A study of the irrigation strategy to maintain winter wheat production and prevent confined groundwater depletion
-
摘要:
我国深层地下水超采最严重的区域当属华北平原的河北省黑龙港地区,该区域的深层承压含水层面临枯竭的安全风险。然而,黑龙港地区作为我国优质冬小麦的重要产区和河北省冬小麦的主产区,肩负着河北省确保冬小麦这一重要口粮稳产的责任。因此,冬小麦生育期的灌溉策略必须在区域尺度上兼顾深层地下水的禁采和冬小麦产量的稳定,这也是当前黑龙港地区这个“华北平原地下水超采综合治理行动方案”重点实施区域的有关部门所亟需的。本文基于分布式农业水文模型的模拟研究及进一步的估算,表明:就黑龙港地区整体而言,在现状灌溉情形下冬小麦生育期多年平均所用的深层地下水开采量和其他用途的深层地下水开采量分别约为9.62×108 m3和12.47×108 m3。考虑到该区域生活和工业所用的深层地下水开采量目前大多已被南水北调中线工程的引水所置换,我们建议:进一步增加“南水北调东线一期工程北延应急供水工程”和“引黄入冀补淀工程”置换黑龙港地区冬小麦井灌所用深层地下水的水量,以满足外调引水9.62×108 m3用于冬小麦生育期进行渠灌的需求,如此才能既确保该地区冬小麦稳产又遏制深层地下水的超采态势。若外调引水量只可以分别满足在冬小麦生育期灌水3次、2次和1次的灌溉定额,则每年在冬小麦生育期所需的外调引水量分别约为8.21×108 m3、5.47×108 m3和2.74×108 m3。然而,与现状灌溉情形相比,冬小麦总产将分别减少约8%、34%和56%。总之,本研究可为相关部门就兼顾禁采深层地下水与稳定冬小麦产量而规划外调引水方案提供一定的参考。
Abstract:The most serious area with groundwater over-exploitation of deep aquifers in China is the Heilonggang region of Hebei Province in the North China Plain (NCP), where deep confined aquifers are facing the risk of depletion. However, as an important producer of high-quality winter wheat in China and the main producer in Hebei Province, this region shoulders the important responsibility of ensuring edible grain security in Hebei Province. Thus, banning deep groundwater exploitation and stabilizing winter wheat yield must be taken into account at the regional scale when proposing irrigation strategy for winter wheat. This is urgently needed by the relevant departments in this key implementation area of the comprehensive treatment action plan for groundwater over-exploitation in the NCP. Simulation using the distributed agro-hydrological model and further estimation show that the average amounts of deep groundwater exploitation for winter wheat irrigation under the current irrigation schedule and for other purposes are approximately 9.62×108 m3 and 12.47×108 m3, respectively, in the whole region. Considering that deep groundwater exploitation for domestic and industrial use has been mostly replaced by water diversion from the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion (SNWD) project in this region, we propose to further increase the water supplies from the northern extension emergency project of the eastward route of SNWD and from the Yellow River to the Baiyangdian Lake of Hebei Province diversion project to replace the deep groundwater used for winter wheat well irrigation. If the water supplies from these external water diversion projects can meet the demand of 9.62×108 m3 for winter wheat canal irrigation, not only can stable winter wheat production be ensured, but deep groundwater over-exploitation can also be curbed. Water amounts of approximately 8.21×108 m3, 5.47×108 m3 and 2.74×108 m3 from external water diversion projects are required to only meet the demand for irrigation three times, twice and once, respectively, during the winter wheat season, while the total winter wheat yield will be reduced by approximately 8%, 34% and 56%, respectively, compared with the current irrigation schedule. In summary, this study can provide a reference for the relevant departments to plan external water diversion schemes considering the banning of deep groundwater exploitation and the stabilization of winter wheat production.
-
Key words:
- deep groundwater /
- banning exploitation /
- winter wheat /
- stabilizing yield /
- water diversion project /
- canal irrigation
-

-
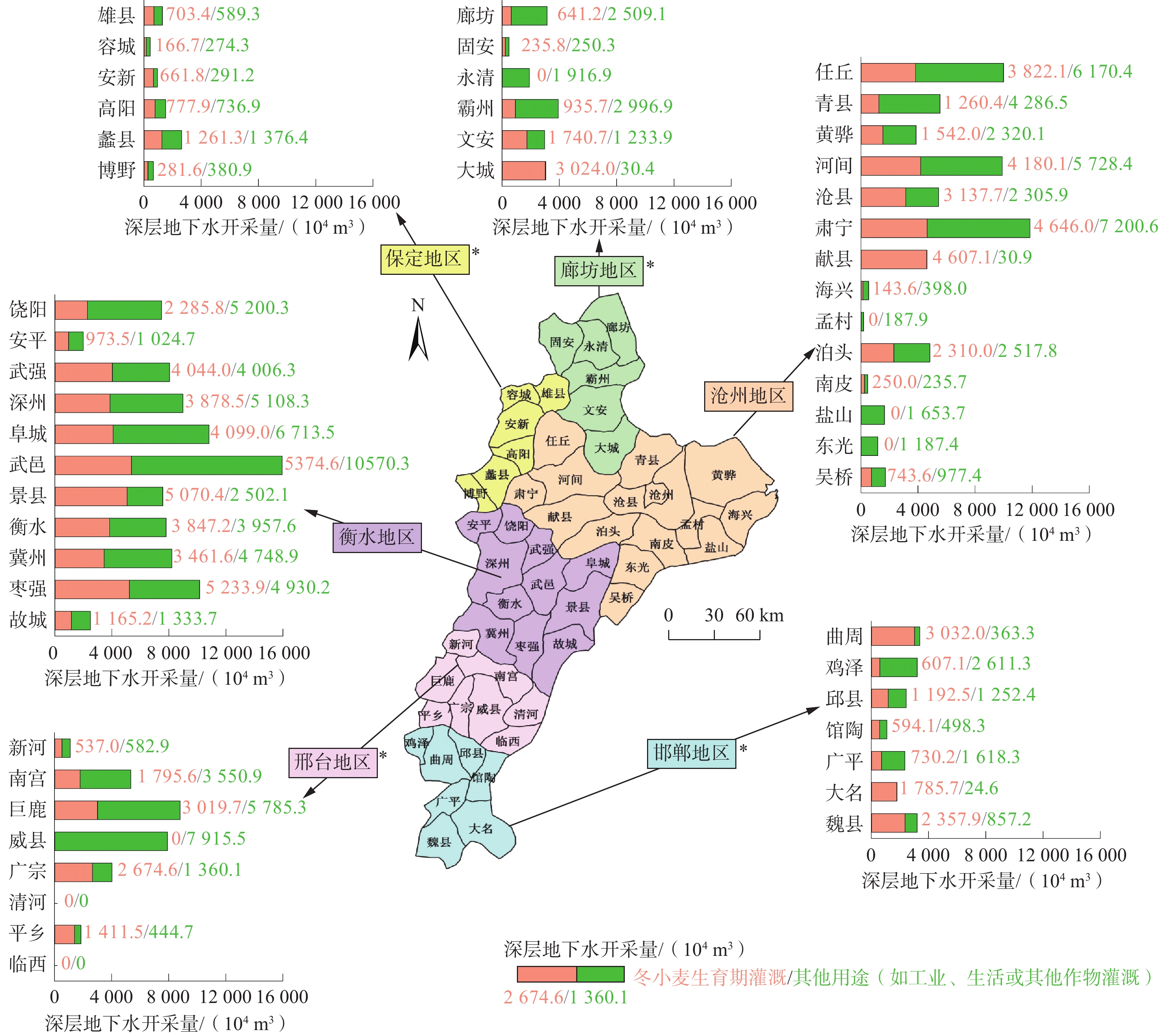
表 1 估算的黑龙港地区范围内在模拟时段多年平均的深层地下水开采量
Table 1. Estimated average exploitation amount of deep groundwater during the simulation period in the Heilonggang region
区域 模拟时段内多年平均的
冬小麦生育期在现状灌溉
情形下所用的深层地下水
开采量/(104 m3)其他用途的深层地下水开采量/(104 m3) 深层地下水
开采量/
(104 m3)廊坊地区* 6577 8937 15514 保定地区* 3852 3649 7501 沧州地区 26643 35201 61844 衡水地区 39434 50096 89530 邢台地区* 9438 19639 29077 邯郸地区* 10300 7225 17525 黑龙港地区 96244 124747 220991 注:*表示的这些地区为各自包含在黑龙港地区内的区域。 表 2 估算的黑龙港地区范围内模拟时段冬小麦生育期在限水灌溉情景下多年平均的井灌所用深层地下水开采量
Table 2. Estimated average deep groundwater exploitation for winter wheat irrigation under the limited irrigation scenarios during the simulation period in the Heilonggang region
区域 模拟时段内多年
平均的冬小麦生育期限水灌溉3 次
所用的深层地下水
开采量/(104 m3)模拟时段内多年
平均的冬小麦生育期限水灌溉2 次
所用的深层地下水
开采量/(104 m3)模拟时段内多年
平均的冬小麦生育期限水灌溉1 次
所用的深层地下水
开采量/(104 m3)廊坊地区* 5123 3415 1708 保定地区* 3040 2027 1013 沧州地区 27382 18255 9127 衡水地区 31015 20677 10338 邢台地区* 7453 4968 2484 邯郸地区* 8105 5403 2702 黑龙港地区 82118 54745 27372 注:*表示的这些地区为各自包含在黑龙港地区内的区域。 表 3 估算的黑龙港地区范围内模拟时段冬小麦生育期在限水灌溉情景下多年平均的冬小麦产量及其与现状灌溉情形相比的变幅
Table 3. Estimated average winter wheat yield and the variation under the limited irrigation scenarios during the simulation period compared with the current irrigation schedule in the Heilonggang region
限水灌溉情景 区域 单产量 总产量 产量/(kg·hm−2) 变幅/% 变化量/(kg·hm−2) 产量/(108 kg) 变幅/% 变化量/(108 kg) 灌水3次 廊坊地区* 3354 −22 −920 2.99 −21 −0.81 保定地区* 3678 −20 −932 3.37 −20 −0.86 沧州地区 4720 12 507 17.06 10 1.55 衡水地区 5064 −9 −508 13.67 −9 −1.39 邢台地区* 3362 −21 −899 4.77 −21 −1.28 邯郸地区* 4365 −17 −907 8.66 −17 −1.74 黑龙港地区 4258 −9 −445 50.52 −8 −4.53 灌水2次 廊坊地区* 2429 −43 −1845 2.16 −43 −1.63 保定地区* 2682 −42 −1928 2.46 −42 −1.76 沧州地区 3393 −19 −820 12.19 −21 −3.32 衡水地区 3612 −35 −1960 9.77 −35 −5.29 邢台地区* 2299 −46 −1962 3.27 −46 −2.78 邯郸地区* 3235 −39 −2037 6.49 −38 −3.91 黑龙港地区 3056 −35 −1647 36.34 −34 −18.69 灌水1次 廊坊地区* 1429 −67 −2845 1.27 −67 −2.53 保定地区* 1623 −65 −2987 1.49 −65 −2.74 沧州地区 2410 −43 −1803 8.59 −45 −6.92 衡水地区 2565 −54 −3007 6.95 −54 −8.11 邢台地区* 1359 −68 −2902 1.94 −68 −4.11 邯郸地区* 2082 −61 −3189 4.22 −59 −6.18 黑龙港地区 2033 −57 −2670 24.46 −56 −30.59 注:*表示的这些地区为各自包含在黑龙港地区内的区域。 -
[1] 陈望和. 河北地下水[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1999
CHEN Wanghe. Groundwater in Hebei Province[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
[2] 张宗祜, 李烈荣. 中国地下水资源(河北卷)[M]. 北京: 中国地图出版社, 2005
ZHANG Zonghu, LI Lierong. Groundwater resources of China-Hebei volume[M]. Beijing: Sinomaps Press, 2005. (in Chinese)
[3] 张兆吉, 费宇红, 陈宗宇, 等. 华北平原地下水可持续利用调查评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009
ZHANG Zhaoji, FEI Yuhong, CHEN Zongyu, et al. Investigation and assessment of groundwater sustainable utilization in the North China Plain[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009. (in Chinese)
[4] 陈秀敏, 李科江, 贾银锁. 河北小麦[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2008
CHEN Xiumin, LI Kejiang, JIA Yinsuo. Wheat in Hebei Province[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
[5] 贾银锁, 郭进考. 河北夏玉米与冬小麦一体化种植[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2009
JIA Yinsuo, GUO Jinkao. Integration planting of summer maize and winter wheat in Hebei Province[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[6] 王慧军. 河北省粮食综合生产能力研究[M]. 石家庄: 河北科学技术出版社, 2010
WANG Huijun. Research of comprehensive grain production capacity in Hebei Province[M]. Shijiazhuang: Science and Technology Press of Hebei Province, 2010. (in Chinese)
[7] FOSTER S,GARDUNO H,EVANS R,et al. Quaternary aquifer of the North China Plain–assessing and achieving groundwater resource sustainability[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2004,12:81 − 93. doi: 10.1007/s10040-003-0300-6
[8] SHI J S,WANG Z,ZHANG Z J,et al. Assessment of deep groundwater over-exploitation in the North China Plain[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2011,2(4):593 − 598. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2011.07.002
[9] HUANG Z Y,PAN Y,GONG H L,et al. Subregional-scale groundwater depletion detected by GRACE for both shallow and deep aquifers in North China Plain[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2015,42:1791 − 1799. doi: 10.1002/2014GL062498
[10] LI P,REN L. Evaluating the effects of limited irrigation on crop water productivity and reducing deep groundwater exploitation in the North China Plain using an agro-hydrological model:II. scenario simulation and analysis[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2019,574:715 − 732.
[11] 任理, 李佩. 华北平原在限水和咸水灌溉及喷灌情景下作物水分生产力的模拟与深层地下水压采量的估算——以河北省黑龙港地区为例[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 2021
REN Li, LI Pei. Simulation of the crop water productivity and estimation of the reduction in deep groundwater exploitation under the scenarios of limited irrigation, saline water irrigation and sprinkler irrigation in the North China Plain: A case study in the Heilonggang region in Hebei Province[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. (in Chinese)
[12] 河北省人民政府. 河北省人民政府关于公布平原区地下水超采区、禁采区和限采区范围的通知[EB/OL]. 2014(2014-06-12). http://info.hebei.gov.cn//eportal/ui?pageId=1962757&articleKey=6272943&columnId=329982.
The General Office of the Hebei People’s Government. The notification of groundwater overexploited, pumping-limited, and pumping-prohibited areas in the plain region of Hebei Province[EB/OL]. 2014(2014-06-12). (in Chinese)
[13] 中华人民共和国水利部, 中华人民共和国财政部, 中华人民共和国国家发展改革委, 等. 联合印发《华北地区地下水超采综合治理行动方案》[EB/OL]. 2019. http://www.mwr.gov.cn/xw/slyw/201902/t20190222_1108258.html.
The Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China, The Ministry of Finance of the People’s Republic of China, National Development and Reform Commission, et al. The notification of comprehensive treatment on groundwater over-exploitation in the North China Plain[EB/OL]. 2019. (in Chinese)
[14] LI P,REN L. Evaluating the effects of limited irrigation on crop water productivity and reducing deep groundwater exploitation in the North China Plain using an agro-hydrological model:I. parameter sensitivity analysis,calibration and model validation[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2019,574:497 − 516.
[15] 河北省人民政府办公厅, 河北省统计局. 河北农村统计年鉴1995—2013[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社: 1995—2013
General Office of People’s Government of Hebei Province, Hebei Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Hebei rural statistical yearbook 1995—2013[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press: 1995—2013. (in Chinese)
[16] “新一轮全国地下水资源评价”项目办公室. “新一轮全国地下水资源评价”附表[R]. 2004
National Groundwater Resources Assessment Project Office. Attached tables of national groundwater resources assessment[R]. 2004. (in Chinese)
[17] 中华人民共和国水利部. 南水北调东线一期工程北延应急供水水头顺利通过穿漳卫新河倒虹吸工程[EB/OL]. 2022. http://szy.mwr.gov.cn/lyxx/202203/t20220328_1567061.html.
The Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. The northern extension emergency project of the eastward route of the South-to-North Water Diversion(SNWD) successfully passed the inverted siphon project through Zhangweixin River [EB/OL]. 2022. (in Chinese)
[18] 中国新闻网. 河北省引黄入冀补淀水利工程正式开工[EB/OL]. 2015. https://www.chinanews.com.cn/sh/2015/10-26/7590301.shtml.
China News Website. Water diversion project from the Yellow River to the Baiyangdian Lake of Hebei Province started[EB/OL]. 2015. (in Chinese)
[19] 河北省水利厅. 河北省水资源公报1999—2012[M]. 石家庄: 河北省水利厅, 1999—2012
Water Resources Department of Hebei Province. Hebei provincial water resources bulletin 1999—2012[M]. Shijiazhuang: Water Resources Department of Hebei Province, 1999—2012. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载:
