Numerical modeling of the impacts of reclaimed water recharge to the Chaobai River channel on the ambient shallow groundwater
-
摘要:
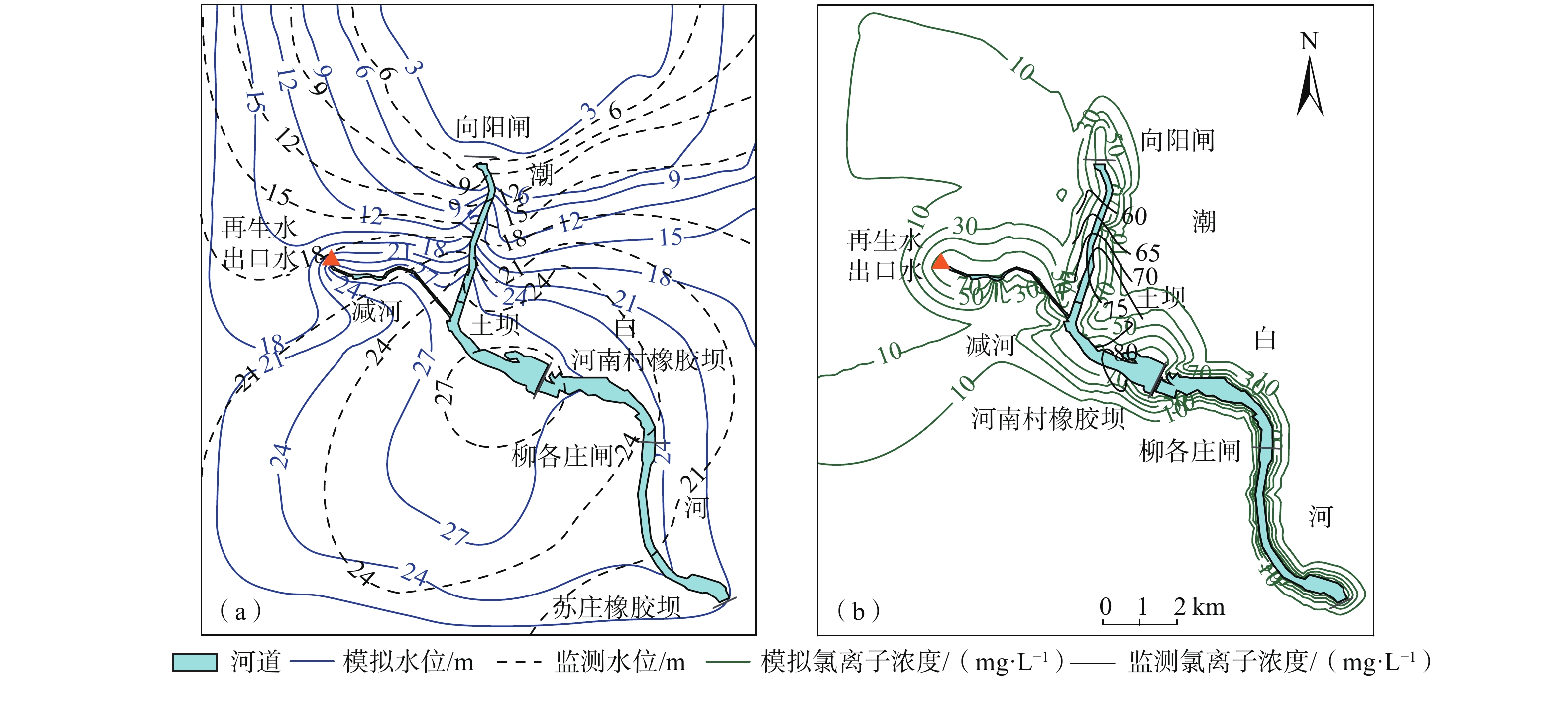
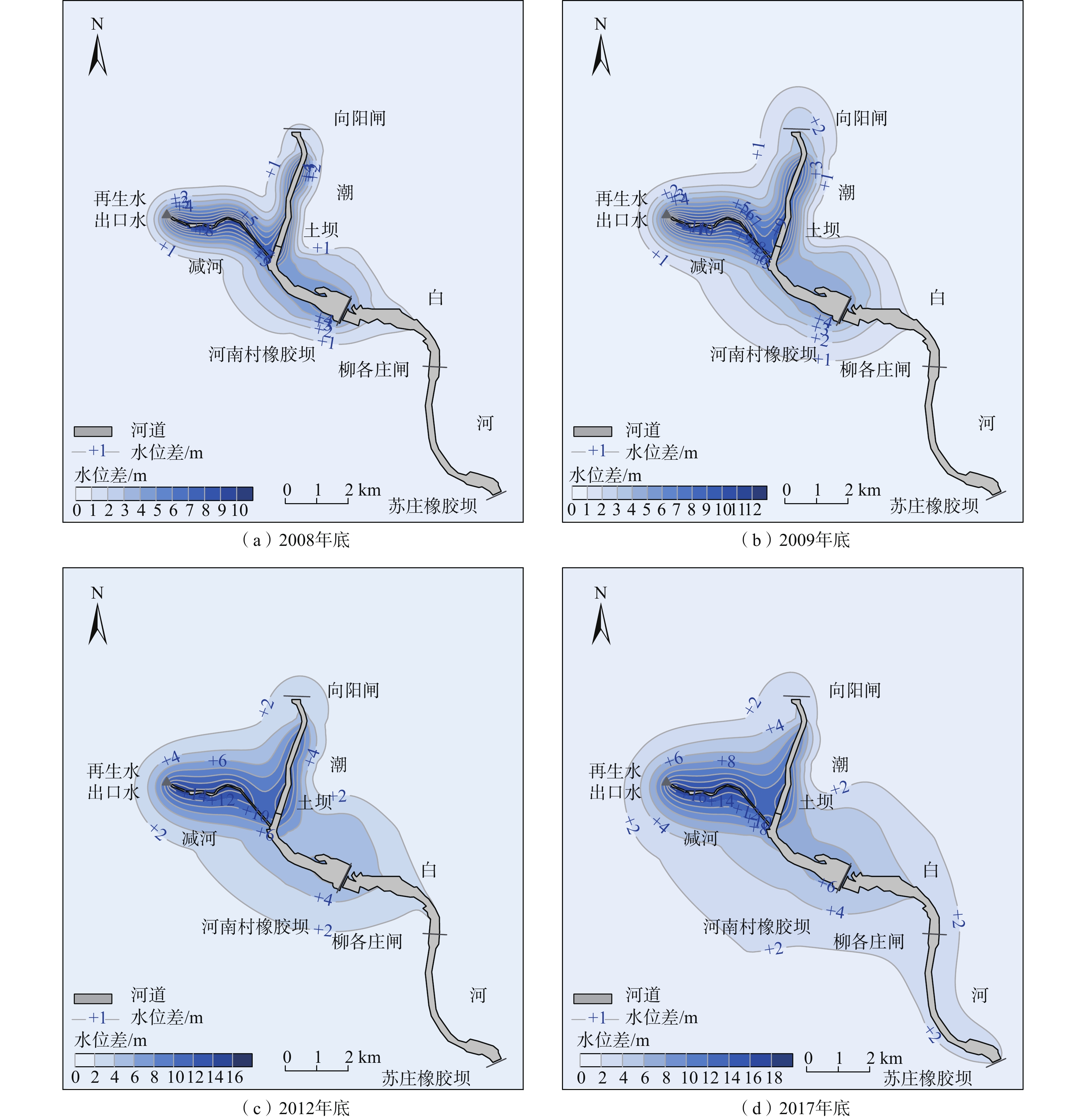
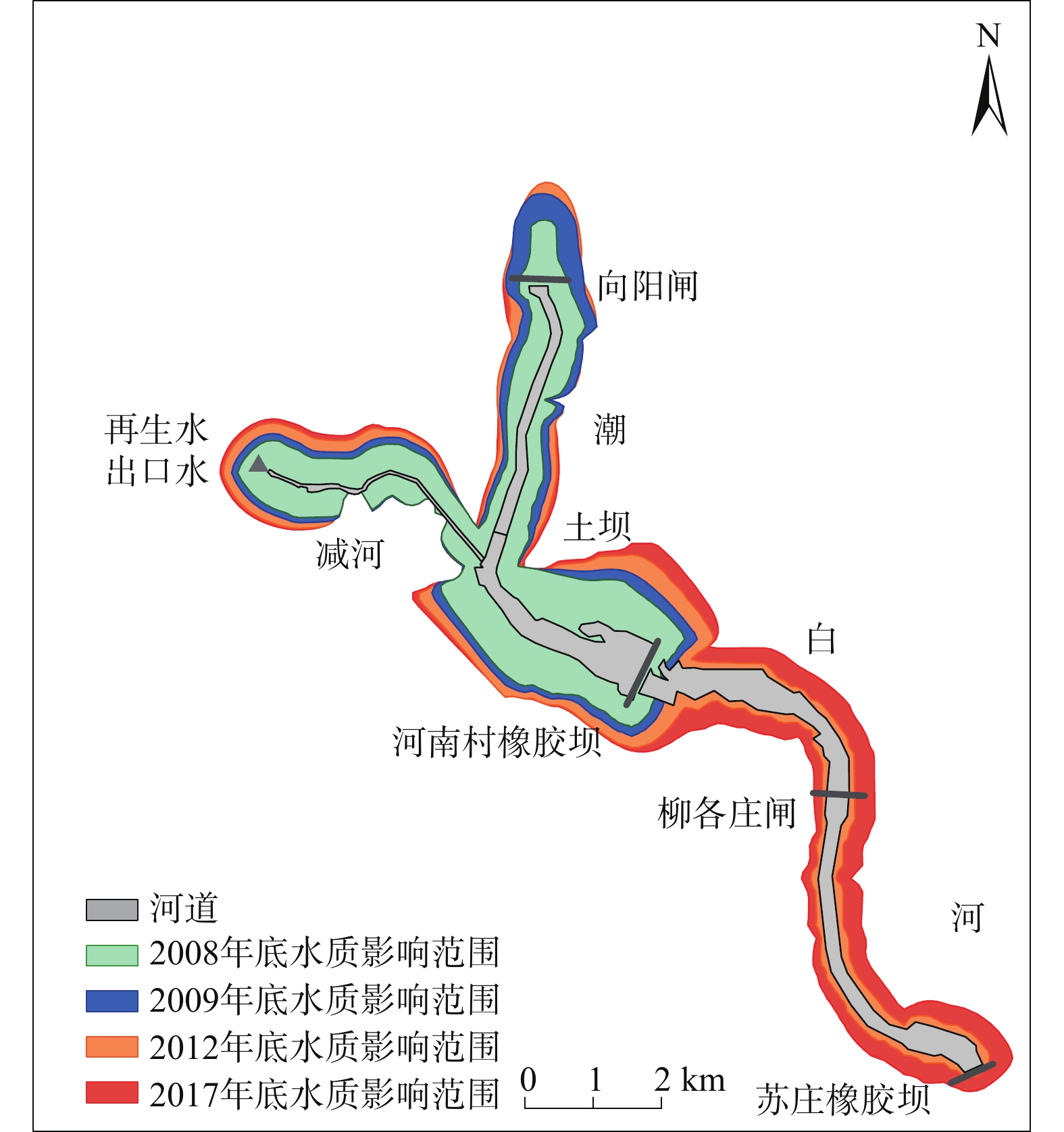
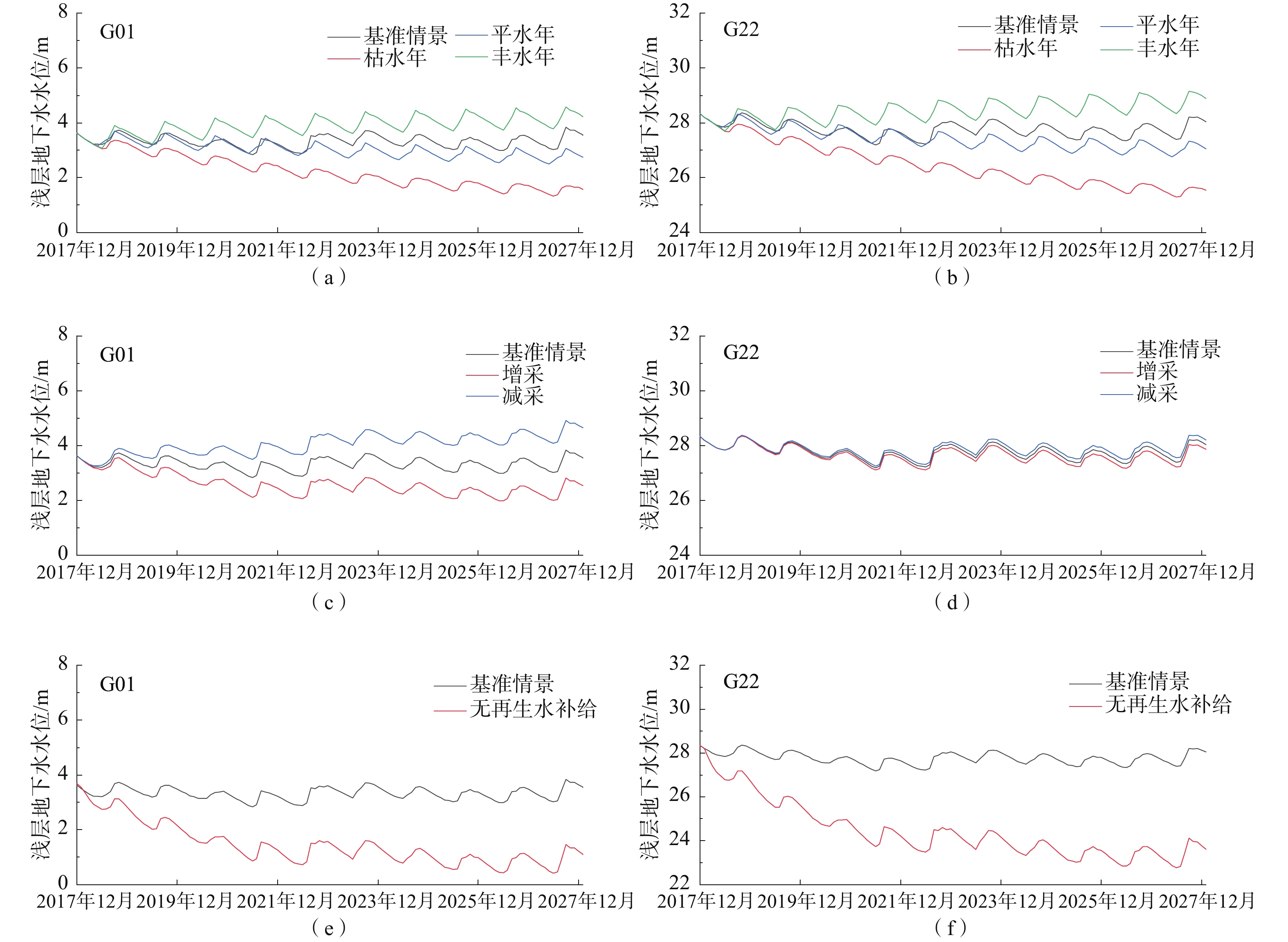
再生水在北京被广泛用于补给河道,2007年底至2017年共有2.3×108 m3再生水补给至潮白河顺义段。其污染物本底值较高(Cl−浓度约62~122 mg/L),通过河床入渗补给到周边的含水层中,对周边地下水产生一定影响,尤其是浅层地下水。为了定量评价再生水补给河道对周边浅层地下水的影响,基于10年(2007—2017)的地下水监测数据,建立了再生水补给河道周边的地下水水流和溶质运移模型,模拟了受水区浅层地下水的水位和Cl−浓度的变化,分析了浅层地下水水量、Cl−负荷和NO3-N负荷的变化。结果表明,再生水补给河道后的前2年(2007—2009),河道周边浅层地下水水位迅速抬升了3~4 m,之后在再生水的持续补给下保持稳定。但受深层地下水开采影响,2007—2014年研究区整体浅层地下水的水量仍在下降。2014年底实施地下水压采措施后,浅层地下水水量从2014年底的3.76×108 m3恢复到了2017年底的3.85×108 m3。周边浅层地下水中的Cl−浓度从再生水补给前的5~75 mg/L变化到了补给后的50~130 mg/L,之后保持稳定。浅层地下水水质受再生水影响的范围从2008年底的11.7 km2扩大到2017年的26.7 km2,影响区内的Cl−负荷从2008年底的1.8×103 t增加到2017年底的3.8×103 t,NO3-N负荷从2008年的29.8 t下降到2017年的11.9 t。尽管研究显示影响范围外的浅层地下水质受再生水影响不明显,但潜在的咸化和污染的隐患不容忽视,需要在后续研究中进一步明确。
Abstract:Reclaimed water has been widely used to recharge river channels in Beijing, with 2.3×108 m3 of reclaimed water recharge to the Shunyi section of the Chaobai River from the end of 2007 to 2017. It has a high background value of pollutants (Cl− concentration ranging from 62 to 122 mg/L) and recharges the ambient aquifers, which has an impact on the ambient groundwater through riverbank filtration, particularly on the shallow groundwater. Based on 10-year series groundwater monitoring data (2007−2017), we conducte a 3D groundwater flow and solute transport model to simulate the variations of the shallow groundwater table and chloride concentrations, and analyze the variations in groundwater storage, Cl− loads, and NO3-N loads in the shallow aquifers near the Chaobai River receiving reclaimed water. The results demonstrate that the ambient groundwater table swiftly rose by about 3−4 m following the reclaimed water replenishment from 2007 to 2009, and stayed steady under the condition of continuous replenishment of reclaimed water. However, affected by the exploitation of deep groundwater, the groundwater storage in the unconfined aquifer still decreased overall from 2007 to 2014. After reducing the groundwater extraction since 2014, the shallow groundwater storage recovered from 3.76×108 m3 at the end of 2014 to 3.85×108 m3 at the end of 2017. Cl− concentrations in the ambient shallow groundwater changed from a range of 5−75 mg/L before the recharge to 50−130 mg/L after the recharge (2007−2009), and then remained stable. The areas of shallow groundwater quality affected by reclaimed water infiltration expanded from 11.7 km2 in 2008 to 26.7 km2 in 2017. The Cl− loads in the affected areas increased from 1.8×103 t in 2008 to 3.8×103 t in 2017. The NO3-N loads decreased from 29.8 t in 2008 to 11.9 t in 2017. Although the results show that the shallow groundwater quality outside the affected area is not significantly affected by the reclaimed water, the potential salinization and pollution cannot be ignored and need to be further clarified in the subsequent studies.
-
Key words:
- reclaimed water /
- groundwater /
- numerical model /
- groundwater level /
- water quality /
- Chaobai River
-

-
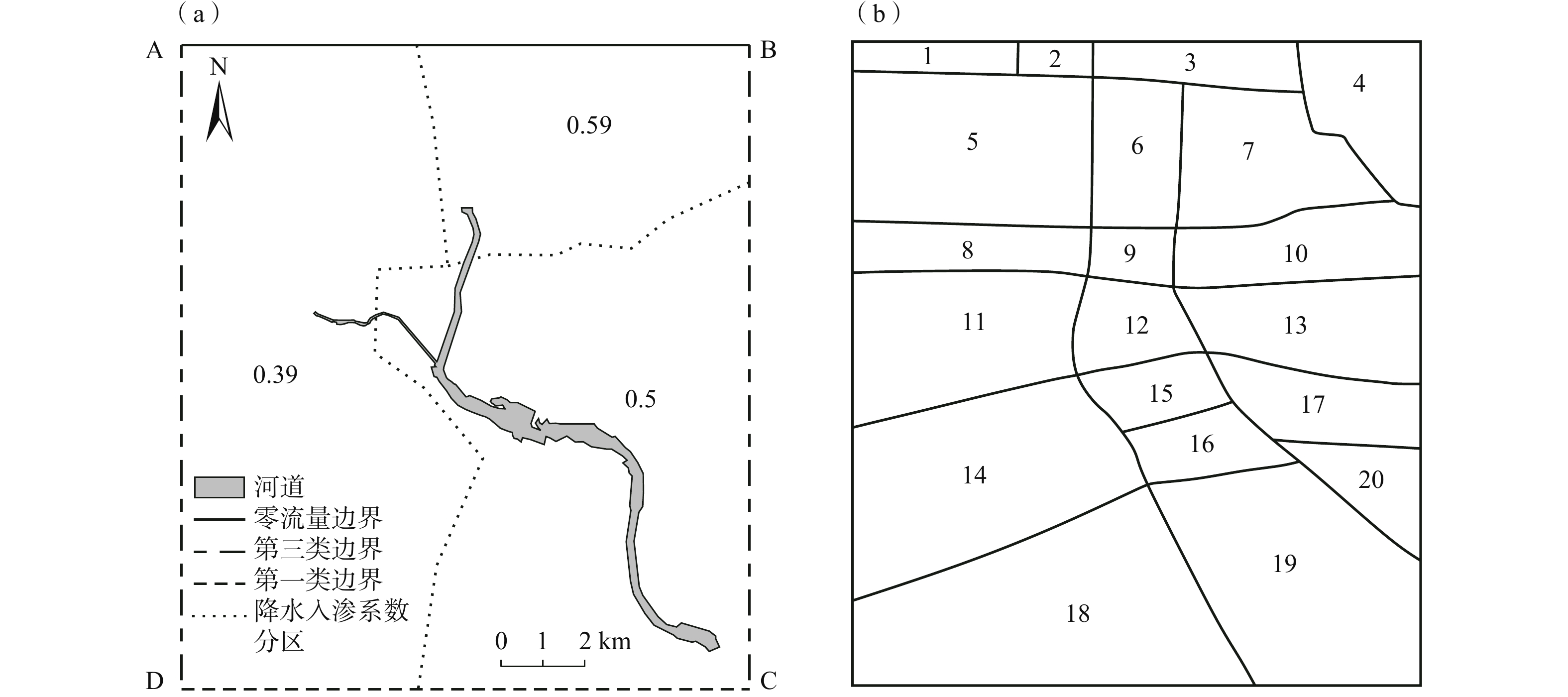
表 1 校准后的模型参数
Table 1. Hydrogeological parameters used in the calibrated model
水文地质单元 K/(10−4 m·s−1) S n αL/m αT/m 潜水含水层 0.1~9.5 0.11~0.26 0.11~0.26 1.5~12 0.1~1.2 第1弱透水层 3×10−5~5×10−4 1.1×10−4~1.5×10−4 0.07~0.11 0.5~0.7 0.05~0.07 第1承压含水层 0.5~9.9 3×10−6~1.4×10−4 0.08~0.24 1~12 0.1~1.2 第2、3弱透水层 9×10−5~0.1 1×10−5~1.5×10−4 0.07~0.16 0.5~0.85 0.05~0.08 第2、3承压含水层 0.6~9 2×10−5~4×10−4 0.11~0.24 1.2~12 0.12~1.2 表 2 模型预测情景设计
Table 2. Scenario design for the groundwater model
情景 降水量
/(mm·a−1)地下水开采量
/(107 m3·a−1)再生水补给量
/(107 m3·a−1)基准情景 592.8~1053.1 4.26 2.89 1 454.8 4.26 2.89 2 574.6 4.26 2.89 3 710.9 4.26 2.89 4 592.8~1053.1 3.57 2.89 5 592.8~1053.1 4.94 2.89 6 592.8~1053.1 4.26 0 表 3 2007年底至2017年底潜水含水层水均衡统计
Table 3. Groundwater budget in the unconfined aquifer from December, 2007 to Deccember, 2017
补给 水量/(108 m3) 比例 排泄 水量/(108 m3) 比例 降水入渗 7.57 84.6% 越流 9.97 97.4% 侧向流入 0.78 8.7% 侧向流出 0.23 2.2% 再生水入渗 0.59 6.7% 蒸发 0.04 0.4% 补给总量 8.94 100% 排泄总量 10.24 100.0% 总补排差/(108 m3) −1.30 -
[1] WENDLING Z A, EMERSON J W, DE SHERBININ A, et al. 2020 environmental performance index[J/OL]. New Haven, CT: Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy, 2020(2021-01-12)[2021-04-23]. epi. yale. edu.
[2] ANGELAKIS A N,GIKAS P. Water reuse:Overview of current practices and trends in the world with emphasis on EU states[J]. Water Utility Journal,2014,8(67):e78.
[3] DENG S,YAN X,ZHU Q,et al. The utilization of reclaimed water:Possible risks arising from waterborne contaminants[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,254:113020. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113020
[4] ZHU Z,DOU J. Current status of reclaimed water in China:An overview[J]. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination,2018,8(3):293 − 307. doi: 10.2166/wrd.2018.070
[5] 周军,杜炜,张静慧,等. 北京市再生水行业的现状与发展[J]. 中国建设信息(水工业市场),2009(9):12 − 14. [ZHOU Jun,DU Wei,ZHANG Jinghui,et al. Status and development of Beijing reclaimed water industry[J]. Information of China Construction Water-Industry Market,2009(9):12 − 14. (in Chinese)
[6] 北京市水务局. 北京市水资源公报(2003年度)[R]. 北京: 北京市水务局, 2004
Beijing Water Authority. Beijing water resources bulletin (2003)[R]. Beijing: Beijing Water Authority, 2004. (in Chinese)
[7] 北京市水务局. 北京市水资源公报(2020年度)[R]. 北京: 北京市水务局, 2021
Beijing Water Authority. Beijing water resources bulletin (2021)[R]. Beijing: Beijing Water Authority, 2021. (in Chinese)
[8] 胡立堂,郭建丽,张寿全,等. 永定河生态补水的地下水水位动态响应[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):5 − 11. [HU Litang,GUO Jianli,ZHANG Shouquan,et al. Response of groundwater regime to ecological water replenishment of the Yongding River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):5 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] HE Z,HAN D,SONG X,et al. Variations of groundwater dynamics in alluvial aquifers with reclaimed water restoring the overlying river,Beijing,China[J]. Water,2021,13(6):806. doi: 10.3390/w13060806
[10] 姜瑞雪,韩冬梅,宋献方,等. 再生水补给河道周边水体特征—以北京潮白河顺义段为例[J]. 资源科学,2020,42(12):2419 − 2433. [JIANG Ruixue,HAN Dongmei,SONG Xianfang,et al. Impacts of reclaimed water recharge to a river channel on ambient water bodies:A case study of the Chaobai River in Beijing[J]. Resources Science,2020,42(12):2419 − 2433. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.12.13
[11] 李丛舟. 再生水河道渗透补给下的地下水水质演化特征分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2019
LI Congzhou. Analysis of evolution characteristics of groundwater quality under river infiltration recharge with reclaimed water[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 刘立才,单悦,黄俊雄,等. 河道再生水入渗的水岩相互作用机理研究[J]. 水资源保护,2018,34(1):31 − 35. [LIU Licai,SHAN Yue,HUANG Junxiong,et al. Interaction mechanism experiment of water and rocks in infiltration of reclaimed water[J]. Water Resources Protection,2018,34(1):31 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2018.01.06
[13] LI J, FU J, ZHANG H, et al. Spatial and seasonal variations of occurrences and concentrations of endocrine disrupting chemicals in unconfined and confined aquifers recharged by reclaimed water: A field study along the Chaobai River, Beijing[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2013, 450–451: 162–168.
[14] 吴苗苗. 再生水回灌过程中典型磺胺类抗生素的行为特性研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2015
WU Miaomiao. The behavior of typical sulfanomides in soil by groundwater recharge with reclaimed water[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 北京市水务局. 北京市水资源公报(2007年度)[R]. 北京: 北京市水务局, 2008
Beijing Water Authority. Beijing water resources bulletin (2007)[R]. Beijing: Beijing Water Authority, 2008. (in Chinese)
[16] 北京市水科学技术研究院. 引温济潮工程受水区地表地下水环境监测评价(2017年度)[R]. 北京: 北京市水科学技术研究院, 2017
Beijing Water Science And Technology Institution. Environmental monitoring and assessment of surface water and groundwater in the water receiving area of the “Yin Wen Ji Chao” Project (2017)[R]. Beijing: Beijing Water Science and Technology Institution, 2017 . (in Chinese)
[17] 熊燕娜. 再生水入渗过程中三氮迁移转化模拟柱实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2009
XIONG Yanna. The simulated columns tests on the nitrogen transformation and biodegradation during the reclaimed water Infiltration through the vadose[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 国家气象科学数据中心. 中国地面气候资料月值数据集[EB/OL]. (2019-11-07)[2021-02-22]. http://data.cma.cn/data/cdcdetail/dataCode/SURF_CLI_CHN_MUL_MON.html
China Meteorological Administration Data Center. Monthly Data Set of Surface Climatological Data for Beijing[EB/OL]. (2019-11-07)[2021-02-22]. http://data.cma.cn/data/cdcdetail/dataCode/SURF_CLI_CHN_MUL_MON.html.(in Chinese)
[19] 霍思远. 潜水位下降对入渗补给的影响研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2015
HUO Siyuan. Research on the effect of water table decline on vertical groundwater recharge[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 郑凡东. 再生水作为河湖景观用水的地下水环境效应研究——以潮白河为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2012
ZHENG Fandong. A case study on effects of reclaimed water use for scenic water on groundwater environment in Chaobai River[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] ZHANG Y,YU Y. Evaluating the impact of percolated reclaimed water from river-channel reservoir on groundwater using tracers in Beijing,Northern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2021,80(4):138. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09449-1
[22] 刘庄,晁建颖,张丽,等. 中国非点源污染负荷计算研究现状与存在问题[J]. 水科学进展,2015,26(3):432 − 442. [LIU Zhuang,CHAO Jianying,ZHANG Li,et al. Current status and problems of non-point source pollution load calculation in China[J]. Advances in water science,2015,26(3):432 − 442. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] LI S,BIAN R,LI B,et al. Hyporheic zone geochemistry of a multi-aquifer system used for managed aquifer recharge in Beijing,China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2021,131:105032. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105032
[24] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 生活饮用水卫生标准: GB 5749-2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006
National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Sanitary standards of drinking water: GB 5749-2006 [S]. Beijing: China Quality and Standards Publishing & Media Co. Ltd. , 2006. (in Chinese)
[25] PAN W,HUANG Q,HUANG G. Nitrogen and organics removal during riverbank filtration along a reclaimed water restored river in Beijing,China[J]. Water,2018,10(4):491. doi: 10.3390/w10040491
[26] LI C,LI B,BI E. Characteristics of hydrochemistry and nitrogen behavior under long-term managed aquifer recharge with reclaimed water:A case study in north China[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2019,668:1030 − 1037. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.375
[27] 熊凯, 宫兆宁, 张磊, 等. 再生水补水条件下土壤全氮空间分布特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2017,47(6):1829 − 1837. [XIONG Kai, GONG Zhaoning, ZHANG Lei, et al. Spatial distribution of total soil nitrogen under reclaimed water recharge[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2017,47(6):1829 − 1837. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] TRAUTH N,MUSOLFF A,KNÖLLER K,et al. River water infiltration enhances denitrification efficiency in riparian groundwater[J]. Water Research,2018,130:185 − 199. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.11.058
[29] 刘鑫,左锐,王金生,等. 地下水水位波动带三氮迁移转化过程研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):27 − 36. [LIU Xin,ZUO Rui,WANG Jinsheng,et al. Advances in researches on ammonia,nitrite and nitrate on migration and transformation in the groundwater level fluctuation zone[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):27 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 夏绮文,李炳华,何江涛,等. 潮白河再生水生态补给河道区浅层地下水氮转化[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,34(3):618 − 628. [XIA Qiwen,LI Binghua,HE Jiangtao,et al. Nitrogen transformation of shallow groundwater in the river area of ecological recharge of reclaimed water in Chaobai River[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,34(3):618 − 628. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.07.22
[31] BÖHLKE J K,SMITH R L,MILLER D N. Ammonium transport and reaction in contaminated groundwater:Application of isotope tracers and isotope fractionation studies[J]. Water Resources Research,2006,42(5):W05411.
-




 下载:
下载: