The response regularity of temperature and humidity of surface soil on slopes in high-cold and humid areas
-
摘要:
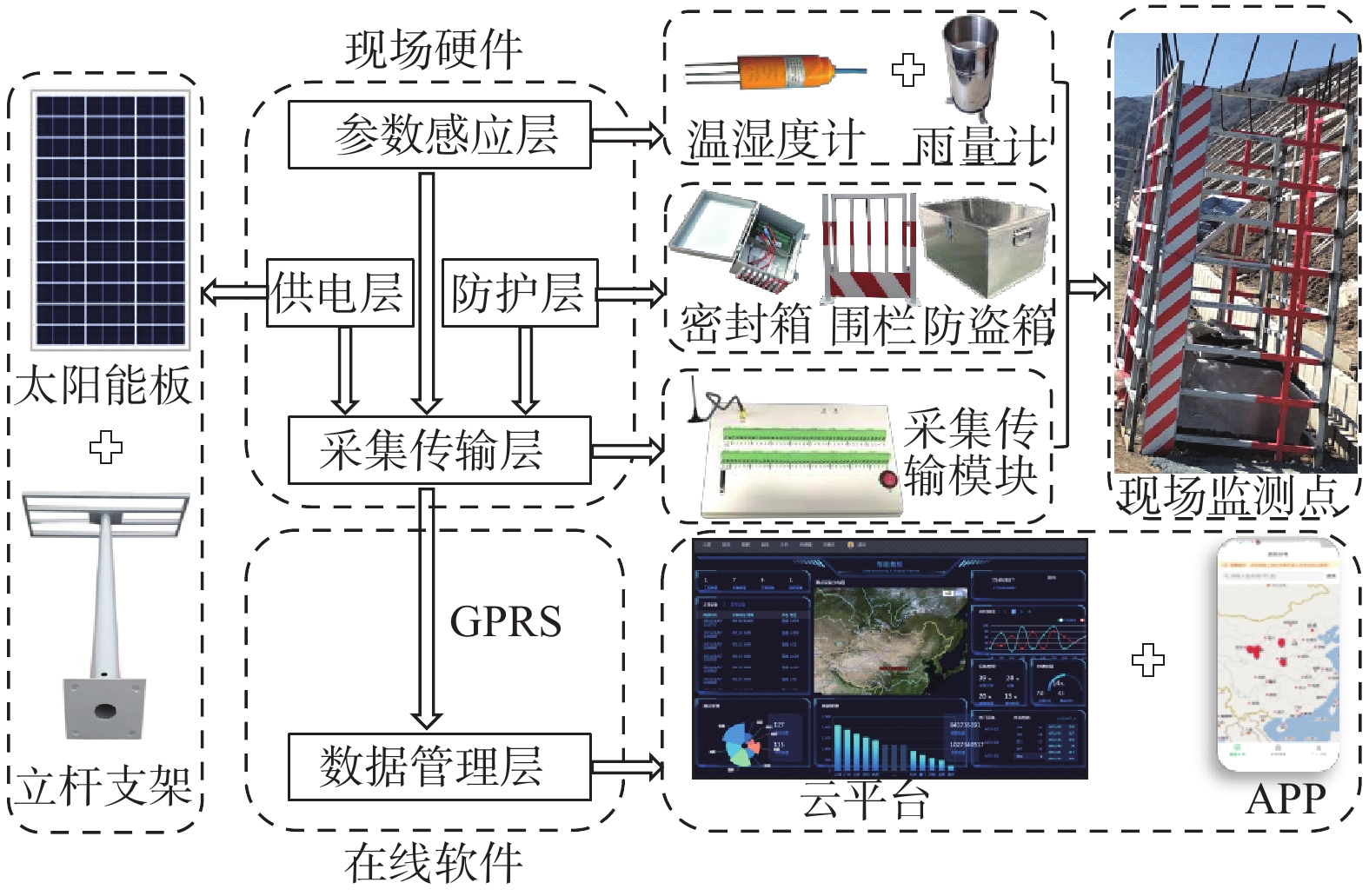
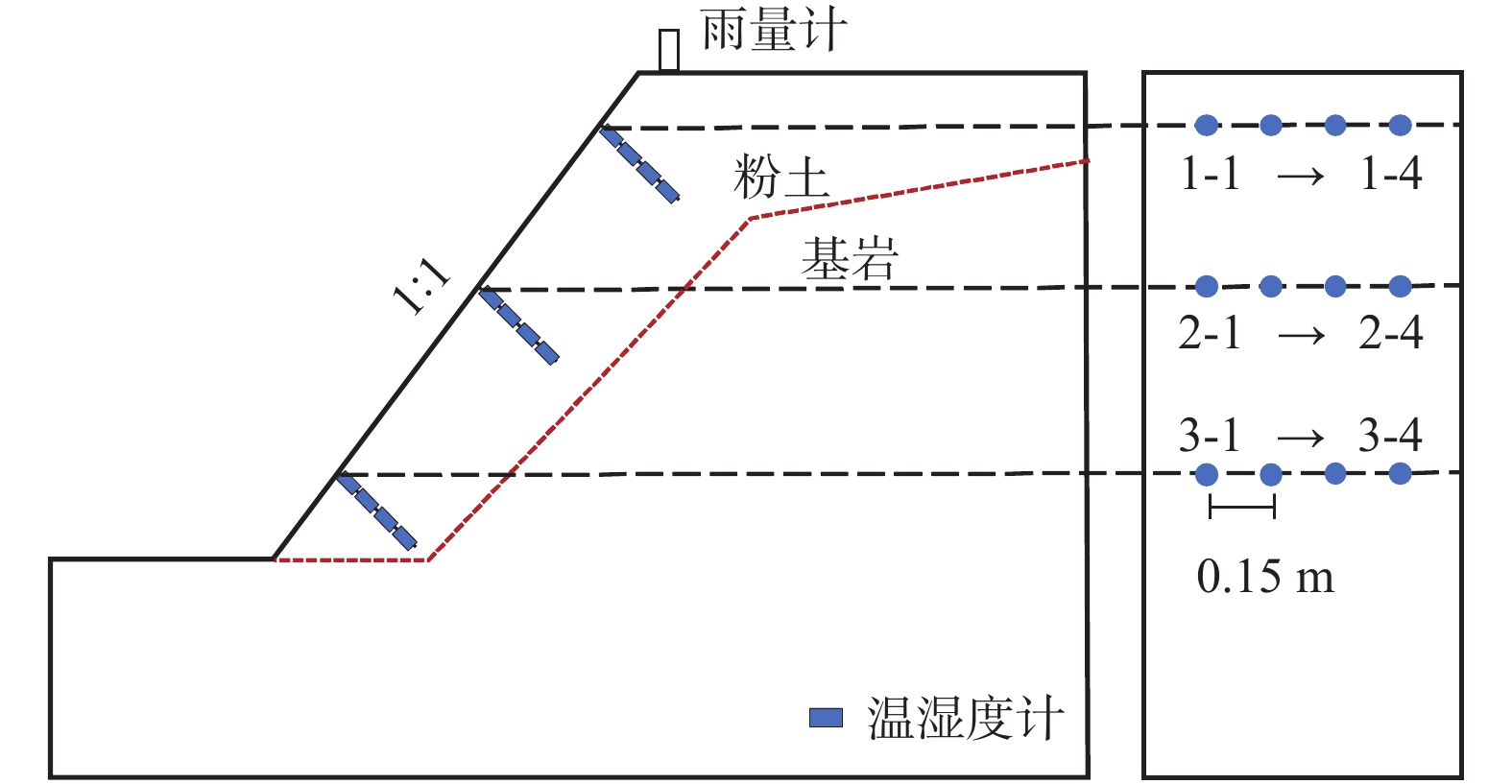
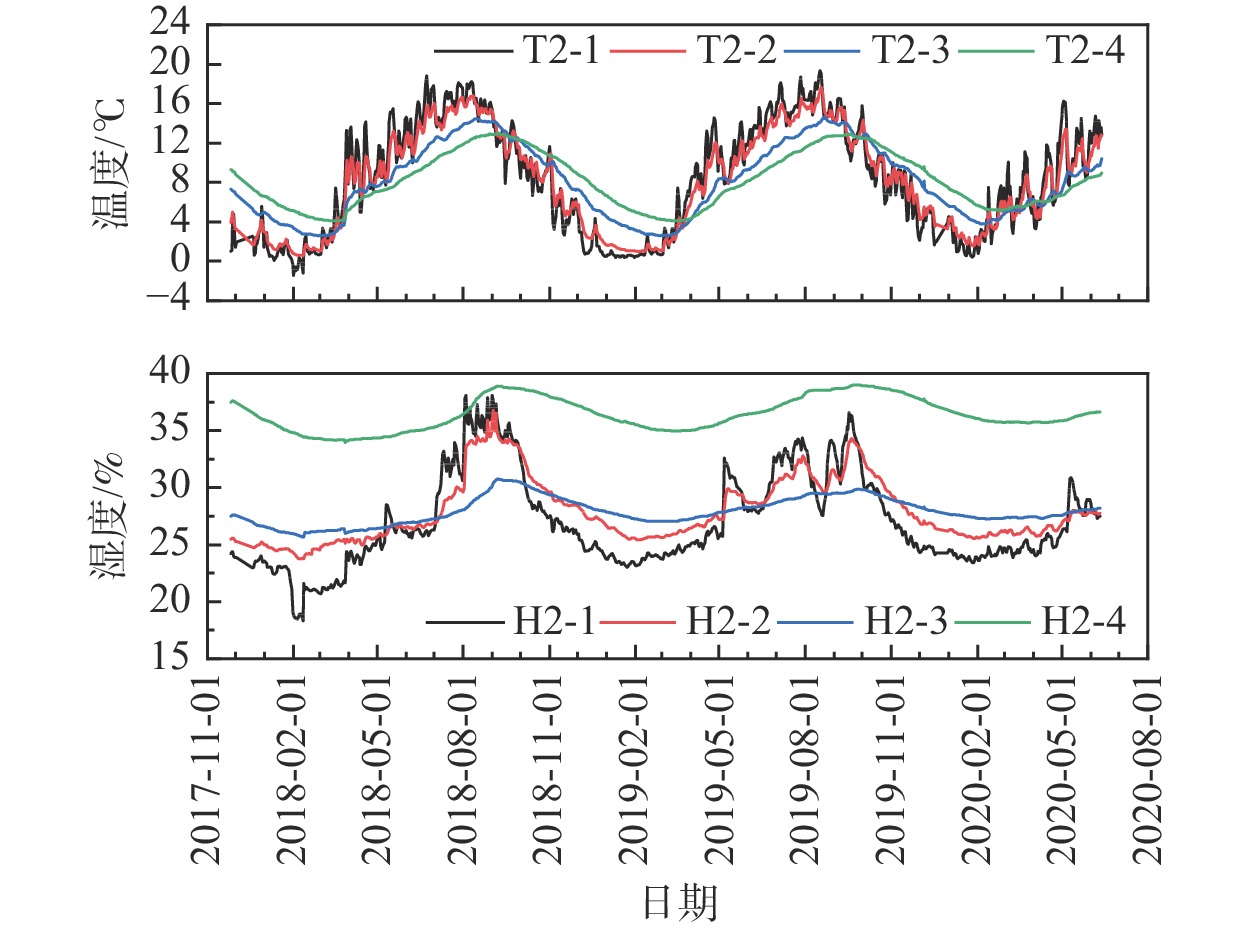
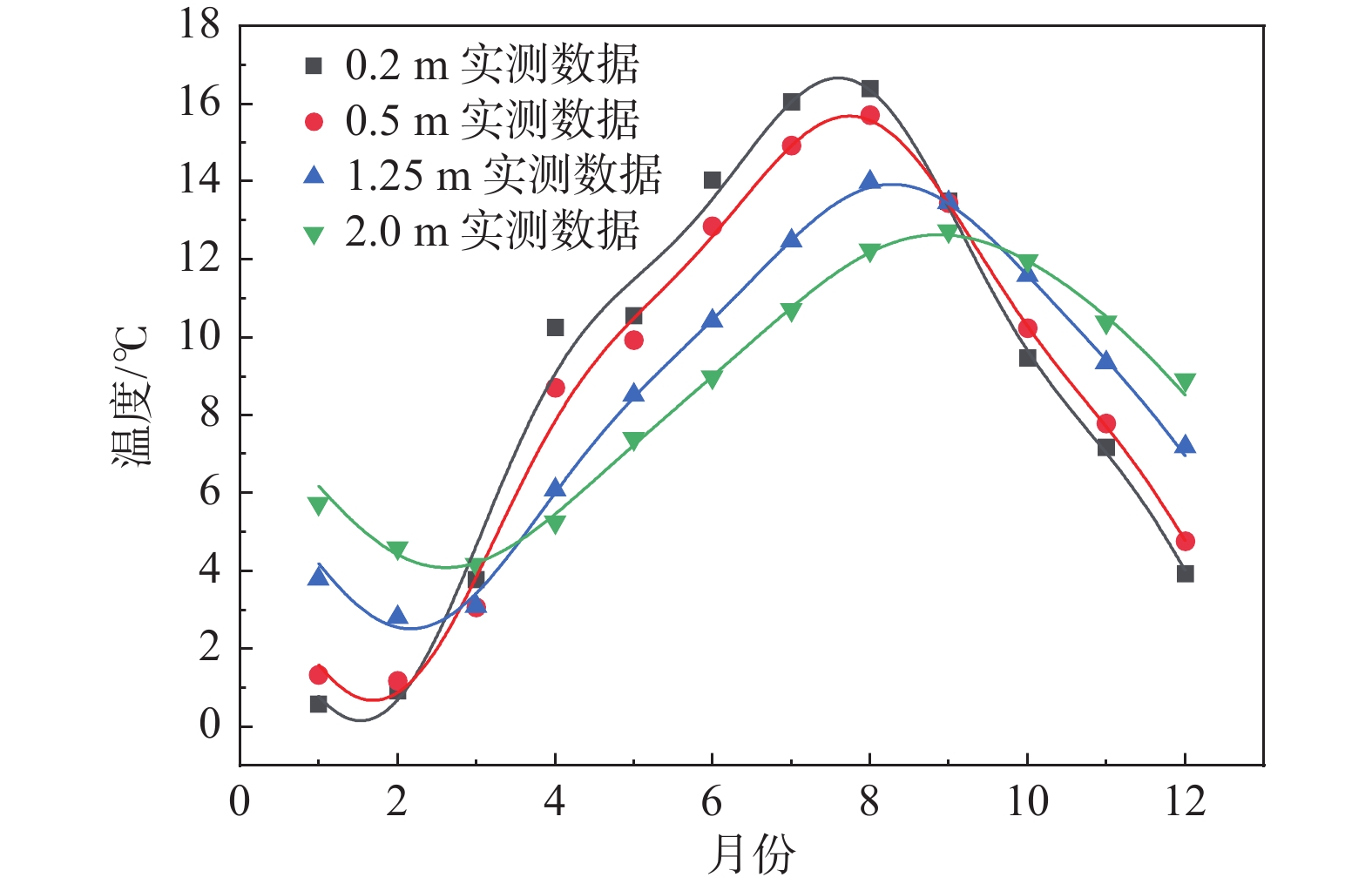
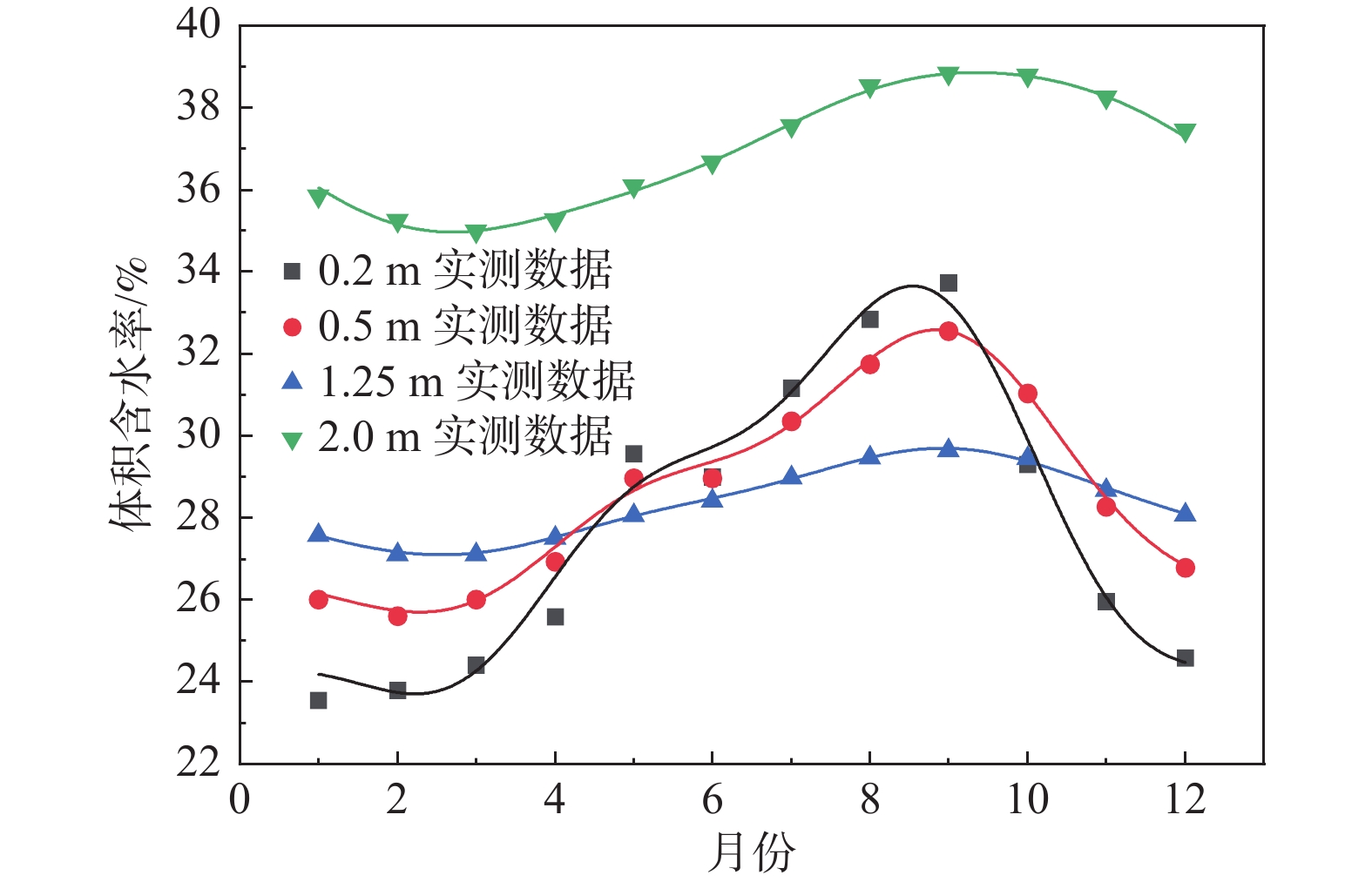
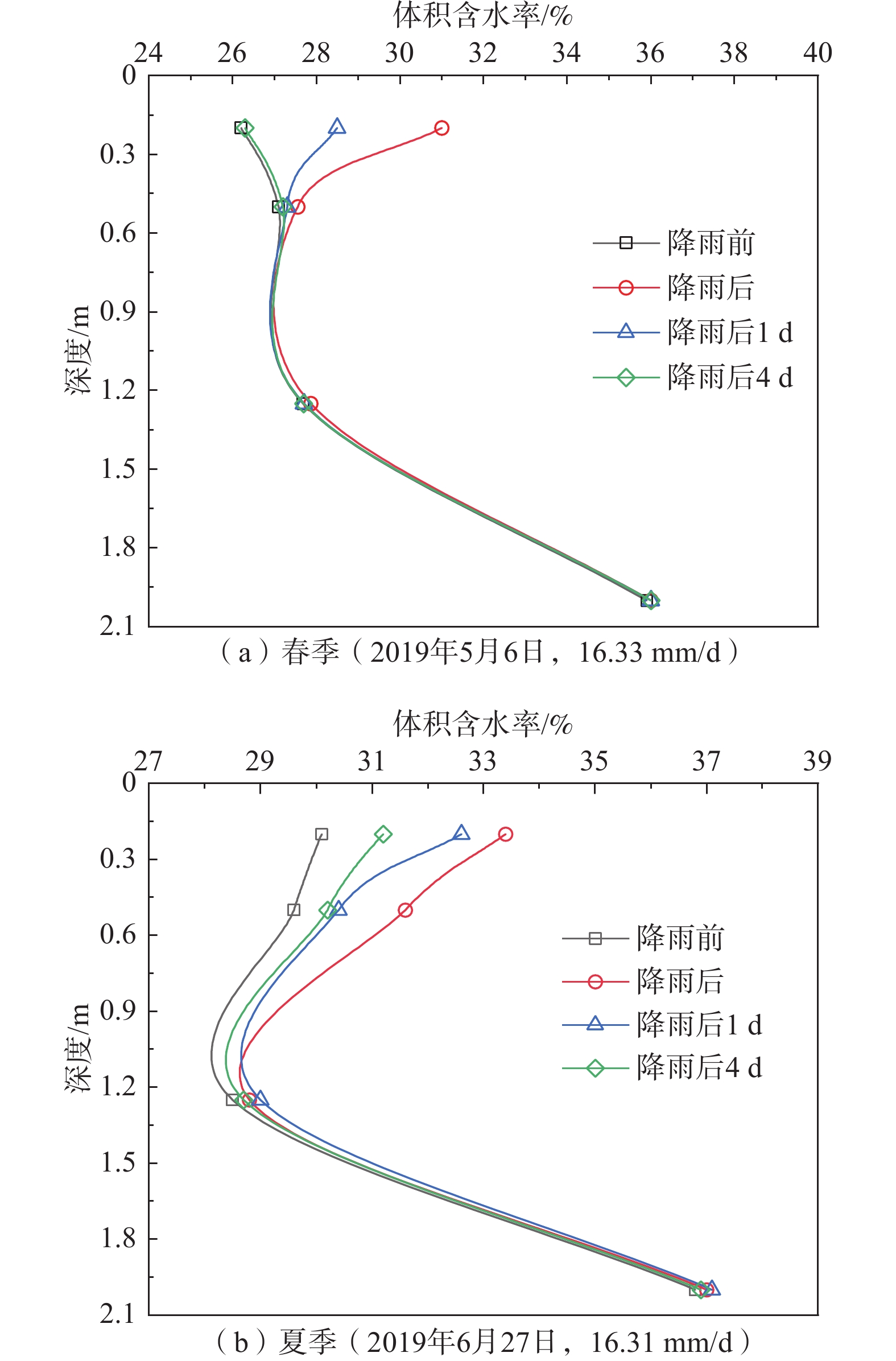
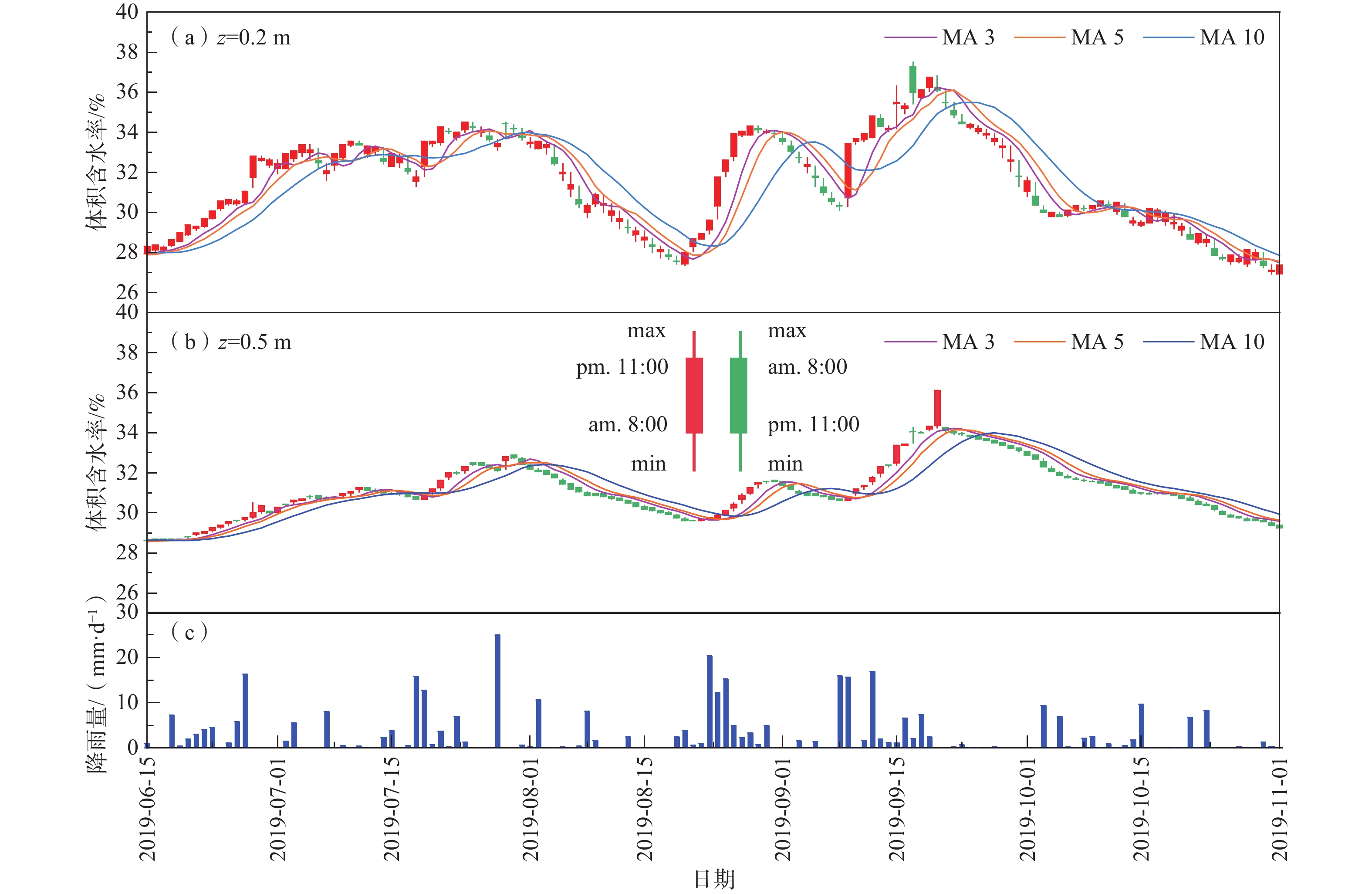
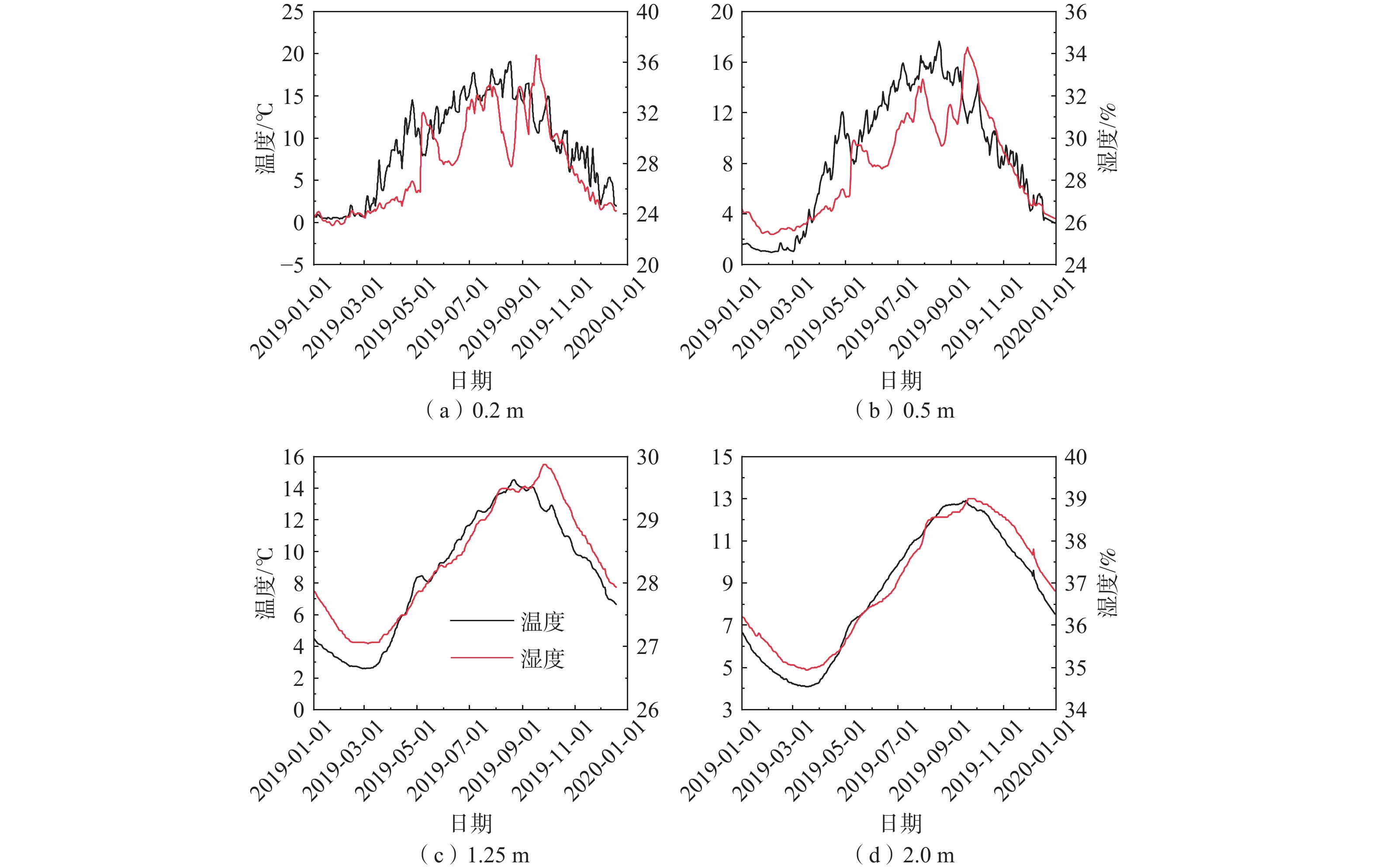
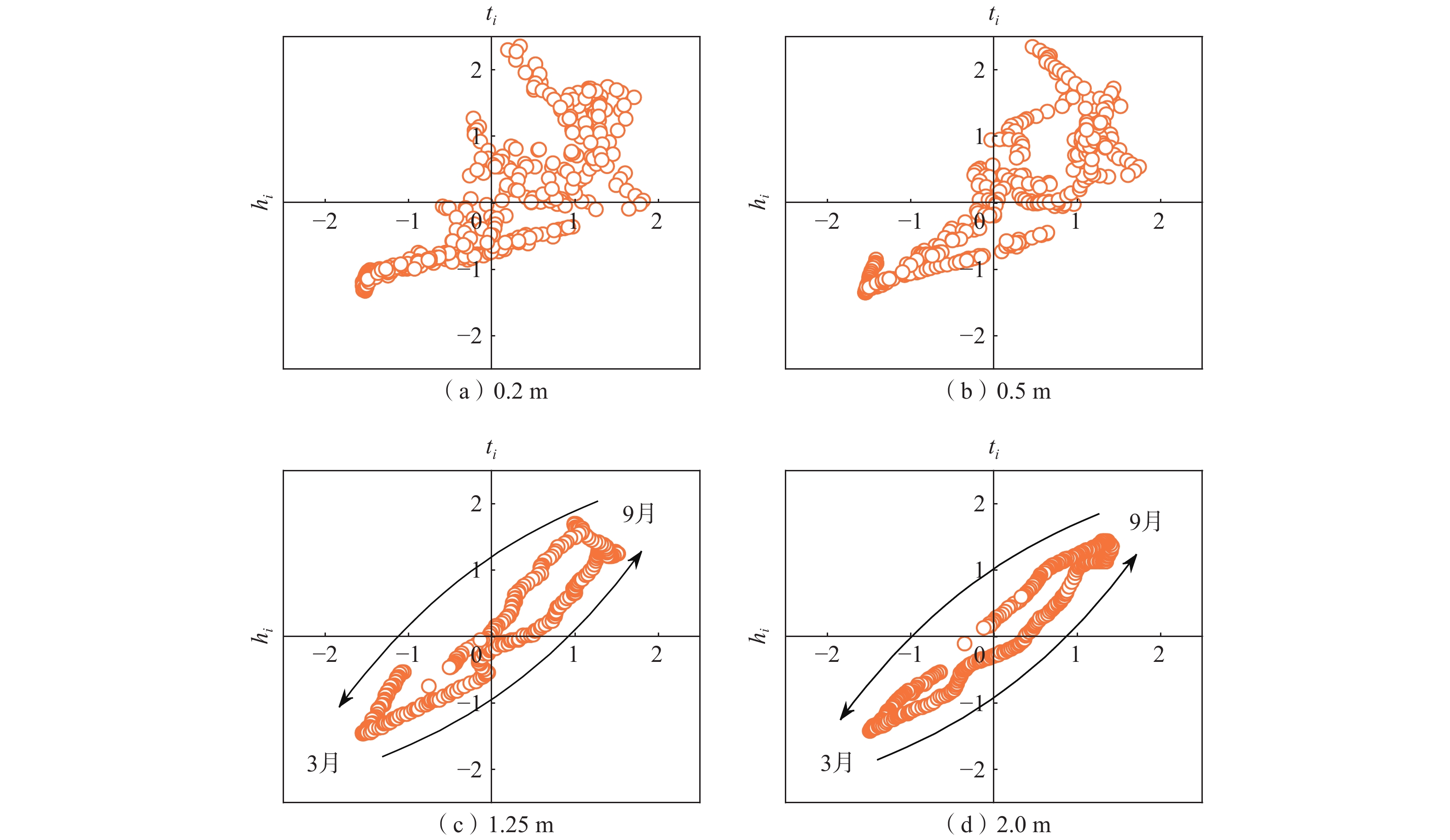
基于长期原位监测对高寒阴湿区边坡土体温湿响应规律研究存在的不足,选取甘肃双达高速公路沿线土-岩二元结构边坡为研究对象,构建远程监测系统对边坡浅层土体温温度及大气降雨开展了为期2年多的现场监测,结合傅里叶模型与Pearson相关性分析方法,揭示了边坡土体水热迁移及降雨入渗规律,分析了边坡土体温湿度相互作用效应。研究结果表明:(1)边坡浅层土体温湿度随时间呈简谐式周期变化,且变化幅度随埋深逐渐减小,2 m深度处土体月平均温度变化具有一定滞后性,滞后时间约为30 d。(2)年内3月与9月,土体月平均温度曲线出现“纽结”现象,使边坡呈现出由春夏季表热而内凉向秋冬季表寒而内温转变的趋势。(3)春季降雨期,土体含水率增长仅发生在50 cm深度以内;夏季降雨期,降雨引起更深层土体含水率变化,因雨水持续性补充,浅层土体湿度长时间保持在35%以上。(4)土体温湿度存在较高的正相关关系,随土体埋深增加温湿度相关性增强,不同时期温湿度相互影响程度不同,年内温湿度相关性表现出“循环圈”效应。研究成果可为进一步认识边坡土体水文响应规律、水-热相关性与坡面侵蚀机理提供一定参考。
Abstract:Previous studies on the temperature and humidity of slopes in cold and humid areas based on long-term in-situ monitoring are insufficient. Therefore, a soil-rock slope along the Shuangda Expressway in Gansu Province is selected as the research object, and the humidity and temperature of shallow soil and rainfall are monitored for more than two years based on the constructed remote monitoring system. Combination of the Fourier model and Pearson correlation analysis, the soil moisture-heat migration at different depths and rainfall infiltration law are explored, and the interaction relationship between temperature and humidity is analyzed. The results show that the temperature and humidity of shallow soil change periodically in a harmonic way, and the variation range decreases gradually with the depth. In March and September, the temperature curves of each soil layer showed a ‘knot’ phenomenon, which impels the slope to change from one condition characterized by hot outside and cold inside in spring and summer to another condition characterized by cold outside and warm inside in autumn and winter. The change in mean monthly temperature of soil at a depth of 2 m has a certain lag, and the lag time is about 30 days. The depth of rainfall infiltration can occur only within the depth of 50 cm in spring, while the rainfall can infiltrate into deeper soil in summer, and the moisture content of soil stays above 35% because of sustained replenishment by rain. Soil temperature and humidity have a highly positive correlation, the correlation increases with soil depth and the correlation in different periods shows a "circulating ring" effect. The research results may provide some reference for further understanding the eco-hydrological response of soil, the water-heat correlation and the mechanism of surface erosion in terms of slope.
-

-
表 1 监测时段内边坡温湿度情况
Table 1. Slope temperature and humidity conditions during the monitoring period
监测点 温度/℃ 湿度/% 平均值±标准差 最小值 最大值 平均值±标准差 最小值 最大值 1-1 10.31±6.030 −2.6 23.5 − − − 2-1 8.74±5.715 −3.1 22.5 27.37±3.968 18.06 39.50 3-1 10.32±5.677 0.1 21.0 27.11±1.723 23.31 35.62 1-2 10.04±5.098 0.7 18.5 26.89±1.487 23.94 31.06 2-2 8.52±4.859 0.5 18.0 28.15±2.762 23.69 37.44 3-2 10.08±4.925 1.2 18.1 28.70±1.284 25.56 32.12 1-3 9.39±3.891 2.2 15.1 29.07±2.085 26.87 39.44 2-3 8.43±3.585 2.5 14.7 28.04±1.157 25.69 30.81 3-3 9.17±3.581 2.5 14.8 29.89±1.272 27.06 33.25 1-4 8.91±3.004 3.3 13.6 32.50±1.022 30.87 34.56 2-4 8.46±2.745 4.0 13.1 36.55±1.408 34.12 39.06 3-4 8.73±2.619 3.6 13.0 34.48±1.067 32.25 37.50 表 2 边坡土体水-热Pearson相关性分析结果
Table 2. Pearson correlation analysis results of water-heat of slope soil
温/湿度 T0.2 m T0.5 m T1.25 m T2.0 m H0.2 m H0.5 m H1.25 m H2.0 m T0.2 m 1 0.979 0.856 0.674 0.805 0.778 0.711 0.534 T0.5 m 0.979 1 0.928 0.774 0.843 0.839 0.803 0.644 T1.25 m 0.856 0.928 1 0.948 0.856 0.915 0.955 0.867 T2.0 m 0.674 0.774 0.948 1 0.757 0.878 0.985 0.978 H0.2 m 0.805 0.843 0.856 0.757 1 0.941 0.794 0.641 H0.5 m 0.778 0.839 0.915 0.878 0.941 1 0.923 0.808 H1.25 m 0.711 0.803 0.955 0.985 0.794 0.923 1 0.955 H2.0 m 0.534 0.644 0.867 0.978 0.641 0.808 0.955 1 -
[1] 佘诗刚,林鹏. 中国岩石工程若干进展与挑战[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(3):433 − 457. [SHE Shigang,LIN Peng. Some developments and challenging issues in rock engineering field in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(3):433 − 457. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.03.001
[2] HUGGEL C. Recent extreme slope failures in glacial environments:Effects of thermal perturbation[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2009,28(11/12):1119 − 1130.
[3] XU Q J,YIN H L,CAO X F,et al. A temperature-driven strength reduction method for slope stability analysis[J]. Mechanics Research Communications,2009,36(2):224 − 231. doi: 10.1016/j.mechrescom.2008.07.004
[4] 叶万军,杨更社,彭建兵,等. 冻融循环导致洛川黄土边坡剥落病害产生机制的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(1):199 − 205. [YE Wanjun,YANG Gengshe,PENG Jianbing,et al. Test research on mechanism of freezing and thawing cycle resulting in loess slope spalling hazards in Luochuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(1):199 − 205. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.01.023
[5] 曾磊,赵贵章,胡炜,等. 冻融条件下浅层黄土中温度与水分的空间变化相关性[J]. 地质通报,2015,34(11):2123 − 2131. [ZENG Lei,ZHAO Guizhang,HU Wei,et al. Spatial variation characteristics of temperature and moisture in shallow loess layer under freezing-thawing condition[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2015,34(11):2123 − 2131. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.11.019
[6] 王铁行,李宁,谢定义. 土体水热力耦合问题研究意义、现状及建议[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(3):488 − 493. [WANG Tiehang,LI Ning,XIE Dingyi. Necessity and means in research on soil coupled heat-moisture-stress issues[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2005,26(3):488 − 493. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.03.031
[7] WANG T H,SU L J. Experimental study on moisture migration in unsaturated loess under effect of temperature[J]. Journal of Cold Regions Engineering,2010,24(3):77 − 86. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CR.1943-5495.0000015
[8] 张正, 马学宁, 朱启有. 兰州地区黄土水平冻胀力分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(1):102 − 107. [ZHANG Zheng, MA Xuening, ZHU Qiyou. Experimental analysis of horizontal frost heaving force of loess in Lanzhou City of Gansu Province Area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(1):102 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 马稚桐,王文科,赵明,等. 半干旱地区地表-地下水系统水热运移与裸土蒸发研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):7 − 14. [MA Zhitong,WANG Wenke,ZHAO Ming,et al. Hydrothermal transfer and bare soil evaporation in surface-groundwater systems in semi-arid areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):7 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] TAYLOR R V,SEASTEDT T R. Short- and long-term patterns of soil moisture in alpine tundra[J]. Arctic and Alpine Research,1994,26(1):14 − 20. doi: 10.2307/1551871
[11] 杨梅学,姚檀栋,王绍令,等. 藏北高原土壤的温湿特征[J]. 地理研究,1999,18(3):312 − 317. [YANG Meixue,YAO Tandong,WANG Shaoling,et al. The features of soil temperature and moisture on Northern Xizang Plateau[J]. Geographical Research,1999,18(3):312 − 317. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.1999.03.013
[12] 赵逸舟,马耀明,马伟强,等. 藏北高原土壤温湿变化特征分析[J]. 冰川冻土,2007,29(4):578 − 583. [ZHAO Yizhou,MA Yaoming,MA Weiqiang,et al. Variations of soil temperature and soil moisture in northern Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2007,29(4):578 − 583. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 马剑,刘贤德,李广,等. 祁连山北麓中段青海云杉林土壤水热时空变化特征[J]. 干旱区地理,2020,43(4):1033 − 1040. [MA Jian,LIU Xiande,LI Guang,et al. Spatial and temporal variations of soil moisture and temperature of Picea Crassifolia forest in north piedmont of central Qilian Mountains[J]. Arid Land Geography,2020,43(4):1033 − 1040. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李静,盛煜,吴吉春,等. 祁连山大通河源多年冻土区浅层土壤水热时空变化特征[J]. 冰川冻土,2014,36(4):994 − 1001. [LI Jing,SHENG Yu,WU Jichun,et al. Spatial and temporal variations of the superficial hydro-thermal characteristics in permafrost regions in the source areas of the Datong River,Qilian Mountains[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2014,36(4):994 − 1001. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 车宗玺,李进军,汪有奎,等. 祁连山西段草地土壤温度、水分变化特征[J]. 生态学报,2018,38(1):105 − 111. [CHE Zongxi,LI Jinjun,WANG Youkui,et al. Characteristics of soil temperature and water content variation in the western Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(1):105 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] JODRY C,PALMA L S,FARGIER Y,et al. 2D-ERT monitoring of soil moisture seasonal behaviour in a river levee:A case study[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics,2019,167:140 − 151. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2019.05.008
[17] LACAVA T,BROCCA L,CALICE G,et al. Soil moisture variations monitoring by AMSU-based soil wetness indices:A long-term inter-comparison with ground measurements[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2010,114(10):2317 − 2325. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.05.008
[18] WAGNER W,REIMER C,BAUER-MARSCHALLINGER B,et al. Long-term soil moisture time series analyses based on active microwave backscatter measurements[J]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry,Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences,2015,40(7):545 − 550.
[19] 陈棠茵,朱宝龙. 温度、湿度循环条件下砂岩物理特性试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(1):74 − 78. [CHEN Tangyin,ZHU Baolong. Experimental study of physical properties of sandstone under the cycling conditions of temperature and humidity[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(1):74 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2014.01.008
[20] 李彦龙,王俊,王铁行. 温度梯度作用下非饱和土水分迁移研究[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(10):2839 − 2844. [LI Yanlong,WANG Jun,WANG Tiehang. Moisture migration of unsaturated soil due to thermal gradients[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2016,37(10):2839 − 2844. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 蔡国庆,赵成刚,刘艳. 非饱和土土-水特征曲线的温度效应[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(4):1055 − 1060. [CAI Guoqing,ZHAO Chenggang,LIU Yan. Temperature effects on soil-water characteristic curve of unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(4):1055 − 1060. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.04.008
[22] 王铁行,陆海红. 温度影响下的非饱和黄土水分迁移问题探讨[J]. 岩土力学,2004,25(7):1081 − 1084. [WANG Tiehang,LU Haihong. Moisture migration in unsaturated loess considering temperature effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2004,25(7):1081 − 1084. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2004.07.016
[23] 王铁行,卢靖,岳彩坤. 考虑温度和密度影响的非饱和黄土土-水特征曲线研究[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(1):1 − 5. [WANG Tiehang,LU Jing,YUE Caikun. Soil-water characteristic curve for unsaturated loess considering temperature and density effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2008,29(1):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.01.001
[24] 赵利云, 张茂省, 孙萍萍, 等. 基于原位监测的浅层黄土斜坡水分运移规律分析[J]. 地质与资源,2021,30(4):492 − 498. [ZHAO Liyun, ZHANG Maosheng, SUN Pingping, et al. Analysis of water movement law in shallow loess slope based on in situ monitoring[J]. Geology and Resources,2021,30(4):492 − 498. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: