An experimental study of the engineering properties and erosion resistance of guar gum-reinforced loess
-
摘要:
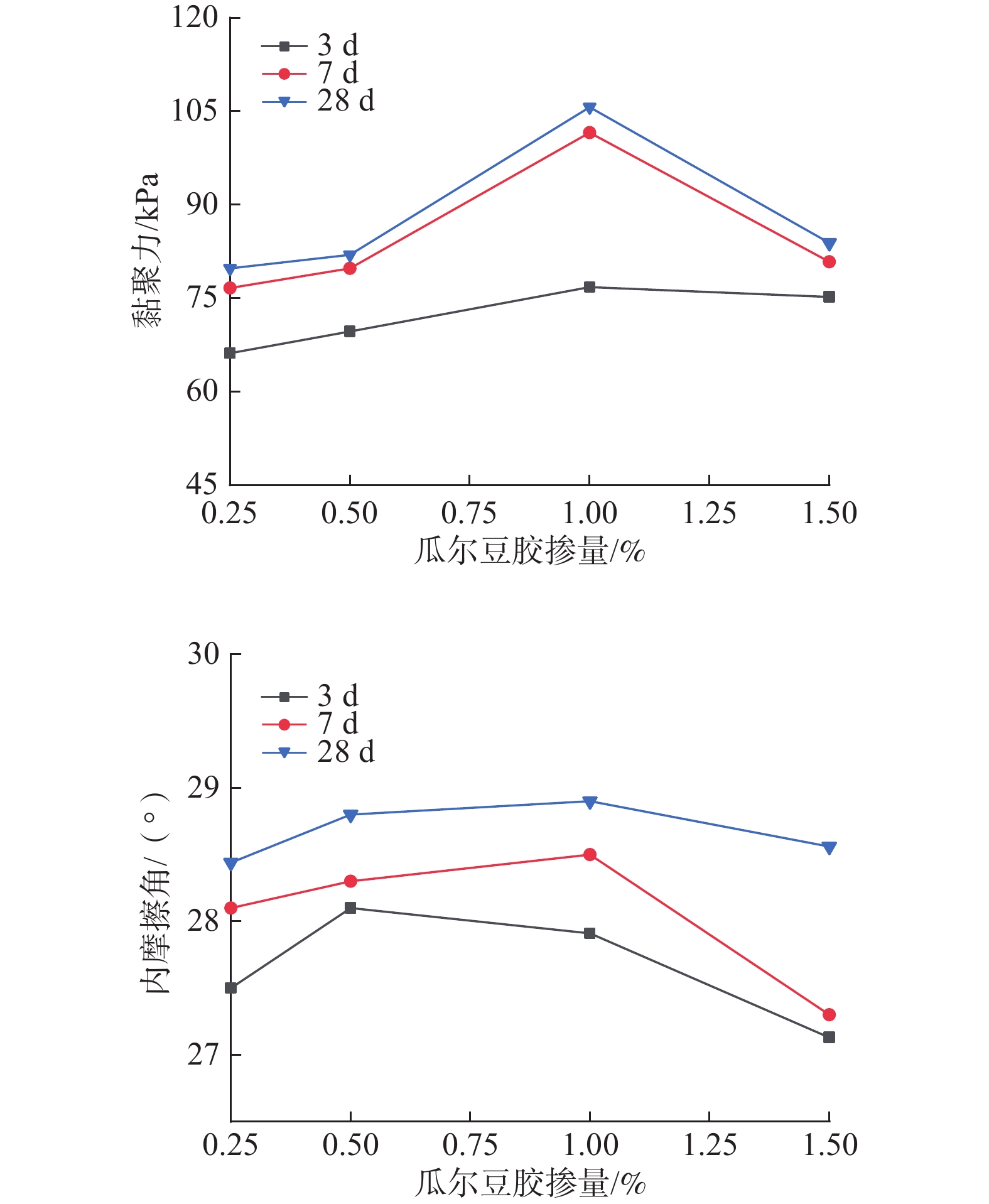
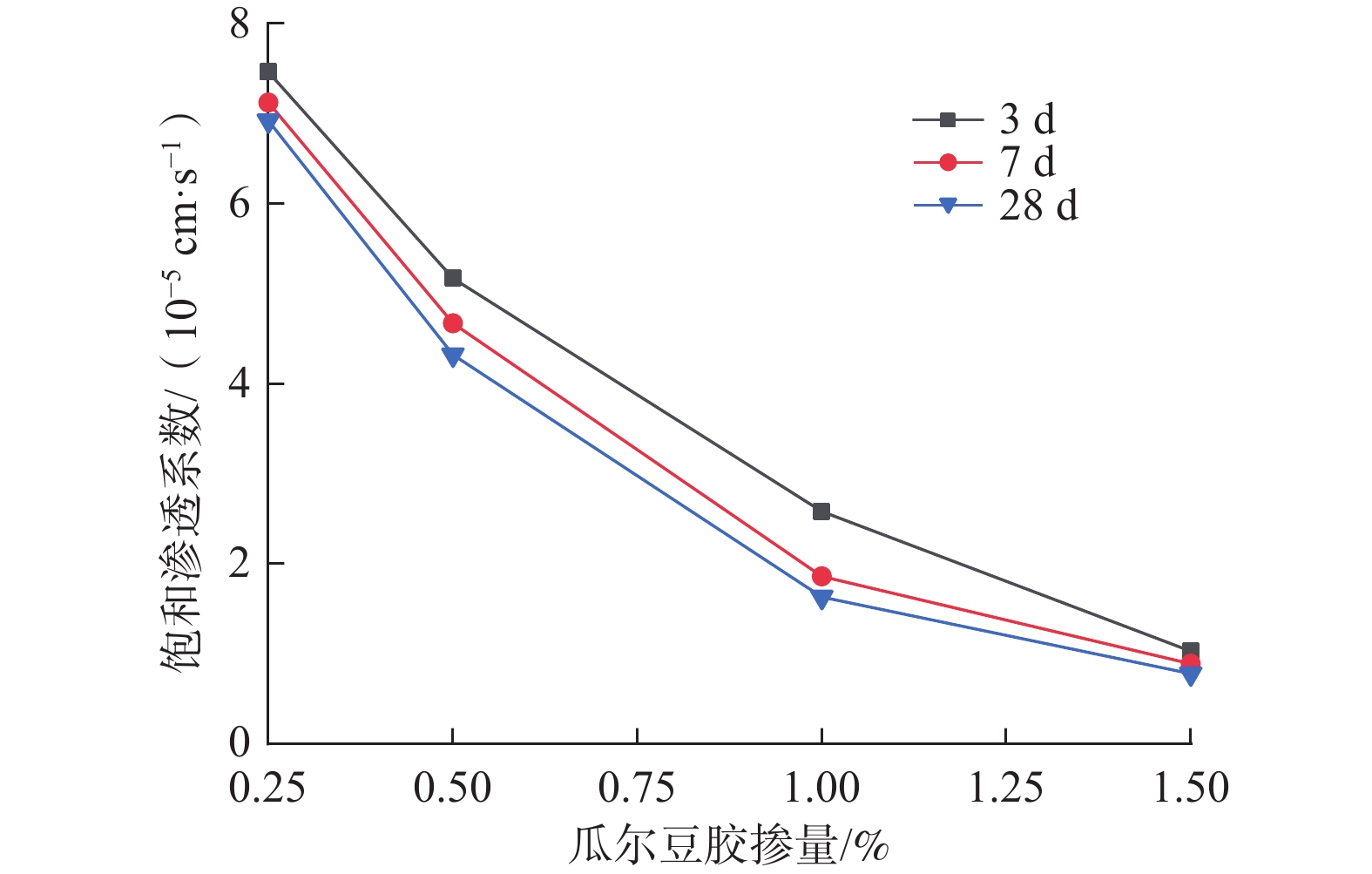
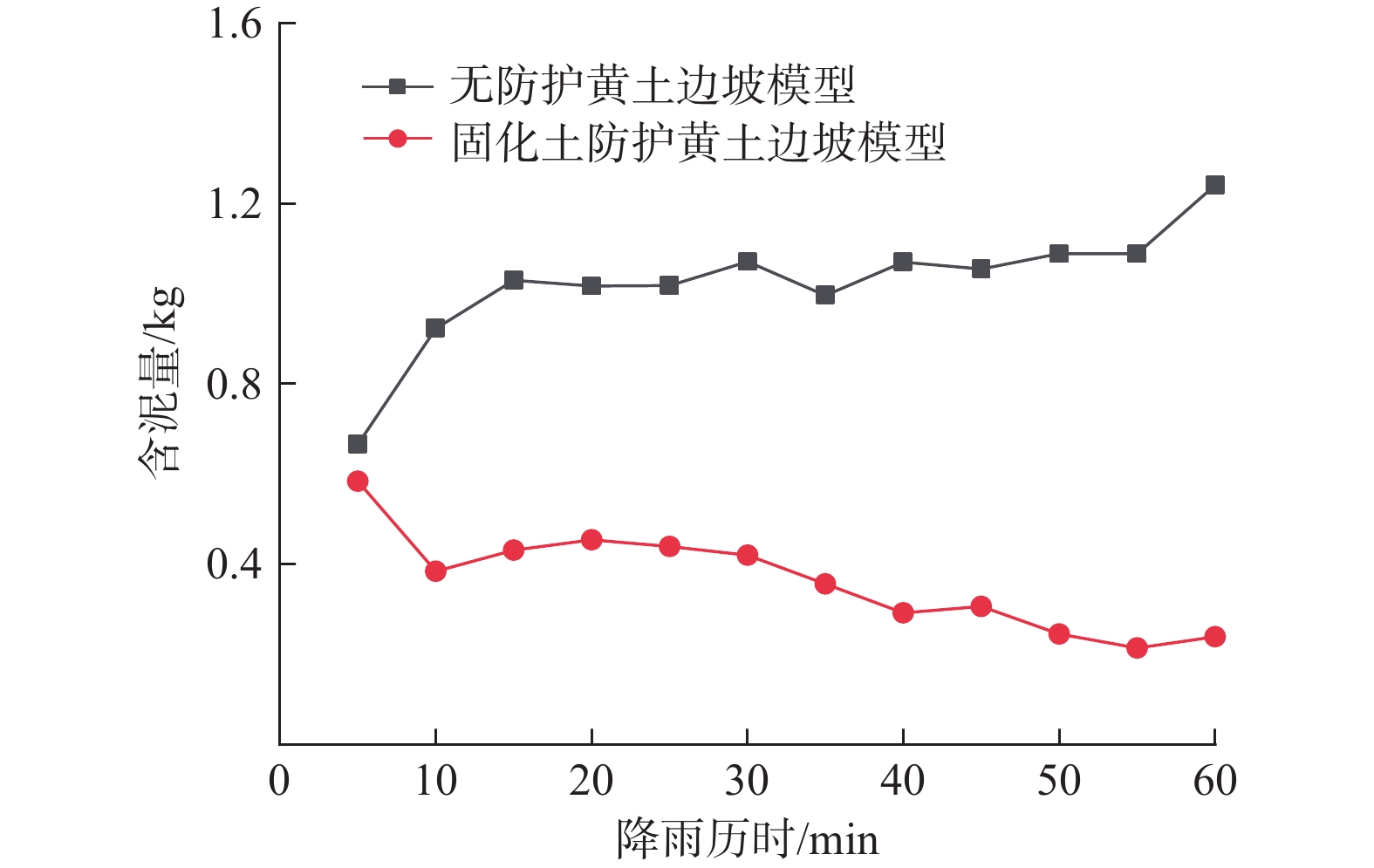
为了减少暴雨冲刷条件下黄土边坡侵蚀的发生,提出采用瓜尔豆胶固化黄土对边坡坡面进行防护。基于直剪试验、渗透试验以及模拟暴雨边坡冲刷试验,研究了瓜尔豆胶固化黄土的工程特性及抗冲蚀能力,并对比素黄土与固化黄土的微观结构,探讨了瓜尔豆胶对黄土的加固机制。试验结果表明:瓜尔豆胶可有效增强黄土的抗剪强度和抗渗透性,固化黄土的黏聚力和内摩擦角呈现相同的变化趋势,即随瓜尔豆胶掺量增加而先增加后减小,随养护龄期增长而增加,饱和渗透系数随瓜尔豆胶掺量增加和养护龄期增长而减小;瓜尔豆胶掺量1.0%,养护龄期7 d的固化黄土相比于素黄土,黏聚力和内摩擦角提升了53.7%和5.6%,饱和渗透系数降低了78.3%;瓜尔豆胶固化黄土在暴雨冲刷条件下的坡面防护效果明显,相比于无防护边坡,坡面的累计冲刷量降低了64.4%,平均流速提升了55.2%;瓜尔豆胶对黄土的加固机制主要在于其水化反应产生的高黏度水凝胶能够填充孔隙和胶结黄土颗粒。本研究可为瓜尔豆胶固化黄土在边坡坡面防护工程中的应用及推广提供试验支撑。
Abstract:To reduce the erosion of the loess slope under the condition of rainstorms, the loess cured by guar gum is used to protect the slope surface. The engineering properties and erosion resistance of the guar gum-reinforced loess are studied by conducting the direct shear test, penetration test, slope scour test in simulated rainstorm, and the curing mechanism of guar gum is studied by contrasting the microstructure characteristics of plain loess and reinforced loess. The results show that the guar gum can effectively enhance the shear strength and the anti-permeability of loess. The cohesion and internal friction angle of the reinforced loess show the same trend, and they increase first and then decrease with the increasing guar gum content, and increase with the increasing curing age. The saturated permeability coefficient decreases with the increasing guar gum content and curing age. Compared with plain loess, the cohesion and internal friction angle of 7 d cured loess with 1.0% guar gum content increases by 53.7% and 5.6%, and the saturated permeability coefficient decreases by 78.3%. The slope protection effect of the guar gum-reinforced loess under rainstorm scour condition is obvious. Compared with the slope without protection, the cumulative scour amount of the slope decreases by 64.4%, and the average slope flow rate increases by 55.2%. The strengthening mechanism of guar gum on loess mainly lies in the high viscosity hydrogel produced by its hydration reaction to fill the pores and cement loess particles. This study provides test support for the application and promotion of the guar gum-reinforced loess in slope protection engineering.
-
Key words:
- guar gum /
- reinforced loess /
- shear strength /
- anti-permeability /
- erosion resistance /
- microstructure
-

-
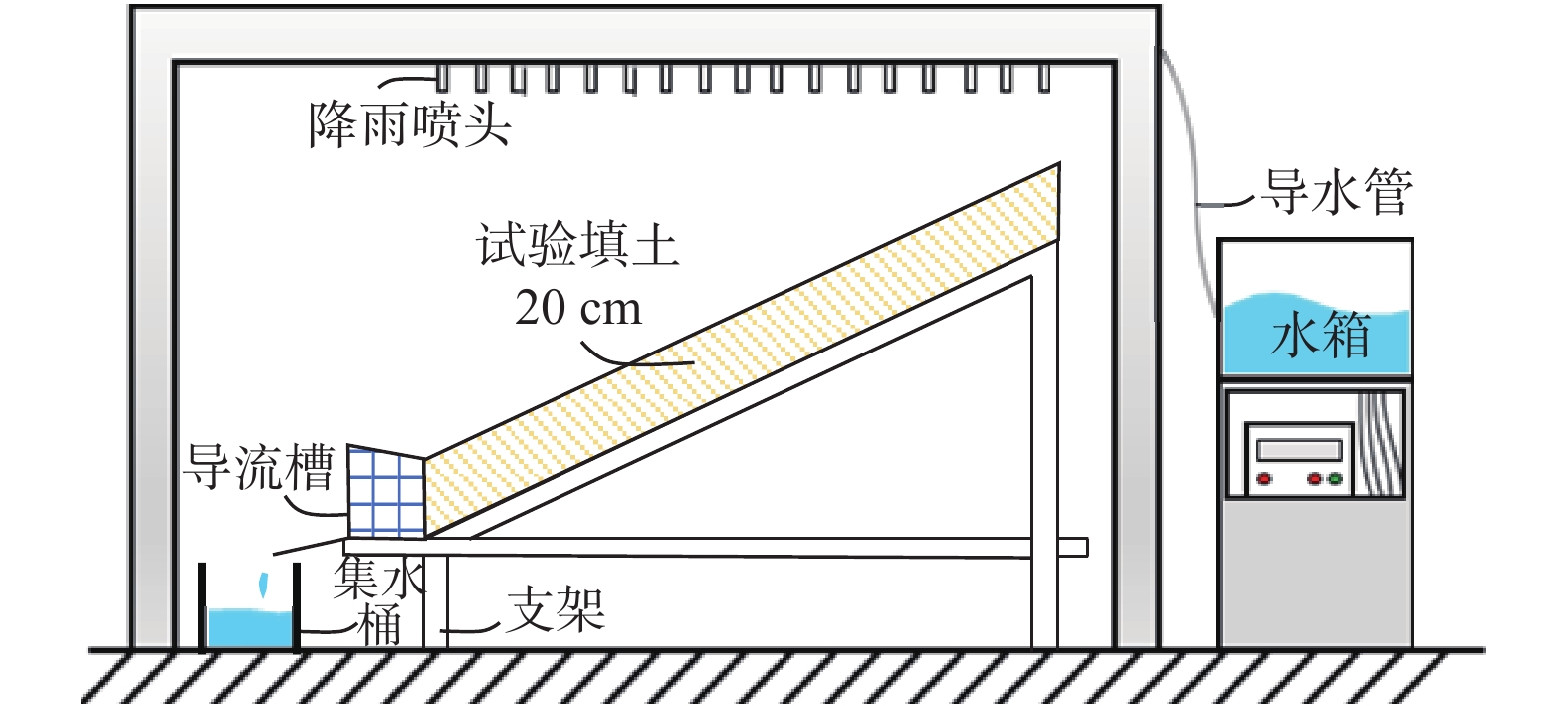
表 1 人工降雨模拟器的技术参数
Table 1. Technical parameters of the artificial rainfall simulator
型号 降雨强度/
(mm·h−1)有效降雨
面积/m2有效降雨
高度/m雨滴直径/
mmDIK-6000 10~80 1.0404 2 1.7~3.0 表 2 不同试样的黏聚力及内摩擦角
Table 2. Cohesion and internal friction angle of different samples
瓜尔豆胶掺量/% 养护龄期/d 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 0.00 7 66.08 27.0 0.25 3 66.17 27.5 7 76.62 28.1 28 79.78 28.4 0.50 3 69.65 28.1 7 79.78 28.3 28 81.95 28.8 1.00 3 76.77 27.9 7 101.56 28.5 28 105.64 28.9 1.50 3 75.18 27.1 7 80.82 27.3 28 83.87 28.6 表 3 不同试样的饱和渗透系数
Table 3. Saturation permeability coefficient of different samples
瓜尔豆胶掺量/% 养护龄期/d 饱和渗透系数/(10−5 cm·s−1) 0.00 7 8.56 0.25 3 7.46 7 7.12 28 6.92 0.50 3 5.17 7 4.67 28 4.32 1.00 3 2.58 7 1.86 28 1.63 1.50 3 1.03 7 0.89 28 0.78 表 4 各时段边坡坡面的含泥量与流速
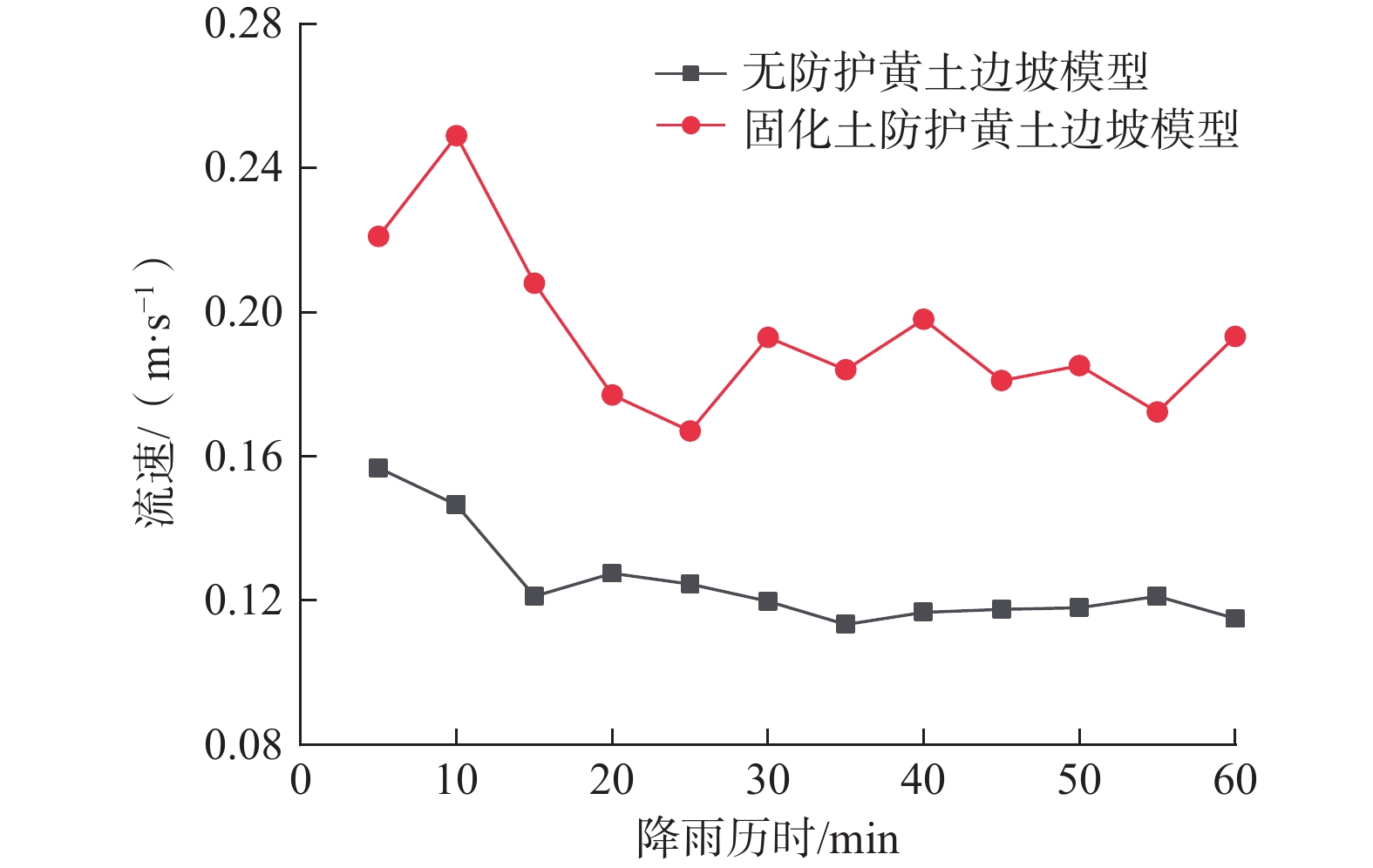
Table 4. Mud content and velocity of slope in each period
防护类型 参数 时间/min 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 无防护 含泥量/kg 0.666 0.923 1.030 1.017 1.018 1.071 0.996 1.070 1.055 1.089 1.089 1.241 流速/ (m·s−1) 0.157 0.147 0.121 0.128 0.125 0.120 0.113 0.117 0.118 0.118 0.121 0.115 固化土防护 含泥量/kg 0.584 0.384 0.431 0.454 0.439 0.420 0.356 0.292 0.306 0.245 0.214 0.239 流速/ (m·s−1) 0.221 0.249 0.208 0.177 0.167 0.193 0.184 0.198 0.181 0.185 0.172 0.193 -
[1] 唐泽军, 雷廷武, 张晴雯, 等. 雨滴溅蚀和结皮效应对土壤侵蚀影响的试验研究[J]. 土壤学报,2004,41(4):632 − 635. [TANG Zejun, LEI Tingwu, ZHANG Qingwen, et al. Quantitative determination of the impacts of raindrop splash and crust on soil erosion with ree experimental data[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2004,41(4):632 − 635. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2004.04.022
TANG Zejun, LEI Tingwu, ZHANG Qingwen, et al. Quantitative determination of the impacts of raindrop splash and crust on soil erosion with ree experimental data[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2004, 41(4): 632-635. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2004.04.022
[2] LIU J, CHEN Z H, KANUNGO D P, et al. Topsoil reinforcement of sandy slope for preventing erosion using water-based polyurethane soil stabilizer[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,252:125 − 135. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.03.003
[3] PUPPALA A J, PEDARLA A. Innovative ground improvement techniques for expansive soils[J]. Innovative Infrastructure Solutions,2017,2(1):1 − 15. doi: 10.1007/s41062-016-0049-0
[4] 安宁, 晏长根, 王亚冲, 等. 聚丙烯纤维加筋黄土抗侵蚀性能试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(2):501 − 510. [AN Ning, YAN Changgen, WANG Yachong, et al. Experimental study on anti-erosion performance of polypropylene fiber-reinforced loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(2):501 − 510. (in Chinese with English abstract)
AN Ning, YAN Changgen, WANG Yachong, et al. Experimental study on anti-erosion performance of polypropylene fiber-reinforced loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(2): 501-510. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 沙琳川, 王桂尧, 张永杰, 等. 含水率与加筋率对加筋土抗剪强度的影响规律研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):51 − 58. [SHA Linchuan, WANG Guiyao, ZHANG Yongjie, et al. A study of influence of water content and reinforcement ratio on the shear strength of reinforced soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(2):51 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SHA Linchuan, WANG Guiyao, ZHANG Yongjie, et al. A study of influence of water content and reinforcement ratio on the shear strength of reinforced soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(2): 51-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 徐岗, 裴向军, 袁进科, 等. 改性纳米硅材料加固松散砂土的工程特性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):142 − 149. [XU Gang, PEI Xiangjun, YUAN Jinke, et al. A study of the engineering characteristics of reinforced loose sand by modified nano-Si materials[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):142 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XU Gang, PEI Xiangjun, YUAN Jinke, et al. A study of the engineering characteristics of reinforced loose sand by modified nano-Si materials[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 142-149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] CHANG I, IM J, CHO G C. Introduction of microbial biopolymers in soil treatment for future environmentally-friendly and sustainable geotechnical engineering[J]. Sustainability,2016,8(3):251. doi: 10.3390/su8030251
[8] SHARMA G, SHARMA S, KUMAR A, et al. Guar gum and its composites as potential materials for diverse applications: A review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,199:534 − 545. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.053
[9] 祝艳波, 李红飞, 巨之通, 等. 黄土抗剪强度与耐崩解性能综合改良试验研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(4):221 − 233. [ZHU Yanbo, LI Hongfei, JU Zhitong, et al. Improvement of shear strength and anti-disintegration performance of compacted loess[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(4):221 − 233. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.04.027
ZHU Yanbo, LI Hongfei, JU Zhitong, et al. Improvement of shear strength and anti-disintegration performance of compacted loess[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(4): 221-233. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.04.027
[10] 周天宝, 张福海, 周炳生, 等. 生物聚合物固化粉土室内试验与机理研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2019,36(1):107 − 110. [ZHOU Tianbao, ZHANG Fuhai, ZHOU Bingsheng, et al. Laboratory experiment and mechanism of solidified soil of biopolymer[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2019,36(1):107 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20170797
ZHOU Tianbao, ZHANG Fuhai, ZHOU Bingsheng, et al. Laboratory experiment and mechanism of solidified soil of biopolymer[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2019, 36(1): 107-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20170797
[11] ORTS W J, SOJKA R E, GLENN G M. Biopolymer additives to reduce erosion-induced soil losses during irrigation[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2000,11(1):19 − 29. doi: 10.1016/S0926-6690(99)00030-8
[12] 贺智强, 樊恒辉, 王军强, 等. 木质素加固黄土的工程性能试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(3):731 − 739. [HE Zhiqiang, FAN Henghui, WANG Junqiang, et al. Experimental study of engineering properties of loess reinforced by lignosulfonate[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(3):731 − 739. (in Chinese with English abstract)
HE Zhiqiang, FAN Henghui, WANG Junqiang, et al. Experimental study of engineering properties of loess reinforced by lignosulfonate[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(3): 731-739. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘钊钊, 王谦, 钟秀梅, 等. 木质素改良黄土的持水性和水稳性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(12):2582 − 2592. [LIU Zhaozhao, WANG Qian, ZHONG Xiumei, et al. Water holding capacity and water stability of lignin-modified loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(12):2582 − 2592. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Zhaozhao, WANG Qian, ZHONG Xiumei, et al. Water holding capacity and water stability of lignin-modified loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(12): 2582-2592. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] CHANG I, IM J, PRASIDHI A K, et al. Effects of Xanthan gum biopolymer on soil strengthening[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2015,74:65 − 72. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.10.026
[15] CHANG I, PRASIDHI A K, IM J, et al. Soil strengthening using thermo-gelation biopolymers[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2015,77:430 − 438. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.12.116
[16] CHANG I, CHO G C. Strengthening of Korean residual soil with β-1, 3/1, 6-glucan biopolymer[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2012,30:30 − 35. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.11.030
[17] SUJATHA E R, SAISREE S. Geotechnical behaviour of guar gum-treated soil[J]. Soils and Foundations,2019,59(6):2155 − 2166. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2019.11.012
[18] AYELDEEN M K, NEGM A M, EL SAWWAF M A. Evaluating the physical characteristics of biopolymer/soil mixtures[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2016,9(5):1 − 13.
[19] AYELDEEN M, NEGM A, EL-SAWWAF M, et al. Enhancing mechanical behaviors of collapsible soil using two biopolymers[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2017,9(2):329 − 339. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.11.007
[20] CHEN R, ZHANG L Y, BUDHU M. Biopolymer stabilization of mine tailings[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2013,139(10):1802 − 1807. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000902
[21] STUPP S I, BRAUN P V. Molecular manipulation of microstructures: Biomaterials, ceramics, and semiconductors[J]. Science,1997,277(5330):1242 − 1248. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5330.1242
[22] 周春梅, 王宇, 吕雷, 等. 雨滴溅蚀下压实黄土变形破坏规律研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(6):93 − 98. [ZHOU Chunmei, WANG Yu, LYU Lei, et al. Research on deformation of compacted loess under raindrop splash erosion[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(6):93 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU Chunmei, WANG Yu, LYU Lei, et al. Research on deformation of compacted loess under raindrop splash erosion[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(6): 93-98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 乔勇虎, 郭东静, 陈锡云. 泾河南小河沟流域自然降雨特性[J]. 水土保持学报,2017,31(5):133 − 138. [QIAO Yonghu, GUO Dongjing, CHEN Xiyun. Characteristics of natural rainfall of Nanxiaohegou Basin in Jinghe River[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2017,31(5):133 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
QIAO Yonghu, GUO Dongjing, CHEN Xiyun. Characteristics of natural rainfall of Nanxiaohegou Basin in Jinghe River[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(5): 133-138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 左烽林, 钟守琴, 冉卓灵, 等. 紫色土丘陵区新改土坡面产流产沙及水动力学参数特征[J]. 水土保持学报,2018,32(1):59 − 66. [ZUO Fenglin, ZHONG Shouqin, RAN Zhuoling, et al. Characteristics of sediment and hydrodynamic parameters of new reconstructed slope soil in the hill area with purple soils[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,32(1):59 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZUO Fenglin, ZHONG Shouqin, RAN Zhuoling, et al. Characteristics of sediment and hydrodynamic parameters of new reconstructed slope soil in the hill area with purple soils[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(1): 59-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 袁和第, 信忠保, 蒋秋玲, 等. 连续降雨作用下褐土坡面侵蚀及其水动力学特征[J]. 水土保持学报,2020,34(4):14 − 20. [YUAN Hedi, XIN Zhongbao, JIANG Qiuling, et al. Slope erosion and its hydrodynamic characteristic of cinnamon soil under continuous rainfall[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,34(4):14 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YUAN Hedi, XIN Zhongbao, JIANG Qiuling, et al. Slope erosion and its hydrodynamic characteristic of cinnamon soil under continuous rainfall[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(4): 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] ZHANG G H, LIU G B, TANG K M, et al. Flow detachment of soils under different land uses in the loess plateau of China[J]. Transactions of the ASABE,2008,51(3):883 − 890. doi: 10.13031/2013.24527
[27] ZHANG X C, ZHANG G H, GARBRECHT J D, et al. Dating sediment in a fast sedimentation reservoir using cesium-137 and lead-210[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,2015,79(3):948 − 956. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2015.01.0021
-



 下载:
下载: