Types of water film on the surface of loess and related mineral particles and their quantitative characterization
-
摘要:
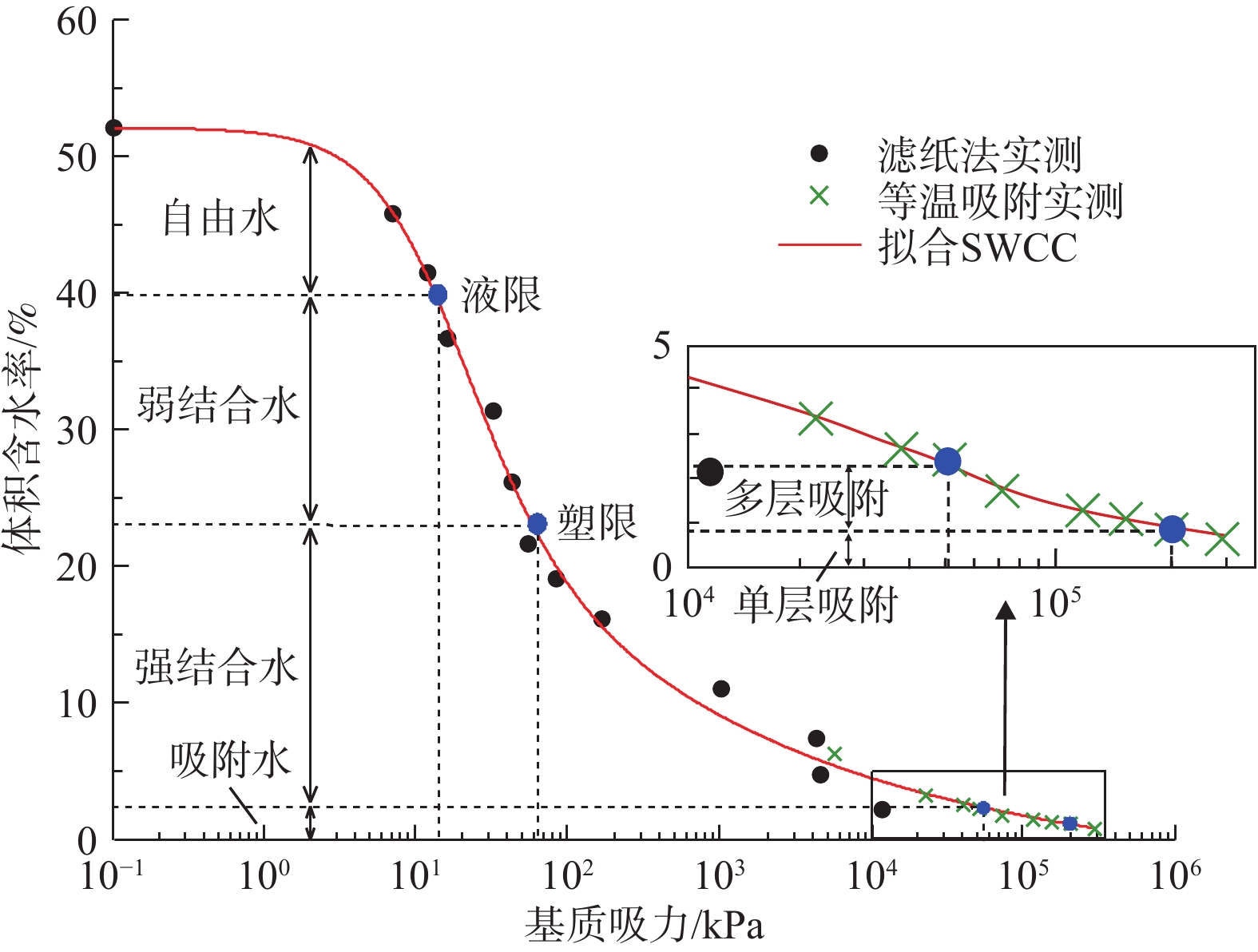
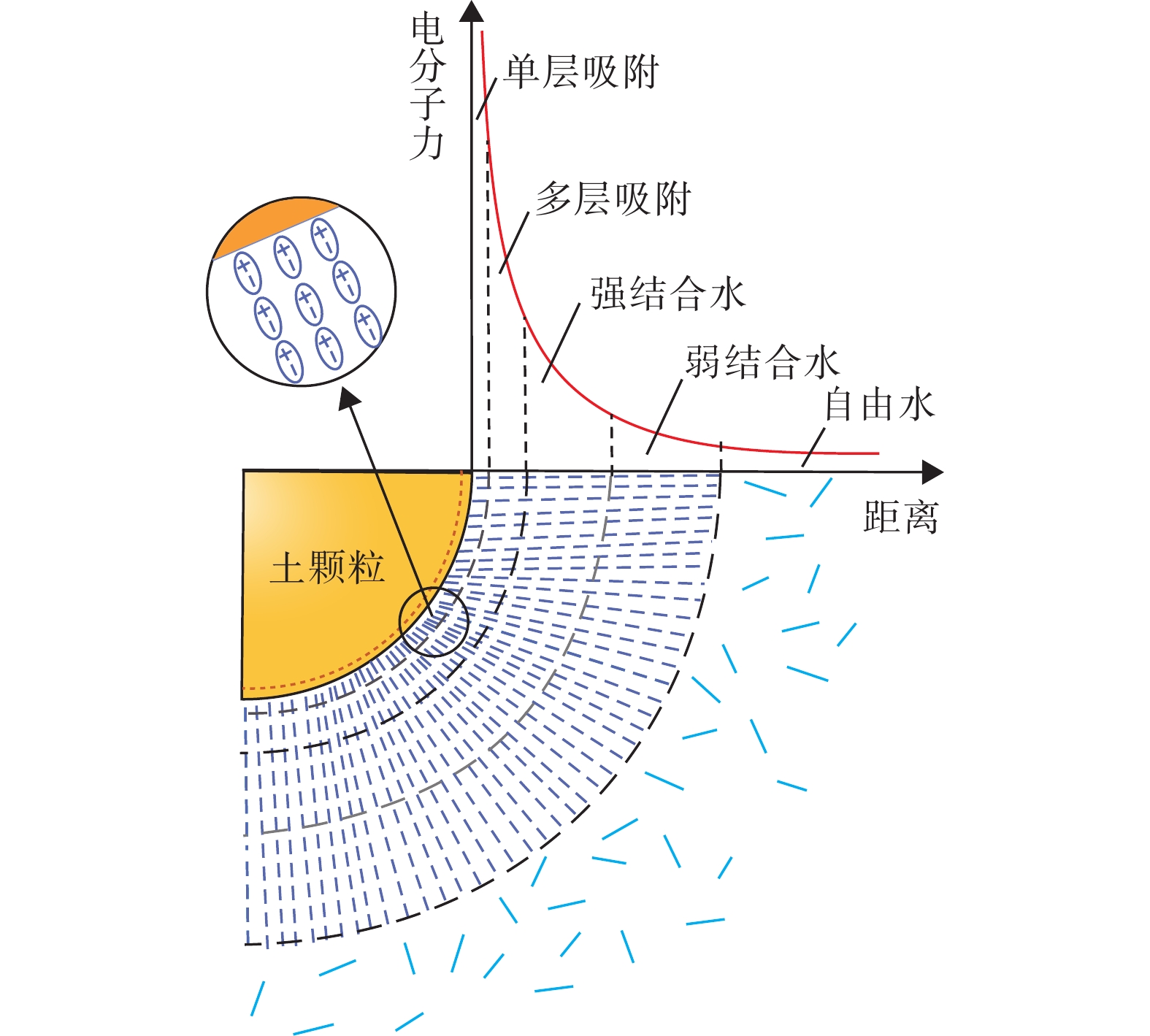
黏性土中细粒表面水膜是影响其物理力学性质的内在因素。经典土力学一般将土粒表面水膜分为强结合水和弱结合水,即所谓双电层模型,弱结合水的存在是土具有可塑性的原因,强弱结合水的界限含水率为塑限,该模型很好地解释了黏性土的稠度变化及其有关的物理力学行为。然而,通过等温吸附试验发现,土粒表面还存在吸附水膜,对非饱和土高吸力段的物理力学特性有重要影响。为此,本文将黄土颗粒表面水膜分为单层吸附水、多层吸附水、强结合水、弱结合水和自由水5种类型。取甘肃正宁Q2最顶层的L2黄土试样,采用等温吸附和液限、塑限测试,对该黄土样和其中的单矿物颗粒各水膜之间的界限含水率进行了定量表征,并测试黄土试样的土水特征曲线(SWCC),在SWCC上界定了这些界限含水率与基质吸力的关系。当水汽压很低时,土粒表面的吸力来自水的偶极分子与颗粒表面离子间的静电引力,形成单层吸附水,水膜厚度为1个水分子直径;离颗粒表面超出水分子直径的地方,吸力来自范德华力,水的偶极子相互靠拢呈定向排列,形成了多层吸附水;当土粒周围水分增加,颗粒表面未平衡掉的分子引力又可吸引更多的极化水分子,此时在吸附水的周围形成结合水,结合水又分为强结合水和弱结合水;吸附水和结合水膜以外的水为自由水。
-
关键词:
- 黄土 /
- 矿物颗粒 /
- 水膜类型 /
- 界限含水率 /
- 土水特征曲线(SWCC)
Abstract:The surface water film of fine particles in cohesive soil is an internal factor that affects the physical and mechanical properties of the soil. In the classical soil mechanics, the water film on the surface of soil particles is generally divided into two layers: strong bound water and weak bound water, i. e., the so-called electric double layer model. The existence of weak bound water is the reason for the plasticity of soil, thus, the plastic limit is the boundary moisture content of strong bound water and weak bound water. The model perfectly explains the consistency change and related physical and mechanical behavior of cohesive soil. However, through the isothermal adsorption test, it is found that there is an adsorbed water film on the surface of the soil particles, which has an important impact on the physical and mechanical properties of the unsaturated soil in the high suction section. Therefore, this paper divides the water film on the surface of soil into five types: monolayer adsorbed water, multi-layer adsorbed water, strong bound water, weak bound water and free water. The L2 loess specimen was taken from the topmost layer of Q2 in Zhengning of Gansu Province and are used to conduct isothermal adsorption test, liquid limit test and plastic limit test, respectively, to achieve the internal minerals that make up the loess and quantitative characterization of the types of water film on the particle surface.The soil-water characteristic curves (SWCC) of the loess specimen are tested. Combined with the above test results, the relationship between these boundary moisture contents and the matrix suction is defined on the SWCC. When the water vapor pressure is very low, the suction on the surface of the soil particles comes from the electrostatic attraction between the dipole molecules of water and the ions on the surface of the particles, forming a single layer of the adsorbed water, and the thickness of the water film is one water molecule diameter. In the place beyond the water molecular diameter from the particle surface, the suction comes from the van der Waals force, and the dipoles of water are oriented toward each other, forming multi-layer adsorbed water. When the moisture around the soil particles increases, the unbalanced molecular attraction on the surface of the particles can attract more polarized water molecules, the bound water is formed around the adsorbed water, which is divided into strong bound water and weak bound water. The water outside the adsorbed water and the bound water film is free water.
-

-
图 1 土颗粒周围的水膜类型(改自张一敏[11])
Figure 1.
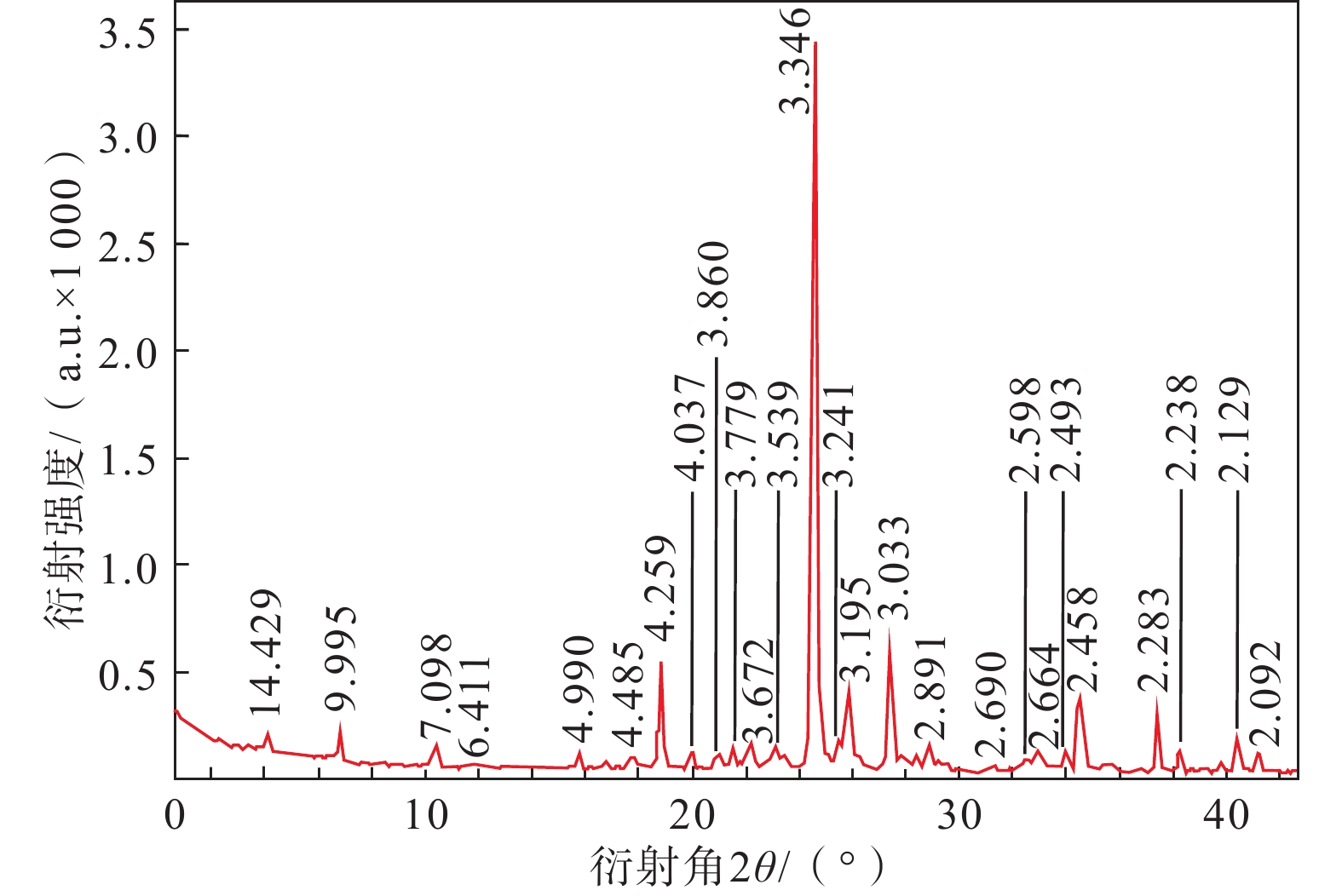
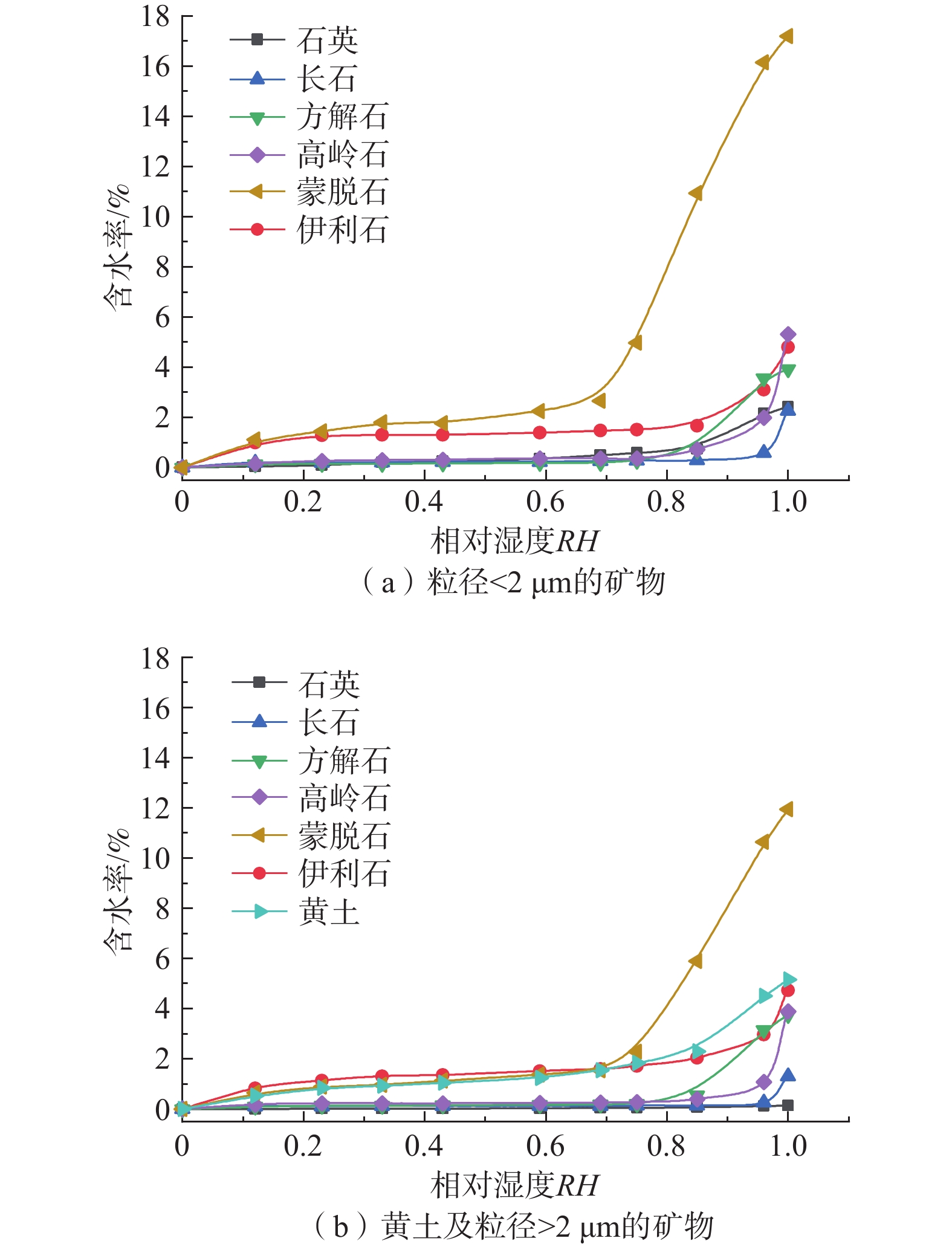
表 1 黄土及各矿物试样X-射线衍射分析结果
Table 1. Results of X-ray diffraction analysis of loess and minerals
样品
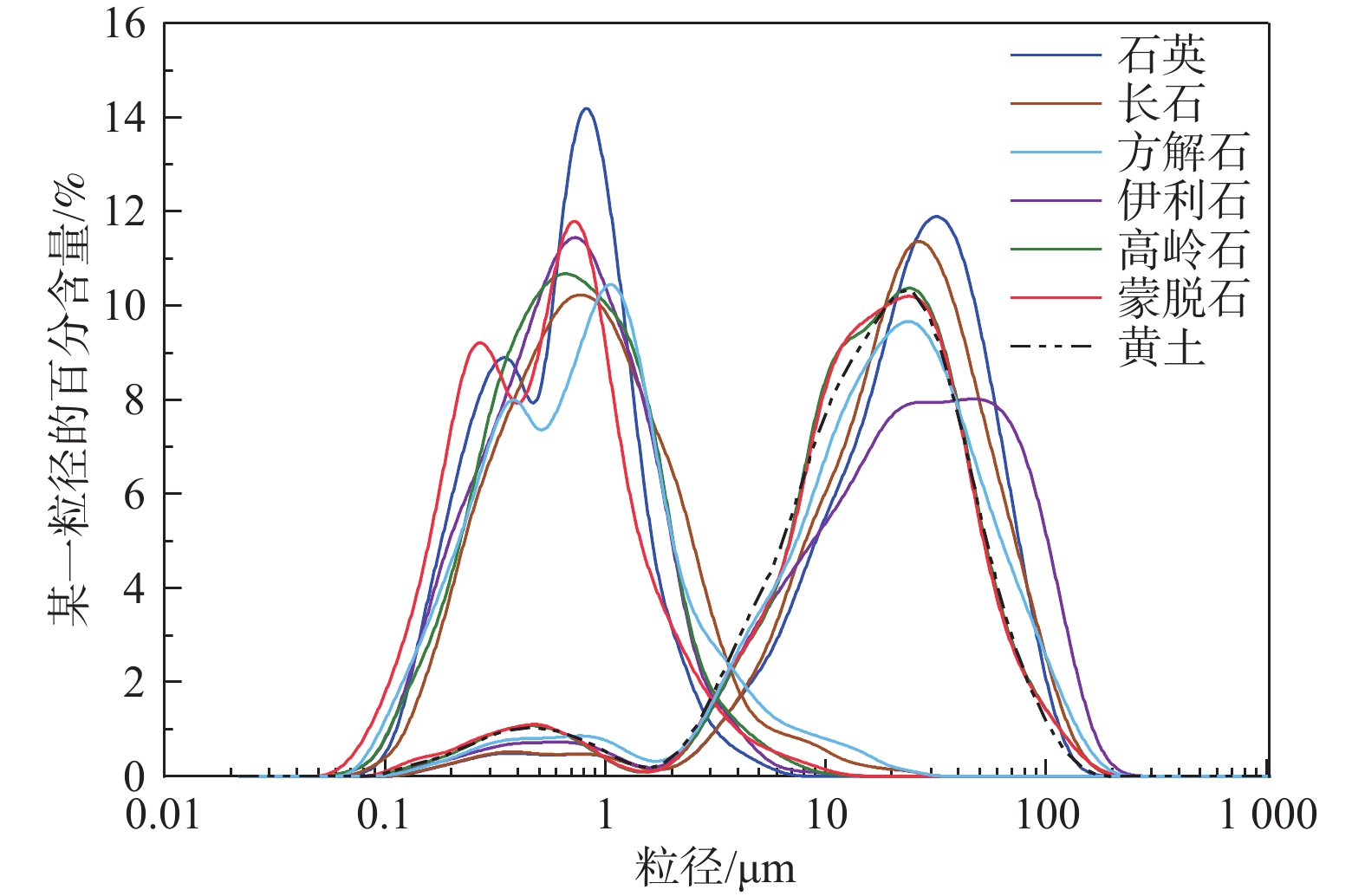
名称矿物含量/% 石英 长石 方解石 白云石 蒙脱石 伊利石 高岭石 绿泥石 黄土 48.1 13.0 15.4 3.2 7.8 7.1 2.9 2.5 石英 93.2 / 3.0 / / 3.8 / / 长石 / 96.8 / / 3.2 / / 方解石 0.3 / 99.7 / / / / / 蒙脱石 9.2 / / / 90.8 / / / 伊利石 5.1 2.5 / / / 92.4 / 高岭石 / 6.2 / / 2.3 91.5 / 表 2 不同过饱和溶液对应的相对湿度值
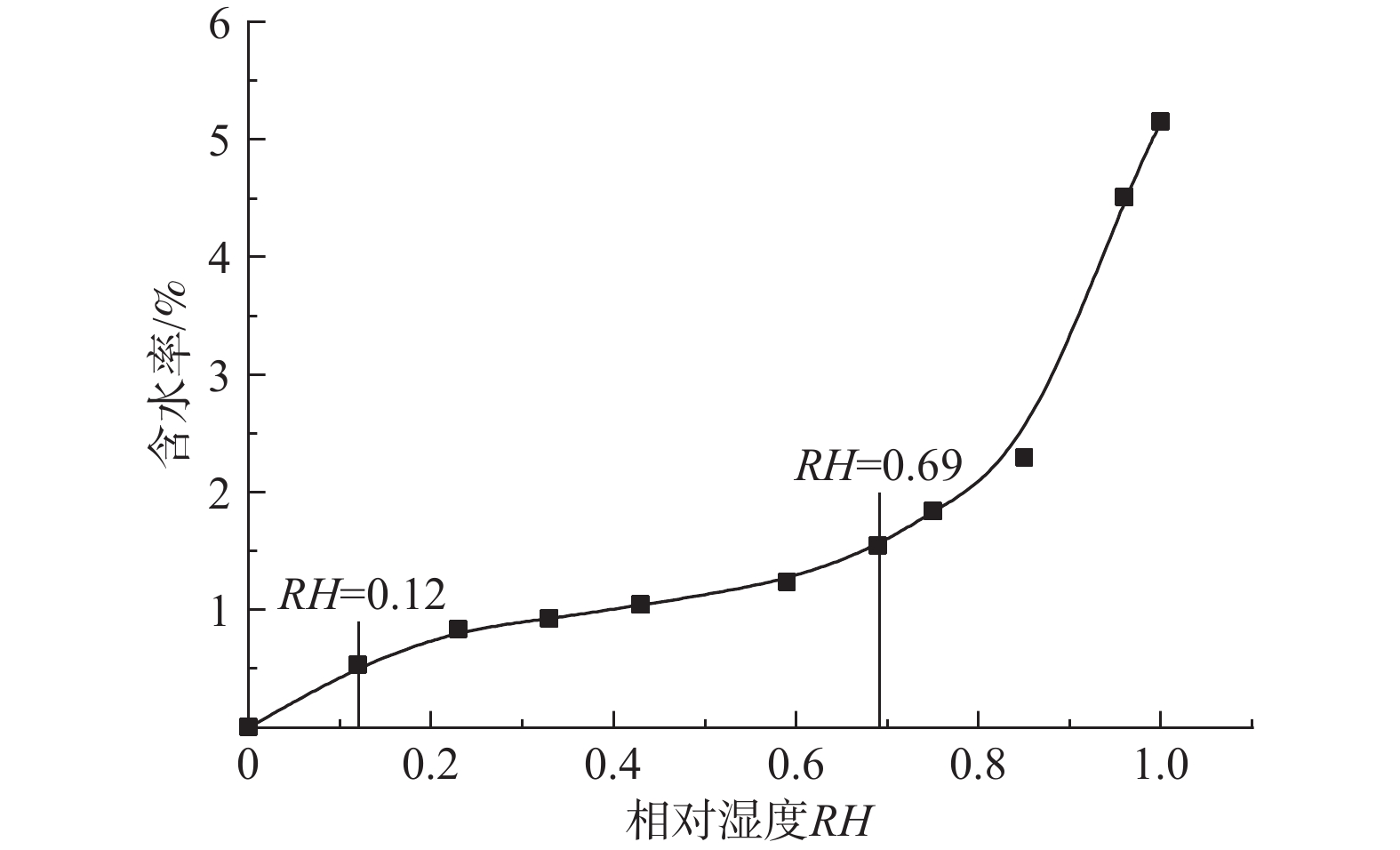
Table 2. Relative humidity of different supersaturated solutions
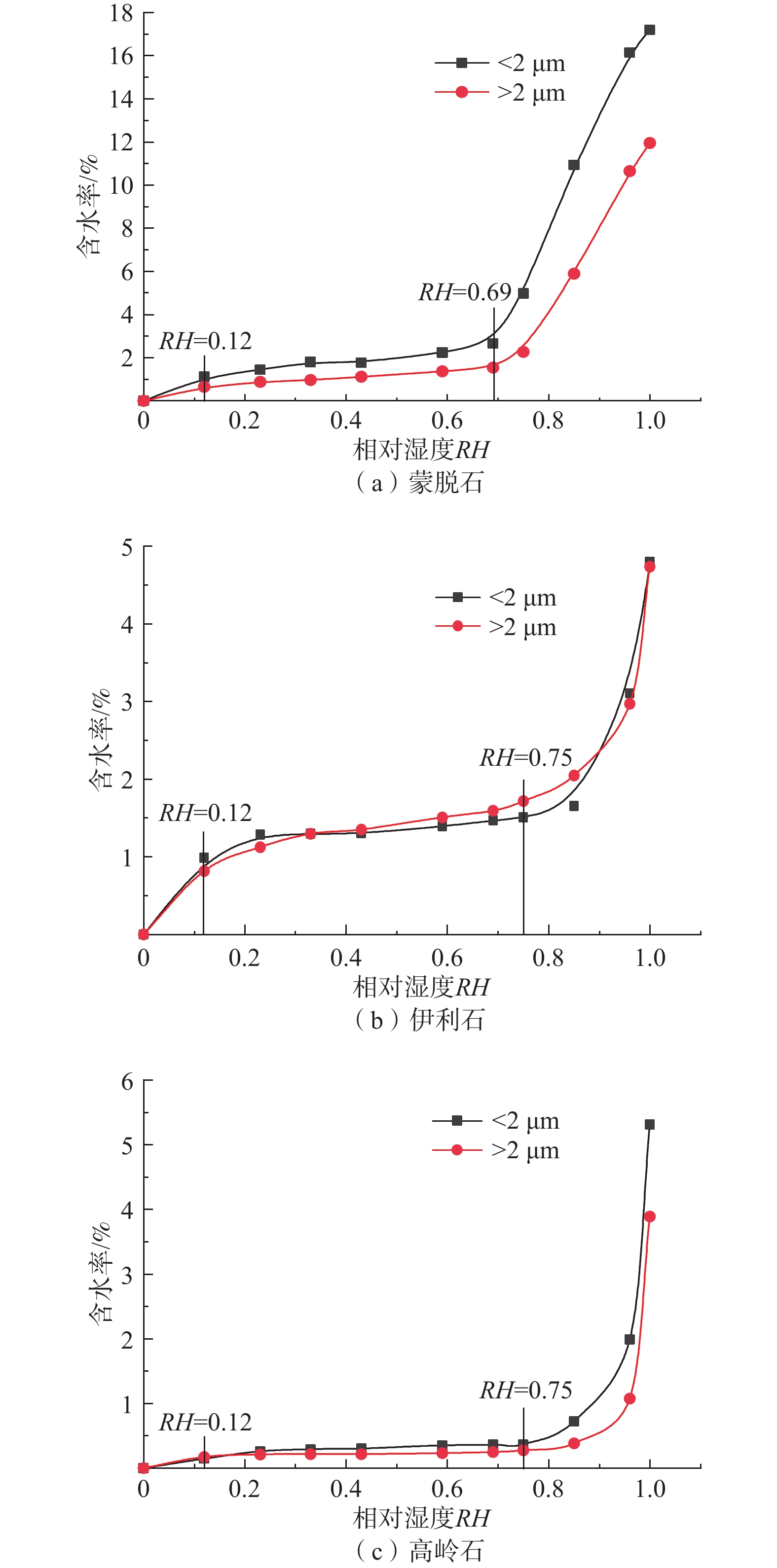
溶液 RH 溶液 RH LiCl 0.12 KI 0.69 CH3COOK 0.23 NaCl 0.75 MgCl2 0.33 KCl 0.85 K2CO3 0.43 K2SO4 0.96 NaBr 0.59 H2O 1.00 表 3 黄土试样及其黏土矿物的液限、塑限测定结果
Table 3. Liquid limit and plastic limit of the loess specimen and clay minerals
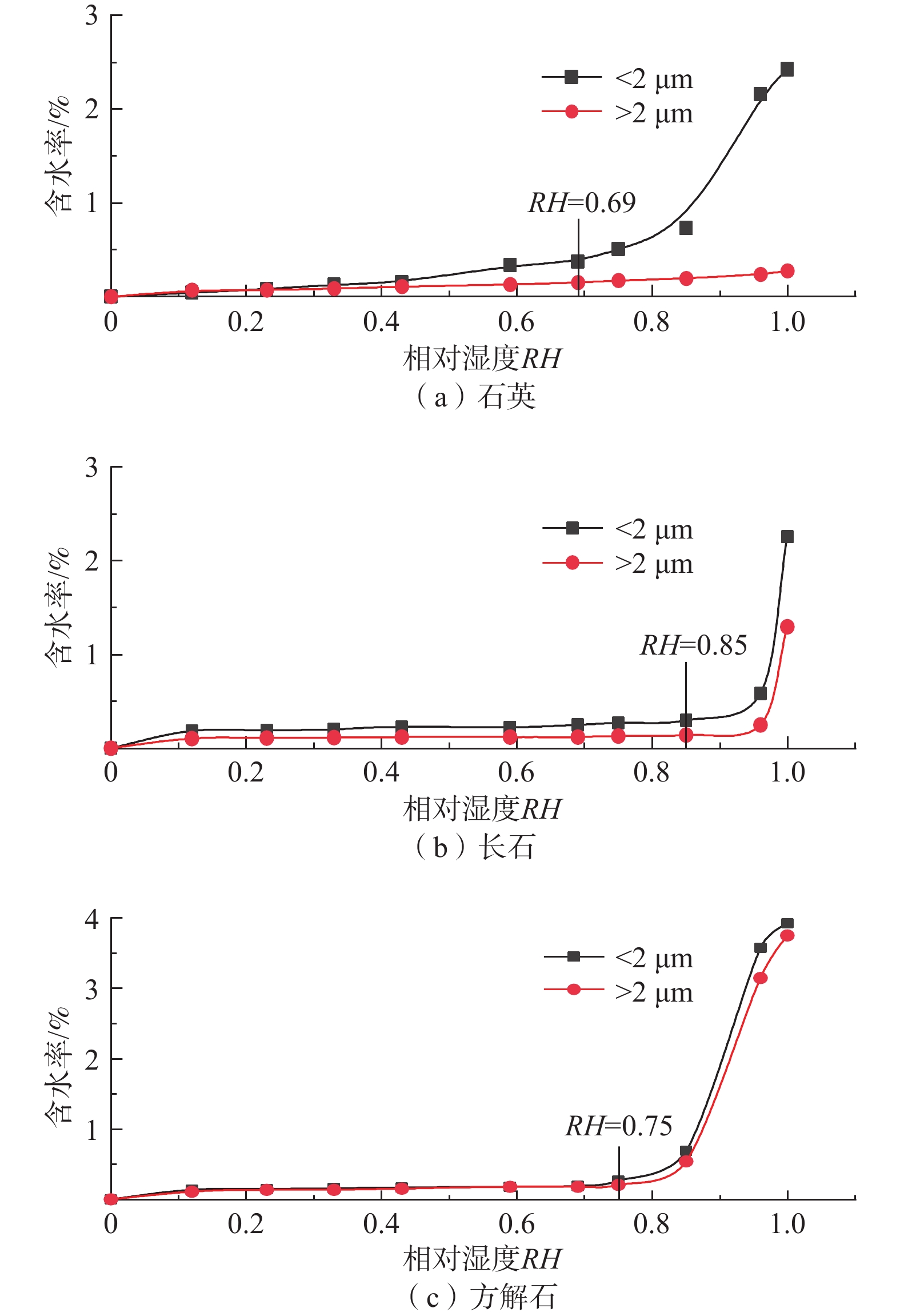
样品名称 塑限wP/% 液限wL/% 黄土 16.3 28.2 蒙脱石 25.8 80.1 伊利石 9.6 62.5 高岭石 6.6 39.3 表 4 各水膜类型的界限含水率
Table 4. Boundary water contents of the water film
试样名称 ws/% wm/% wP /% wL/% 黄土 0.53 1.55 16.3 28.2 石英 >2 μm 0.05 − − − <2 μm 0.49 − − − 长石 >2 μm 0.14 − − − <2 μm 0.30 − − − 方解石 >2 μm 0.21 − − − <2 μm 0.26 − − − 蒙脱石 >2 μm 0.65 1.54 25.8 80.1 <2 μm 1.11 2.66 伊利石 >2 μm 0.81 1.71 9.6 62.5 <2 μm 0.99 1.47 高岭石 >2 μm 0.17 0.28 6.6 39.3 <2 μm 0.26 0.37 表 5 单层吸附含水率的试验值和经验公式计算值
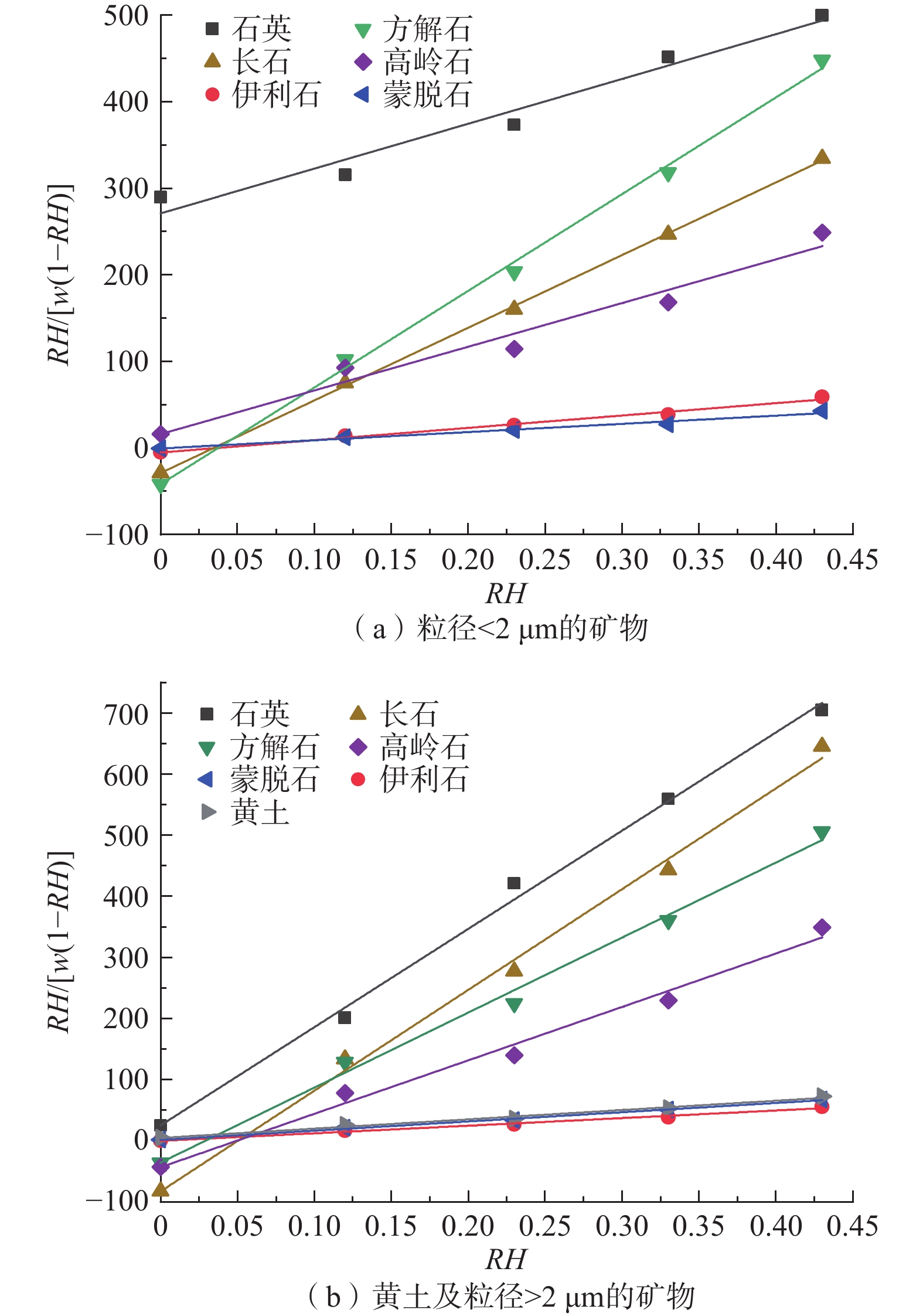
Table 5. Experimental results of the single-layer adsorption moisture content and empirical formula calculation results
试样名称 BET计算值
ws1/%试验值
ws2/%(ws1− ws2)/% 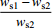 /%
/%黄土 0.638 0.531 0.107 20.2 石英 >2 μm 0.061 0.054 0.007 13.0 <2 μm 0.337 0.493 −0.156 −31.6 长石 >2 μm 0.098 0.143 −0.045 −31.5 <2 μm 0.223 0.296 −0.073 −24.7 方解石 >2 μm 0.164 0.206 −0.042 −20.4 <2 μm 0.193 0.264 −0.071 −26.9 蒙脱石 >2 μm 0.655 0.649 0.006 0.9 <2 μm 1.061 1.109 −0.048 −4.3 伊利石 >2 μm 0.805 0.813 −0.008 −1.0 <2 μm 0.728 0.988 −0.260 −26.3 高岭石 >2 μm 0.120 0.175 −0.055 −31.4 <2 μm 0.192 0.261 −0.069 −26.4 -
[1] 李强,李同录,乔志甜,等. 非饱和土粒间毛细作用的微观不连续变形分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(3):834 − 842. [LI Qiang,LI Tonglu,QIAO Zhitian,et al. Microscopic discontinuity deformation analysis of capillary in unsaturated soil[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(3):834 − 842. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-140
[2] 赵明华,刘小平,彭文祥. 水膜理论在非饱和土中吸力的应用研究[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(7):1323 − 1327. [ZHAO Minghua,LIU Xiaoping,PENG Wenxiang. Application of aqueous film theory to study of unsaturated soil’s suction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2007,28(7):1323 − 1327. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.07.007
[3] 李广信. 高等土力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004
LI Guangxin. Advanced Soil Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[4] LU N,ZHANG C. Soil sorptive potential:concept,theory,and verification[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2019,145(4):04019006. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002025
[5] 曾立峰, 邵龙潭, 牛庚, 等. 考虑孔隙水微观赋存形态的非饱和粉土有效应力方程及其验证[J/OL]. 水文地质工程地质, (2022-03-09)[2022-03-21]. https://kns.cnki.net/kns8/DefaultResult/Index?dbcode
ZENG Lifeng, SHAO Longtan, NIU Geng, et al. Effective Force Equation of Unsaturated Silt Soil Considering Microscopic Deposit Form of Pore Water and Its Verification[J/OL]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, (2022-03-09)[2022-03-21]. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 田慧会,韦昌富. 基于核磁共振技术的土体吸附水含量测试与分析[J]. 中国科学:技术科学,2014,44(3):295 − 305. [TIAN Huihui,WEI Changfu. A NMR-based testing and analysis of adsorbed water content[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica),2014,44(3):295 − 305. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 何攀,许强,刘佳良,等. 基于核磁共振与氮吸附技术的黄土含盐量对结合水膜厚度的影响研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):142 − 149. [HE Pan,XU Qiang,LIU Jialiang,et al. An experimental study of the influence of loess salinity on combined water film thickness based on NMR and nitrogen adsorption technique[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):142 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201910002
[8] BAKER R,FRYDMAN S. Unsaturated soil mechanics:critical review of physical foundations[J]. Engineering Geology,2009,106(1/2):26 − 39.
[9] 王铁行,李彦龙,苏立君. 黄土表面吸附结合水的类型和界限划分[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(5):942 − 948. [WANG Tiehang,LI Yanlong,SU Lijun. Types and boundaries of bound water on loess particle surface[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,36(5):942 − 948. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201405019
[10] 袁建滨. 粘土中结合水特性及其测试方法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012
YUAN Jianbin. The study for properties of bound water on clayey soils and their quantitative methods[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张一敏. 球团理论与工艺[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002
ZHANG Yimin. Pellet theory and technology[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002. (in Chinese)
[12] HABIBAGAHI K. Temperature effect and the concept of effective void ratio[J]. Indian Geotechnical Journal,1977,7(1):14 − 34.
[13] SKEMPTION A W,NORTHEY R D. The sensitivity of clays[J]. Géotechnique,1952,3(1):30 − 53.
[14] 李亚斌. 黄土及相关黏土矿物吸附结合水的定量研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018
LI Yabin. Quantitative study on the adsorption bound water of loess and related clay minerals[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 张乃娴. 粘土矿物研究方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990
ZHANG Naixian. Research methods of clay minerals[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1990. (in Chinese)
[16] 中华人民共和国水利部. 土工试验规程: SL 237—1999[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 1999
Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Specification of soil test: SL 237—1999[S]. Beijing: China Water Power Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
[17] 李彦龙. 非饱和黄土结合水特性及水分迁移问题研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2015
LI Yanlong. Bound water properties and moisture migration in unsaturated loess[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] ZHOU B C,LU N. Correlation between atterberg limits and soil adsorptive water[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2021,147(2):04020162. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002463
[19] LANGMUIR I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass,mica and platinum[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,1918,40(9):1361 − 1403. doi: 10.1021/ja02242a004
[20] BRUNAUER S,EMMETT P H,TELLER E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,1938,60(2):309 − 319. doi: 10.1021/ja01269a023
[21] LIKOS W J,LU N. Water vapor sorption behaviour of smectite-kaolinite mixtures[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals,2002,50(5):553 − 561. doi: 10.1346/000986002320679297
[22] RIDLEY A M,DINEEN K,BURLAND J B,et al. Soil matrix suction:some examples of its measurement and application in geotechnical engineering[J]. Géotechnique,2003,53(2):241 − 253.
[23] 王竹溪. 热力学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1955
WANG Zhuxi. Thermodynamics [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1955. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: