Geological storage conditions and potential assessment of CO2 in deep saline aquifers in Lindian of Heilongjiang Province
-
摘要:
CO2地质储存是减少碳排放、缓解温室效应的有效措施。经地热勘探与综合研究,黑龙江林甸地区埋藏深度940~2062 m的中生代白垩系泉头组三四段、青山口组和姚家组砂岩层状地层中蕴含丰富的咸水,溶解性总固体可达2000~9000 mg/L,孔隙发育较好,水流速缓慢,其上盖层以白垩系嫩江组、四方台组、明水组的层状泥质岩为主,厚度为800~1300 m,未被主要断裂带穿透,封闭良好,决定了其可以作为储存CO2的良好地质储体。同时,大庆市紧邻林甸地区,化工企业众多,碳源集中且充足,规模大,距离短,为研究区的CO2地质储存提供了有利条件。因林甸地区油气资源匮乏,缺少石油井,本次工作首次利用地热勘探井,根据CO2地质储存技术机理,采用国际权威潜力评估公式,开展了深部咸水层CO2地质储存的潜力评估。结果表明,其深部咸水层CO2理论储存量为478.91×108 t,有效储存量为11.49×108 t,储存潜力较大,未来可作为大庆、齐齐哈尔等邻近城市减碳的地质储存场所。此项工作的开展,为林甸地区下一步实施CO2地质储存适宜性评价、目标靶区筛选和场地选址及示范工程建设提供了技术支撑。
Abstract:Geological storage of CO2 is an effective measure to reduce carbon emission and mitigate greenhouse effect. Through geothermal exploration and comprehensive research, it is found that the sandstone stratified strata of the Third and Fourth Member of the Quantou Formation, the Qingshankou Formation and the Yaojia Formation of the Cretaceous age in the Lindian area of Heilongjiang Province, with the burial depth of about 940−2062 m, contain rich saline water with TDS of 2000−9000 mg/L, and are of well-developed pores and slow groundwater flow. The caprock is dominated by pelite stratified strata of the Nenjiang Formation, Sifangtai Formation and Mingshui Formation of the Cretaceous age, with a thickness of about 800−1300 m. It has not been penetrated by major fault zones and is well closed, which determines that it can be used as a good geological reservoir for CO2 storage. At the same time, Lindian is close to the city of Daqing, with numerous chemical enterprises, concentrated and sufficient carbon sources, and large scale and short distance, providing favorable conditions for CO2 geological storage in the study area. Due to the lack of oil and gas resources and oil wells in the Lindian area, this work uses geothermal exploration wells for the first time. According to the mechanism of CO2 geological storage technology and the international authoritative potential assessment formula, the potential assessment of CO2 geological storage of deep saline aquifers in this area is carried out. The results show that the theoretical CO2 storage in the deep salt aquifers is 478.91×108 t, the effective CO2 storage is 11.49×108 t, which is of large storage potential. In the future, it can provide geological storage sites for carbon reduction in Daqing, Qiqihar and other neighboring cities. The implementation of this work provides technical support for the next implementation of CO2 geological storage suitability evaluation, objective target area and site selection and demonstration projects in the Lindian area.
-
Key words:
- saline aquifer /
- CO2 geological storage /
- geological condition /
- potential assessment
-

-
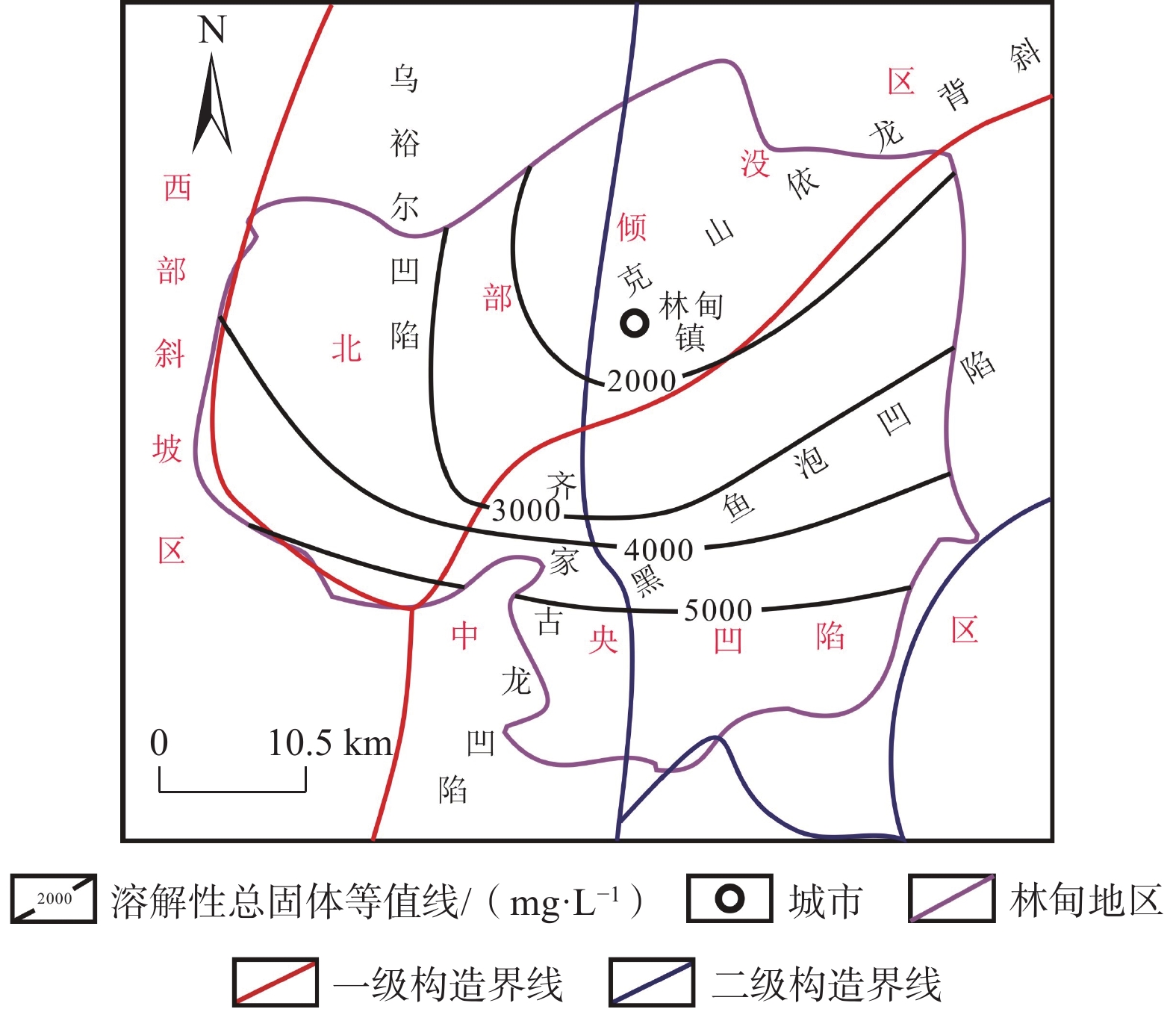
图 3 林甸地区断裂分布图(据文献[27]修改)
Figure 3.
图 4 滨北地区姚家组—青山口组水文地质图[27]
Figure 4.
表 1 林甸地区CO2地质储存主要储层厚度、孔隙度与渗透率
Table 1. Statistical table of thickness, porosity and permeability of main reservoirs of CO2 geological storage in the Lindian area
储 层 厚度/m 孔隙度/% 渗透率/(10−3 μm2) 组 段 姚家组 二、三段 3.4~33.2 7.5~31.5 2.4~1440.0 一段 2.2~32.6 12.0~28.0 11.3~544.0 青山
口组二、三段 90.5~209.6 8.2~29.2 11.0~426.0 一段 1.8~30.5 9.8~27.8 2.1~95.3 泉头组 四段 4.0~57.2 8.8~25.9 0.8~82.0 三段 5.1~57.3 10.1~21.8 3.1~79.8 表 2 乌裕尔凹陷、克山—依龙背斜、黑鱼泡凹陷与齐家—古龙凹陷深部咸水层储存量计算参数
Table 2. Storage parameters of deep saline aquifers in the Wuyuer depression, the Keshan-yilong anticline, the Heiyupao depression and the Qijia-gulong depression
储 层 储层面积
/km2储层平均
厚度/m储层岩石
平均孔隙度/%初始地层水的平均
密度/(kg·m−3)液流逆流后被圈闭的
CO2平均饱和度/%CO2在地层水中的
平均溶解度/(mol·kg−1)储层中CO2的
平均密度/(kg·m−3)乌裕尔凹陷 姚家组二三段 1215 9.7 15.88 996.96 47.4 1.247 638.56 姚家组一段 13.8 18.03 997.05 40.7 1.243 639.09 青山口组二三段 163.4 15.17 997.43 46.2 1.263 676.21 青山口组一段 12.3 15.32 999.44 45.5 1.288 712.39 泉头组四段 28.8 18.00 999.66 40.4 1.295 723.07 泉头组三段 29.2 17.90 1000.05 40.7 1.319 747.39 克山—
依龙背斜姚家组二三段 597 14.5 25.76 992.75 30.0 1.222 569.36 姚家组一段 28.3 21.84 992.89 35.4 1.226 582.26 青山口组二三段 181.6 20.60 993.47 37.2 1.243 636.97 青山口组一段 6.9 15.20 994.04 45.8 1.257 671.80 泉头组四段 30.4 15.96 994.24 46.8 1.268 684.59 泉头组三段 40.7 17.46 994.55 42.3 1.292 702.04 黑鱼泡凹陷 姚家组二三段 1404 14.3 14.93 994.46 46.5 1.197 601.50 姚家组一段 13.2 16.21 994.92 44.6 1.203 609.84 青山口组二三段 158.1 15.14 994.43 47.3 1.223 628.14 青山口组一段 9.9 14.94 993.78 47.6 1.247 645.22 泉头组四段 16.5 13.19 993.55 51.6 1.258 647.34 泉头组三段 22.4 14.32 993.61 48.3 1.273 652.91 齐家—
古龙凹陷姚家组二三段 345 24.4 18.31 991.98 39.9 1.153 497.1 姚家组一段 21.2 15.85 991.83 44.4 1.158 509.65 青山口组二三段 188.6 17.03 991.28 42.2 1.176 539.82 青山口组一段 6.2 9.98 990.65 58.9 1.196 564.59 泉头组四段 57.2 15.25 990.32 45.6 1.206 575.33 泉头组三段 34.8 11.42 989.60 54.7 1.223 587.24 表 3 林甸地区深部咸水层CO2储存量
Table 3. CO2 storage scale of deep saline aquifers in the Lindian area
计算区 残余气体储存量
/(108 t)溶解储存量/(108 t) 理论储存量/
(108 t)有效储存量/
(108 t)乌裕尔凹陷 152.75 15.53 168.28 4.04 克山—依龙背斜 88.14 12.16 100.30 2.41 黑鱼泡凹陷 147.19 13.90 161.09 3.86 齐家—古龙凹陷 43.93 5.31 49.24 1.18 合计 432.01 46.90 478.91 11.49 -
[1] IPCC. Climate change 2001: The third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change[R]. Cambridge: Cambridge University, 2001.
[2] SAM H. An overview of the underground disposal of carbon dioxide[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,1997,38:S193 − S198. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(96)00268-3
[3] GUNTER W D,GENTZIS T,ROTTENFUSSER B A,et al. Deep coalbed methane in Alberta,Canada:A fuel resource with the potential of zero greenhouse gas emissions[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,1997,38:S217 − S222. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(96)00037-4
[4] WINTER E M,BERGMAN P D. Availability of depleted oil and gas reservoirs for disposal of carbon dioxide in the United States[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,1993,34(9/10/11):1177 − 1187.
[5] BACHU S,SHAW J. Evaluation of the CO2 sequestration capacity in Alberta’s oil and gas reservoirs at depletion and the effect of underlying aquifers[J]. Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology,2003,42(9):51 − 61.
[6] HOLLOWAY S. Underground sequestration of carbon dioxide:A viable greenhouse gas mitigation option[J]. Energy,2005,30(11/12):2318 − 2333.
[7] 江怀友,沈平平,宋新民,等. 世界气候变暖及二氧化碳埋存现状与展望[J]. 古地理学报,2008,10(3):323 − 328. [JIANG Huaiyou,SHEN Pingping,SONG Xinmin,et al. Global warming and current status and prospect of CO2 underground storage[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2008,10(3):323 − 328. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2008.03.012
[8] 许志刚,陈代钊,曾荣树,等. CO2地下地质埋存原理和条件[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2009,31(1):91 − 97. [XU Zhigang,CHEN Daizhao,ZENG Rongshu,et al. The theory and conditions of geological storage of CO2[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition),2009,31(1):91 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 文冬光,郭建强,张森琦,等. 中国二氧化碳地质储存研究进展[J]. 中国地质,2014,41(5):1716 − 1723. [WEN Dongguang,GUO Jianqiang,ZHANG Senqi,et al. The progress in the research on carbon dioxide geological storage in China[J]. Geology in China,2014,41(5):1716 − 1723. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.05.025
[10] 郭建强, 文冬光, 张森琦, 等. 中国二氧化碳地质储存适宜性评价与示范工程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014
GUO Jianqiang, WEN Dongguang, ZHANG Senqi, et al. Carbon dioxide geological storage suitability evaluation and demonstration project in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014. (in Chinese)
[11] BACHU S. Sequestration of CO2 in geological media:Criteria and approach for site selection in response to climate change[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2000,41(9):953 − 970. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(99)00149-1
[12] TSANG C F,BENSON S M,KOBELSKI B,et al. Scientific considerations related to regulation development for CO2 sequestration in brine formations[J]. Environmental Geology,2002,42(2/3):275 − 281.
[13] WHITE C M,SMITH D H,JONES K L,et al. Sequestration of carbon dioxide in coal with enhanced coalbed methane recovery:A review[J]. Energy & Fuels,2005,19(3):659 − 724.
[14] 李小春,刘延锋,白冰,等. 中国深部咸水含水层CO2储存优先区域选择[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(5):963 − 968. [LI Xiaochun,LIU Yanfeng,BAI Bing,et al. Ranking and screening of CO2 saline aquifer storage zones in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(5):963 − 968. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.05.015
[15] 巫润建,李国敏,黎明,等. 松辽盆地咸含水层埋存CO2储存容量初步估算[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(1):100 − 104. [WU Runjian,LI Guomin,LI Ming,et al. Estimation of CO2 storage capacity in deep saline aquifer in Songliao sedimentary basin[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(1):100 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.01.014
[16] LI D Y,LIU Q F,WENIGER P,et al. High-pressure sorption isotherms and sorption kinetics of CH4 and CO2 on coals[J]. Fuel,2010,89(3):569 − 580. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.06.008
[17] 韩燚,梁荣柱. 深部盐水层二氧化碳储量的计算新方法[J]. 西部探矿工程,2011,23(6):112 − 115. [HAN Yi,LIANG Rongzhu. The new means of estimation of CO2 storage capacity in deep saline aquifer[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering,2011,23(6):112 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2011.06.039
[18] 金超,曾荣树,田兴有. 松辽盆地南部保康体系上白垩统CO2埋存条件与潜力[J]. 地球科学,2013,38(6):1229 − 1239. [JIN Chao,ZENG Rongshu,TIAN Xingyou. CO2 storage conditions and capacity of Upper Cretaceous series in Baokang sedimentary system in the southwest of Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science,2013,38(6):1229 − 1239. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 李琦,魏亚妮,刘桂臻. 中国沉积盆地深部CO2地质封存联合咸水开采容量评估[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2013,11(4):93 − 96. [LI Qi,WEI Yani,LIU Guizhen. Assessment of CO2 storage capacity and saline water development in sedimentary basins of China[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2013,11(4):93 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] LI L,ZHAO N,WEI W,et al. A review of research progress on CO2 capture,storage,and utilization in Chinese Academy of Sciences[J]. Fuel,2013,108:112 − 130. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.08.022
[21] BACHU S. Review of CO2 storage efficiency in deep saline aquifers[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2015,40:188 − 202. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.01.007
[22] 刁玉杰,朱国维,金晓琳,等. 四川盆地理论CO2地质利用与封存潜力评估[J]. 地质通报,2017,36(6):1088 − 1095. [DIAO Yujie,ZHU Guowei,JIN Xiaolin,et al. Theoretical potential assessment of CO2 geological utilization and storage in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2017,36(6):1088 − 1095. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.06.021
[23] 张冰,梁凯强,王维波,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地深部咸水层CO2有效地质封存潜力评价[J]. 非常规油气,2019,6(3):15 − 20. [ZHANG Bing,LIANG Kaiqiang,WANG Weibo,et al. Evaluation of effective CO2 geological sequestration potential of deep saline aquifer in Ordos Basin[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas,2019,6(3):15 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8471.2019.03.003
[24] ZHU Q L,WANG C,FAN Z H,et al. Optimal matching between CO2 sources in Jiangsu province and sinks in Subei-Southern South Yellow Sea Basin,China[J]. Greenhouse Gases:Science and Technology,2019,9(1):95 − 105. doi: 10.1002/ghg.1835
[25] 张晓娟. 准噶尔盆地CO2地质利用与储存潜力研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020
ZHANG Xiaojuan. Study on CO2 geological utilization and storage capacity in Junnggar Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 桑树勋, 刘世奇, 王文峰, 等. 深部煤层CO2地质存储与煤层气强化开发有效性理论及评价[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 403 − 435
SANG Shuxun, LIU Shiqi, WANG Wenfeng, et al. Coal bed methane in deep coal seam geological storage of CO2 and theories of strengthening development effectiveness and evaluation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020: 403 − 435. (in Chinese)
[27] 大庆市地热研究课题组. 大庆市林甸地区地热资源特征及地热资源评价研究[R]. 大庆: 大庆石油学院, 大庆市地热开发办, 1998
Daqing geothermal research group. Characteristics and evaluation of geothermal resources in Lindian area of Daqing City[R]. Daqing: Daqing Petroleum Institute, Daqing Geothermal Development Office, 1998. (in Chinese)
[28] 施尚明,孙小洁,于清华. 松辽盆地林甸地区地温场特征[J]. 大庆石油学院学报,1998,22(4):77 − 79. [SHI Shangming,SUN Xiaojie,YU Qinghua. Geotemperature field characterastics in Lindian region of Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute,1998,22(4):77 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 汪在君. 松辽盆地北部的地热资源及其开发利用方向[J]. 自然资源学报,2003,18(1):8 − 12. [WANG Zaijun. The geothermal resource of the northern Songliao Basin and direction for its development and utilization[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2003,18(1):8 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2003.01.002
[30] 杨永智,沈平平,宋新民,等. 盐水层温室气体地质埋存机理及潜力计算方法评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2009,39(4):744 − 748. [YANG Yongzhi,SHEN Pingping,SONG Xinmin,et al. Greenhouse gas geo-sequestration mechanism and capacity evaluation in aquifer[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2009,39(4):744 − 748. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] BRUANT R G J,GUSWA A J,CELIA M A,et al. Safe storage of CO2 in deep saline aquifers[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2002,36(11):240A − 245A.
[32] 张洪涛,文冬光,李义连,等. 中国CO2地质埋存条件分析及有关建议[J]. 地质通报,2005,24(12):1107 − 1110. [ZHANG Hongtao,WEN Dongguang,LI Yilian,et al. Conditions for CO2 geological sequestration in China and some suggestions[J]. Regional Geology of China,2005,24(12):1107 − 1110. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.12.004
[33] BACHU S,HAUG K,MICHAEL K,et al. Deep injection of acid gas in western Canada[J]. Developments in Water Science,2005,52:623 − 635.
[34] 陈瑞军,王继革,贾志,等. 深部地热流体温度场中稳态静水压力研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(6):123 − 128. [CHEN Ruijun,WANG Jige,JIA Zhi,et al. A study of steady-state hydrostatic pressure in deep geothermal fluid temperature field[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(6):123 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] HOLTZ, M H. Optimization of CO2 sequestered as a residual phase in brine-saturated formations[C]//Second Annual Conference on Carbon Sequestration: Developing & validating the technology base to reduce carbon intensity. Alesandria Virginia: GCCC Digital Publication, 2003.
[36] DUAN Z H,SUN R,ZHU C,et al. An improved model for the calculation of CO2 solubility in aqueous solutions containing Na+,K+,Ca2+,Mg2+,Cl−,and
$ {\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ [37] 于立松,张卫东,吴双亮,等. 二氧化碳在深部盐水层中溶解封存规律的研究进展[J]. 新能源进展,2015,3(1):75 − 80. [YU Lisong,ZHANG Weidong,WU Shuangliang,et al. Research on dissolved sequestration of CO2 In deep saline aquifers[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy,2015,3(1):75 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2015.01.012
[38] 张川如, 虞绍永. 二氧化碳气井测试与评价方法[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1999
ZHANG Chuanru, YU Shaoyong. Test and evaluation methods for carbon dioxide gas wells[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
[39] 罗伟,张洋,刘宁,等. 松辽盆地中央坳陷区北部咸水层CO2储存场地适宜性评价与储量计算[J]. 安全与环境工程,2015,22(5):52 − 58. [LUO Wei,ZHANG Yang,LIU Ning,et al. Assessment of site suitability and the capacity of CO2 storage in deep aquifer in the northern central depression of Songliao Basin[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2015,22(5):52 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[40] 宋铁军,万玉玉,张文强,等. 基于灰色关联分析法的松辽盆地CO2地质储存适宜性评价[J]. 地质通报,2017,36(10):1874 − 1883. [SONG Tiejun,WAN Yuyu,ZHANG Wenqiang,et al. Suitability assessment of geological sequestration of CO2 in Songliao Basin based on gray relational analysis method[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2017,36(10):1874 − 1883. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.10.018
[41] 雷宏武,李佳琦,许天福,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地深部咸水层二氧化碳地质储存热-水动力-力学(THM)耦合过程数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2015,45(2):552 − 563. [LEI Hongwu,LI Jiaqi,XU Tianfu,et al. Numerical simulation of coupled thermal-hydrodynamic-mechanical(THM) processes for CO2 geological sequestration in deep saline aquifers at Ordos Basin,China[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition),2015,45(2):552 − 563. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: