Response of water cycle to precipitation in Shizhiyan underground river system in Huixian wetland of Guilin
-
摘要:
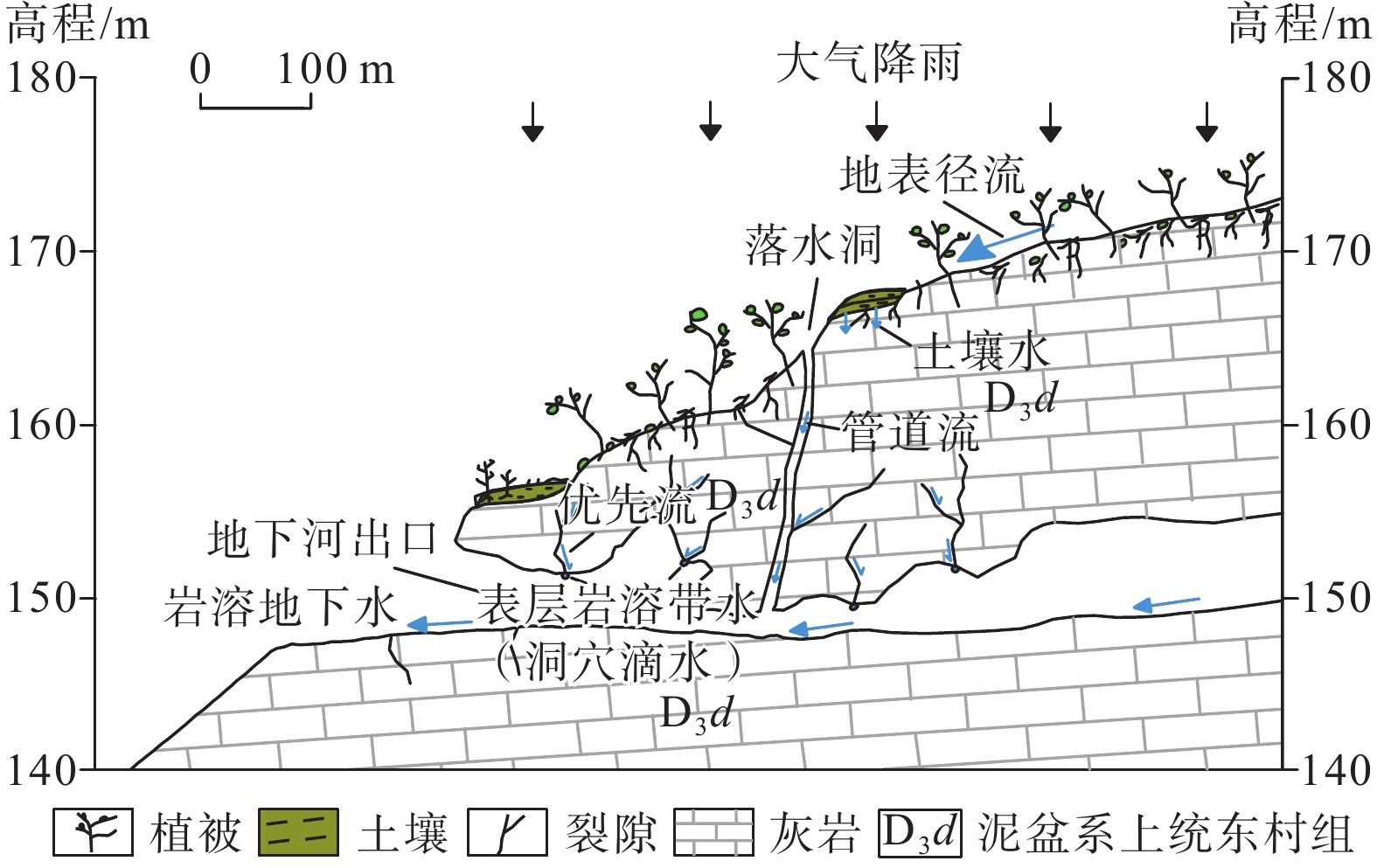
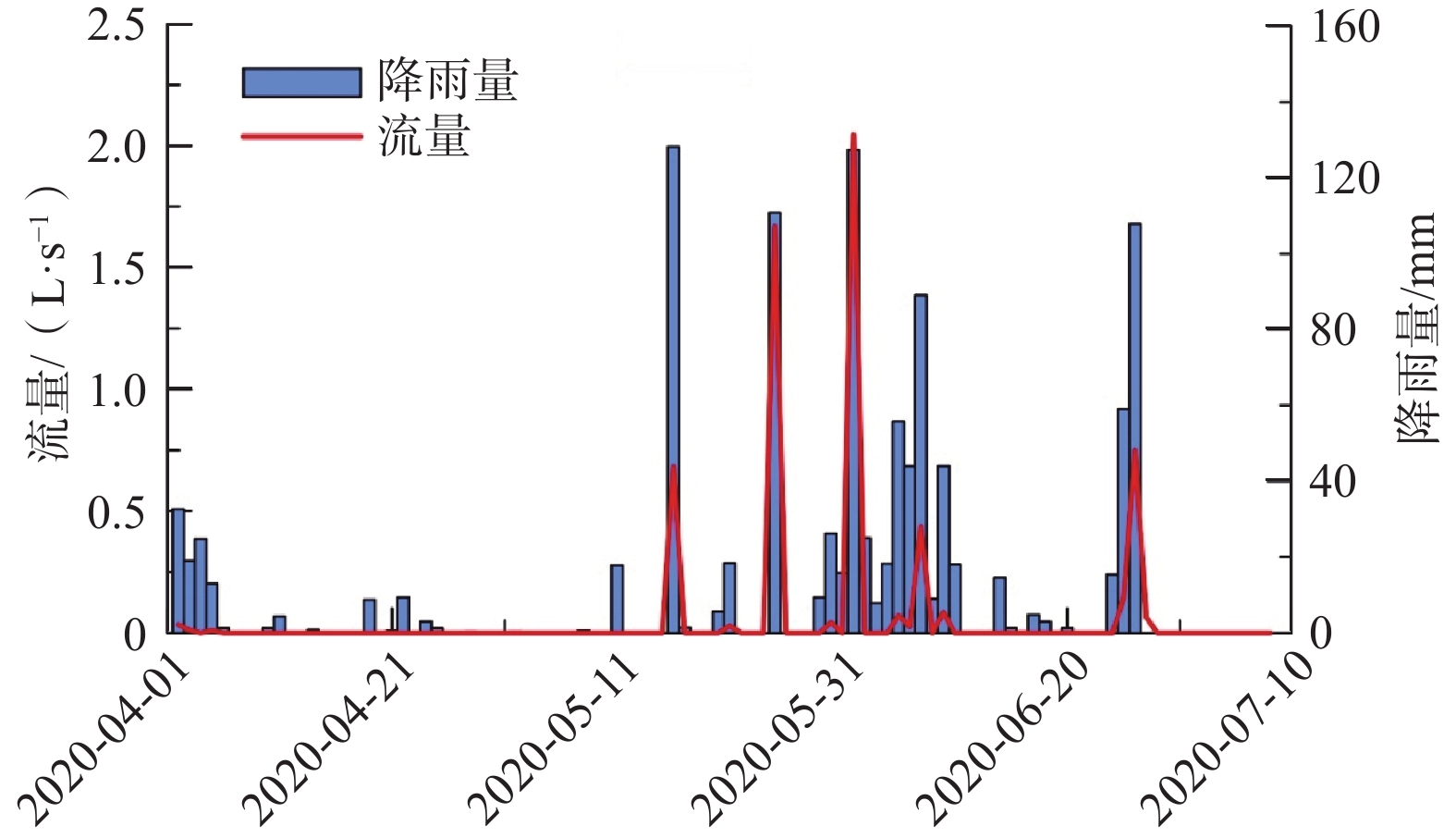
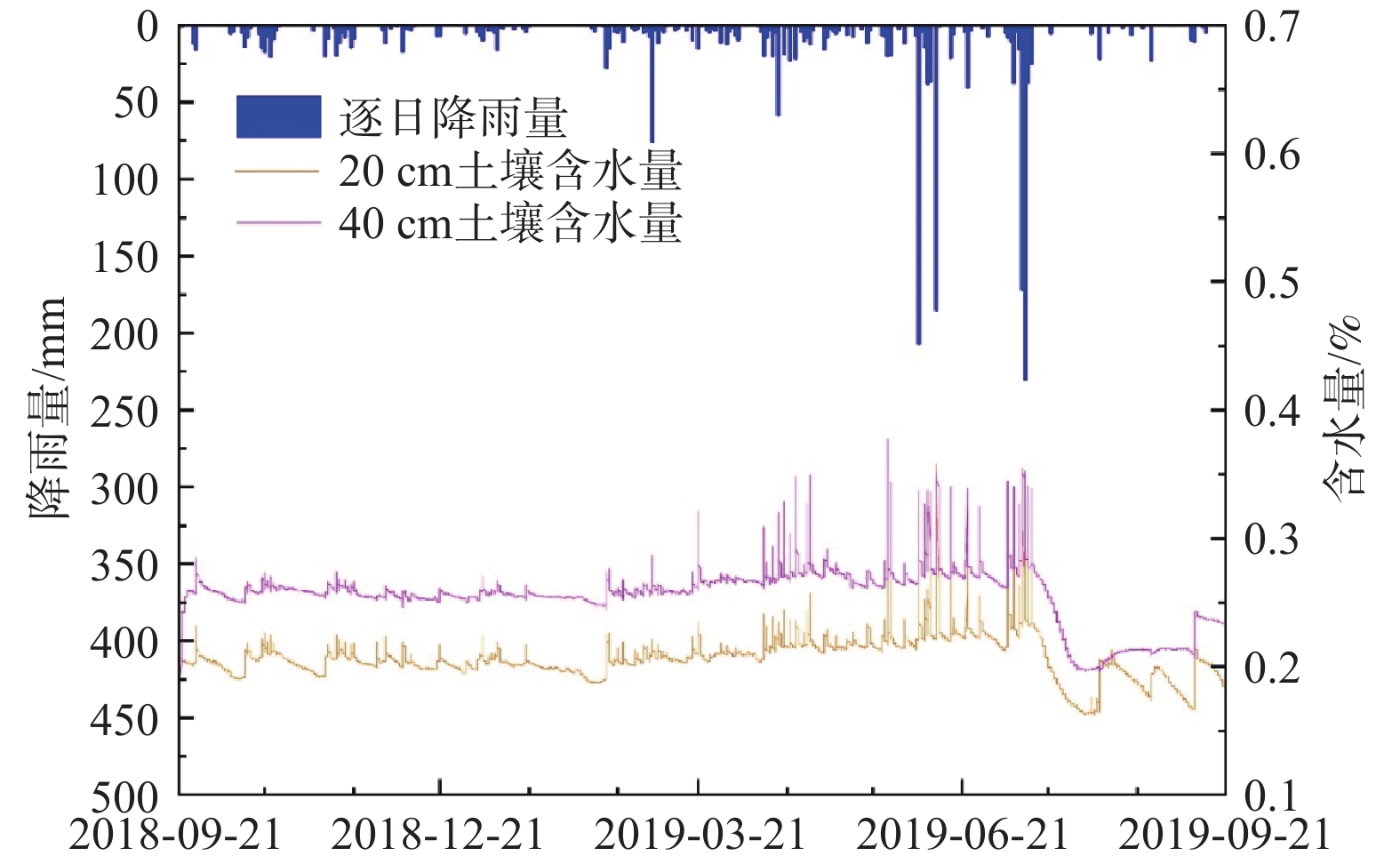
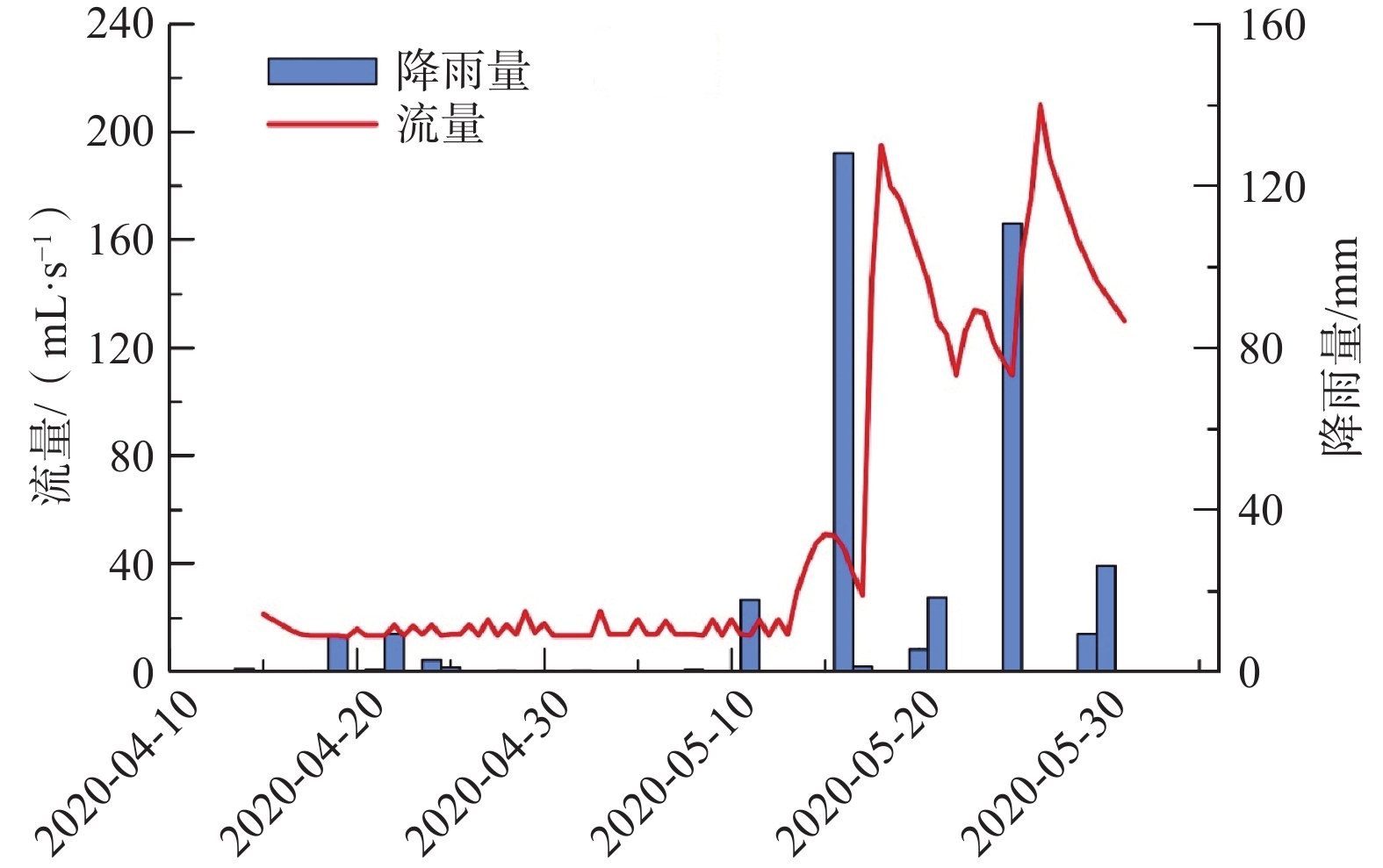
岩溶湿地是西南岩溶生态系统的重要调节器,对该地区的可持续发展有重要意义,而水循环作为维系岩溶湿地健康运转的核心因素,已经成为当前的研究热点。2020年4月15日—5月30日野外监测了桂林会仙湿地狮子岩地下河系统参数,采用水文动态分析与水均衡等方法,开展了地下河系统水循环研究。结果表明:(1)地表径流、土壤水、表层岩溶带水和岩溶地下水均对大气降雨响应敏感,但敏感程度有差异,其中岩溶地下水的敏感性最高,地表径流和表层岩溶带水的敏感性较弱,土壤水的敏感性受深度影响较大。(2)不同等级降雨中地下河系统的各类水变化量的比例有差异。本次研究中,小雨(24 h累计降雨量范围为4.2~10 mm)时系统内土壤水变化量比例最大,约为75.87%;中雨(24 h累计降雨量为17.8 mm)时土壤水变化量和岩溶地下水变化量的比例最大,分别约为43.38%和44.12%,大雨(24 h累计降雨量为24 mm)和大暴雨(24 h累计降雨量范围为110.8~128.2 mm)时岩溶地下水变化量比例最大,约为66.48%。(3)研究区调蓄系数平均值约为0.53,明显高于其他岩溶地区,表现出较强的调蓄能力,且随着降雨量的增大,调蓄系数逐渐减小。(4)地下河系统水循环概念模型包含大气降雨、地表径流、土壤水、表层岩溶带水和岩溶地下水之间的转化关系及转化量,建立概念模型可为岩溶湿地水资源开发利用和湿地保护提供理论基础。
Abstract:Karst wetland is an important regulator of karst ecosystems in southwest China and is of great significance to the sustainable development of the region. Water cycle, as the core factor to maintain the healthy operation of karst wetlands, has become a hot topic in current researches. Based on the field monitoring data of the Shizhiyan underground river system in the Guilin Huixian Wetland from April 15, 2020 to May 30, 2020, hydrological dynamic analysis and water balance are used to study the water cycle of the underground river system. The results show that (1) surface runoff, soil water, surface karst zone water and karst groundwater are sensitive to atmospheric rainfall, but the sensitivity degree is different. The sensitivity of karst groundwater is the highest, the sensitivity of surface runoff and surface karst zone water is weak, and the sensitivity of soil water is greatly affected by depth. (2) The proportion of all kinds of water circulation in the underground river system is different at different grades of rainfall, and the proportion of soil water in the system is the largest in light rain (24 h cumulative rainfall ranges from 4.2 mm to 10 mm), which accounts for about 75.87%. The proportion of soil water and karst groundwater in moderate rain (24 h cumulative rainfall is 17.8 mm) is the largest, which is about 43.38% and 44.12%, respectively. The proportion of karst groundwater in heavy rain (24 h cumulative rainfall is 24 mm) and heavy rainstorm (24 h cumulative rainfall ranges from 110.8 mm to 128.2 mm) is the largest, accounting for about 66.48%. (3) The average coefficient of regulation and storage in the study area is about 0.53, which is significantly higher than that of other karst areas, showing strong regulation and storage capacity. With the increasing rainfall, the coefficient of regulation and storage gradually decreases. (4) The conceptual model of water cycle of underground river system includes the transformation relationship and transformation amount among atmospheric rainfall, surface runoff, soil water, surface karst zone water and karst groundwater. The establishment of the conceptual model can provide a theoretical basis for the development and utilization of water resources and wetland protection of karst wetland.
-
Key words:
- wetland /
- karst /
- water cycle /
- storage coefficient /
- hydrological processes
-

-
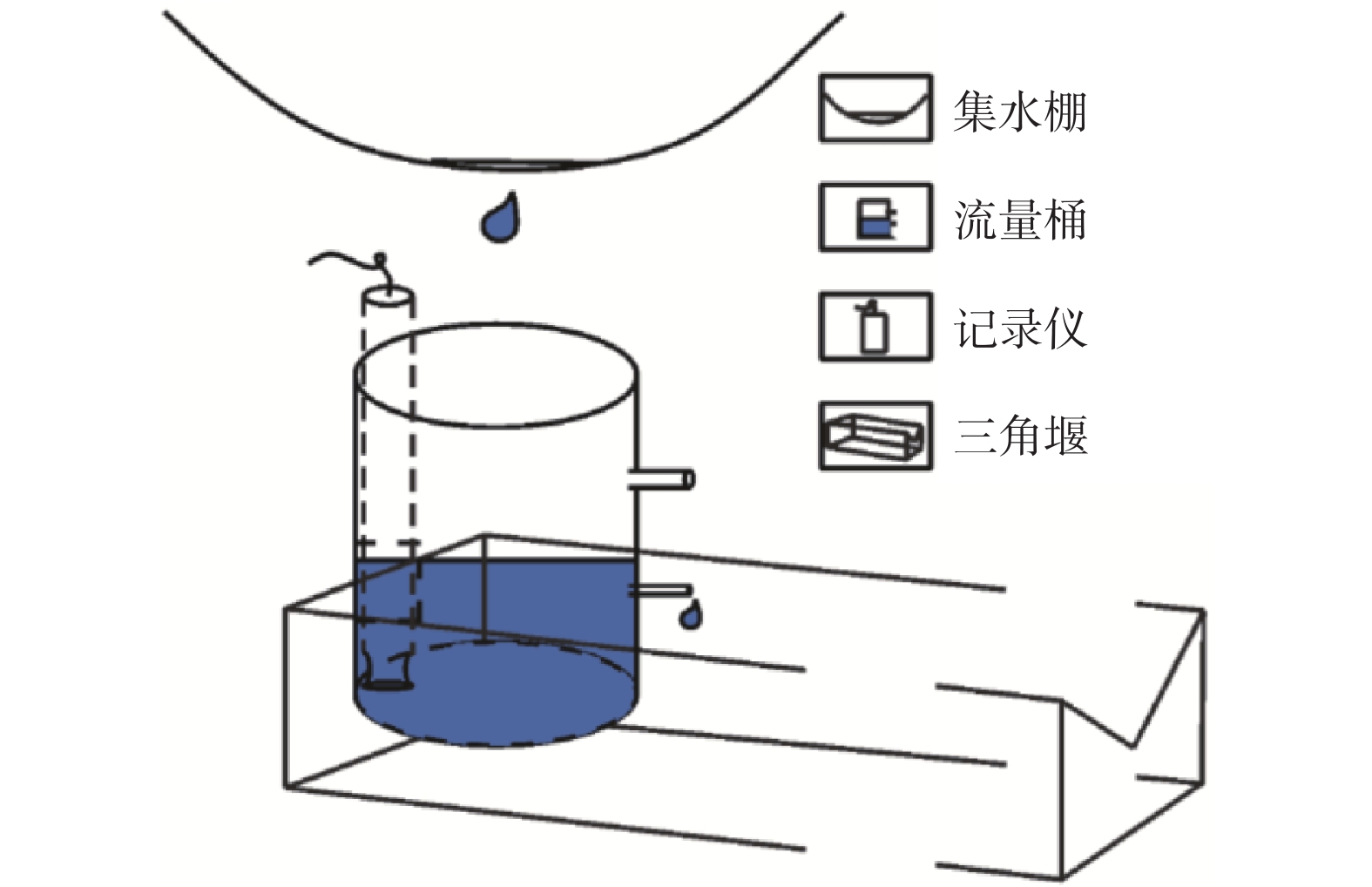
图 4 洞穴滴水监测装置示意图[14]
Figure 4.
表 1 不同类型水的监测特征
Table 1. Monitoring characteristics of different types of water
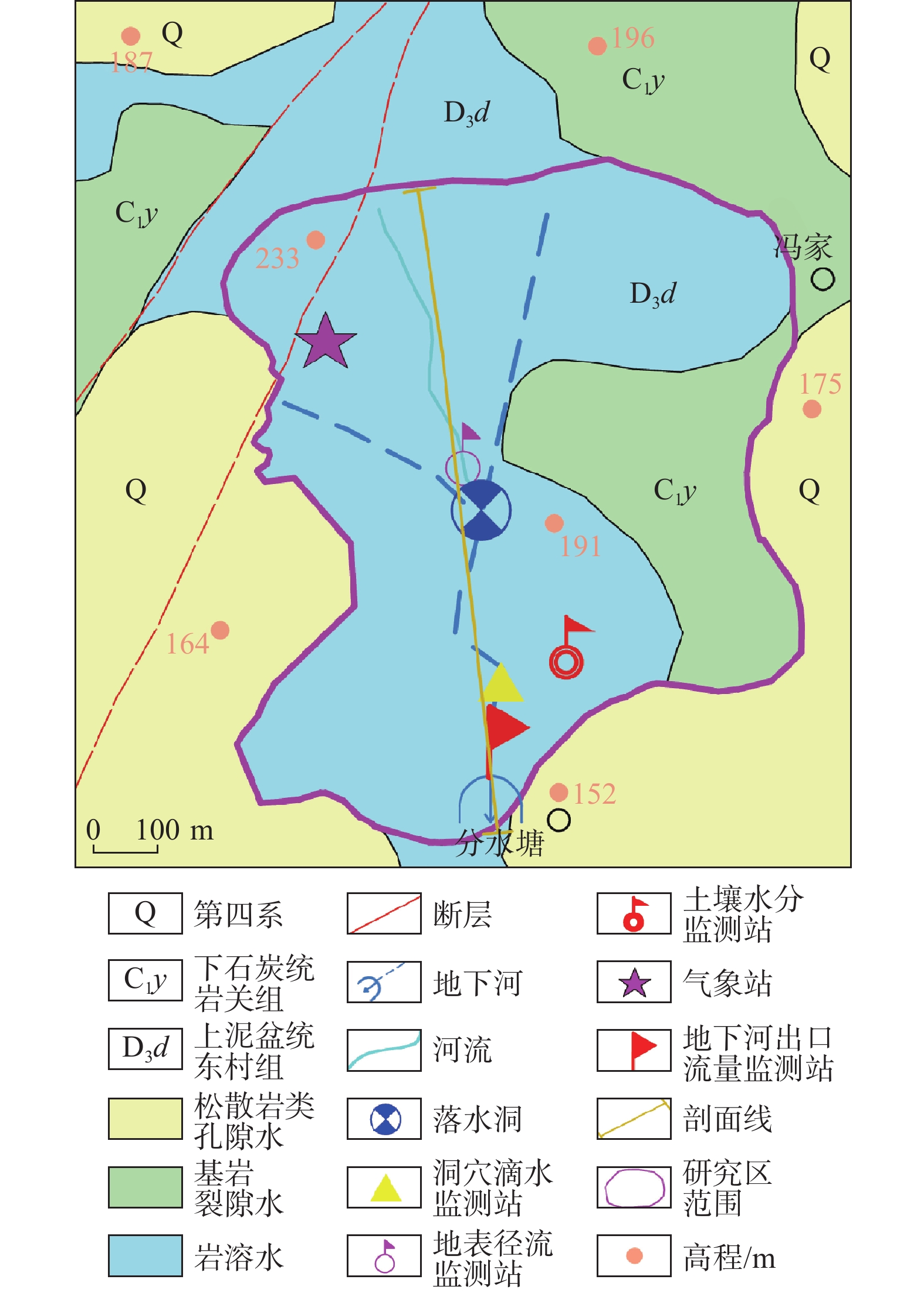
类型 监测时间 监测设备 监测地点 监测频率 备注 大气降雨 2018年9月—
2020年6月美国Onset HOBO型翻斗
式雨量桶自动记录仪分水塘村西北800 m 15 mim1次 地表径流 2020年4月—6月 矩形堰和渠道 分水塘村北500 m 5 mim1次 土壤水 2018年9月—
2019年9月美国WatchDog 2400型
土壤水分自动监测仪分水塘村北300 m 15 mim1次 监测深度为20 ,40 cm 表层岩溶水(洞穴滴水) 2020年4月—5月 洞穴滴水监测装置(专项开发) 分水塘村北狮子岩洞穴内 15 mim1次 洞穴滴水监测的
布设面积约为15.5 m2岩溶地下水(地下河出口流量) 2020年1月—6月 矩形堰和渠道 分水塘村 5 mim1次 表 2 不同降雨等级下各类型水变化量比例的计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of water circulation under different levels of rainfall
序号 降雨等级 24 h累计降雨量/mm 地表径流变化量比例/% 土壤水变化量比例/% 表层岩溶水变化量比例/% 岩溶地下水变化量比例/% 1 小雨 4.2 0.00 87.47 0.00 12.53 2 小雨 8.8 0.00 72.27 0.00 27.73 3 小雨 9.4 0.00 67.85 0.00 32.15 4 中雨 17.8 0.00 43.38 12.50 44.12 5 大雨 25 0.71 33.33 14.80 51.16 6 大暴雨 110.8 2.08 7.30 24.52 66.10 7 大暴雨 128.2 2.11 6.35 24.69 66.85 -
[1] 吕玉香,胡伟,杨琰. 岩溶关键带水循环过程研究进展[J]. 水科学进展,2019,30(1):123 − 138. [LYU Yuxiang,HU Wei,YANG Yan. Research progress of hydrological cycle in Karst critical zone[J]. Advances in Water Science,2019,30(1):123 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 曹建华,袁道先,章程,等. 受地质条件制约的中国西南岩溶生态系统[J]. 地球与环境,2004,32(1):1 − 8. [CAO Jianhua,YUAN Daoxian,ZHANG Cheng,et al. Karst ecosystem constrained by geological conditions in southwest China[J]. Earth and Environment,2004,32(1):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 吴泽燕,章程,蒋忠诚,等. 岩溶关键带及其碳循环研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2019,34(5):488 − 498. [WU Zeyan,ZHANG Cheng,JIANG Zhongcheng,et al. Advance of karst critical zone and its carbon cycle[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2019,34(5):488 − 498. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.05.0488
[4] HAO Y H,CAO B B,CHEN X,et al. A piecewise grey system model for study the effects of anthropogenic activities on karst hydrological processes[J]. Water Resources Management,2013,27(5):1207 − 1220. doi: 10.1007/s11269-012-0231-x
[5] 梁桂星,覃小群,崔亚莉,等. 分布式水文模型在岩溶地区的改进与应用研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):60 − 67. [LIANG Guixing,QIN Xiaoqun,CUI Yali,et al. Improvement and application of a distributed hydrological model in Karst regions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):60 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] SHAO Y X,WANG Y X,XU X Q,et al. Occurrence and source apportionment of PAHs in highly vulnerable karst system[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2014,490:153 − 160. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.128
[7] 陈舟,赵贵清,王志光,等. 岩溶区某磷石膏堆放场渗漏特征分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):144 − 150. [CHEN Zhou,ZHAO Guiqing,WANG Zhiguang,et al. Leakage characteristics of a phosphorus gypsum storage site in Karst area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):144 − 150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 陈国富,姜光辉,周文亮,等. 岩溶石山区山坡表层径流水文动态特征对比分析:以桂林丫吉试验场为例[J]. 水文,2013,33(5):58 − 63. [CHEN Guofu,JIANG Guanghui,ZHOU Wenliang,et al. Comparative analysis of surface runoff hydrologic dynamic characteristics in Karst mountainous areas:taking yaji experimental station as study case[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2013,33(5):58 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2013.05.011
[9] 周文亮. 岩溶山区包气带洞穴滴水水文水化学过程与水量研究—以硝盐洞研究为例[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2014
ZHOU Wenliang. Hydrochemical process and water volume of dripping water in vadose cave in Karst mountainous area: A case study of saltpeter cave[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 宋洋,迟宝明,谷洪彪,等. 基于水化学及D、18O的柳江盆地东宫河流域地下水循环特征解析[J]. 水土保持研究,2015,22(2):90 − 95. [SONG Yang,CHI Baoming,GU Hongbiao,et al. Study on groundwater cycle in Donggong River Basin using data of hydrochemistry,D and 18O[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2015,22(2):90 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 郭小娇,龚晓萍,袁道先,等. 典型岩溶包气带洞穴滴水水文过程研究:以桂林硝盐洞为例[J]. 地球学报,2017,38(4):537 − 548. [GUO Xiaojiao,GONG Xiaoping,YUAN Daoxian,et al. Research on hydrological processes of cave dripping water in a typical Karst vadose zone:A case study of Xiaoyan Cave,Guilin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2017,38(4):537 − 548. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.11
[12] LUO M M,CHEN Z H,CRISS R E,et al. Method for calibrating a theoretical model in karst springs:An example for a hydropower station in South China[J]. Hydrological Processes,2016,30(25):4815 − 4825. doi: 10.1002/hyp.10950
[13] 罗明明. 南方岩溶水循环的物理机制及数学模型研究: 以香溪河岩溶流域为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2017
LUO Mingming. The physical machanism and methematical model of Karst water circulation: A case study of the Xiangxi River Karst Basin, South China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 郭小娇,姜光辉,汤庆佳,等. 典型岩溶石山包气带洞穴水流的水文过程浅析[J]. 中国岩溶,2014,33(2):176 − 183. [GUO Xiaojiao,JIANG Guanghui,TANG Qinjia,et al. Analysis of hydrological process of drip water in the aeration zone of a typical karst stone hill[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2014,33(2):176 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 吴乔枫,刘曙光,蔡奕,等. 流域非闭合特性对岩溶地区水文过程模拟的影响[J]. 水利学报,2017,48(4):457 − 466. [WU Qiaofeng,LIU Shuguang,CAI Yi,et al. Effect of unclosed characteristics of the basin on hydrological modeling in Karst regions[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2017,48(4):457 − 466. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 陈晓宏,颜依寒,李诚,等. 溶蚀丘陵型岩溶流域概念性水文模型及其应用[J]. 水科学进展,2020,31(1):1 − 9. [CHEN Xiaohong,YAN Yihan,LI Cheng,et al. Conceptual hydrological model of corrosional hill karst watershed and its application[J]. Advances in Water Science,2020,31(1):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 孙斌,彭玉明. 济南泉域边界条件、水循环特征及水环境问题[J]. 中国岩溶,2014,33(3):272 − 279. [SUN Bin,PENG Yuming. Boundary condition,water cycle and water environment changes in the Jinan spring region[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2014,33(3):272 − 279. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11932/zgyr20140302
[18] 孙斌,邢立亭,彭玉明,等. 济南十大泉群特征、形成模式及水循环差异性浅析[J]. 中国岩溶,2021,40(3):409 − 419. [SUN Bin,XING Liting,PENG Yuming,et al. Characteristics,formation models and water cycle differences of ten major spring groups in Jinan city[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2021,40(3):409 − 419. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 李向全,张春潮,侯新伟. 采煤驱动下晋东大型煤炭基地地下水循环演变特征:以辛安泉域为例[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(9):3015 − 3026. [LI Xiangquan,ZHANG Chunchao,HOU Xinwei. Characteristics of groundwater circulation and evolution in Jindong large coal base driven by coal mining:An example of Xin’an spring area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(9):3015 − 3026. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 朱磊. 普者黑峰林湖盆区稳定同位素水文过程研究[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2016
ZHU Lei. Stable isotope hydrology process research in Puzhehei peak forest-lake basin[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] ZHANG Z C,CHEN X,GHADOUANI A,et al. Modelling hydrological processes influenced by soil,rock and vegetation in a small karst basin of southwest China[J]. Hydrological Processes,2017,25(15):2456 − 2470.
[22] 李向全,马剑飞,张春潮,等. 川藏铁路格聂山和察雅段构造岩溶发育规律及岩溶地下水循环模式研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):34 − 45. [LI Xiangquan,MA Jianfei,ZHANG Chunchao,et al. Evolution regularity of the plateau tectonic Karst and the relevant Karst groundwater circulation mode in Mount Genie and Zaya sections along the Sichuan-Xizang Railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):34 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 陈静,罗明明,廖春来,等. 中国岩溶湿地生态水文过程研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(6):221 − 230. [CHEN Jing,LUO Mingming,LIAO Chunlai,et al. Review of eco-hydrological process in Karst wetlands of China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2019,38(6):221 − 230. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 王月,尹辉,李晖,等. 桂林会仙岩溶湿地生态环境保护与生态补偿研究[J]. 湖北农业科学,2015,54(1):66 − 69. [WANG Yue,YIN Hui,LI Hui,et al. Ecological environment protection and ecological compensation to Huixian karst wetland in Guilin[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2015,54(1):66 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 赵一,邹胜章,申豪勇,等. 会仙湿地岩溶地下水系统水位动态特征与均衡分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2021,40(2):325 − 333. [ZHAO Yi,ZOU Shengzhang,SHEN Haoyong,et al. Dynamic characteristics and equilibrium of water level of the Karst groundwater system beneath the Huixian wetland[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2021,40(2):325 − 333. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 朱丹尼,邹胜章,周长松,等. 桂林会仙岩溶湿地水位动态特征及水文生态效应[J]. 中国岩溶,2021,40(4):661 − 670. [ZHU Danni,ZOU Shengzhang,ZHOU Changsong,et al. Dynamic characteristics of water Level and hydro-ecological effects in Huixian Karst wetland in Guilin[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2021,40(4):661 − 670. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 陈植华, 陈刚, 靖娟利, 等. 西南岩溶石山表层岩溶带岩溶水资源调蓄能力初步评价[C]//中国岩溶地下水与石漠化治理. 桂林: 广西科学出版社, 2003: 180-188
CHEN Zhihua, CHEN Gang, JING Juanli, et al. Preliminary evaluation on the capacity of karst water resources regulation and storage in the surface karst zone of karst stone mountain in southwest China[C]//Karst Groundwater and Rock Desertification Control in China. Guilin: Guangxi Science Press, 2003: 180-188. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 邹胜章,张文慧,梁小平,等. 表层岩溶带调蓄系数定量计算:以湘西洛塔赵家湾为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2005,32(4):37 − 42. [ZOU Shengzhang,ZHANG Wenhui,LIANG Xiaoping,et al. Quantitative calculation of regulating coefficient for epikarsk zone:Case study of Zhaojiawan,Luota,West of Hunan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2005,32(4):37 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.04.010
[29] 罗明明,陈植华,周宏,等. 岩溶流域地下水调蓄资源量评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(6):14 − 20. [LUO Mingming,CHEN Zhihua,ZHOU Hong,et al. Assessment of regulating groundwater resources in karst watersheds[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2016,43(6):14 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2016.06.03
-



 下载:
下载: