Influence of organic matter content and ingredient on the physical and mechanical properties of peat soils
-
摘要:
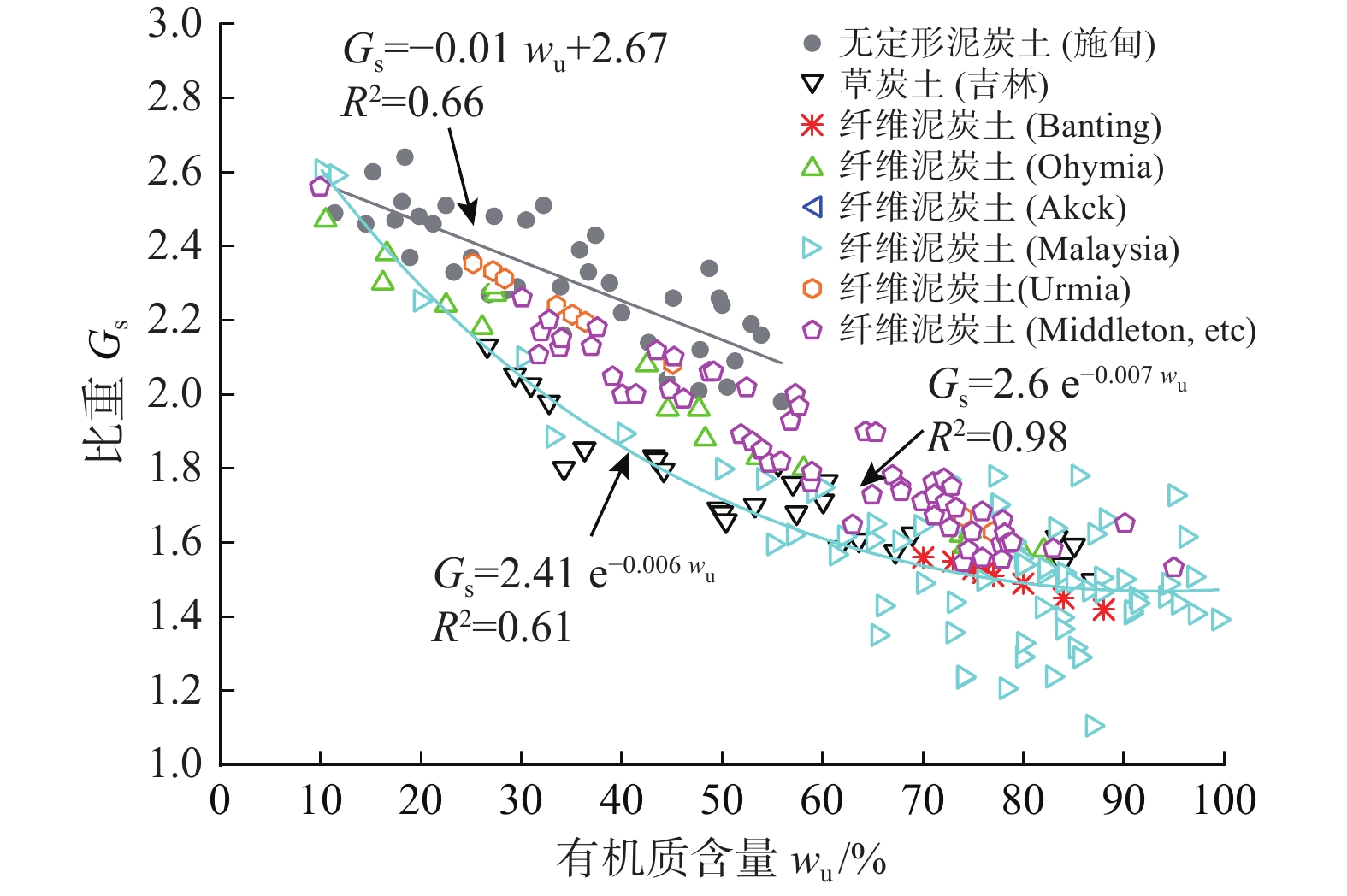
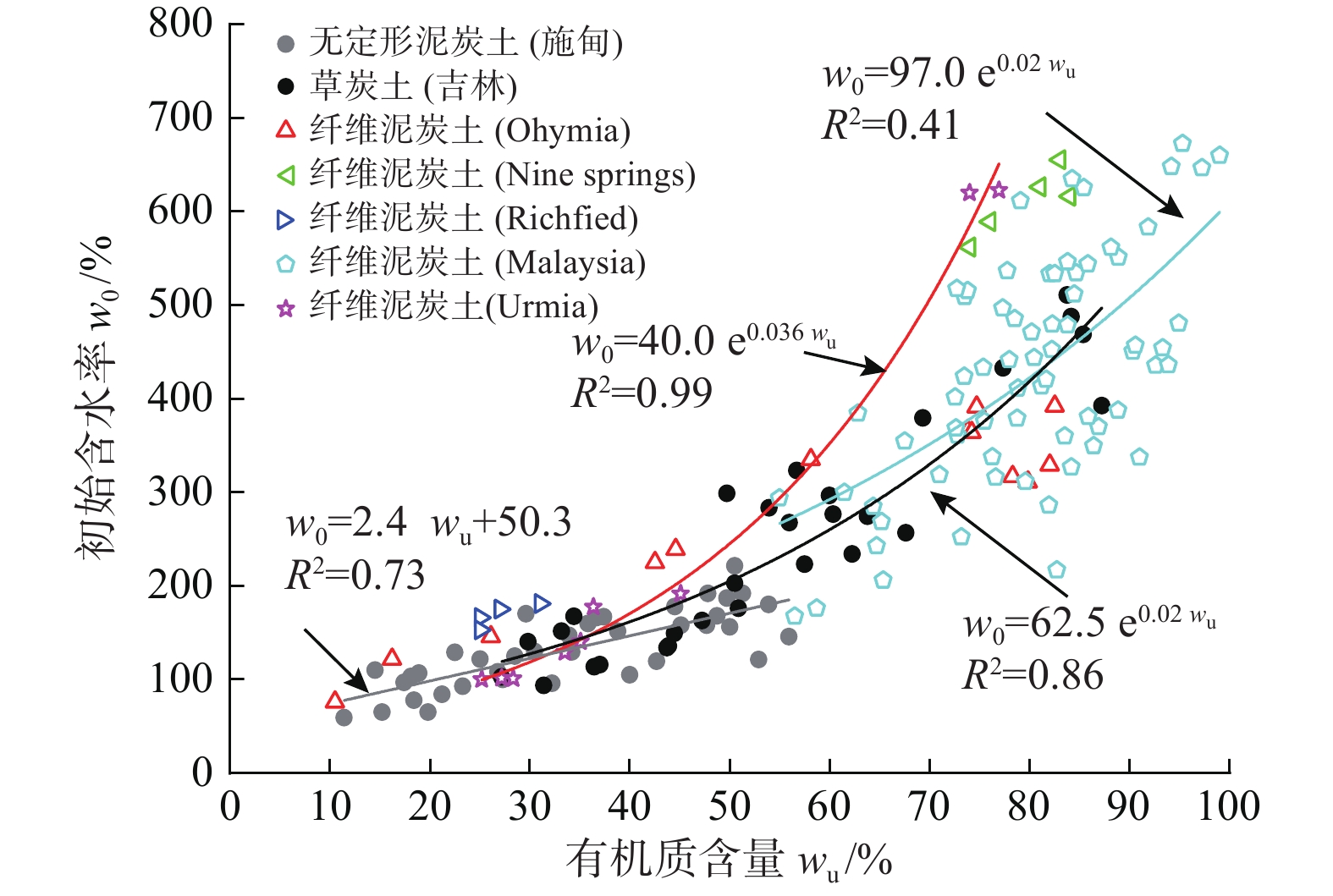
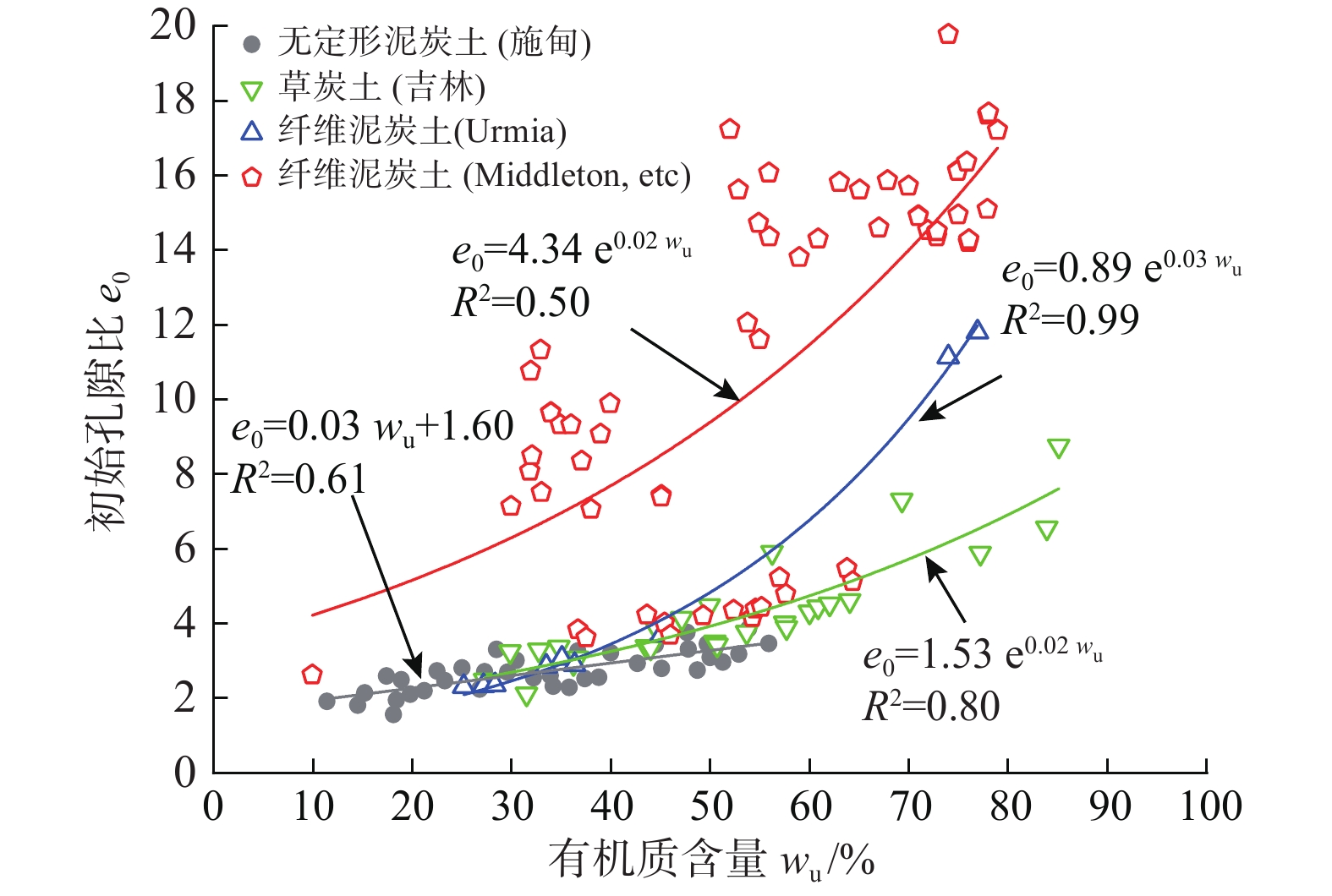
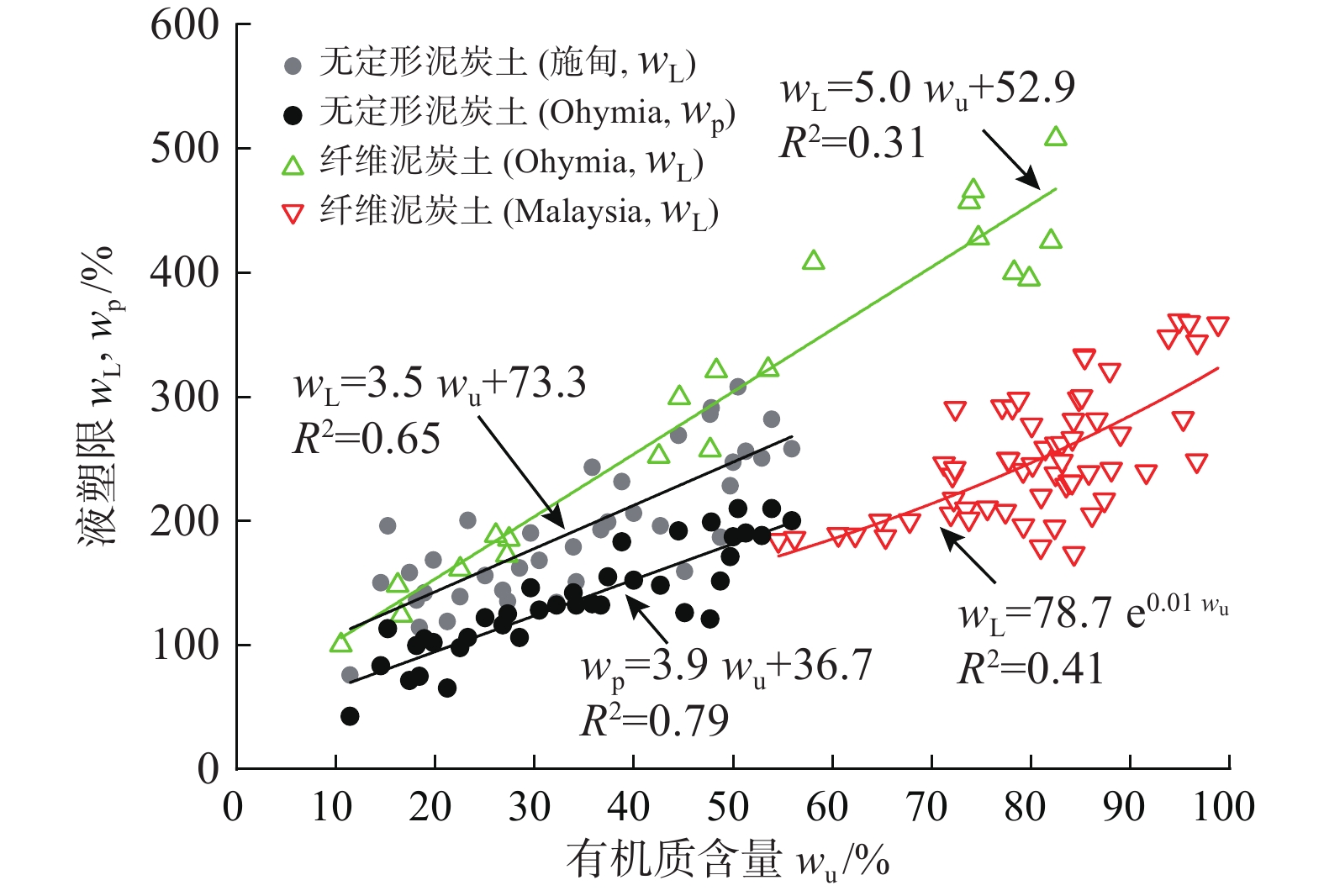
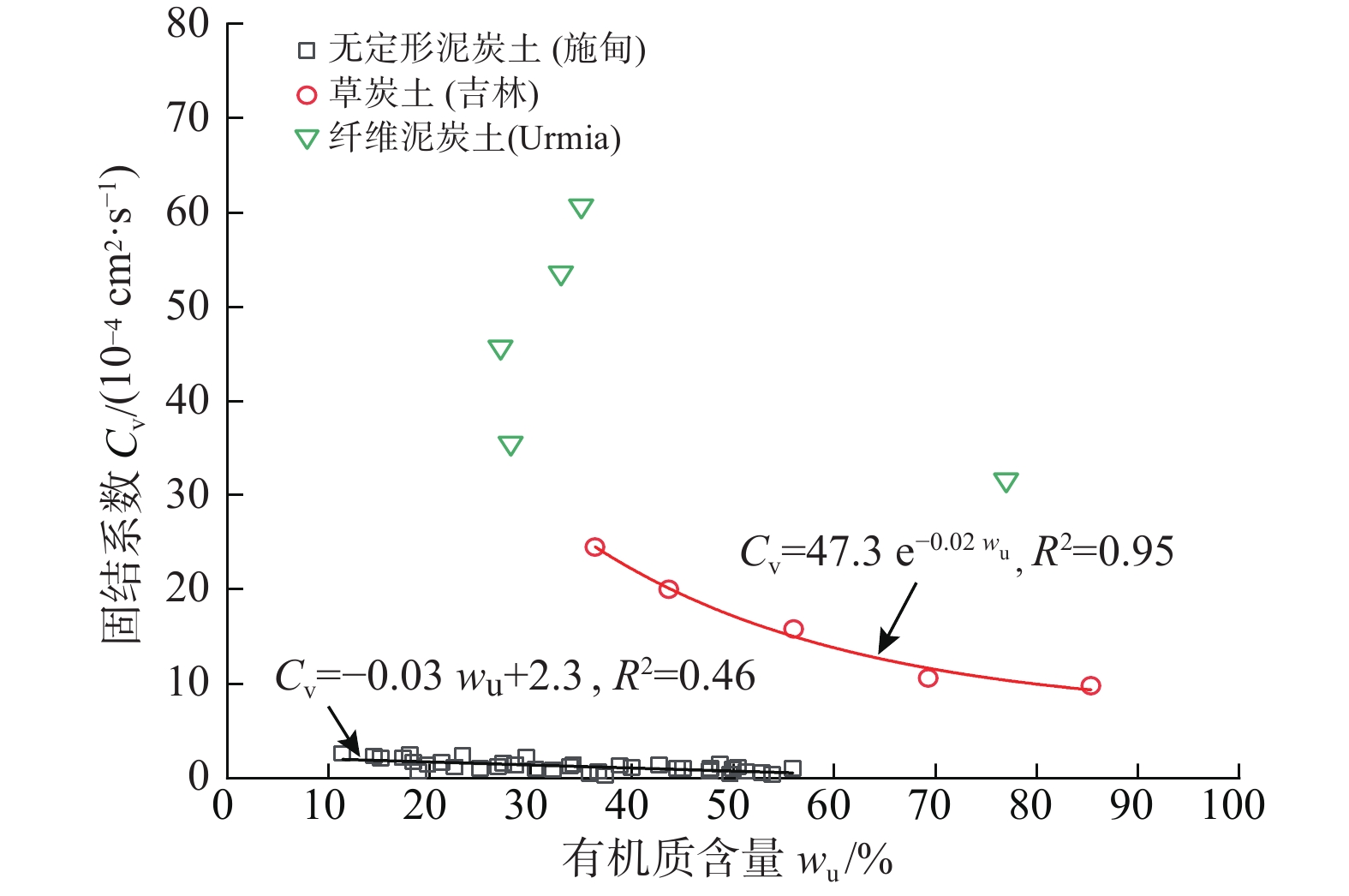
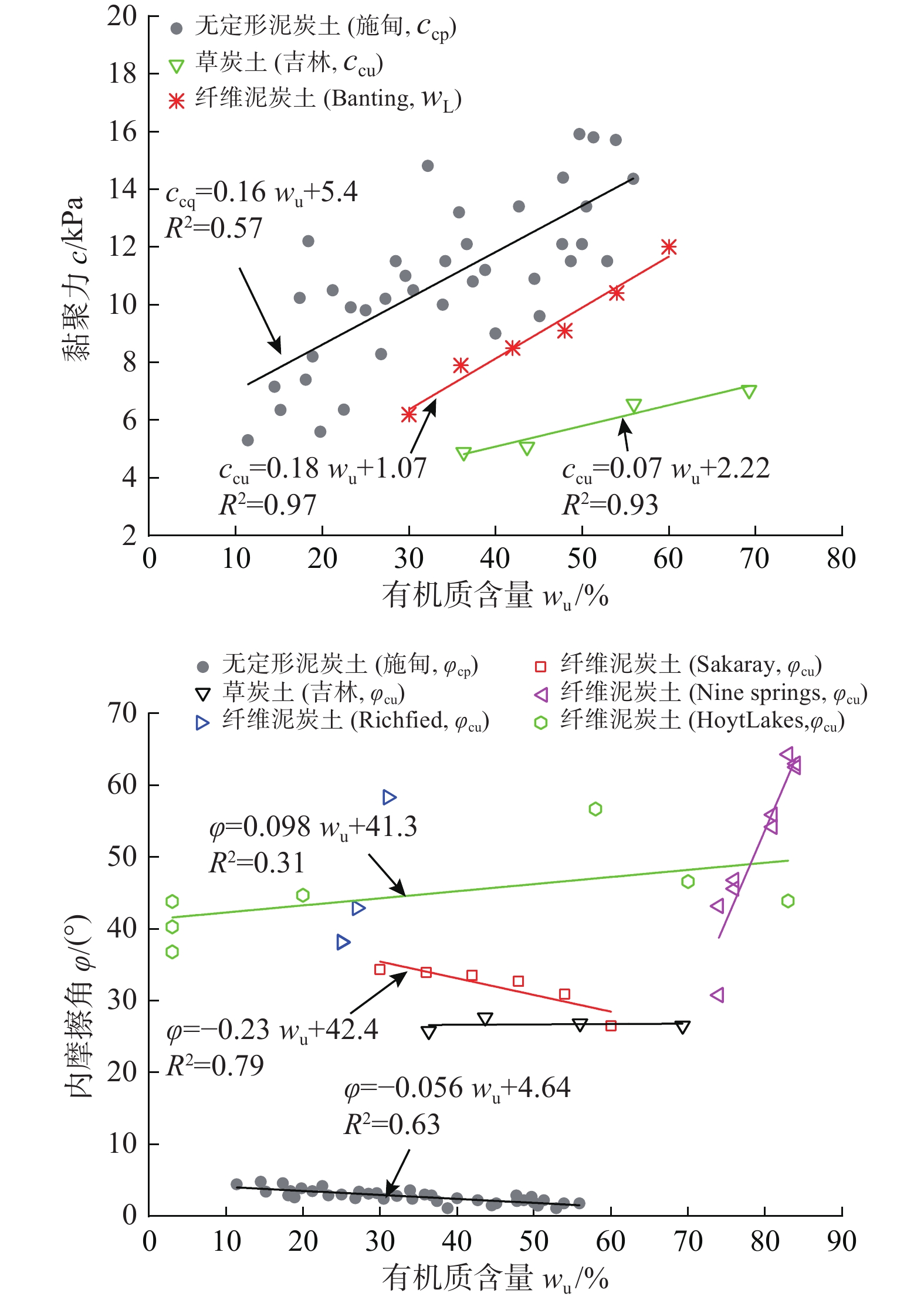
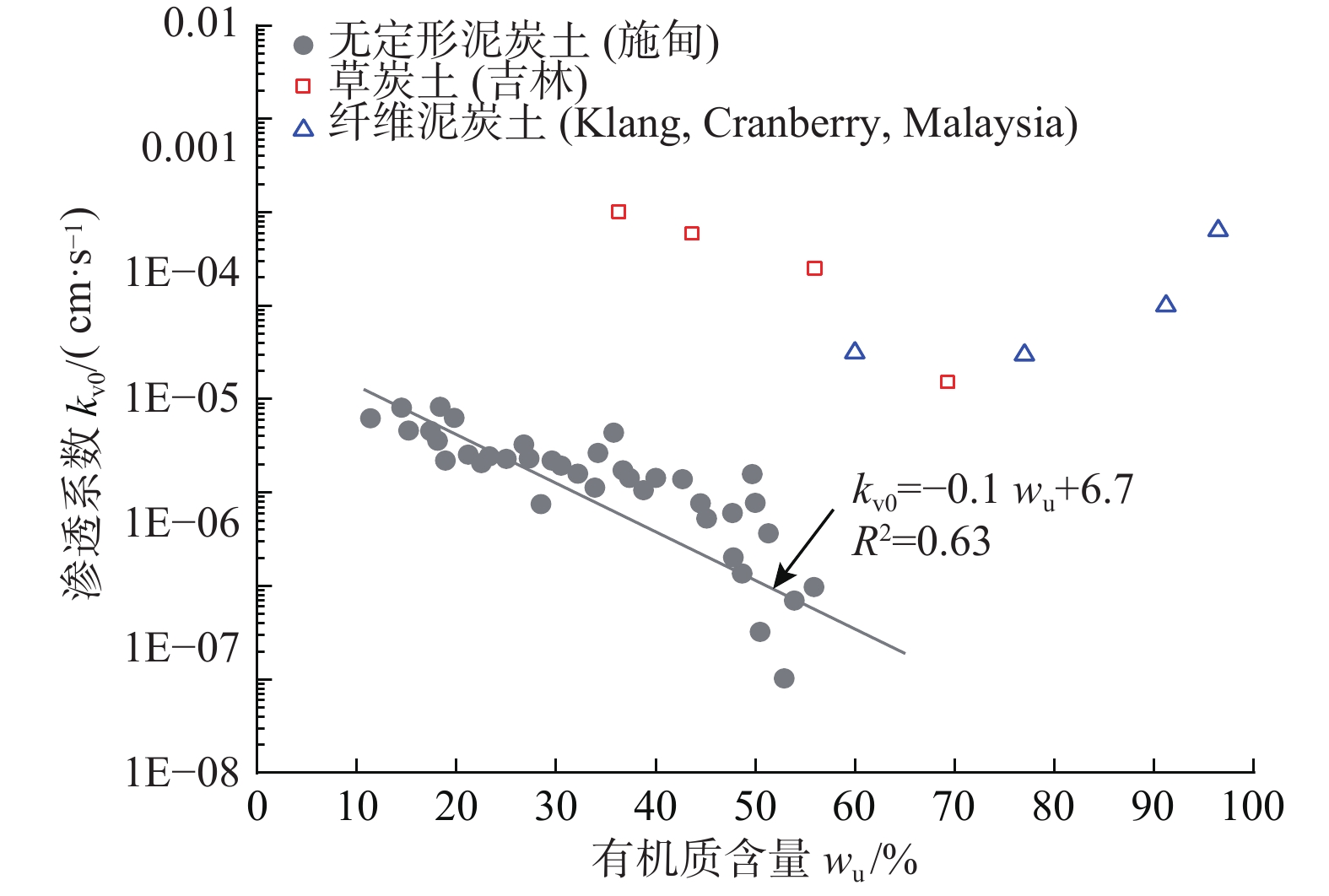
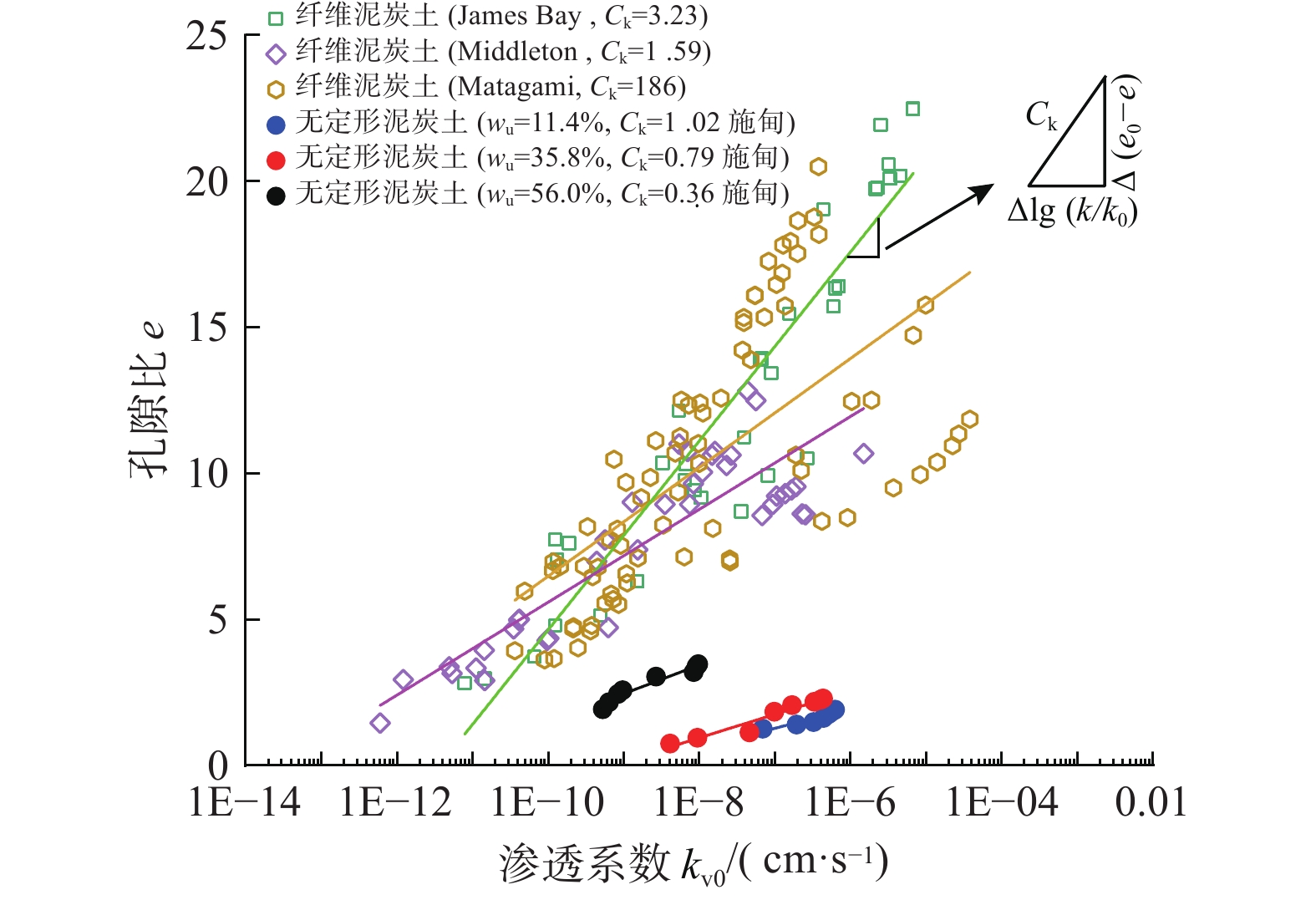
富含有机物质是泥炭土工程性质不良的主要原因。不同有机质含量及组分的泥炭土,其物理力学性质差异很大。为明确有机质含量的影响,对数十组不同有机质含量无定形泥炭土试样进行一系列室内试验,系统分析了物理、变形、强度及渗透性随有机质含量的变化规律;为比较有机质组分不同导致的工程性质差异,将以上无定形泥炭土物理力学指标与纤维泥炭土试验数据进行系统分析。结果表明:无定形泥炭土基本物理力学指标与有机质含量间有一定的线性关系,其中,初始孔隙比(e0)、天然含水率(w0)、液塑限(wL、wp)、黏聚力(c)随有机质含量增加线性增大,比重(Gs)、固结系数(Cv)和内摩擦角(φ)随有机质含量增大而减小。相较无定形泥炭土,纤维泥炭土比重小、含水率大、孔隙比大。抗剪强度方面,无定形泥炭土黏聚力随有机质含量增大而增大,较纤维泥炭土略高;内摩擦角随有机质含量增大而有下降趋势,约为纤维泥炭土的1/5~1/14。渗透性方面,无定形泥炭土的初始渗透系数(kv0)及渗透指数(Ck)随有机质含量增大而减小,且普遍小于纤维泥炭土。
Abstract:Peat soil is rich in organic matter, which is the main reason for its poor engineering properties. The content and compositions of organic matter of peat soil lead to the various physical and mechanical properties of this kind of soil. In order to clarify the influence of organic matter content, a series of laboratory tests are conducted on dozens of groups of amorphous peat soil samples with different organic matter content, and the laws of physics, deformation, strength and permeability with organic matter content are systematically analyzed. In order to compare the difference in engineering properties caused by the different organic matter components, the experimental data of the fiber peat soil from domestic and foreign literatures are collected and compared systematically with the physical and mechanical indexes of the amorphous peat soil. The results show that there is a certain linear relationship between the basic physical and mechanical indexes of the amorphous peat soil and the organic matter content. Among them, the initial void ratio (e0), natural moisture content (w0), liquid plastic limit (wp, wL), cohesion (c) increases linearly with the increase of the organic matter content. Specific gravity (Gs), consolidation coefficient (Cv) and internal friction angle (φ) decrease with the increase in organic matter content. Compared with the amorphous peat soil, the fiber peat soil is characterized by small specific gravity, high water content and a large void ratio. In terms of shear strength, the cohesive force of the amorphous peat increases with the increase of organic matter content, which is slightly higher than that of the fiber peat soil. The internal friction angle has a downward trend with the increase of organic matter content, which is about 1/5~1/14 that of the fiber peat soil. In terms of permeability, the initial permeability coefficient (kv0) and permeability index (Ck) of the amorphous peat soil decrease with the increase in organic matter content, and are generally smaller than those of the fiber peat soil.
-

-
表 1 施甸泥炭土基本物理力学指标
Table 1. Basic physical and mechanical indexes of the Shidian peat soil
指标参数 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 天然含水率w0/% 38 59.3 221.5 132.8 颗粒比重Gs 38 1.9 2.6 2.3 天然孔隙比e0 38 1.6 3.9 1.6 饱和度Sr /% 38 80.7 98.2 93.8 液限wL /% 38 75.7 307.9 192.3 塑限wp /% 38 26.3 210.0 101.4 有机质含量wu /% 38 10.4 58.0 25.3 固结系数Cv /(10−4cm2·s−1) 38 1.1 8.3 4.0 黏聚力c /kPa 38 5.3 15.9 10.9 内摩擦角φ/ (°) 38 1.1 4.8 2.8 渗透系数kv0/ (cm·s−1) 38 2.1×10−9 1.3×10−6 5.4×10−7 表 2 泥炭土物理力学指标统计表
Table 2. Physical and mechanical indexes of the peat soil
泥炭土
产地Von
Post值有机质含量
wu/%纤维含量
wf/%颗粒比重
Gs含水率
w0/%孔隙比
e0液限
wL/%塑限
wP/%黏聚力
c/kPa内摩擦角
φ/(°)渗透系数
kv0/(cm·s−1)固结系数Cv/
(10−4cm2·s−1)来源 施甸 H8~H10 10~58 <5 1.90~2.60 59.3~221.5 1.6~3.9 75.7~
307.926.3~
210.05.3~15.9 1.1~4.8 0.8×10−7~
3.5×10−70.9~2.6 本文 Nine
springsH2~H3 74~84 75~92 — 562~655 — — — — 30.0~64.3 — — Edil et al[3] Richfied H3 25~31 37~45 — 153~181 — — — — 38.1~58.3 — — Hoyt
LakesH4~H5 3~70 50~58 — — — — — — 36.8~56.7 — — 吉林 H4~H6 27~88 65~50 1.50~2.10 100~510 2.2~10.8 27.5~
87.5— 4.9~7.0 25.8~27.7 1×10−9~
1×10−29.9~24.5 吕岩等[4] Malaysia H2~H4 10~95 — 1.10~2.60 167.5~672.5 1.0~8.1 173.7~
361.2— — — — — Huat et al[5] Banting H2~H5 70~88 — 1.42~2.6 181~350 4.1~10.5 285.0~
330.0— 6.2~12 26.5~34.3 — — Huat et al[5] Ackc H5 1.4~98 — 1.46~2.67 560~890 — — — — — — — Skempton
et al[6]滇池 H7~H10 22.94~32.44 — 1.84~2.55 103.8~306.7 — — — 11.6~22.2 2.2~17.2 4.9×10−7~
1.0×10−3— 蒋忠信[22] Ohmiv H3~H4 30~80 — 1.60~2.30 330~1200 7.0~18.0 100.0~
505.056.7~
368.0— — — — Yamaguchi[24] James
bayH3~H4 96 — 1.50~1.64 1000~1340 18.0~23.5 — — — — 1.3×10−9~
1.0×10−2— Mesri et al[26] Middieton H3~H4 90~95 — 1.53~1.65 510~850 8.3~14.2 — — — — 10−10~10−5 — Turkey
ACH3~H4 22.3~71.7 — 1.63~2.14 118.3~211.7 3.2~4.7 310.2~
320— 1.7 16.2 — 2.4~6.2 Ulusay[27] Turkey
SKH5~ H7 55~58 — 1.66~2.44 105.0~559.0 2.7~3.3 147.5~
317.2— 1.6 16.2 — 1.7~22.5 Urmia H3~H6 25~77 — 1.63~2.35 102~671 2.4~11.2 — — — — 1.3×10−8~
1.6×10−60.3~253.7 Badv
et al[28]Middleton,
etcH2~H3 9.9~95 20~60.4 1.54~2.56 — 2.6~19.8 — — — — — — Cranberry
BogsnittH2~H4 60 ~77 40~52 1.48~1.52 759~946 — 580.0~
600.0375~
400— — 3.1×10−5~
2.9×10−52.5~1503 Elsaysed
et al[29]Bogs H2~H4 — — — — — — — — — 1.0×10−7~
4.0×10−4— Hanrahan[30] Muskeg H3~H4 84.2~95.4 — 1.41~1.7 605~1290 10.3~17.5 — — — — 1.0×10−4 — Samson[31] Matagam H2~H4 68~99.3 40~80 — 660~1591 — — — — — 5.0×10−5~
5.0×10−3— Lefebvre[32] Middleton H3 — — — 610~850 — — — — — 6.0×10−6~
5.0×10−5— Mesri[33] Wisconsin H1~H3 — 20~64 1.41~1.94 240~600 — — — — — 2.0×10−8~
5.0×10−5— Dhowian [34] Surfers
ParadiseH2~H3 63~68 — 1.57 168~247 — 259.0~
305.0125~
207— — 2.4×10−5~
1.4×10−33.6~128.4 Al-Ani [35] Banyuasin
regency and
SumatraH1~H4 >80 >20 1.39~1.90 200~700 3.0~15.0 — — — — 1.9×10−4~
4.9×10−49.8~57.4 Sutejo
et al[36]Klang H4 88.6~99.1 90.25~
90.491.23~1.48 572.9~690.9 8.0~9.6 — — — — 6.3×10−4 38.1~164.9 Ali[37] Thompson H2~H5 — — — 612~1161 — — — — — 8.0×10−5 — Earl[38] Minnesota H2~H3 — 87.3 — — — — — — — >18.0×10−4 — Boelter[39] -
[1] WONG L S, HASHIM R, ALI F H. A review on hydraulic conductivity and compressibility of peat[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences,2009,9(18):3207 − 3218. doi: 10.3923/jas.2009.3207.3218
[2] HOBBS N B. Mire morphology and the properties and behaviour of some British and foreign peats[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology,1986,19(1):7 − 80. doi: 10.1144/GSL.QJEG.1986.019.01.02
[3] EDIL T B, Wang X. Shear strength and K0 of peats and organic soils[J]. Geotechnics of High Water Content Materials,2000:209 − 225.
[4] 吕岩, 佴磊, 徐燕, 等. 有机质对草炭土物理力学性质影响的机理分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2011,33(4):655 − 660. [LYU Yan, NIE Lei, XU Yan, et al. The mechanism of organic matter effect on physical and mechanical properties of turfy soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2011,33(4):655 − 660. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] HUAT B B K, ASADI A, KAZEMIAN S. Experimental investigation on geomechanical properties of tropical organic soils and peat[J]. American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences,2009,2(1):184 − 188.
[6] SKEMPTON A W, PETLEY D J. Ignition loss and other properties of peats and clays from avonmouth, King's Lynn and cranberry moss[J]. Géotechnique,1970,20(4):343 − 356.
[7] SANTAGATA M, BOBET A, JOHNSTON C T, et al. One-dimensional compression behavior of a soil with high organic matter content[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2008,134(1):1 − 13. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2008)134:1(1)
[8] HUAT B B K, KAZEMIAN S, PRASAD A, et al. State of an art review of peat: General perspective[J]. International Journal of Physical Sciences,2011,6(8):1988 − 1996.
[9] OLGUN M, YıLDıZ M. Effect of organic fluids on the geotechnical behavior of a highly plastic clayey soil[J]. Applied Clay Science,2010,48(4):615 − 621. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.03.015
[10] ZENG L L, HONG Z S, WANG C, et al. Experimental study on physical properties of clays with organic matter soluble and insoluble in water[J]. Applied Clay Science,2016,132/133:660 − 667. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2016.08.018
[11] RASHID M A, BROWN J D. Influence of marine organic compounds on the engineering properties of a remoulded sediment[J]. Engineering Geology,1975,9(2):141 − 154. doi: 10.1016/0013-7952(75)90036-8
[12] BOOTH J S, DAHL A G. A note on the relationships between organic matter and some geotechnical properties of a marine sediment[J]. Marine Geotechnology,1986,6(3):281 − 297. doi: 10.1080/10641198609388191
[13] 牟春梅, 李佰锋. 有机质含量对软土力学性质影响效应分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2008,35(3):42 − 46. [MU Chunmei, LI Baifeng. Influence of organic matter on mechanical character of soft soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2008,35(3):42 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2008.03.011
[14] ODELL R T, THORNBURN T H, MCKENZIE L J. Relationships of atterberg limits to some other properties of Illinois soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1960,24(4):297 − 300. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1960.03615995002400040025x
[15] WILLIAM H BUSCH , GEORGE H KEL. The physical properties of Peru-Chile continental margin sediments: the influence of coastal upwelling on sediment properties[J]. SEPM Journal of Sedimentary Research,1981,51(3):705 − 719.
[16] BENNETT R H, LEHMAN L, HULBERT M H, et al. Interrelationships of organic carbon and submarine sediment geotechnical properties[J]. Marine Geotechnology,1985,6(1):61 − 98. doi: 10.1080/10641198509388180
[17] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard test method for moisture, ash, and organic matter of peat and other organic soils: D 2974—87 [S]. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: American Society for Testing and Materials, 1989.
[18] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard test method for laboratory determination of the fiber content of peat samples by dry mass: D 1997—91[S]. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: American Society for Testing and Materials, 1991.
[19] 中华人民共和国交通部. 公路土工试验规程: JTG E40—2007[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2007.
Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Test methods of soils for highway engineerin: JTG E40—2007[S]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 200. (in Chinese)
[20] LONG M. Review of peat strength, peat characterisation and constitutive modelling of peat with reference to landslides[J]. Studia Geotechnica et Mechanica,2005,27(3/4):67 − 90.
[21] 桂跃, 付坚, 吴承坤, 等. 高原湖相泥炭土渗透特性研究及机制分析[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(11):3197 − 3207. [GUI Yue, FU Jian, WU Chengkun, et al. Hydraulic conductivity of lacustrine peaty soil in plateau areas and its mechanism analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2016,37(11):3197 − 3207. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 蒋忠信. 滇池泥炭土-地质·工程[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 1994.
JIANG Zhongxin. Dianchi peaty soil[M]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University Press, 1994. (in Chinese)
[23] ZWANENBURG C. The influence of anisotropy on the consolidation behaviour of peat[J]. TU Delft: Delft University of Technology. 2005.
[24] YAMAGUCHI H, OHIRA Y, KOGURE K. Volume change characteristics of undisturbed fibrous peat[J]. Soils and Foundations,1985,25(2):119 − 134. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.25.2_119
[25] VON POST L. Sveriges geologiska undersoknings torvinventering och nogra av dess hittils vunna resultat[J]. Svenska Mosskulturforeningens Tidskrift, Jonkoping, Sweden,1921,36:1 − 37.
[26] MESRI G, AJLOUNI M. Engineering properties of fibrous peats[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2007,133(7):850 − 866. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:7(850)
[27] ULUSAY R, TUNCAY E, HASANCEBI N. Geo-engineering properties and settlement of peaty soils at an industrial site (Turkey)[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2010,69(3):397 − 410. doi: 10.1007/s10064-010-0290-2
[28] BADV K, SAYADIAN T. An investigation into the geotechnical characteristics of Urmia peat[J]. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology - Transactions of Civil Engineering,2012,36(C2):167 − 180.
[29] ELSAYED A, PAIKOWSKY S, KURUP P. Characteristics and engineering properties of peaty soil underlying cranberry bogs[C]//Geo-Frontiers Congress 2011. March 13−16, 2011, Dallas, Texas, USA. Reston, VA, USA: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2011: 2812 − 2821.
[30] HANRAHAN E T. An investigation of some physical properties of peat[J]. Géotechnique,1954,4(3):108 − 123.
[31] SAMSON L, ROCHELLE P L. Design and performance of an expressway constructed over peat by preloading[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1972,9(4):447 − 466. doi: 10.1139/t72-044
[32] LEFEBVRE G, LANGLOIS P, LUPIEN C, et al. Laboratory testing and in situ behaviour of peat as embankment foundation[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1984,21(2):322 − 337. doi: 10.1139/t84-033
[33] MESRI G, STARK T D, AJLOUNI M A, et al. Secondary compression of peat with or without surcharging[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,1997,123(5):411 − 421. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1997)123:5(411)
[34] DHOWIAN A W, EDIL T B. Consolidation behavior of peats[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal,1980,3(3):105. doi: 10.1520/GTJ10881J
[35] AL-ANI H, OH E, CHAI G. Engineering properties of peat in estuarine environment[C]//Foundation and Soft Ground Engineering. 2013.
[36] SUTEJO Y, SAGGAFF A, RAHAYU W, et al. Hydraulic conductivity and compressibility characteristics of fibrous peat[J]. IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering,2019,620:012053. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/620/1/012053
[37] ALI F H, SING W L, HASHIM R. Engineering properties of improved fibrous peat[J]. Scientific Research & Essays, 2010, 5(2).
[38] DE GUZMAN E M B, ALFARO M C. Geotechnical properties of fibrous and amorphous peats for the construction of road embankments[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2018,30(7):04018149. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002325
[39] BOELTER D H. Physical properties of peats as related to degree of decomposition[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1969,33(4):606 − 609. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1969.03615995003300040033x
[40] 黄昌勇. 土壤学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
HUANG Changyong. Soil science[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
[41] 张亚玲, 赵晓彦, 严群. 云母影响水泥软黏土强度的试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):101 − 108. [ZHANG Yaling, ZHAO Xiaoyan, YAN Qun. Experimental research on the influence of mica on strength of cement-reinforced soft clay[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):101 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] TAVENAS F, JEAN P, LEBLOND P, et al. The permeability of natural soft clays. Part II: Permeability characteristics[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1983,20(4):645 − 660. doi: 10.1139/t83-073
[43] YAMAGUCHI H, OHIRA Y, KOGURE K, et al. Undrained shear characteristics of normally consolidated peat under triaxial compression and extension conditions[J]. Soils and Foundations,1985,25(3):1 − 18. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.25.3_1
-




 下载:
下载: