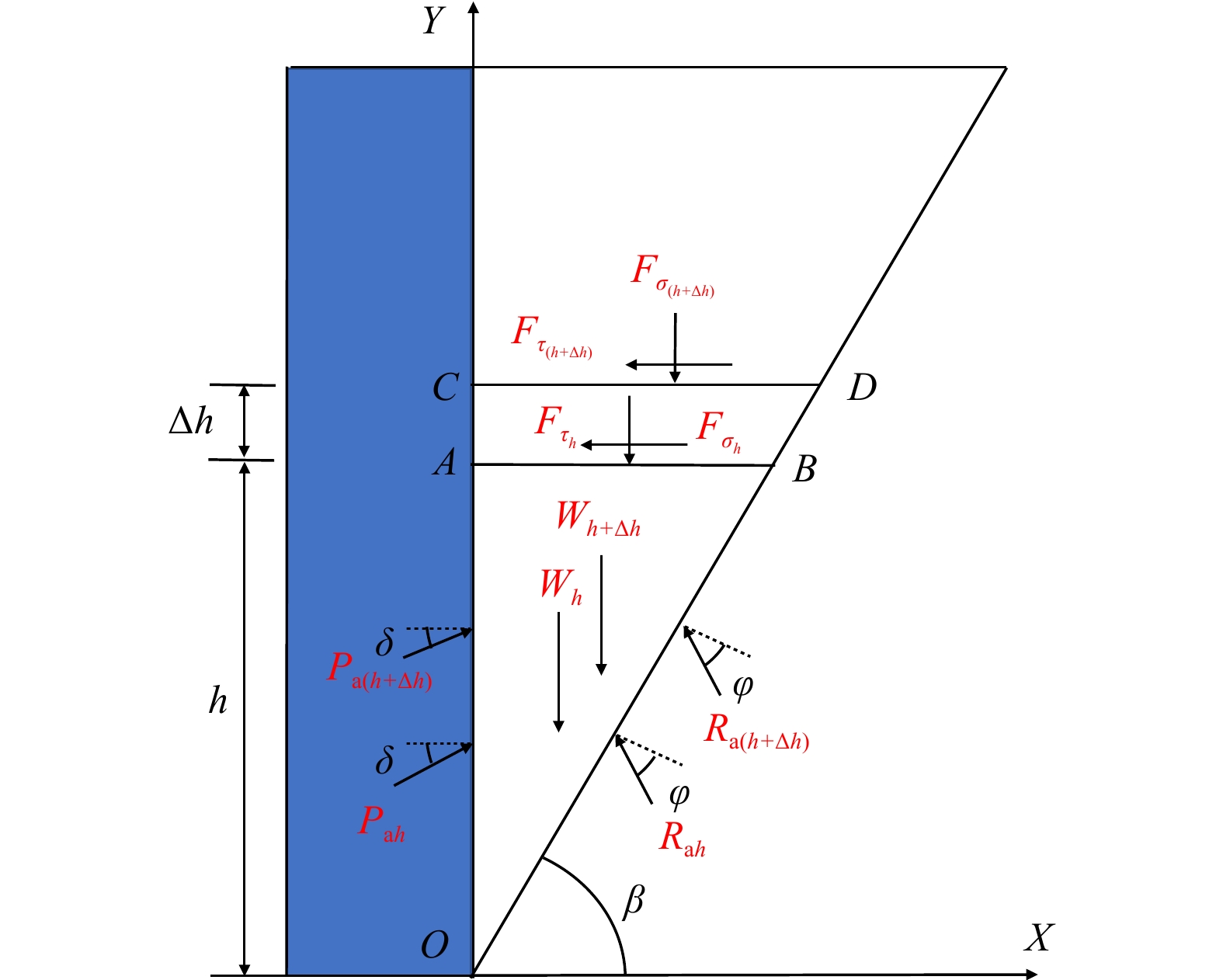
An active earth pressure analysis method of retaining wall considering the influence of uneven interfacial stress distribution
-
摘要:
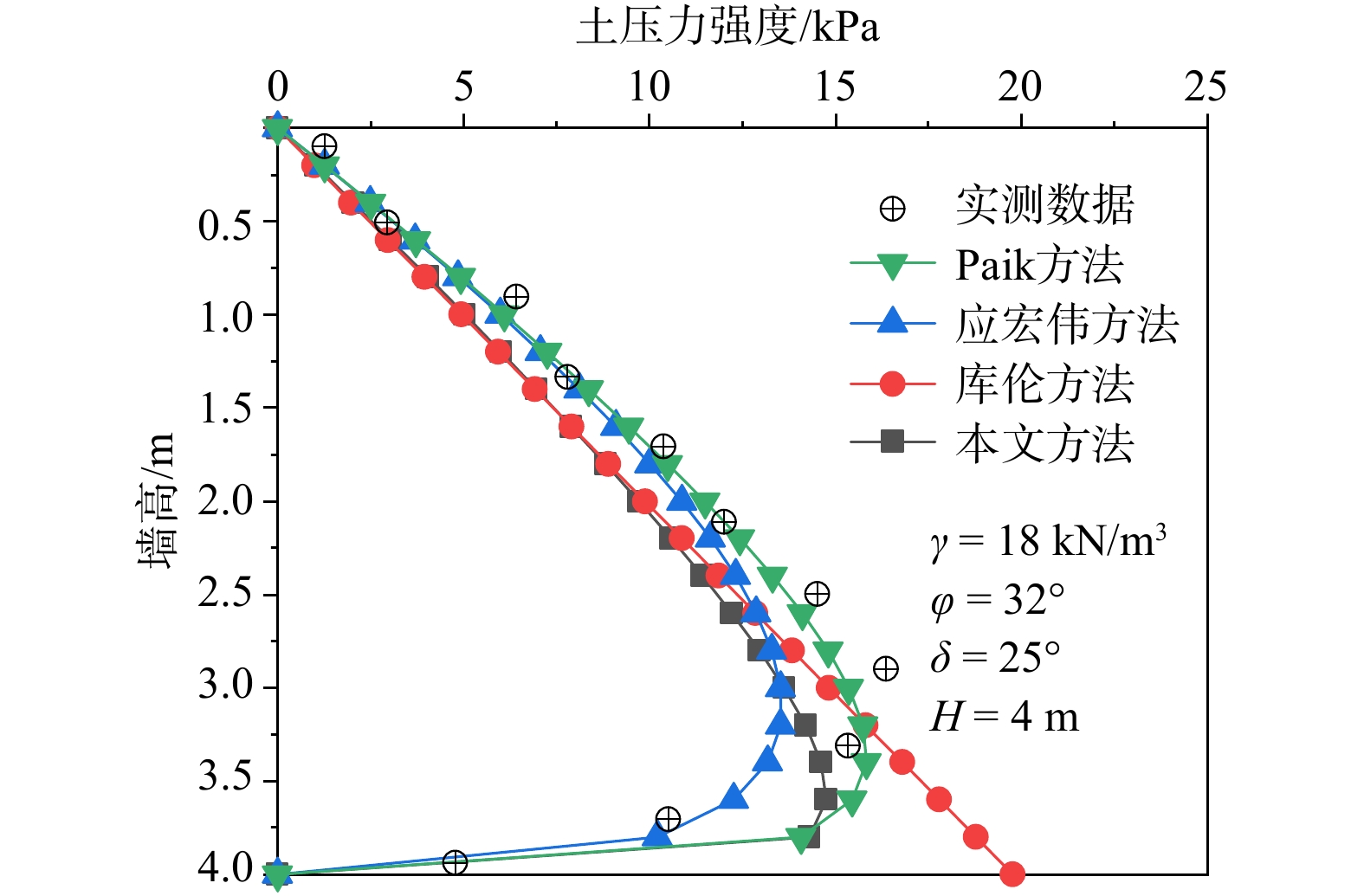
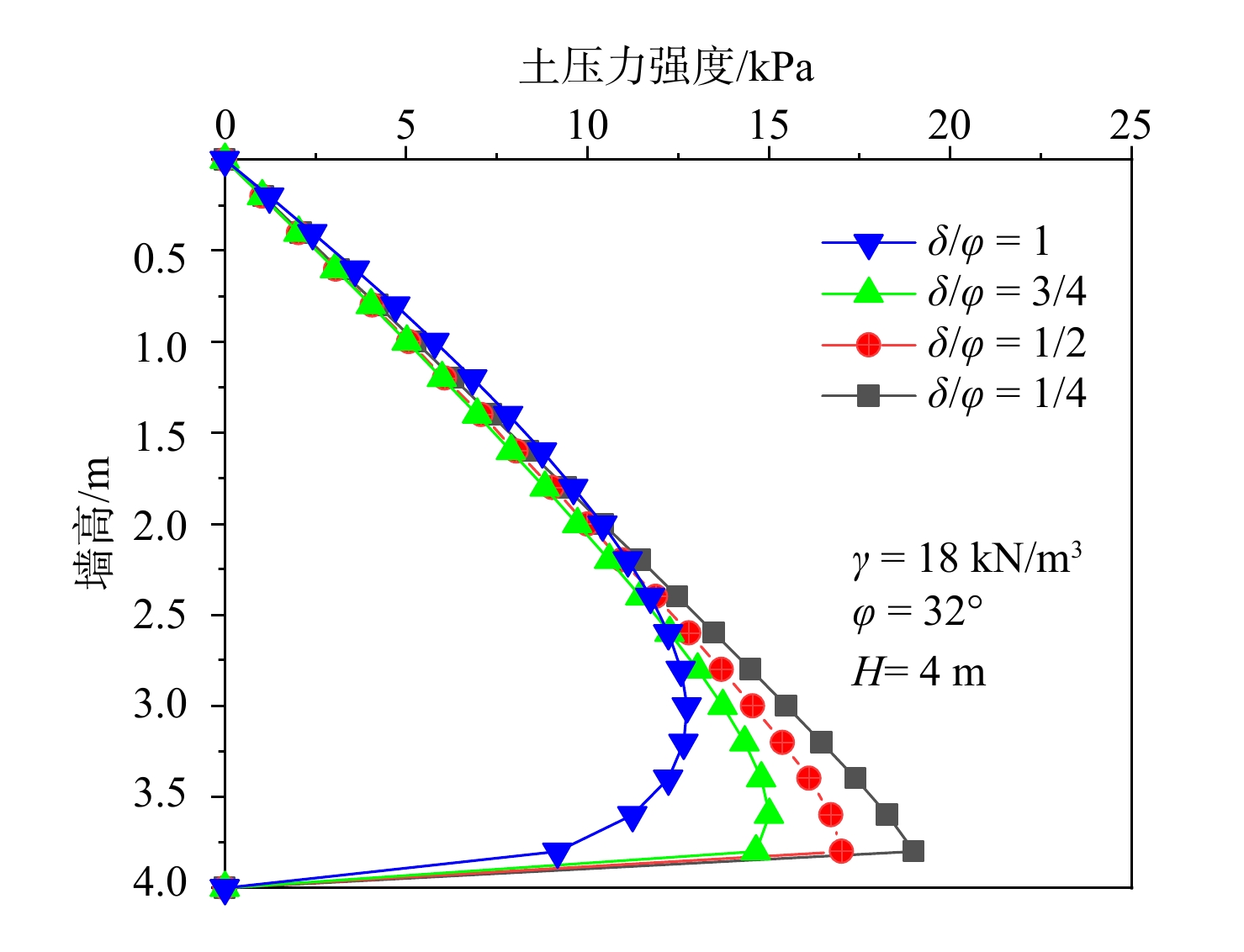
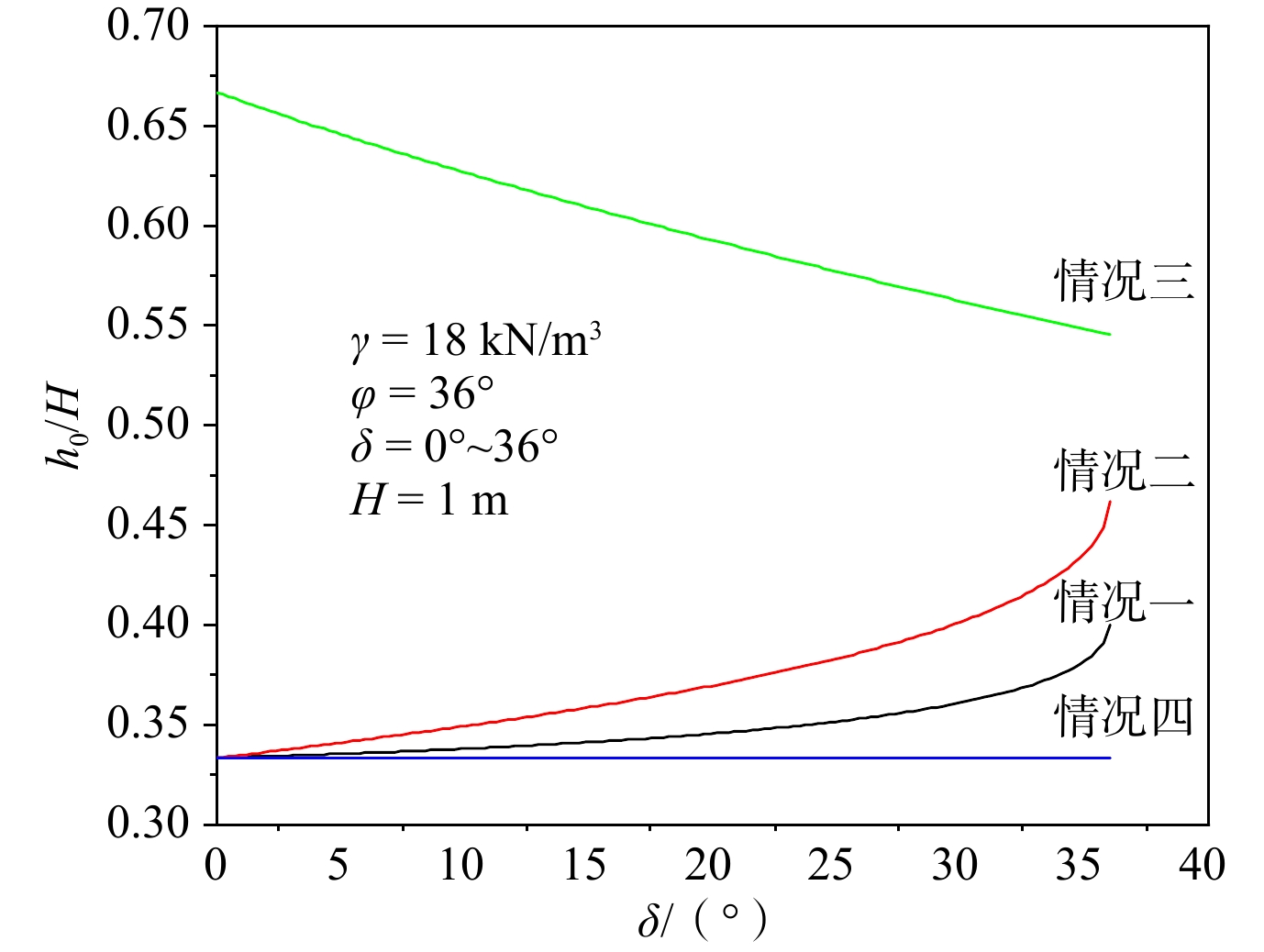
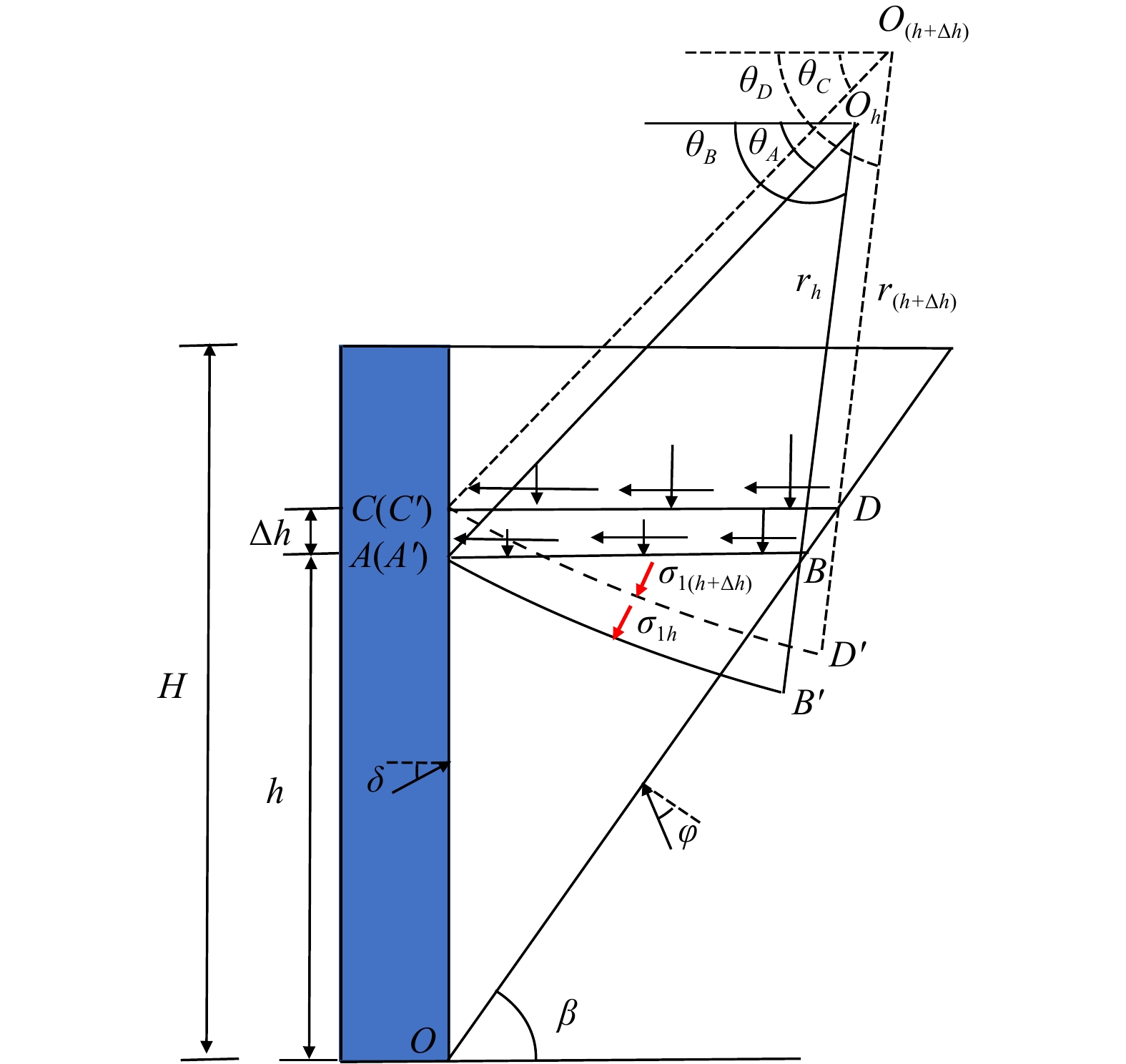
目前关于挡土墙土压力的计算多采用水平分层研究方法,该法在计算分析中常假设分层单元界面上的竖向正应力和水平剪切应力均匀分布,未考虑界面应力分布不均匀对土压力计算结果的影响。为此,本文基于现有的墙后填土应力分布及主应力偏转规律,将界面上不均匀分布的剪应力和正应力等效为作用在楔体单元边界的集中力,通过楔体单元受力分析及其静力平衡条件,建立了可以考虑单元界面剪应力和正应力分布不均匀影响的挡土墙主动土压力分析新方法,并探讨了不均匀界面应力对土压力计算结果的影响。研究结果表明:分层单元不均匀界面应力作为滑动楔体内部土体的内力不会对土压力合力的大小产生影响,但会对土压力分布和土压力合力作用点位置产生影响,且相对于水平剪切应力,竖向正应力对土压力计算结果的影响更大。通过对比论证,发现在考虑界面应力分布不均匀情况下,计算结果可以更准确地描述土压力的分布规律,土压力分布曲线的拐点随着墙土接触摩擦角
$\delta $ $\varphi $ $\delta /\varphi $ Abstract:At present, calculation of the earth pressure of retaining walls mostly adopts the horizontal layered research method. In the calculation and analysis with this method, it is often assumed that the vertical normal stress and horizontal shear stress on the interface of the layered element are uniformly distributed, and influence of the uneven distribution of the interface stress on the earth pressure calculation results is not considered. Based on the existing backfill stress distribution and principal stress deflection law, the shear stress and normal stress that are unevenly distributed on the interface are equivalent to the concentrated force acting on the boundary of the wedge element. Based on the analysis of its static equilibrium conditions, a new method for the active earth pressure analysis of retaining walls that can consider the influence of uneven distribution of shear stress and normal stress at the element interface is established, and the influence of uneven interface stress on the calculation results of earth pressure is discussed. The research results show that the non-uniform interfacial stress of the layered element, as the internal force of the soil inside the sliding wedge, will not affect the magnitude of the resultant earth pressure, but will affect the distribution of the earth pressure and the position of the resultant action point, and it is relative to the resultant earth pressure. Horizontal shear stress and vertical normal stress have greater influence on the calculation results of earth pressure. By comparison and demonstration, it is found that the calculation results can describe the distribution law of earth pressure with reasonable accuracy when considering the uneven distribution of interface stress. The inflection point of the earth pressure distribution curve increases with the decreasing
$\delta $ $\varphi $ $\delta /\varphi $ -

-
[1] TSAGARELI Z V. Experimental investigation of the pressure of a loose medium on retaining walls with a vertical back face and horizontal backfill surface[J]. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering,1965,2(4):197 − 200. doi: 10.1007/BF01706095
[2] FANG Y S,ISHIBASHI I. Static earth pressures with various wall movements[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1986,112(3):317 − 333. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1986)112:3(317
[3] 周应英,任美龙. 刚性挡土墙主动土压力的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,1990,12(2):19 − 26. [ZHOU Yingying,REN Meilong. An experimental study on active earth pressure behind rigid retaining wall[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1990,12(2):19 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1990.02.003
[4] CHANG M F. Lateral earth pressures behind rotating walls[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1997,34(4):498 − 509. doi: 10.1139/t97-016
[5] O’NEAL T S,HAGERTY D J. Earth pressures in confined cohesionless backfill against tall rigid walls—A case history[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2011,48(8):1188 − 1197. doi: 10.1139/t11-033
[6] 顾慰慈. 挡土墙土压力计算[M]. 北京: 中国建材工业出版社, 2002: 235 − 258
GU Weici. Earth pressure calculation of retaining wall [M]. Beijing: China Building Materials Industry Press, 2002: 235 − 258. (in Chinese)
[7] HANDY R. The arch in soil arching[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1985,111(3):302 − 318. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:3(302
[8] PAIK K H,SALGADO R. Estimation of active earth pressure against rigid retaining walls considering arching effects[J]. Géotechnique,2003,53(7):643 − 653. doi: 10.1680/geot.2003.53.7.643
[9] 应宏伟,蒋波,谢康和. 考虑土拱效应的挡土墙主动土压力分布[J]. 岩土工程学报,2007,29(5):717 − 722. [YING Hongwei,JIANG Bo,XIE Kanghe. Distribution of active earth pressure against retaining walls considering arching effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2007,29(5):717 − 722. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.05.014
[10] 章瑞文,徐日庆. 土拱效应原理求解挡土墙土压力方法的改进[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(4):1057 − 1060. [ZHANG Ruiwen,XU Riqing. Solution of problem of earth pressure on retaining wall calculated by method of soil arching effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2008,29(4):1057 − 1060. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.04.038
[11] 俞缙,周亦涛,蔡燕燕,等. 基于土拱效应的刚性挡墙墙后主动土压力[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(12):2306 − 2310. [YU Jin,ZHOU Yitao,CAI Yanyan,et al. Active earth pressure against rigid retaining wall considering soil-arching effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(12):2306 − 2310. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 朱建明,赵琦. 考虑土拱效应的挡土墙主动土压力与被动土压力统一解[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(9):2501 − 2506. [ZHU Jianming,ZHAO Qi. Unified solution to active earth pressure and passive earth pressure on retaining wall considering soil arching effects[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(9):2501 − 2506. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] ZHOU Y T,CHEN Q S,CHEN F Q,et al. Active earth pressure on translating rigid retaining structures considering soil arching effect[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering,2018,22(8):910 − 926. doi: 10.1080/19648189.2016.1229225
[14] 胡卫东,曹文贵,曾律弦,等. 考虑摩擦条件下临近既有建筑物的有限土体土压力上限解[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(5):73 − 79. [HU Weidong,CAO Wengui,ZENG Lyuxian,et al. Upper bound solution of earth pressure for limited soils adjacent to existing buildings considering friction energy consumption[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(5):73 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.05.10
[15] 王佳宇,曹文贵,王雨波,等. 基于圆弧主应力迹线的黏性土主动土压力分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):81 − 88. [WANG Jiayu,CAO Wengui,WANG Yubo,et al. An analysis of active earth pressure of cohesive soil based on the layering of principal stress traces[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):81 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202103006
[16] XIE Y,LESHCHINSKY B. Active earth pressures from a log-spiral slip surface with arching effects[J]. Géotechnique Letters,2016,6(2):149 − 155. doi: 10.1680/jgele.16.00015
[17] HOSSEIN K M,REZA K A,MEHDI A. Active earth pressures for non-planar to planar slip surfaces considering soil arching[J]. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2020,14(7):730 − 739. doi: 10.1080/19386362.2018.1503439
[18] 涂兵雄,贾金青. 考虑土拱效应的黏性填土挡土墙主动土压力研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(5):1064 − 1070. [TU Bingxiong,JIA Jinqing. Research on active earth pressure behind rigid retaining wall from clayey backfill considering soil arching effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(5):1064 − 1070. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.05.025
[19] 同济大学数学系. 高等数学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007
Department of Mathematics, Tongji University. Advanced mathematics [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007. (in Chinese)
-









 下载:
下载: