Geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the seawater-recharged geothermal systems in Yantian of Fujian, China
-
摘要:
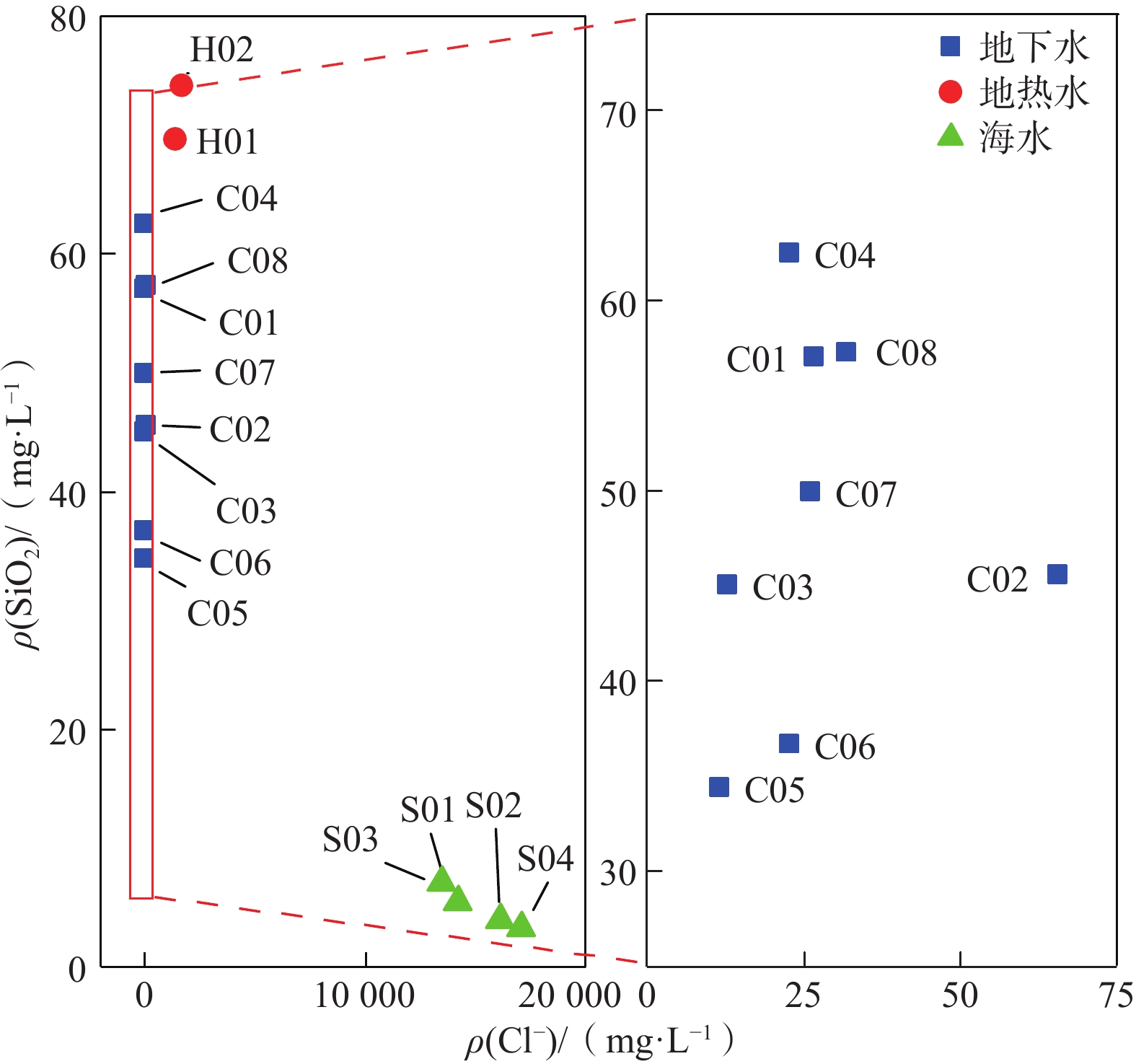
海水补给型地热系统具有补给资源量大,但温度低、水质咸化等特点,查明沿海地热水循环补给条件和成因机制,对东南沿海地热资源的合理开发利用和保护具有重要意义。在泉州官桥盐田地热区分别采集了地热水、地下水和海水样品14个,利用水化学同位素特征分析和地球化学温标法,揭示了官桥盐田地热水循环补给和地热资源成因机制。结果表明:地热水水化学类型为Cl—Na型水,与海水水化学类型一致;H01和H02的溶解性固体总量(TDS)分别为2610 mg/L和3 090 mg/L,地下水以TDS小于400 mg/L的
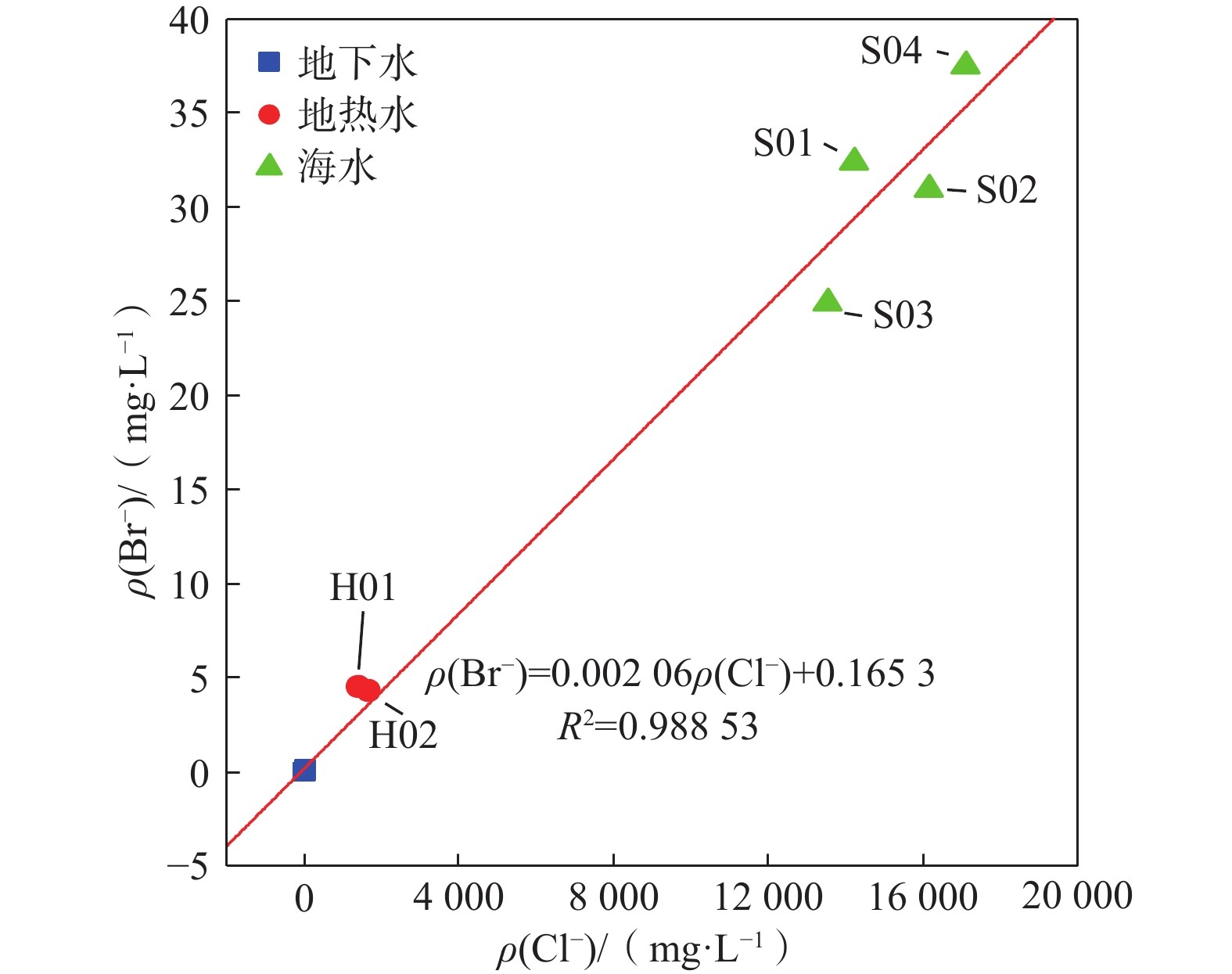
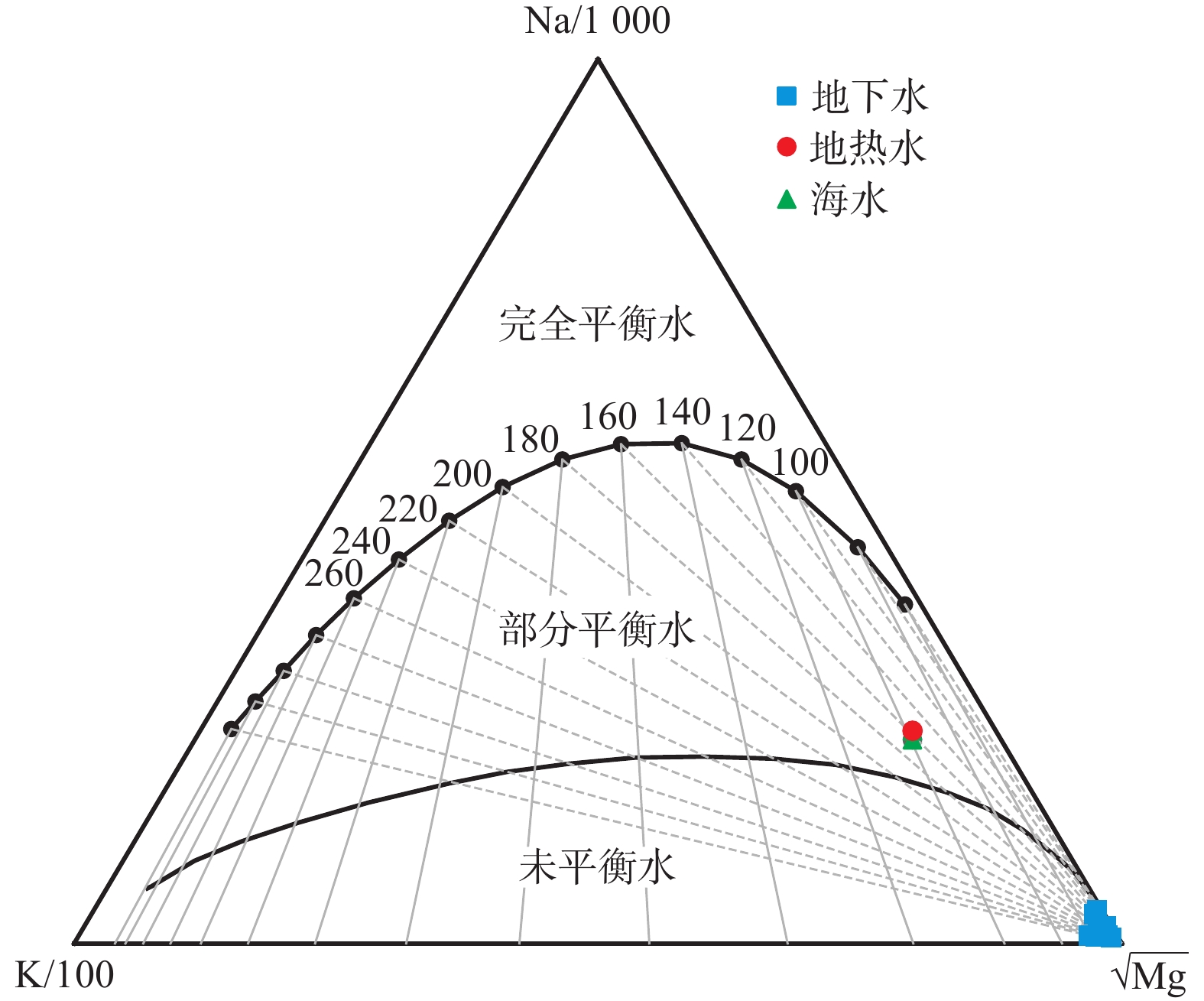
$ {\rm{HCO}}_3$ Abstract:Seawater-recharged geothermal systems are characterized by abundant recharge, low temperature and salinization. Ascertaining the circulation recharge conditions and genetic mechanisms of geothermal water in coastal areas of southeast China is of important significance in the rational exploration, utilization and protection of geothermal resources in these areas. In this study, 14 samples of geothermal water, groundwater and seawater are collected from the Yantian geothermal field near Guanqiao Town in Fujian Province, China and the hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics are analyzed. The circulation recharge of the geothermal water and the genetic mechanisms of the geothermal resources in the geothermal field are revealed using geothermometers. The results show that hydrochemical type of the geothermal water in the Yantian geothermal field is of Cl—Na type, which is similar to that of the seawater. Total dissolved solids of geothermal water samples H01 and H02 are 2 610 mg/L and 3 090 mg/L, respectively. By contrast, the groundwater in the geothermal field is dominated by the HCO3—Na type, and the groundwater samples have TDS of less than 400 mg/L. Moreover, the geothermal water is rich in Br−, which is not detected in the groundwater. These results indicate that modern seawater or ancient seawater in marine sedimentary layers is a recharge source of the geothermal water. As shown by the results of H01 and H02 calculated using the Cl− mixing model, geothermal water samples H01 and H02 have seawater mixing ratios of 9.13% and 10.76%, respectively, and H01 is mixed with more groundwater after being exposed to Quaternary sediments. The comprehensive analyses show that the geothermal water in the Yantian geothermal field is primarily recharged by seawater and its chemical composition is significantly affected by seawater mixing. Furthermore, the comprehensive analyses also suggest that the deep geothermal water is mixed with groundwater or seawater twice or more times as it rises upward, thus forming shallow geothermal reservoirs with a temperature of 89 °C to 121 °C, as estimated by using the SiO2 geothermometer and the multi-mineral equilibrium method.
-
Key words:
- geothermal water /
- hydrogeochemistry /
- environmental isotope /
- geothermometer /
- seawater recharge
-

-
表 1 官桥盐田地下水化学测试结果表
Table 1. List of hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in Yantian
样品
编号井深
/mρ(K+)
/(mg∙L−1)ρ(Na+)
/(mg∙L−1)ρ(Ca2+)
/(mg∙L−1)ρ(Mg2+)
/(mg∙L−1)ρ(Cl−)
/(mg∙L−1)ρ( 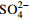 )
)
/(mg∙L−1)ρ(  )
)
/(mg∙L−1)ρ(  )
)
/(mg∙L−1)ρ(Br−)
/(mg∙L−1)TDS
/(mg∙L−1)ρ(SiO2)
/(mg∙L−1)pH δD
/‰δ18O
/‰H01 50.0 19.67 534.90 415.10 2.53 1 418.00 109.20 67.12 0.00 4.51 2 610.0 69.60 7.03 −41.00 −6.20 H02 500.0 22.57 683.20 456.70 3.73 1 667.00 115.30 76.41 0.00 4.29 3 090.0 74.11 7.15 −39.75 −5.82 C01 100.0 5.60 17.80 13.78 3.99 26.55 2.26 54.92 0.00 <0.10 167.9 57.00 6.51 −40.00 −6.10 C02 100.0 6.11 42.56 41.27 12.85 65.32 14.65 56.14 0.00 0.13 369.5 45.54 6.47 −41.00 −6.20 C03 100.0 2.25 23.81 27.27 6.26 12.92 12.02 115.90 0.00 <0.10 212.3 45.03 6.81 −45.00 −6.70 C04 90.0 0.95 31.91 35.77 2.68 22.70 9.58 151.30 0.00 <0.10 244.0 62.45 7.55 −46.00 −6.80 C05 164.0 0.98 70.32 32.04 3.30 11.53 64.47 183.10 0.00 <0.10 314.1 34.39 7.79 −41.00 −6.30 C06 110.0 0.92 32.43 47.12 0.87 22.70 4.05 170.20 0.00 <0.10 245.0 36.69 7.22 −37.00 −5.10 C07 109.0 2.20 21.35 31.72 9.85 26.20 2.28 102.50 0.00 <0.10 259.0 49.93 7.17 −41.00 −6.30 C08 100.0 5.17 19.10 25.27 5.66 31.78 3.47 73.83 0.00 <0.10 217.0 57.25 6.62 −37.00 −5.10 S01 − 279.70 7 645.00 309.90 942.00 14 233.00 1 750.00 1 240.00 0.00 32.35 25 310.0 5.47 7.24 − − S02 − 322.50 8 590.00 349.50 1 077.00 16 154.00 1 900.00 135.90 0.00 30.94 29 000.0 3.92 7.63 − − S03 − 274.20 7 355.00 303.30 912.00 13 535.00 1 582.00 141.80 0.00 24.86 24 050.0 7.13 7.24 − − S04 − 344.40 9 435.00 374.30 1 176.00 17 115.00 2 116.00 135.90 0.00 37.51 31 160.0 3.24 7.84 − − 注:“−”表示无数据;“0.00”表示低于检出限;ρ表示质量浓度。 -
[1] 沈照理,王焰新,郭华明. 水-岩相互作用研究的机遇与挑战[J]. 地球科学,2012,37(2):207 − 219. [SHEN Zhaoli,WANG Yanxin,GUO Huaming. Opportunities and challenges of water-rock interaction studies[J]. Earth Science,2012,37(2):207 − 219. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] KONG Yanlong,PANG Zhonghe,SHAO Haibing,et al. Recent studies on hydrothermal systems in China:A review[J]. Geothermal Energy,2014,2:19. doi: 10.1186/s40517-014-0019-8
[3] 史杰,汪美华,马小军,等. 新疆塔什库尔干县曲曼地热田地下热水同位素研究[J]. 地球学报,2022,43(5):645 − 653. [SHI Jie,WANG Meihua,MA Xiaojun,et al. Isotope and hydrogeochemical characteristics of the Quman high temperature geothermal field in Taxkorgan,Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2022,43(5):645 − 653. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 熊亮萍,汪集旸,庞忠和. 漳州热田的对流热流和传导热流的研究[J]. 地球物理学报,1990,33(6):702 − 711. [XIONG Liangping,WANG Jiyang,PANG Zhonghe. Convective and conductive heat flows in zhangzhou geothermal field,Fujian province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,1990,33(6):702 − 711. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1990.06.010
[5] 张七道,刘振南,尹林虎,等. 深变质岩区地热流体化学特征及成因—以滇西陇川盆地温泉为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(6):1838 − 1852. [ZHANG Qidao,LIU Zhennan,YIN Linhu,et al. Chemical characteristics and genesis of geothermal fluid in deep metamorphic rock area:A case of hot springs in Longchuan Basin,Western Yunnan[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(6):1838 − 1852. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 甘浩男,蔺文静,闫晓雪,等. 粤中隐伏岩体区地热赋存特征及热异常成因分析[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(7):2096 − 2106. [GAN Haonan,LIN Wenjing,YAN Xiaoxue,et al. Analysis of geothermal occurrence characteristics and origin of the thermal anomalies in the hidden igneous rock area in the central Guangdong[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(7):2096 − 2106. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.017
[7] ÁRMANNSSON H. The fluid geochemistry of Icelandic high temperature geothermal areas[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2016,66:14 − 64. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.10.008
[8] 孙红丽,马峰,蔺文静,等. 西藏高温地热田地球化学特征及地热温标应用[J]. 地质科技情报,2015,34(3):171 − 177. [SUN Hongli,MA Feng,LIN Wenjing,et al. Geochemical characteristics and geothermometer application in high temperature geothermal field in Xizang[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2015,34(3):171 − 177. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 汪洋,张旭虎,蒲丛林,等. 河北廊坊南部地区地热水化学特征及成因机制[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(9):1698 − 1706. [WANG Yang,ZHANG Xuhu,PU Conglin,et al. The hydrochemical characteristics of geothermal water and its formation in the south Langfang,Hebei Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2022,41(9):1698 − 1706. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 史猛, 张杰, 殷焘, 等. 胶东半岛中低温对流型地热资源水化学特征分析[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(增刊1): 138 − 148
SHI Meng, ZHANG Jie, YIN Tao, et al. Hydrochemistry characteristic analysis of low-medium temperature convective geothermal resources in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(Sup 1): 138 − 148. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 徐钫一鸣,卢国平. 广东海岸带型新洲地热田水化学及海水入侵水动力特征[J]. 安全与环境工程,2017,24(1):1 − 10. [XU Fangyiming,LU Guoping. Hydrochemical characteristics of Xinzhou geothermal field,coastal Guangdong and the hydrodynamic characteristics of seawater intrusion in the field[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2017,24(1):1 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 林韵,高磊,李绍恒,等. 广东江门地热水水文地球化学特征及来源分析[J]. 环境化学,2020,39(2):512 − 523. [LIN Yun,GAO Lei,LI Shaoheng,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and source identification of geothermal waters in Jiangmen,Guangdong Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2020,39(2):512 − 523. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019030606
[13] LIU Yanguang,LIU Bing,LU Chuan,et al. Reconstruction of deep fluid chemical constituents for estimation of geothermal reservoir temperature using chemical geothermometers[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2017(2):87 − 95.
[14] 王晓翠,孙海龙,袁星芳. 胶东典型花岗岩热储地下热水水化学特征及热储研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):186 − 194. [WANG Xiaocui,SUN Hailong,YUAN Xingfang. A study of the hydrochemical characteristics and geothermal water of typical granite geothermal reservoir in the Jiaodong area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):186 − 194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] CRAIG H. The geochemistry of the stable carbon isotopes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1953,3(2/3):53 − 92.
[16] 郑西来, 郭建青. 二氧化硅地热温标及其相关问题的处理方法[J]. 地下水, 1996, 18(2): 85-88
ZHENG Xilai, GUO Jianqing. Silica geothermometer and related methods of dealing with problems[J], Groundwater. 1996, 18(2): 85-88. (in Chinese)
[17] FOURNIER R O. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems[J]. Geothermics,1977,5(1/2/3/4):41 − 50.
[18] FOURNIER R O,ROWE J J. Estimation of underground temperatures from the silica content of water from hot springs and wet-steam wells[J]. American Journal of Science,1966,264(9):685 − 697. doi: 10.2475/ajs.264.9.685
[19] FOURNIER R O,TRUESDELL A H. An empirical Na–K–Ca geothermometer for natural waters[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1973,37(5):1255 − 1275. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90060-4
[20] FOURNIER R O,THOMPSON J M,AUSTIN C F. Interpretation of chemical analyses of waters collected from two geothermal wells at Coso,California[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1980,85(B5):2405 − 2410. doi: 10.1029/JB085iB05p02405
[21] ARNORSSON S. Application of the silica geothermometer in low temperature hydrothermal areas in Iceland[J]. American Journal of Science,1975,275(7):763 − 784. doi: 10.2475/ajs.275.7.763
[22] REED M,SPYCHER N. Calculation of pH and mineral equilibria in hydrothermal waters with application to geothermometry and studies of boiling and dilution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1984,48(7):1479 − 1492. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90404-6
[23] PANG Zhonghe,REED M. Theoretical chemical thermometry on geothermal waters:Problems and methods[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1998,62(6):1083 − 1091. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00037-4
[24] 熊绍柏,金东敏,孙克忠,等. 福建漳州地热田及其邻近地区的地壳深部构造特征[J]. 地球物理学报,1991,34(1):55 − 63. [XIONG Shaobai,JIN Dongmin,SUN Kezhong,et al. Some characteristics of deep structure of the Zhangzhou geothermal field and it’s neighbourhood in the Fujian Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,1991,34(1):55 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1991.01.006
[25] ZHANG Ying,LUO Jun,FENG Jianyun. Characteristics of geothermal reservoirs and utilization of geothermal resources in the southeastern coastal areas of China[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2020,8(2):134 − 142.
[26] 李亭昕,蔺文静,甘浩男,等. 东南沿海干热岩资源成因模式探讨及勘查进展[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(2):187 − 200. [LI Tingxin,LIN Wenjing,GAN Haonan,et al. Research on the genetic model and exploration progress of hot dry rock resources on the southeast coast of China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(2):187 − 200. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.02.018
[27] LIN Wenjing, WANG Guiling, GAN Haonan, et al. Heat generation and accumulation for hot dry rock resources in the igneous rock distribution areas of southeastern China[J]. Lithosphere, 2022, 2021(Special 5): 2022.2039112.
[28] 廖志杰. 福建无岩浆热源的深循环水热系统[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(1): 85 − 98
LIAO Zhijie. Deep-circulation hydrothermal systems without magmatic heat source in Fujian Province[J], Geoscience, 2012, 26(1): 85 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 韩庆之, 庄庆祥. 漳州盆地地下热水的来源和运移途径的初步研究[J]. 地球科学, 1988, 13(3): 271-277
HAN Qingzhi, ZHUANG Qingxiang. On the source and pathway of hot water in Zhangzhou Basin, Fujian[J], Earth Science, 1988, 13(3): 271-277. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 范蔚茗,MENZIES M A,尹汉辉,等. 中国东南沿海深部岩石圈的性质和深部作用过程初探[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,1993,17(1):23 − 30. [FAN Weiming,MENZIES M A,YIN Hanhui,et al. Nature and processes of the lower lithosphere of the southeast China coast[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,1993,17(1):23 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 裘中良. 厦门地热资源及成因研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018
QIU Zhongliang. Study on geothermal resources and its causes in Xiamen[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 陆晨明,刘春雷,李亚松,等. 泉州官桥地区地热勘探靶区及成因模式探讨[J]. 地质论评,2021,67(5):1345 − 1356. [LU Chenming,LIU Chunlei,LI Yasong,et al. Exploration target area of geothermal resources in Guanqiao area,Quanzhou,and its genetic model[J]. Geological Review,2021,67(5):1345 − 1356. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2021.08.053
[33] 马振波,马艳飞,张平,等. 广域电磁法在福建洪塘镇地热勘查中的应用[J]. 矿产勘查,2021,12(3):661 − 667. [MA Zhenbo,MA Yanfei,ZHANG Ping,et al. Application of wide area electromagnetic method in geothermal exploration of Hongtang Town,Fujian Province[J]. Mineral Exploration,2021,12(3):661 − 667. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2021.03.019
[34] 蔺文静,陈向阳,甘浩男,等. 东南沿海厦门湾-漳州盆地地热地质特征及干热岩勘查方向[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(7):2066 − 2077. [LIN Wenjing,CHEN Xiangyang,GAN Haonan,et al. Geothermal,geological characteristics and exploration direction of hot dry rocks in the Xiamen Bay-Zhangzhou Basin,southeastern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(7):2066 − 2077. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.014
[35] LIU Chunlei,LI Yasong,CAO Shengwei,et al. Effects of seawater recharge on the formation of geothermal resources in coastal areas and their mechanisms:A case study of Xiamen City,Fujian Province,China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2022,10:872620. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.872620
[36] 王大纯, 张人权, 史毅虹, 等. 水文地质学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1986
WANG Dachun, ZHANG Renquan, SHI Yihong, et al. General hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1986. (in Chinese)
[37] 陈衍婷,杜文娇,陈进生,等. 厦门地区大气降水氢氧同位素组成特征及水汽来源探讨[J]. 环境科学学报,2016,36(2):667 − 674. [CHEN Yanting,DU Wenjiao,CHEN Jinsheng,et al. Composition of hydrogen and oxygen isotopic of precipitation and source apportionment of water vapor in Xiamen area[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2016,36(2):667 − 674. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] YURTSEVER Y. Worldwide survey of stable isotopes in precipitation[R]. Rep. Sect. Isotope Hydrol., IAEA, 1975.
[39] GIGGENBACH W F. Geothermal solute equilibria derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1988,52(12):2749 − 2765. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3
[40] 史杰,乃尉华,李明,等. 新疆曲曼高温地热田水文地球化学特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(3):165 − 172. [SHI Jie,NAI Weihua,LI Ming,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of high temperature geothermal field of the Quman geothermal field in Xinjiang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(3):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] SPYCHER N,PEIFFER L,SONNENTHAL E L,et al. Integrated multicomponent solute geothermometry[J]. Geothermics,2014,51:113 − 123. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2013.10.012
[42] TIAN Jiao,LI Yiman,ZHOU Xiaocheng,et al. Geochemical characteristics of hydrothermal volatiles from southeast China and their implications on the tectonic structure controlling heat convection[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2021,9:786051. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.786051
-




 下载:
下载: