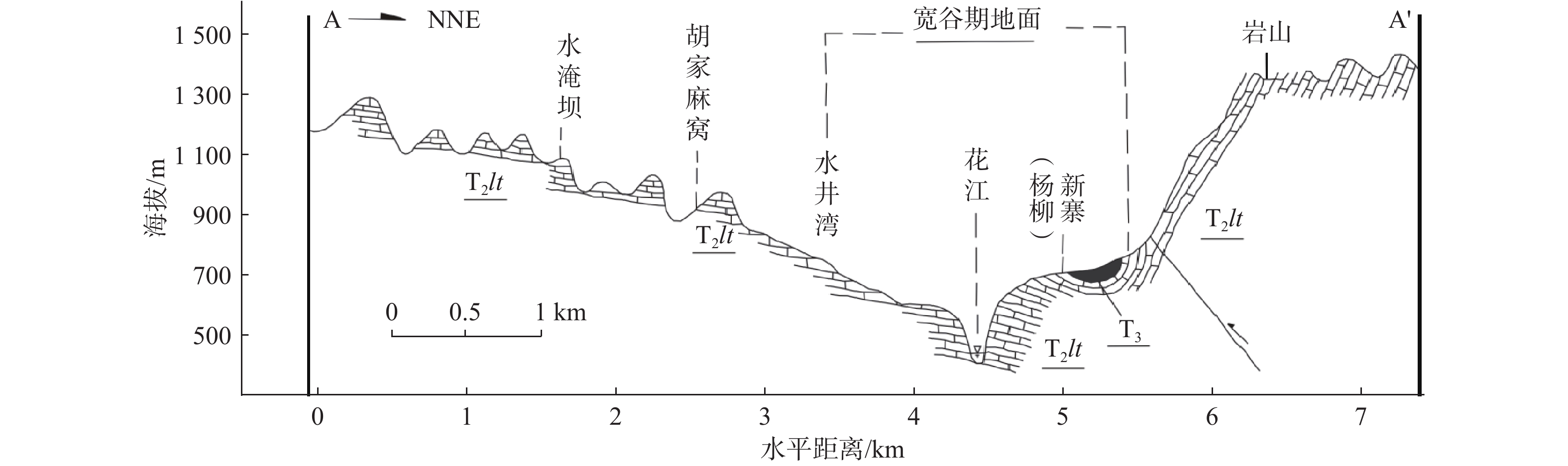
Spatial distribution characteristics of soil thickness in the Zhenfeng-GuanlingHuajiang karst rocky desertification area in Guizhou Province
-
摘要:
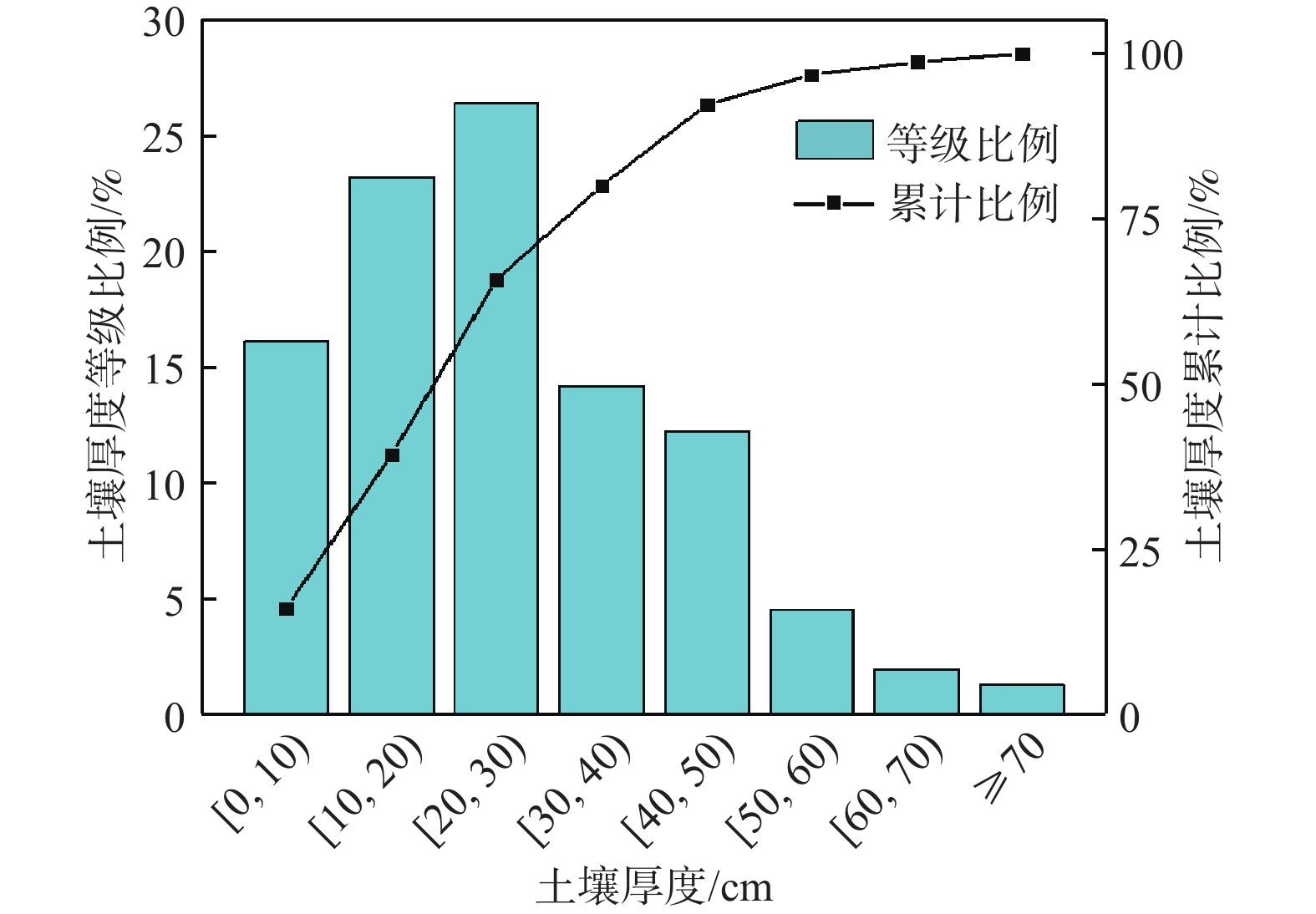
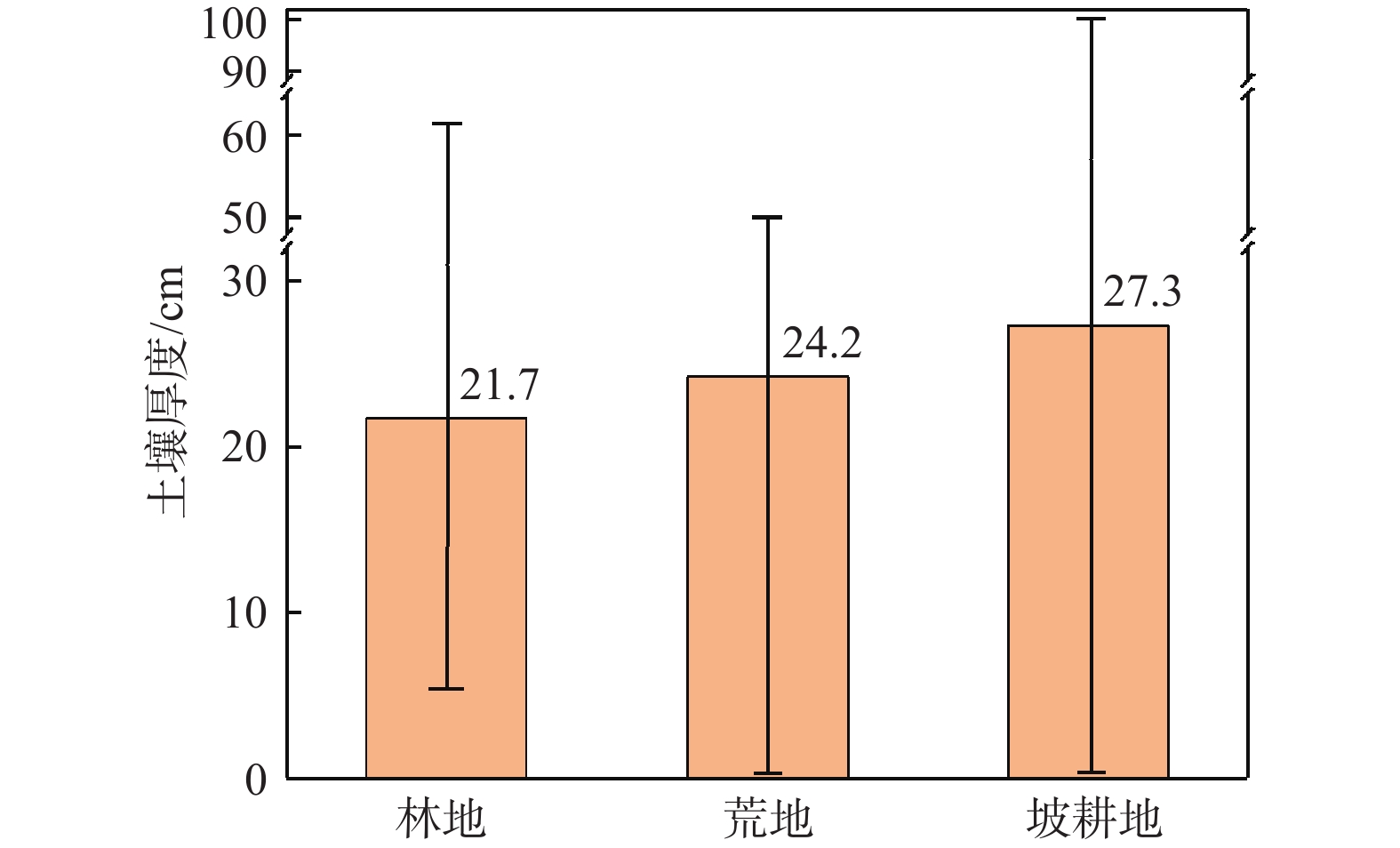
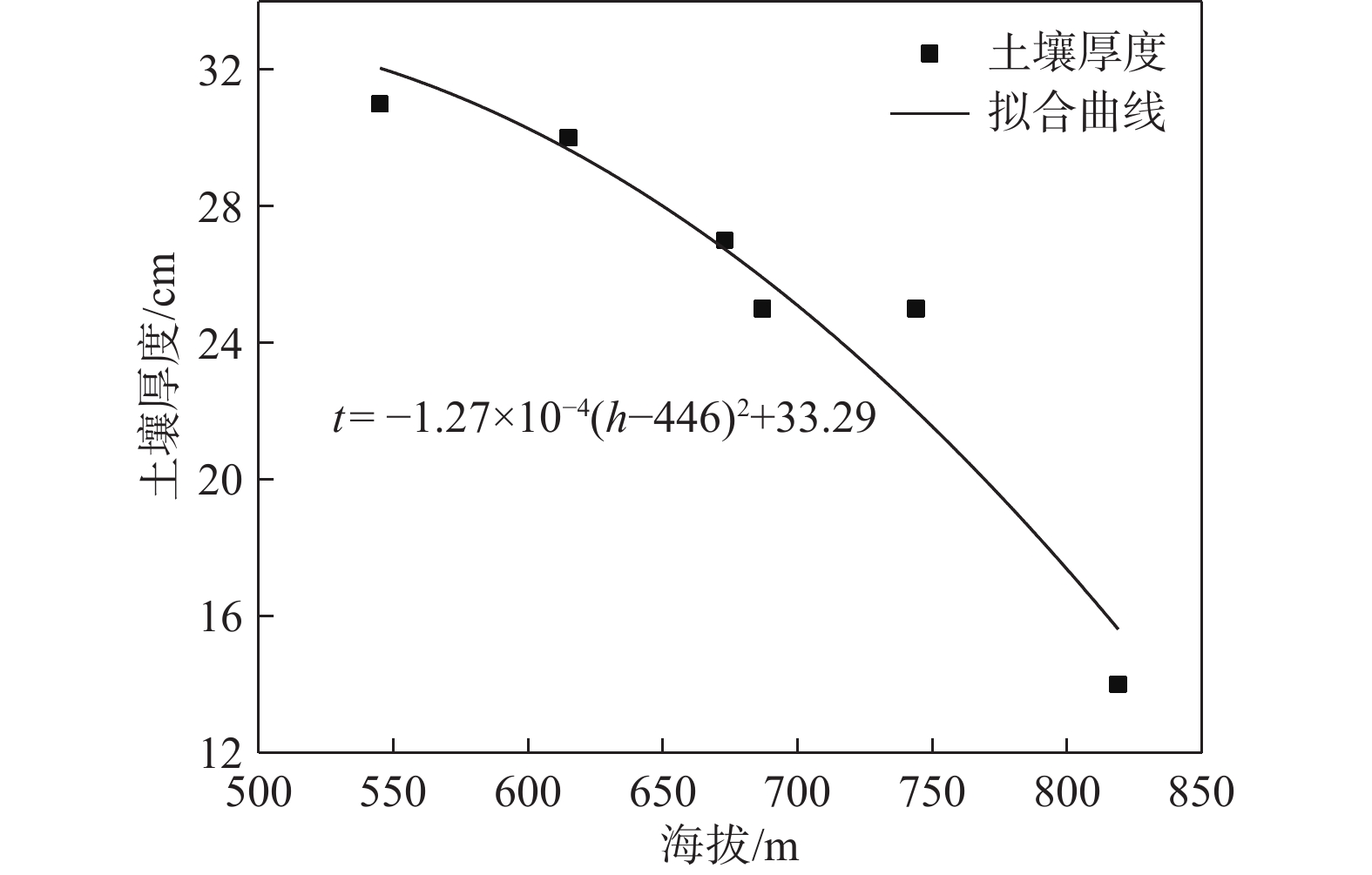
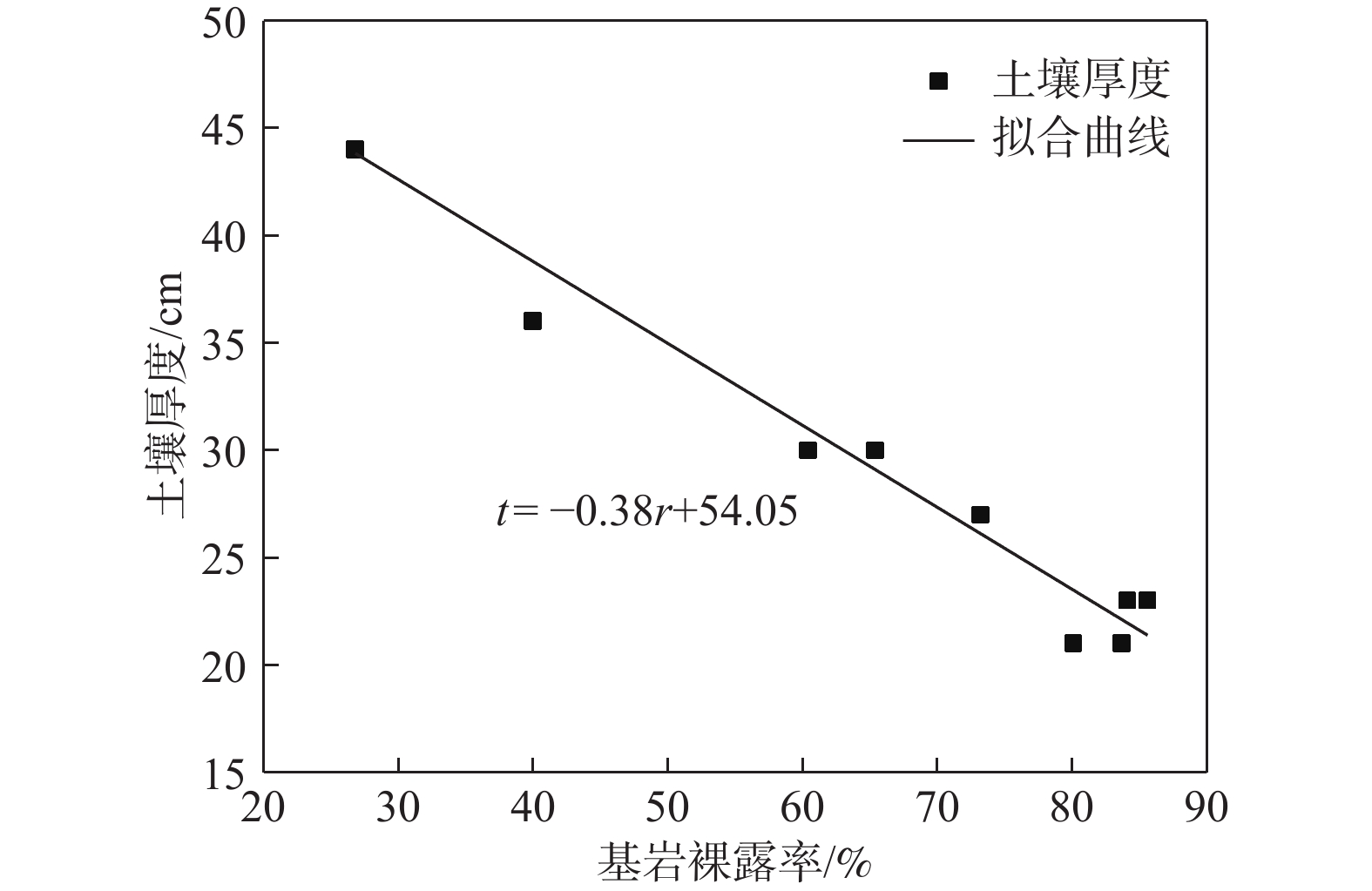
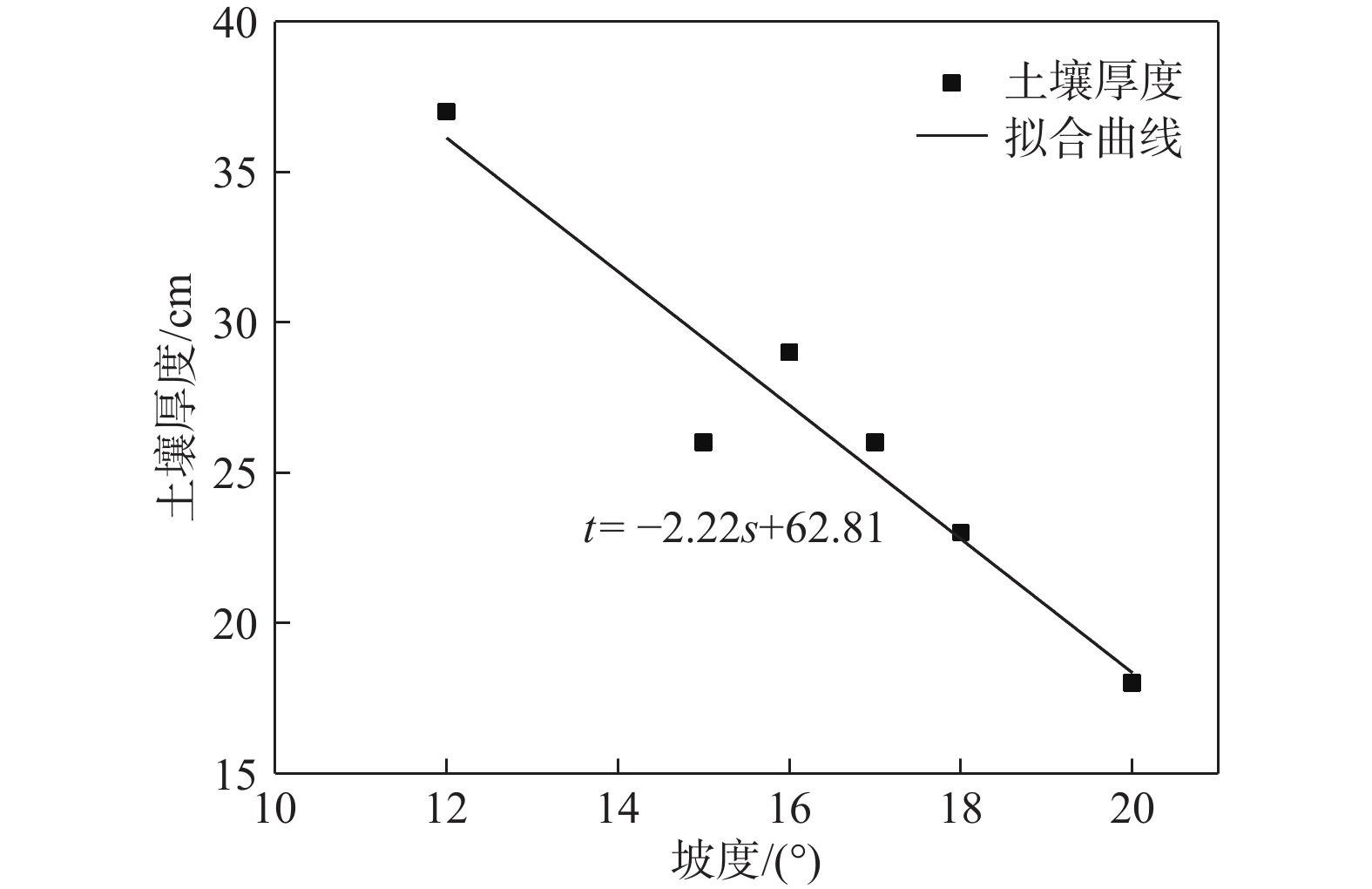
土壤厚度与石漠化发展程度有着密切的关系,土壤也是石漠化地区生态恢复以及农业生产的基础。为了研究典型高原峡谷中-强度石漠化地区的土壤厚度空间分布规律,在土壤厚度野外调查的基础上,利用地统计学方法分析了贵州典型石漠化地区——贞丰—关岭花江小流域土壤厚度空间分布特征及主要影响因素。结果表明:(1)研究区土壤平均厚度仅为26 cm,土壤平均厚度表现为坡耕地>荒地>林地;(2)土壤厚度空间变异性以强度为主,荒地的土壤厚度空间分布连续程度优于林地和坡耕地,林地的土壤厚度空间分布有明显突变性,坡耕地的土壤厚度具有点状分布特征,有耕作物附近土壤厚度较大;(3)土壤厚度与海拔、基岩裸露率、坡度之间均有明显负相关关系;(4)自然和人为因素综合影响下的土壤强侵蚀是研究区土壤厚度分布极为不均的主要原因,对该区域石漠化的治理可以采用工程措施与生物措施相结合的方法。研究结果对研究区石漠化因地制宜地防治及其他地区水土流失防治、生态恢复、农业合理生产具有一定的参考价值。
Abstract:Soil thickness is closely related to the development degree of rocky desertification, and soil is the basis of ecological restoration and agricultural production in karst rocky desertification areas. In order to examine the spatial distribution law of soil thickness in typical plateau rocky desertification areas, by combining field investigation of soil thickness with geostatistic methods, this paper analyzes the spatial distribution characteristics of soil thickness and its influencing factors in the karst plateau gorge area of the Zhenfeng-Guanling Huajiang small watershed in Guizhou. The results show that the average soil thickness in the study area is only 26 cm, and the average thickness of soil is: Slope farmland > wasteland > forest land. The spatial variability of soil thickness in the study area is mainly intensity. The spatial distribution continuity of soil thickness in wasteland is better than that of forest land and slope farmland. The spatial distribution of soil thickness in forest land has obvious mutation. The soil thickness in slope farmland is characterized by point distribution, and the soil thickness near crops is large. There are significant negative correlations between soil thickness and altitude, bedrock exposure rate and slope. Serious soil erosion under natural and man-made effect is the main reason for the uneven distribution of soil thickness in the study area, and the combination of engineering measures and biological measures can be used to control rocky desertification in the study area. The results are of guiding significance for the control of rocky desertification in the study area and control of soil erosion, ecological restoration and rational agricultural production in other similar areas.
-
Key words:
- karst rocky desertification /
- plateau canyon /
- land use /
- soil thickness /
- spatial distribution
-

-
表 1 各采样单元土壤厚度
Table 1. Soil thickness information of the investigation units
调查单元编号 土地利用类型 主要植被 海拔
/m基岩裸露率
/%斜坡倾向
/(°)坡度
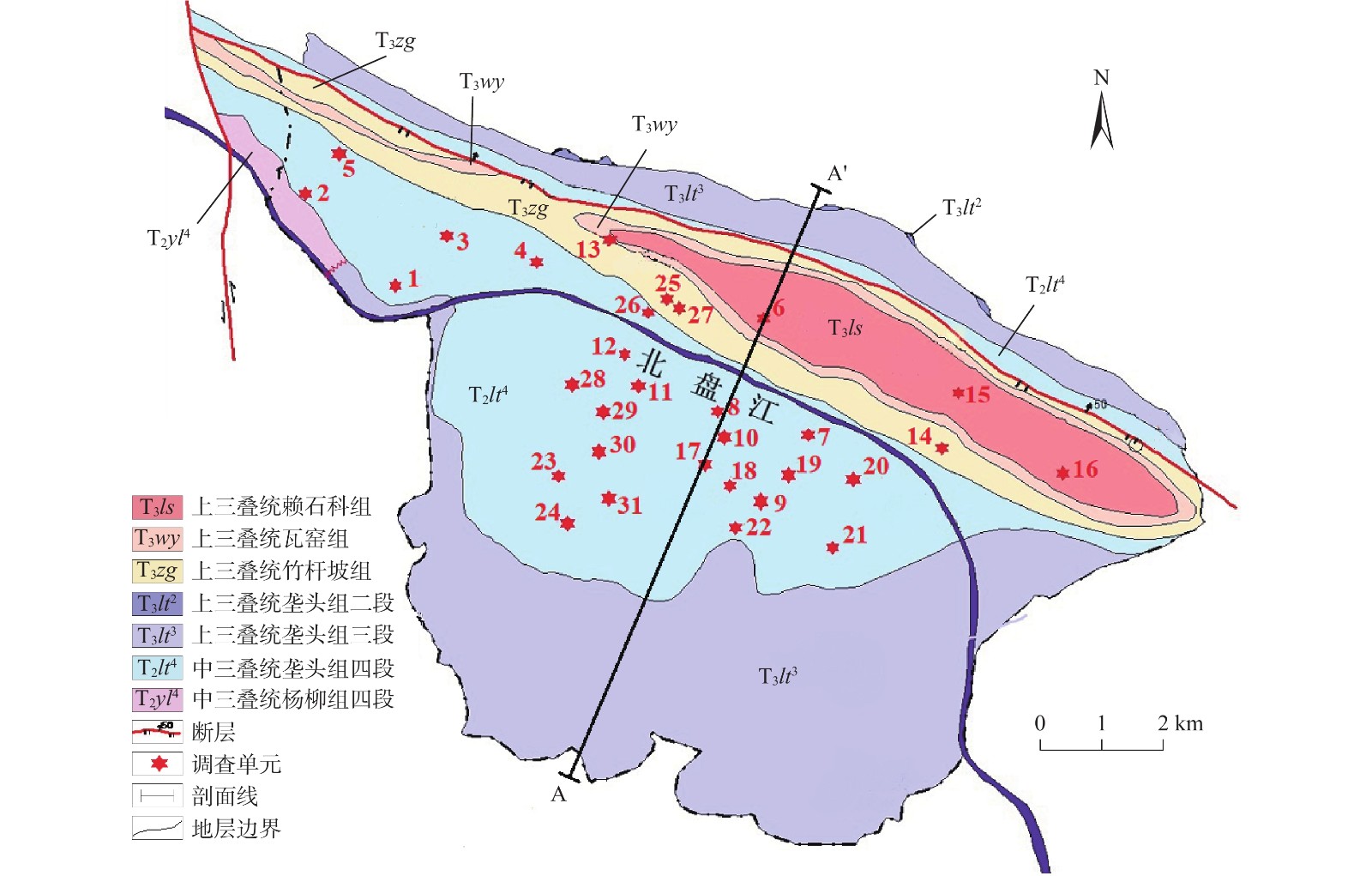
/(°)土壤厚度描述性统计 最大值/cm 最小值/cm 平均值/cm 标准差 变异系数/% Plot 1 坡耕地 仙人掌、花椒 744 84.1 65 15 40 10 28 9.57 34 Plot 2 坡耕地 花椒 820 60.0 11 29 100 15 44 24.74 57 Plot 3 荒地 乔木、杂草 702 60.0 30 16 50 10 36 16.99 48 Plot 4 坡耕地 仙人掌、花椒 665 79.2 0 20 25 10 18 6.87 37 Plot 5 坡耕地 花椒、玉米 676 85.6 334 18 58 10 36 19.80 55 Plot 6 坡耕地 花椒 618 73.0 330 15 40 0 33 14.97 58 Plot 7 林地 柚木 542 63.8 255 15 45 5 18 14.04 77 Plot 8 荒地 杂草 677 80.9 18 16 35 20 27 5.10 19 Plot 9 坡耕地 玉米 871 72.8 10 17 50 10 33 14.62 44 Plot 10 坡耕地 金银花、花椒 774 75.1 30 12 50 18 37 11.68 32 Plot 11 坡耕地 花椒、仙人掌 689 63.4 60 16 50 20 33 9.95 30 Plot 12 坡耕地 火龙果 537 18.5 225 19 55 15 37 13.61 37 Plot 13 荒地 无 612 26.8 140 15 37 0 19 13.45 72 Plot 14 林地 柚木 555 83.7 210 11 62 15 32 15.62 49 Plot 15 坡耕地 大豆、花椒、玉米 767 61.1 15 16 80 25 59 16.41 28 Plot 16 坡耕地 花椒 717 71.9 30 18 40 15 28 7.07 25 Plot 17 坡耕地 花椒 813 64.2 258 14 8 5 6 1.41 24 Plot 18 坡耕地 花生、花椒 547 66.6 5 14 55 20 36 11.58 32 Plot 19 坡耕地 花椒 737 66.2 34 13 45 5 25 15.67 63 Plot 20 坡耕地 花椒 685 65.9 196 14 30 5 18 8.06 45 Plot 21 坡耕地 玉米、花椒 749 67.6 230 16 32 5 21 10.87 51 Plot 22 荒地 杂草 826 72.0 223 17 30 8 23 7.80 34 Plot 23 坡耕地 荒草、花椒 775 74.2 121 17 40 10 23 10.80 46 Plot 24 林地 灌木、荒草 1189 0.0 40 20 15 15 15 0.00 0 Plot 25 坡耕地 火龙果、杂草 596 12.3 130 15 73 0 18 18.22 62 Plot 26 荒地 杂草 654 0.0 140 15 40 0 25 10.20 41 Plot 27 荒地 杂草 596 55.5 170 22 42 0 15 10.51 69 Plot 28 坡耕地 花椒、玉米 692 33.3 60 20 49 0 18 15.10 82 Plot 29 坡耕地 花椒 866 40.2 75 28 35 0 11 11.48 100 Plot 30 坡耕地 核桃、石榴 726 19.5 170 16 50 0 21 16.21 77 Plot 31 坡耕地 仙人掌、红薯 932 60.2 130 19 53 0 17 14.87 85 表 2 典型样地土壤厚度半方差分析参数表
Table 2. Parameters of semi-variance analysis of soil thickness in typical plots
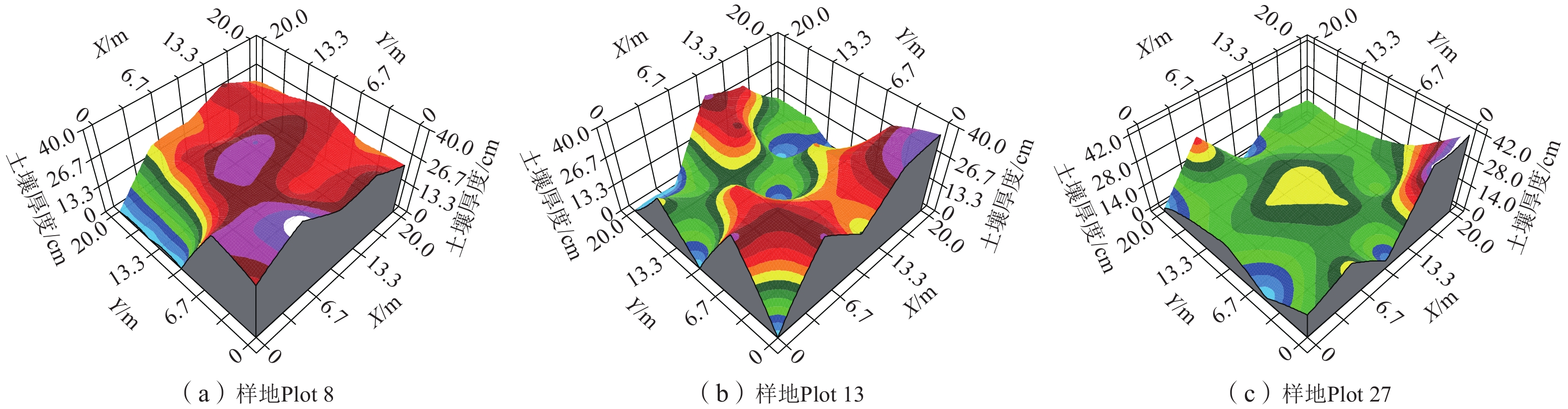
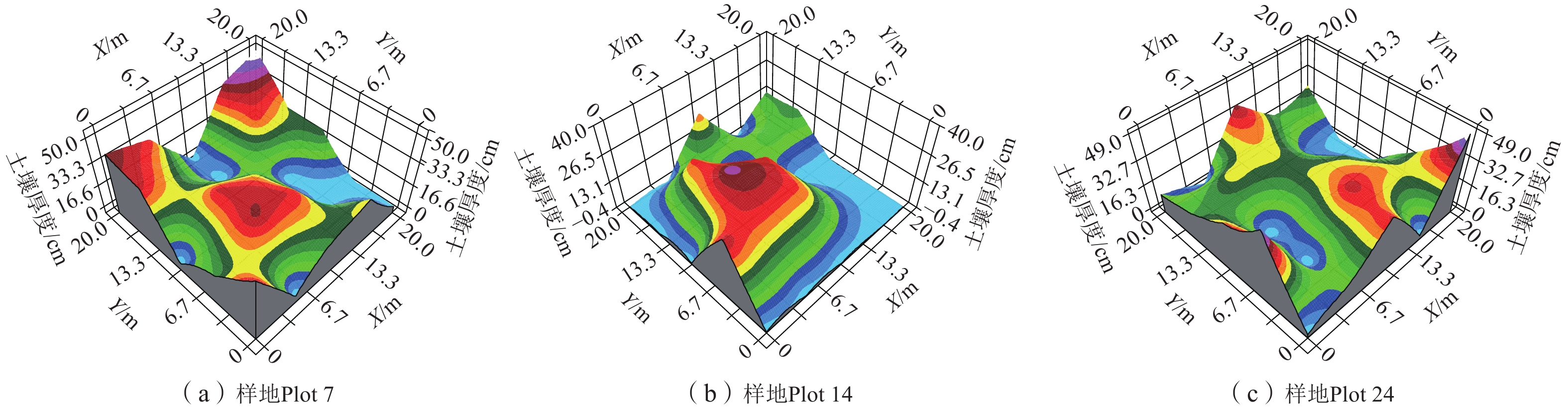
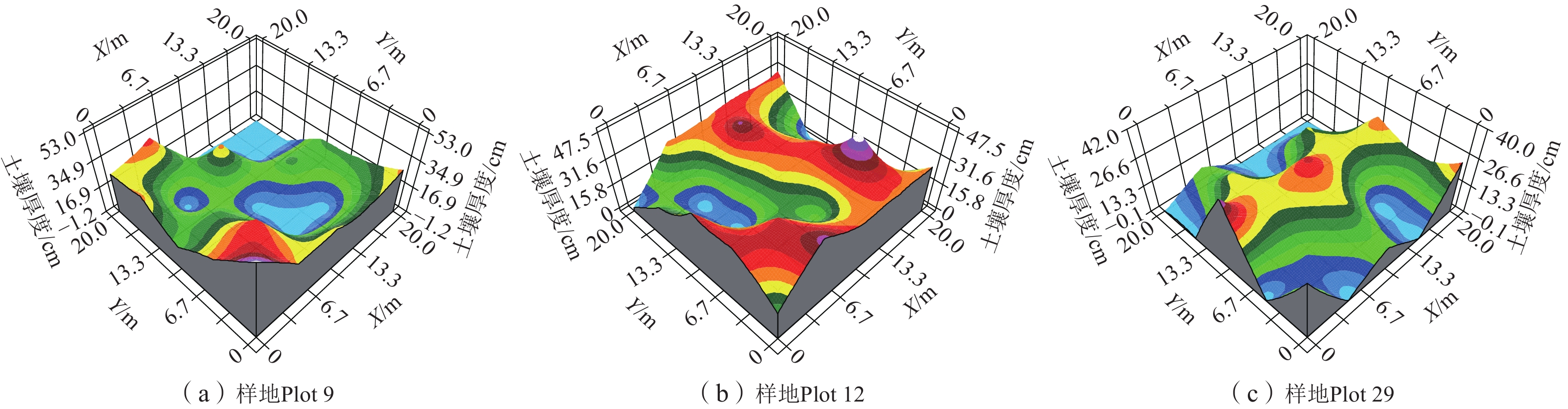
编号 土地利用类型 理论模型 块金值 基台值 块金值/基台值 变程 R2 RSS Plot 8 荒地 高斯模型 177.0 664.9 0.27 31.40 0.519 21732 Plot 13 荒地 高斯模型 40.0 284.6 0.14 12.64 1.000 1.65 Plot 27 荒地 高斯模型 71.6 354.1 0.20 43.00 0.629 1451 Plot 7 林地 球状模型 166.0 742.9 0.22 29.25 0.607 26464 Plot 14 林地 球状模型 11.2 284.6 0.04 7.20 0.715 313 Plot 24 林地 线性模型 71.0 71.0 1.00 14.14 0.929 632 Plot 9 坡耕地 球状模型 25.0 459.3 0.05 7.93 0.509 3922 Plot 12 坡耕地 线性模型 199.8 199.8 1.00 11.77 0.855 18301 Plot 29 坡耕地 指数模型 98.6 342.9 0.29 183.00 0.528 240 -
[1] 卢耀如,张凤娥,刘长礼,等. 中国典型地区岩溶水资源及其生态水文特性[J]. 地球学报,2006,27(5):393 − 402. [LU Yaoru,ZHANG Fenge,LIU Changli,et al. Karst water resources in typical areas of China and their eco-hydrological characteristics[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2006,27(5):393 − 402. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.002
[2] 姚邦杰,刘琦,任标,等. 典型石漠化地区岩溶水系统循环演化分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(5):1179 − 1187. [YAO Bangjie,LIU Qi,REN Biao,et al. Analysis of cyclic evolution of karst water system in typical karst rocky desertification area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(5):1179 − 1187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] LIU Qi,DENG Dapeng,YAO Bangjie,et al. Analysis of the karst springs’ supply sources in rocky desertification area of Guanling–Huajiang,Guizhou,China[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites,2020,35(3):1 − 11.
[4] 闫利会,周忠发,陈全,等. 高原峡谷区喀斯特石漠化演变过程研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(2):112 − 117. [YAN Lihui,ZHOU Zhongfa,CHEN Quan,et al. A study of the evolution process of karst rocky desertification in a karst canyon area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(2):112 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张信宝,刘再华,王世杰,等. 锥峰和塔峰溶丘地貌的表层喀斯特带径流溶蚀形成机制[J]. 山地学报,2011,29(5):529 − 533. [ZHANG Xinbao,LIU Zaihua,WANG Shijie,et al. Dynamic mechanism of runoff corrosion in the epikarst zone on the formation of cone and tower karst landforms[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2011,29(5):529 − 533. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2011.05.003
[6] WANG Miaomiao,CHEN Hongsong,ZHANG Wei,et al. Soil nutrients and stoichiometric ratios as affected by land use and lithology at county scale in a karst area,southwest China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,619/620:1299 − 1307. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.175
[7] CAO Shixiong. A win-win path for institutional change[J]. Time and Society,2016,25(3):493 − 512. doi: 10.1177/0961463X15577275
[8] FENG Qi,MA Hua,JIANG Xuemei,et al. What has caused desertification in China?[J]. Scientific Reports,2015,5:15998. doi: 10.1038/srep15998
[9] 周春衡,付智勇,吴丽萍,等. 喀斯特坡地土层厚度及养分含量空间分布特征[J]. 农业现代化研究,2020,41(3):539 − 548. [ZHOU Chunheng,FU Zhiyong,WU Liping,et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil thickness and soil nutrient content in karst slopes[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization,2020,41(3):539 − 548. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 魏兴琥,李森,罗红波,等. 粤北石漠化过程土壤与植被变化及其相关性研究[J]. 地理科学,2008,28(5):662 − 666. [WEI Xinghu,LI Sen,LUO Hongbo,et al. Changes and correlation of soil and vegetation in process of rock desertification in northern Guangdong Province[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2008,28(5):662 − 666. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2008.05.012
[11] 李森,董玉祥,王金华. 土地石漠化概念与分级问题再探讨[J]. 中国岩溶,2007,26(4):279 − 284. [LI Sen,DONG Yuxiang,WANG Jinhua. Re-discussion on the concept and classification of rocky desertification[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2007,26(4):279 − 284. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2007.04.001
[12] 周运超,罗美. 喀斯特小流域土壤厚度的影响因素[J]. 山地农业生物学报,2017,36(3):1 − 5. [ZHOU Yunchao,LUO Mei. Influencing factors of soil thickness in karst small watershed[J]. Journal of Mountain Agriculture and Biology,2017,36(3):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 尹辉,李晖,蒋忠诚,等. 基于“3S”的广西典型岩溶区土壤厚度空间格局研究[J]. 水土保持研究,2014,21(6):25 − 29. [YIN Hui,LI Hui,JIANG Zhongcheng,et al. Study on spatial pattern of soil thickness in typical karst area in Guangxi based on ‘3S’ technology[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2014,21(6):25 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2014.06.008
[14] 李程程,程星,杨士超. 岩溶山区植物生长的土壤厚度因素研究:以贵州相宝山为例[J]. 贵州师范学院学报,2012,28(9):38 − 41. [LI Chengcheng,CHENG Xing,YANG Shichao. Study on the soil thickness factor of plant growth in karst mountains: Take the Guizhou Xiangbao Mountain as an example[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal College,2012,28(9):38 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7798.2012.09.010
[15] HUANG Xianfei,ZHANG Zhenming,ZHOU Yunchao,et al. Spatial heterogeneity of soil thickness and factors controlling it in a karst basin[J]. Eurasian Soil Science,2021,54(4):478 − 486. doi: 10.1134/S1064229321040074
[16] 尹亮,崔明,周金星,等. 岩溶高原地区小流域土壤厚度的空间变异特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学,2013,11(1):51 − 58. [YIN Liang,CUI Ming,ZHOU Jinxing,et al. Spatial variability of soil thickness in a small watershed of karst plateau[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2013,11(1):51 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2013.01.008
[17] 梁桂星,覃小群,崔亚莉,等. 分布式水文模型在岩溶地区的改进与应用研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):60 − 67. [LIANG Guixing,QIN Xiaoqun,CUI Yali,et al. Improvement and application of a distributed hydrological model in karst regions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):60 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 王涵,刘琦,任标,等. 典型喀斯特石漠化地区降雨产流产沙特征[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版),2019,37(3):6 − 12. [WANG Han,LIU Qi,REN Biao,et al. Characteristics of rainfall runoff and sediment yield in typical karst rocky desertification area[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences),2019,37(3):6 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] ROBERTSON G P,CRUM J R,ELLIS B G. The spatial variability of soil resources following long-term disturbance[J]. Oecologia,1993,96(4):451 − 456. doi: 10.1007/BF00320501
[20] 高峻,何春霞,张劲松,等. 太行山干瘠山地土壤厚度空间变异及草灌群落分布特征[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(6):2080 − 2089. [GAO Jun,HE Chunxia,ZHANG Jinsong,et al. Spatial variability of soil thickness and the distribution characteristics of herb and shrub communities in the arid and barren areas of Taihang Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(6):2080 − 2089. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 易湘生,李国胜,尹衍雨,等. 土壤厚度的空间插值方法比较:以青海三江源地区为例[J]. 地理研究,2012,31(10):1793 − 1805. [YI Xiangsheng,LI Guosheng,YIN Yanyu,et al. Comparison on soil depth prediction among different spatial interpolation methods:A case study in the Three-River Headwaters Region of Qinghai Province[J]. Geographical Research,2012,31(10):1793 − 1805. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 尹亮. 西南岩溶高原石漠化地区小流域土壤厚度空间分异规律研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2012
YIN Liang. Spatial variability of soil thickness in a watershed of highland areas in karst region[D]. Changsha: Hu’nan University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 代希君,彭杰,张艳丽,等. 基于光谱分类的土壤盐分含量预测[J]. 土壤学报,2016,53(4):909 − 918. [DAI Xijun,PENG Jie,ZHANG Yanli,et al. Prediction on soil salt content based on spectral classification[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2016,53(4):909 − 918. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 陈小强,张寿鹏,张连根,等. 岩溶石漠化区吉科小流域治理效果评价[J]. 中国水土保持,2015(6):21 − 23. [CHEN Xiaoqiang,ZHANG Shoupeng,ZHANG Liangen,et al. Evaluation of treatment effect of Jike small watershed in karst rocky desertification area[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China,2015(6):21 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2015.06.006
[25] 张军以,戴明宏,王腊春,等. 西南喀斯特石漠化治理植物选择与生态适应性[J]. 地球与环境,2015,43(3):269 − 278. [ZHANG Junyi,DAI Minghong,WANG Lachun,et al. Plant selection and their ecological adaptation for rocky desertification control in karst region in the southwest of China[J]. Earth and Environment,2015,43(3):269 − 278. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2015.03.001
[26] 喻阳华, 闵芳卿, 盈斌. 顶坛花椒矮化密植方法: CN109168865A[P]. 2019-01-11
YU Yanghua, MIN Fangqing, YING Bin. Zanthoxylum bungeanum dwarfing and dense planting method: CN109168865A[P]. 2019-01-11. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: