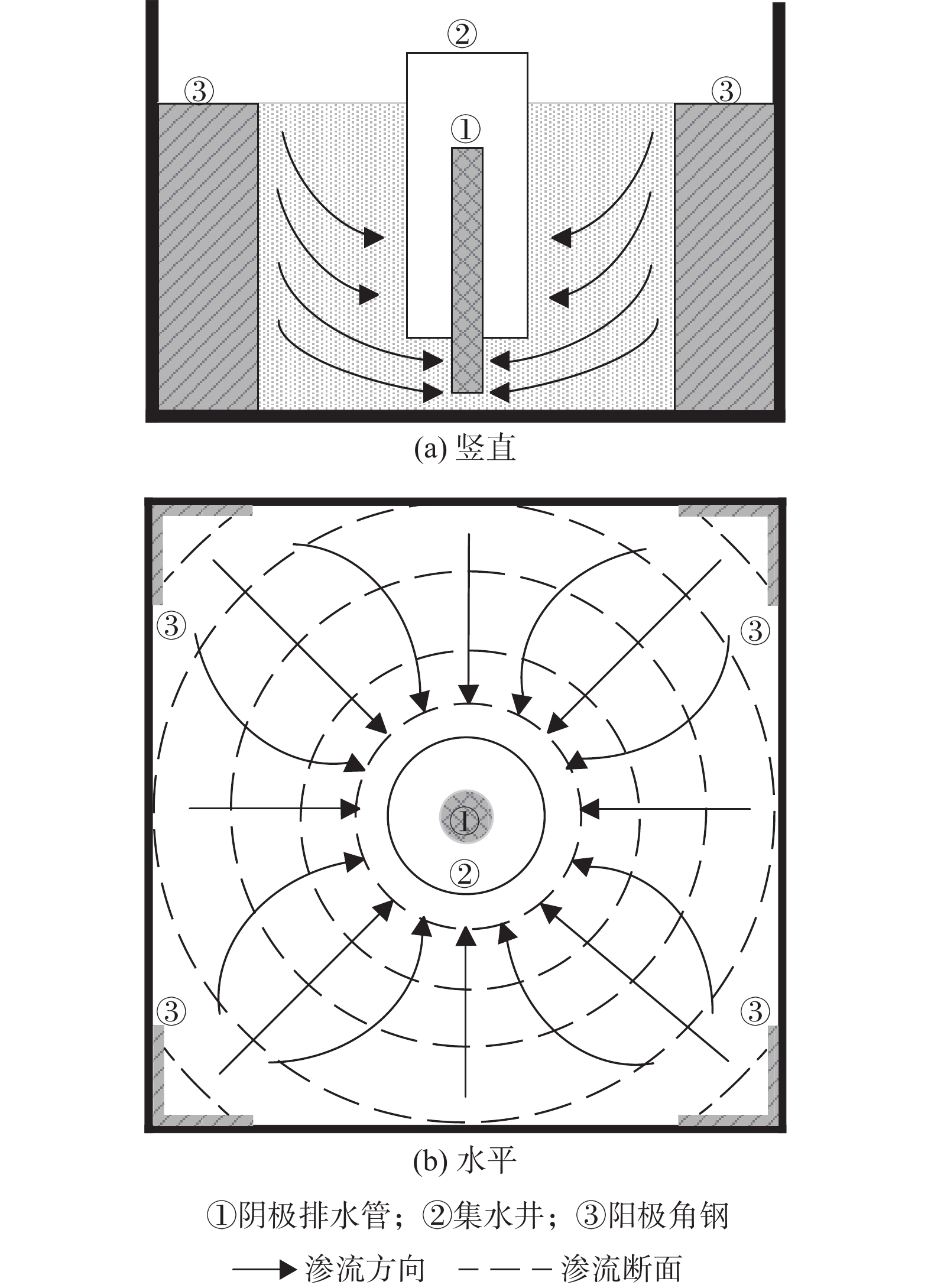
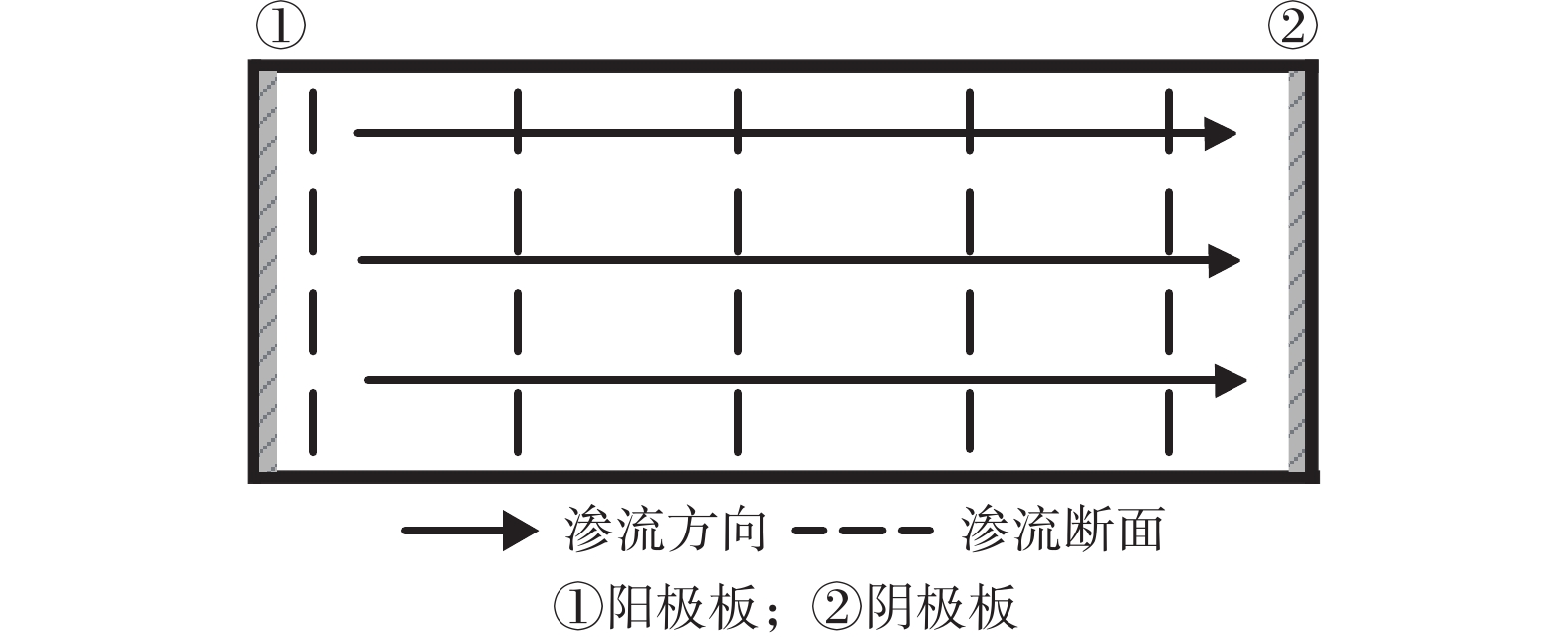
Energy consumption in a large- scale 3D electro-osmosis-hydraulic synergism system for sludge consolidation
-
摘要:
为解决目前电渗应用的高能耗困境及大尺寸模拟困难等问题,提出针对低渗透性、高含水率土体的电动-水力渗流协同作用的三维固结方法。自行研制了一套阴极-集水-排水协同作用的多功能集排水系统,采用间歇式抽水代替连续抽水。采用三维电动-水力渗流固结系统对取自贡湖湾湿地和白旄堆场的2种不同太湖底泥进行了电渗试验研究,同时对白旄堆场太湖底泥进行了传统一维电渗固结试验,并对2种试验条件下的单位体积排水能耗和单位体积单位排水量能耗等关键指标进行了对比。结果表明:三维集水井设计可大大降低土体阴极附近电阻,间断性提高系统电流,提高排水效率,降低电渗总能耗;间歇式抽水可间歇性降低系统内总电流,利用电动-水力协同作用,保持系统渗流的连续性;三维电动-水力渗流固结系统的电流呈周期性减小—增大模式,并且降低速率较慢,尤其对于有机质含量较高的土体,电渗过程电流始终保持在一个较高的水平,提高了排水固结效率。三维电动-水力渗流固结系统的单位体积排水能耗和单位体积单位排水量能耗分别约为一维电渗系统的2/3和1/30。在高含水量软土固结排水中具有显著的节能效果。三维电动-水力渗流固结系统可以提高排水固结效率、大幅度降低能耗,为实际工程应用提供了可靠的理论、设计依据和数据支持,具有很好的推广价值。
Abstract:The 3D electro-osmosis-hydraulic synergistic consolidation method is proposed based on the theory of electroosmosis and consolidation to solve the problem of the high energy consumption and large-scale simulation of practice conditions for low permeability and high-water content soils. A set of multi-functional catchment drainage systems combining the synergistic action of the cathode-catchment-intermittent pumping mode is developed. Consolidation of two types of Taihu lake sediments from the Gonghuwan wetland and Baimao Storage site are investigated using this system. Two key indicators of energy consumption per unit volume and displacement per unit volume of the 3D electro-osmosis-hydraulic synergistic consolidation system and the traditional 1D electroosmosis system are analyzed to illustrate the advantage of the 3D system. The results show that the design of water collecting well can greatly reduce the resistance near the soil cathode, intermittently improve the system current, improve the drainage efficiency and reduce the energy consumption. Intermittent pumping can intermittently reduce the system current, and maintain the continuity of system seepage by using the electric and hydraulic synergistic effect. A decrease-increase periodic decrease mode of the current for the 3D electrohydraulic seepage consolidation system is observed. The decrease rate of the current is slower than that of the 1D electro-osmotic system, especially for the soil with high organic matter content, the current in the electroosmotic process is maintained at a relatively higher level, which improves the drainage consolidation efficiency. The energy consumption per unit volume and displacement per unit volume of the 3D electro-hydraulic seepage consolidation system are about 2/3 and 1/30 that of the 1D electro-osmotic system, respectively. The 3D electro-hydraulic seepage consolidation system has remarkable energy saving effect in consolidation and drainage of soft soil with high water content. The 3D electroosmosis-hydraulic consolidation system can greatly improve the drainage consolidation efficiency, greatly reduce energy consumption and better guide the application of the proposed method to the electro-osmotic consolidation of high-water content sludge and another related field.
-

-
表 1 试验所用土体采集地点及物理性质
Table 1. Sampling location and physical properties of soil used in the test
编号 采集地点 液限/% 塑限/% 1号太湖底泥 贡湖湾湿地 51.0 16.5 2号太湖底泥 太湖白旄堆场 44..0 23.0 表 2 试验条件
Table 2. Test conditions
工况 试验土样 试验装置 土样尺寸 试验
电压/V初始含
水率/%S1 1号太湖底泥 三维电渗装置 50 cm×50 cm×25 cm 30 55.0 C1 2号太湖底泥 三维电渗装置 50 cm×50 cm×25 cm 30 55.0 C2 2号太湖底泥 一维电渗装置 20 cm×10 cm×10 cm 30 55.0 -
[1] 刘松玉,周建,章定文,等. 地基处理技术进展[J]. 土木工程学报,2020,53(4):93 − 110. [LIU Songyu,ZHOU Jian,ZHANG Dingwen,et al. State of the art of the ground improvement technology in China[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2020,53(4):93 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 郑凌逶,谢新宇,谢康和,等. 电渗法加固地基试验及应用研究进展[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2017,51(6):1064 − 1073. [ZHENG Lingwei,XIE Xinyu,XIE Kanghe,et al. Test and application research advance on foundation reinforcement by electro-osmosis method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2017,51(6):1064 − 1073. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 林伟岸,江文豪,詹良通. 考虑真空加载过程及堆载随时间变化下砂井地基的普遍固结解析解[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(7):1828 − 1838. [LIN Weian,JIANG Wenhao,ZHAN Liangtong. General analytical solution for consolidation of sand-drained foundation considering the vacuum loading process and the time-dependent surcharge loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(7):1828 − 1838. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.1649
[4] BHOSLE S,DESHMUKH V. Experimental studies on soft marine clay under combined vacuum and surcharge preloading with PVD[J]. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,15(4):461 − 470. doi: 10.1080/19386362.2018.1496004
[5] NGUYEN T N,BERGADO D T,KIKUMOTO M,et al. A simple solution for prefabricated vertical drain with surcharge preloading combined with vacuum consolidation[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2021,49(1):304 − 322. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2020.10.004
[6] 金志伟,阎长虹,李良伟,等. 低含水率盾构泥浆的真空-电渗联合泥水分离技术试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):103 − 110. [JIN Zhiwei,YAN Changhong,LI Liangwei,et al. An experimental study of vacuum negative pressure incorporated with electro-osmosis in mud-water dehydration for shield slurry with low water content[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):103 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201906033
[7] WANG Jun, ZHAO Ran, CAI Yuanqiang,et al. Vacuum preloading and electro-osmosis consolidation of dredged slurry pretreated with flocculants[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,246:123 − 130. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.09.024
[8] WU Jun,XUAN Youjin,DENG Yongfeng,et al. Combined vacuum and surcharge preloading method to improve lianyungang soft marine clay for embankment widening project:A case[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2021,49(2):452 − 465. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2020.10.013
[9] XUE Zhijia,XIONG Qi. Electro-osmotic chemical behavior of clayey soil under various boundary conditions[J]. Journal of Central South University,2021,28(5):1493 − 1504. doi: 10.1007/s11771-021-4717-7
[10] ZHANG Heng, ZHOU Guoxiang, WU Junliang,et al. Mechanism for soil reinforcement by electroosmosis in the presence of calcium chloride[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications,2017,204(4):424 − 433. doi: 10.1080/00986445.2016.1273833
[11] 刘飞禹,吴文清,海钧,等. 絮凝剂对电渗处理河道疏浚淤泥的影响[J]. 中国公路学报,2020,33(2):56 − 63. [LIU Feiyu,WU Wenqing,HAI Jun,et al. Effect of flocculants on electro-osmotic treatment of river dredged sludge[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2020,33(2):56 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2020.02.005
[12] 沈美兰,周太全,李吴刚. 高岭土电渗固结特性及数值模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):78 − 85. [SHEN Meilan,ZHOU Taiquan,LI Wugang. A study of the Kaolin electro-osmotic consolidation characteristics and their numerical simulation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):78 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王耀明, 王柳江, 刘斯宏, 等. 非饱和黏土的一维电渗排水解析理论[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(增刊2): 3767 − 3774
WANG Yaoming, WANG Liujian, LIU Sihong, et al. One-dimensional analytical theory of electro-osmotic drainage for unsaturated clayey soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(Sup 2): 3767 − 3774. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 龚明星,王档良,詹贵贵. 考虑有效电势变化的软土一维电渗固结理论[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(4):61 − 66. [GONG Mingxing,WANG Dangliang,ZHAN Guigui. 1-D electro-osmotic consolidation theory considering variation in effective potential in soft soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(4):61 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2015.04.11
[15] 陶燕丽,周建,龚晓南,等. 铁和铜电极对电渗效果影响的对比试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(2):388 − 394. [TAO Yanli,ZHOU Jian,GONG Xiaonan,et al. Comparative experiment on influence of ferrum and cuprum electrodes on electroosmotic effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(2):388 − 394. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] DALHAT MU’AZU N,ESSA M H. Comparative performance evaluation of anodic materials for electro-kinetic removal of Lead (II) from contaminated clay soil[J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:An International Journal,2020,29(1):69 − 95. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2019.1673698
[17] XUE Zhijia,TANG Xiaowei,YANG Qing,et al. Influence of salt content on clay electro-dewatering with copper and stainless steel anodes[J]. Drying Technology,2019,37(15):2005 − 2019. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2018.1555709
[18] 胡俞晨,王钊,庄艳峰. 电动土工合成材料加固软土地基实验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2005,27(5):582 − 586. [HU Yuchen,WANG Zhao,ZHUANG Yanfeng. Experimental studies on electro-osmotic consolidation of soft clay using EKG electrodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2005,27(5):582 − 586. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.05.020
[19] GLENDINNING S,LAMONT-BLACK J,JONES C. Treatment of sewage sludge using electrokinetic geosynthetics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2007,139(3):491 − 499. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.046
[20] FOURIE A B,JOHNS D G,JONES C J F P. Dewatering of mine tailings using electrokinetic geosynthetics[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2007,44(2):160 − 172. doi: 10.1139/t06-112
[21] 谢新宇,郑凌逶,谢康和,等. 电势梯度与电极间距变化的滨海软土电渗模型试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2019,52(1):108 − 114. [XIE Xinyu,ZHENG Lingwei,XIE Kanghe,et al. Experimental study on electro-osmosis of marine soft soil with varying potential gradient and electrode spacing[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2019,52(1):108 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.20181121.001
[22] WEN Liang. Influence of the electric voltage gradient,electrode spacing and electrode radius on slurry dewatering by vertical electro-osmosis[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science,2020,15(11):11326 − 11339.
[23] 刘飞禹,宓炜,王军,等. 逐级加载电压对电渗加固吹填土的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(12):2582 − 2591. [LIU Feiyu,MI Wei,WANG Jun,et al. Influence of applying stepped voltage in electroosmotic reinforcement of dredger fill[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(12):2582 − 2591. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] ZHANG Heng,MA Qinguo,SU Wenji,et al. On the dewatering of electroosmotic soil using intermittent current incorporated with calcium chloride[J]. Environmental Technology,2019,42(3):468 − 478.
[25] FU Hongtao,FANG Ziquan,WANG Jun,et al. Experimental comparison of electroosmotic consolidation of Wenzhou dredged clay sediment using intermittent current and polarity reversal[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology,2018,36(1):131 − 138.
[26] 庄艳峰. 电渗排水固结的设计理论和方法[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016,38(增刊 1):152 − 155. [ZHUANG Yanfeng. Theory and design method for electro-osmotic consolidation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2016,38(Sup 1):152 − 155. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2016S1028
[27] 温晓贵,胡平川,周建,等. 裂缝对电渗模型尺寸效应影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(11):2054 − 2060. [WEN Xiaogui,HU Pingchuan,ZHOU Jian,et al. Experimental research on influence of cracks on size effect of electro-osmosis model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,36(11):2054 − 2060. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201411011
[28] LING Jianming,HAN Bingye,XIE Yan,et al. Laboratory and field study of electroosmosis dewatering for pavement subgrade soil[J]. Journal of Cold Regions Engineering,2017,31(4):04017010.1 − 04017010.16.
[29] 王柳江, 陈强强, 刘斯宏, 等. 水平排水板真空预压联合电渗处理软黏土模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(增刊2): 3516 − 3525
WANG Liujiang, CHEN Qiangqiang, LIU Sihong, et al. Model test on treatment of soft clay under combined vacuum preloading with electro-osmosis using prefabricated horizontal drain[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(Sup 2): 3516 − 3525. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] ESRIG M I. Pore pressures,consolidation,and electrokinetics[J]. ASCE Soil Mechanics and Foundation Division Journal,1968,94(4):899 − 921. doi: 10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001178
-




 下载:
下载: