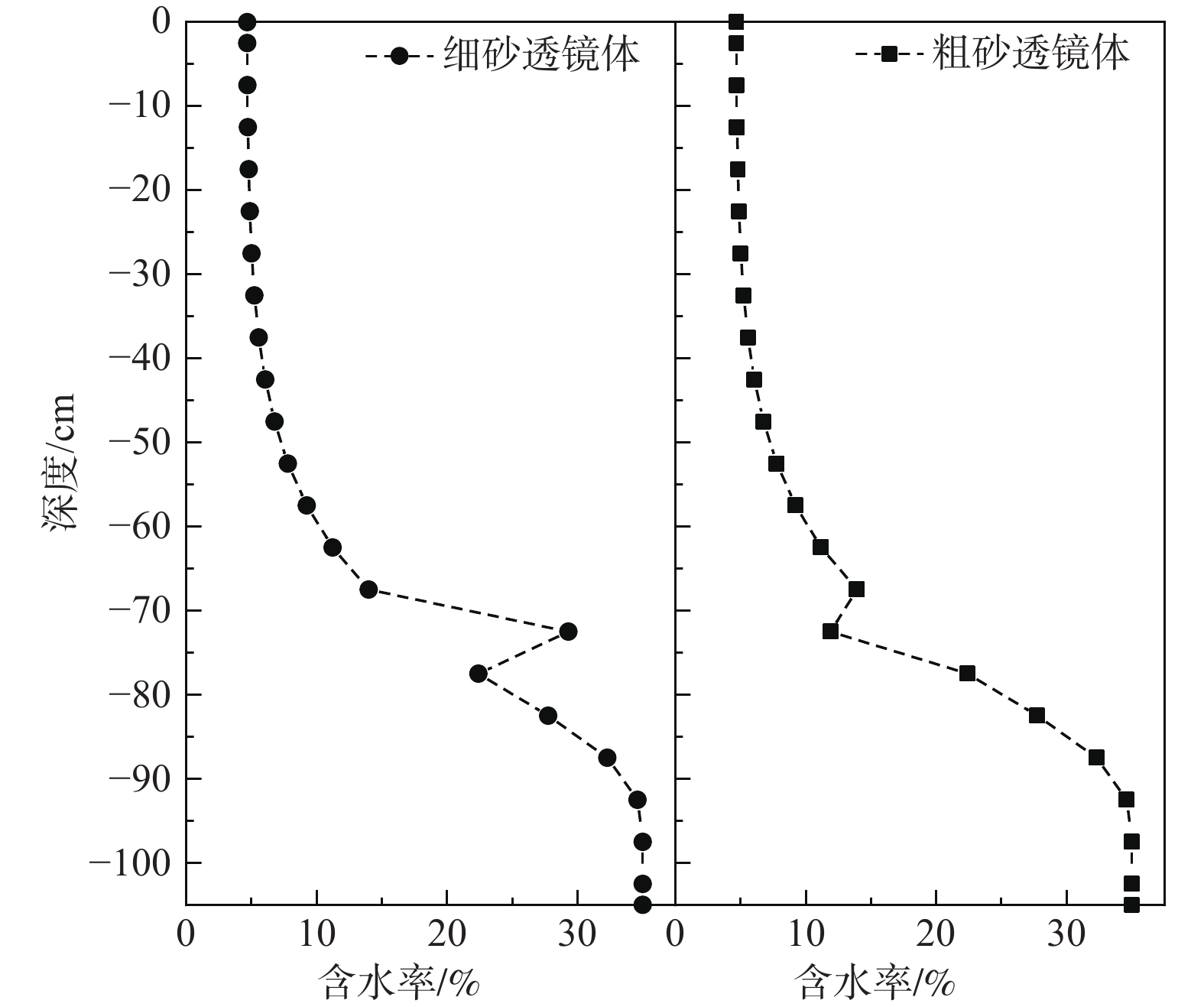
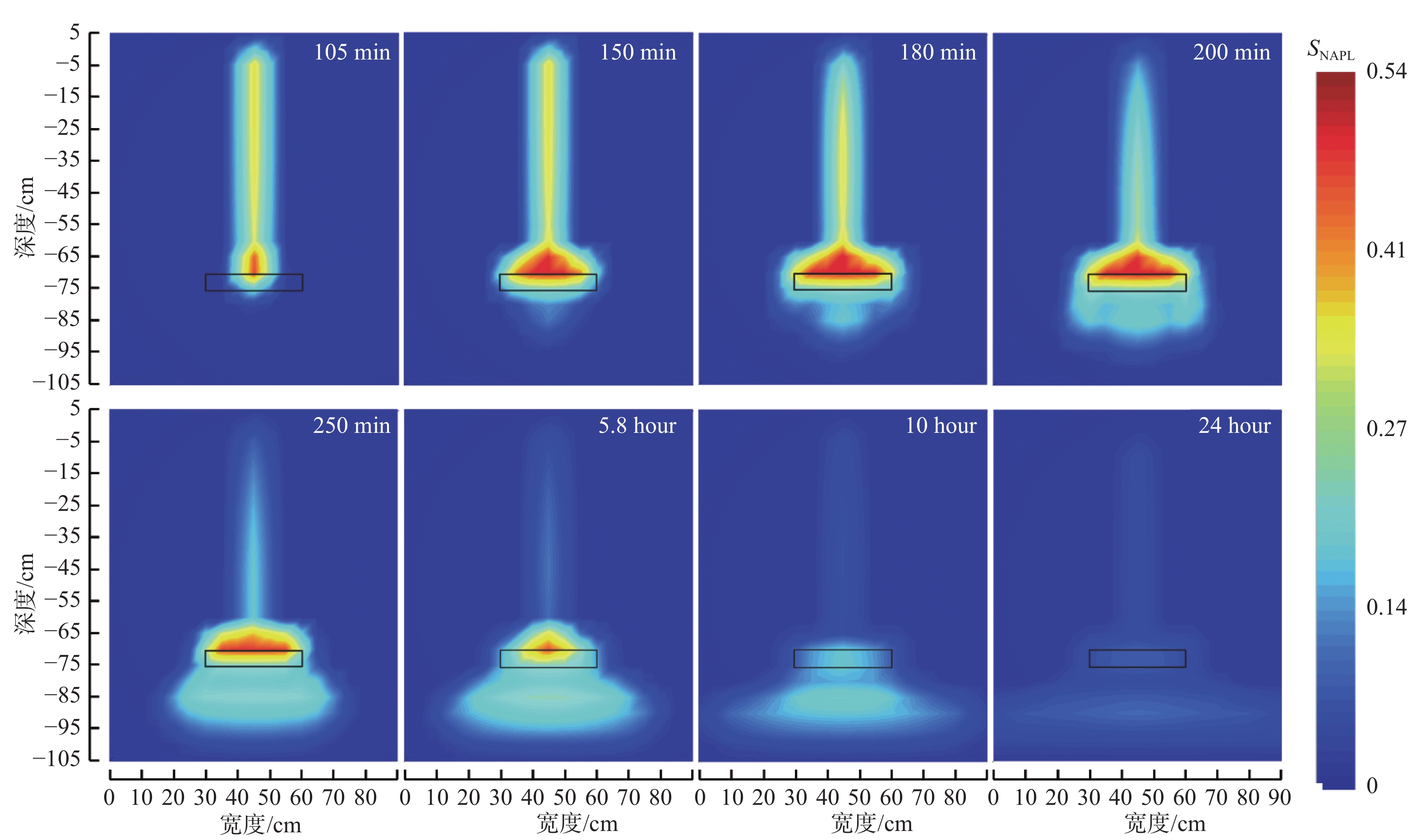
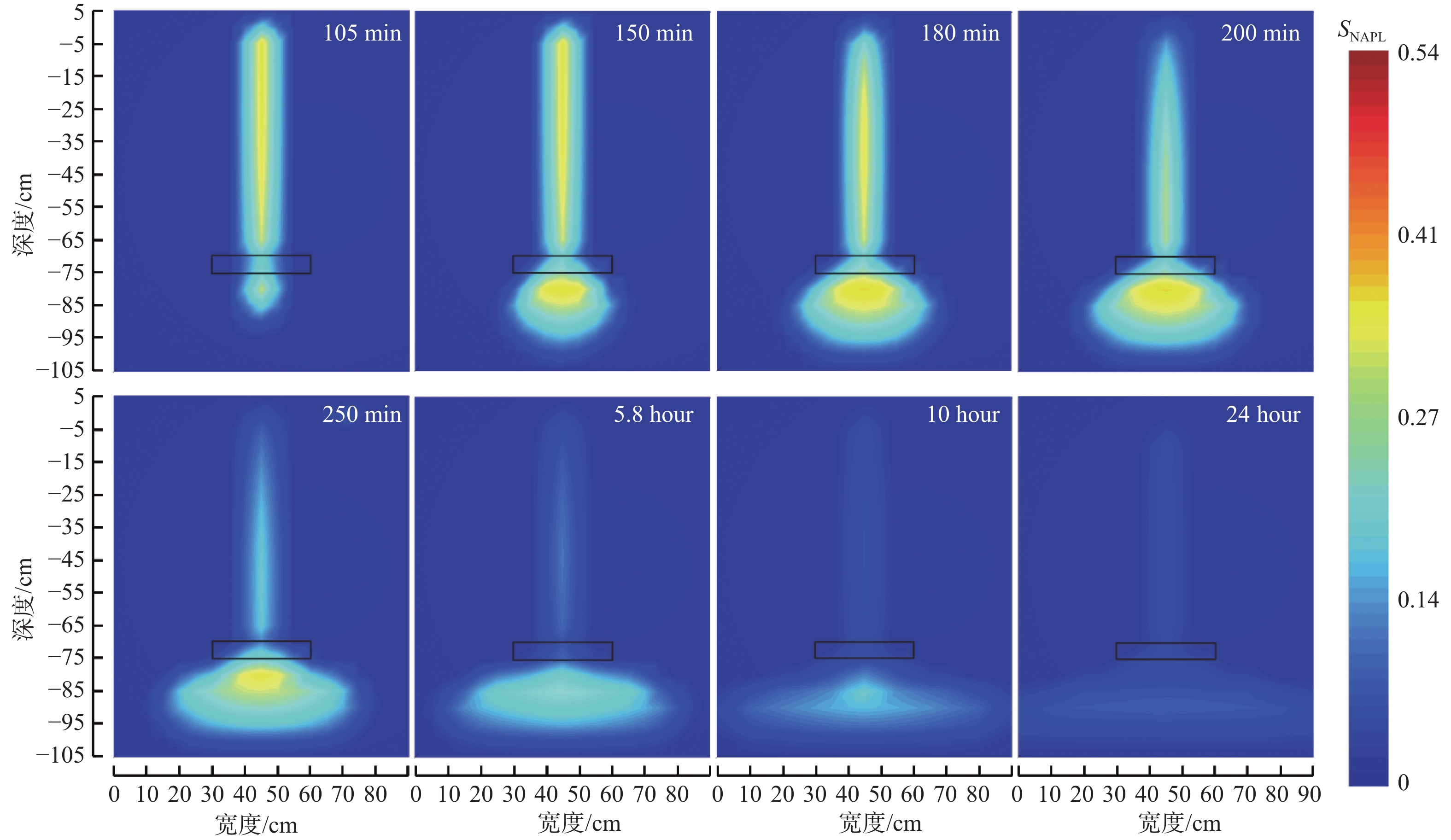
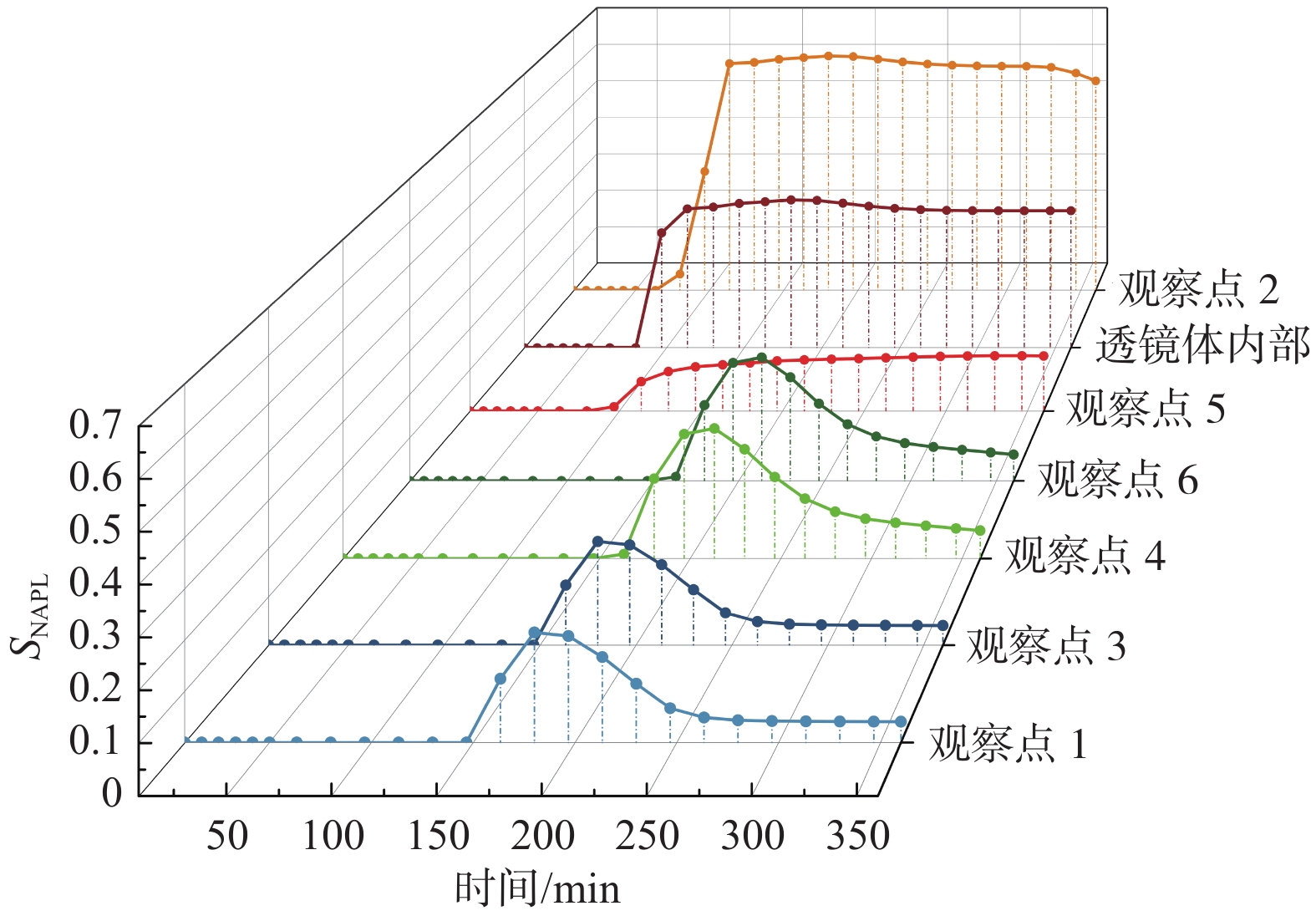
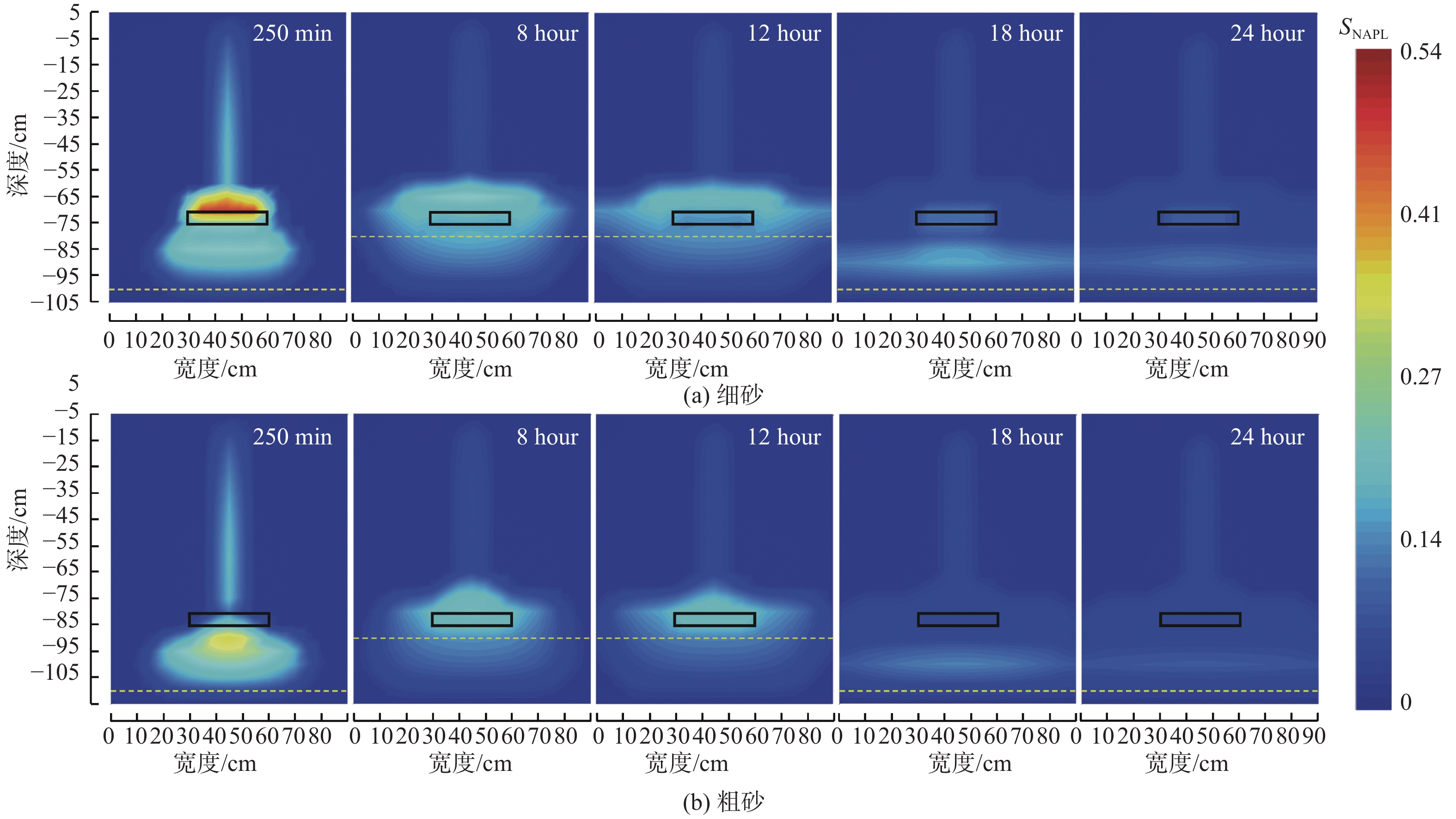
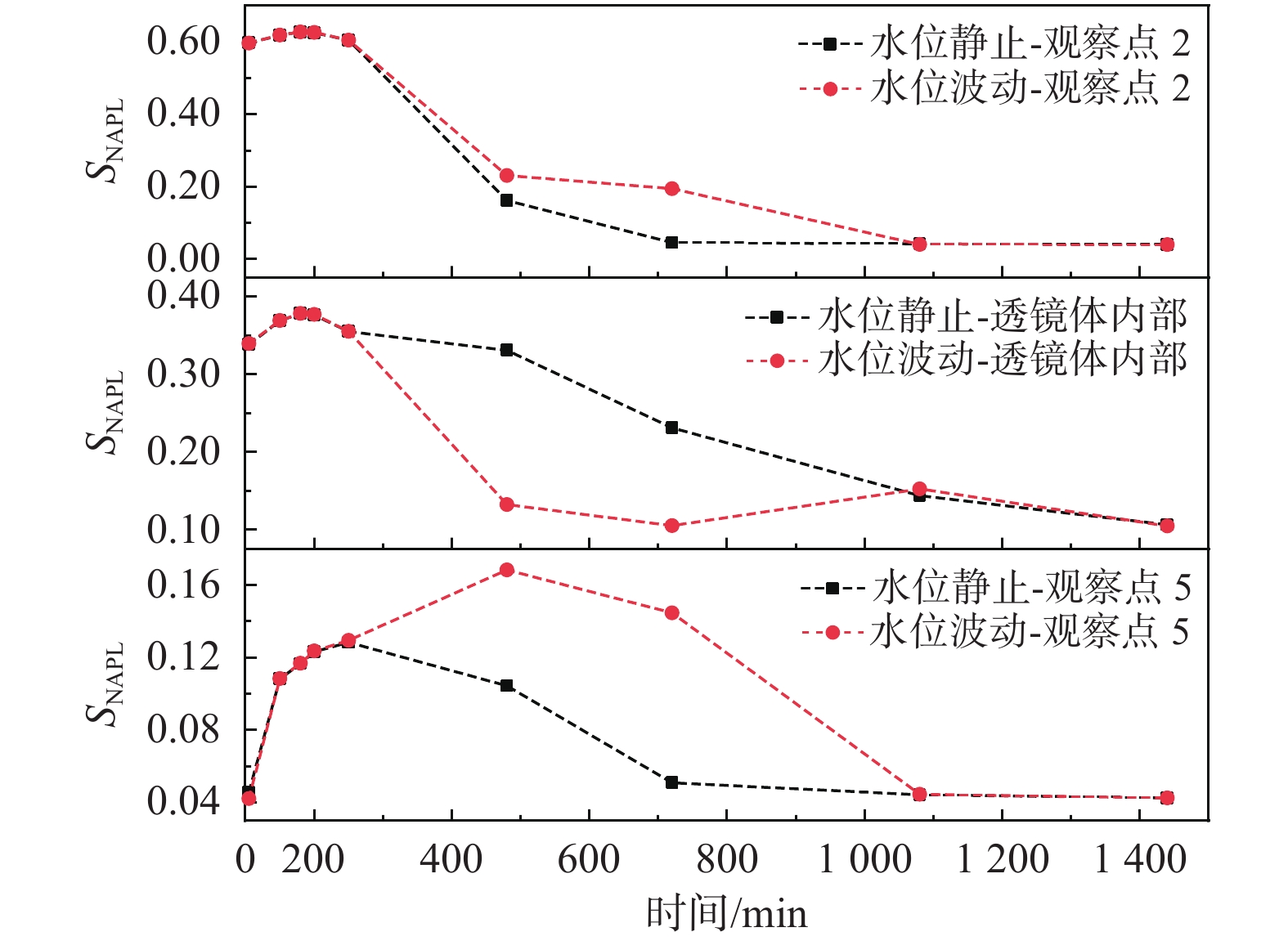
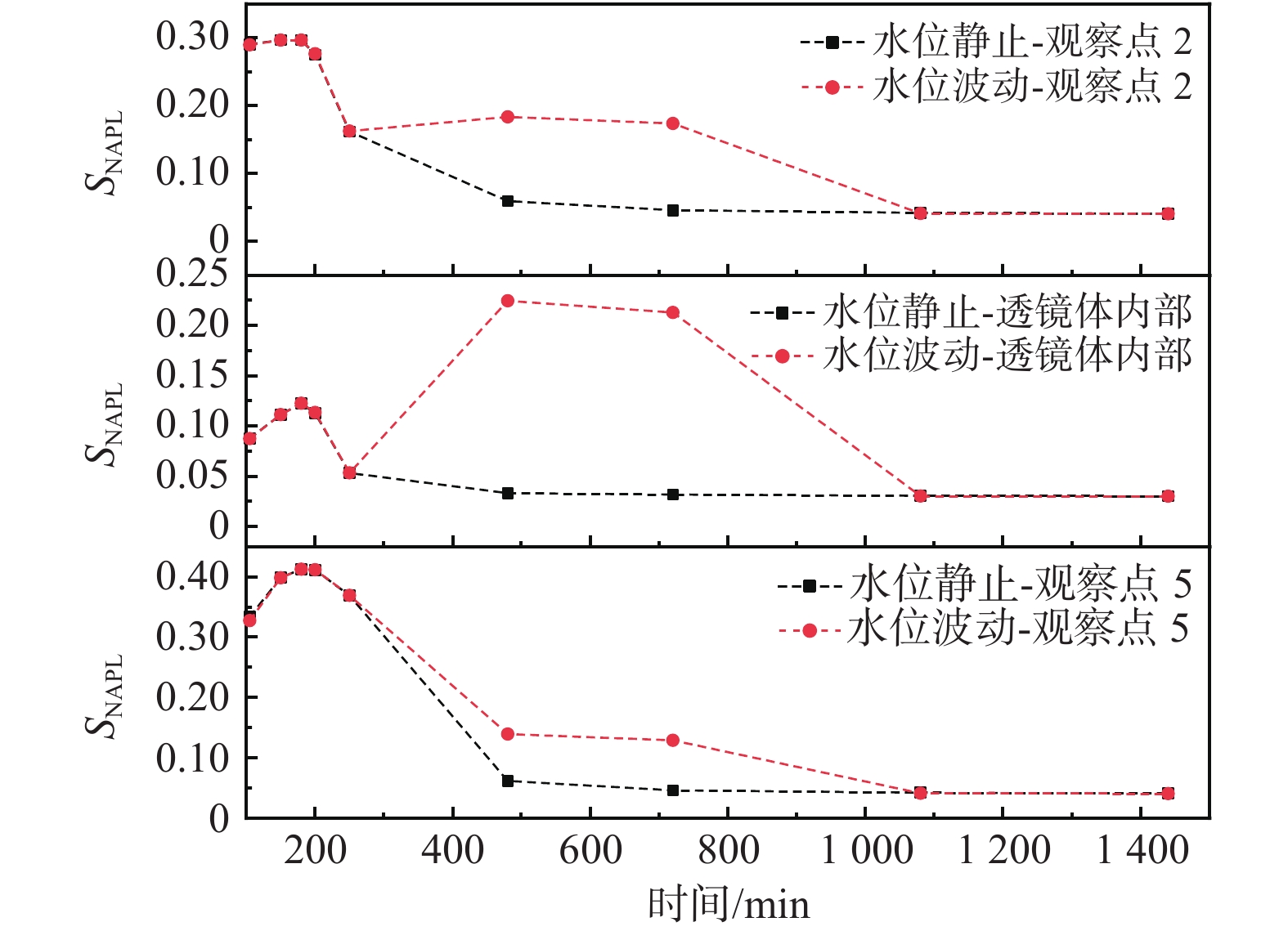
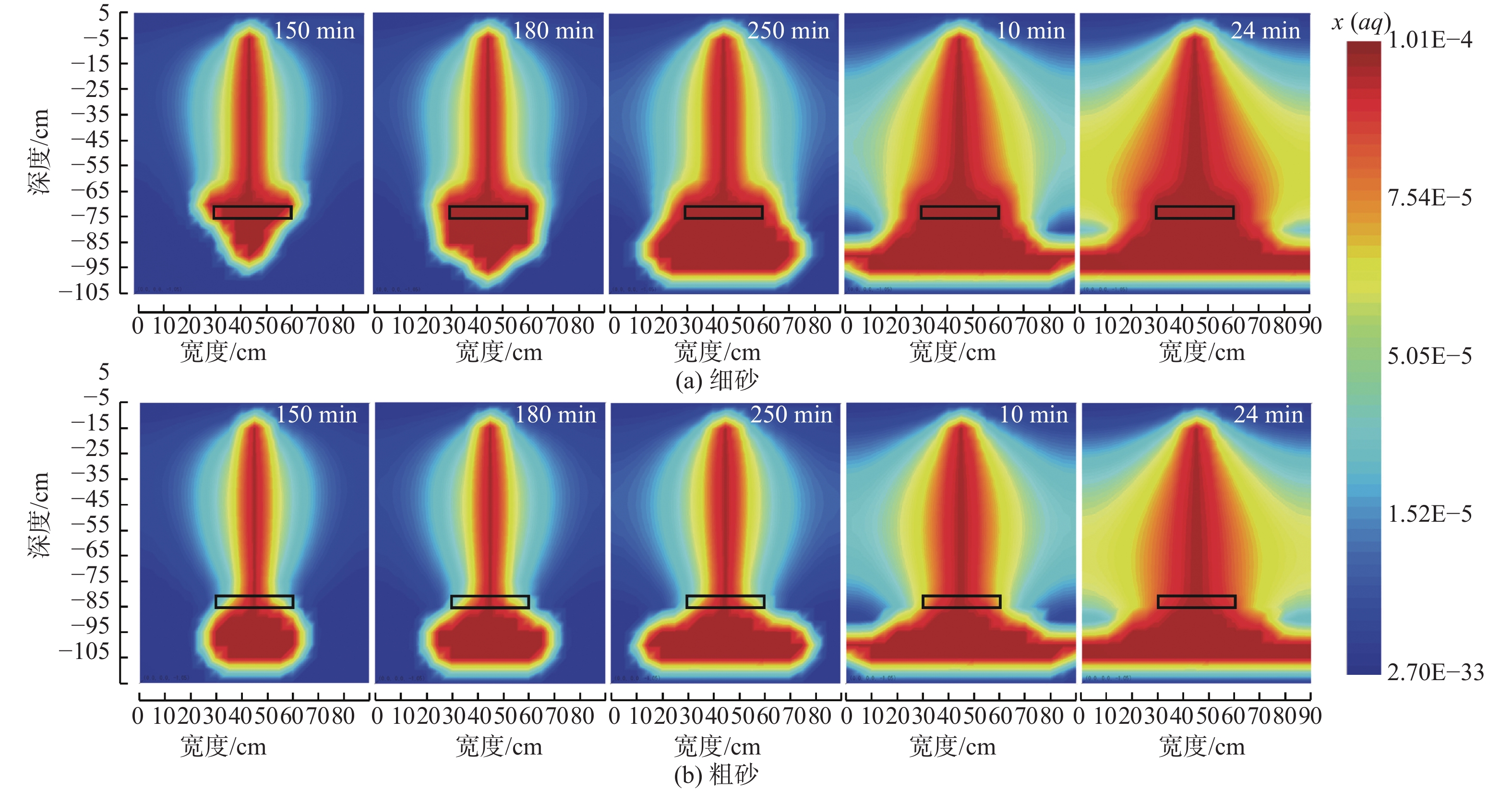
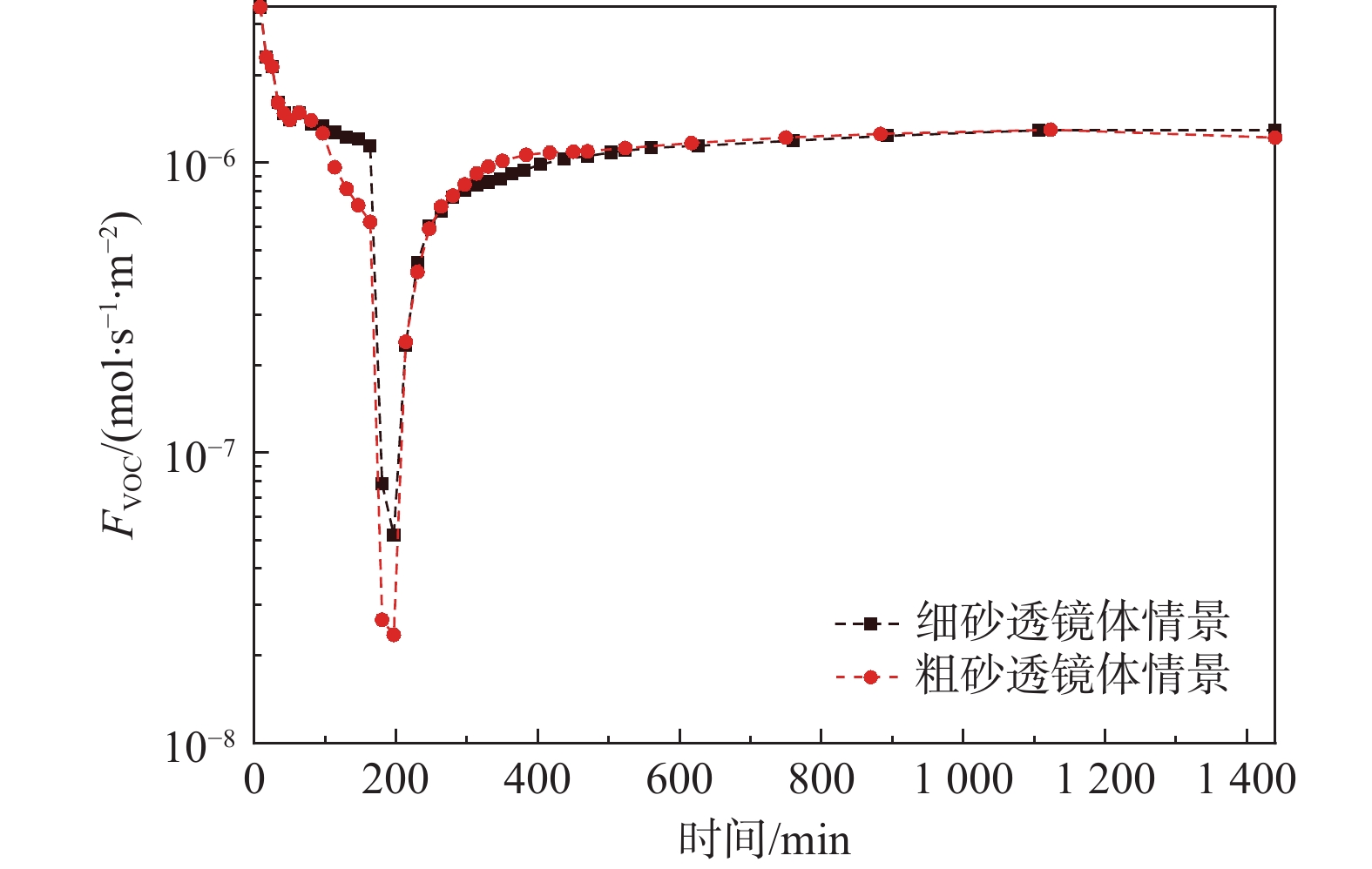
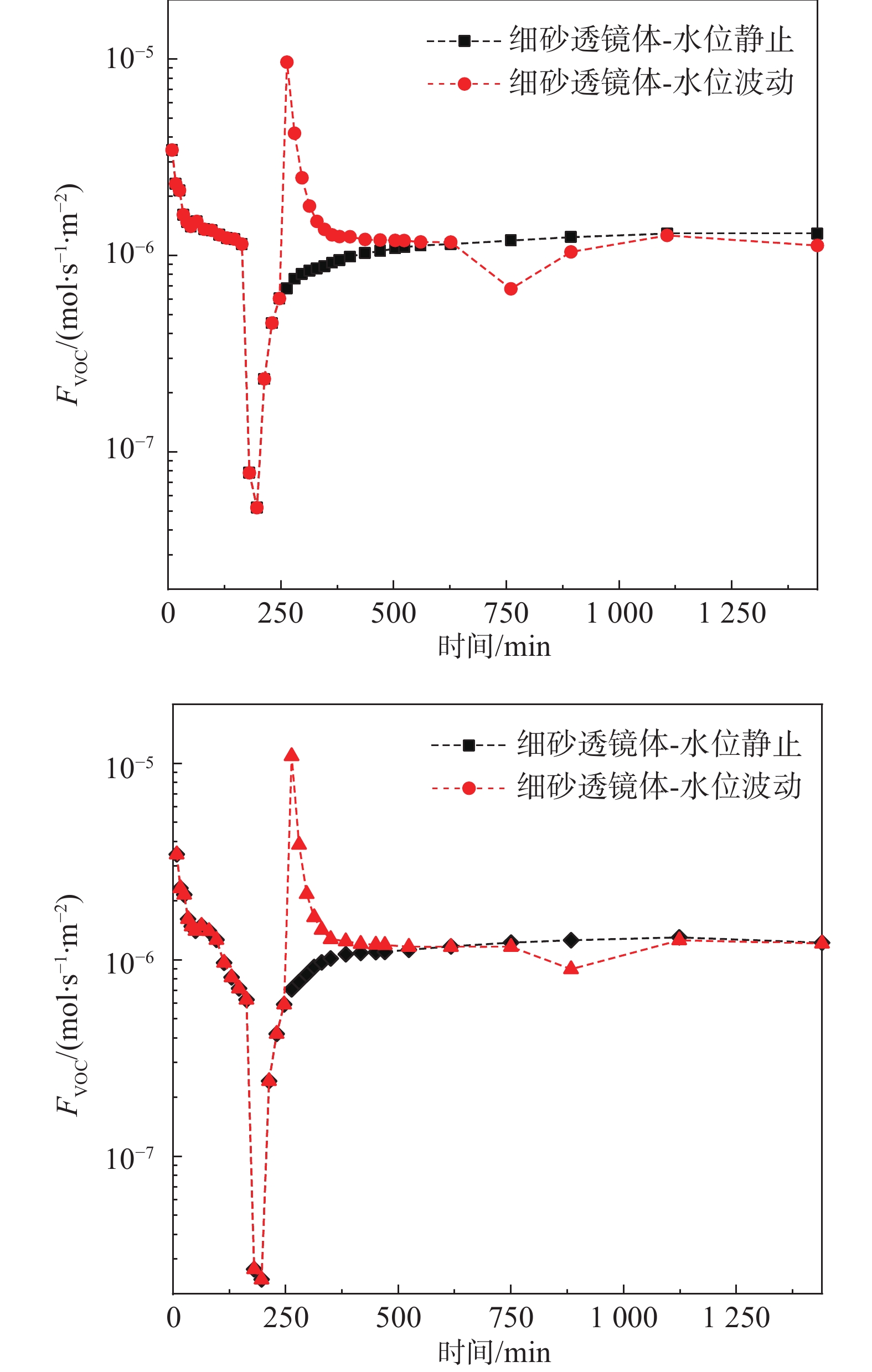
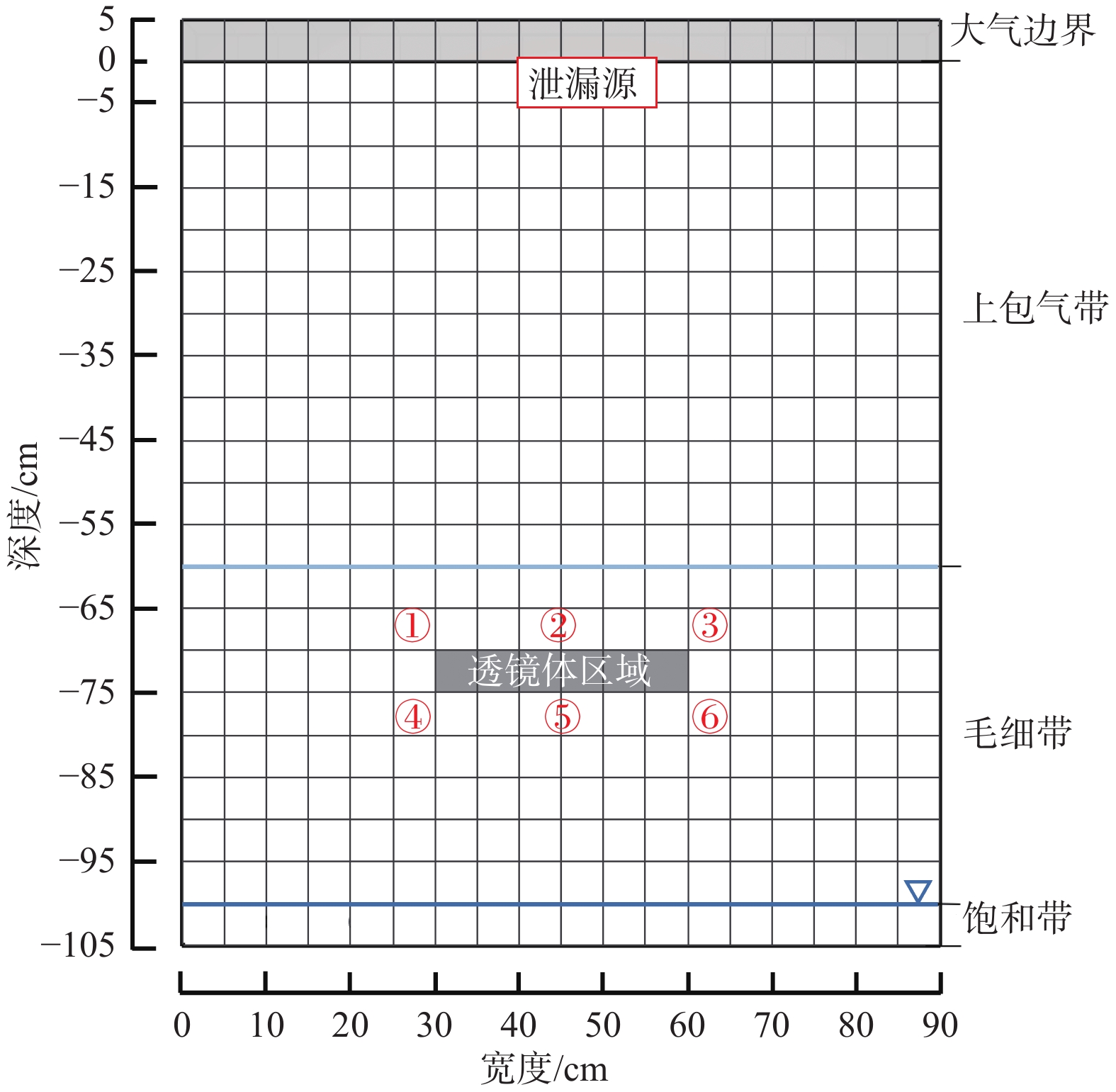
轻质非水相液体(LNAPLs)在土壤包气带中具有多相态特征,非均质性、地下水位波动等因素将显著增加包气带内LNAPLs污染的复杂程度。已有研究多关注于揭示包气带内自由相LNAPLs的污染过程,少有更为深入地探究水位波动时非均质结构对LNAPLs迁移及各相态分布规律的影响。基于TOUGH2程序构建包气带多相流数值模型,以揭示透镜体结构与地下水位波动共同作用下LNAPLs迁移过程及相态分布。研究结果表明:(1)含水率变化是LNAPLs迁移分布的主要控制因素,包气带内受透镜体介质岩性、水位波动影响所呈现的含水率变化直接控制LNAPLs迁移规律及分布特征;(2)水位恒定时,细砂透镜体使LNAPL呈“蓄积穿透-横向扩展-绕流”迁移,粗砂透镜体则是LNAPL垂向迁移的“优势通道”,水位波动引起的细砂透镜体含水率变化使“绕流”显著增强,粗砂透镜体则进一步呈现“优势空间”作用;(3)水位恒定时,细砂透镜体模型中LNAPL滞留于透镜体内部,粗砂模型中LNAPL则集中于透镜体下方,水位波动下透镜体附近LNAPL分布范围扩展,两模型LNAPL分布面积较水位恒定时分别增大51%、63%;(4)两模型中LNAPL挥发通量均呈“先减小-后增大”规律,并受LNAPL-气体接触条件及LNAPL分布状况共同作用,水位波动打破三相平衡状态,主要表现为水位抬升阶段LNAPL挥发增强,此时两模型中平均挥发量较水位恒定时增大124%~126%。研究为非均质石油污染场地中的LNAPL污染过程认识提供了科学的理论依据。
Abstract:Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids (LNAPLs) in vadose zone is of multi-phase characteristics, while factors such as heterogeneity and groundwater fluctuation are expected to significantly increase the complexity of LNAPLs contamination in vadose zone. Previous studies have mostly focused on revealing the contamination process of free-phase LNAPLs, few have explored deeply the influence of the heterogeneous structure on the migration and phase distribution pattern of LNAPLs when the water table fluctuates. A numerical model of multiphase flow in vadose zone is established based on TOUGH2 to reveal the migration and phase distribution of LNAPLs under the joint effect of different lithological lenses and water table fluctuation. The results show that (1) the migration and distribution regularity of LNAPLs in vadose zone is predominantly controlled by the variation in water content, which is presented under the effect of heterogeneity and water fluctuation. (2) In the steady groundwater scenario, LNAPL migrates in an “accumulation-lateral expansion-flow bypass” pattern around the fine-sand lens, while the coarse-sand lens acts as the "preferential route" for the vertical movement of LNAPL. Flow around the fine-sand lens is significantly enhanced by the variation in water content induced by groundwater fluctuation, and the coarse-sand lens further exhibits the "preferential space" effect. (3) When the water table is steady, LNAPL are concentrated inside and below the lens body in the fine-sand and coarse-sand lens models, respectively. In the fluctuating groundwater scenario, a greater range of LNAPL is presented in the vicinity of the lens with the distribution area in each model is 51% and 63% larger than that in the steady scenario. (4) Volatile flux of LNAPL, affected by the LNAPL-gas exposure conditions and the distribution of LNAPL, shows a "decreasing-then increasing" pattern in both models. The three-phase equilibrium state is disrupted by groundwater fluctuation, which is manifested by the enhanced volatilization during the stage of groundwater elevation, when the average volatile flux in the two models is 124%~126% higher compared to the steady scenario.This research provides a theoretical basis for the understanding of LNAPL pollution process in heterogeneous contaminated sites.
-
Key words:
- LNAPL /
- vadose zone /
- heterogeneity /
- numerical model
-

-
介质类型 中砂 细砂 粗砂 孔隙度 0.35 0.40 0.30 饱和渗透率/(m2) 2.37×10−11 1.48×10−12 2.26×10−10 颗粒比重/(kg∙m−3) 1650.00 1510.00 1749.00 相对渗透率
Stone模型Swr 0.05 0.15 0.03 Snr 0.04 0.08 0.03 Sgr 0.00 0.00 0.00 n 2.93 3.00 3.00 毛细压力
van-
Genuchten模型m 0.66 0.67 0.67 Slr 0.02 0.12 0.02 P0−1 5.105×10−4 3.75×10−4 6.02×10−4 Pmax 5×105 1×107 5×105 Sls 1.00 1.00 1.00 表 2 甲苯相关参数[24]
Table 2. Toluene-relevant parameters
参数 气相中扩散系数/(m2∙s−1) 水相中扩散系数/(m2∙s−1) NAPL相扩散系数/(m2∙s−1) 水中溶解度/(mol∙mol−1) 数值 8.8×10−6 6.0×10−10 6.0×10−10 1.01×10−4 -
[1] YOON H, WERTH C J, BARKAN C P L, et al. An environmental screening model to assess the consequences to soil and groundwater from railroad-tank-car spills of light non-aqueous phase liquids[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,165(1-3):332 − 344. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.121
[2] 刘玉兰, 程莉蓉, 丁爱中, 等. NAPL泄漏事故场地地下水污染风险快速评估与决策[J]. 中国环境科学,2011,31(7):1219 − 1224. [LIU Yulan, CHENG Lirong, DING Aizhong, et al. Quick assessment of groundwater risk after NAPL spill and its application in site emergency management[J]. China Environmental Science,2011,31(7):1219 − 1224. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 刘汉乐, 周启友, 徐速. 非饱和带中非均质条件下LNAPL运移与分布特性实验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2006,33(5):52 − 57. [LIU Hanle, ZHOU Qiyou, XU Su. An experimental investigation of LNAPL migration and redistribution in unsaturated heterogeneous porous media[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2006,33(5):52 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.05.012
[4] DUNN A M, SILLIMAN S E. Air and water entrapment in the vicinity of the water table[J]. Groundwater,2003,41(6):729 − 734. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2003.tb02414.x
[5] ALAZAIZA M Y D, NGIEN S K, COPTY N, et al. Assessing the influence of infiltration on the migration of light non-aqueous phase liquid in double-porosity soil media using a light transmission visualization method[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2019,27(2):581 − 593. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1904-1
[6] 王莹莹, 郭秀军, 邵帅, 等. 土壤毛细带内油污染区探地雷达异常特征分析及状态评价[J]. 地球物理学进展,2018,33(5):2172 − 2180. [WANG Yingying, GUO Xiujun, SHAO Shuai, et al. Abnormal features analysis and status evaluation for oil contaminated site in capillary zone based on ground penetrating radar[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2018,33(5):2172 − 2180. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/pg2018BB0365
[7] 束善治, 梁宏伟, 袁勇. 轻非水相液体在非均质地层包气带中运移和分布特征数值分析[J]. 水利学报,2002,33(11):31 − 37. [SHU Shanzhi, LIANG Hongwei, YUAN Yong. Numerical analysis of transportation and distribution of light non-aqueous phase liquids in partially saturated heterogeneous soils[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2002,33(11):31 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2002.11.006
[8] SLEEP B E, SEHAYEK L, CHIEN C C. A modeling and experimental study of light nonaqueous phase liquid (LNAPL) accumulation in wells and LNAPL recovery from wells[J]. Water Resources Research,2000,36(12):3535 − 3545. doi: 10.1029/2000WR900224
[9] SOOKHAK LARI K, KING A, RAYNER J L, et al. Quantifying the benefits of in-time and in-place responses to remediate acute LNAPL release incidents[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2021,287:112356. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112356
[10] DOBSON R, SCHROTH M H, ZEYER J. Effect of water-table fluctuation on dissolution and biodegradation of a multi-component, light nonaqueous-phase liquid[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2007,94(3/4):235 − 248. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2007.07.007
[11] 罗凌云. LNAPL在包气带形成的透镜体形状及水位波动对其的影响[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.
LUO Lingyun. The shape of lens formed of LNAPL in vadose zone and the influence of the fluctuation of the water table[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 刘汉乐, 张晨富, 刘宝臣, 等. 轻非水相液体在不同粒径多孔介质中的运移与分布特性[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(2):105 − 110. [LIU Hanle, ZHANG Chenfu, LIU Baochen, et al. Experimental investigation of migration and distribution characteristics of LNAPL contaminants in porous media of different particle sizes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(2):105 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 任璇. LNAPLs在包气带层状非均质界面迁移规律的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019.
REN Xuan. Study on migration law of LNAPLs at layered heterogeneous interface in vadose zone[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王颖, 陈雷, 杨洋, 等. 基于TMVOC的地下水位波动带苯系物迁移转化模拟[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(3):634 − 642. [WANG Ying, CHEN Lei, YANG Yang, et al. Numerical simulation of BTEX migration in groundwater table fluctuation zone based on TMOVC[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(3):634 − 642. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 杨明星. 石油有机污染组分在水位波动带中的分异演化机理研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014.
YANG Mingxing. Fate and transport of petroleum organic compounds in water table fluctuation zone[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] SCHROTH M H, ISTOK J D, SELKER J S. Three-phase immiscible fluid movement in the vicinity of textural interfaces[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,1998,32(1):1 − 23.
[17] 陶佳辉, 施小清, 康学远, 等. 轻非水相液体污染源区结构的影响因素数值分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(6):132 − 140. [TAO Jiahui, SHI Xiaoqing, KANG Xueyuan, et al. Numerical analyses of factors affecting the LNAPL source-zone architecture[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(6):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] SIMANTIRAKI F, AIVALIOTI M, GIDARAKOS E. Implementation of an image analysis technique to determine LNAPL infiltration and distribution in unsaturated porous media[J]. Desalination,2009,248(1):705 − 715.
[19] WIPFLER E L, NESS M, BREEDVELD G D, et al. Infiltration and redistribution of LNAPL into unsaturated layered porous media[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2004,71(1−4):47 − 66. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2003.09.004
[20] 刘月峤, 丁爱中, 刘宝蕴, 等. 地下水位波动带中石油烃污染迁移转化规律综述[J]. 科学技术与工程,2018,18(24):172 − 178. [LIU Yueqiao, DING Aizhong, LIU Baoyun, et al. A review of the petroleum hydrocarbon contamination transformation performance in the zone of intermittent saturation[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2018,18(24):172 − 178. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.24.025
[21] BAEDECKER M J, EGANHOUSE R P, BEKINS B A, et al. Loss of volatile hydrocarbons from an LNAPL oil source[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2011,126(3-4):140 − 152. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2011.06.006
[22] 赵科锋, 王锦国, 曹慧群. 含单裂隙非饱和带中轻非水相流体修复的数值模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):43 − 55. [ZHAO Kefeng, WANG Jinguo, CAO Huiqun. Numerical simulation oflight non-aqueous phase liquids remediation in the unsaturated zone with single fractures[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):43 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] PRUESS K, BATTISTELLI A. TMVOC, A numerical simulator for three-phase non-isothermal flows of multicomponent hydrocarbon mixtures in saturated-unsaturated heterogeneous media[R]. Berkeley, CA, USA: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2002.
[24] 王颖, 汪洋, 唐军, 等. 基于TMVOC的水位波动带土壤气相抽提模拟[J]. 中国环境科学,2020,40(1):350 − 356. [WANG Ying, WANG Yang, TANG Jun, et al. Numerical simulation of SVE in groundwater table fluctuation zone based on TMVOC[J]. China Environmental Science,2020,40(1):350 − 356. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.01.039
[25] 李永涛. LNAPLs在包气带中运移机理及模拟研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2010.
LI Yongtao. Study on migration mechanism and simulation of light nonaqueous-phase liquids in vadose zone[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 浦烨枫, 江思珉, 栗现文, 等. DNAPLs在低渗透性夹层影响下的迁移和分布特征研究[J]. 工程勘察,2015,43(12):43 − 47. [PU Yefeng, JIANG Simin, LI Xianwen, et al. Study on migration and distribution of DNAPLs affected by layers with low permeability[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2015,43(12):43 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] KARADAG K, YATI I, BULBUL SONMEZ H. Effective clean-up of organic liquid contaminants including BTEX, fuels, and organic solvents from the environment by poly(alkoxysilane) sorbents[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2016,174:45 − 54.
[28] 朱振慧, 高宗军, 张晓海, 等. 轻质非水相流体(柴油)在多孔介质中的垂向运移[J]. 环境工程学报,2015,9(4):1842 − 1848. [ZHU Zhenhui, GAO Zongjun, ZHANG Xiaohai, et al. Vertical migration of LNAPLs(diesel) in porous medium[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2015,9(4):1842 − 1848. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150452
[29] GRIBOVSZKI Z, SZILAGYI J, KALICZ P. Diurnal fluctuations in shallow groundwater levels and streamflow rates and their interpretation-A review[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2010,385(1/2/3/4):371 − 383.
[30] HA J H, SEAGREN E A, SONG X. Oxygen transport across the capillary fringe in LNAPL pool-source zones[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2014, 140(12): 1 − 11.
[31] KIM J, CORAPCIOGLU M Y. Modeling dissolution and volatilization of LNAPL sources migrating on the groundwater table[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2003,65(1/2):137 − 158. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7722(02)00105-5
-



 下载:
下载: