Controlling factors identification of groundwater system evolution based on numerical simulation in the typical arid-inland basin
-
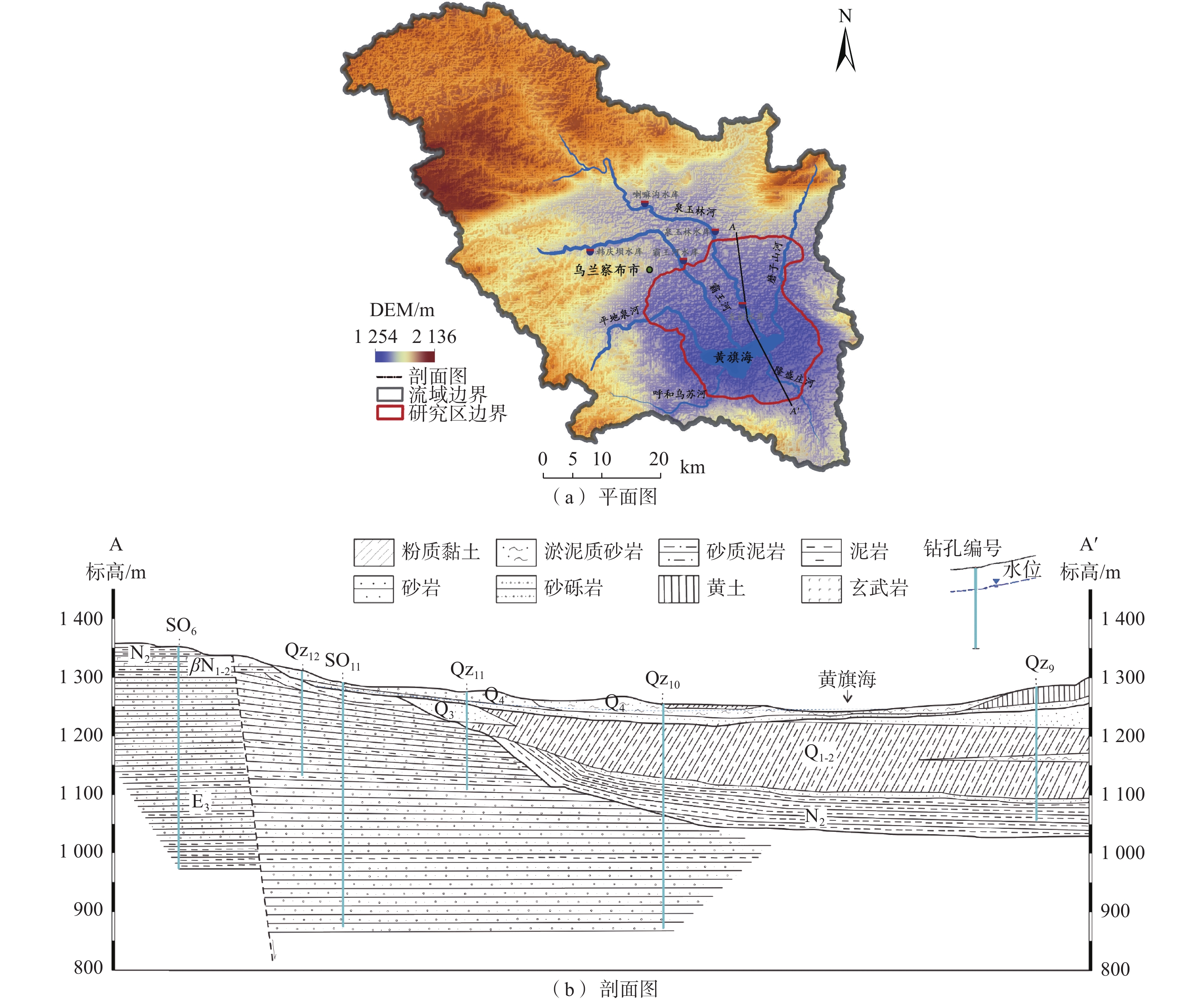
摘要:
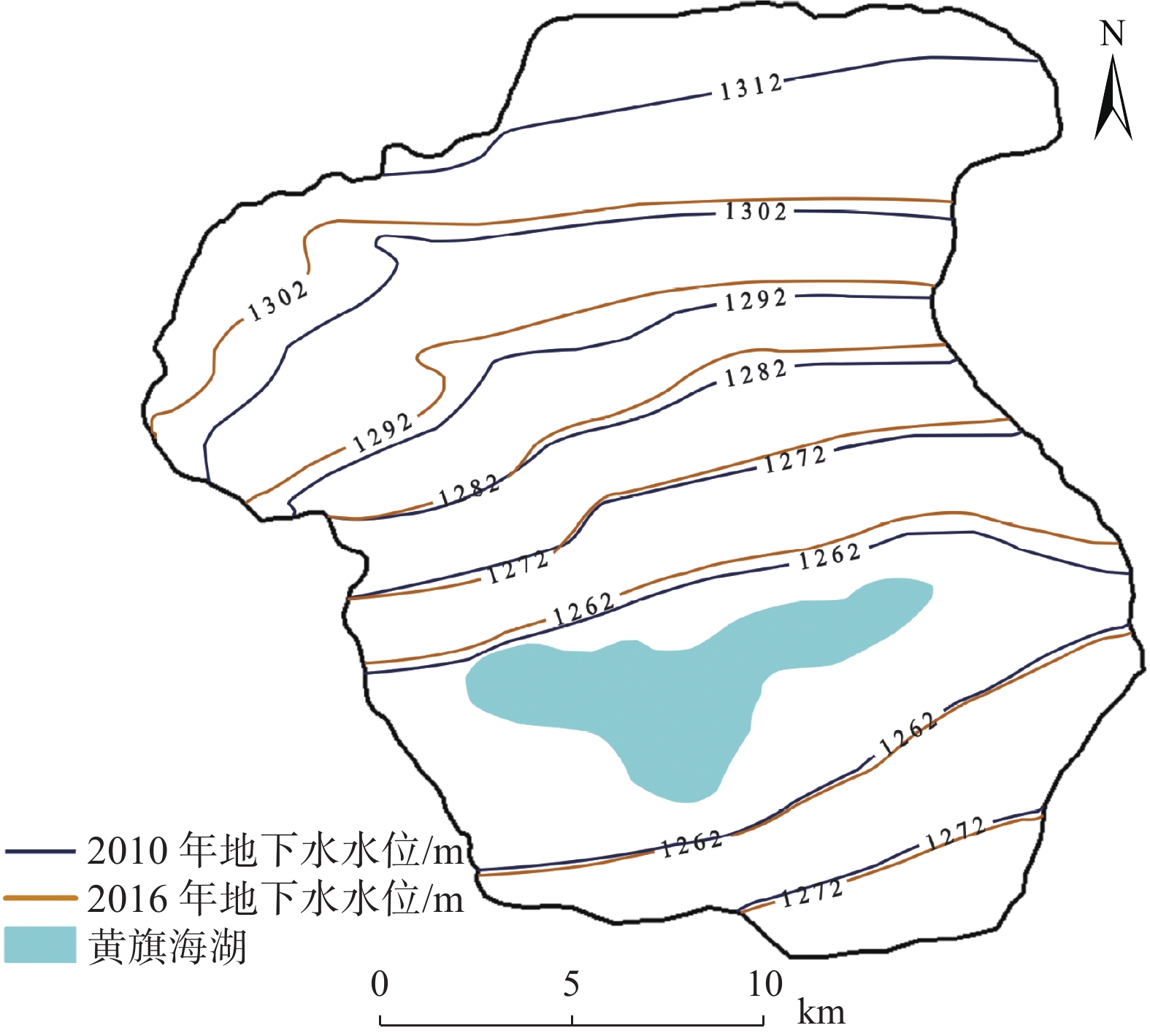
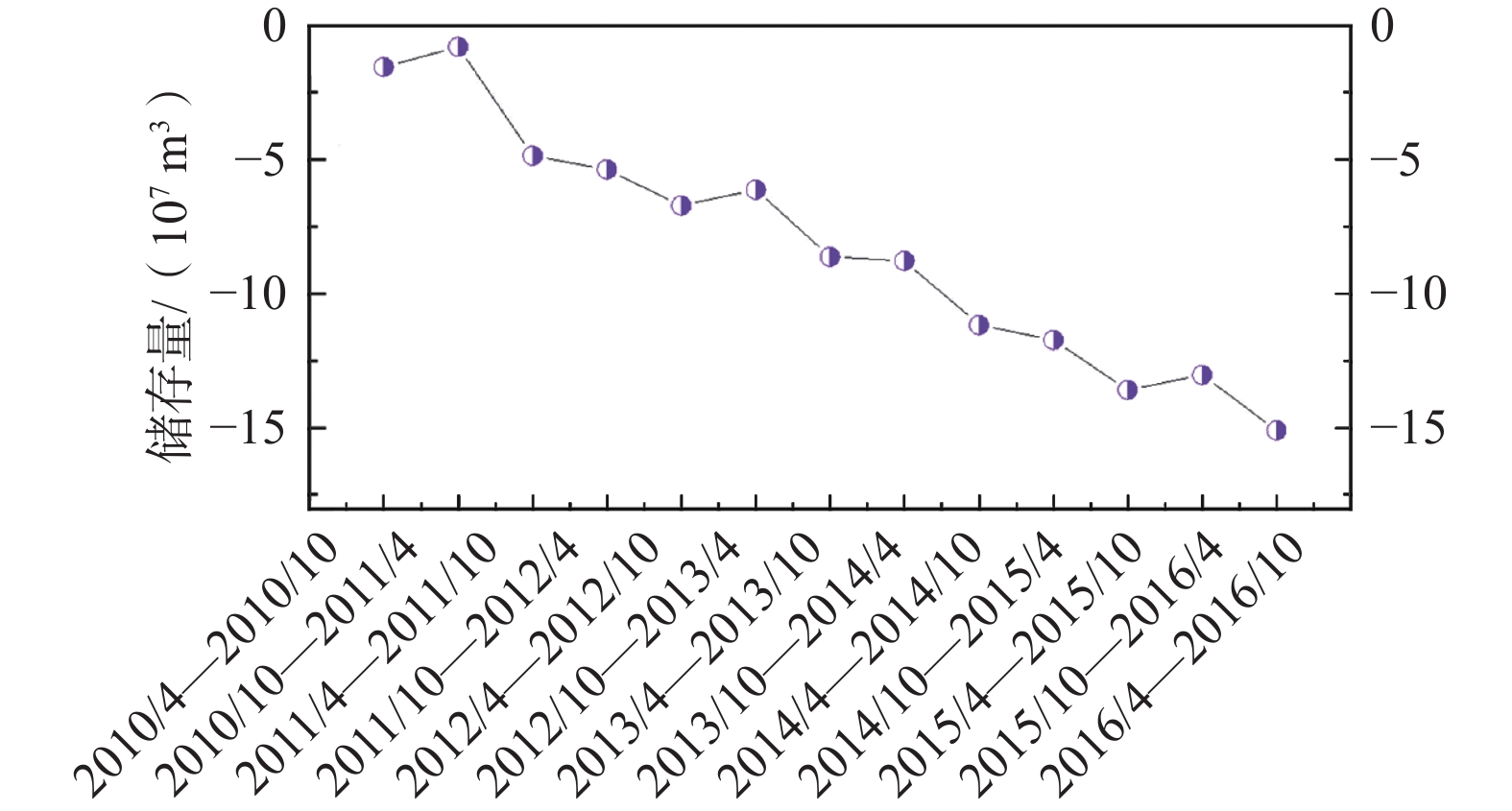
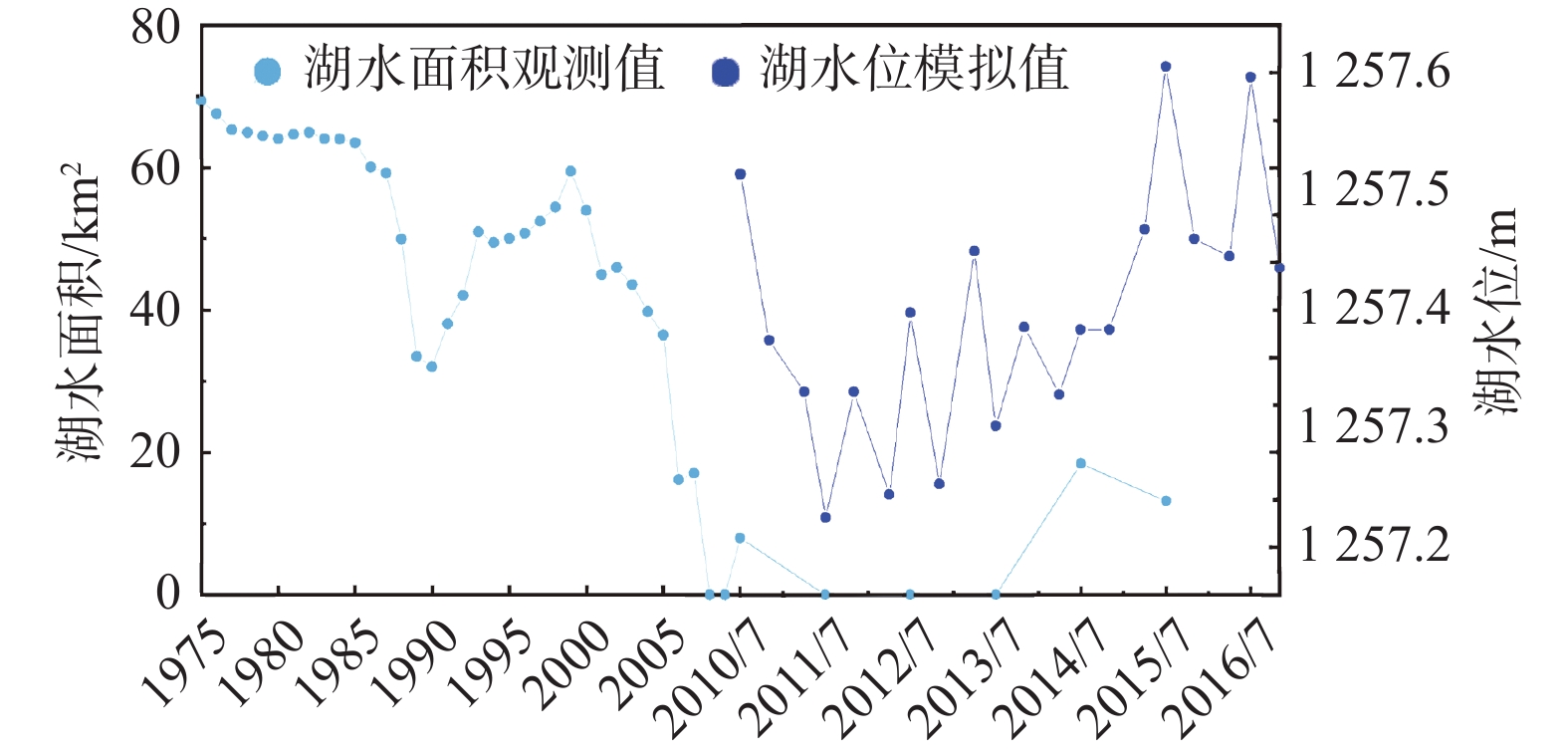
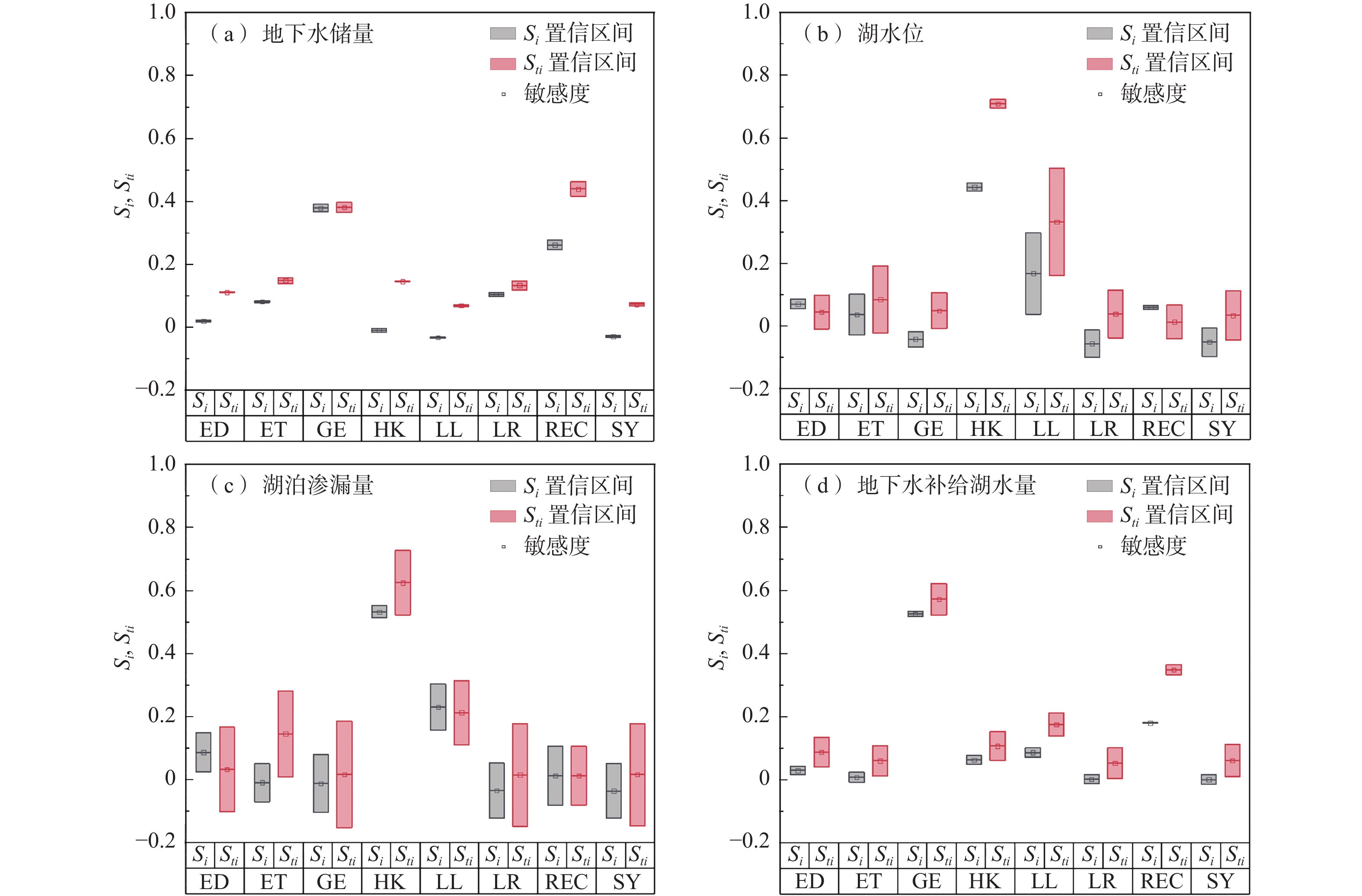
地下水资源是推动干旱区社会经济发展的基础动力,也是影响内陆湖泊及周边生态环境的关键因素。内蒙古黄旗海盆地作为干旱区内陆河流域的典型,近年来地下水水位不断下降,黄旗海湖区面积持续减小,甚至面临干涸的风险。为定量分析黄旗海盆地地下水资源时空演变及黄旗海湖水-地下水的转化关系,利用数值模拟技术构建黄旗海盆地地下水流数值模型,利用该区2010—2016年水位长观数据对模型进行识别和验证。模拟结果表明,模拟期黄旗海盆地地下水储量累计亏空达1.5×108 m3,地下水过度开采是该区水资源呈现负均衡的根本原因。在此基础上,采用Sobol全局敏感性分析方法进一步识别影响该区地下水资源演变的主要控制因素,分别利用湖水位、湖泊渗漏量、地下水储存量和地下水补给湖水量等4个目标函数对影响地下水系统演变的8个主要参数进行敏感性评估。结果显示,不同参数对不同目标的敏感性差异明显,前2个目标主要受渗透系数与湖床渗漏速率的影响,后2个目标主要受人工开采和降雨灌溉补给的影响,而超采地下水则是该区地下水资源枯竭及黄旗海湖泊面积萎缩的主控因素。本研究结果可为黄旗海盆地地下水资源可持续利用及周边生态环境保护提供技术支撑与决策依据。
Abstract:Groundwater resource is the basic power for the socio-economic development of arid-inland basins, and is also the major factor affecting the ecological environment of the Huangqihai Lake. As a typical study area of arid-inland basins, with the lowering of groundwater levels in recent years, the total area of the Huangqihai Lake decreases and even faces the risk of drying up. To quantitatively analyze the spatial-temporal evolution of groundwater resources in the Huangqihai Basin and the transformation relationship between lake water and groundwater, a numerical simulation model of groundwater flow in the Huangqihai Basin is established. The model is calibrated and validated by using long-term observation data from 2010 to 2016. The simulation results show that the accumulative deficit of groundwater storage in the Huangqihai Basin is 1.5×108 m3 from 2010 to 2016, and over-exploitation of groundwater is the critical reason for the negative water balance in this area. The Sobol method is used to identify the controlling factors affecting the changes of groundwater resources in this area. The sensitivity of eight main parameters affecting the groundwater system is evaluated by using four objective functions: lake stage, lake leakage, groundwater storage and groundwater discharge to lake. There are significant differences in sensitivity analysis results of model parameters under different objective functions. The first two functions are significantly affected by the horizontal permeability and lake leakage rate, while the last two are mainly affected by exploitation and recharge from precipitation and irrigation. It is proved that the influence of over-exploitation of groundwater is the main controlling factor of the depletion of water resources and shrinking of lake area in the Huangqihai Basin. The results of this study can provide technical support and scientific decision making for the sustainable utilization of groundwater resources and the protection of surrounding ecological environment in the Huangqihai Basin.
-

-
表 1 模型源汇项参数取值范围
Table 1. Values assigned to the source and sink terms
源汇项 数值 降雨入渗补给系数 0.04~0.21 最大蒸发速率/(m·d−1) 0.0001~0.00082 极限蒸发深度/m 5 田间灌溉补给系数 0.288 开采强度/(m3·d−1) 0.2×104~58.3×104 湖底垂向渗透系数/(cm·s−1) 7×10−6 湖面蒸发速率/(m·d−1) 0.00321 湖面降水速率/(m·d−1) 0.0006 表 2 地下水均衡表
Table 2. Water budget of the aquifer system
时间 流入/(107 m3) 总流入
/(107 m3)流出/(107 m3) 总流出
/(107 m3)储变量
/(107 m3)降水灌溉补给 侧向补给 湖泊渗漏 蒸散发 地下水补给湖泊 开采量 2010年4月—2010年10月 3.625 1.958 0.0073 5.591 3.137 0.539 3.449 7.125 −1.535 2010年10月—2011年4月 1.408 1.873 0.0021 3.284 1.089 0.586 0.863 2.538 0.746 2011年4月—2011年10月 1.811 1.378 0.0025 3.192 2.535 0.578 4.136 7.250 −4.059 2011年10月—2012年4月 0.884 1.378 0.0018 2.264 0.901 0.589 1.284 2.774 −0.510 2012年4月—2012年10月 4.302 1.832 0.0017 6.136 2.804 0.587 4.090 7.481 −1.345 2012年10月—2013年4月 1.637 1.811 0.0003 3.448 1.019 0.606 1.230 2.855 0.593 2013年4月—2013年10月 3.486 1.526 0.0007 5.012 3.090 0.595 3.830 7.515 −2.503 2013年10月—2014年4月 1.047 1.510 0.0001 2.557 1.005 0.609 1.087 2.701 −0.145 2014年4月—2014年10月 3.164 1.344 0.0004 4.508 2.503 0.596 3.801 6.90 −2.391 2014年10月—2015年4月 0.884 1.335 0.0005 2.220 0.836 0.602 1.339 2.776 −0.556 2015年4月—2015年10月 3.350 1.381 0.0013 4.732 2.223 0.589 3.787 6.599 −1.867 2015年10月—2016年4月 1.572 1.405 0.0013 2.978 0.788 0.599 1.034 2.421 0.557 2016年4月—2016年10月 3.941 1.613 0.0024 5.556 2.891 0.685 4.044 7.619 −2.063 表 3 敏感性分析的模型参数与输入量
Table 3. Model parameters and their ranges of the input values for the sensitivity analysis
模型参数或输入 缩写 代表水文过程 取值范围 地下水侧向补给流量/(m3·a−1) LR 边界条件 1024~96000 渗透系数/(m·d−1) HK 地下水流动 4.4~92.8 给水度 SY 地下水流动 0.128~0.24 地下水抽水量/(m3·d−1) GE 人工取水 0~26525 面状入渗补给速率/(m·d−1) REC 气象驱动/农业回灌 2.1×10−6~4.7×10−4 蒸发速率/(m·d−1) ET 蒸散发 8×10−5~2.7×10−3 最大蒸发深度/m ED 蒸散发 4~6 湖床渗流速率/(L·d−1) LL 湖床渗漏 2.4×10−3~3.6×10−3 -
[1] LALL U, JOSSET L, RUSSO T. A snapshot of the world’s groundwater challenges[J]. Annual Review of Environment and Resources,2020,45:171 − 194. doi: 10.1146/annurev-environ-102017-025800
[2] 周爱国, 马瑞, 张晨. 中国西北内陆盆地水分垂直循环及其生态学意义[J]. 水科学进展,2005,16(1):127 − 133. [ZHOU Aiguo, MA Rui, ZHANG Chen. Vertical water cycle and its ecological effect in inland basins, Northwest China[J]. Advances in Water Science,2005,16(1):127 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2005.01.023
[3] 胡汝骥, 樊自立, 王亚俊, 等. 中国西北干旱区的地下水资源及其特征[J]. 自然资源学报,2002,17(3):321 − 326. [HU Ruji, FAN Zili, WANG Yajun, et al. Groundwater resources and their characteristics in arid lands of Northwestern China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2002,17(3):321 − 326. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2002.03.012
[4] 张建云, 贺瑞敏, 齐晶, 等. 关于中国北方水资源问题的再认识[J]. 水科学进展,2013,24(3):303 − 310. [ZHANG Jianyun, HE Ruimin, QI Jing, et al. A new perspective on water issues in North China[J]. Advances in Water Science,2013,24(3):303 − 310. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] CHEN M M, LIU J G. Historical trends of wetland areas in the agriculture and pasture interlaced zone:A case study of the Huangqihai Lake Basin in Northern China[J]. Ecological Modelling,2015,318:168 − 176. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.12.012
[6] 薛禹群, 吴吉春. 地下水数值模拟在我国—回顾与展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1997,24(4):21 − 24. [XUE Yuqun, WU Jichun. Review and prospect of groundwater numerical simulation in China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1997,24(4):21 − 24. (in Chinese)
[7] 吴剑锋, 朱学愚. 由MODFLOW浅谈地下水流数值模拟软件的发展趋势[J]. 工程勘察,2000(2):12 − 15. [WU Jianfeng, ZHU Xueyu. Development trend of numerical simulation software for subsurface flow from MODFLOW[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2000(2):12 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] WEIX L, BAILEY R T, RECORDS R M, et al. Comprehensive simulation of nitrate transport in coupled surface-subsurface hydrologic systems using the linked SWAT-MODFLOW-RT3D model[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software,2019,122:104242.
[9] 王庆永, 贾忠华, 刘晓峰, 等. Visual_MODFLOW及其在地下水模拟中的应用[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2007,18(5):90 − 92. [WANG Qingyong, JIA Zhonghua, LIU Xiaofeng, et al. Visual MODFLOW and its application to groundwater simulation[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2007,18(5):90 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-643X.2007.05.023
[10] ZHANG D, YANG Y, WU J F, et al. Global sensitivity analysis on a numerical model of seawater intrusion and its implications for coastal aquifer management:A case study in Dagu River Basin, Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2020,28(7):2543 − 2557. doi: 10.1007/s10040-020-02219-6
[11] 孟世豪,崔亚莉,田芳,等. 基于MODFLOW-SUB建立变渗透系数的地下水流-地面沉降模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(2):550 − 559. [MENG Shihao, CUI Yali, TIAN Fang, et al. Modeling of groundwater flow-land subsidence with variable hydraulic conductivity based on MODFLOW-SUB[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(2):550 − 559. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] SALTELLI A K, CHAN K, SCOTT E M. Sensitivity Analysis [M]. NewYork: Wiley, 2000.
[13] 吴吉春, 陆乐. 地下水模拟不确定性分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版),2011,47(3):227 − 234. [WU Jichun, LU Le. Uncertainty analysis for groundwater modeling[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences),2011,47(3):227 − 234. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] FREY H C, PATIL S R. Identification and review of sensitivity analysis methods[J]. Risk Analysis,2002,22(3):553 − 578. doi: 10.1111/0272-4332.00039
[15] BEVEN K. Prophecy, reality and uncertainty in distributed hydrological modelling[J]. Advances in Water Resources,1993,16(1):41 − 51. doi: 10.1016/0309-1708(93)90028-E
[16] 束龙仓, 王茂枚, 刘瑞国, 等. 地下水数值模拟中的参数灵敏度分析[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2007,35(5):491 − 495. [SHU Longcang, WANG Maomei, LIU Ruiguo, et al. Sensitivity analysis of parameters in numerical simulation of groundwater[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences),2007,35(5):491 − 495. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] WU J C, ZENG X K. Review of the uncertainty analysis of groundwater numerical simulation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(25):3044 − 3052. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5950-8
[18] LIU J G, LIU Q Y, YANG H. Assessing water scarcity by simultaneously considering environmental flow requirements, water quantity, and water quality[J]. Ecological Indicators,2016,60:434 − 441. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.07.019
[19] SALTELLI A, TARANTOLA S, CHAN K P S. A quantitative model-independent method for global sensitivity analysis of model output[J]. Technometrics,1999,41(1):39 − 56. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1999.10485594
[20] SALTELLI A, RATTO M, ANDRES T, et al. Global sensitivity analysis: The primer[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley& SonsLtd, 2008.
[21] 郑菲, 施小清, 吴吉春, 等. 深部咸水层CO2地质封存数值模拟参数的全局敏感性分析—以苏北盆地盐城组为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2014,44(1):310 − 318. [ZHENG Fei, SHI Xiaoqing, WU Jichun, et al. Global parametric sensitivity analysis of numerical simulation for CO2 geological sequestration in saline aquifers:A case study of Yancheng formation in Subei Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2014,44(1):310 − 318. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] SOBOL I M. Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation,2001,55(1/2/3):271 − 280.
[23] WU B, ZHENG Y, TIAN Y, et al. Systematic assessment of the uncertainty in integrated surface water-groundwater modeling based on the probabilistic collocation method[J]. Water Resources Research,2014,50(7):5848 − 5865. doi: 10.1002/2014WR015366
[24] 罗跃, 叶淑君, 吴吉春, 等. 地面沉降模型的参数全局敏感性[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2018,52(10):2007 − 2013. [LUO Yue, YE Shujun, WU Jichun, et al. Global sensitivity analysis of parameters in land subsidence model[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2018,52(10):2007 − 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2018.10.021
-



 下载:
下载: