A study of the relationship between ecological water conveyance and water surface area of the Qingtu Lake based on GSFLOW
-
摘要:
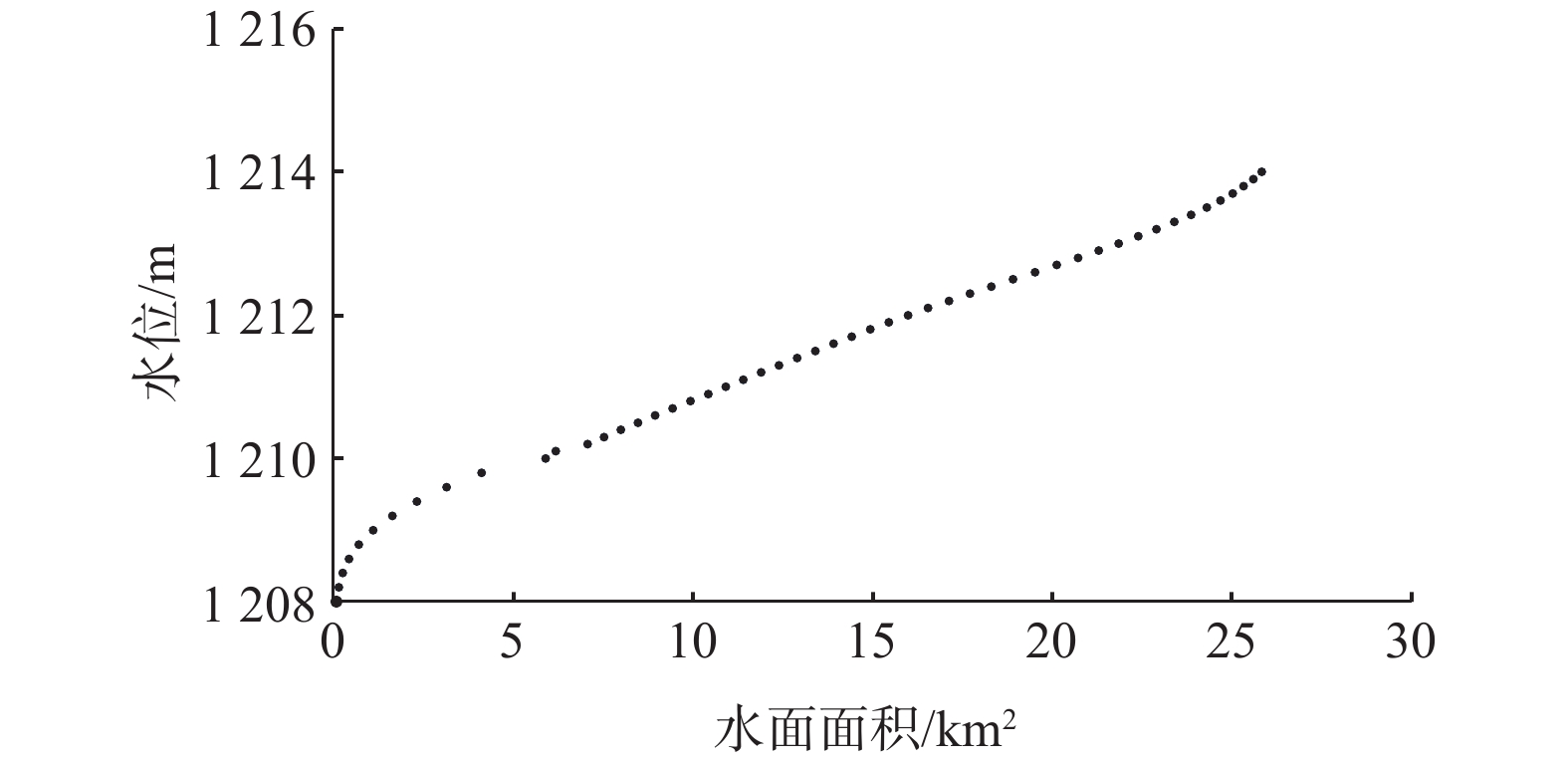
西北地区水资源匮乏,生态环境脆弱,如何科学处理生产用水与生态用水的关系一直是西北干旱区水资源开发利用中关注和研究的热点难点课题之一。关于流域中上游生态输水与尾闾湖水域面积(或湿地面积)关系的定量化研究较少。以我国西北干旱区河西走廊石羊河流域的尾闾湖—青土湖为例,利用GSFLOW建立了区域地表水-地下水耦合模型,其中采用LAK模块及SFR2模块分别处理湖泊和输水渠道,在此基础上预测了不同生态输水方案下湖泊湖面面积的变化情况,分析了青土湖生态输水量-湖水面积关系,确定了青土湖生态输水的合理范围。研究结果显示:当前3100×104 m3/a的生态输水量可以保证青土湖维持年内最高湖水水位1212.23 m(平均水位1211.68 m),稳定最大面积可达16.27 km2;当输水量为2000×104~3700×104 m3/a时,随输水量增大水面面积线性增加,面积变化率相对稳定;当输水量为3700×104~4500×104 m3/a时,水面面积随生态输水量增多,面积增大率逐渐减小;当输水量大于4500×104 m3/a时,水面面积随生态输水增多增大幅度很小,特别是当生态输水量大于5500×104 m3/a时,面积变化率趋近于0。从维持当前青土湖水面面积和向青土湖生态输水的效益考虑,红崖山水库向青土湖的生态输水量应保持在3100×104~4500×104 m3/a。研究成果对于确定西北干旱区合理生态需水,协调生态、经济、社会用水可持续发展具有一定的参考价值。
-
关键词:
- 青土湖 /
- 生态输水-水面面积关系 /
- 数值模拟 /
- 地下水-地表水耦合模型
Abstract:Water resources are scarce and ecological environment is fragile in the arid regions of northwest China. How to scientifically deal with the relationship between production water and ecological water has always been one of the hotspot and difficult issues in the field of water resources development and utilization in northwest arid areas. However, there are few quantitative studies on the relationship between the ecological water conveyance from the middle and upper reaches of the basin to the downstream terminal lake (wetland) and the area of the terminal lake (wetland). In this paper, Qingtu Lake, the terminal lake of the Shiyang River Basin in Gansu Province, is taken as an example. A coupled model of surface water and groundwater is established using GSFLOW software, among which, LAK module and SFR2 module are used to treat the lake and water channel, respectively. Based on this, the changes of surface area of the Qingtu Lake under different ecological water conveyance schemes are predicted. The appropriate range of ecological water conveyance to the Qingtu Lake is determined. The results show that the current ecological water conveyance of 3100×104 m3/a can ensure the highest water level of Qingtu Lake of 1212.23 m (the average water level of 1211.68 m) and the corresponding water surface area of 16.27 km2. The relationship between ecological water conveyance and water surface area is as follow. When the water delivery is in the range of 2000×104−3700×104 m3/a, the water surface area increases obviously and the area change rate is relatively stable with the increase of water conveyance; when the water delivery is in the range of 3700×104−4500×104 m3/a, the increasing water surface area gradually decreases and the area change rate gradually decreases with the increasing water conveyance; and when the water conveyance is more than 4500×104 m3/a, the increase of water surface area with the increasing ecological water conveyance is very small, especially when the ecological water conveyance is more than 5500×104 m3/a, the change rate of water surface area tends to 0. Considering the demand for maintaining the current water surface area of the Qingtu Lake and the benefits of ecological water conveyance, the ecological water conveyance volume from the Hongyashan reservoir to the Qingtu lake should be in range of 3100×104−4500×104 m3/a. The results are of certain reference value in determining the local ecological water demand and maintaining the coordinated and sustainable development of local ecology, economy and society.
-

-
图 4 PRMS与MODFLOW耦合模式[20]
Figure 4.
图 6 湖区钻孔分布及地层剖面[19]
Figure 6.
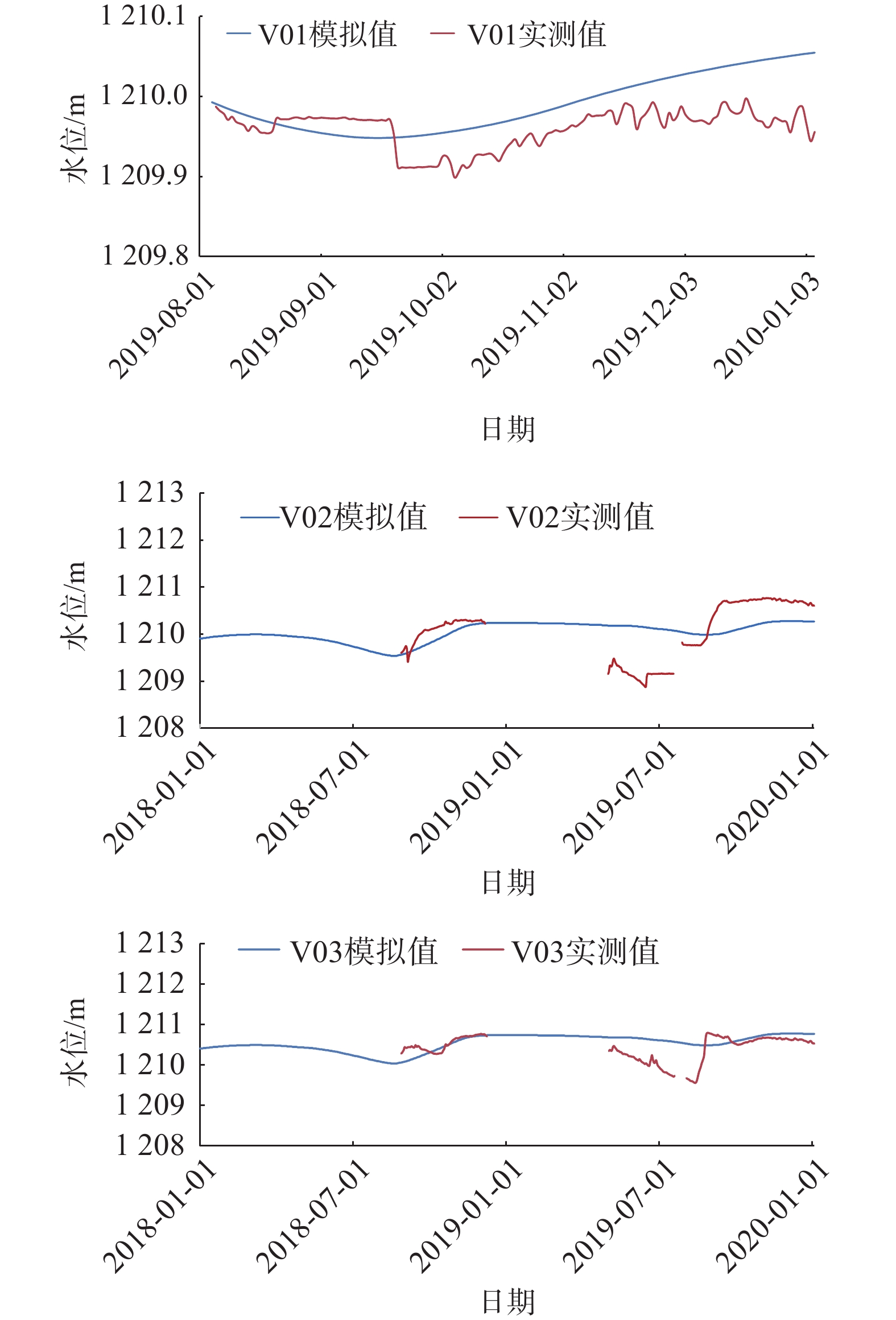
表 1 不同生态输水方案下2039年预测湖泊水均衡情况
Table 1. Predicted lake water balance in 2039 under different ecological water conveyance schemes
/104 m3 生态
输水量补给项 排泄项 均衡量 降水量 生态入湖输水量 蒸散发量 湖泊补给地下水量 3100 147 2170 2550 14 −247 4500 162 3150 2810 463 40 6000 165 4200 2862 1518 −15 -
[1] 孙自永,王俊友,葛孟琰,等. 基于水稳定同位素的地下水型陆地植被识别:研究进展、面临挑战及未来研究展望[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(1):11 − 20. [SUN Ziyong,WANG Junyou,GE Mengyan,et al. Isotopic approaches to identify groundwater dependent terrestrial vegetation:Progress,challenges,and prospects for future research[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(1):11 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张晓晓,张钰,徐浩杰,等. 河西走廊三大内陆河流域出山径流变化特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2014,28(4):66 − 72. [ZHANG Xiaoxiao,ZHANG Yu,XU Haojie,et al. Mountainous runoff change in three inland river basin in Hexi Corridor and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2014,28(4):66 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2014.04.034
[3] 赵军,杨建霞,朱国锋. 生态输水对青土湖周边区域植被覆盖度的影响[J]. 干旱区研究,2018,35(6):1251 − 1261. [ZHAO Jun,YANG Jianxia,ZHU Guofeng. Effect of ecological water conveyance on vegetation coverage in surrounding area of the qingtu lake[J]. Arid Zone Research,2018,35(6):1251 − 1261. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2018.06.01
[4] 刘淑娟,袁宏波,刘世增,等. 石羊河尾闾水面形成区土壤颗粒的分形特征[J]. 水土保持通报,2013,33(6):285 − 289. [LIU Shujuan,YUAN Hongbo,LIU Shizeng,et al. Characteristics of soil particle fractal dimension after formation of water area in tail-streams of Shiyang River[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2013,33(6):285 − 289. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2013.06.051
[5] 刘淑娟,马剑平,刘世增,等. 青土湖水面形成过程对荒漠植物多样性的影响[J]. 水土保持通报,2016,36(1):27 − 32. [LIU Shujuan,MA Jianping,LIU Shizeng,et al. Effects of qingtu lake water area formation on diversity of plants in desert region[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2016,36(1):27 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2016.01.006
[6] 陈政融,刘世增,刘淑娟,等. 青土湖水面形成对区域典型植被分布的影响[J]. 中国农学通报,2015,31(21):177 − 183. [CHEN Zhengrong,LIU Shizeng,LIU Shujuan,et al. Effect of water body forming on the distribution of typical vegetation in qingtu lake[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2015,31(21):177 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] QIAO S F,MA R,SUN Z Y,et al. The effect of water transfer during non-growing season on the wetland ecosystem via surface and groundwater interactions in arid northwestern China[J]. Remote Sensing,2020,12(16):2516. doi: 10.3390/rs12162516
[8] 林勇,李丰顺. 估算地下水补给量的新方法-SWATMOD耦合模型简介[J]. 科技视界,2017(3):251. [LIN Yong,LI Fengshun. Estimation of groundwater recharge by the new method-SWATMOD coupling model introduction[J]. Science & Technology Vision,2017(3):251. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19694/j.cnki.issn2095-2457.2017.03.191
[9] PERKINS S P,SOPHOCLEOUS M. Development of a comprehensive watershed model applied to study stream yield under drought conditions[J]. Ground Water,1999,37(3):418 − 426. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1999.tb01121.x
[10] 雷凯文,卢宏玮. 基于MIKESHE的流域表层土壤含水量时空变化特征分析[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020,48(6):50 − 54. [LEI Kaiwen,LU Hongwei. Spatial and temporal variation of surface soil moisture content based on MIKESHE[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(6):50 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] GRAHAM N, REFSGAARD A. MIKE SHE: A distributed physically based modelling system for surface water/groundwater interactions[C]//Proceedings of MODFLOW 2001 and other modelling odysseys. Golden: Colorado, 2001: 321 − 327.
[12] 吴斌,王赛,王文祥,等. 基于地表水-地下水耦合模型的未来气候变化对西北干旱区水资源影响研究:以黑河中游为例[J]. 中国地质,2019,46(2):369 − 380. [WU Bin,WANG Sai,WANG Wenxiang,et al. Impact of future climate change on water resources in the arid regions of Northwest China based on surface water-groundwater coupling model:a case study of the middle reaches of the Heihe River[J]. Geology in China,2019,46(2):369 − 380. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 何君. 基于GSFLOW的片麻岩地区地表水和地下水耦合作用分析[J]. 陕西水利,2018(6):17 − 19. [HE Jun. Analysis of coupling effect of surface water and groundwater in gneiss area based on GSFLOW[J]. Shaanxi Water Resources,2018(6):17 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16747/j.cnki.cn61-1109/tv.2018.06.006
[14] MARKSTROM S L, NISWONGER R G, REGAN R S, et al. GSFLOW—coupled groundwater and surface-water flow model based on the integration of the precipitation-runoff modeling system (PRMS) and the modular ground-water flow model (MODFLOW-2005): US Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 6-D1[M]. Reston: US Geological Survey, 2008: 240.
[15] 陈喜. 生态脆弱区地下水合理开发及生态功能退变防控机制与基础研究[R]. 天津: 天津大学, 2021
CHEN Xi. Mechanism and basic research on rational development of groundwater and prevention and control of ecological function degeneration in ecologically fragile areas[R]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2021. (in Chinese)
[16] CHEN P P,LIU H M,WANG Z M,et al. Vegetation dynamic assessment by NDVI and field observations for sustainability of China ’s Wulagai River Basin[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2021,18(5):2528. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052528
[17] 屈慧慧,裴亮,桑学锋,等. 基于MNDWI特征空间的水体追踪识别方法研究[J]. 测绘工程,2021,30(2):32 − 35. [QU Huihui,PEI Liang,SANG Xuefeng,et al. A method of water body tracking and recognition based on feature space of MNDWI[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping,2021,30(2):32 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19349/j.cnki.issn1006-7949.2021.02.006
[18] 邵景力. 生态脆弱区地下水合理开发与生态保护的监控-预警与对策综合研究[R]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2021
SHAO Jingli. Comprehensive research on monitoring-early warning and countermeasure of reasonable groundwater development and ecological protection in ecologically fragile areas [R]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2021. (in Chinese)
[19] 马瑞. 重要湿地地下水调控及水生态功能保护关键技术与示范[R]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2021
MA Rui. Key technologies and demonstration of groundwater regulation and protection of water ecology function in important wetlands [R]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2021. (in Chinese)
[20] HARBAUGH AW. MODFLOW-2005, the US geological survey modular ground-water model-the ground-water flow process: US geological survey techniques and methods 6-A16[M]. Reston: US Geological Survey, 2005.
[21] MICHAEL L, MERRITT, LEONARD F, et al. Documentation of a computer program to simulate lake-aquifer interaction using the MODFLOW ground-water flow model and the MOC3D solute-transport model: US Geological Survey Water Resources Investigations Report 00-4167[R]. Reston: US Geological Survey, 2001: 146.
[22] MERRITT M L, KONIKOW L F. Documentation of a computer program to simulate lake-aquifer interaction using the MODFLOW ground water flow model and the MOC3D solute-transport model[R]. Reston: US Geological Survey, 2000.
[23] GUO Y T,SHAO J L,ZHANG Q L,et al. Relationship between water surface area of qingtu lake and ecological water delivery:A case study in northwest China[J]. Sustainability,2021,13(9):4684. doi: 10.3390/su13094684
-




 下载:
下载: