Influences of lithology and structure of the vadose zone on groundwater ecological function
-
摘要:
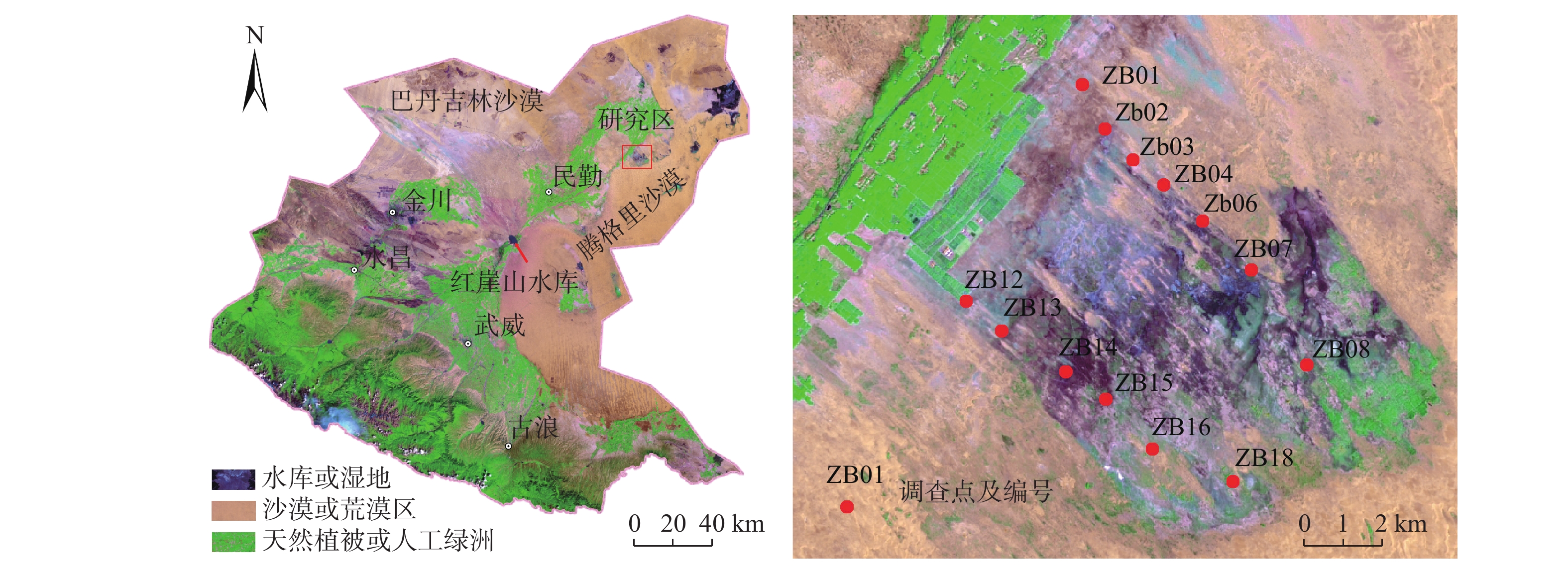
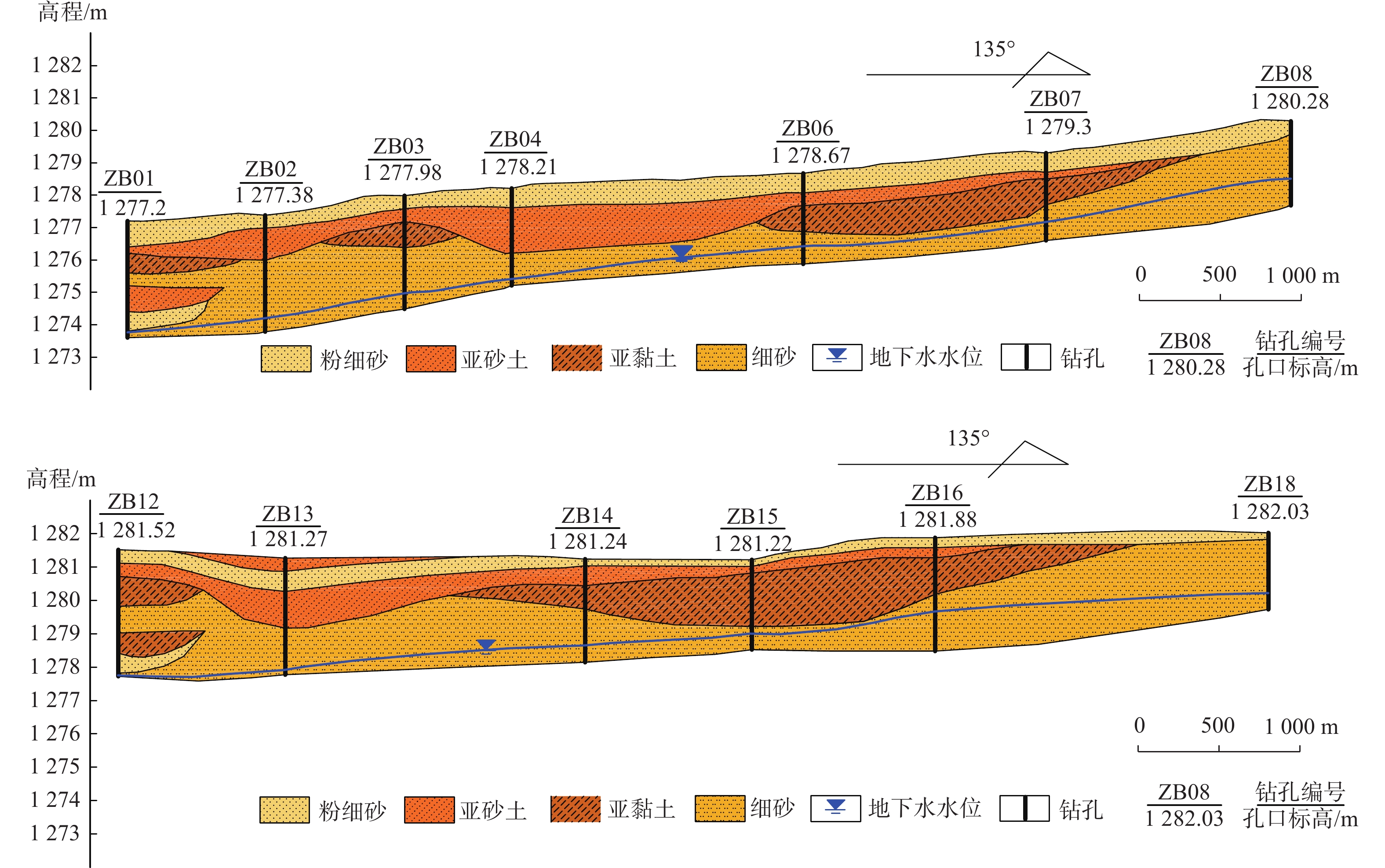
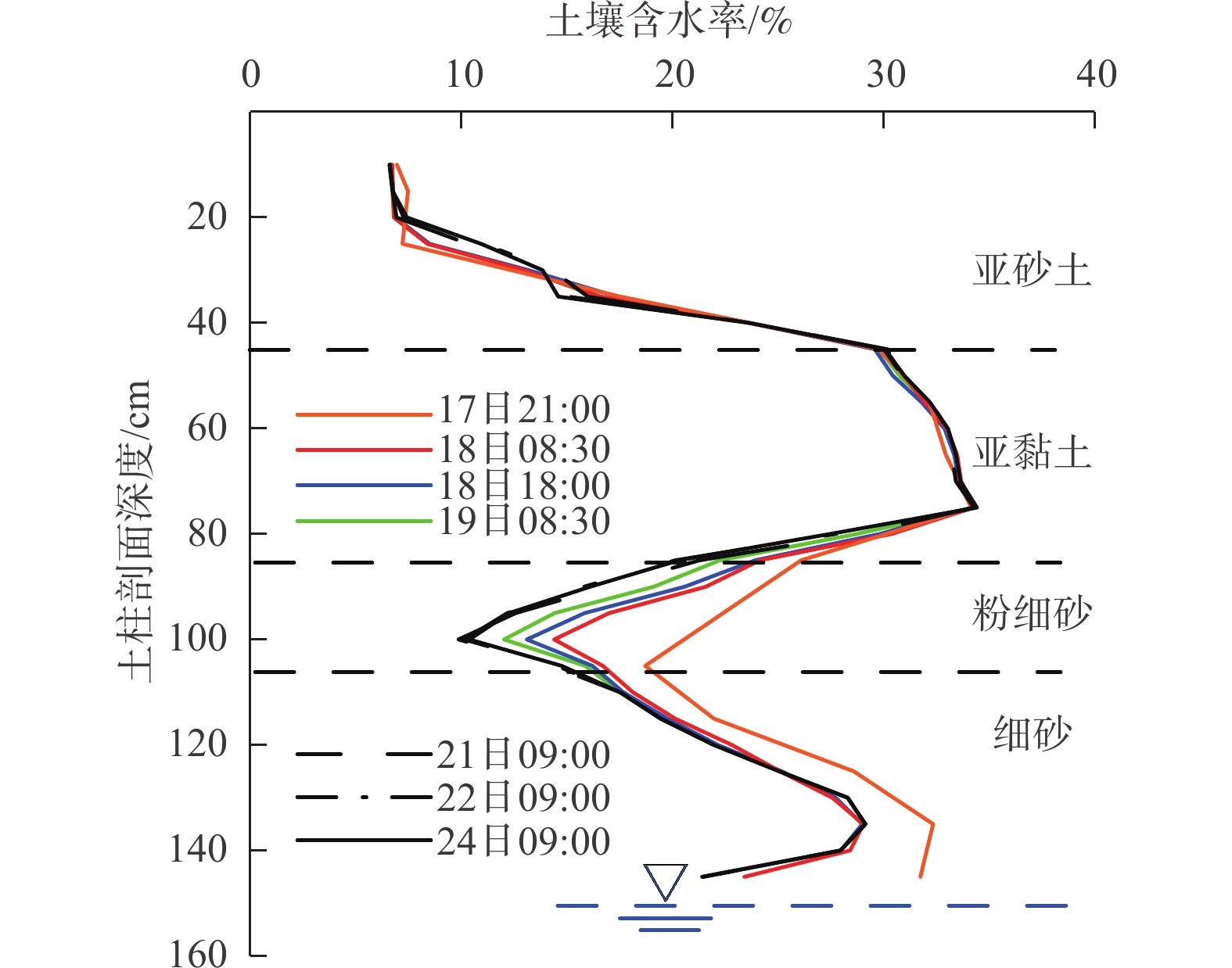
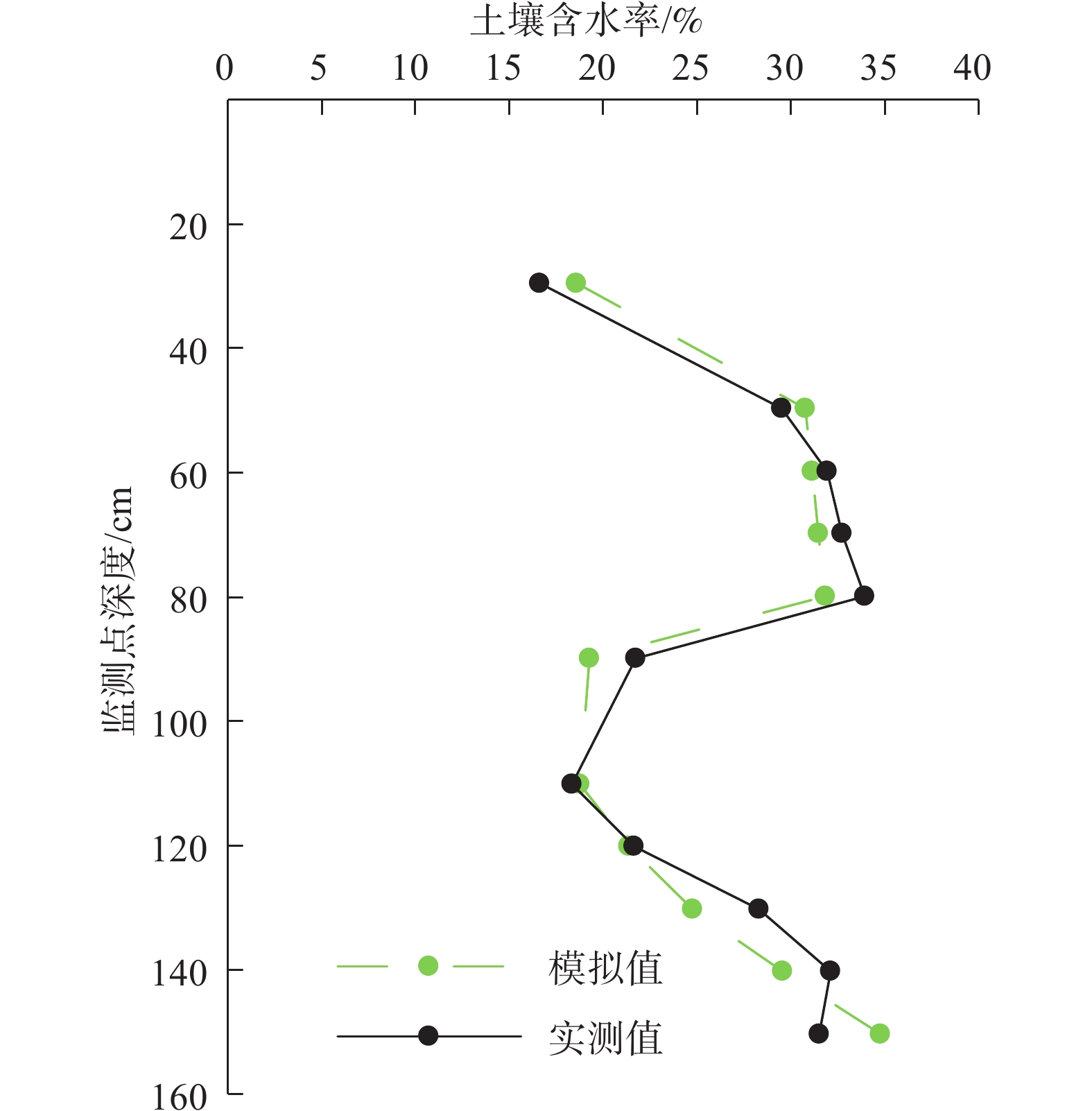
西北内陆流域下游区天然植被对地下水生态功能具有强烈依赖性,而包气带岩性结构对地下水生态功能具有明显影响,但是在目前的研究中,缺乏定量分析评判。以甘肃石羊河流域下游天然绿洲区为研究区,基于包气带岩性结构野外调查、室内土柱试验和Hydrus1-D数值模拟,研究包气带岩性结构与地下水耦合作用的生态效应,分析不同岩性结构包气带获取地下水供给水分和持水能力差异,定量对比不同包气带岩性结构对地下水生态功能影响特征,得到以下认识:(1)在地下水水位埋深增大和减小的情况下,不同包气带岩性结构对地下水生态功能影响不同;(2)当地下水水位埋深逐渐减小时,在相同植被条件下,包气带岩性颗粒越细,其支持毛细水上升高度和速度越大,土壤获得地下水的补给水分越快越多,对地表植被的生长越有利;(3)当地下水水位埋深大幅增大后,旱区包气带的有效持水量具有继续维持陆表植被存活的生态效应,中等岩性颗粒的有效持水量最大,对维持植被的生态效应最明显。与单一岩性相比,多种岩性的组合结构有效持水量较大,生态效应更强。研究结果加深了对包气带在地下水生态功能中调节作用的认识,可以为旱区水资源的精细化管理及生态保护提供科学依据。
Abstract:The natural vegetation in the lower reaches in the inland basins of northwest China is strongly dependent on the groundwater ecological function, and the lithology and structure of the vadose zone has a significant impact on the groundwater ecological function. However, there is a lack of systematic and specific research on how to quantitatively analyze and evaluate the degree of influence. The natural oasis area in the lower reaches of the Shiyang River Basin in Gansu Province is taken as the research area, and field investigation, soil column test and numerical simulation with Hydrus1-D are carried out to study the ecological effect of the coupling effect between the vadose zone and groundwater. The difference of water supply ability and water holding ability of the vadose zone with different lithologic structure is analyzed, and the influences of lithology and structure of the vadose zone on the groundwater ecological function is quantitatively compared. The results show that (1) the lithological structure of different vadose zones has different effects on the groundwater ecological function when the groundwater depth increases or decreases. (2) When the groundwater depth decreases gradually, under the same vegetation condition, the finer the lithologic particles in the vadose zone, the higher the height and speed of the supporting capillary water rises, and the faster the soil obtains groundwater recharge, and the more beneficial it is to the growth of the surface vegetation. (3) The effective water holding capacity of the vadose zone in the arid area has ecological effect of maintaining the survival of land surface vegetation after the local groundwater depth increases greatly. The effective water holding capacity of the medium lithologic particles is the largest, which has the most obvious ecological effect on maintaining vegetation. Compared with a single lithology, the combination of multiple lithologies is more conducive to hold larger effective water capacity and stronger ecological effect. The results will be helpful to strengthen the understanding of the regulation of the vadose zone in groundwater ecological function, and can provide a scientific basis for the fine management of water resources and ecological protection in arid regions.
-

-
表 1 模拟模型岩性确定依据
Table 1. Lithology of the simulation model
岩性 厚度
/cm不同岩性粒径占比/% 干容重
/(g·cm−3)0.05~2 mm 0.002~0.05
mm< 0.002 mm 亚砂土 40 75.7 22.0 2.3 1.35 亚黏土 40 46.0 51.6 2.4 1.44 粉细砂 20 86.2 11.9 1.9 1.51 细 砂 50 > 0.075 mm,占比85.7%;≤ 0.075 mm,占比14.3% 1.60 表 2 校正识别后不同岩性土壤水力特性参数
Table 2. Corrected hydraulic characteristic parameters of different lithology soils
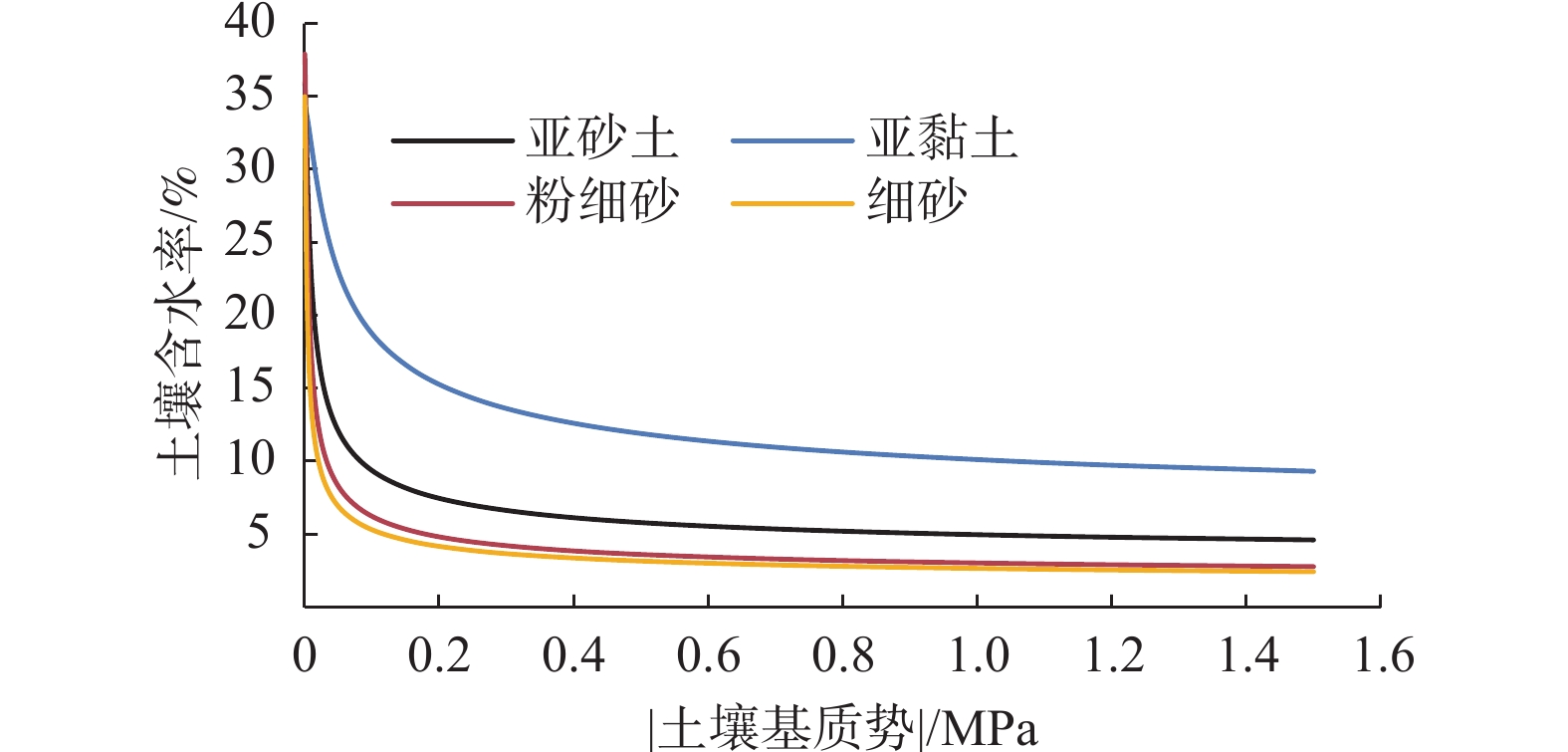
岩性 残余含水率/% 饱和含水率/% 进气值倒数 形状系数 饱和渗透系数/(cm·d−1) 凋萎含水率/% 亚砂土 3.07 35.99 0.0239 1.52 117.33 4.62 亚黏土 5.35 34.27 0.005 1.46 47.85 9.32 粉细砂 1.79 37.91 0.045 1.55 305.67 2.79 细 砂 1.44 35 0.075 1.5 642.98 2.44 表 3 释水50 d后不同岩性包气带有效持水量
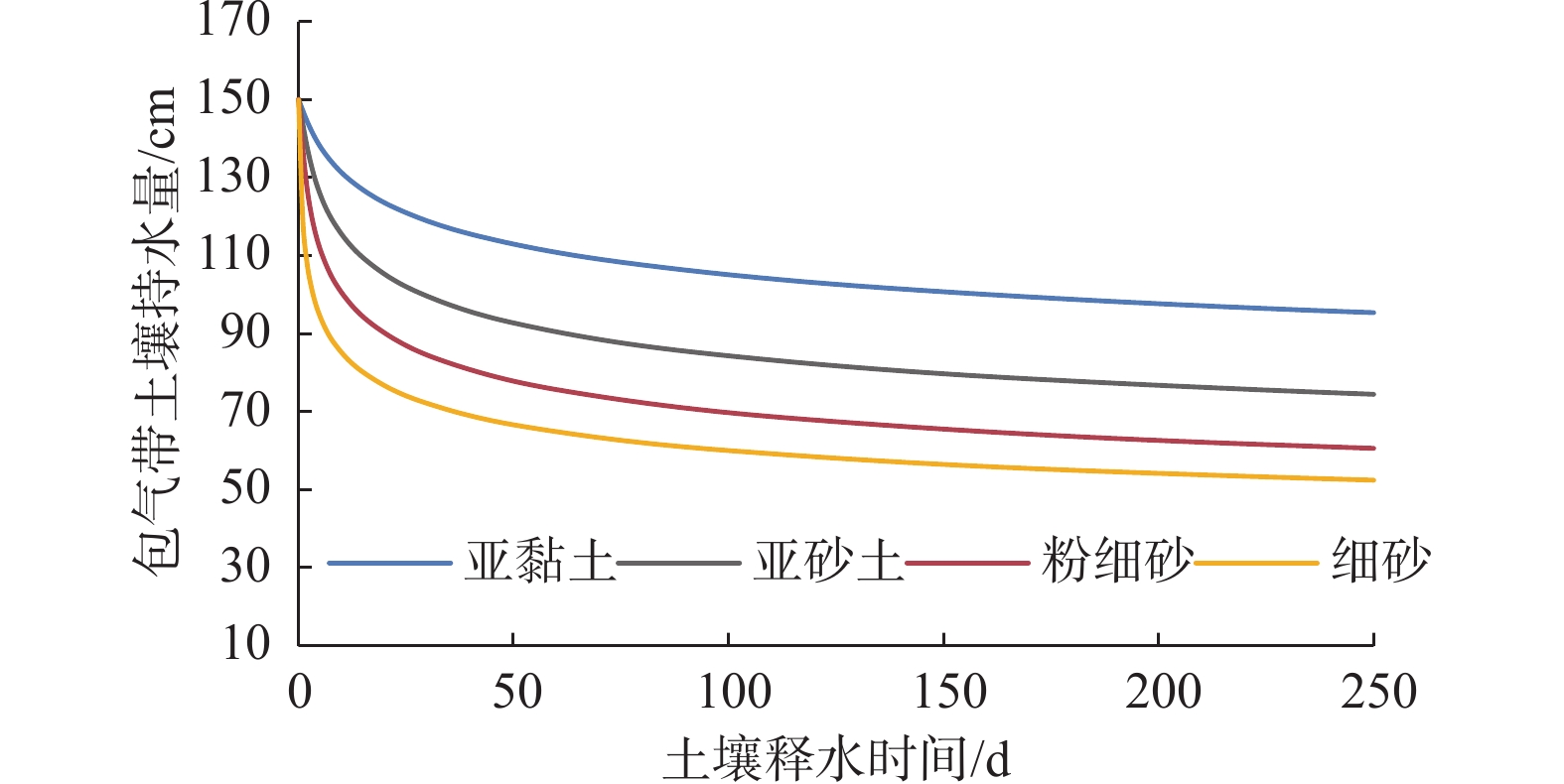
Table 3. Effective water holding capacity in the vadose zone of different lithologies after 50 days of water release
/cm 岩性 亚黏土 亚砂土 粉细砂 细砂 土壤凋萎含水量 46.60 23.10 13.95 12.20 土壤持水量 113.00 92.78 77.87 66.67 土壤有效持水量 66.40 69.68 63.92 54.47 注:土壤凋萎含水量=包气带厚度×凋萎含水率;土壤有效持水量=土壤持水量-土壤凋萎含水量。 表 4 释水50 d后不同结构包气带有效持水量
Table 4. Effective water holding capacity in the vadose zone of different structures after 50 days of water release
/cm 岩性结构 上粗
下细上细
下粗细粒
夹层粗粒
夹层土壤凋萎含水量 29.40 29.40 19.08 39.72 土壤持水量 86.14 102.97 81.24 114.68 土壤有效持水量 56.74 73.57 62.16 74.96 注:土壤凋萎含水量=包气带厚度×凋萎含水率;土壤有效持水量=土壤持水量-土壤凋萎含水量。 -
[1] 孙自永,王俊友,葛孟琰,等. 基于水稳定同位素的地下水型陆地植被识别:研究进展、面临挑战及未来研究展望[J]. 地质科技情报,2020,39(1):11 − 20. [SUN Ziyong,WANG Junyou,GE Mengyan,et al. Isotopic approaches to identify groundwater dependent terrestrial vegetation:Progress,challenges,and prospects for future research[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2020,39(1):11 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0102
[2] 王文科,宫程程,张在勇,等. 旱区地下水文与生态效应研究现状与展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2018,33(7):702 − 718. [WANG Wenke,GONG Chengcheng,ZHANG Zaiyong,et al. Research status and prospect of the subsurface hydrology and ecological effect in arid regions[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2018,33(7):702 − 718. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.07.0702
[3] 武选民, 史生胜, 黎志恒, 等. 西北黑河下游额济纳盆地地下水系统研究(上)[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2002, 29(1): 16 − 20. [WU Xuanmin, SHI Shengsheng, LI Zhiheng, et al. The study on the groundwater flow system of Ejina Basin in lower reaches of the Heihe River in Northwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2002, 29(1): 16 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 凤蔚,李文鹏,邵新民,等. 黑河流域中游盆地地下水动态特征及其调蓄能力分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(3):11 − 21. [FENG Wei,LI Wenpeng,SHAO Xinmin,et al. Research on the dynamic characteristics of groundwater and regulation capability of aquifers in the intermediate section of Heihe River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(3):11 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] LIU M,NIE Z L,CAO L,et al. Comprehensive evaluation on the ecological function of groundwater in the Shiyang River watershed[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2021,9(4):326 − 340.
[6] HUANG F,ZHANG Y,ZHANG D,et al. Environmental groundwater depth for groundwater-dependent terrestrial ecosystems in arid/semiarid regions:A review[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2019,16:763.
[7] 王金哲,张光辉,王茜,等. 西北干旱区地下水生态功能评价指标体系构建与应用[J]. 地质学报,2021,95(5):1573 − 1581. [WANG Jinzhe,ZHANG Guanghui,WANG Qian,et al. Construction and application of evaluation index system of groundwater ecological function in northwest arid area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2021,95(5):1573 − 1581. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.05.018
[8] 崔浩浩,张冰,冯欣,等. 不同土体构型土壤的持水性能[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2016,34(4):1 − 5. [CUI Haohao,ZHANG Bing,FENG Xin,et al. Soil water-holding properties of different soil body configuration[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2016,34(4):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2016.04.01
[9] 葛建,黄德文,高旭,等. 分层土壤的持水性能研究[J]. 西南农业学报,2019,32(9):2126 − 2132. [GE Jian,HUANG Dewen,GAO Xu,et al. Water retention capacity of drained soil columns with grained layers[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2019,32(9):2126 − 2132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 贾利民,郭中小,龙胤慧,等. 干旱区地下水生态水位研究进展[J]. 生态科学,2015,34(2):187 − 193. [JIA Limin,GUO Zhongxiao,LONG Yinhui,et al. Research advances in ecological groundwater level in arid areas[J]. Ecological Science,2015,34(2):187 − 193. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2015.02.028
[11] 赵文智,周宏,刘鹄. 干早区包气带土壤水分运移及其对地下水补给研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2017,32(9):908 − 918. [ZHAO Wenzhi,ZHOU Hong,LIU Hu. Advances in moisture migration in vadose zone of dryland and recharge effects on groundwater dynamics[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2017,32(9):908 − 918. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.09.0899
[12] 乔晓英,王文科,姜桂华,等. 西北干旱内陆盆地地下水生态功能的探讨[J]. 水资源保护,2005(5):6 − 10. [QIAO Xiaoying,WANG Wenke,JIANG Guihua,et al. Study on ecological function of groundwater in northwest arid inland basin[J]. Water Resources Protection,2005(5):6 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2005.05.002
[13] 陶正平,黄金廷,崔旭东. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部风积沙覆基岩型包气带结构的生态意义[J]. 地下水,2007(6):54 − 55. [TAO Zhengping,HUANG Jinting,CUI Xudong. The Eco-significance of the Sand-sandrock Vadose Zone Structure in the North of the Erdos Basin[J]. Groundwater,2007(6):54 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2007.06.017
[14] 陈敏建,张秋霞,汪勇,等. 西辽河平原地下水补给植被的临界埋深[J]. 水科学进展,2019,30(1):24 − 33. [CHEN Minjian,ZHANG Qiuxia,WANG Yong,et al. Critical depth of recharge of the vegetation by groundwater in the West Liaohe Plain[J]. Advances in Water Science,2019,30(1):24 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2019.01.003
[15] 周宏. 干旱区包气带土壤水分运移能量关系及驱动力研究评述[J]. 生态学报,2019,39(18):6586 − 6597. [ZHOU Hong. Review of studies on the relationship between soil water movement and energyand their driving forces in the vadose zone of arid regions[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2019,39(18):6586 − 6597. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 钱鞠, 常娟, 马海燕, 等. 民勤县水资源综合规划报告[R]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2013
QIAN Ju, CHANG Juan, MA Haiyan, et al. Comprehensive water resources planning of Minqin County[R]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2013. (in Chinese)
[17] HUANG F,OCHOA C G,CHEN X,et al. Modeling oasis dynamics driven by ecological water diversion and implications for oasis restoration in arid endorheic basins[J]. Journal of Hydrology ,2021,593:125774.
[18] 曹乐,聂振龙,刘敏,等. 民勤绿洲天然植被生长与地下水埋深变化关系[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):25 − 33. [CAO Le,NIE Zhenlong,LIU Min,et al. Changes in natural vegetation growth and groundwater depth and their relationship in the Minqin oasis in the Shiyang River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):25 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201907010
[19] 王金哲, 张光辉, 严明疆, 等. 干旱区地下水功能评价与区划体系指标权重解析[J]. 农业工程学报. 2020, 36(22): 133 − 143
WANG Jinzhe, ZHANG Guanghui, YAN Mingjiang, et al. Index weight analysis of groundwater function evaluation and zoning system in arid areas[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(22): 133 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王金哲, 张光辉, 崔浩浩, 等. 适宜西北内陆区地下水功能区划的体系指标属性与应用[J]. 水利学报. 2020, 51(7): 796 − 804
WANG Jinzhe, ZHANG Guanghui, CUI Haohao, et al. System index attribute and application of groundwater function zoning in northwest inland area of China[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2020, 51(7): 796 − 804. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王国帅,史海滨,李仙岳,等. 基于HYDRUS-1D模型的荒漠绿洲水盐运移模拟与评估[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(8):87 − 98. [WANG Guoshuai,SHI Haibin,LI Xianyue,et al. Simulation and evaluation of soil water and salt transport in desert oases of Hetao Irrigation District using HYDRUS-1D model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2021,37(8):87 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.08.010
[22] 钟韵,费良军,傅渝亮,等. 多因素影响下土壤上升毛管水运动特性HYDRUS模拟及验证[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(5):83 − 89. [ZHONG Yun,FEI Liangjun,FU Yuliang,et al. HYDRUS simulation and verification of movement characteristics of upward capillary water flow in soil as affected by multi-factor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2018,34(5):83 − 89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 乔照华. 土壤凋萎系数的影响因素研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2008(2):82 − 84. [QIAO Zhaohua. Study on the influence factors of wilting point[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water engineering,2008(2):82 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] TA SAN S,DEMIR Y. Comparative Analysis of MLR,ANN,and ANFIS Models for Prediction of Field Capacity and Permanent Wilting Point for Bafra Plain Soils[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis,2020,51:604 − 621.
[25] OSTOVARI Y,ASGARI K,CORNELIS W. Performance evaluation of pedotransfer functions to predict field capacity and perma-nent wilting point using UNSODA and HYPRES Dataset[J]. Arid Land Research and Management,2015,29:383 − 398.
[26] 王鑫,肖武,刘慧芳,等. 锡林浩特矿区土壤水分特征曲线和有效含水量预测[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(4):169 − 177. [WANG Xin,XIAO Wu,LIU Huifang,et al. Soil moisture characteristic curve and prediction of available water content of overburden in Xilinhot Mining Area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(4):169 − 177. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.04.018
[27] WIECHETECK L H,GIAROLA N F B,DE LIMA R P,et al. Comparing the classical permanent wilting point concept of soil (−15,000 hPa) to biological wilting of wheat and barley plants under contrasting soil textures[J]. Agricultural Water Management,2020,230:105965.
[28] 白致威,段兴武,丁剑宏,等. 土壤有效含水量的经验估算模型—以黑土为例[J]. 中国农学通报,2015,31(20):153 − 159. [BAI Zhiwei,DUAN Xingwu,DING Jianhong,et al. Experience estimation model of soil available water-holding capacity:A case study of black soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2015,31(20):153 − 159. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15030063
[29] CUI H,ZHANG G,WANG J,et al. Influence of multi-layered structure of vadose zone on ecological effect of groundwater in arid area:A case study of Shiyang River Basin,Northwest China[J]. Water,2022,14:59.
[30] 张阳阳,陈喜,高满,等. 内陆干旱区典型旱生植物蒸腾耗水量模拟研究[J]. 生态学报,2021,41(19):7751 − 7762. [ZHANG Yangyang,CHEN Xi,GAO Man,et al. Simulation of transpiration for typical xeromorphic plants in inland arid region of Northwestern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(19):7751 − 7762. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 张阳阳,陈喜,高满,等. 基于元数据分析的西北干旱区生态地下水水位埋深及其影响因素[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2020,18(5):57 − 65. [ZHANG Yangyang,CHEN Xi,GAO Man,et al. Meta-analysis of ecological depth to groundwater table and its influencing factors in aird region of northwest China[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2020,18(5):57 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 邵明安, 王全九, 黄明斌. 土壤物理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006
SHAO Mingan, WANG Quanjiu, HUANG Mingbin. Soil physics[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[33] 史文娟,沈冰,汪志荣,等. 层状土壤毛管水最大上升高度分析[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2007,25(1):94 − 97. [SHI Wenjuan,SHEN Bing,WANG Zhirong,et al. Maximum height of upward capillary water movement in layered soil[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2007,25(1):94 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7601.2007.01.019
-




 下载:
下载: