Numerical simulation of three-dimensional soil-groundwater coupled chromium contamination based on FEFLOW
-
摘要:
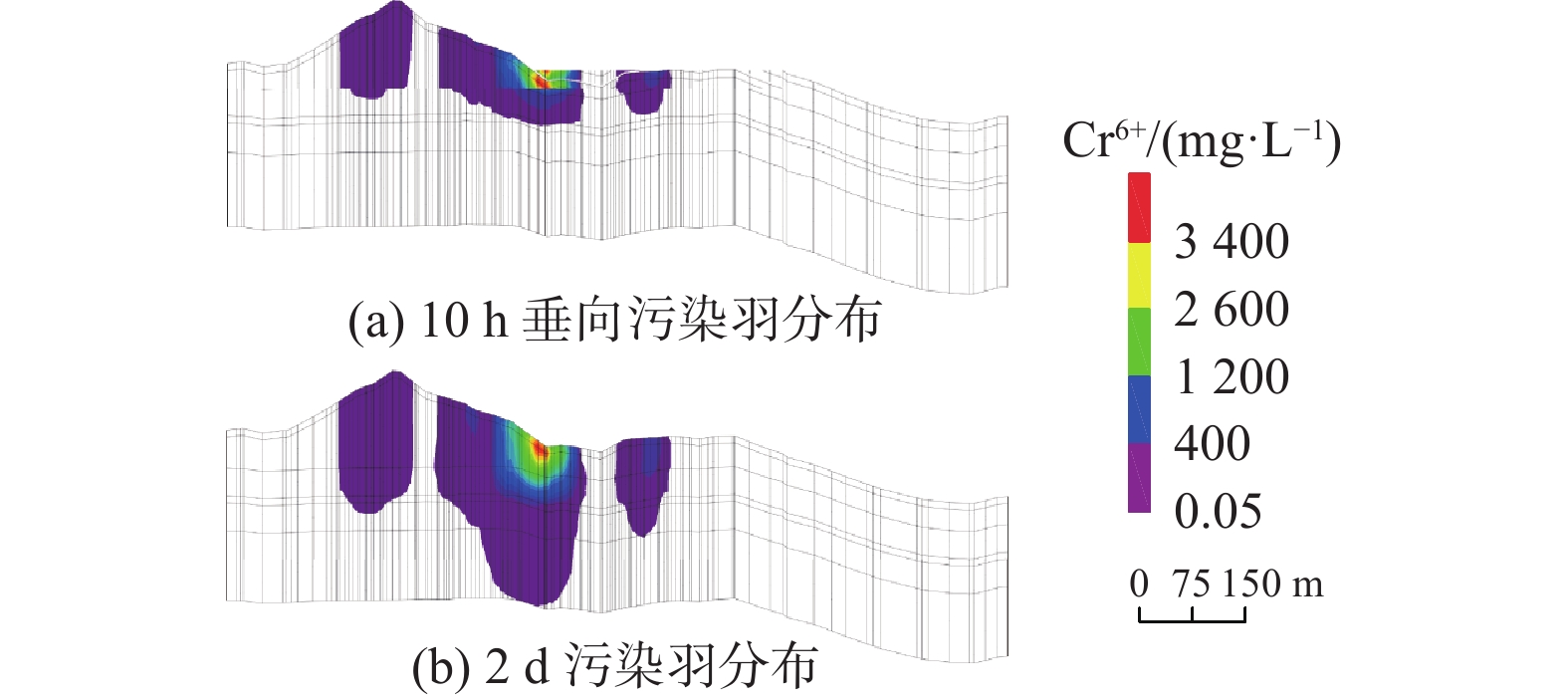
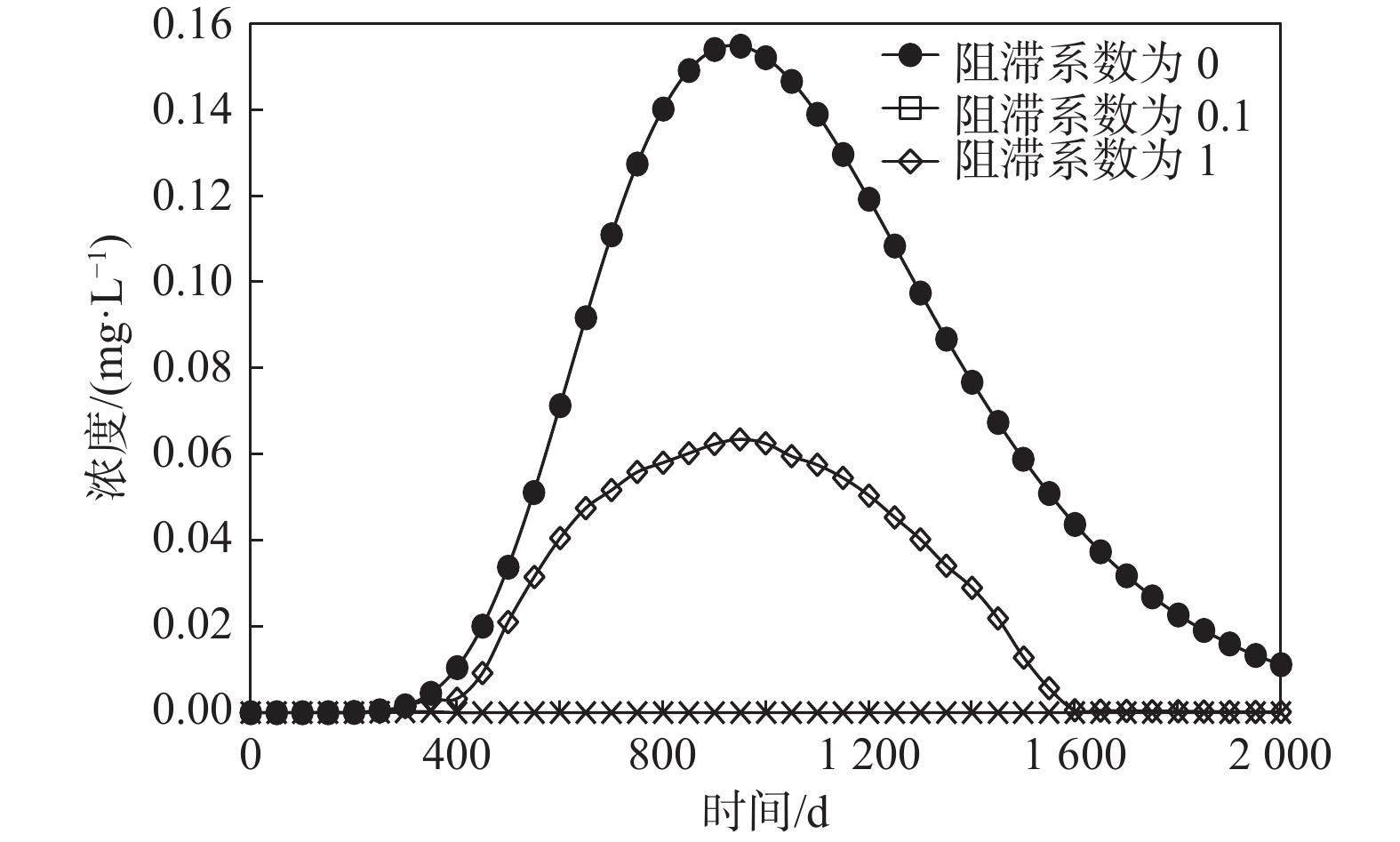
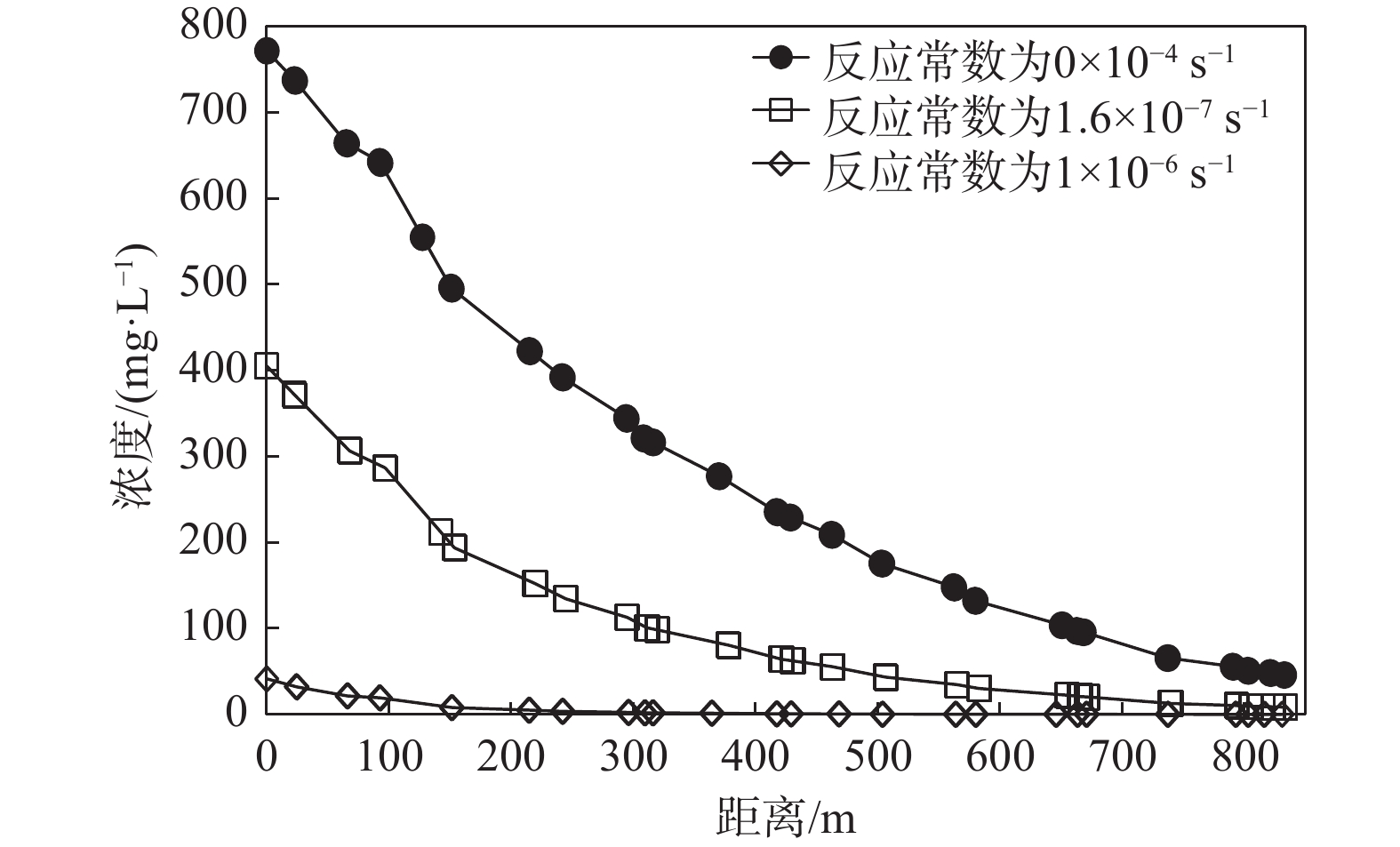
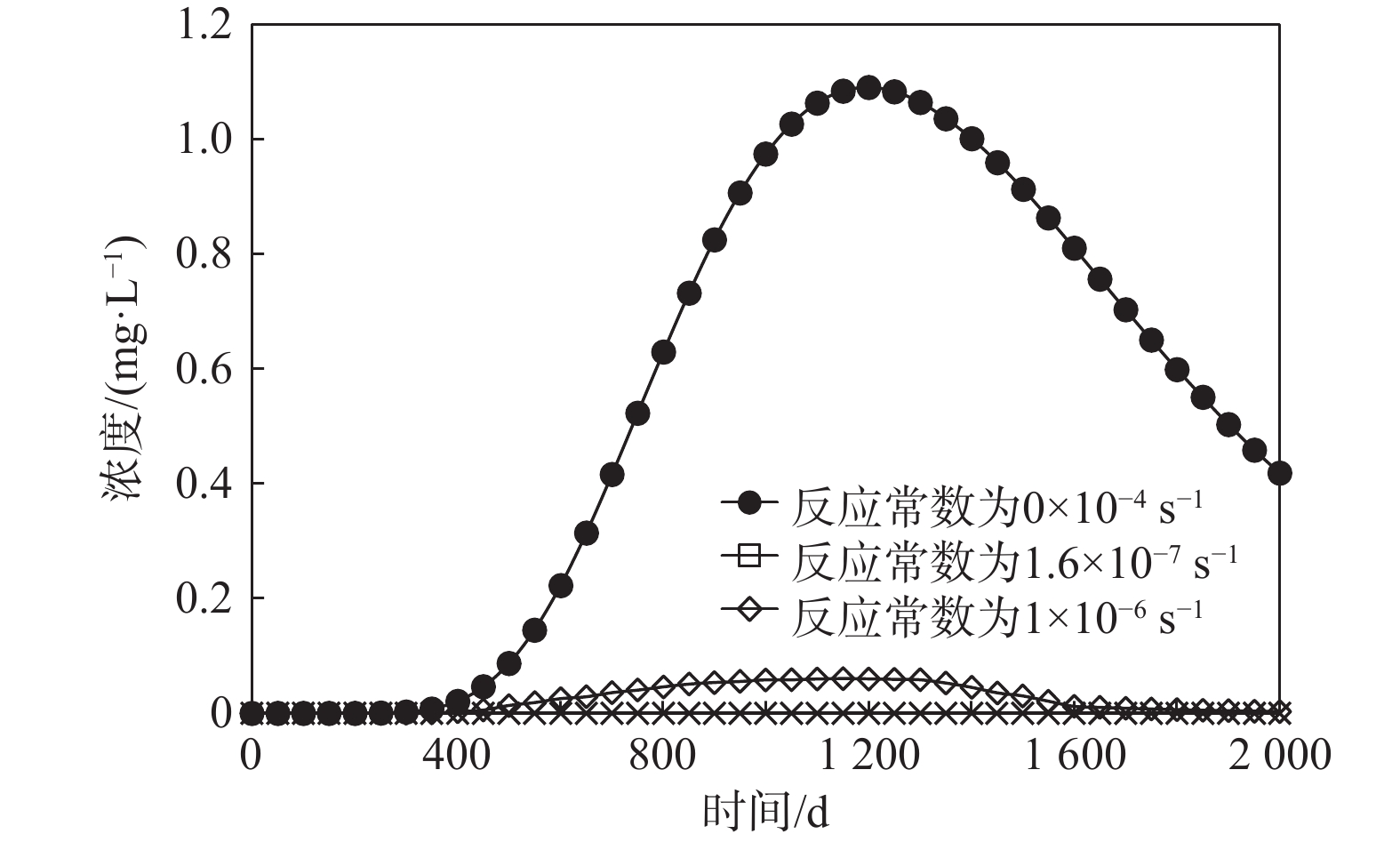
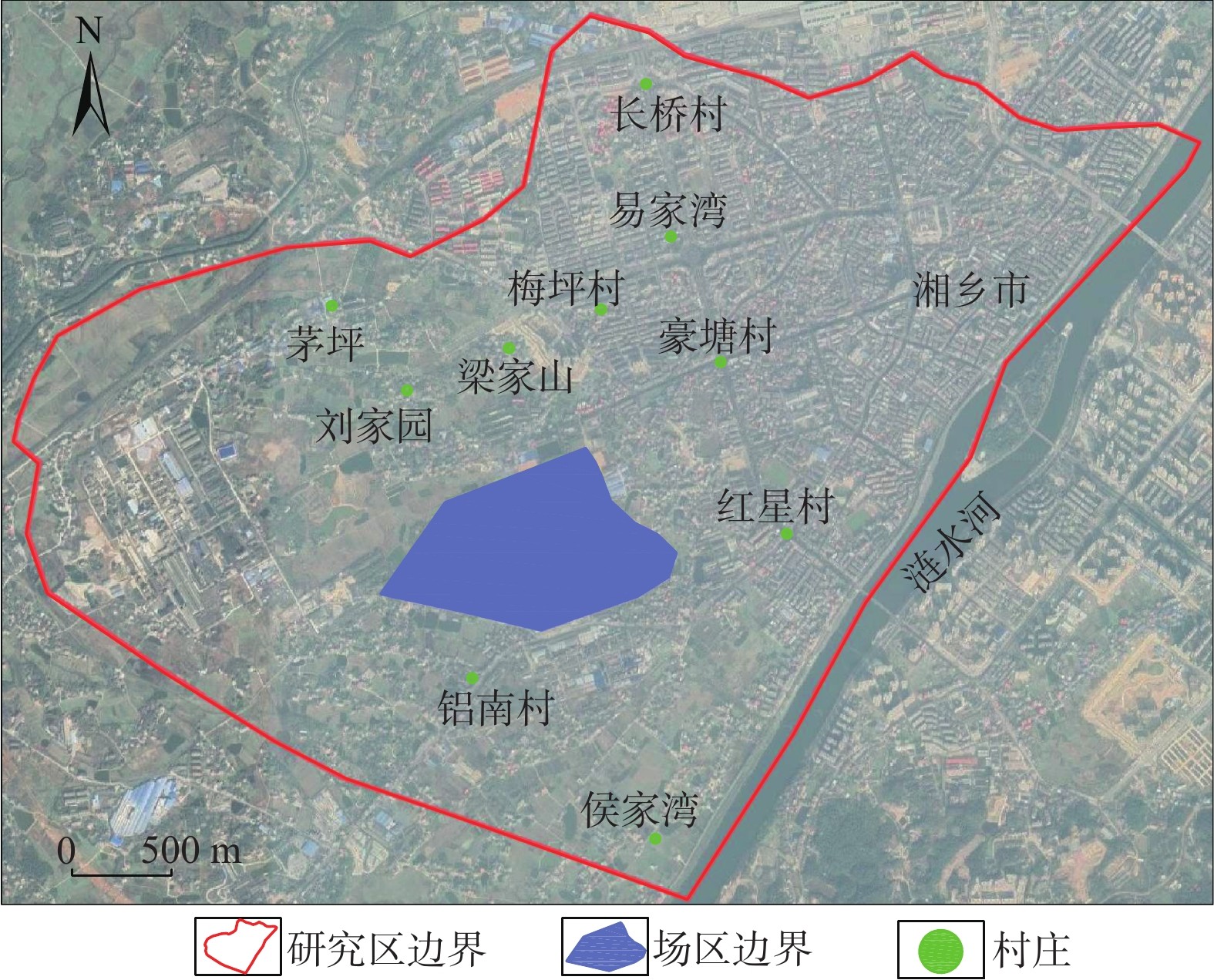
`土壤-地下水耦合数值模拟是定量刻画水流和溶质运移的主要手段。现有大范围场地尺度的研究受到数据采集难度及模拟计算量的限制,多是将土壤和地下水分成两个系统,这种方式不利于模型之间的计算反馈,易出现计算误差,因此将土壤和地下水作为整体系统研究具有重要意义。为精确刻画实际场地土壤-地下水系统中污染物迁移规律,揭示变饱和反应溶质迁移模型的参数敏感性,以某铬污染场地为研究对象,基于现场试验及前人研究所获数据,采用Galerkin有限元法建立三维土壤-地下水模型,定量描述六价铬在土壤-地下水中的迁移规律。在此基础上,通过改变补给条件,研究潜水面在土壤-地下水系统中的波动。并讨论阻滞系数和反应常数对溶质运移的影响。结果表明:在土壤中,污染物最大水平迁移距离为场地东南侧300 m;地下水中污染晕最大分布面积约为1.632 km2;垂向上土壤中的六价铬仅需15.6 h即可下渗至潜水面,第6天贯穿含水层。当潜水面随着补给量变化而波动时,地下水中六价铬会随水流进入土壤,影响土壤中污染分布。对溶质运移参数的讨论显示,当反应常数由0增大至10−6 s-1时,迁移出场区边界时地下水中污染物浓度约减少2000 mg/L,较难迁移至涟水河。基于FEFLOW的数值模型,能够解决各系统之间交互性差的问题,提供较为精确的模拟结果。
Abstract:Soil-groundwater coupled numerical simulation is the main method to quantitatively describe the flow and solute transport in a groundwater system. The existing researches on a large-scale site are limited by the difficulty of data acquisition and the amount of simulation calculation. Most of them divide the soil and groundwater into two systems, and it is of great significance to study the soil and groundwater as a whole system. In order to accurately depict the migration of contaminants in the soil-groundwater system of the actual site and reveal the parameter sensitivity of the variable saturation reaction solute transport model, in this paper, a 3D soil-groundwater model is established by using the Galerkin finite element method to quantitatively describe the migration of hexavalent chromium in soil-groundwater based on the data obtained from field tests and previous studies. The fluctuation of phreatic surface in the soil-groundwater system is studied by changing the recharge conditions. The effects of retardation coefficient and reaction constant on solute transport are discussed. The results show that in the soil, the maximum horizontal migration distance of contaminants is 300 m to the southeast of the site; the maximum distribution area of contamination halo in groundwater is about 1.632 km2; the vertical hexavalent chromium in soil only needs 15.6 h to infiltrate into the phreatic surface, and penetrates through the aquifer in the sixth day. When the groundwater level fluctuates with the change of recharge, hexavalent chromium in groundwater will enter the soil with the water flow, affecting the distribution of contamination in the soil. The discussion of solute transport parameters shows that when the reaction constant increases from 0 to 10-6s-1, the concentration of the contaminants in groundwater decreases by about 2000 mg/L at the boundary of the migration site, which makes it difficult to migrate to the Lianshui River. The numerical model based on FEFLOW can solve the problem of poor interaction between systems and provide more accurate simulation results.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- groundwater /
- coupling simulation /
- contaminants transport /
- FEFLOW
-

-
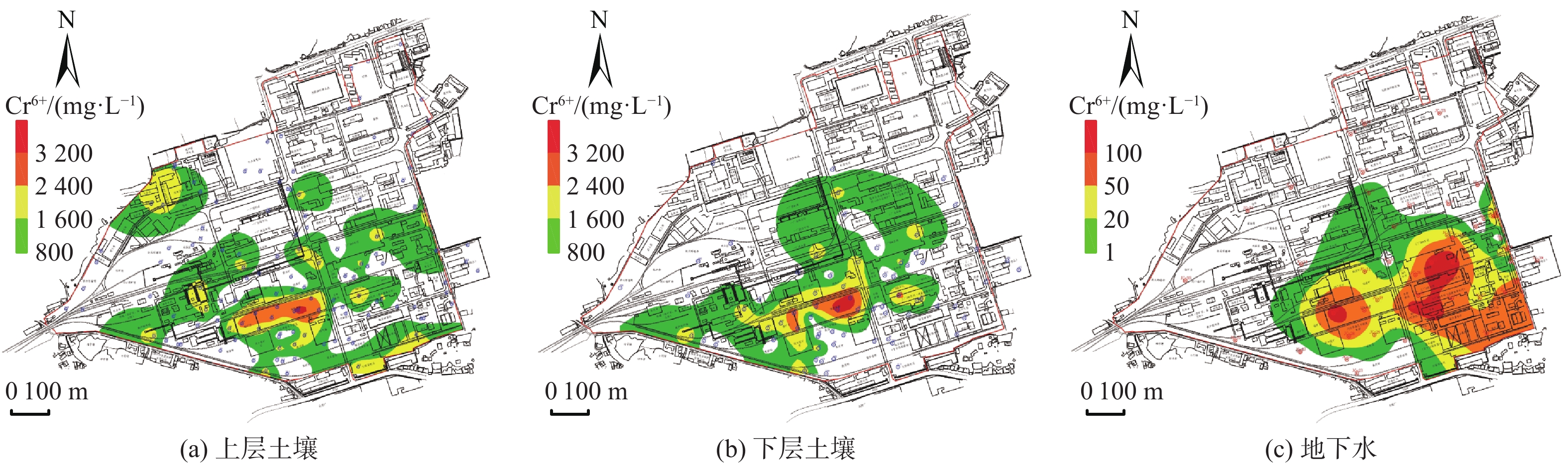
表 1 六价铬检测结果
Table 1. Statistics of soil test results
层位 标准限值/(mg·L−1) 分析总数/个 超标
个数/个超标率/% 最大值/(mg·L−1) 最小值/(mg·L−1) 平均值/(mg·L−1) 相对偏差/% 上层土壤 30 203 29 14.3 3410 <1.0 283 733 下层土壤 30 94 17 18.1 3430 <1.0 414 876 地下水 0.1 45 23 51.1 109 <0.01 21.2 30.6 表 2 研究区水文地质参数取值表
Table 2. Values of hydrogeological parameters in the study area
参数 非饱和区 饱和区 第一亚层 第二亚层 第二层 第三层 第四层 第五层 Kxx/(m·d−1) 0.0864 0.0864 0.1 1 33 4 Kyy/(m·d−1) 0.0864 0.0864 0.1 1 33 4 Kzz/(m·d−1) 0.0864 0.0864 0.01 0.1 3.3 0.4 孔隙度 0.5 0.1 0.05 0.1 0.3 0.1 最大饱和度 1 1 1 / / / 剩余饱和度 0.12 0.12 0.12 / / / 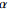 /m−1
/m−11.2 1.2 1.2 / / / n 3 3 3 / / / 表 3 溶质运移模型参数取值表
Table 3. Parameter values of the solute transport model
参数 非饱和区 饱和区 第一亚层 第二亚层 第二层 第三层 第四层 第五层 弥散系数/
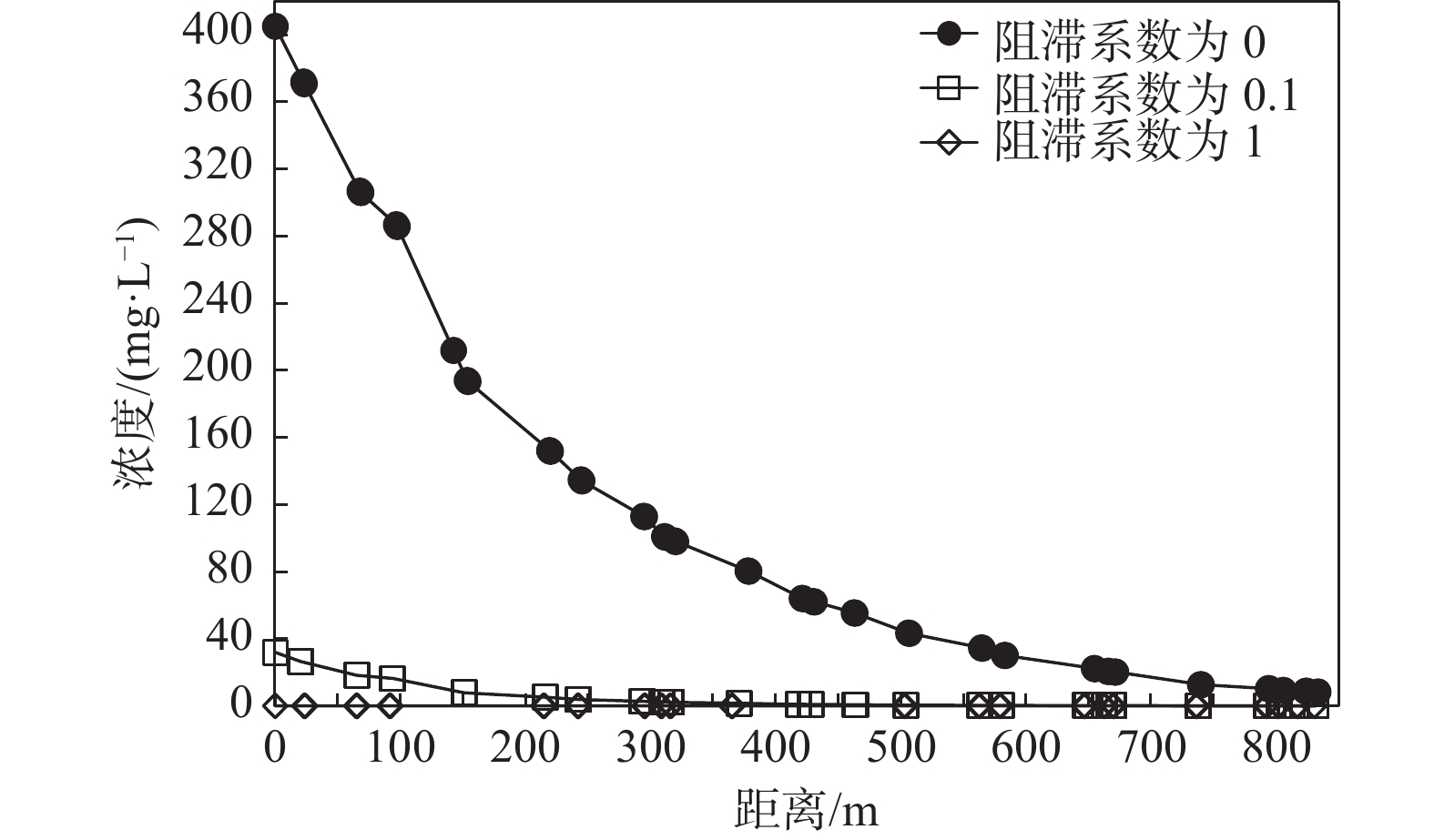
(10−9m2·s−1)200 200 200 2300 2300 2300 纵向弥散度/m 1 1 1 100 100 100 横向弥散度/m 0.2 0.2 0.2 20 20 20 阻滞系数 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.01 0.01 0.01 反应系数/
(10−4·s−1)0.0016 0.0016 0.0016 0.0016 0.0016 0.0016 表 4 污染晕面积表
Table 4. Contaminant halo area
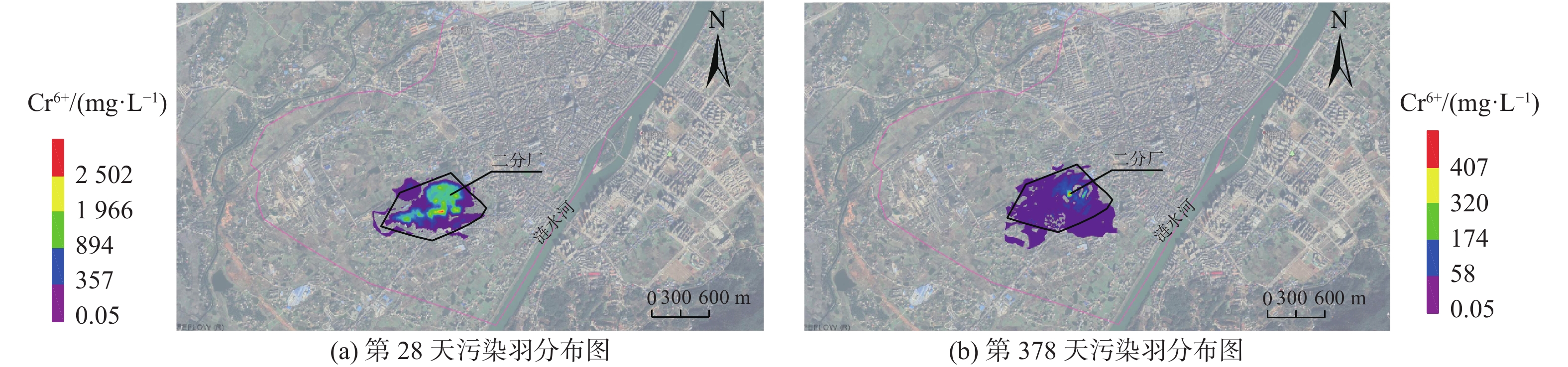
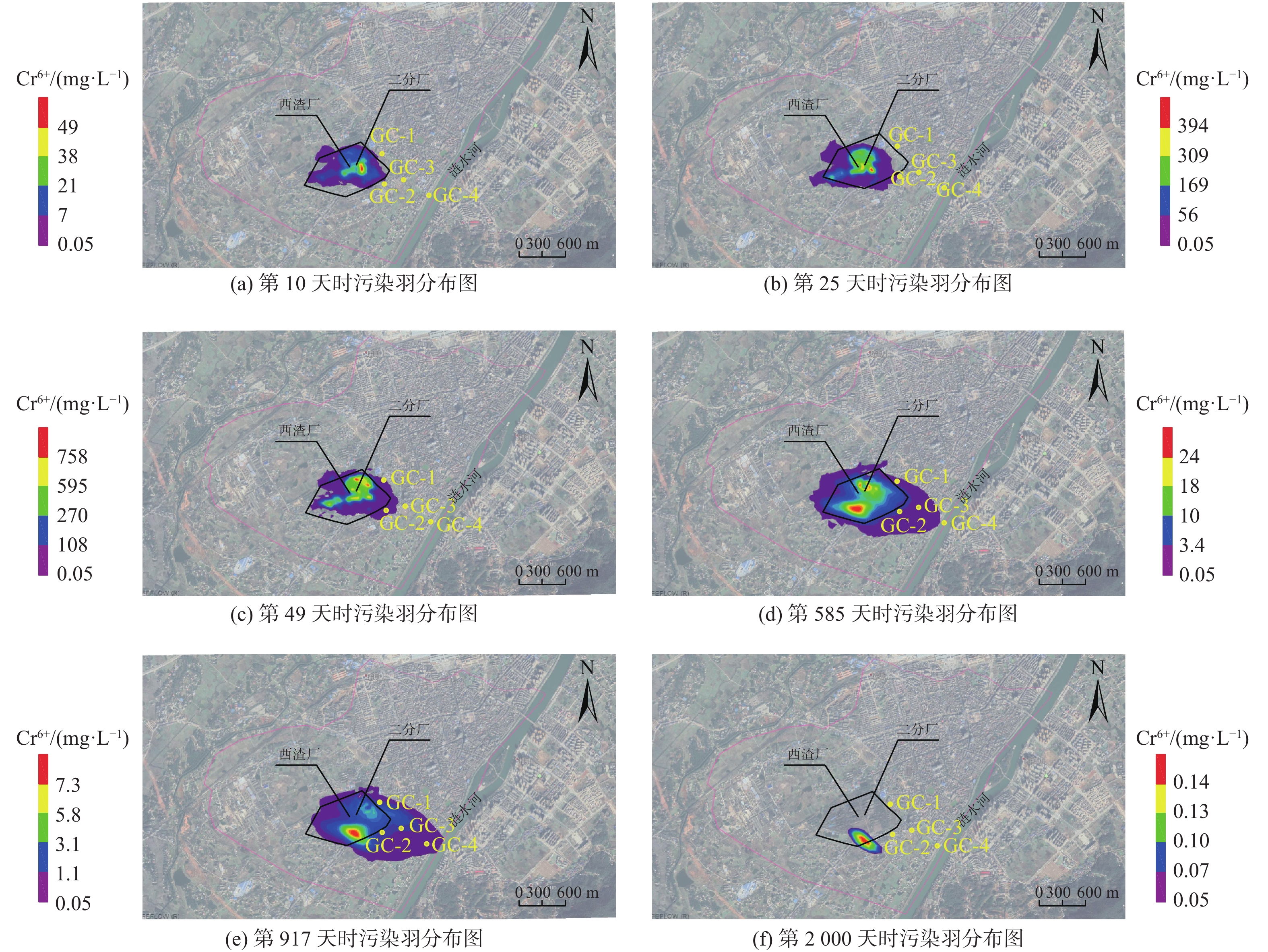
时间/d 面积/km2 时间/d 面积/km2 100 0.831 1100 1.416 200 1.030 1200 1.350 300 1.246 1300 1.255 400 1.321 1400 1.055 500 1.413 1500 0.876 600 1.478 1600 0.601 700 1.569 1700 0.376 800 1.596 1800 0.241 917 1.632 1900 0.0018 1000 1.465 2000 0.0014 -
[1] 陈晨, 胡立新, 叶力. 清洁场项目地下水污染迁移研究[J]. 世界生态学,2018,7(2):80 − 88. [CHEN Chen, HU Lixin, YE Li. Study on groundwater pollution transfer in clean field project[J]. International Journal of Ecology,2018,7(2):80 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12677/IJE.2018.72012
[2] HAVARD P L, PRASHER S O, BONNELL R B. LINKFLOW a water flow computer model for water table management: Part1. Model development[J]. Transactions of the ASAE,1995,38(2):481 − 488. doi: 10.13031/2013.27856
[3] FACCHI A, ORTUANI B, MAGGI D, et al. Coupled SVAT-groundwater model for water resources simulation in irrigated alluvial plains[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software,2004,19(11):1053 − 1063.
[4] TWARAKAVI N K C, ŠIMUNEK J, SOPHIA S. Evaluating interactions between groundwater and vadose zone using the HYDRUS-based flow package for MODFLOW[J]. Vadose Zone Journal,2008,7(2):757 − 768. doi: 10.2136/vzj2007.0082
[5] BERGVALL M. Hydrogeological modeling to improve remediation strategies for a drinking water aquifer contaminated by an aqueous phase liquid[D]. Umea: Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, 2011.
[6] 张旭洋, 林青, 黄修东, 等. 大沽河流域土壤水-地下水流耦合模拟及补给量估算[J]. 土壤学报,2019,56(1):101 − 113. [ZHANG Xuyang, LIN Qing, HUANG Xiudong, et al. Soil water groundwater coupling simulation and recharge estimation in Dagu River Basin[J]. Acta pedologica Sinica,2019,56(1):101 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] NISWONGER R G, PRUDIC D E. Modeling variably saturated flow using kinematic waves in MODFLOW[J]. Groundwater Recharge in a Desert Environment: The Southwestern United States, 2004, 9(1):101 − 112.
[8] NISWONGER R G, PRUDIC D E , REGAN R S. Documentation of the unsaturated-zone flow (UZF1) package for modeling unsaturated flow between the land surface and the water table with MODFLOW-2005[R]. Reston: U. S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods, 2006.
[9] YAKIREVICH A, BORISOV V, SOREK S. A quasi three-dimensional model for flow and transport in unsaturated and saturated zones: 1. Implementation of the quasi two-dimensional case[J]. Advances in Water Resources,1998,21(8):679 − 689. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1708(97)00031-6
[10] 林琳, 杨金忠, 史良胜, 等. 区域饱和-非饱和地下水流运动数值模拟[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版),2005,38(6):53 − 58. [LIN Lin, YANG Jinzhong, SHI Liangsheng, et al. Saturated and unsaturated groundwater flow numerical simulation in large scale zone[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University,2005,38(6):53 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 查元源, 朱焱, 杨金忠. 基于改进积分型Richards方程的区域地下水饱和-非饱和水流耦合模型[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),2013,45(1):107 − 116. [ZHA Yuanyuan, ZHU Yan, YANG Jinzhong. A regional coupled groundwater model for unsaturated-saturated flow based on modified integrated richards equation[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2013,45(1):107 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 查元源. 饱和-非饱和水流运动高效数值算法研究及应用[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2014: 5 − 7.
ZHA Yuanyuan. Research on cost-effective algorithm for unsaturated-saturated flow and its application[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2014: 5 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 朱焱. 区域拟三维饱和-非饱和水流与溶质运移模型研究与应用[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2013: 5 − 7.
ZHU Yan. Study on quasi-3D water flow and solute transport model in regional scales and its application[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2013: 5 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] ZHOU Y, WANG Y X, ZWAHLEN F , et al. FEFLOW modeling of groundwater-surface water system of Maozui area of Jianghan Plain, Central China[C] //The 7th International Conference on Calibration and Reliability Groundwater Modeling(modelCARE2009). Wuhan, 2009: 241 − 244.
[15] HUO Z L, FENG S Y, KANG S Z, et al. Simulation of effects of agricultural activities on groundwater level by combining FEFLOW and GIS[J]. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research,2007,50(5):839 − 846. doi: 10.1080/00288230709510358
[16] 胡健, 张祥达, 魏志诚. 基于FEFLOW在地下水数值模拟中的应用综述[J]. 地下水,2020,42(1):9 − 13. [HU Jian, ZHANG Xiangda, WEI Zhicheng. Literature review of the groundwater numerical simulation method based on the application of FEFLOW[J]. Ground water,2020,42(1):9 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] DIERSCH H J G, PERROCHET P. On the primary variable switching technique for simulating unsaturated-saturated flows[J]. Advances in Water Resources,1999,23(3):271 − 301.
[18] HUYAKORN P S, MERCER J W, WARD D S. Finite element matrix and mass balance computational schemes for transport in variably saturated porous media[J]. Water Resources Research,1985,21(3):346 − 358. doi: 10.1029/WR021i003p00346
[19] DIERSCH H J G . Finite element modeling of flow, mass and heat transport in porous and fractured media[M]. Berlin: Groundwater Modelling Centre DHI-WASY GmbH, 2014: 1 − 19.
[20] PANDAY S , HUYAKORN P S , THERRIEN R , et al. Improved three-dimensional finite-element techniques for field simulation of variably saturated flow and transport[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,1993, 12(1/2): 3 − 33.
[21] ŠIMŮNEK J, ŠEJNA M, SAITO H , et al. The HYDRUS-1D software package for simulating the one-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media[R]. California: University of California Riverside, 2008.
[22] 陈彦, 吴吉春. 含水层渗透系数空间变异性对地下水数值模拟的影响[J]. 水科学进展,2005,16(4):483 − 487. [CHEN Yan, WU Jichun. Effect of the spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity in aquifer on the numerical simulation of groundwater[J]. Advances in water science,2005,16(4):483 − 487. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 刘兆昌. 地下水系统的污染与控制[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1991.
LIU Zhaochang. Pollution and control of groundwater system[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1991. (in Chinese)
[24] SEFEROU P , SOUPIOS P, KOURGIALAS N N, et al. Olive-oil mill wastewater transport under unsaturated and saturated laboratory conditions using the geoelectrical resistivity tomography method and the FEFLOW model[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2013,21(6):1219 − 1234. doi: 10.1007/s10040-013-0996-x
[25] GELHAR L W, WELTY C, REHFELDT K R. A critical review of data on field-scale dispersion in aquifers[J]. Water Resources Research,1992,28(7):1955 − 1974. doi: 10.1029/92WR00607
[26] 孙讷正. 地下水污染-数学模型和数值方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989: 33 − 36.
SUN Nezheng. Groundwater pollution mathematical model and numerical method[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1989: 33 − 36. (in Chinese)
[27] 王焰新. 地下水污染与防治[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007: 19 − 32.
WANG Yanxin. Groundwater pollution and control[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007: 19 − 32. (in Chinese)
[28] 姜利国, 梁冰. 非饱和-饱和区域中重金属污染物运移数值模拟[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报:自然科学版,2007,26(增刊 2):74 − 76. [JIANG Liguo,LIANG Bing. Numerical analog simulation of heavy metal pollution transport in variably saturated flow[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science Edition),2007,26(Sup 2):74 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 张俊杰. 包气带中六价铬运移规律的离心试验研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018.
ZHANG Junjie. Study on the migration law of hexavalent chromium in unsaturated zone through centrifugal test[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] WENG C H, HUANG C P, ALLEN H E, et al. Chromium leaching behavior in soil derived from chromite ore processing waste[J]. The Science of The Total Environment,1994,154(1):71 − 86. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(94)90615-7
[31] KHAN A A, MUTHUKRISHNAN M, GUHA B K. Sorption and transport modeling of hexavalent chromium on soil media[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,174(1−3):444 − 454. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.073
[32] 谢水波, 陈泽昂, 张晓健, 等. 宏观弥散度和阻滞系数对地下水中核素迁移模拟的影响[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2007,34(5):78 − 82. [XIE Shuibo, CHEN Zeang, ZHANG Xiaojian, et al. Effect of macrodispersivity and retardation coefficient on retardation coefficient on radionuclide migration simulation[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences),2007,34(5):78 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] KOTAS J , STASICKA Z. Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation[J]. Environmental Pollution,2000,107(3):263 − 283.
-



 下载:
下载: