An analysis of the endowment characteristics and geneses of geothermal resources in the Zhangye Basin
-
摘要:
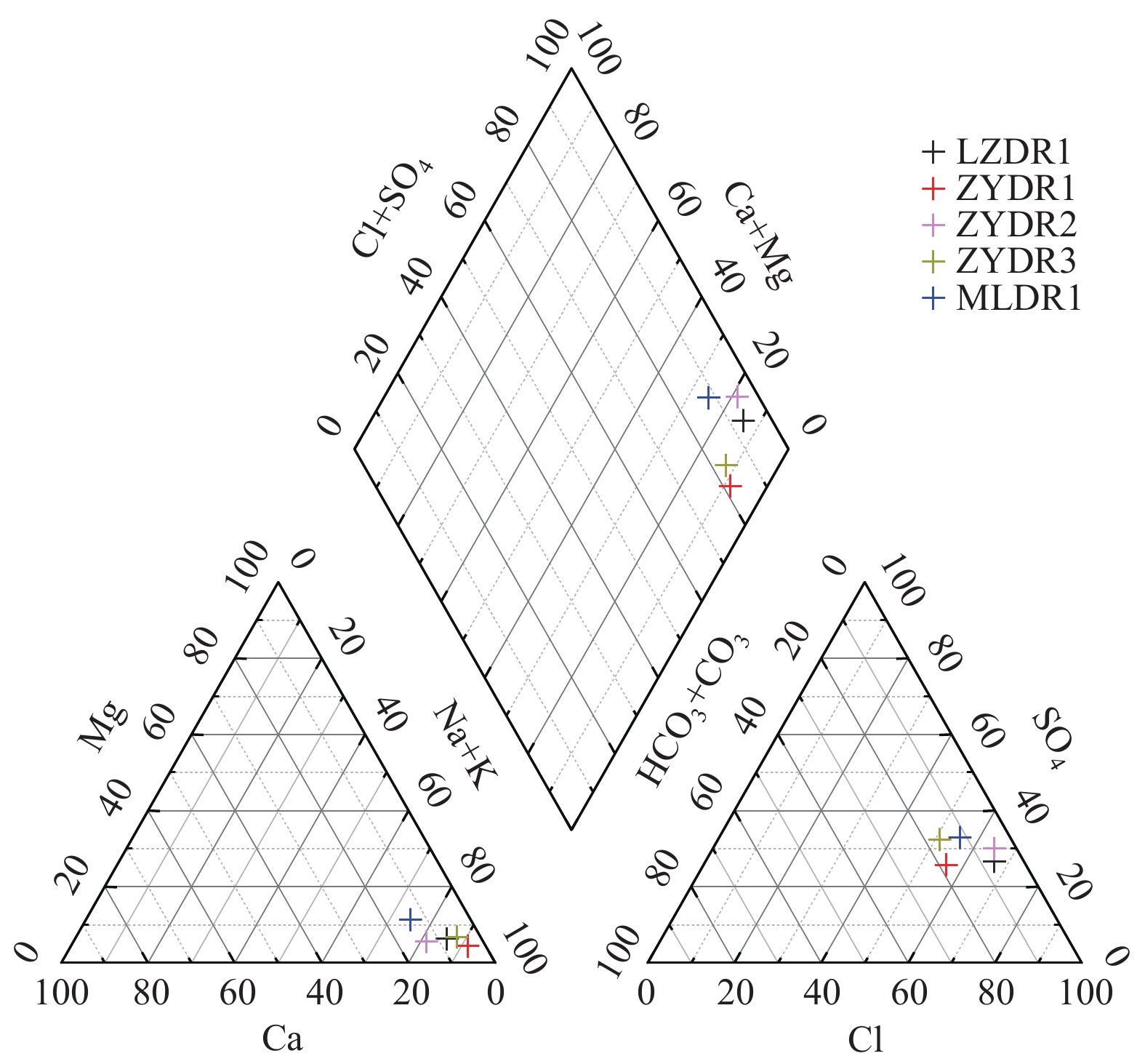
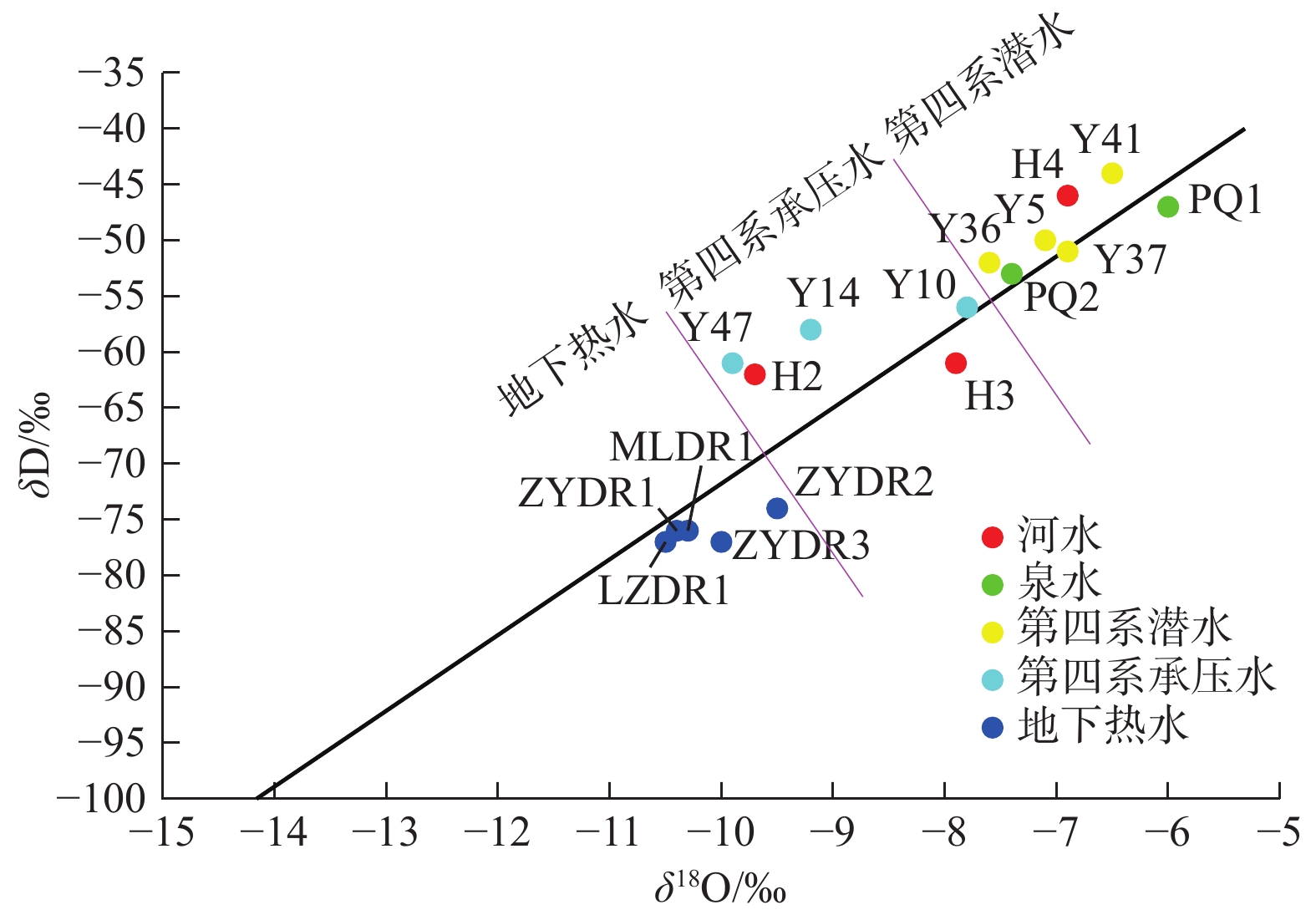
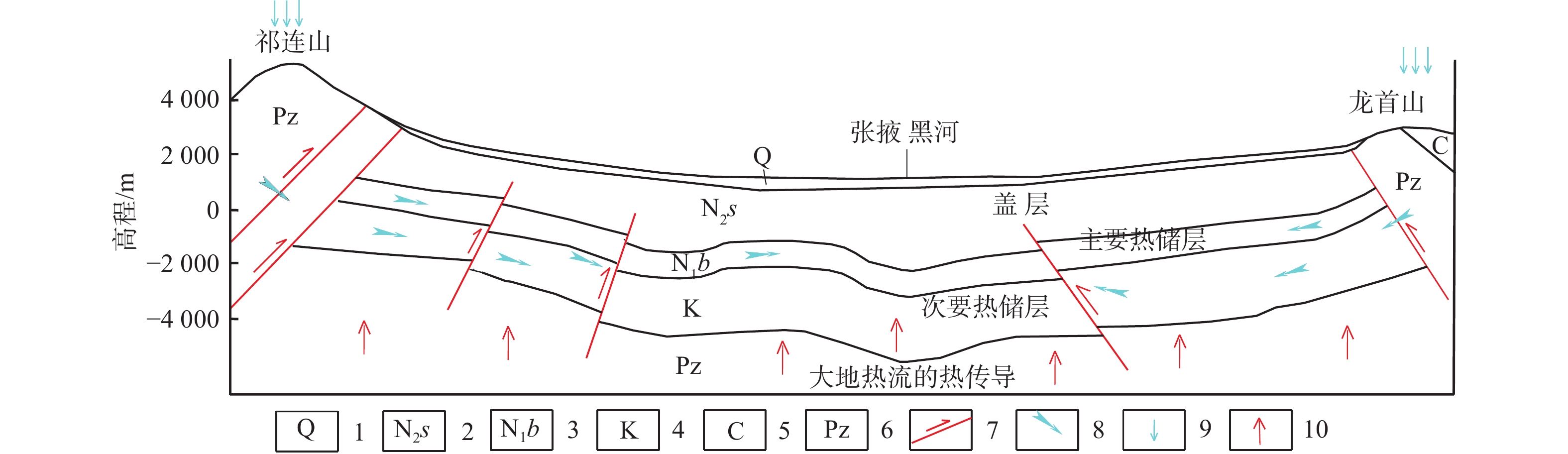
张掖盆地地处甘肃省河西走廊黑河流域中游地区,地势南东高北西低。已有勘探资料显示,张掖盆地赋存丰富的水热型地热资源。通过研究该区域地球物理勘探、钻探、地温测量及水文地球化学等成果资料,分析了张掖盆地地热资源赋存特征,探讨了其成因模式。张掖盆地地热田属沉积盆地型中低温地热田,热储为呈层状分布的新近系白杨河组砂岩、砂砾岩,选择钾镁地球化学温标计算热储温度为47~82 °C,盖层为新近系上新统疏勒河组泥岩及第四系松散地层;地热水类型主要为碎屑岩类孔隙水,根据氢氧同位素特征推断其主要补给来源为南部祁连山区大气降水;祁连山北缘深大断裂和盆地内NNW向基底断裂是地热流体深循环良好的导水通道,地下水接受补给后沿导水断裂带或岩层孔隙裂隙运移,在深部热传导的增温作用下,赋存于碎屑岩类孔隙之中形成了本区的地热资源。水质分析结果表明:本区地热水属于溶滤型的陆相沉积水,水化学类型为Cl·SO4—Na型,F−、SiO2、溶解性总固体、总硬度含量随水温的升高而增大;区内地热水3H值普遍小于2.0 TU,说明形成年代较早;14C分析结果进一步证实,区域地热水形成年龄超过20 ka,反映出地热流体补给路径长、径流缓慢的特点。研究成果可为张掖盆地地热资源勘查和开发利用提供重要参考。
Abstract:As a part of Hexi Corridor in Gansu Province, the Zhangye Basin is located in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin, with high topography in the southeast and low topography in the northwest. The existing exploration data show that the Zhangye basin is rich in hydrothermal geothermal resources. Based on the study of geophysical exploration, geothermal drilling, geo-temperature measurement and hydrogeochemistry, this paper analyzes the occurrence characteristics of geothermal resources and discusses the genetic mode in Zhangye Basin. The geothermal field in the Zhangye basin belongs to the sedimentary basin type of low-medium temperature. The geothermal reservoir is composed of sandstone and glutenite of Neogene Baiyanghe Formation with layered distribution. Temperature of the geothermal reservoir ranges from 47 to 82 °C calculated by using the potassium magnesium geochemical temperature standard. The caprock consists of mudstone of Neogene Shulehe Formation and Quaternary unconsolidated sediments. The geothermal water type is mainly clastic pore water. The characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotope indicate that the main recharge source is atmospheric precipitation in the southern Qilian Mountains. The deep faults in the northern margin of Qilian Mountains and NNW-trending basement faults in the basin are good conduits for deep circulation of the geothermal fluids. After receiving recharge, groundwater migrates along the water-conducting fault zones or rock pore fractures. Heating by the deep heat conduction, it occurs in the pores of clastic rocks and forms geothermal resources in this area. The results of hydrochemical analyses show that the geothermal water in this area belongs to continental sedimentary water containing dissolved water in rock salt formation, and the hydrochemical type is of Cl·SO4—Na. The contents of fluorine, SiO2, total dissolved solids and total hardness increase with the increasing water temperature. The tritium value of hot water in the area is generally less than 2.0 TU, indicating that the formation age is relatively early. The results of carbon-14 analysis further confirm that the formation age of the regional geothermal water is more than 20,000 years, reflecting the characteristics of a long geothermal fluid supply path and slow runoff. The research results can provide important reference for exploration and utilization of geothermal resources in the Zhangye Basin.
-
Key words:
- geothermal resources /
- reservoir /
- hydrogeochemistry /
- geothermal genesis /
- groundwater age /
- Zhangye Basin
-

-
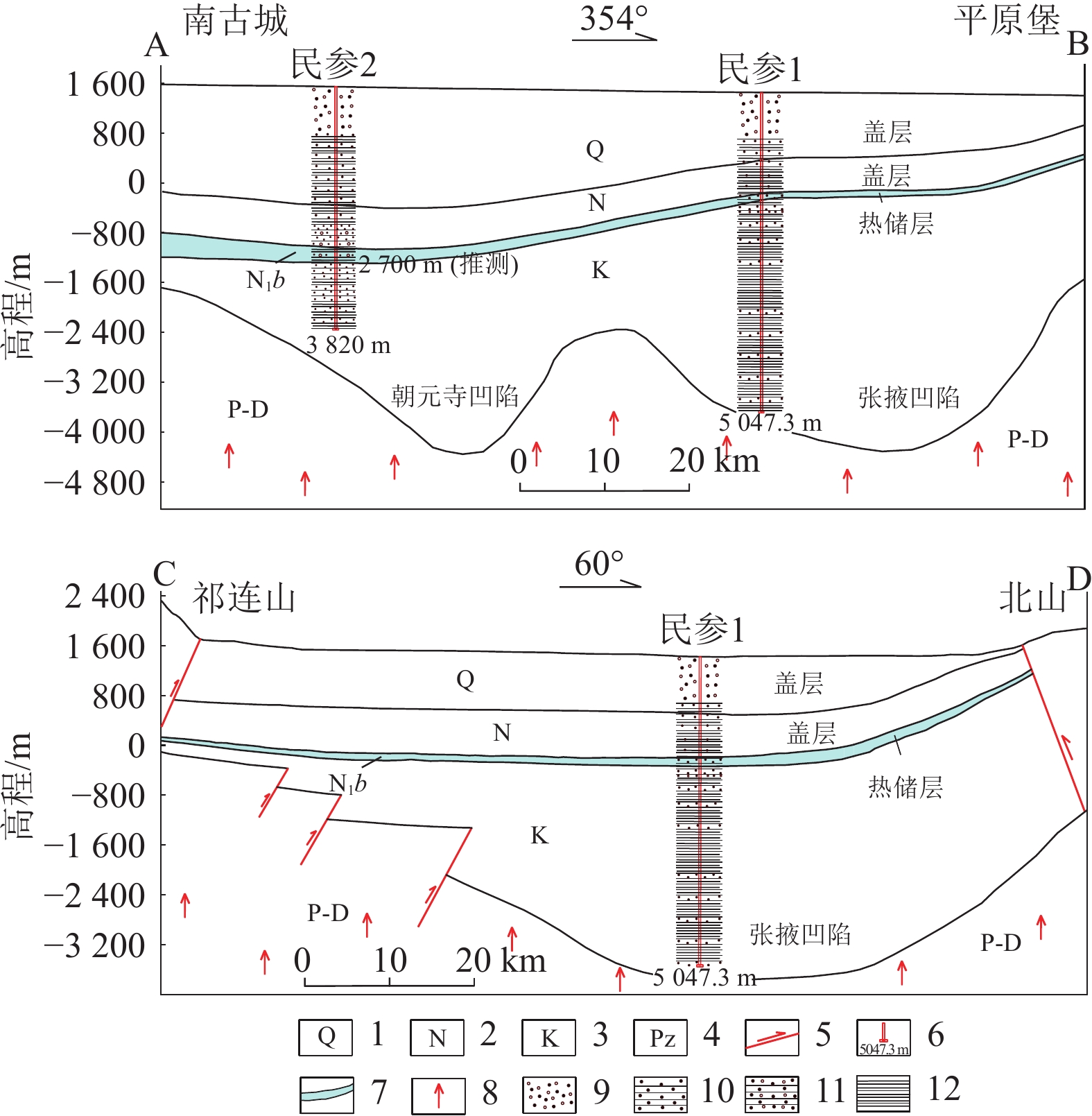
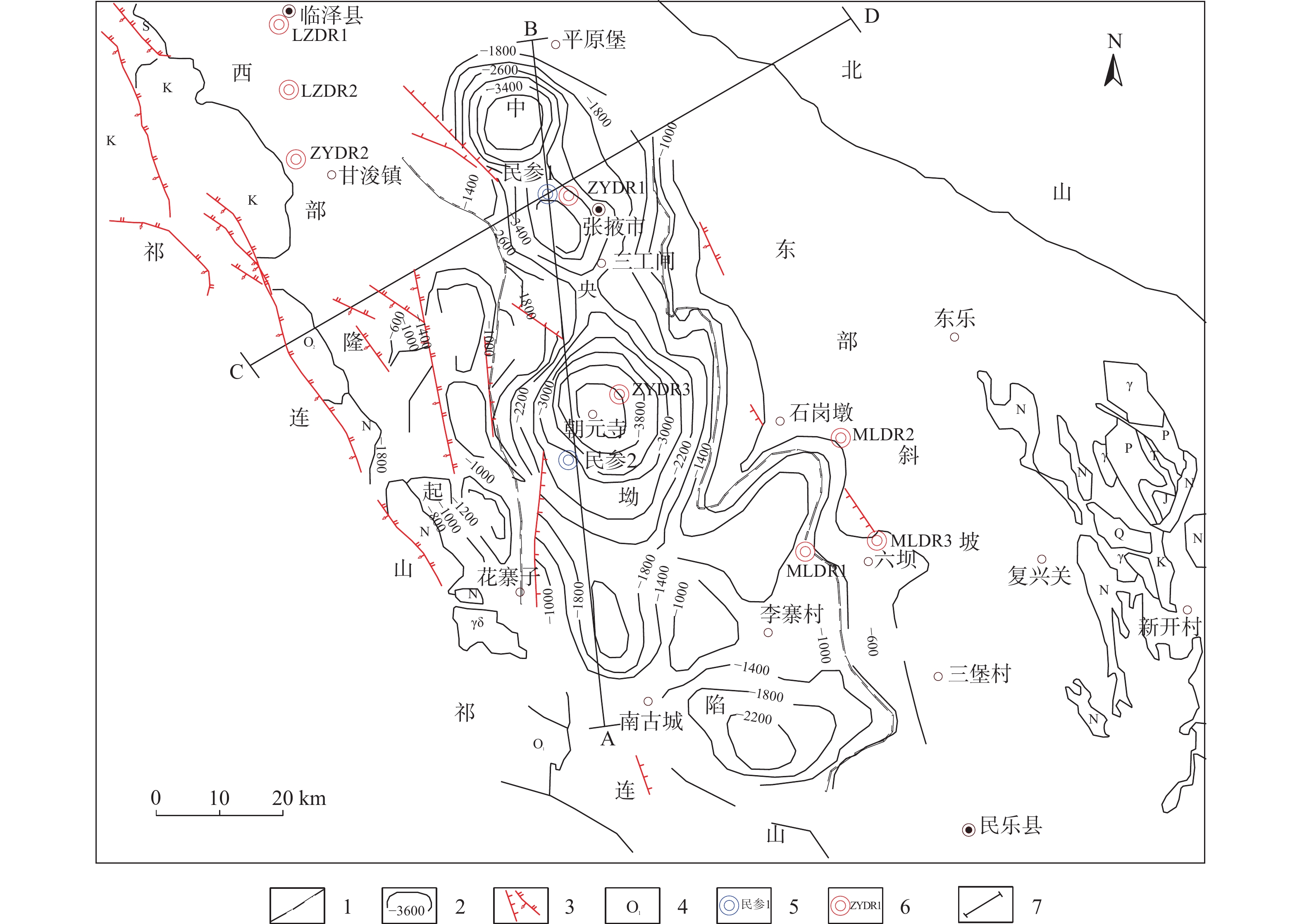
图 1 张掖盆地地震推断构造图(改编自文献[20])
Figure 1.
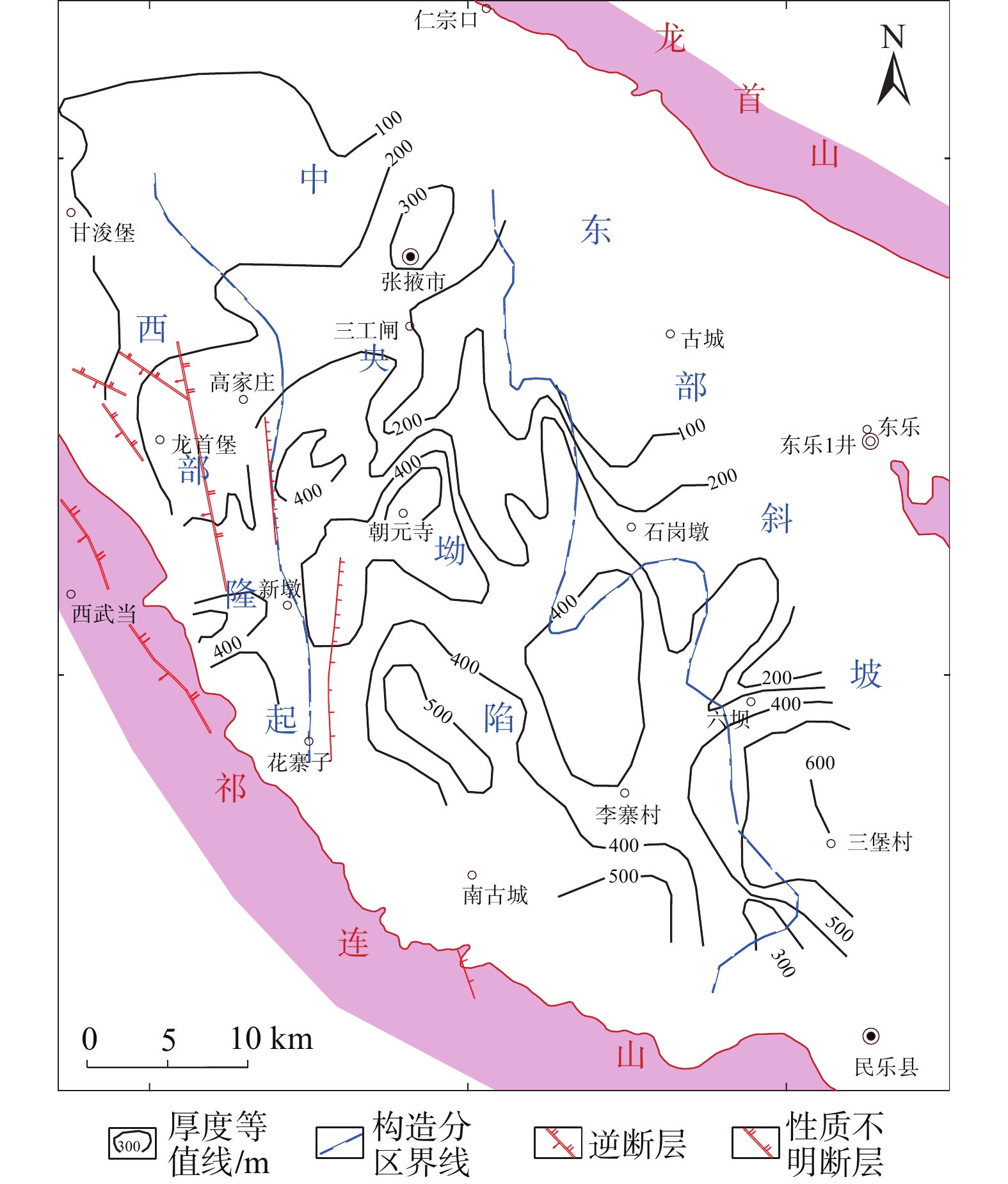
图 3 白杨河组间泉子段厚度等值线图(改编自文献[20])
Figure 3.
表 1 张掖盆地地热勘探孔地层时代及厚度对比表
Table 1. Geological age and thickness of strata tapped by geothermal exploration holes in the Zhangye Basin
地层或侵入岩时代 厚度/m 临泽LZDR1井 民参1井 张掖
ZYDR1井民参2井 甘浚
ZYDR2井体育公园
ZYDR3井民乐
MLDR1井第四系(Q) 412.85 669.10 651.60 685.00 598.00 590.00 644.00 新近系上新统(N2) 287.15 806.00 808.40 1117.00 592.00 1055.00 1154.00 新近系中新统(N1) 304.10 328.00 344.50 358.00 319.10 375.00 390.00 白垩系(K) 缺失 3244.20
(未揭穿)796.72
(未揭穿)1660.00
(未揭穿)120.60 154.03
(未揭穿)缺失 奥陶系(O) 未揭露 未揭露 未揭露 未揭露 423.38
(未揭穿)未揭露 未揭露 加里东期侵入岩 496.49
(未揭穿)未揭露 未揭露 未揭露 未揭露 未揭露 81.18
(未揭穿)表 2 张掖盆地地热勘探孔孔隙型热储统计表
Table 2. Statistics of geothermal reservoirs of pore type tapped by geothermal exploration holes in the Zhangye Basin
孔号 位置 井深
/m水头埋深
/m孔隙型热储岩性 热储底界
埋深/m孔隙型热储总厚度/m 热储底界测温/°C LZDR1 临泽县城南部 1500.59 62.00 砂岩、砂砾岩 1004.40 134.55 40.00 ZYDR1 甘州区滨河新区 2601.22 16.35 砂岩、砂砾岩 1804.50 174.50 49.70 ZYDR2 甘州区甘浚镇 2053.08 212.00 砂岩、砂砾岩 1509.10 165.40 41.50 ZYDR3 沙漠体育公园 2174.00 147.00 砂岩、砂砾岩 2020.00 175.48 58.64 MLDR1 民乐县新天镇 2269.18 69.51 砂岩、砂砾岩 2188.00 193.05 64.60 表 3 张掖盆地地下热水水化学分析结果
Table 3. Hydrochemical analyses of geothermal waters in the Zhangye Basin
孔号 温度
/°CTDS
/(mg∙L−-1)总硬度
/(mg∙L−1)pH ρ/(mg∙L−1) 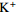

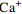
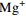
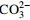

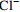
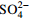
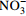

偏硅酸 偏硼酸 锶 锂 硒 铁 溴 游离
CO2LZDR1 45 3 432 374.8 7.6 8.0 1 044 84.2 39.9 0 217.1 1 293 701.6 6.2 1.4 28.36 12.0 5.84 0.23 0.001 0.06 1.16 6.98 ZYDR1 56 4 497 286.7 8.5 13.7 1 409 56.2 35.6 23.8 743.0 1 331 828.0 3.7 2.1 35.4 20.2 3.77 0.62 <0.002 0.02 2.20 8.40 ZYDR2 46 3 513 509.4 7.6 12.1 1 017 142.9 37.0 0 167.5 1 285 804.6 3.5 1.9 31.1 16.0 5.41 0.87 <0.001 0.33 0.77 7.63 ZYDR3 76 5 427 487.9 7.1 46.0 1 586 88.5 64.8 0 773.1 1 449 1 242.0 29.2 3.5 64.2 26.3 5.59 1.48 <0.002 0.58 1.40 51.80 MLDR1 77 5 810 1 131.0 7.7 61.7 1 522 250.0 123.0 0 596.0 1 754 1 408.0 37.2 3.6 59.8 3.2 10.80 1.04 0.027 <0.02 <0.01 106.00 表 4 张掖盆地水样氢、氧同位素分析结果
Table 4. Results of hydrogen and oxygen isotope analyses of geothermal water in the Zhangye Basin
编号 位置 地下水
类型δ18O
/‰δD
/‰3H
/TUH2 鹰落峡 河水 −9.7 −62 58 H3 新河大桥 河水 −7.9 −61 51 H4 乌江大桥 河水 −6.9 −46 49 PQ1 山丹河 泉水 −6.0 −47 55 PQ2 乌江四社 泉水 −7.4 −53 51 Y36 张掖龙渠 潜水 −7.6 −52 55 Y37 张掖甘浚 潜水 −6.9 −51 65 Y5 张掖新墩 潜水 −7.1 −50 57 Y41 张掖大满 潜水 −6.5 −44 47 Y10 张掖城区 承压水 −7.8 −56 39 Y11 张掖城区 承压水 −9.2 −63 21 Y14 张掖城区 承压水 −9.2 −58 16 Y47 张掖乌江 承压水 −9.9 −61 20 LZDR1 临泽沙河 地下热水 −10.5 −77 1.5±0.7 ZYDR1 张掖滨河新区 地下热水 −10.4 −76 <1.0 ZYDR2 张掖甘浚 地下热水 −9.5 −74 <0.5 ZYDR3 张掖党寨 地下热水 −10.0 −77 1.3±0.5 MLDR1 民乐新天镇 地下热水 −10.3 −76 <0.5 表 5 张掖盆地地下热水热储温度估算
Table 5. Estimated temperature of geothermal reservoirs in the Zhangye Basin
孔号 LZDR1 ZYDR1 ZYDR2 ZYDR3 MLDR1 ρ(K+)/(mg·L−1) 8.05 13.73 12.06 46.04 61.70 ρ(Mg2+)/(mg·L−1) 39.92 35.58 37.04 64.80 123.00 实测井口温度/°C 45.00 56.00 46.00 78.00 77.00 估算热储温度/°C 47.82 60.29 57.04 81.49 80.80 表 6 张掖盆地地热勘探孔推测热水循环深度
Table 6. Estimated circulation depth of geothermal water in geothermal exploration holes in the Zhangye Basin
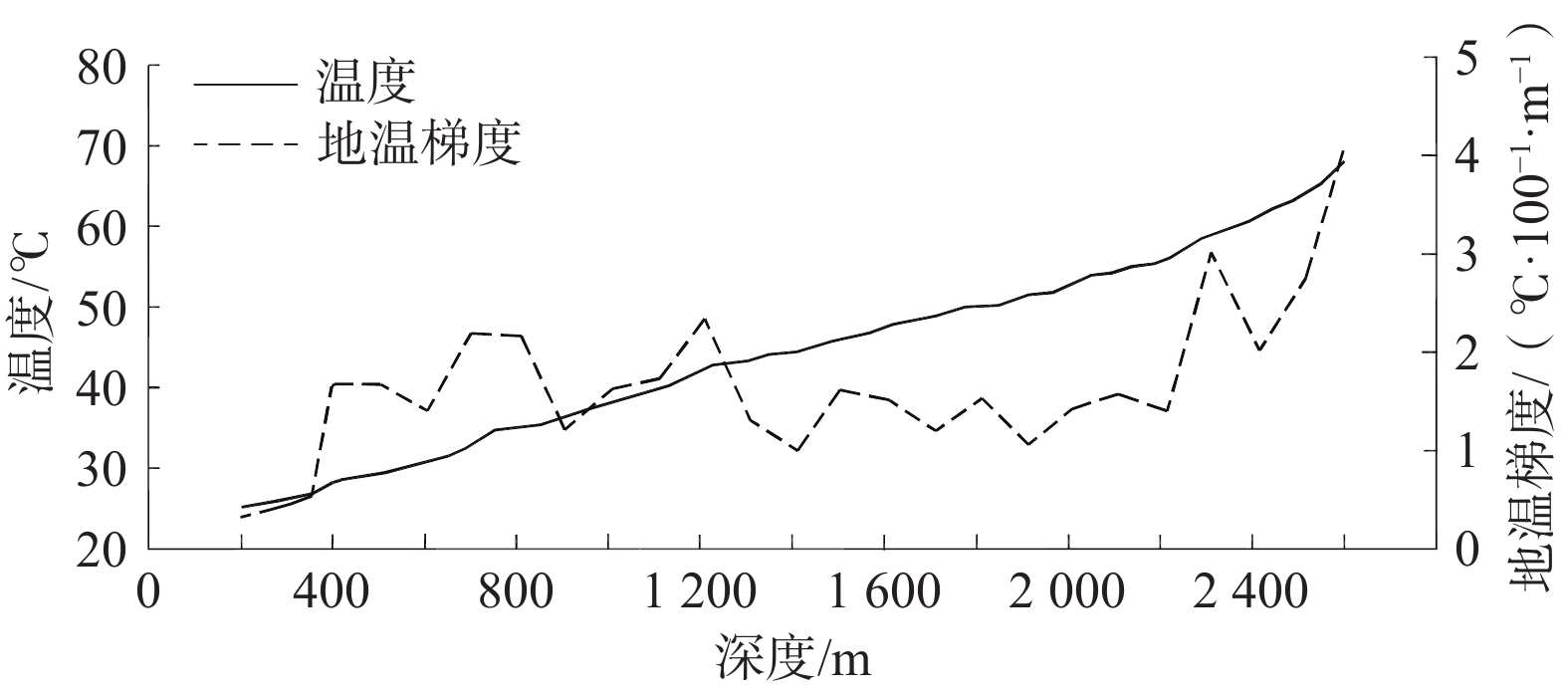
孔号 孔深/m 测温深度/m 测温/°C 地温梯度
/(°C·100−1·m−1)热储底界
埋深/m推测热水循
环深度/mLZDR1 1500.59 1500.00 45.60 2.58 1004.40 1588.91 ZYDR1 2601.22 2600.00 67.14 2.32 1804.50 2301.12 ZYDR2 2053.08 2000.00 47.70 2.04 1509.10 2453.53 ZYDR3 2174.00 2120.00 63.40 2.67 2020.00 2797.42 MLDR1 2269.18 2200.00 64.60 2.63 2188.00 2813.27 -
[1] 汪集旸. 地热学及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015
WANG Jiyang. Geothermics and its applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[2] 周总瑛,刘世良,刘金侠. 中国地热资源特点与发展对策[J]. 自然资源学报,2015,30(7):1210 − 1221. [ZHOU Zongying,LIU Shiliang,LIU Jinxia. Study on the characteristics and development strategies of geothermal resources in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2015,30(7):1210 − 1221. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.07.013
[3] 拓明明,周训,郭娟,等. 重庆温泉及地下热水的分布及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(1):165 − 172. [TA Mingming,ZHOU Xun,GUO Juan,et al. Occurrence and formation of the hot springs and thermal groundwater in Chongqing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(1):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张薇,王贵玲,刘峰,等. 中国沉积盆地型地热资源特征[J]. 中国地质,2019,46(2):255 − 268. [ZHANG Wei,WANG Guiling,LIU Feng,et al. Characteristics of geothermal resources in sedimentary basins[J]. Geology in China,2019,46(2):255 − 268. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 王贵玲,刘彦广,朱喜,等. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘,2020,27(1):1 − 9. [WANG Guiling,LIU Yanguang,ZHU Xi,et al. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2020,27(1):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2020.1.1
[6] 王寿川,刘亚强,张楷,等. 我国地热的开发现状和前景探讨[J]. 制冷技术,2015,35(2):68 − 72. [WANG Shouchuan,LIU Yaqiang,ZHANG Kai,et al. Discussion on status and prospects of geothermal resource development in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Refrigeration Technology,2015,35(2):68 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4468.2015.02.206
[7] 胡志华,高洪雷,万汉平,等. 西藏羊八井地热田水热蚀变的时空演化特征[J]. 地质论评,2022,68(1):359 − 374. [HU Zhihua,GAO Honglei,WAN Hanping,et al. Temporal and spatial evolution of hydrothermal alteration in the Yangbajing geothermal field,Xizang[J]. Geological Review,2022,68(1):359 − 374. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2021.12.105
[8] 龙登红,周小龙,杨坤光,等. 青藏高原东北缘深部地质构造与地热资源分布关系研究[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(3):721 − 731. [LONG Denghong,ZHOU Xiaolong,YANG Kunguang,et al. Research on relationship between the deep structure and geothermal resource distribution in the Northeastern Xizang Plateau[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(3):721 − 731. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 卞跃跃,赵丹. 四川康定地热田地下热水成因研究[J]. 地球学报,2018,39(4):491 − 497. [BIAN Yueyue,ZHAO Dan. Genesis of Geothermal Waters in the Kangding geothermal field,Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2018,39(4):491 − 497. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 张七道,刘振南,尹林虎,等. 深变质岩区地热流体化学特征及成因—以滇西陇川盆地温泉为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(6):1838 − 1852. [ZHANG Qidao,LIU Zhennan,YIN Linhu,et al. Chemical characteristics and genesis of geothermal fluid in deep metamorphic rock area:A case of hot springs in Longchuan Basin,Western Yunnan[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition),2021,51(6):1838 − 1852. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 赵振,秦光雄,罗银飞,等. 西宁盆地地热水特征及回灌结垢风险[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):193 − 204. [ZHAO Zhen,QIN Guangxiong,LUO Yinfei,et al. Characteristics of geothermal water in the Xining Basin and risk of reinjection scaling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):193 − 204. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 史杰,乃尉华,李明,等. 新疆曲曼高温地热田水文地球化学特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(3):165 − 172. [SHI Jie,NAI Weihua,LI Ming,et al. Study on the hydrogeo-chemical characteristics of the Quman high temperature geothermal field in Xinjiang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(3):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 史杰,汪美华,马小军,等. 新疆塔什库尔干县曲曼地热田地下热水同位素研究[J]. 地球学报,2022,43(5):645 − 653. [SHI Jie,WANG Meihua,MA Xiaojun,et al. Isotope and hydrogeochemical characteristics of the Quman high temperature geothermal field in Taxkorgan,Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2022,43(5):645 − 653. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2022.040702
[14] 汪洋,张旭虎,蒲丛林,等. 河北廊坊南部地区地热水化学特征及成因机制[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(9):1698 − 1706. [WANG Yang,ZHANG Xuhu,PU Conglin,et al. The hydrochemical characteristics of geothermal water and its formation in the south Langfang,Hebei Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2022,41(9):1698 − 1706. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.09.017
[15] 刘润川,任战利,叶汉青,等. 地热资源潜力评价—以鄂尔多斯盆地部分地级市和重点层位为例[J]. 地质通报,2021,40(4):565 − 576. [LIU Runchuan,REN Zhanli,YE Hanqing,et al. Potential evaluation of geothermal resources:Exemplifying some municipalities and key strata in Ordos Basin as a study case[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021,40(4):565 − 576. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.04.013
[16] 汪新伟,王婷灏,李海泉,等. 太原盆地岩溶地热系统的形成演化及其地热资源潜力[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(3):716 − 731. [WANG Xinwei,WANG Tinghao,LI Haiquan,et al. Evolution of karst geothermal system and its geothermal resource potential in Taiyuan Basin[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(3):716 − 731. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 刘峰,王贵玲,张薇,等. 江西宁都县北部大地热流特征及地热资源成因机制[J]. 地质通报,2020,39(12):1883 − 1890. [LIU Feng,WANG Guiling,ZHANG Wei,et al. Terrestrial heat flow and geothermal genesis mechanism of geothermal resources in northern Ningdu County,Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2020,39(12):1883 − 1890. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.12.002
[18] 尹政, 田辽西, 张旭儒, 等. 张掖城区及外围地热资源普查报告[R]. 兰州: 甘肃省地矿局水文地质工程地质勘察院, 2018.
YIN Zheng, TIAN Liaoxi, ZHANG Xuru, et al. Geothermal resources survey in Zhangye city and its periphery [R]. Lanzhou: Institute of Hydrogeoloical and Engineering Geology, Gansu Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development, 2018. (in Chinese)
[19] 刘宝睿,杨克绳,刘东艳. 论河西走廊陆盆的演化和最终形成期[J]. 地质论评,2009,55(1):25 − 31. [LIU Baorui,YANG Kesheng,LIU Dongyan. A discussion on evolution and final forming time of the Hexi Corridor continental basin[J]. Geological Review,2009,55(1):25 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2009.01.003
[20] 玉门油田石油地质志编写组. 中国石油地质志-卷十三-玉门油田[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1989: 236 − 261
Compilation group of petroleum geology in Yumen Oilfield. Yumen Oilfield, petroleum geology of China (Vol. 13) [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1989: 236 − 261. (in Chinese)
[21] 魏红军,李百祥. 张掖—民乐盆地地质构造特征与张掖市地热资源开发可行性分析[J]. 甘肃地质,2007,16(4):73 − 76. [WEI Hongjun,LI Baixiang. Characteristics of geological structures in Zhangye—Minle Basin and feasibility study of geothermal resources in Zhangye City[J]. Gansu Geology,2007,16(4):73 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 汪集旸, 熊亮萍, 庞忠和. 中低温对流型地热系统[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993: 117 − 132
WANG Jiyang, XIONG Liangping, PANG Zhonghe. Low-medium temperature geo-thermal system of convective type[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993: 117 − 132. (in Chinese)
[23] 尹政,柳永刚,张旭儒,等. 张掖—民乐盆地中新生界地层结构及对地热的控制作用[J]. 甘肃地质,2021,30(3):49 − 56. [YIN Zheng,LIU Yonggang,ZHANG Xuru,et al. Mesozoic cenozoic stratigraphic structure and its control on geothermal energy in Zhangye— Minle Basin[J]. Gansu Geology,2021,30(3):49 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 王卫星,孙玉东,杨永江,等. 天津市东丽湖地热对井的地质与水文地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探,2010,34(1):44 − 48. [WANG Weixing,SUN Yudong,YANG Yongjiang,et al. Geological and hydrogeochemical characteristics geothermal paired wells in Dongli Lake area Tianjin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2010,34(1):44 − 48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] PAYNE B R. Water balance of Lake Chala and its relation to groundwater from tritium and stable isotope data[J]. Journal of Hydrology,1970,11(1):47 − 58. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(70)90114-9
[26] 冯欣,张亚哲. 深州地区地下水离子比例系数分析研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2014(4):18 − 20. [FENG Xin,ZHANG Yazhe. An analysis of the ions ratio coefficients of groundwater in Shenzhou area[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2014(4):18 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2014.04.006
[27] 尹政,张旭儒,王春磊,等. 张掖—民乐盆地地热田热矿水化学特征及理疗作用研究[J]. 甘肃地质,2022,31(1):72 − 78. [YIN Zheng,ZHANG Xuru,WANG Chunlei,et al. Chemical characteristics and physiotherapy effects of thermal mineral water in Zhangye Basin[J]. Gansu Geology,2022,31(1):72 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 黄锦忠,谭红兵,王若安,等. 我国西北地区多年降水的氢氧同位素分布特征研究[J]. 水文,2015,35(1):33 − 39. [HUANG Jinzhong,TAN Hongbing,WANG Ruoan,et al. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic analysis of perennial meteoric water in northwest China[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2015,35(1):33 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2015.01.006
[29] CHEN Jiansheng,ZHAO Xia,FAN Zhechao,et al. Isotope method for confined groundwater recharge of the lower reaches of the Heihe River,Inner Mongolia,China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2007,81(4):668 − 673. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2007.tb00990.x
[30] MONTOROI J P,GRÜNBERGER O,NASRI S. Groundwater geochemistry of a small reservoir catchment in Central Tunisia[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2002,17(8):1047 − 1060. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00076-8
[31] 张人权. 国外水文地质研究中应用同位素方法的现状[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1981,8(6):55 − 57. [ZHANG Renquan. Application of isotope method in hydrogeological research abroad[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1981,8(6):55 − 57. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.1981.06.023
[32] 王莹,周训,于湲,等. 应用地热温标估算地下热储温度[J]. 现代地质,2007,21(4):605 − 612. [WANG Ying,ZHOU Xun,YU Yuan,et,al. Application of geothermemeters to calculation of temperature of geothermal reservoirs[J]. Geoscience,2007,21(4):605 − 612. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003
[33] 汪集旸,熊亮萍,庞忠和. 利用地热资料确定地下热水循环深度[J]. 科学通报,1990,35(5):378 − 380. [WANG Jiyang,XIONG Liangping,PANG Zhonghe,et al. Using geothermal data to determine the circulation depth of underground hot water[J]. Chinses Science Bulletin,1990,35(5):378 − 380. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/csb1990-35-5-378
-



 下载:
下载: