Consolidation characteristics of the turfy soil in seasonally frozen area
-
摘要:
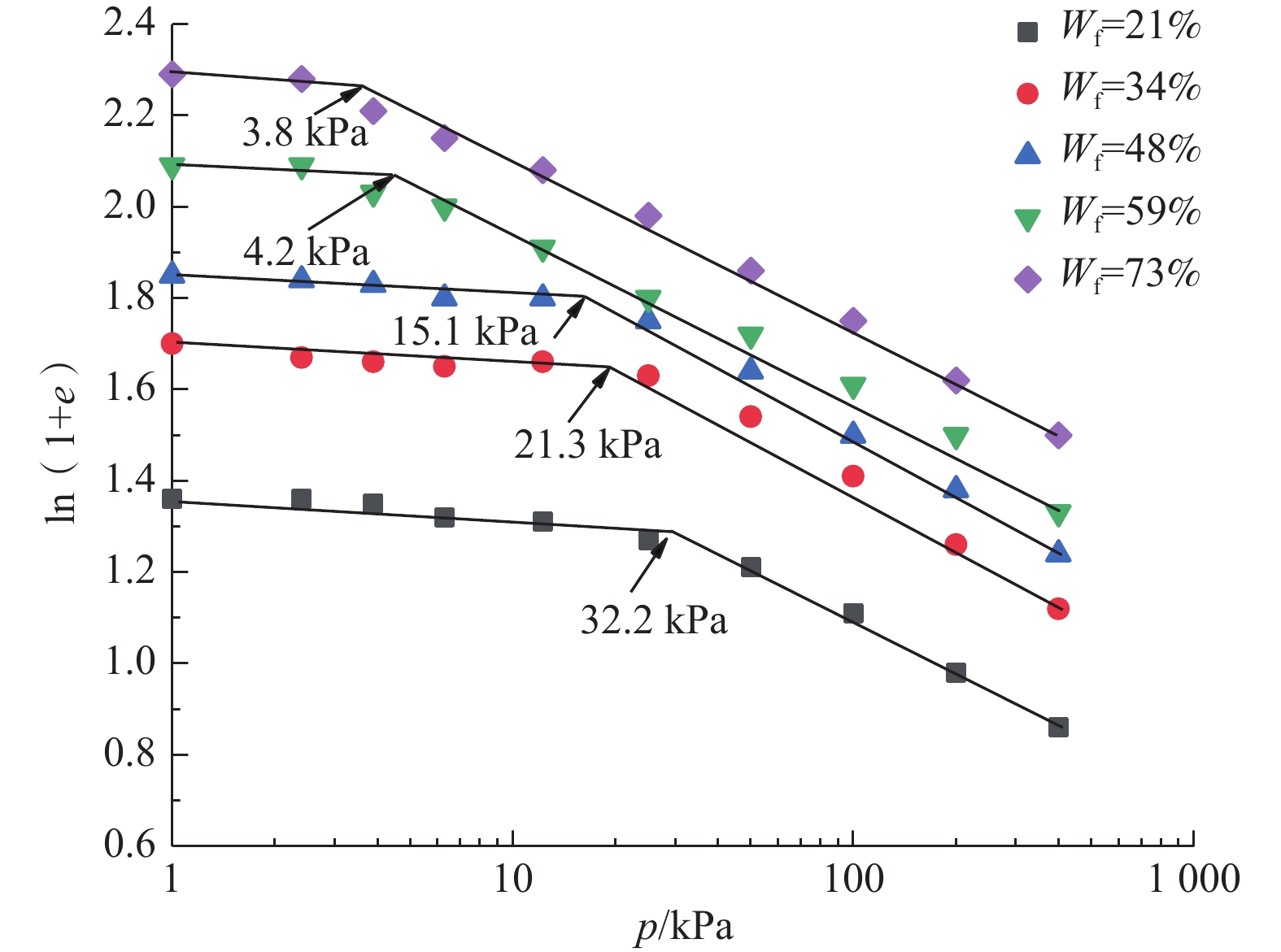
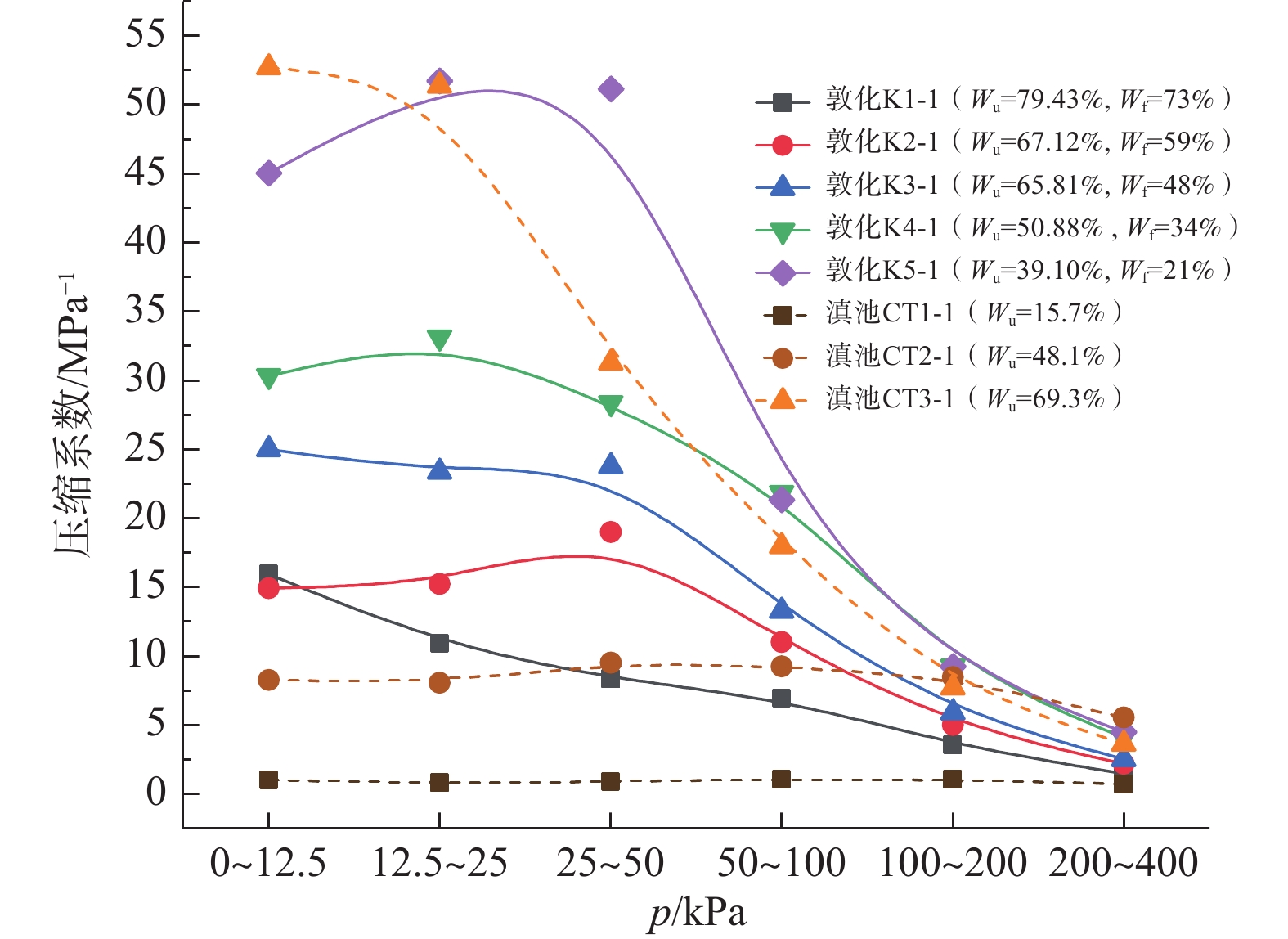
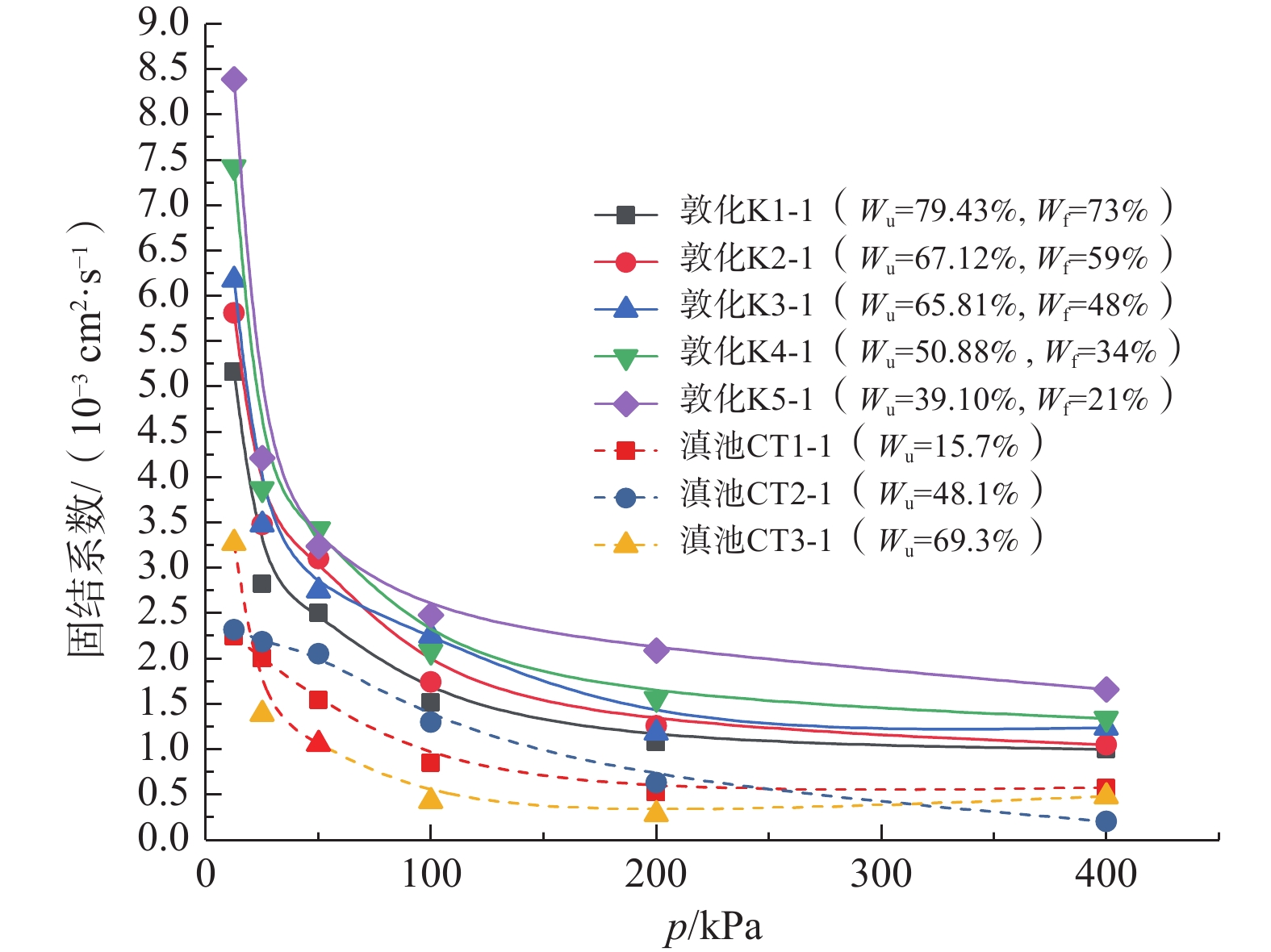
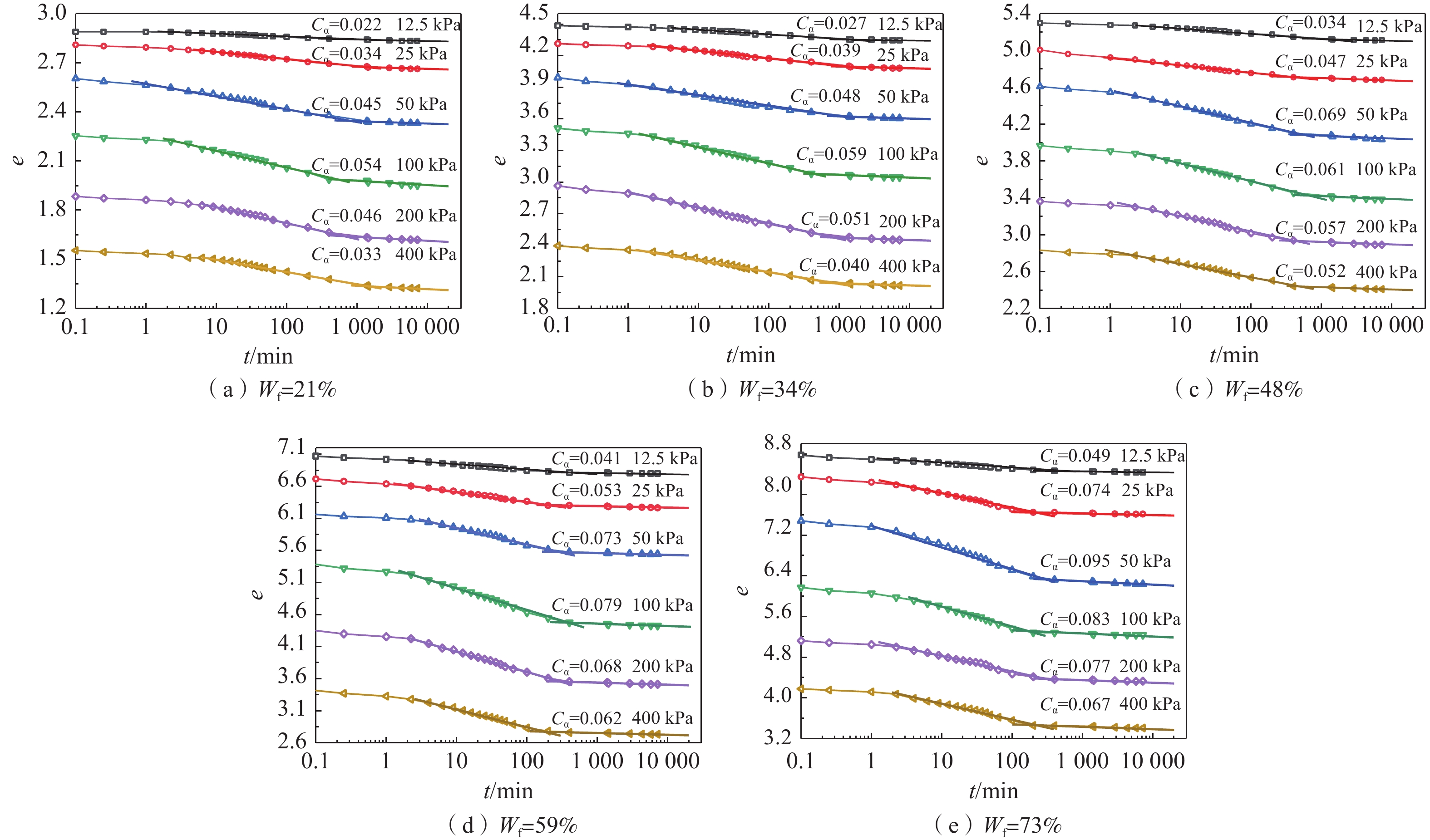
季冻区草炭土的工程性质很差,具有高压缩性的同时蠕变特性明显,路基工后沉降量大。目前针对季冻区草炭土固结压缩蠕变特性的研究仍相对匮乏,亟需对其固结压缩及蠕变特性进行深入研究,为季冻区草炭土路基的沉降预测提供参数依据。选取吉林省敦化市江源镇典型季冻区草炭土为研究对象,通过一维固结压缩试验和一维固结蠕变试验,获得草炭土压缩系数、固结系数和次固结系数分布范围及纤维含量对草炭土主、次固结特性的影响规律。试验表明:分级加载下,草炭土纤维含量越大,压缩性越强,两者呈正相关性;固结系数(Cv)范围为1.00×10−3~8.39×10−3 cm2/s,固结系数随固结压力增大而减小,当固结压力超过200 kPa之后基本稳定。次固结系数(Cα)范围为0.022~0.095,次固结系数随固结压力增大而增大,到达峰值后逐渐减小,峰值时所对应的固结压力介于50~100 kPa之间;当固结压力一定时,纤维含量越大固结蠕变越明显,次固结系数越大。吉林敦化草炭土的次固结系数和压缩指数具有一定的相关性,纤维质量占比为21%、34%、48%、59%、73%的草炭土对应的次固结系数与压缩指数比值(Cα/Cc)分别为0.0452,0.0331,0.0303,0.0246,0.0245。
Abstract:The turfy soil in seasonally frozen regions has very poor engineering properties, with high compressibility and obvious creep characteristics. The settlement of roadbed after construction is large. Therefore, it is urgent to conduct in-depth researches due to the lack of consolidation compression and creep characteristics researches of turfy soil in seasonally frozen regions, so as to provide parameters for the settlement prediction of the turfy soil roadbed in seasonally frozen regions. The typical turfy soil in seasonally frozen region near the Jiangyuan town of the city of Dunhua in Jilin Province is selected as the research object. Through 1D consolidation compression test and 1D consolidation creep test, the distribution range of the compression coefficient, consolidation coefficient and secondary consolidation coefficient of the turfy soil and the influence of fiber content on the primary and secondary consolidation characteristics of the turfy soil are obtained. The experimental results show that under graded loading, the greater the fiber content is, the stronger the compressibility of turfy soil is, showing a positive correlation. Consolidation coefficient (Cv) ranges from 1.00×10−3 to 8.39×10−3 cm2/s. Cv decreases with the increase of consolidation pressure. When the consolidation pressure exceeds 200 kPa, Cv is basically in a stable range. The secondary consolidation coefficient (Cα) ranges from 0.022 to 0.095. Cα increases with the increasing consolidation pressure, then decreases gradually after reaching the peak value when the corresponding consolidation pressure varies between 50 kPa and 100 kPa. When the consolidation pressure is constant, the higher the fiber content is, the more obvious the consolidation creep is, and the higher Cα is. There is a certain correlation between the secondary consolidation coefficient and compression index of the Dunhua turfy soil in Jilin Province. The Cα/Cc numerical values corresponding to the turfy soil with the fiber content of 21%, 34%, 48%, 59% and 73% are 0.0452, 0.0331, 0.0303, 0.0246 and 0.0245, respectively.
-
Key words:
- turfy soil /
- consolidation compression /
- consolidation creep /
- fiber content /
- Cα/Cc
-

-
表 1 吉林敦化草炭土不同深度有机质质量分数(Wu)和纤维质量分数(Wf)
Table 1. Organic matter content and fiber content of the turfy soil at different depths near Dunhua in Jilin
深度/m Wu/% Wf /% 0.0~1.0 53.28~81.35 40.99~73.78 1.0~2.0 36.25~65.81 30.83~49.12 2.0~2.4 38.37~55.25 19.83~37.65 表 2 吉林敦化草炭土样基本物理指标
Table 2. Basic physical indexes of the turfy soil samples near Dunhua in Jilin
深度/m 取样编号 密度ρ/(g·cm−3) 含水率w/% 比重Gs 初始孔隙比e0 有机质质量分数Wu /% 纤维质量占比Wf /% 0.0~0.5 K1-1 0.99 416.83 1.31 8.88 79.43 73 0.5~1.0 K2-1 1.05 392.92 1.62 7.11 67.12 59 1.0~1.5 K3-1 1.09 306.08 1.68 5.33 65.81 48 1.5~2.0 K4-1 1.14 242.18 2.09 4.50 50.88 34 2.0~2.4 K5-1 1.17 198.27 1.96 2.91 39.10 21 表 3 云南滇池土样[18]和云南大理土样[19]基本物理指标
Table 3. Basic physical indexes of Yunnan Dianchi Lake soil samples and Yunnan Dali soil samples
土样
名称深度/
m取样
编号含水率
w/%比重
Gs初始
孔隙比e0有机质
质量分数Wu/%滇池
泥炭土2.5~3.0 CT1-1 64.6 2.4 1.4 15.7 7.5~8.0 CT2-1 203.4 2.1 4.4 48.1 1.0~2.0 CT3-1 406.3 1.5 6.4 69.3 大理
泥炭土1 S1 171.7 41.8 1 S6 162.1 32.1 1 S7 118.0 34.8 表 4 试验方案
Table 4. Test schemes
试验名称 试验目的 Wf/% 加荷序列/
kPa加荷比 历时/d 固结
压缩
试验先期固结
压力分析21 2.4-3.9-6.3-
12.5-25-50-
100-200-400
(12.5 kPa
开始每级1 d)— 7 34 48 59 73 固结
压缩
试验(1)压缩特性分析
(2)主固结特性分析21 12.5-25-50-
100-200-400
(每级1 d)1 6 34 48 59 73 固结
蠕变
试验固结蠕变
特性分析21 12.5-25-50-
100-200-400
(每级7 d)1 42 34 48 59 73 表 5 不同纤维含量草炭土的Cv-p经验关系表达式
Table 5. Cv-P empirical relationship expression of the turfy soil with different fiber contents
Wf/% 拟合公式 相关系数 21 Cv=15.09p0.48 R2=0.96 34 Cv =19.43p0.50 R2=0.97 48 Cv=18.05p0.47 R2=0.94 59 Cv =21.72p0.49 R2=0.96 73 Cv =19.82p0.43 R2=0.93 -
[1] 刘柱, 佴磊. 吉林地区草炭土物理力学指标相关性试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(4):53 − 57. [LIU Zhu, NIE Lei. Experimental research on the correlation of physical mechanics indexes of the turfy soil in the Jilin Area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(4):53 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.04.011
LIU Zhu, NIE Lei. Experimental research on the correlation of physical mechanics indexes of the turfy soil in the Jilin Area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(4): 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.04.011
[2] 徐燕, 佴磊, 胡忠君. 季冻区草炭土工程地质特性研究[J]. 人民长江,2011,42(10):17 − 20. [XU Yan, NAI Lei, HU Zhongjun. Study on engineering geological properties of turfy soil in seasonal frozen region[J]. Yangtze River,2011,42(10):17 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2011.10.005
XU Yan, NAI Lei, HU Zhongjun. Study on engineering geological properties of turfy soil in seasonal frozen region[J]. Yangtze River, 2011, 42(10): 17-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2011.10.005
[3] WHITLOW R. Basic soil mechanics[M]. 3th ed. London: Longman Group Limited, 1995.
[4] RAZALI S N M, BAKAR I, ZAINORABIDIN A. Behaviour of peat soil in instrumented physical model studies[J]. Procedia Engineering,2013,53:145 − 155. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2013.02.020
[5] SANTAGATA M, BOBET A, JOHNSTON C T, et al. One-dimensional compression behavior of a soil with high organic matter content[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2008,134(1):1 − 13. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2008)134:1(1)
[6] JOHARI N N, BAKAR I, RAZALI S M, et al. Fiber effects on compressibility of peat[J]. IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering,2016,136:012036. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/136/1/012036
[7] 桂跃, 余志华, 刘海明, 等. 高原湖相泥炭土固结系数变化规律试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(增刊1): 3259 − 3267
GUI Yue, YU Zhihua, LIU Haiming, et al. Experimental study of the change law of consolidation coefficient of the plateau lacustrine peaty soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(Sup 1): 3259 − 3267. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 吕岩, 佴磊, 徐燕, 等. 有机质对草炭土物理力学性质影响的机理分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2011,33(4):655 − 660. [LYU Yan, NIE Lei, XU Yan, et al. The mechanism of organic matter effect on physical and mechanical properties of turfy soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2011,33(4):655 − 660. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LYU Yan, NIE Lei, XU Yan, et al. The mechanism of organic matter effect on physical and mechanical properties of turfy soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(4): 655-660. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] MACFARLANE I C. The muskeg subcommittee[C]//Proc, Tench Muskeg Research Conf, National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa: Assoc. Ctee. on Soil and Snow Mech, Tech, Memo. 1965, 85: 1 − 5.
[10] 桂跃, 余志华, 刘海明, 等. 高原湖相泥炭土次固结特性及机理分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015,37(8):1390 − 1398. [GUI Yue, YU Zhihua, LIU Haiming, et al. Secondary consolidation properties and mechanism of plateau lacustrine peaty soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,37(8):1390 − 1398. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201508005
GUI Yue, YU Zhihua, LIU Haiming, et al. Secondary consolidation properties and mechanism of plateau lacustrine peaty soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(8): 1390-1398. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201508005
[11] 王竟宇, 王志良, 申林方, 等. 单向压缩状态下滇池泥炭土的蠕变特性研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2020,16(6):1689 − 1695. [WANG Jingyu, WANG Zhiliang, SHEN Linfang, et al. Study on consolidation creep properties of Dianchi peaty soil under one-dimensional compression[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2020,16(6):1689 − 1695. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Jingyu, WANG Zhiliang, SHEN Linfang, et al. Study on consolidation creep properties of Dianchi peaty soil under one-dimensional compression[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2020, 16(6): 1689-1695. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 冯瑞玲, 吴立坚, 张益铭. 泥炭土的固结特性试验研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2019,15(5):1384 − 1392. [FENG Ruiling, WU Lijian, ZHANG Yiming. Study on the consolidation properties of peaty soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2019,15(5):1384 − 1392. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FENG Ruiling, WU Lijian, ZHANG Yiming. Study on the consolidation properties of peaty soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2019, 15(5): 1384-1392. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李育红, 周庆云, 程芸. 滇池湖相泥炭土固结系数及次固结系数研究[J]. 工程勘察,2019,47(5):26 − 32. [LI Yuhong, ZHOU Qingyun, CHENG Yun. Study on the coefficient of consolidation and secondary consolidation of lacustrine peat soil around the Dian Lake[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2019,47(5):26 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Yuhong, ZHOU Qingyun, CHENG Yun. Study on the coefficient of consolidation and secondary consolidation of lacustrine peat soil around the Dian Lake[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2019, 47(5): 26-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] Standard test methods for moisture, ash, and organic matter of peat and other organic soils: ASTMD 2974—14[S]. 2014.
[15] Standard test methods for laboratory determination of the fiber content of peat samples by dry mass: ASTMD 1997—13[S]. 2013.
[16] Standard classification of peat samples by laboratory testing: ASTMD 4497—13[S]. 2007.
[17] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for geotechnical testing method: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[18] 方超. 高原湖相泥炭土工程性质原生各向异性试验研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2019
FANG Chao. Experimental study on inherent anisotropy of engineering properties of plateau lacustrine peat soil[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 彭博. 云南大理地区强泥炭质土固结特性的试验研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2019
PENG Bo. Experimental study on consolidation of peat soil in Dali area of Yunnan[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] ONITSUKA K, HONG Z S, HARA Y, et al. Interpretation of oedometer test data for natural clays[J]. Soils and Foundations,1995,35(3):61 − 70. doi: 10.3208/sandf.35.61
[21] HONG Z S, ONITSUKA K. A method of correcting yield stress and compression index of ariake clays for sample disturbance[J]. Soils and Foundations,1998,38(2):211 − 222. doi: 10.3208/sandf.38.2_211
[22] 沈珠江. 软土工程特性和软土地基设计[J]. 岩土工程学报,1998,20(1):100 − 111. [SHEN Zhujiang. Engineering properties of soft soils and design of soft ground[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1998,20(1):100 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1998.01.025
SHEN Zhujiang. Engineering properties of soft soils and design of soft ground[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1998, 20(1): 100-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1998.01.025
[23] 加瑞, 雷华阳. 有明黏土各向异性固结特性的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(6):2231 − 2238. [JIA Rui, LEI Huayang. Experimental study of anisotropic consolidation behavior of Ariake clay[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(6):2231 − 2238. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIA Rui, LEI Huayang. Experimental study of anisotropic consolidation behavior of Ariake clay[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(6): 2231-2238. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 雷华阳, 任倩, 张文振, 等. 吹填超软土固结特性试验分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(6):1039 − 1045. [LEI Huayang, REN Qian, ZHANG Wenzhen, et al. Consolidation property of ultra soft soil[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(6):1039 − 1045. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LEI Huayang, REN Qian, ZHANG Wenzhen, et al. Consolidation property of ultra soft soil[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(6): 1039-1045. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] MESRI G, GODLEWSKI P M. Time and stress compressibility interrelationship[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division,1977,103(5):417 − 430. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0000421
[26] WALKER L K. Undrained creep in a sensitive clay[J]. Géotechnique,1969,19(4):515 − 529.
[27] O’KELLY B C. Compression and consolidation anisotropy of some soft soils[J]. Geotechnical & Geological Engineering,2006,24(6):1715 − 1728.
[28] 孙德安, 申海娥. 上海软土的流变特性试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(3):74 − 78. [SUN Dean, SHEN Haie. Experimental study on rheology behaviour of Shanghai soft clay[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(3):74 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.03.016
SUN Dean, SHEN Haie. Experimental study on rheology behaviour of Shanghai soft clay[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(3): 74-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.03.016
[29] 邓岳保, 陈菲, 刘干斌, 等. 宁波土层的流变固结试验及流变模型参数研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(5):46 − 51. [DENG Yuebao, CHEN Fei, LIU Ganbin, et al. A study of the rheological consolidation test and rheological model parameters for the Ningbo soil layer[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(5):46 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DENG Yuebao, CHEN Fei, LIU Ganbin, et al. A study of the rheological consolidation test and rheological model parameters for the Ningbo soil layer[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(5): 46-51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] BERRY P L, VICKERS B. Consolidation of fibrous peat[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division,1975,101(8):741 − 753. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0000183
-




 下载:
下载: