Probabilistic classification prediction of rockburst intensity in a deep buried high geo-stress rock tunnel during engineering investigation
-
摘要:
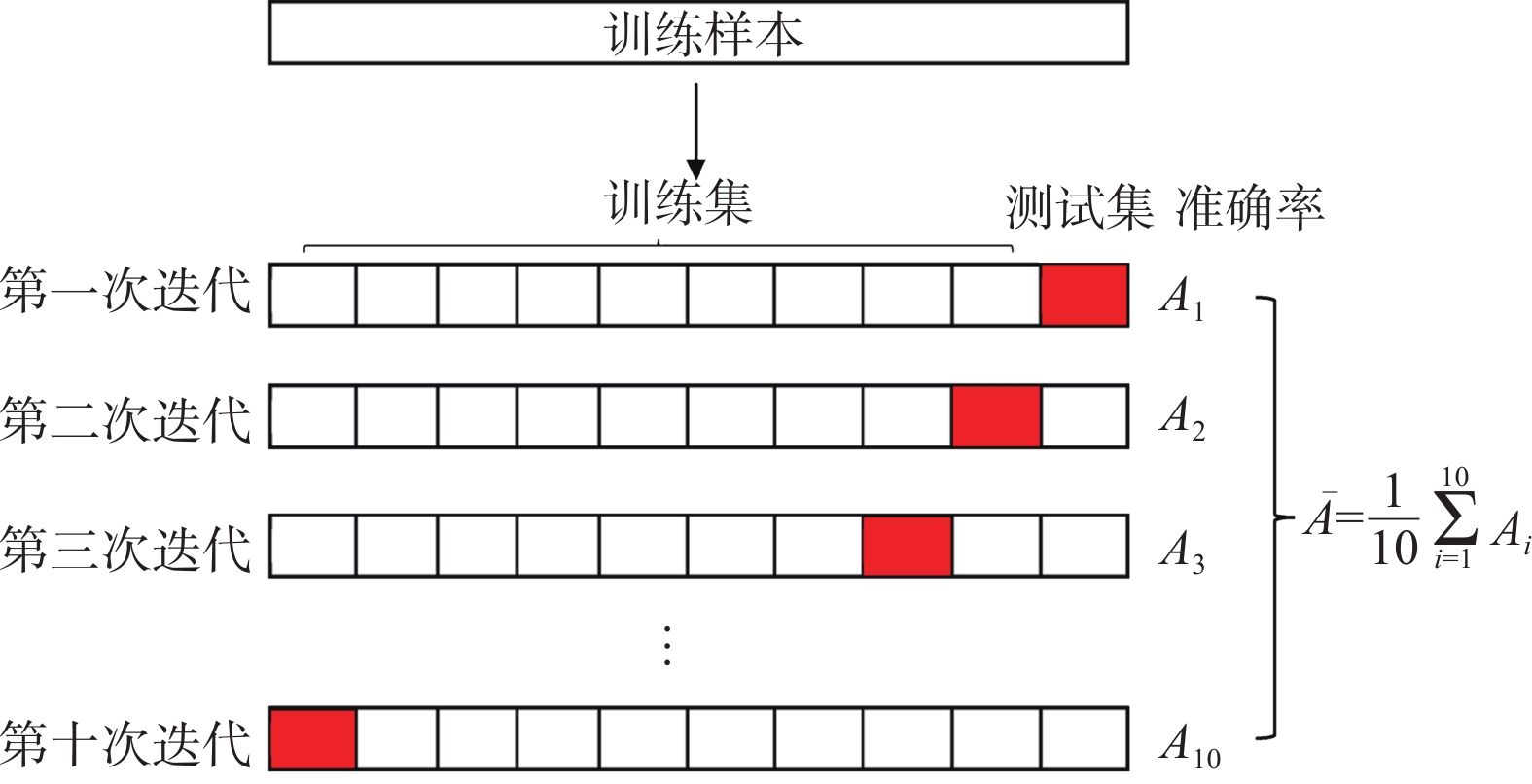
岩爆是地下工程开挖过程中硬质岩体存储的弹性应变能突然、迅速释放的动态过程。我国西南山区正在建设或拟建大量深埋长大隧道,勘察阶段岩爆的准确预测对有效设计和控制投资十分重要。从隧道工程勘察阶段线路比选与设计需求出发,针对隧道勘查期岩爆灾害预测指标获取难、预测精度低的问题,以该阶段岩爆预测指标的易获取性为前提,利用贝叶斯网络解决不确定性问题的有效性来反映岩爆烈度与各影响因素的相关关系。基于473组岩爆灾害案例,采用4个预测指标(地应力、地质构造、围岩级别和岩石强度)来构建岩爆烈度朴素贝叶斯概率分级预测模型,利用十折交叉验证方法确定模型预测精度达84.47%。将该模型应用于雅安—叶城高速公路跑马山1号隧道岩爆段落,预测结果显示:28次岩爆预测中有24次正确、4次错误,准确率高达85.71%;其中2组错误预测中,现场判别为轻微-中等岩爆,而本文模型预测为轻微岩爆。验证结果表明所建立的贝叶斯网络模型具有良好的预测性能,研究成果可为我国西南山区深埋长大硬岩隧道勘察设计期岩爆灾害预测提供技术支撑。
Abstract:Rockburst is a dynamic process of a sudden and rapid release of elastic strain energy stored in hard rock mass during underground excavation. The occurrence of rockburst disaster during tunnel construction will cause serious consequences such as casualties, equipment damage and construction delay. With a large number of deep-buried long tunnels to be constructed in southwestern mountainous areas of China, the prediction of rockburst disaster is of great importance. In this paper, to fulfil the requirement of tunnel alignment and design during engineering investigation stage, on the premise of the availability of rockburst prediction indexes in this stage, the Bayesian network is used to reflect the relationship between rockburst intensity and various influencing factors. Based on 473 groups of rockburst cases, the naive Bayesian probability classification model is constructed to predict the rockburst intensity by using four prediction indexes—geo-stress, geological structure, surrounding rock grade and surrounding rock strength. The prediction accuracy of the model is found to be 84.47% using the 10-fold cross validation method. At the same time, this model is applied to the rockburst section of Paomashan No. 1 Tunnel of Ya’an—Yecheng Expressway. The results show that the prediction accuracy is 85.71% in the 28 tunnel section applications, and the established Bayesian network model has a good prediction performance. The proposed method can provide a good support to the rockburst prediction during the investigation of deep-buried long tunnels located in Southwest China.
-

-
表 1 岩爆案例数据来源统计及岩爆烈度的分布
Table 1. Statistics of rockburst cases and the distribution of rockburst intensity
隧道名称 岩爆案例/个 锦屏二级水电站勘探平洞 97 锦屏二级水电站A辅助洞 109 二郎山隧道C2标左线 71 二郎山隧道C2标右线 42 秦岭隧道Ⅱ线进口 52 福堂隧道A6标左洞 67 福堂隧道A6标右洞 29 西康铁路秦岭隧道 13 郭仓山隧道 5 通渝隧道 2 大相岭隧道 11 表 2 预测变量间相关系数
Table 2. Correlation coefficients of prediction factors
岩石强度 围岩级别 地应力 地质构造 岩石强度 1 −0.37 0.24 −0.22 围岩级别 −0.37 1 −0.30 0.25 地应力 0.24 −0.30 1 −0.38 地质构造 −0.22 0.25 −0.38 1 表 3 预测指标节点离散化取值
Table 3. Threshold values for prediction factor discretization
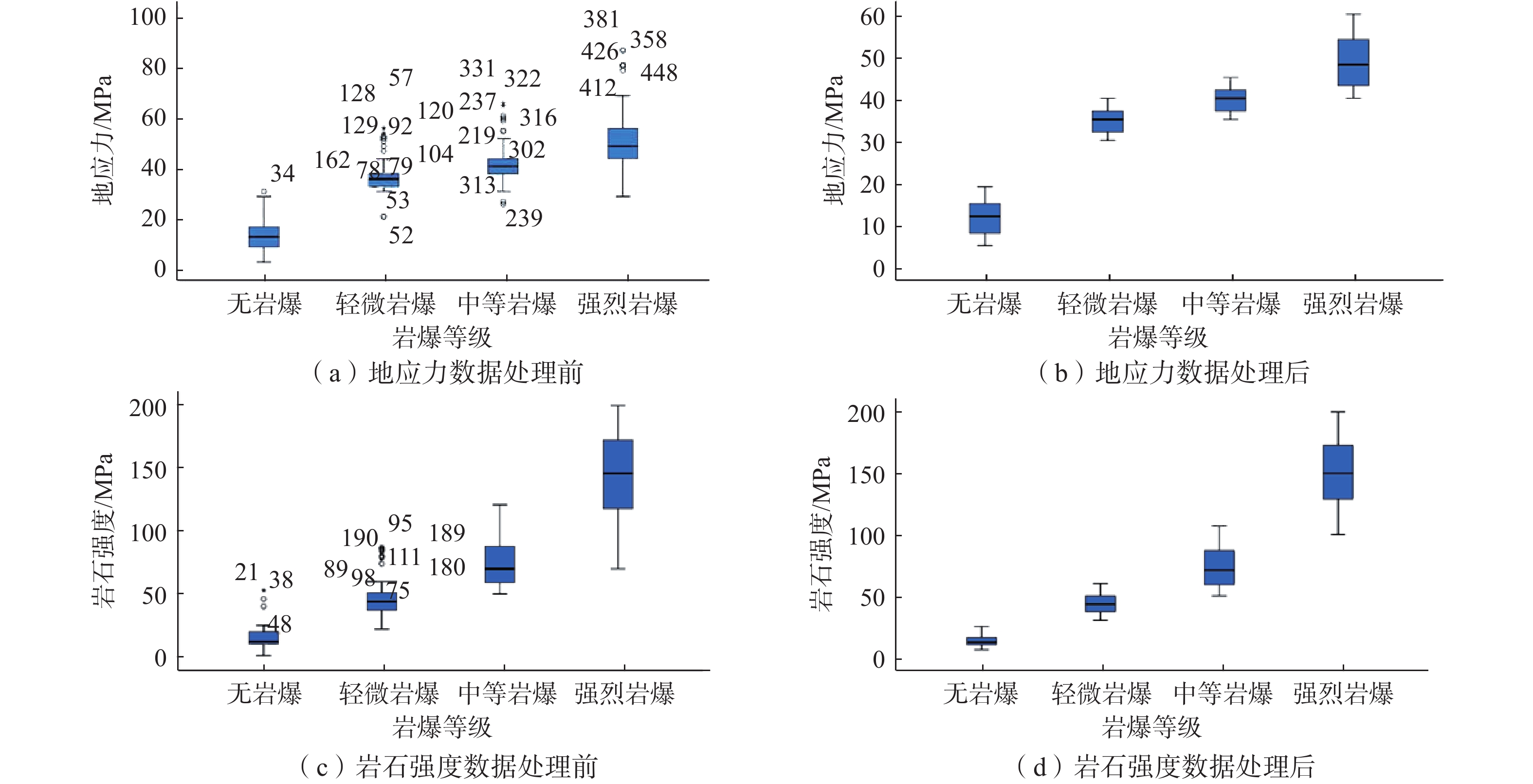
指标 岩爆烈度 围岩级别 地应力/MPa 地质构造 岩石强度/MPa 描述 无岩爆【0】(51) Ⅰ【1】(49) σ≥40(166) 无地质构造【1】(46) 坚硬岩Rc≥60 (358) 轻微岩爆【1】(167) Ⅱ【2】(212) 40>σ≥30(129) 褶皱核部【2】(57) 较坚硬岩60>Rc≥30 (14) 中等岩爆【2】(139) Ⅲ【3】(174) 30>σ≥20(97) 断层附近【3】(67) 较软岩30>Rc≥15(20) 强烈岩爆【3】(116) Ⅳ【4】(23) σ<20 (31) 褶皱两翼及断层破碎带【4】(79) 软岩Rc<15(31) Ⅴ【5】(15) 注:方括号内数字为赋值情况;圆括号内数据为区间样本数。 表 4 模型十折交叉验证的准确率和混淆矩阵
Table 4. Accuracy and confusion matrix of the model for 10-fold cross-validation
验证组 准确率 混淆矩阵 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 1 77.08% 5 0 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度0 17 0 0 轻微岩爆 0 7 5 2 中等岩爆 0 0 2 10 强烈岩爆 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 2 85.42% 5 0 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度0 13 3 1 轻微岩爆 0 0 11 3 中等岩爆 0 0 0 12 强烈岩爆 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 3 94.44% 5 0 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度0 16 1 0 轻微岩爆 0 3 11 1 中等岩爆 0 0 0 12 强烈岩爆 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 4 93.75% 5 0 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度0 16 1 0 轻微岩爆 0 2 12 0 中等岩爆 0 0 0 12 强烈岩爆 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 5 87.5% 5 1 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度0 15 2 0 轻微岩爆 0 1 10 3 中等岩爆 0 0 0 12 强烈岩爆 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 6 79.17% 5 0 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度0 17 0 0 轻微岩爆 0 7 4 3 中等岩爆 0 0 0 12 强烈岩爆 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 7 81.25% 5 0 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度0 14 3 0 轻微岩爆 1 5 8 1 中等岩爆 0 0 0 12 强烈岩爆 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 8 95.83% 5 0 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度0 16 1 0 轻微岩爆 0 1 13 2 中等岩爆 0 0 0 12 强烈岩爆 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 9 77.08% 5 0 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度0 14 3 0 轻微岩爆 0 4 7 3 中等岩爆 0 0 1 11 强烈岩爆 预测烈度 无岩爆 轻微岩爆 中等岩爆 强烈岩爆 No. 10 73.17% 6 0 0 0 无岩爆 实
际
烈
度2 12 0 0 轻微岩爆 0 3 6 4 中等岩爆 0 0 2 6 强烈岩爆 表 5 跑马山1号隧道岩爆基础信息与烈度预测结果
Table 5. Basic information of rockburst and the predicted results of Paomashan No.1 tunnel
序号 桩号 围岩级别 岩石强度 地应力/MPa 地质构造 预测结果(概率) 实际情况 1 ZK1+775 Ⅲ 较坚硬 25.7126 无 轻微岩爆(68.7%) 轻微岩爆 2 ZK1+790 Ⅲ 较坚硬 25.8002 无 轻微岩爆(68.7%) 轻微岩爆 3 ZK1+792 Ⅲ 较坚硬 25.8294 无 轻微岩爆(68.7%) 轻微岩爆 4 ZK2+401 Ⅲ 较坚硬 29.5962 无 轻微岩爆(68.7%) 轻微岩爆 5 ZK2+404—ZK2+407 Ⅲ 较坚硬 29.6254 无 轻微岩爆(68.7%) 轻微岩爆 6 ZK2+394 Ⅲ 较坚硬 29.5962 无 轻微岩爆(68.7%) 中等岩爆 7 ZK2+396 Ⅲ 较坚硬 29.5962 无 轻微岩爆(68.7%) 轻微-中等岩爆 8 ZK2+398—ZK2+400.5 Ⅲ 较坚硬 29.5962 无 轻微岩爆(68.7%) 轻微岩爆 9 ZK2+403—ZK2+408 Ⅲ 坚硬 29.5816 无 中等岩爆(91.8%) 中等岩爆 10 ZK2+465 Ⅲ 坚硬 29.4794 无 中等岩爆(91.8%) 中等岩爆 11 ZK2+475 Ⅲ 坚硬 29.5378 无 中等岩爆(91.8%) 轻微岩爆 12 ZK2+483—ZK2+485 Ⅲ 坚硬 29.3626 无 中等岩爆(91.8%) 中等岩爆 13 ZK2+490—ZK2+492 Ⅲ 坚硬 29.4502 无 中等岩爆(91.8%) 中等岩爆 14 ZK2+789.4 Ⅲ 较坚硬 32.049 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 15 ZK2+800 Ⅲ 较坚硬 31.976 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 16 ZK2+801.4 Ⅲ 较坚硬 31.976 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 17 ZK2+807.4 Ⅲ 较坚硬 31.9614 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微-中等岩爆 18 ZK2+810.4 Ⅲ 较坚硬 31.903 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 19 K1+949.2—K1+953.2 Ⅳ 较软岩 27.3186 无 无岩爆(100%) 无岩爆 20 K1+962.2—K1+966.2 Ⅳ 较软岩 27.377 无 无岩爆(100%) 无岩爆 21 K1+966.2—K1+969.2 Ⅳ 较软岩 27.377 无 无岩爆(100%) 无岩爆 22 K2+580 Ⅲ 较坚硬 31.2022 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 23 K2+905.5 Ⅲ 较坚硬 30.589 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 24 K2+911.5—K2+914.5 Ⅲ 较坚硬 30.735 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 25 K2+920.5 Ⅲ 较坚硬 30.881 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 26 K2+926.5 Ⅲ 较坚硬 31.027 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 27 K2+934.9 Ⅲ 较坚硬 31.173 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 28 K2+946.9 Ⅲ 较坚硬 31.3482 无 轻微岩爆(83.4%) 轻微岩爆 -
[1] 贾金晓. 米仓山隧道岩爆综合集成预测及处治措施研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016
JIA Jinxiao. Study of meta-synthesis prediction methods and treatment measures on rock burst in the Micangshan tunnel[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] ZHOU J,LI X B,SHI X Z. Long-term prediction model of rockburst in underground openings using heuristic algorithms and support vector machines[J]. Safety Science,2012,50(4):629 − 644. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2011.08.065
[3] 陈仕阔,李涵睿,周航,等. 基于岩爆危险性评价的川藏铁路某深埋硬岩隧道线路方案比选研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):81 − 90. [CHEN Shikuo,LI Hanrui,ZHOU Hang,et al. Route selection of deep-lying and hard rock tunnel in the Sichuan-Xizang Railway based on rock burst risk assessment[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):81 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202103099
[4] 唐杰灵,李天斌,曾鹏,等. 岩爆柔性防护网及其动力特性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(4):793 − 802. [TANG Jieling,LI Tianbin,ZENG Peng,et al. Study on rockburst flexible protective net and its dynamic characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(4):793 − 802. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] RUSSENES B F. Analysis of rock spalling for tunnels in steep valley sides(in Norwegian) [R]. Trondheim: Norwegian Institute of Technology, 1974.
[6] KIDYBIŃSKI A. Bursting liability indices of coal[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1981,18(4):295 − 304.
[7] 张镜剑,傅冰骏. 岩爆及其判据和防治[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(10):2034 − 2042. [ZHANG Jingjian,FU Bingjun. Rockburst and its criteria and control[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(10):2034 − 2042. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.10.010
[8] 徐林生,王兰生,李天斌,等. 二郎山公路隧道岩爆特征与预测研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,1999,10(2):55 − 59. [XU Linsheng,WANG Lansheng,LI Tianbin,et al. Study on the character of rockburst and its forecasting in the Erlang mountain tunnel[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,1999,10(2):55 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.1999.02.010
[9] 冯夏庭. 地下峒室岩爆预报的自适应模式识别方法[J]. 东北大学学报,1994,15(5):471 − 475. [FENG Xiating. Adaptive pattern recognition to predict rockbursts in underground openings[J]. Journal of Northeastern University,1994,15(5):471 − 475. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 冯夏庭,赵洪波. 岩爆预测的支持向量机[J]. 东北大学学报,2002,23(1):57 − 59. [FENG Xiating,ZHAO Hongbo. Prediction of rockburst using support vector machine[J]. Journal of Northeastern University,2002,23(1):57 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李天斌,肖学沛. 地下工程岩爆预测的综合集成方法[J]. 地球科学进展,2008,23(5):533 − 540. [LI Tianbin,XIAO Xuepei. Comprehensively integrated methods of rockburst prediction in underground engineering[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2008,23(5):533 − 540. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.05.014
[12] 何怡帆,李天斌,曹海洋. 隧道施工期岩爆危险性评价的属性识别模型及工程应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):102 − 111. [HE Yifan,LI Tianbin,CAO Haiyang. Attribute recognition model of fatalness assessment of rockburst in tunnel construction and its application[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘磊磊,张绍和,王晓密. 基于物元矩阵和理想点法的岩爆烈度预测[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2016,12(1):205 − 212. [LIU Leilei,ZHANG Shaohe,WANG Xiaomi. Prediction of rockburst intensity based on matter-element matrix and ideal point method[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2016,12(1):205 − 212. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 徐琛,刘晓丽,王恩志,等. 基于组合权重–理想点法的应变型岩爆五因素预测分级[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(12):2245 − 2252. [XU Chen,LIU Xiaoli,WANG Enzhi,et al. Prediction and classification of strain mode rockburst based on five-factor criterion and combined weight-ideal point method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(12):2245 − 2252. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201712013
[15] 董源,裴向军,张引,等. 基于组合赋权-云模型理论的岩爆预测研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2018,14(增刊1):409 − 415. [DONG Yuan,PEI Xiangjun,ZHANG Yin,et al. Prediction of rock burst-based on combination weighting and cloud model theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2018,14(Sup1):409 − 415. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王迎超,靖洪文,张强,等. 基于正态云模型的深埋地下工程岩爆烈度分级预测研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(4):1189 − 1194. [WANG Yingchao,JING Hongwen,ZHANG Qiang,et al. A normal cloud model-based study of grading prediction of rockburst intensity in deep underground engineering[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(4):1189 − 1194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] LI N,JIMENEZ R. A logistic regression classifier for long-term probabilistic prediction of rock burst hazard[J]. Natural Hazards,2018,90(1):197 − 215. doi: 10.1007/s11069-017-3044-7
[18] PU Y Y,APEL D B,XU H W. Rockburst prediction in kimberlite with unsupervised learning method and support vector classifier[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2019,90:12 − 18. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2019.04.019
[19] LI T Z,LI Y X,YANG X L. Rock burst prediction based on genetic algorithms and extreme learning machine[J]. Journal of Central South University,2017,24(9):2105 − 2113. doi: 10.1007/s11771-017-3619-1
[20] 付平,张新辉,刘元坤,等. 滇中香炉山引水隧洞工程区地应力场特征及断裂影响模糊综合评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):123 − 132. [FU Ping,ZHANG Xinhui,LIU Yuankun,et al. Characteristics of in-situ stress field and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of the influence of active faults on the water diversion engineering of Xianglushan tunnel area in central Yunnan[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):123 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 徐林生,王兰生. 岩爆形成机理研究[J]. 重庆大学学报(自然科学版),2001,24(2):115 − 117. [XU Linsheng,WANG Lansheng. Study on the mechanism of rockburst[J]. Journal of Chongqing University (Natural Science Edition),2001,24(2):115 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 邢军,王建斌,蒋蕾,等. 圭嘎拉高速公路隧道地应力特征及岩爆预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(2):170 − 178. [XING Jun,WANG Jianbin,JIANG Lei,et al. In-situ stress characteristics and rock burst prediction of the Guigala Expressway tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(2):170 − 178. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 彭华,崔巍,马秀敏,等. 南水北调西线第一期工程调水区水压致裂地应力测量及其工程意义[J]. 地质力学学报,2006,12(2):182 − 190. [PENG Hua,CUI Wei,MA Xiumin,et al. Hydrofracturing in-situ stress measurements of the water diversion area in the first stage of the South-North Water Diversion Project(western line)[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2006,12(2):182 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 徐俊帅,徐金明,涂齐亮. 基于地应力和岩体强度的岩爆预判[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):52 − 58. [XU Junshuai,XU Jinming,TU Qiliang. Prediction of rock burst based on field geostress and rock mass strength[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):52 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2018.05.09
[25] 张鹏,孙治国,王秋宁,等. 木寨岭深埋隧道北段地应力测量与围岩稳定性分析[J]. 地质力学学报,2017,23(6):893 − 903. [ZHANG Peng,SUN Zhiguo,WANG Qiuning,et al. In-situ stress measurement and stability analysis of surrounding rocks in the north section of deep buried tunnel in Muzhailing[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2017,23(6):893 − 903. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 杨树新,姚瑞,崔效锋,等. 中国大陆与各活动地块、南北地震带实测应力特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报,2012,55(12):4207 − 4217. [YANG Shuxin,YAO Rui,CUI Xiaofeng,et al. Analysis of the characteristics of measured stress in Chinese mainland and its active blocks and North-South seismic belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2012,55(12):4207 − 4217. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.032
[27] 李天斌, 孟陆波, 王兰生. 高地应力隧道稳定性及岩爆、大变形灾害防治[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016
LI Tianbin, MENG Lubo, WANG Lansheng. Stability of high-stress tunnels and prevention of large-scale rockburst disasters [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. (in Chinese)
[28] JENSEN F V, NIELSEN T D. Bayesian networks and decision graphs[M]. New York: Springer, 2007.
[29] PEARL J. A constraint propagation approach to probabilistic reasoning[J]. arXiv preprint: 1304.3422, 2013.
[30] FENG X D,JIMENEZ R. Predicting tunnel squeezing with incomplete data using bayesian networks[J]. Engineering Geology,2015,195:214 − 224. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.06.017
[31] KORB K B, NICHOLSON A E. Bayesian artificial intelligence [M]. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2010.
-




 下载:
下载: